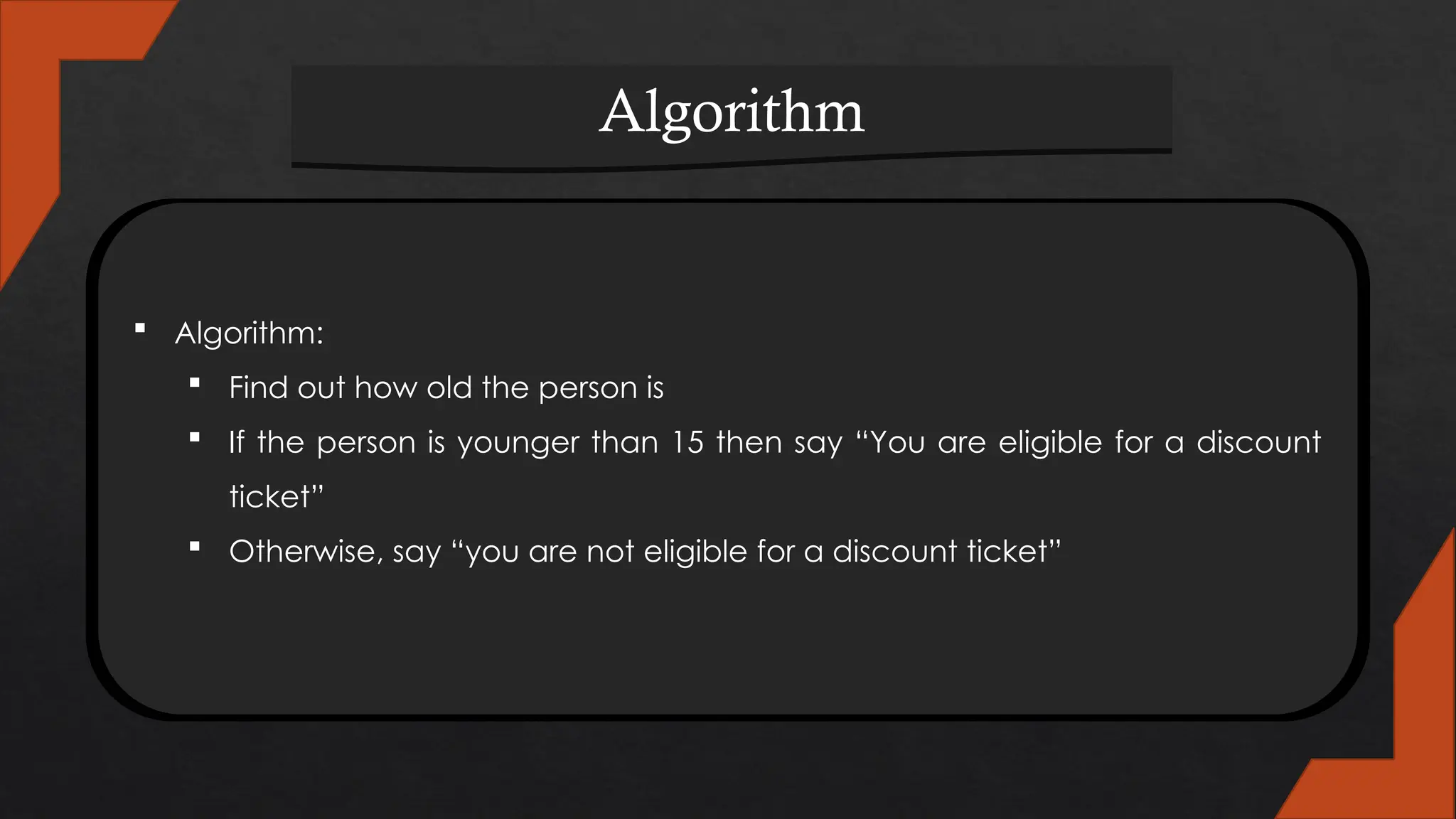
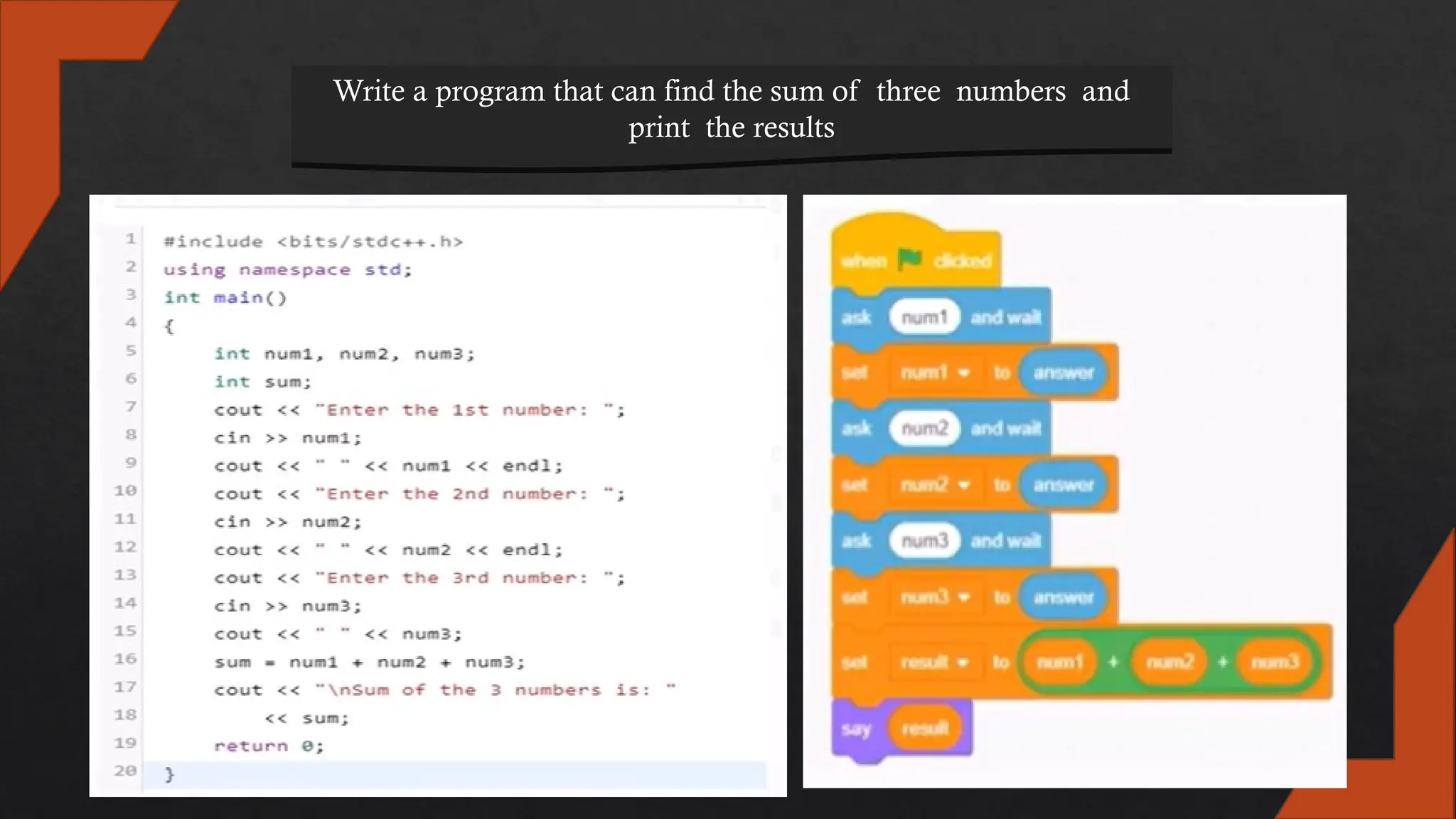
The document explains computational thinking, defining it as solving problems like a computer scientist using techniques such as decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. It describes algorithms as processes or sets of rules for problem-solving, emphasized in computer science as essential for programming. Examples are provided, illustrating how algorithms are used in daily tasks and the steps involved in writing computer programs.