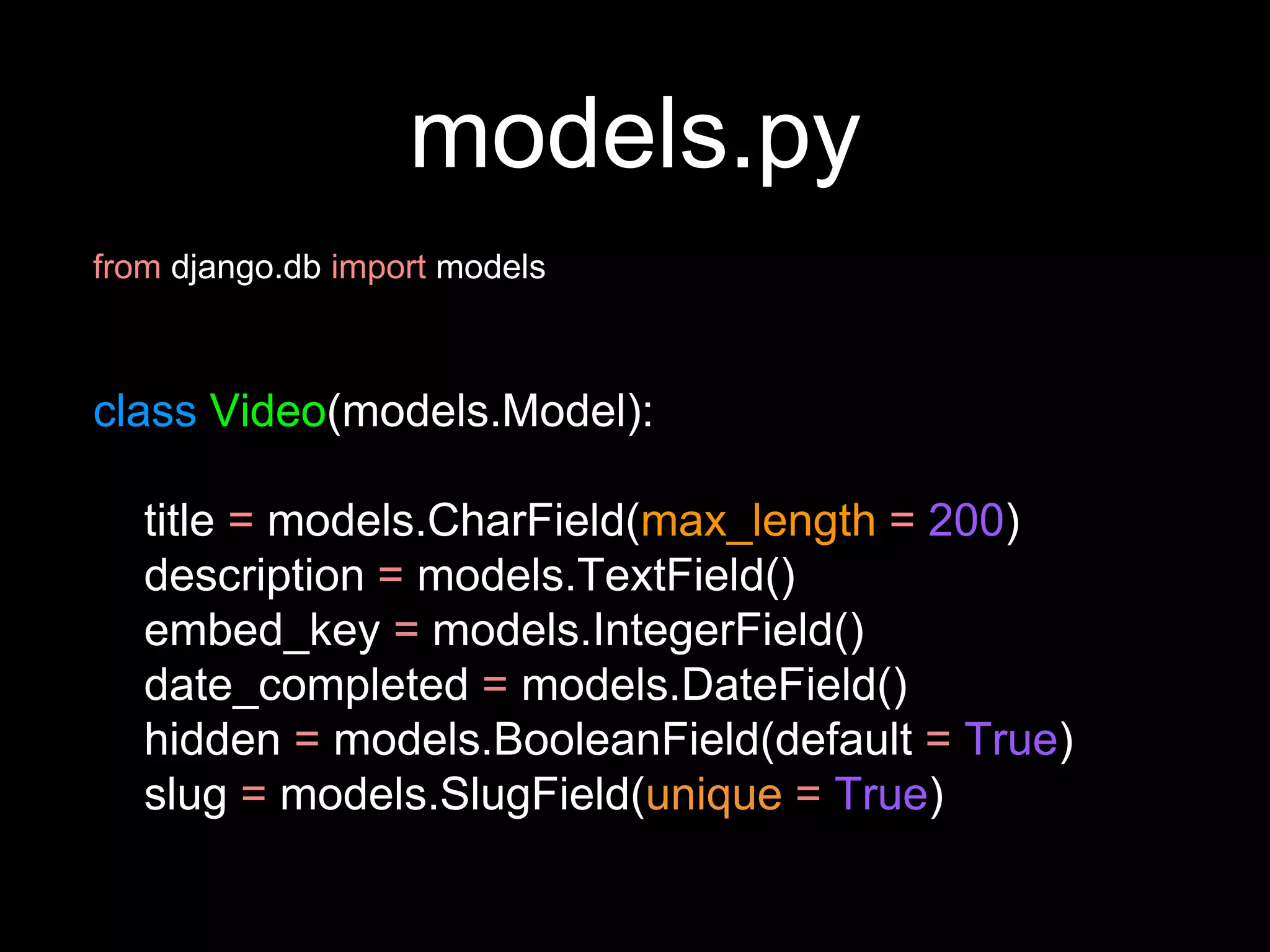
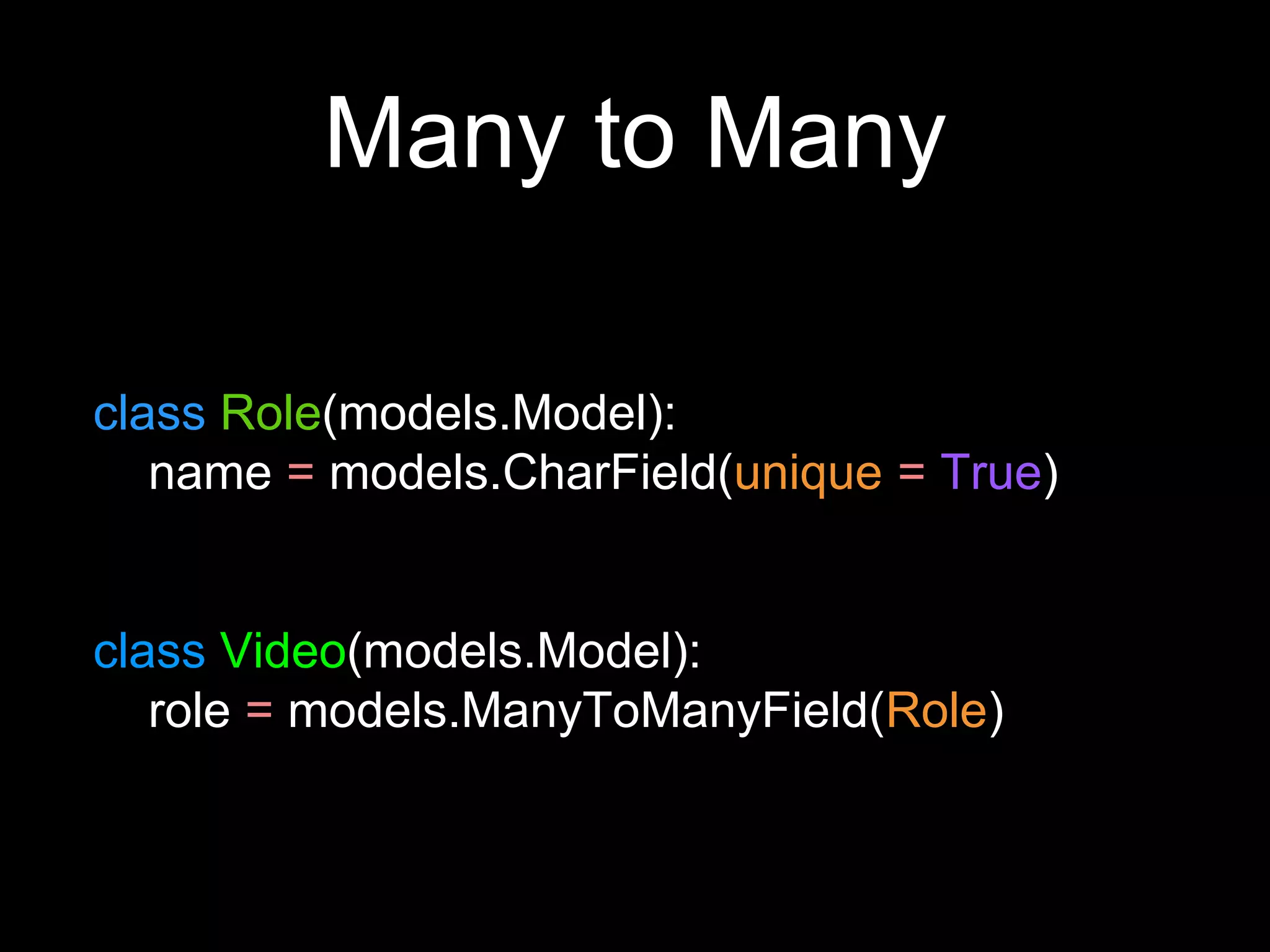
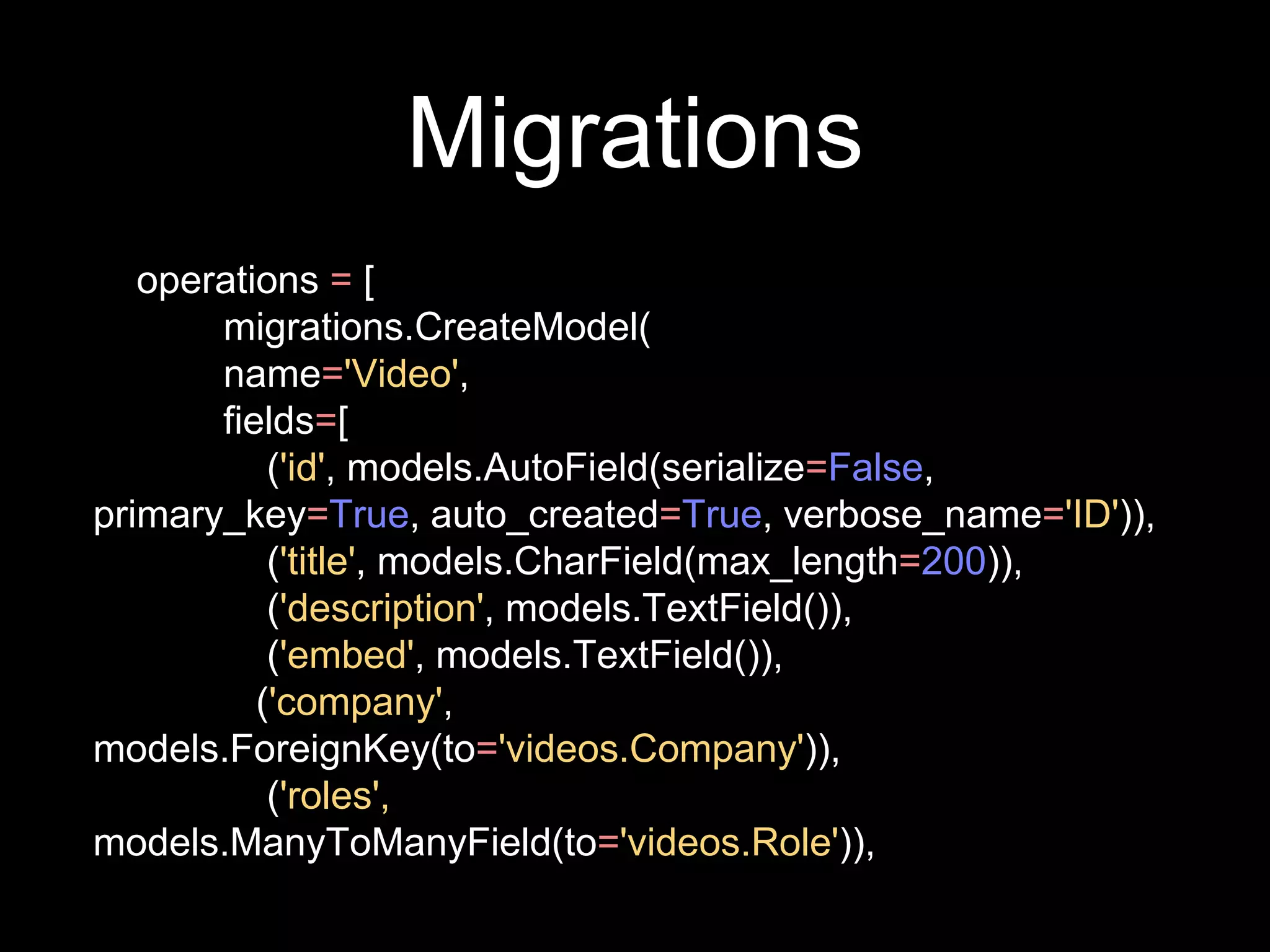
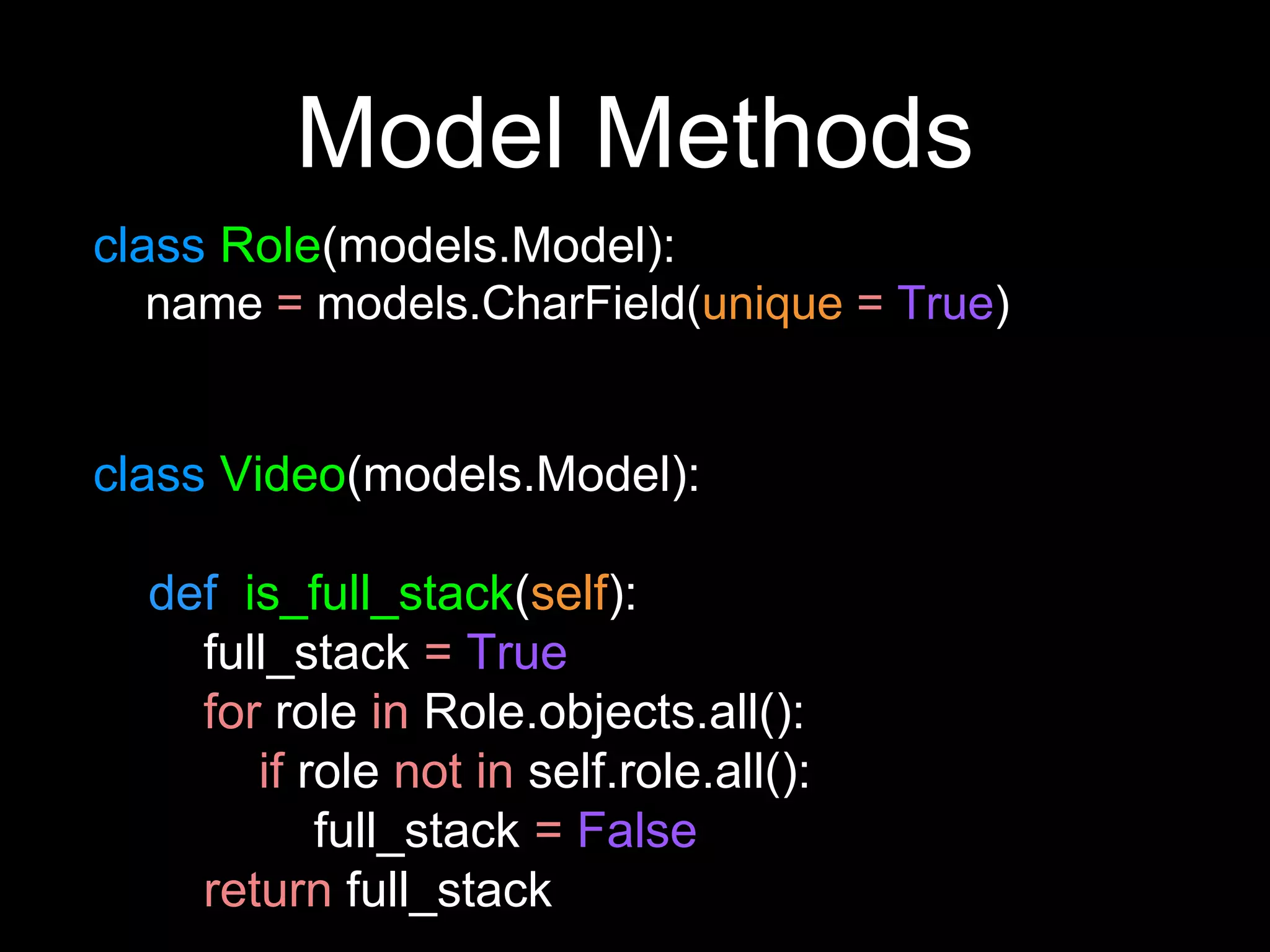
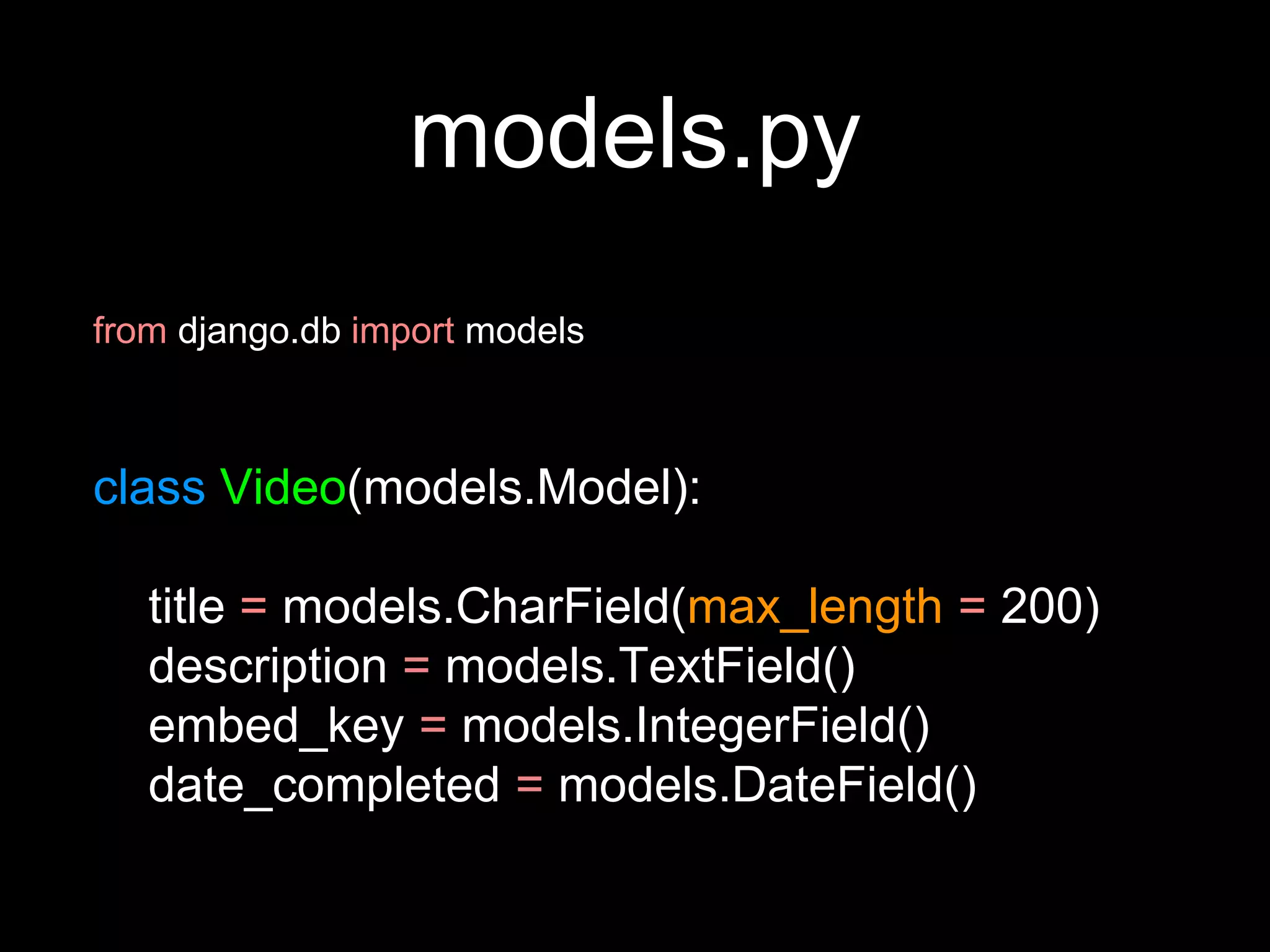
The document provides an overview of Django models, which are used to manage data within a web application. It explains the structure of models, including field definitions and relationships such as many-to-one and many-to-many. Additionally, it covers querying data through Django's ORM and practical examples of model methods and validation techniques.











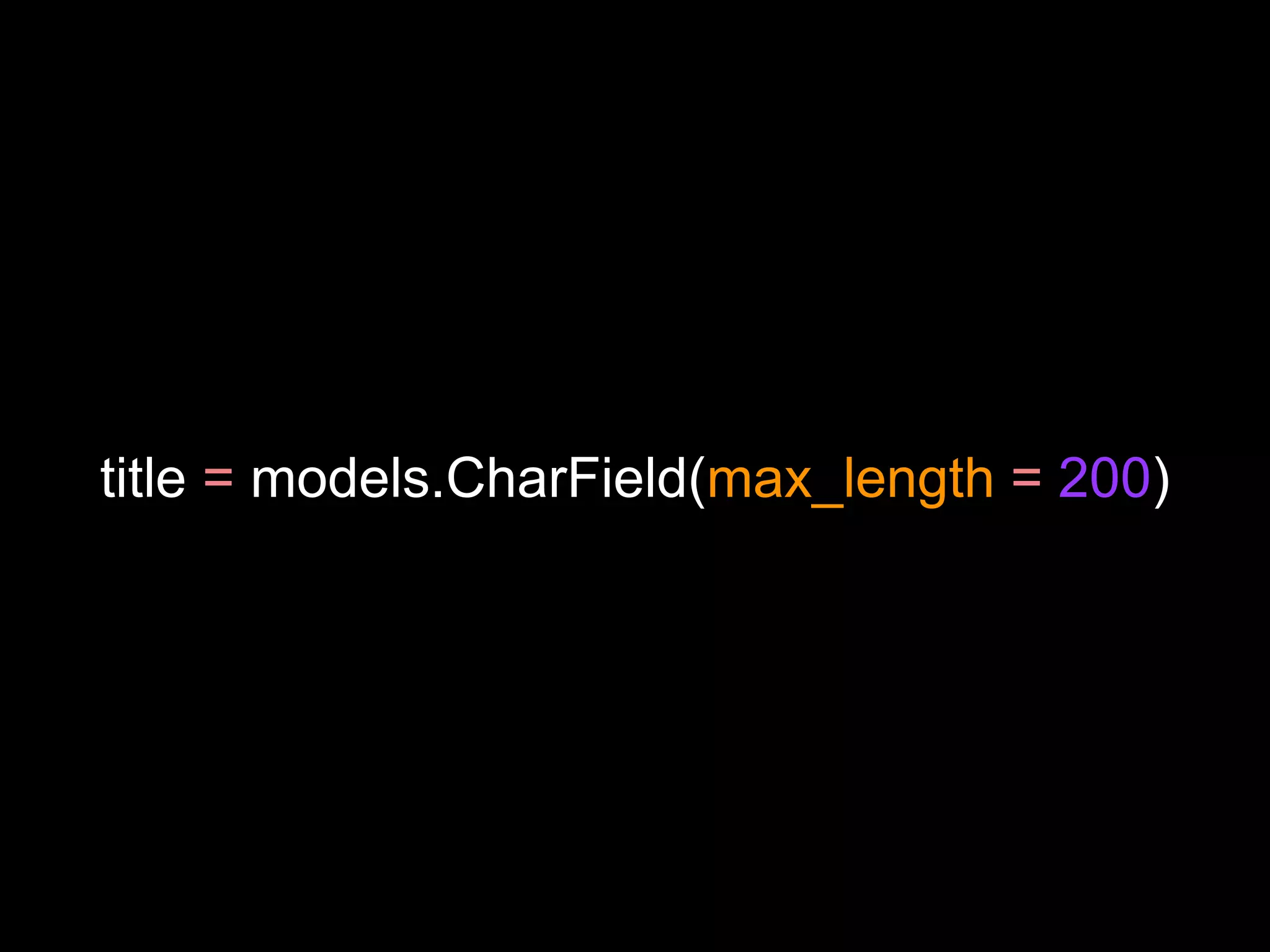



![Validators
(validate = [email_validator])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phillypug-djangomodels-150918192447-lva1-app6892/75/An-Overview-of-Models-in-Django-21-2048.jpg)
![models.py
from django.db import models
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
def validate_embed(value):
valid_embed = (checks embed at vimeo.com)
if not valid_embed:
raise ValidationError(‘That embed code does not
exist at vimeo.com’)
class Video(models.Model):
embed = integerField(validators = [validate_embed])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phillypug-djangomodels-150918192447-lva1-app6892/75/An-Overview-of-Models-in-Django-22-2048.jpg)