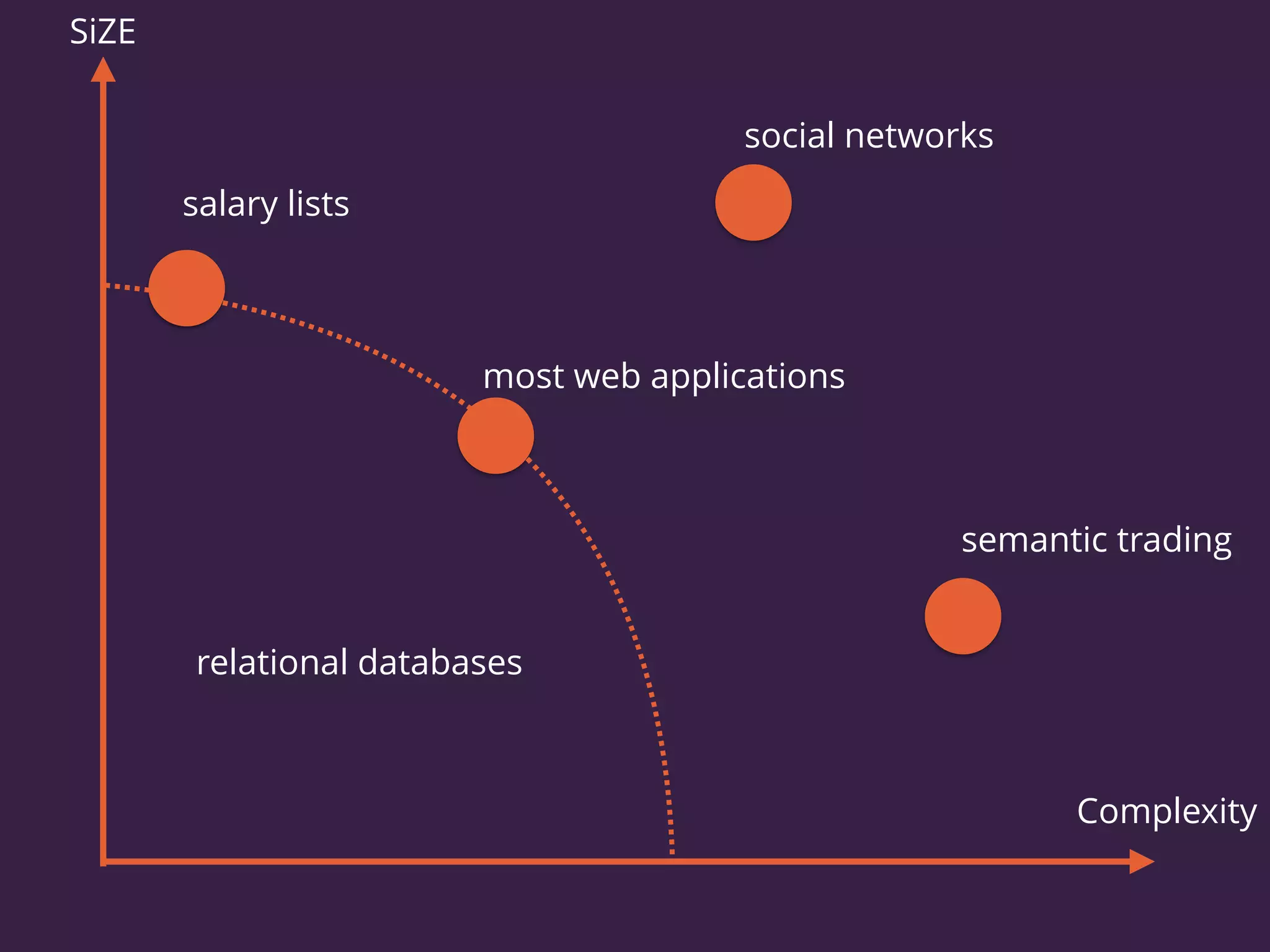
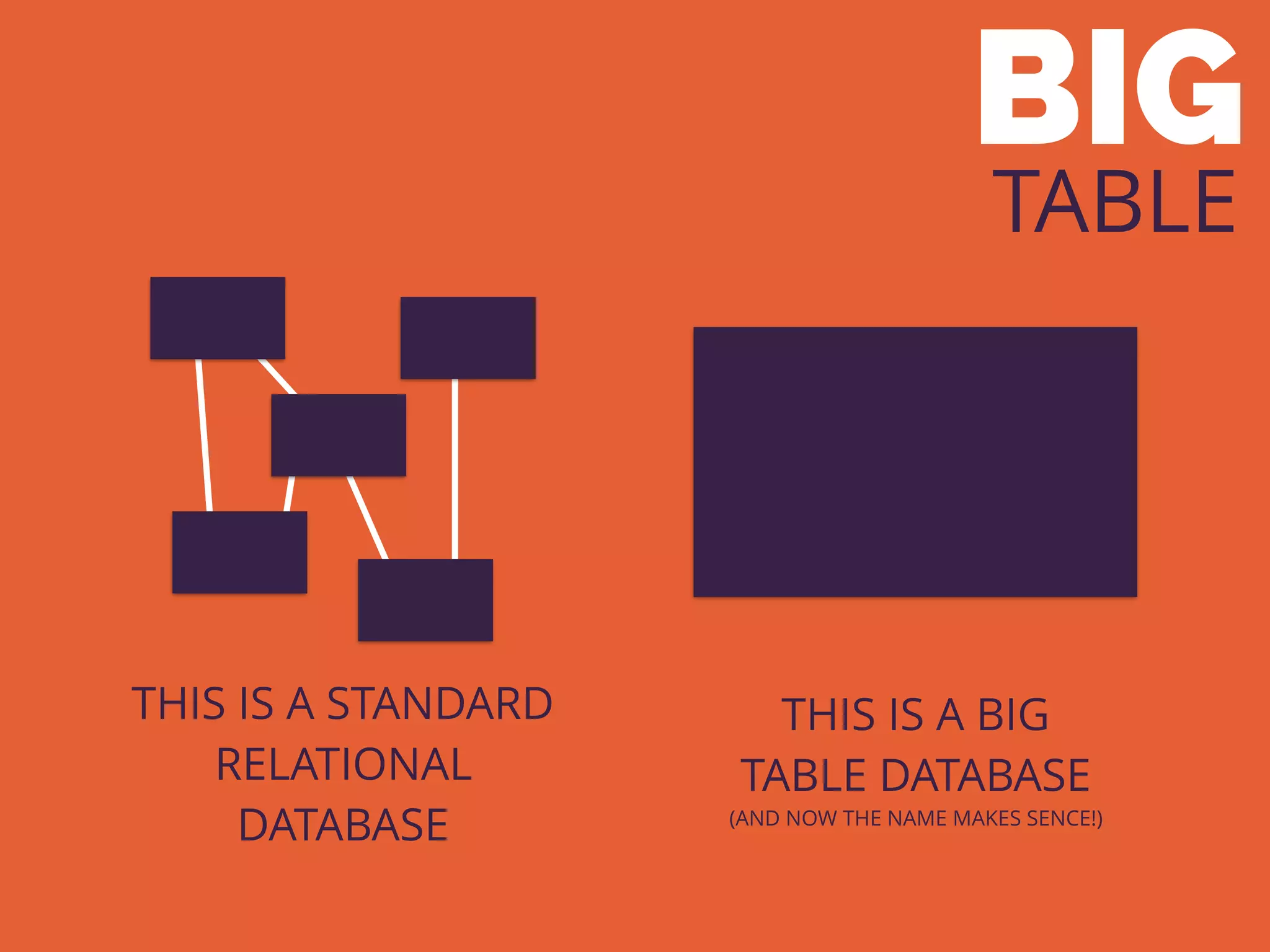
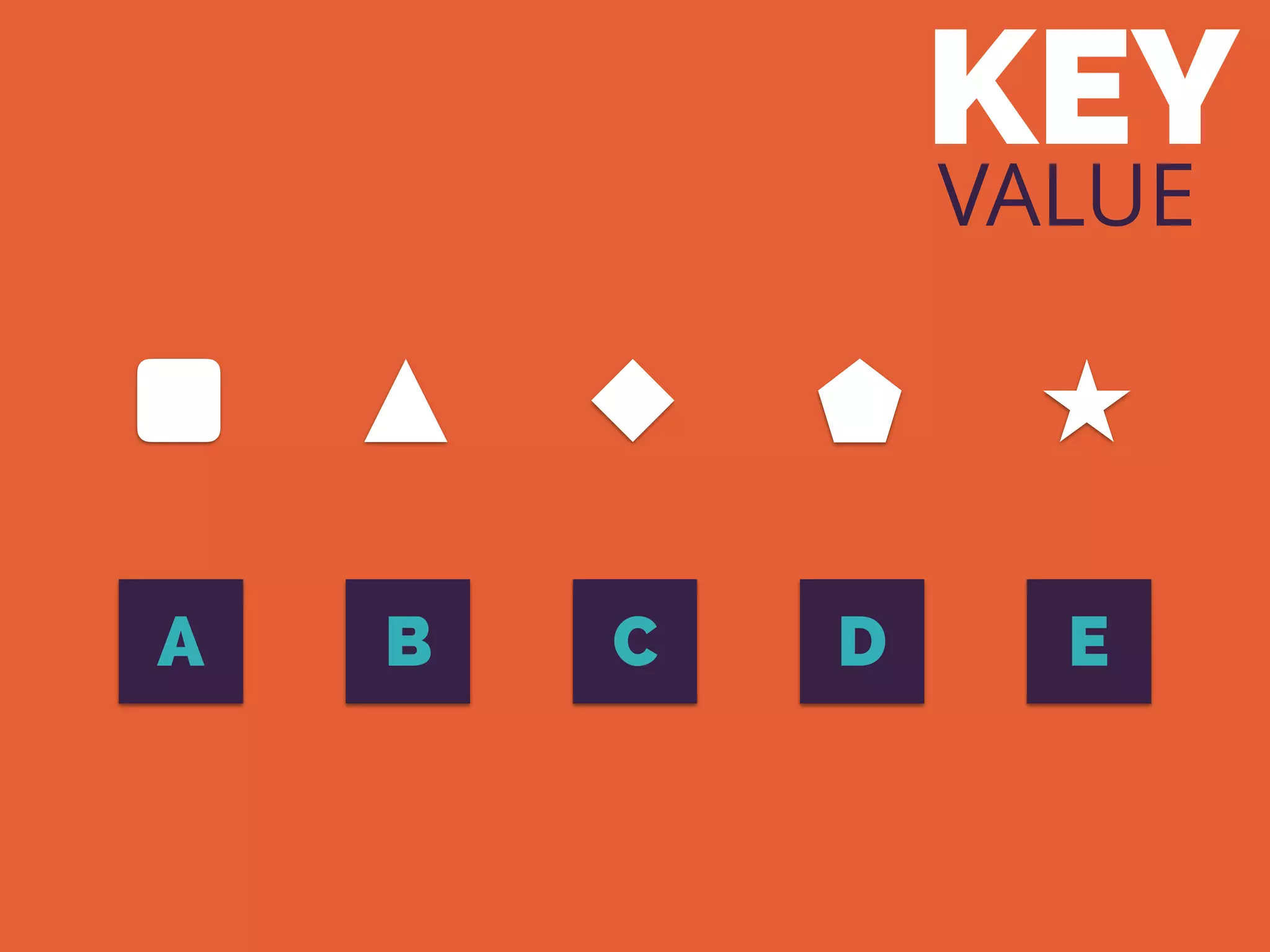
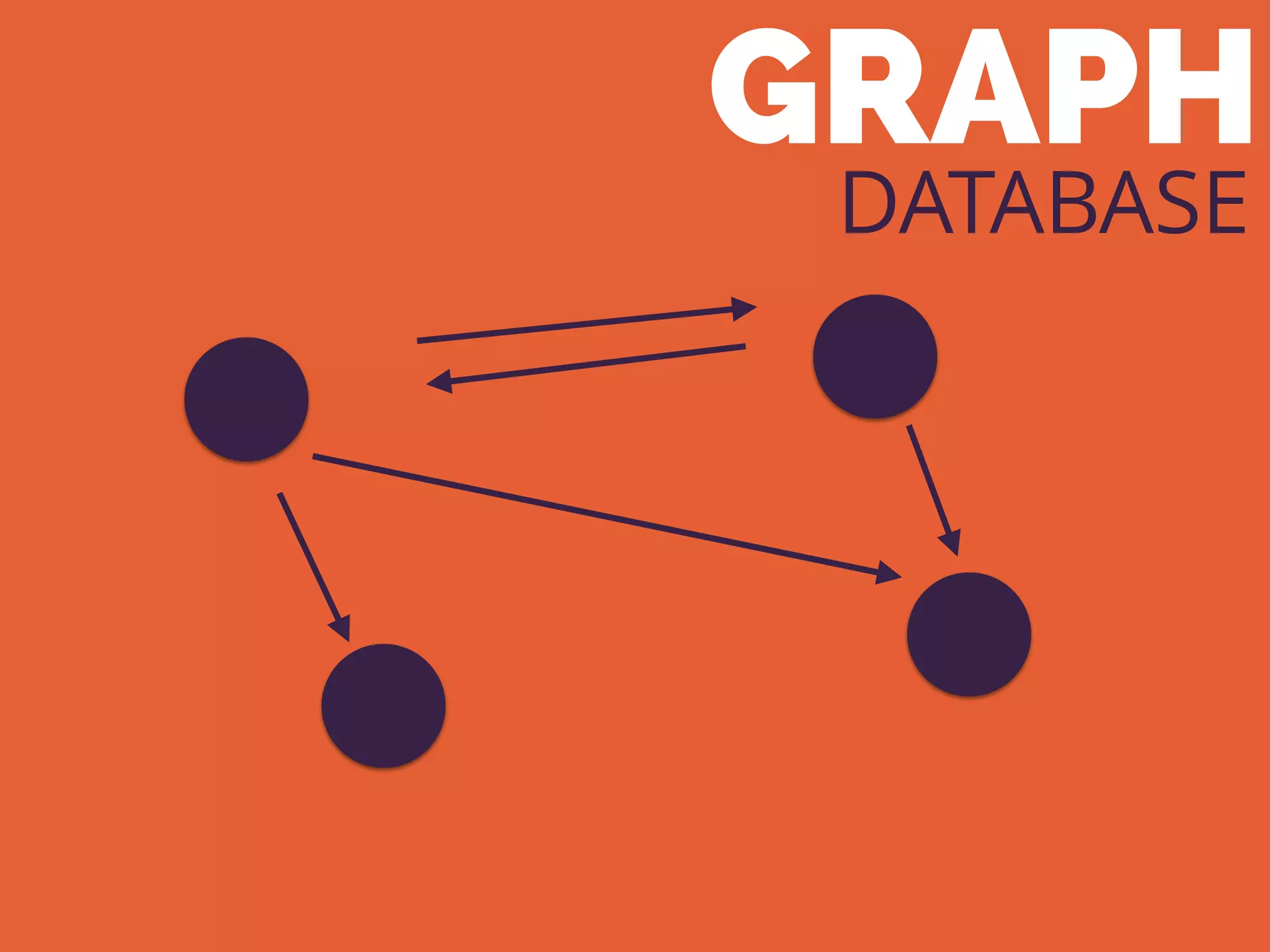
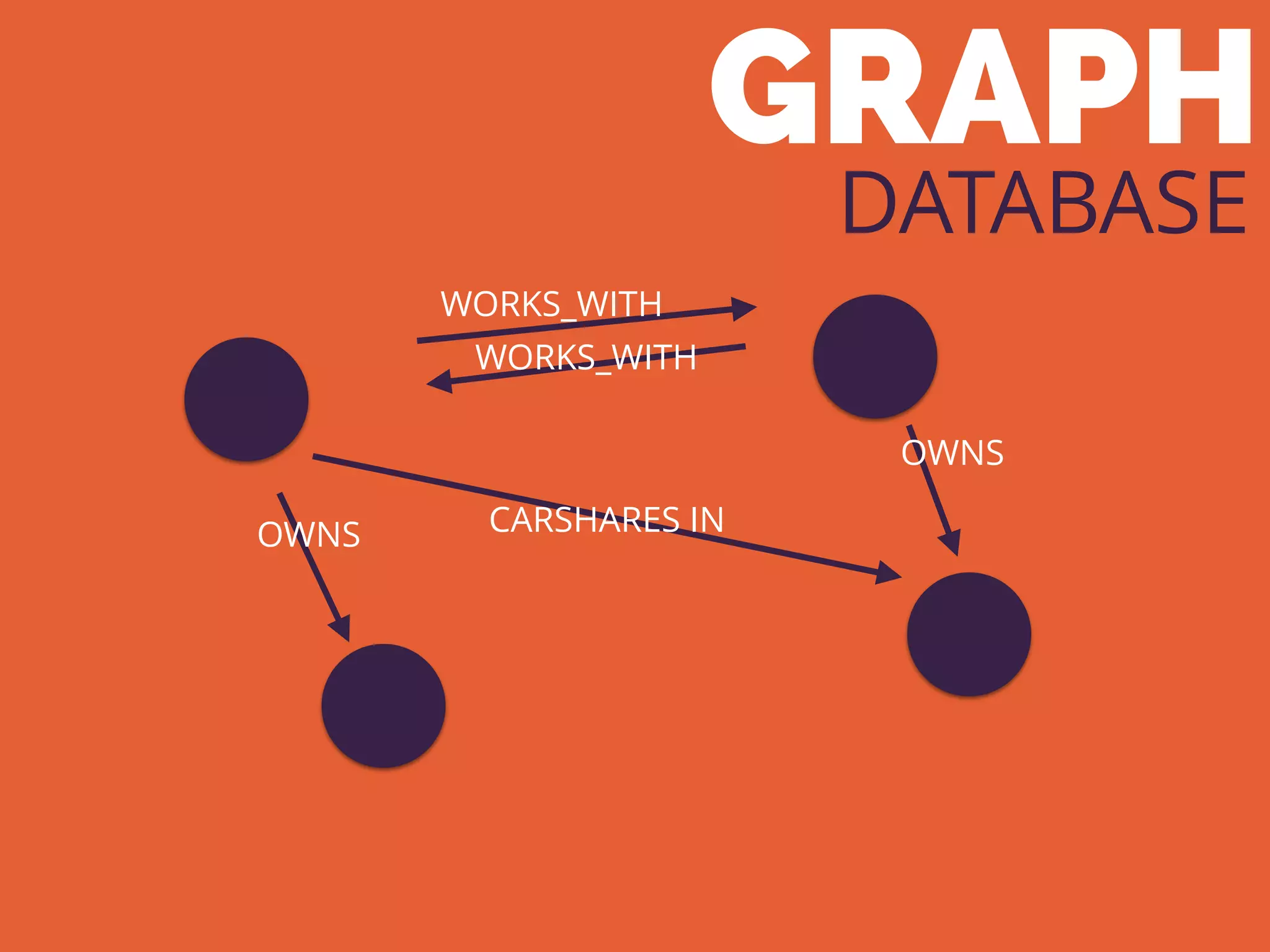
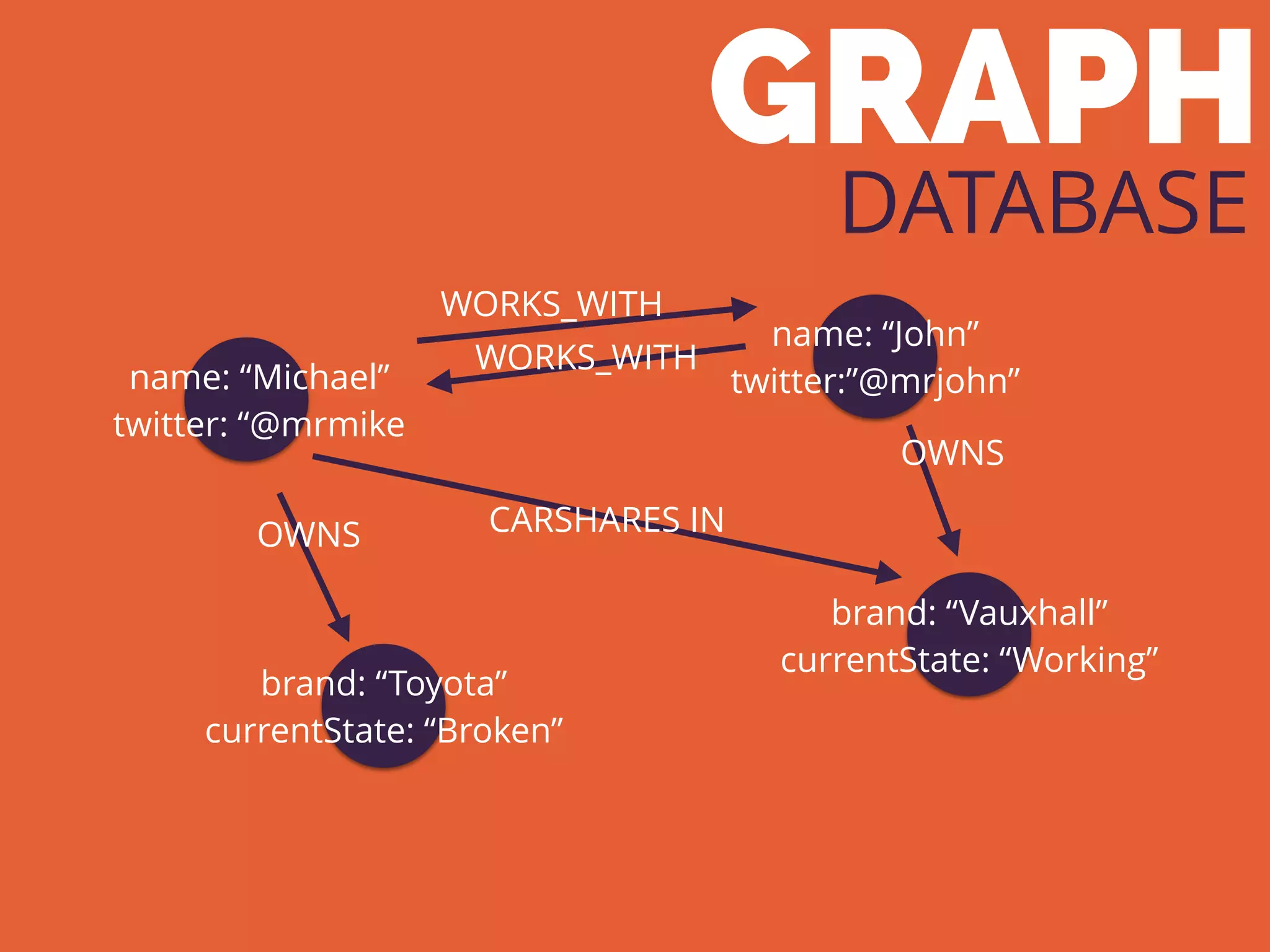
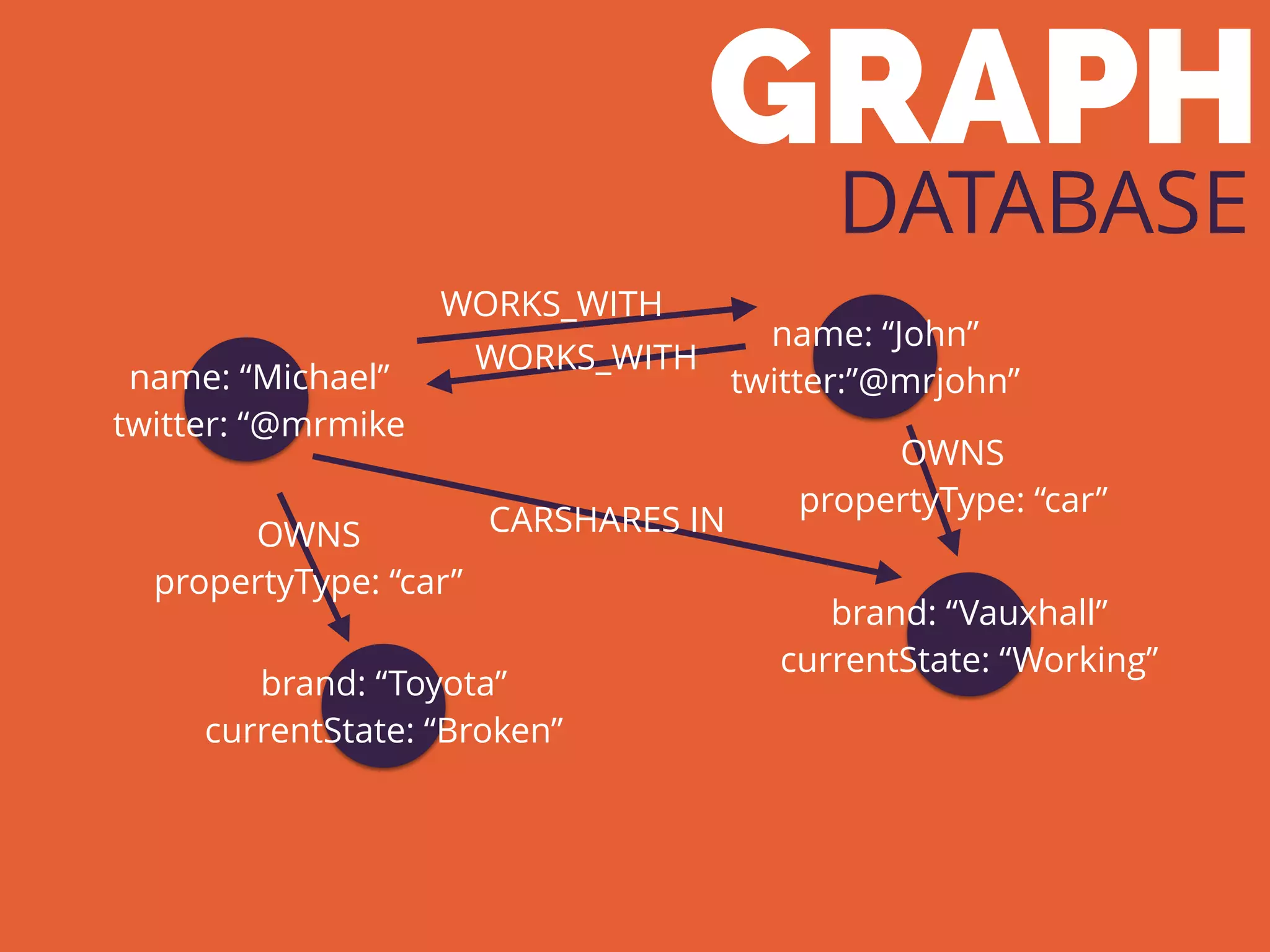
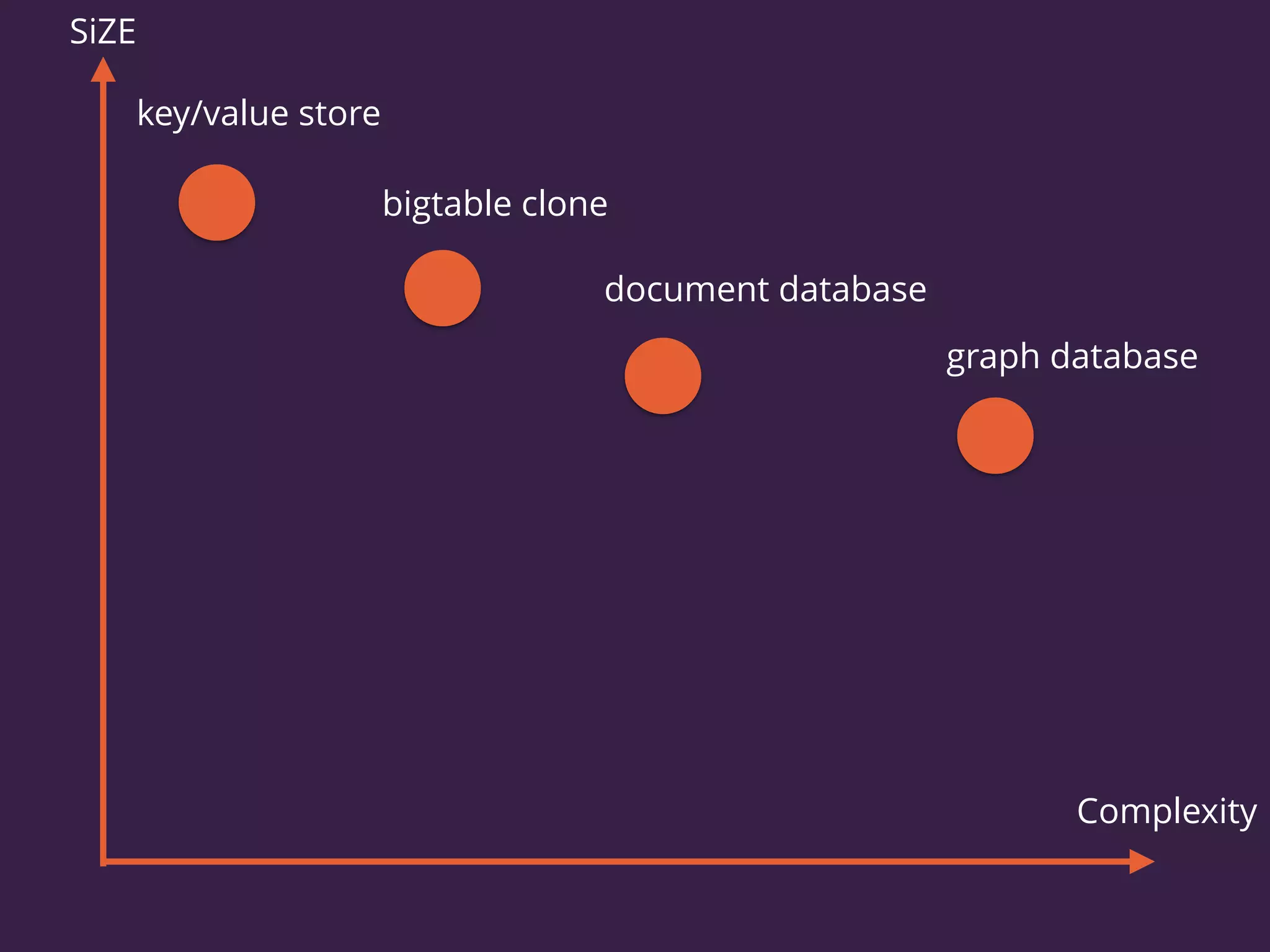
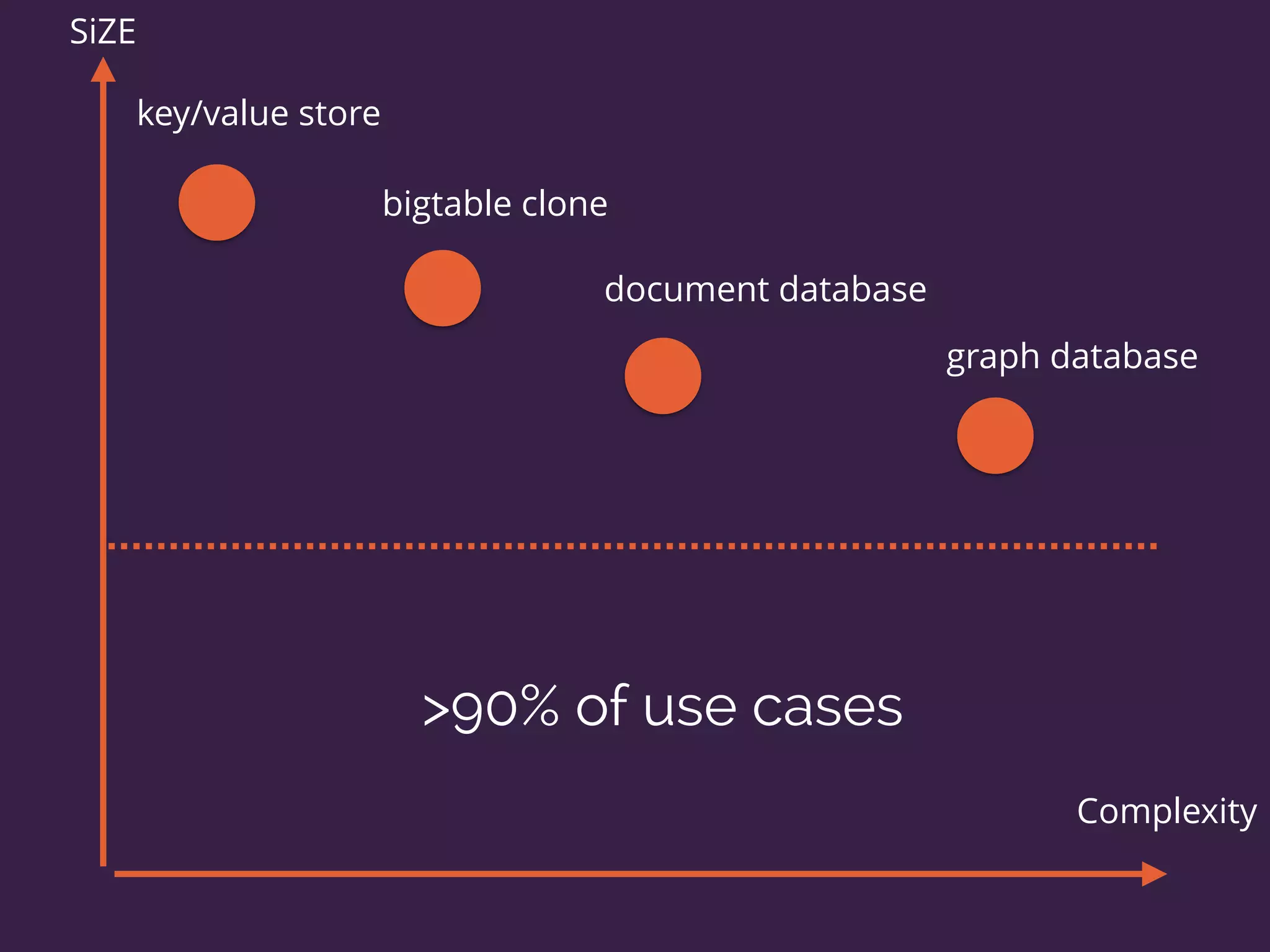
The document discusses the increasing need for NoSQL databases due to the growing volume and complexity of data as traditional relational databases struggle with scalability and flexibility. It outlines various NoSQL database types, such as key-value stores, document stores, and graph databases, highlighting their pros and cons, and when to use them compared to SQL. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of understanding both SQL and NoSQL architectures to optimize data management solutions.