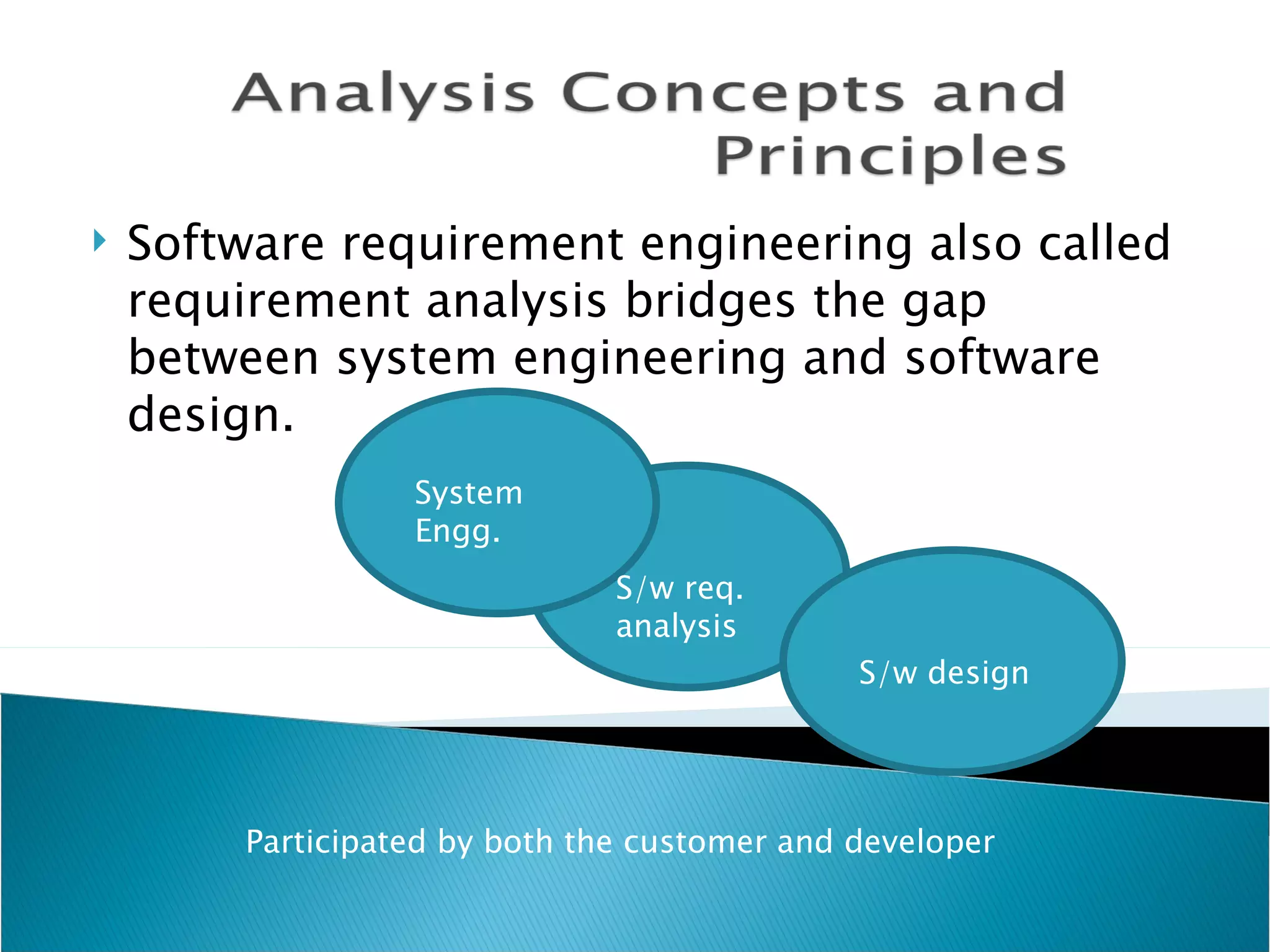
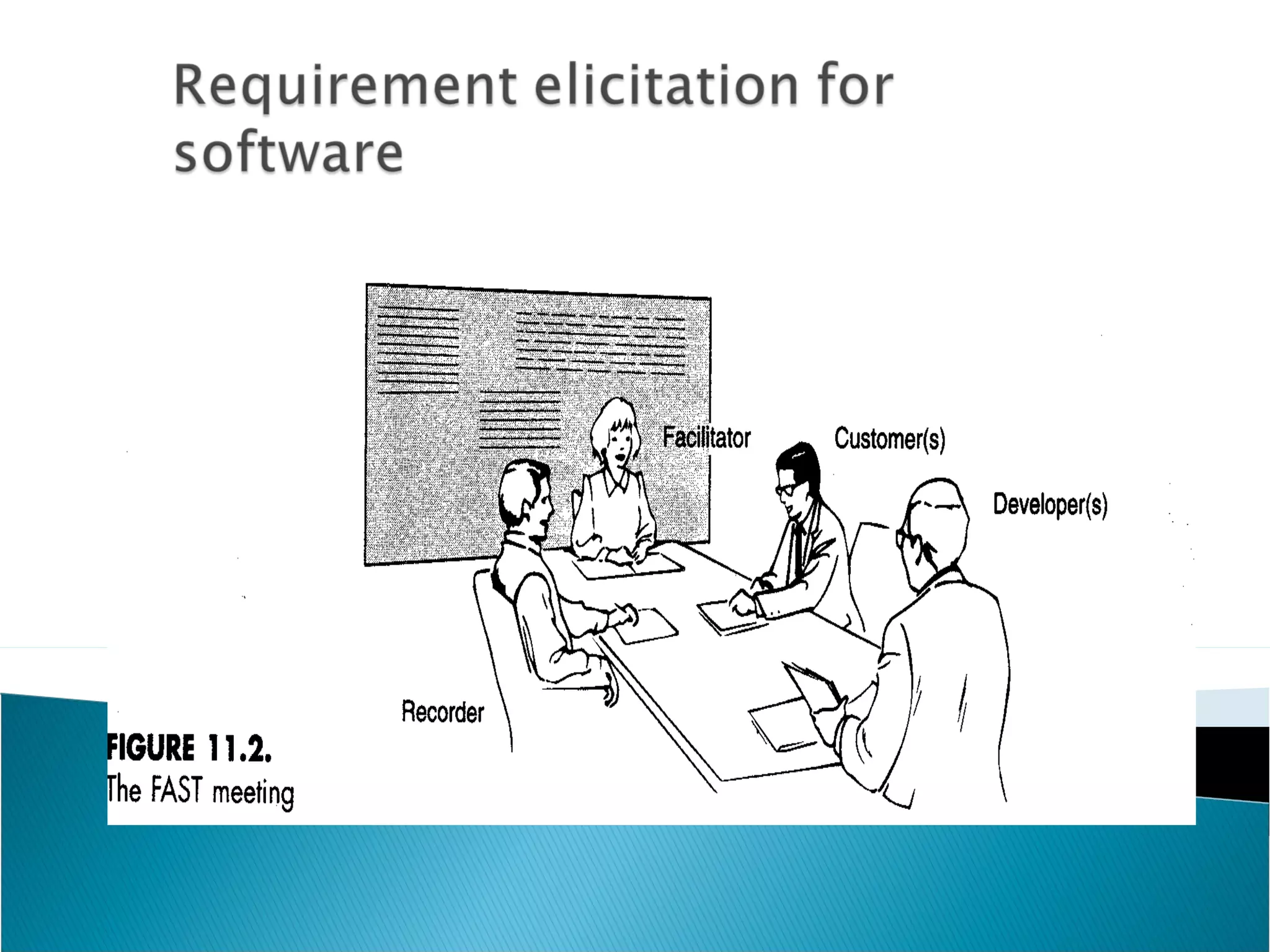
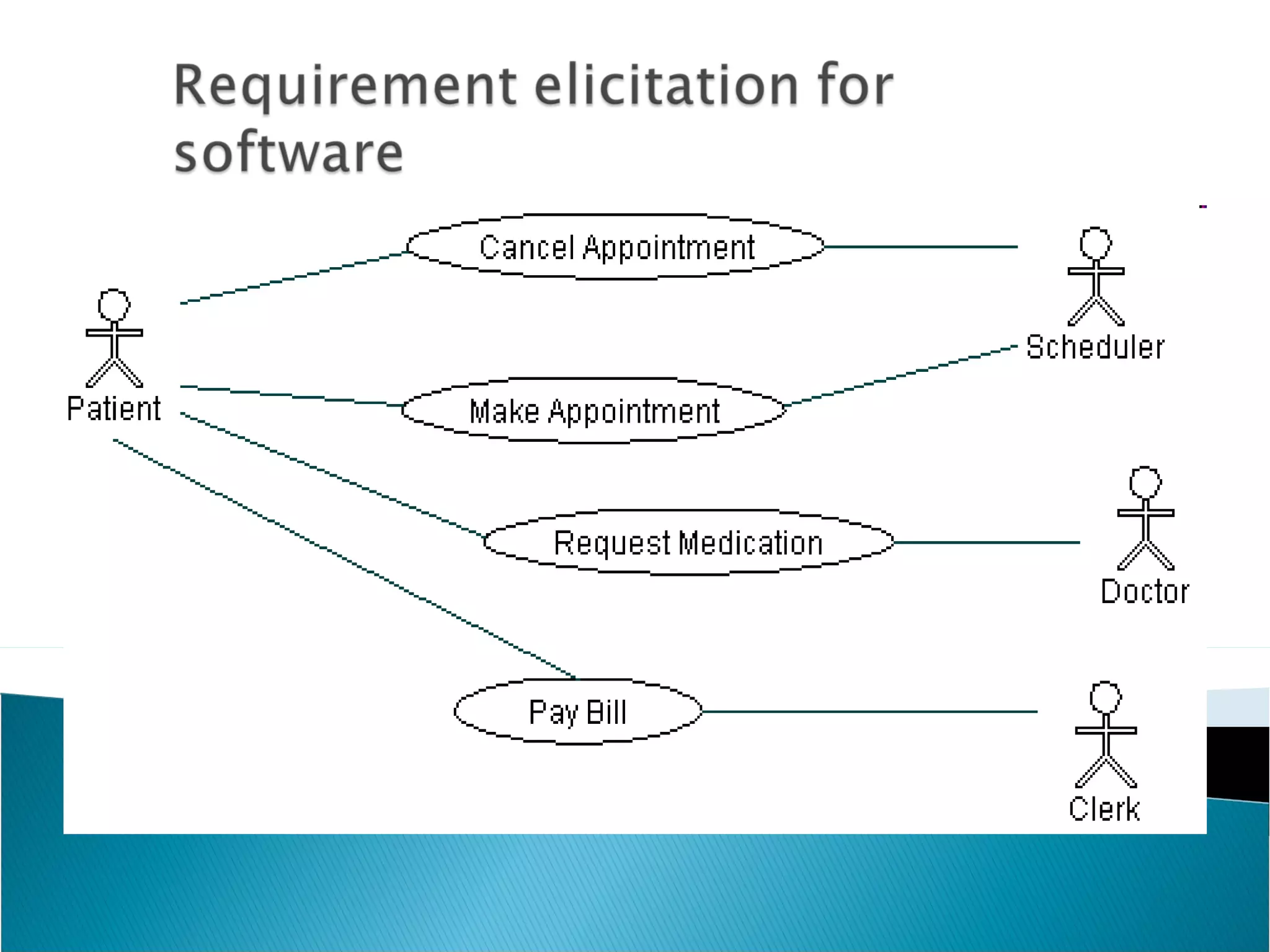
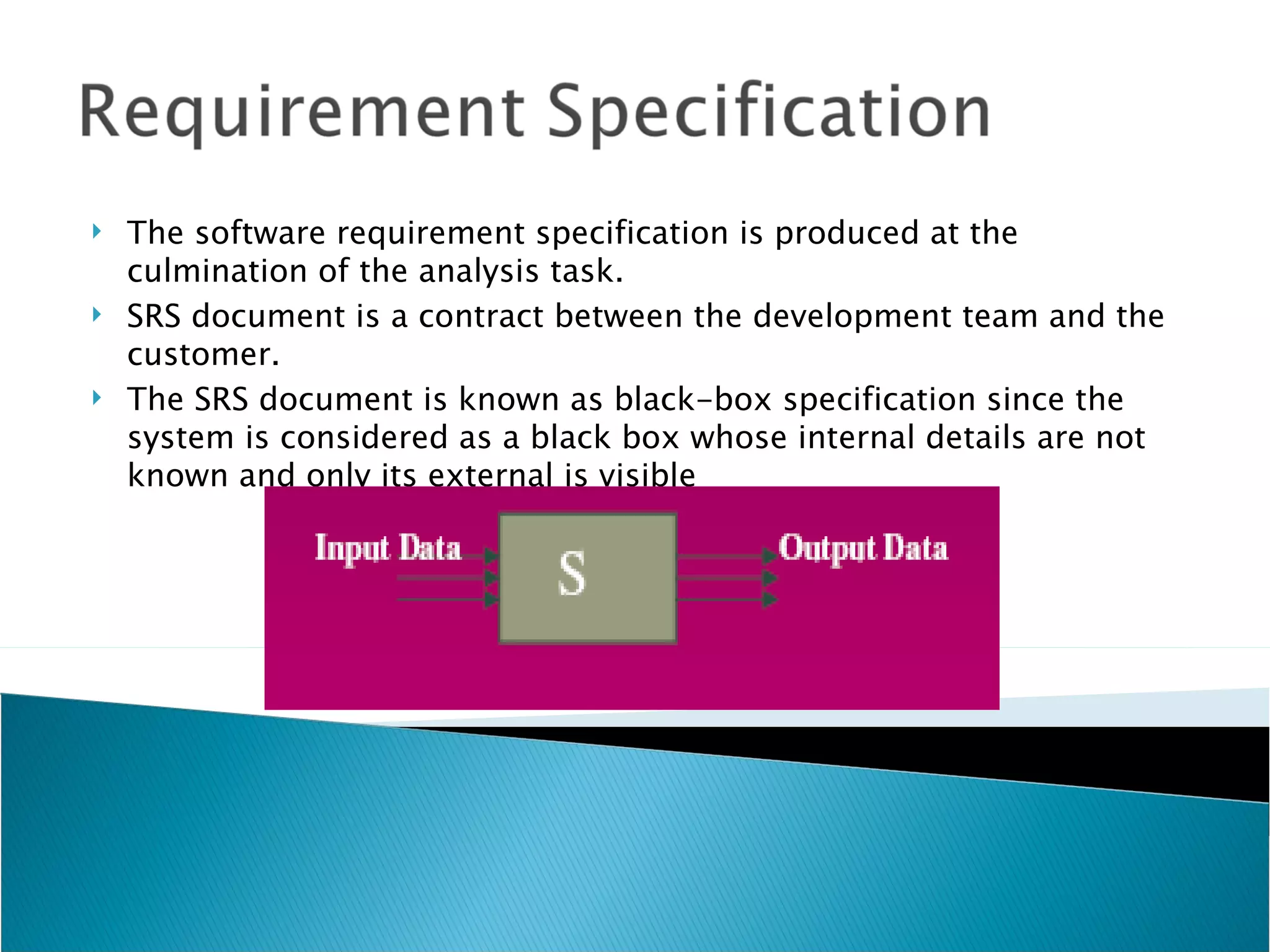
Software requirement engineering bridges the gap between system engineering and software design. It involves gathering requirements through elicitation techniques like interviews and facilitated application specification technique (FAST), analyzing requirements, modeling them, specifying them in documents like use cases, and reviewing the requirements specification. Quality function deployment translates customer needs into technical requirements. Rapid prototyping helps validate requirements by constructing a partial system implementation using tools like 4GLs, reusable components, or formal specification languages. The software requirements specification document is produced at the end of analysis and acts as a contract between developers and customers.