The document outlines the configuration and execution flow of Angular modules, detailing how they can be set up before the application starts. It explains the use of constants, values, services, factories, and providers for dependency injection and data sharing across components. Additionally, it describes the ngRoute module for handling routing within an Angular app, showcasing how to define routes and templates.


![This phase is the only part of the Angular flow that can
be modified before the app starts up.
The only services that can be injected in this block
are and ;
angular
.module('myApp', [])
.config(['provider', 'constant', function(provider, constant){
//Configuration logic
}]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-3-2048.jpg)
![Executed at begining of the application;
Similar with the in other programming
languages;
Any service can be injected here.
angular
.module('myApp', [])
.config(function(){})
.run(['$rootScope', function($rootScope){
$rootScope.globalValue = 'Global Foo';
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-4-2048.jpg)



![angular
.module('myApp', [])
.constant('apiUrl', 'http://localhost:8080')
.config(['apiUrl', function(apiUrl){
//apiUrl can be used here
}])
.run(['$rootScope', function($rootScope){
//apiUrl can be used here
}]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-8-2048.jpg)

![angular
.module('myApp', [])
.value('objectValue', {
foo: 'bar',
setFoo: function(val){
this.foo = val;
}
})
.config(function(){
//objectValue can not be injected here
})
.run(['$rootScope', 'objectValue',
function($rootScope, objectValue){
$rootScope.foo = objectValue.foo;
$rootScope.changeFoo = function(val){
objectValue.setFoo(val);
};
}
]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-10-2048.jpg)
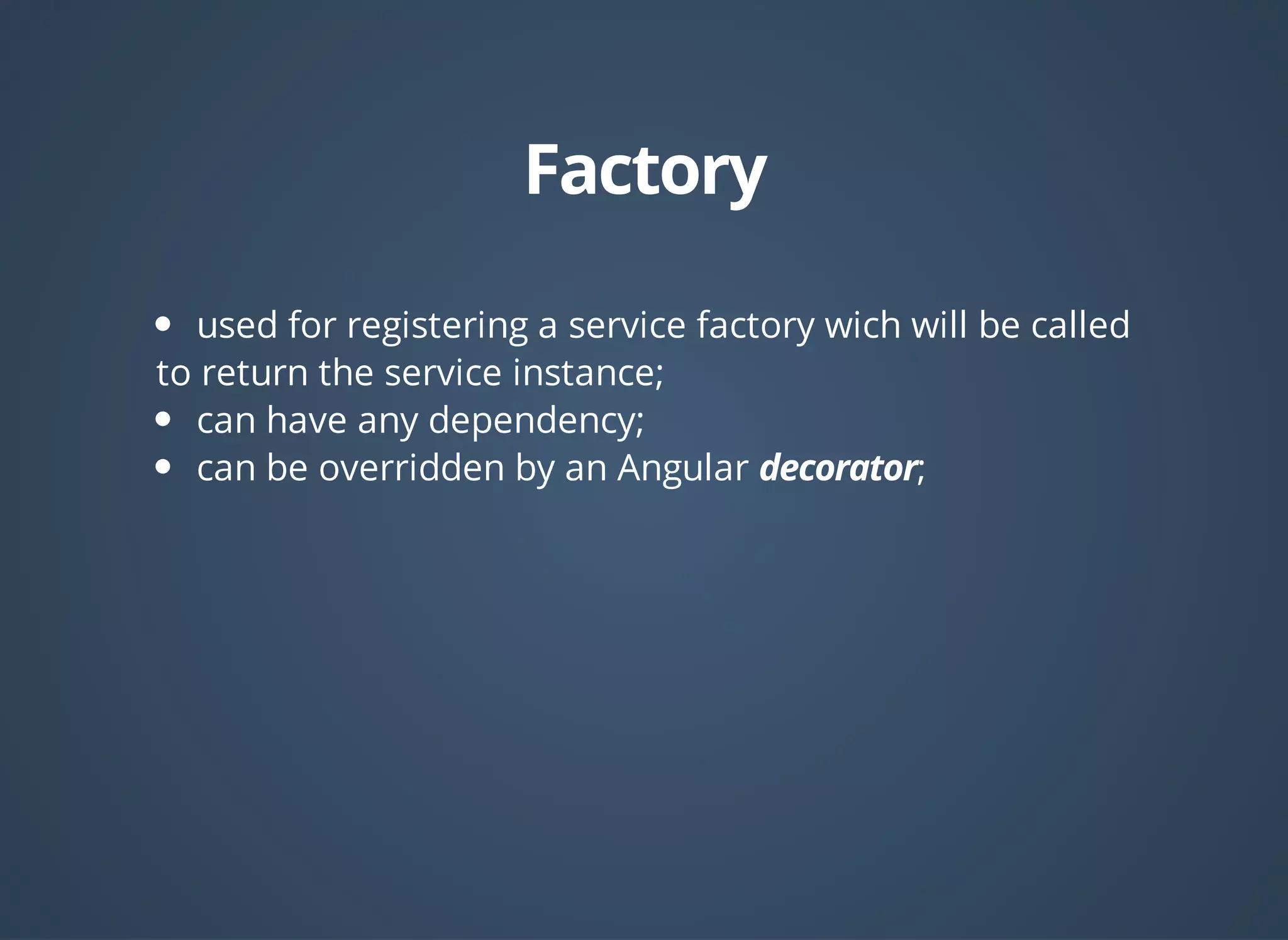
![angular
.module('myApp', [])
.factory('myFactory', function(){
var data; //private variable
return {
fetchData: function(){
//business to populate data
},
getData: function(){
return data;
}
}
})
.run(['$rootScope', 'myFactory',
function($rootScope, myFactory){
myFactory.fetchData();
$rootScope.data = myFactory.getData()
}
]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-12-2048.jpg)
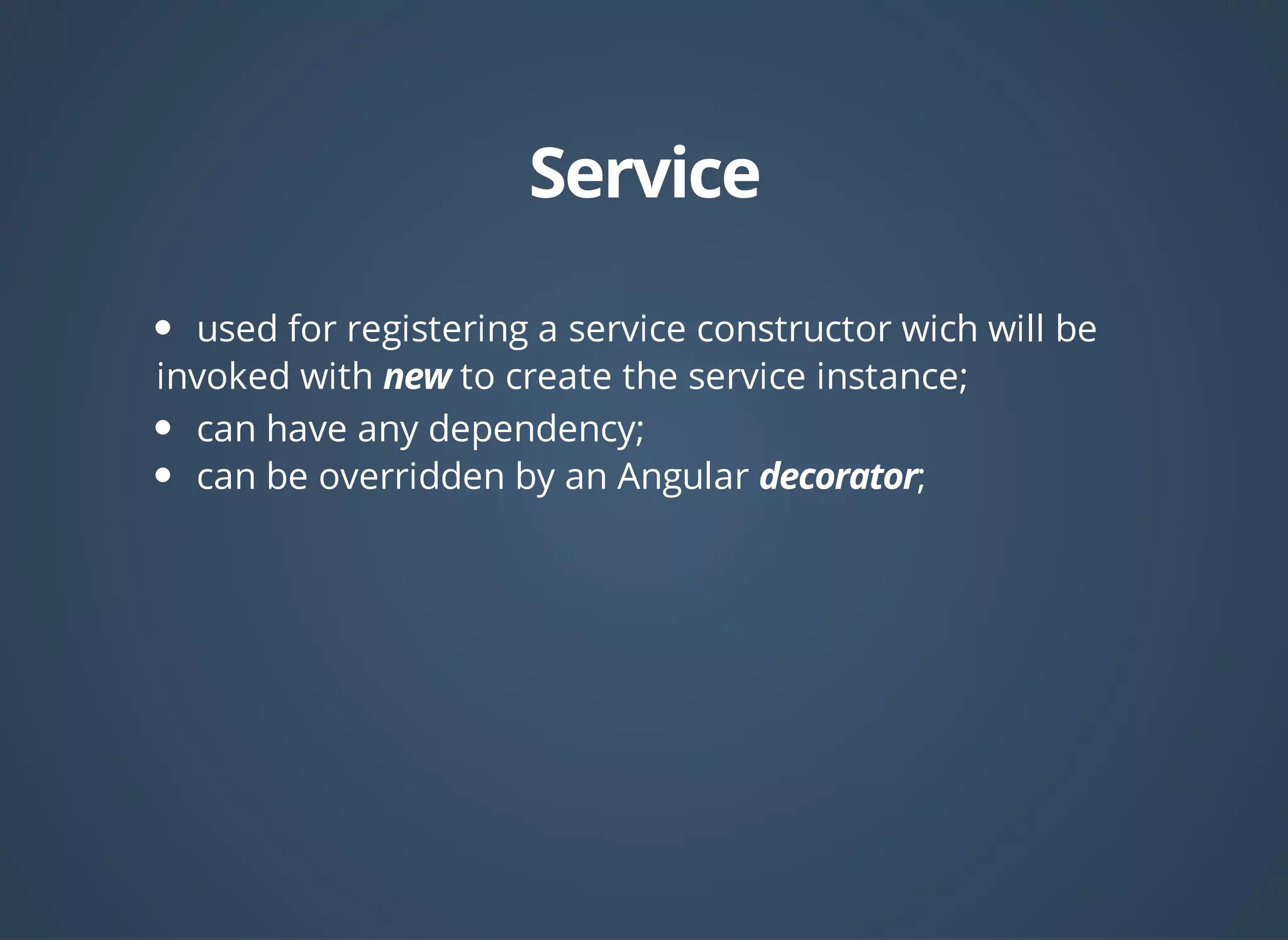
![angular
.module('myApp', [])
.service('myService', function(){
var data; //private variable
this.fetchData= function(){
//business to populate data
};
this.getData= function(){
return data;
};
})
//Same as
.factory('myService', function(){
var Service = function(){
var data; //private variable
this.fetchData= function(){
//business to populate data
};
this.getData= function(){
return data;
};
};
return new Service();
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-14-2048.jpg)

![angular
.module('myApp', [])
.provider('myFactory', function(){
var configVar = 'value';
//The factory Service - can have any dependency
this.$get = [function(){
var data; //private variable
return{
fetchData: function(){
//business to populate data
},
getData: function(){
return data;
}
};
}];
//Config method
this.config = function(config){
configVar = config;
};
})
.config(['myFactoryProvider', function(myFactoryProvider){
myFactoryProvider.config('Overriden value');
}])
.run(['$rootScope', 'myFactory',
function($rootScope, myFactory){
myFactory.fetchData();
$rootScope.data = myFactory.getData()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-16-2048.jpg)


![angular
.module('myApp', [])
.factory('myFactory', function(){
//implementation here
})
.config(['$provide', function($provide){
$provide.decorator('myFactory', ['$delegate', function($delegate){
//$delegate is the original service instance
//add a new method
$delegate.newMethod = function(){
return 'This method was added by the decorator';
};
//return the original decorated method
return $delegate;
}]);
}]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-19-2048.jpg)



![angular
.module('myApp', ['ngRoute'])
.config(['$routeProvider', function($routePro
$routeProvider
.when('/', {
template: '<h2>{{page}}</h2>',
controller: ['$scope', function($
$scope.page = 'home';
}]
})
.when('/about', {
template: '<h2>{{page}}</h2>',
controller: ['$scope', function($
$scope.page = 'about';
}]
})
.otherwise({redirectTo: '/'});
}]);
<html ng-app="myApp">
<head>...</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>My app</h1>
<ul>
<li><a href="#/">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#/about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</header>
<div class="content">
<div ng-view></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Plunker Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular-dependency-injection-140812031940-phpapp01/75/AngularJS-dependency-injection-23-2048.jpg)
