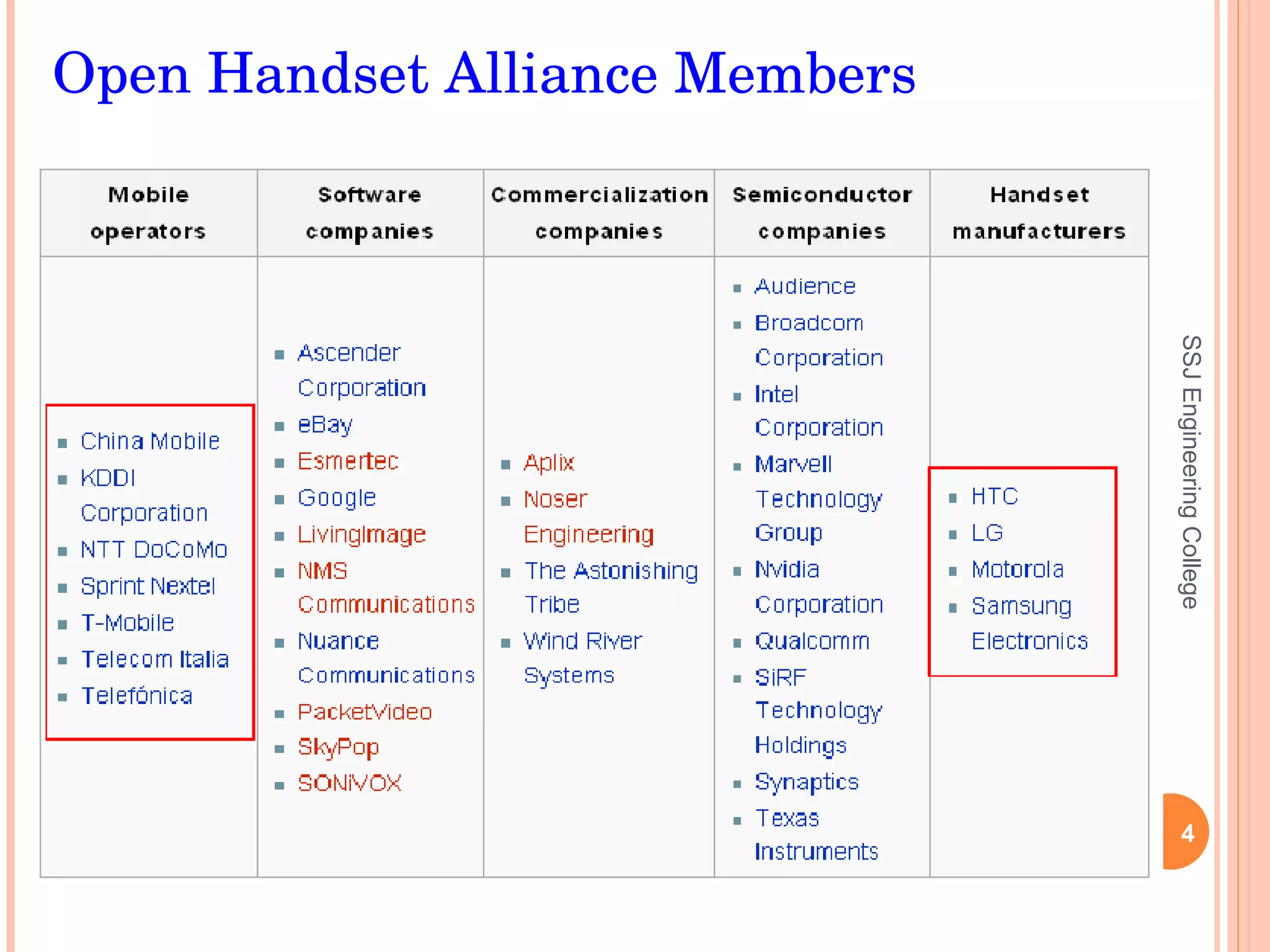
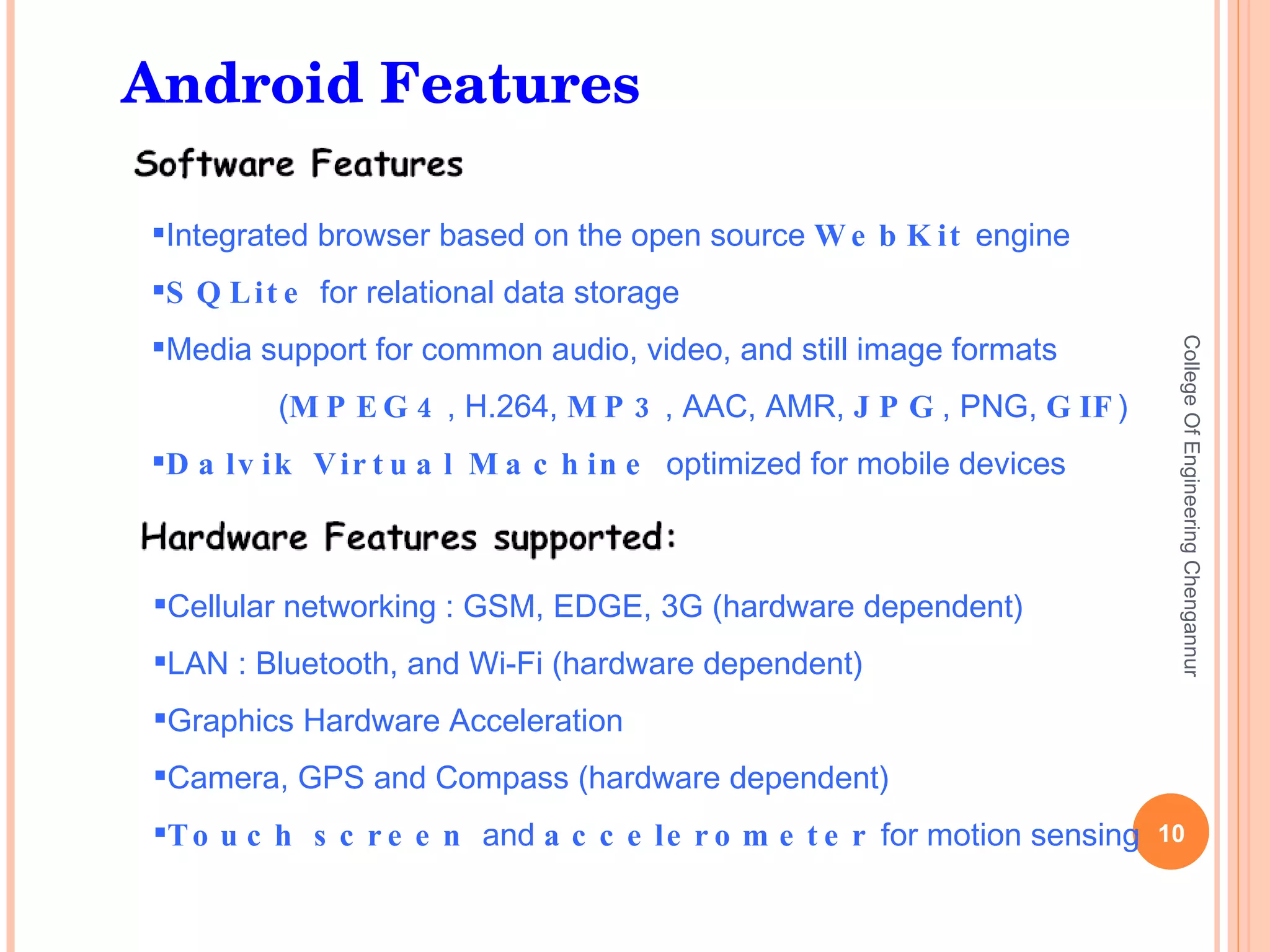
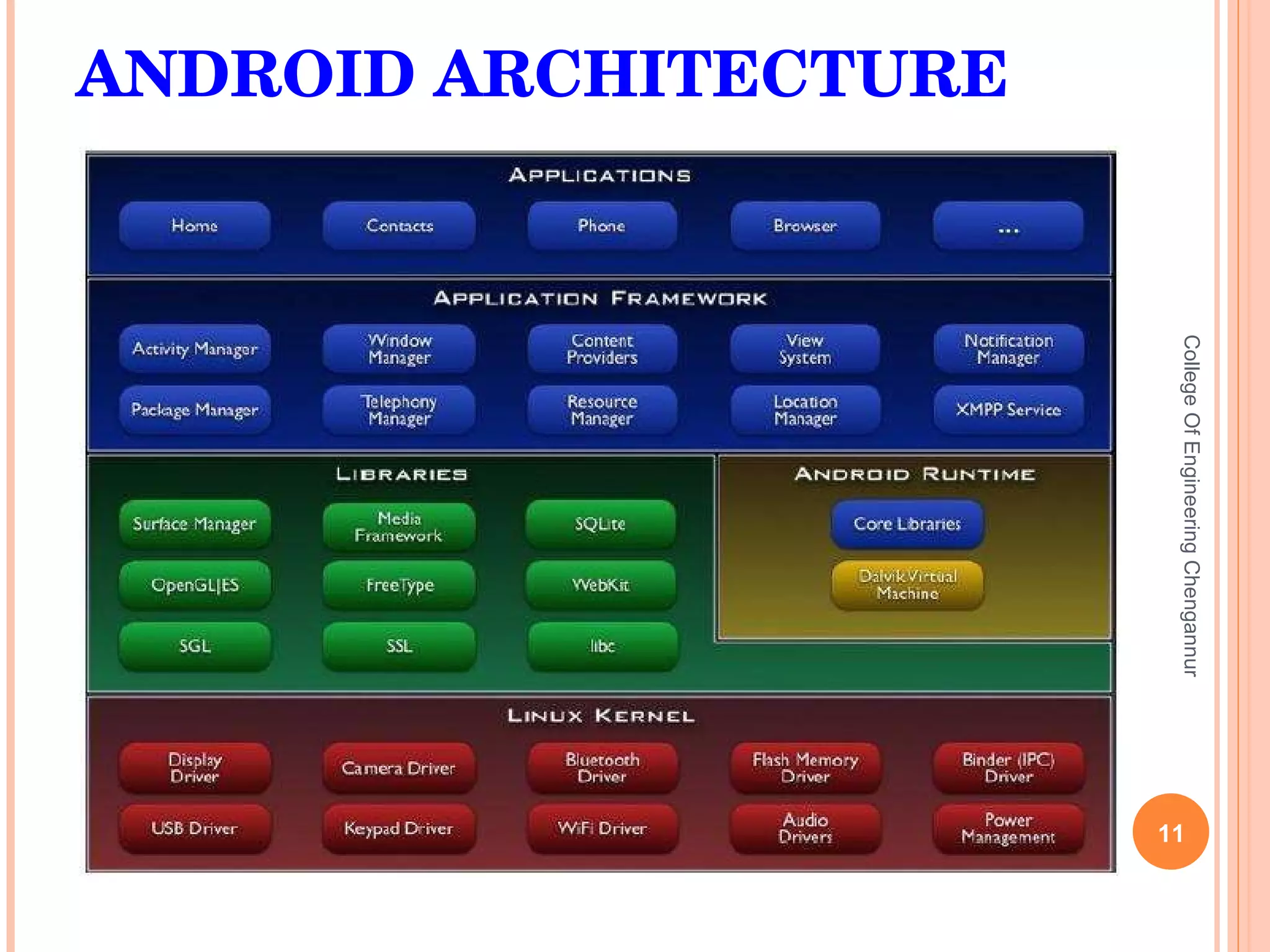
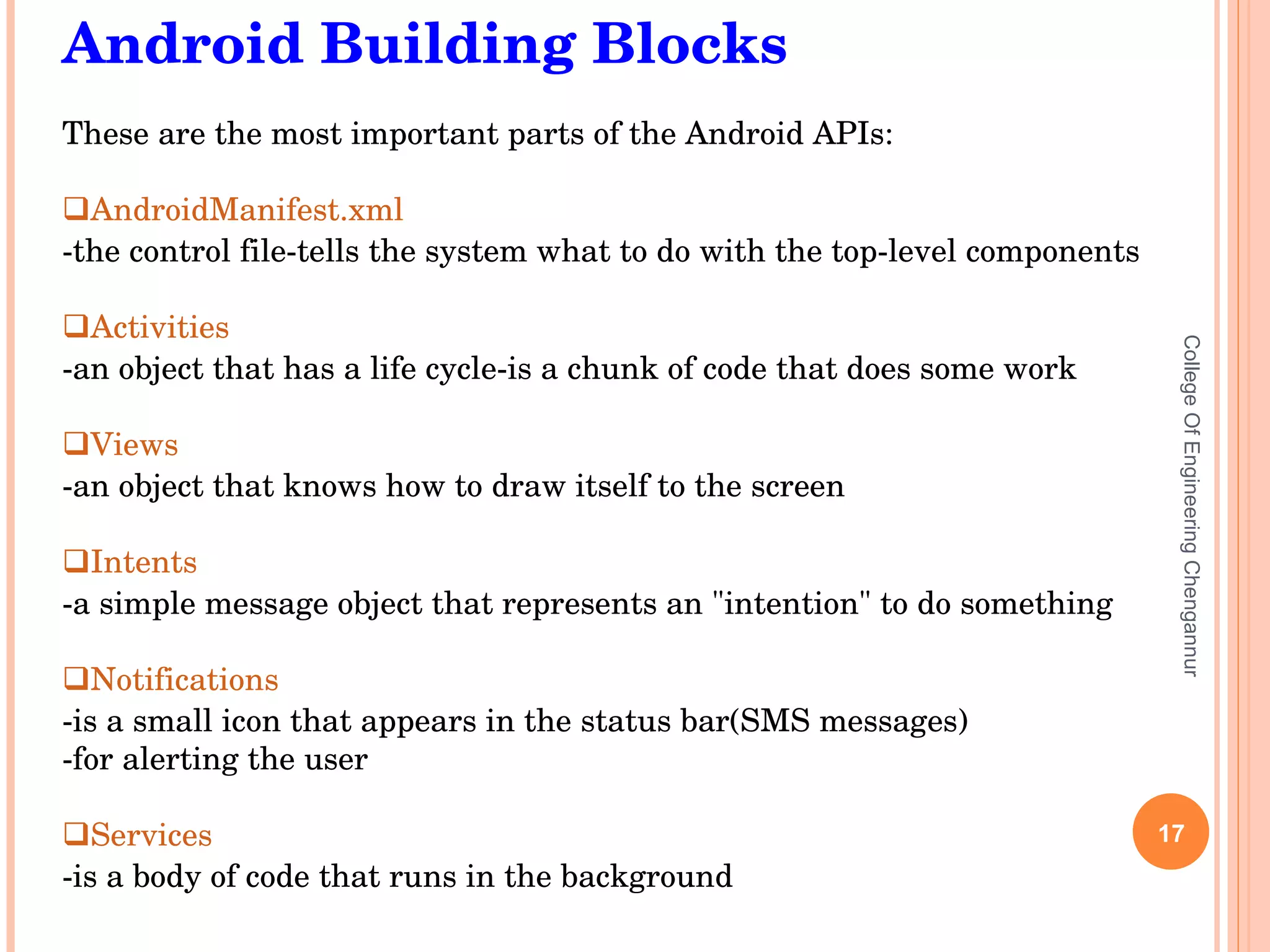
The document discusses the Android open source platform. It provides an overview of the Open Handset Alliance project led by Google to develop Android. Key information presented includes the architecture and building blocks of Android applications, the development tools available, and the lifecycle process Android uses to manage applications and processes based on importance.