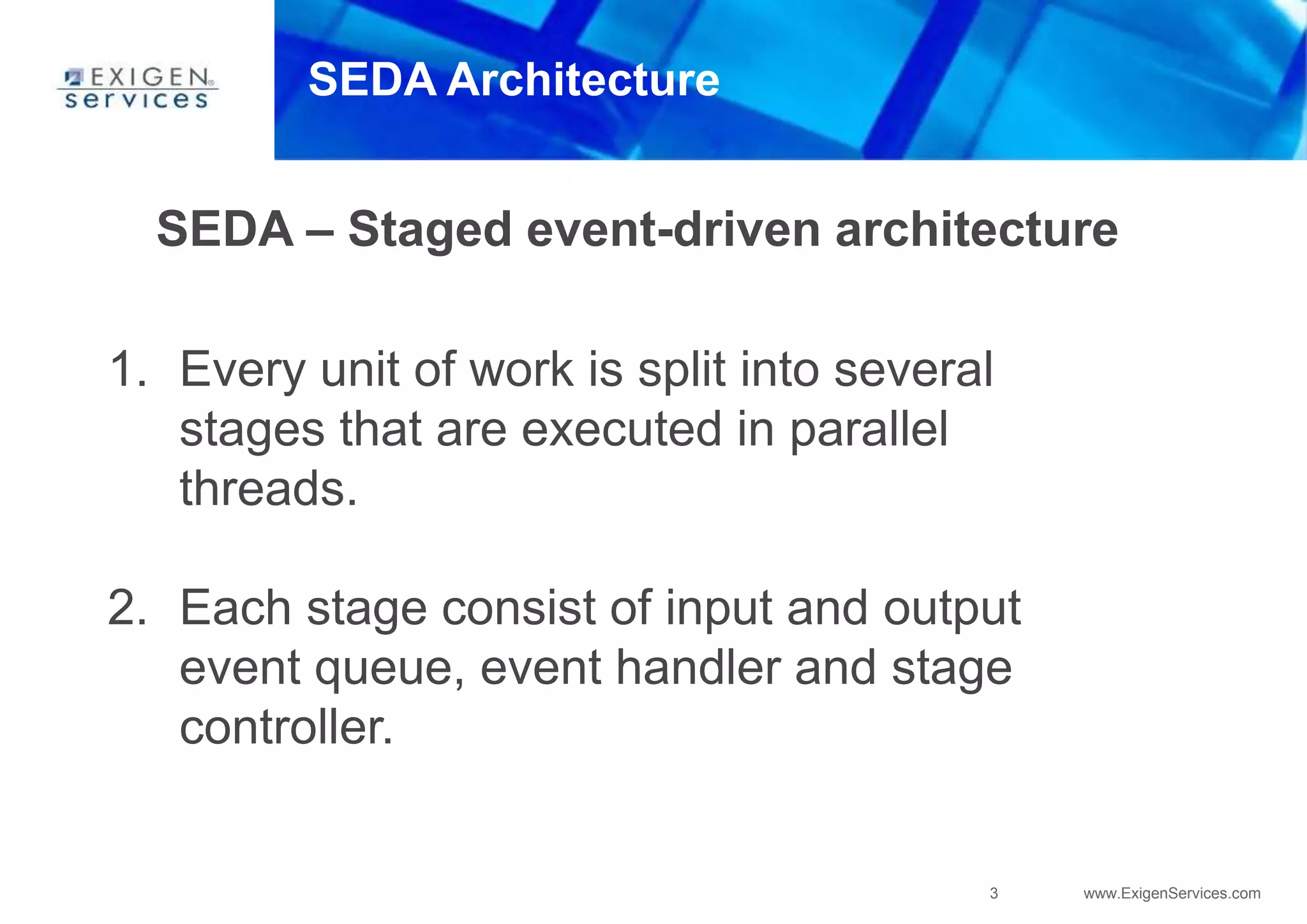
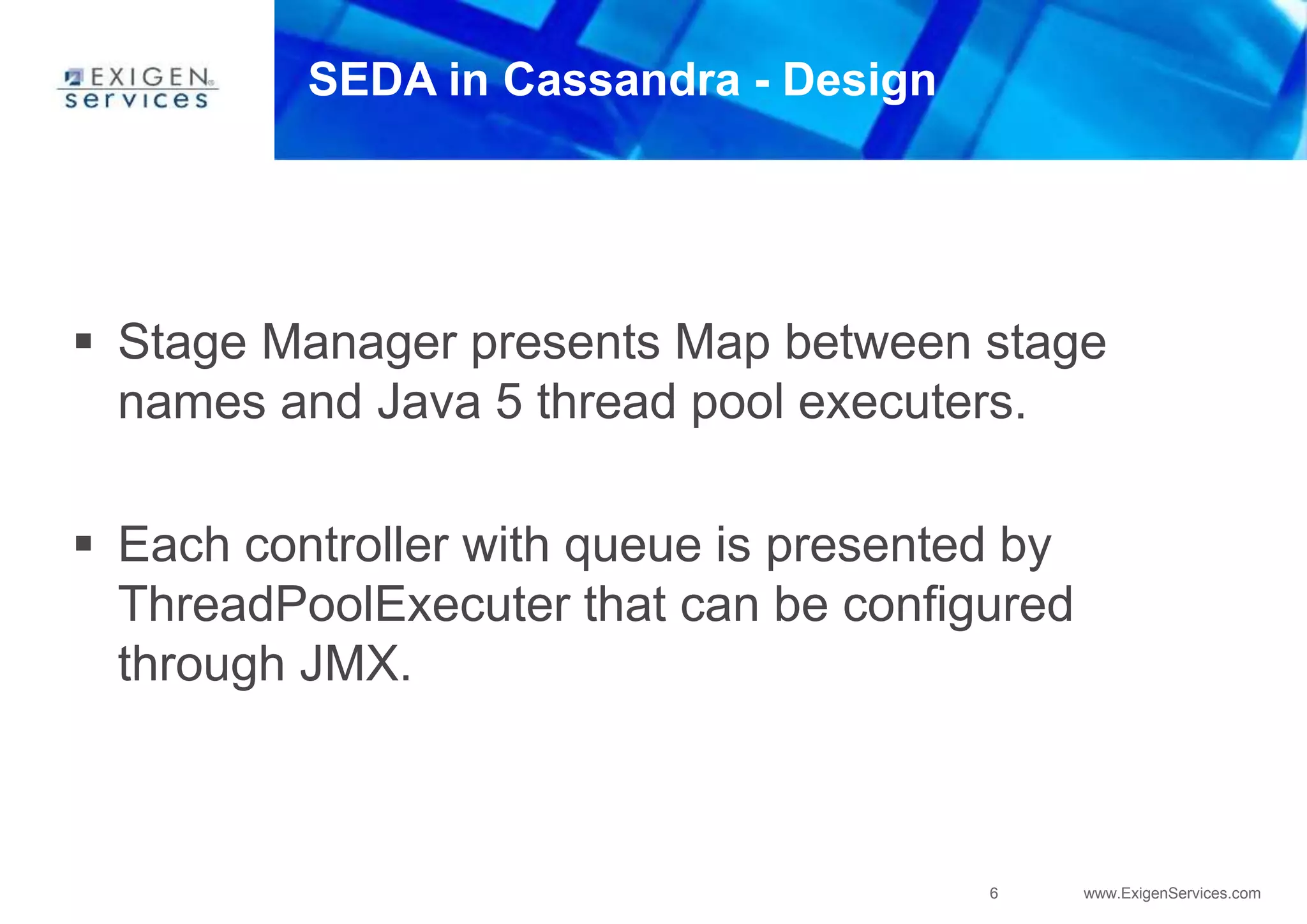
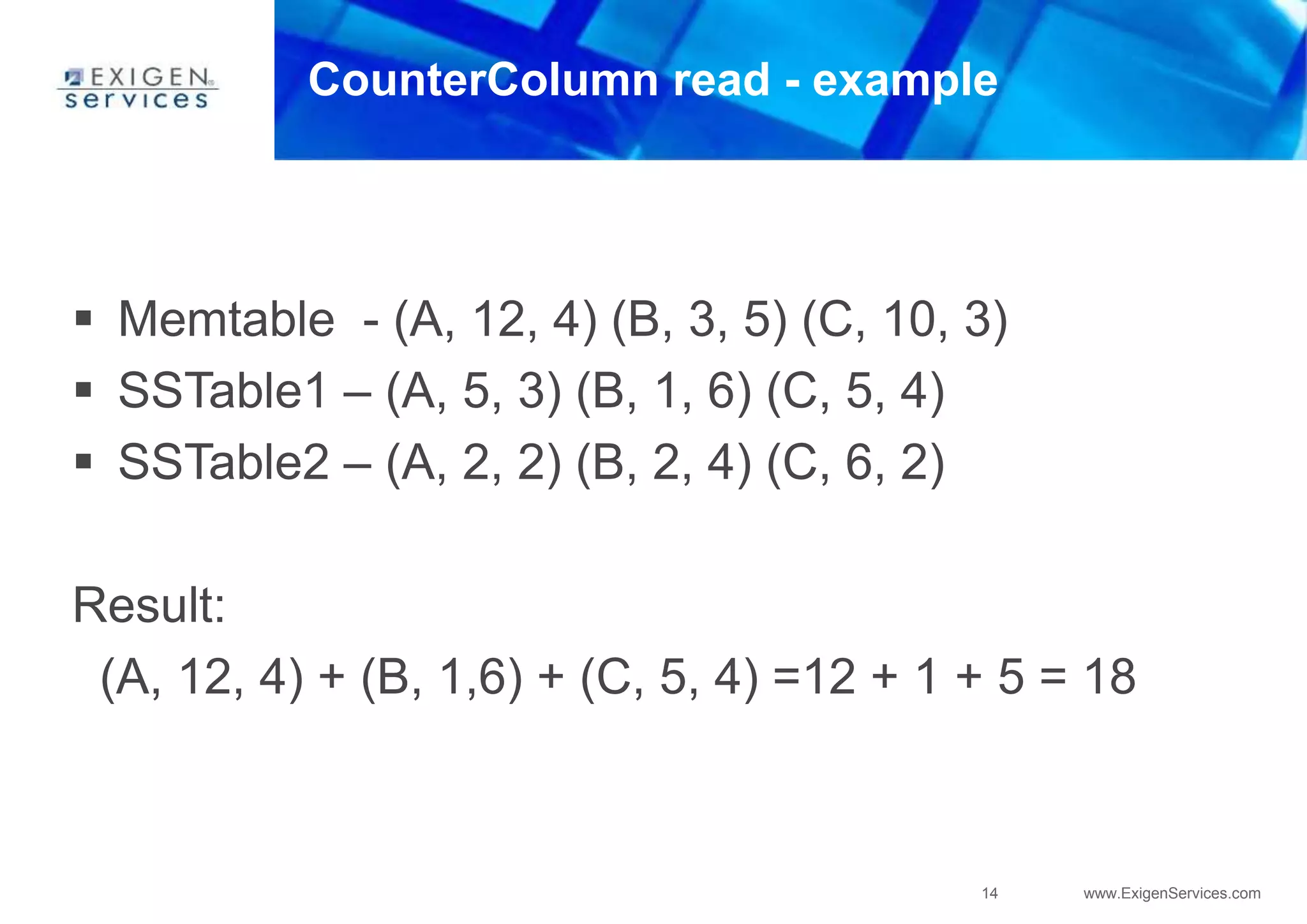
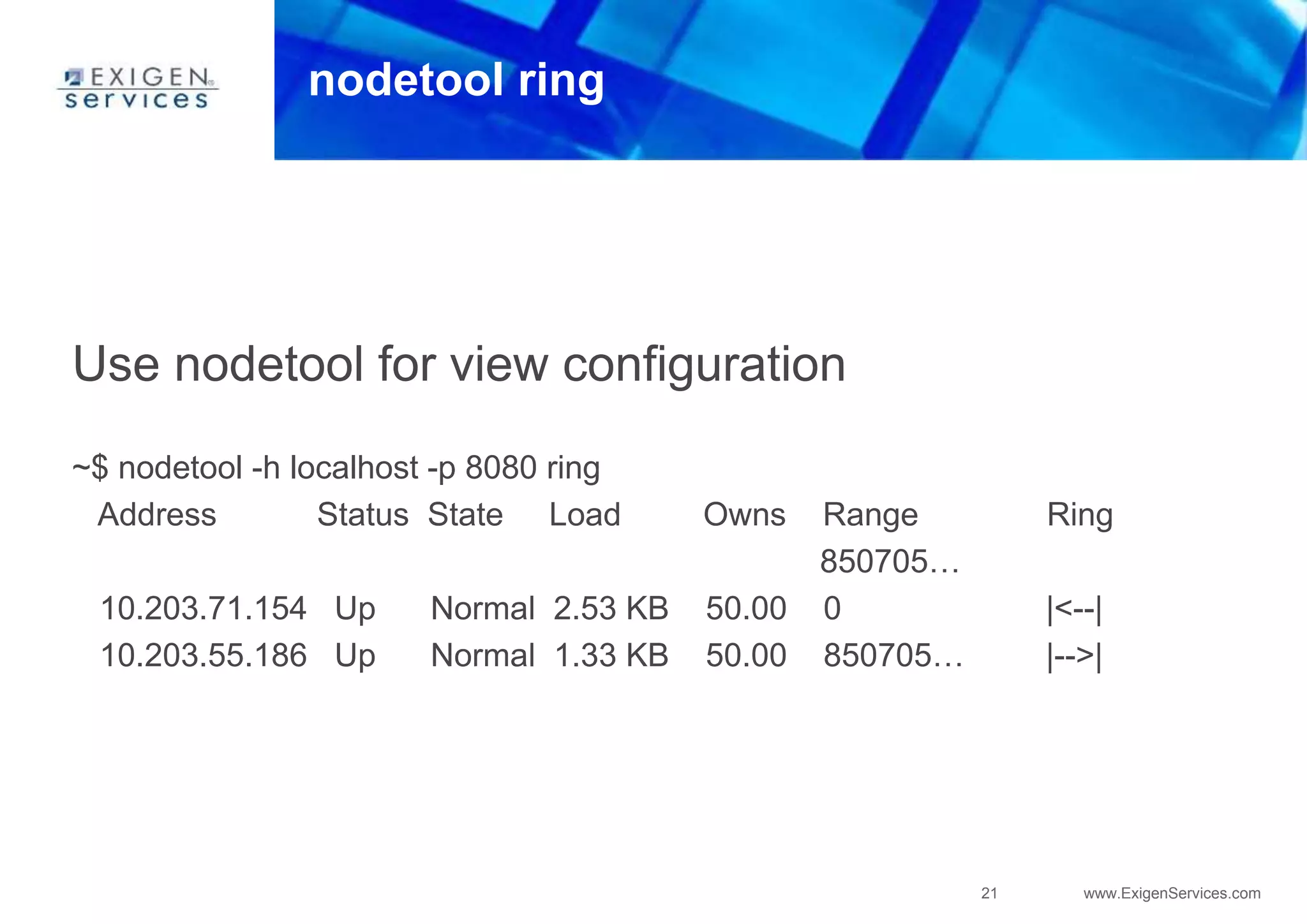
Cassandra uses a SEDA (Staged Event-Driven Architecture) model where work is split into parallel stages. Each stage has input/output queues, an event handler, and a controller. This architecture provides well-conditioned system load and prevents overcommitting resources. In Cassandra, SEDA is used for operations like reads, writes, gossip, and anti-entropy. Counters use a structure containing replica IDs, values, and logical clocks to allow incremental updates across replicas. Secondary indexes allow queries by column values but are currently limited to equality comparisons due to using hash indexes instead of B-trees.





![8 www.ExigenServices.com
TTL column attribute
TTL column is column value of which expires after
given period of time.
Useful to store session token.
set test[row1][col2] = 'val2' with ttl=60;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-8-2048.jpg)

![10 www.ExigenServices.com
CounterColumn internals
CounterColumn structure:
name
…….
[
(replicaId1, counter1, logical clock1),
(replicaId2, counter2, logical clock2),
………………..
(replicaId3, counter3, logical clock3)
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-10-2048.jpg)
![11 www.ExigenServices.com
CounterColumn write (before)
UPDATE CounterCF SET count_me = count_me + 2
WHERE key = 'counter1‘
[
(A, 10, 2),
(B, 3, 4),
(C, 6, 7)
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-11-2048.jpg)
![12 www.ExigenServices.com
CounterColumn write (after)
A is leader
[
(A, 10 + 2, 2 + 1),
(B, 3, 4),
(C, 6, 7)
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-12-2048.jpg)




![18 www.ExigenServices.com
Installing and launching Cassandra
Starting command-line client interface:
bin/cassandra-cli.bat
bin/cassandra-cli.sh
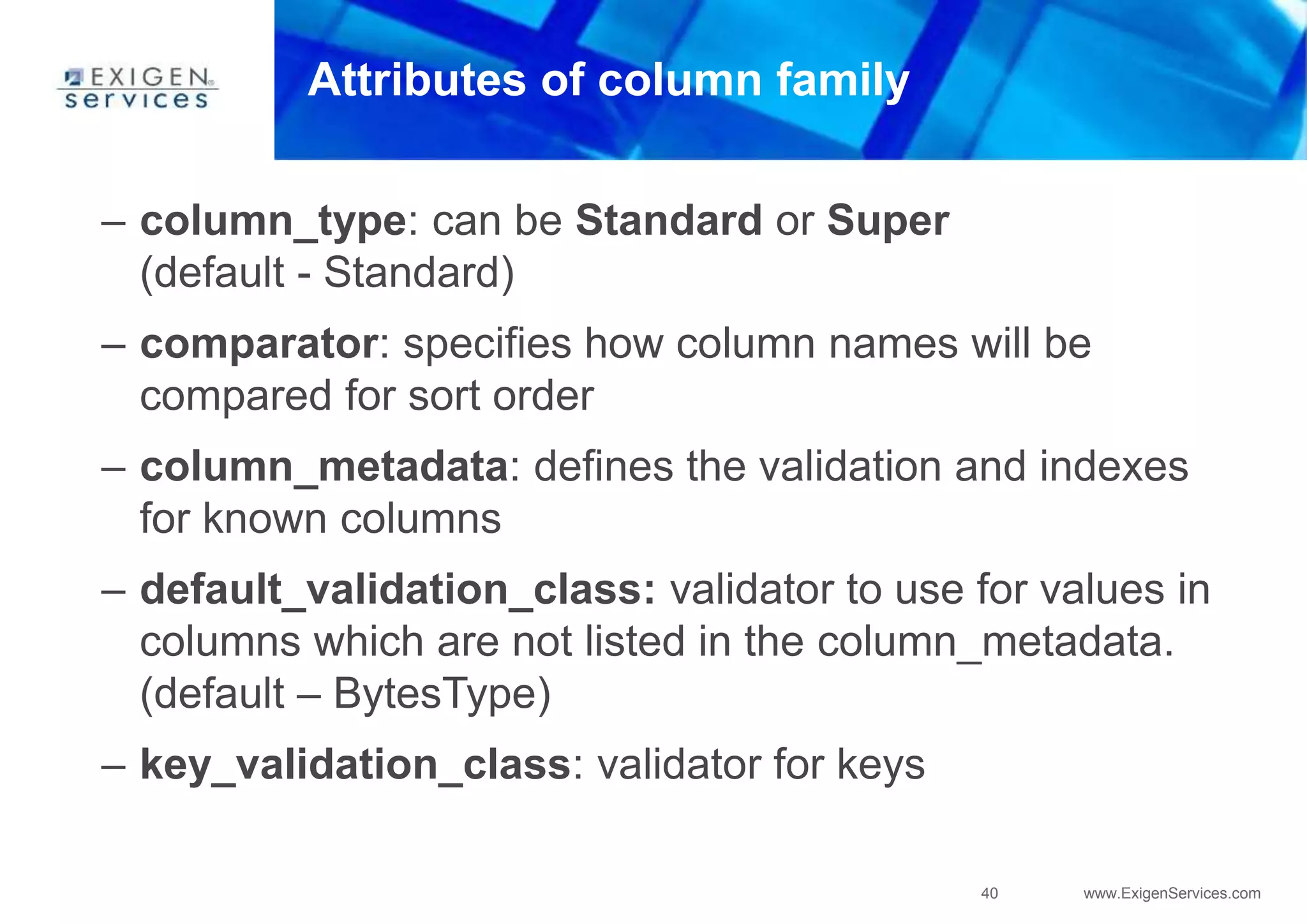
– you see [username@keyspace] at the beginning of every line](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-18-2048.jpg)


![22 www.ExigenServices.com
Connecting to server
Connect from command line:
connect <HOSTNAME>/<PORT> [<USERNAME> ‘<PASSWORD>’];
Examples:
connect localhost/9160;
connect 127.0.0.1/9160 user ‘password’;
Connect when staring command line client:
cassandra-cli
–h,––host <HOSTNAME>
–p,––port <PORT>
–k,––keyspace <KEYSPACE>
–u,––username <USERNAME>
–p,––password <PASSWORD>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-22-2048.jpg)
![23 www.ExigenServices.com
Describing environment
show cluster name;
show keyspaces;
show api version;
describe cluster;
describe keyspace [<KEYSPACE>];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-23-2048.jpg)

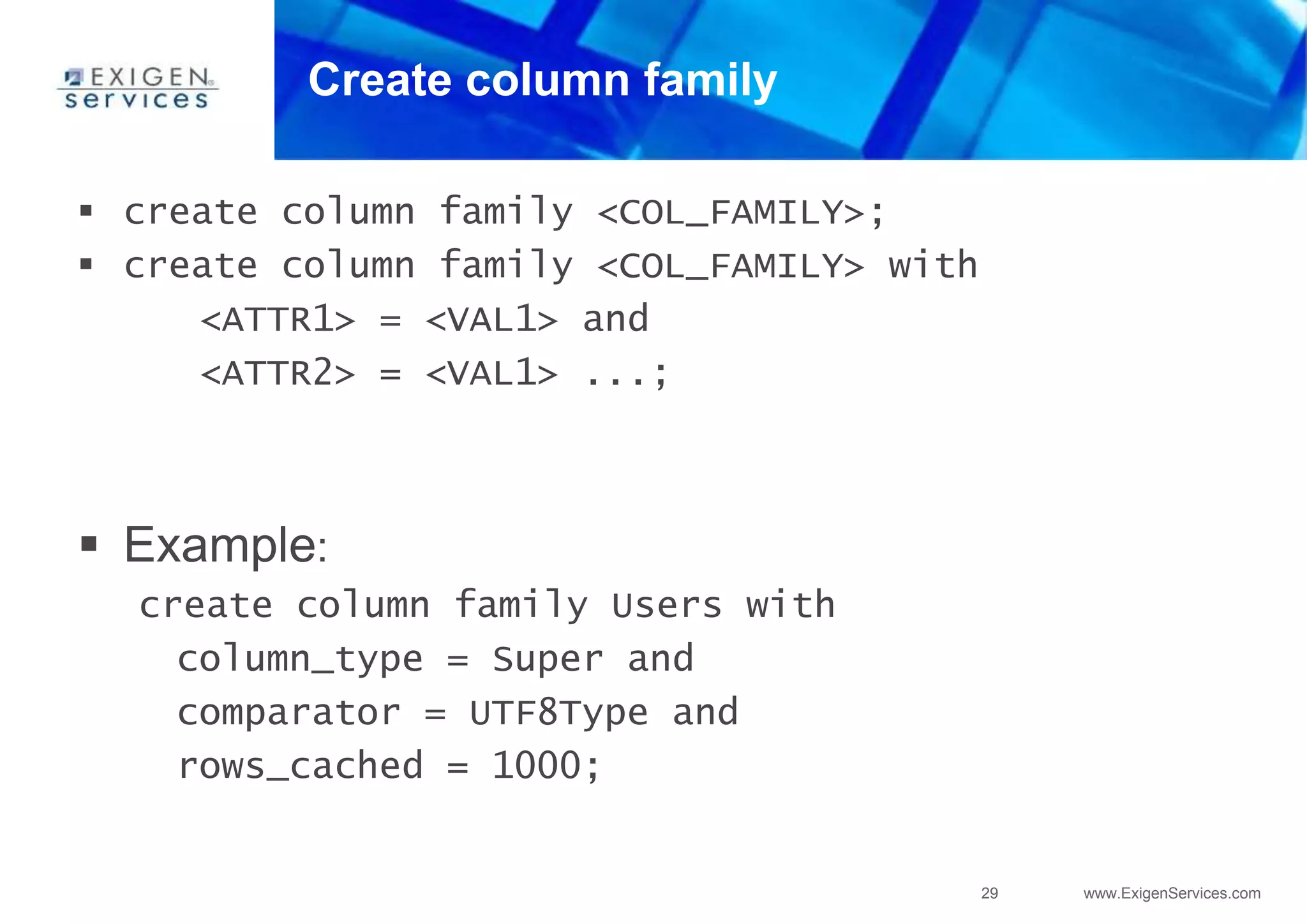
![25 www.ExigenServices.com
Create keyspace
Example:
create keyspace Keyspace1
with placement_strategy =
‘org.apache.cassandra.locator.NetworkTopologyStrategy’
and strategy_options =
[{replication_factor: 4}];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-25-2048.jpg)

![27 www.ExigenServices.com
Switch to keyspace
use <KEYSPACE>;
use <KEYSPACE> [<USERNAME> ‘<PASSWORD>’];
If you don’t specify username and password then
credentials supplied to the ‘connect’ statement will
be used
If the server doesn’t support authentication it will
ignore credentials](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-27-2048.jpg)
![28 www.ExigenServices.com
Switch to keyspace
Example:
use Keyspace1 user1 ‘qwerty123’;
When you use keyspace you’ll see [user1@Keyspace1] at the
beginning of every line](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-28-2048.jpg)

![31 www.ExigenServices.com
Writing data
To write data use set command:
set Customers[‘ivan’][‘name’] = ‘Ivan’;
set Customers[‘makar’][‘info’][‘age’] = 96;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-31-2048.jpg)
![32 www.ExigenServices.com
Reading data
To read data use get command:
get Customers[‘ivan’][‘name’];
- this will display ‘Ivan’
get Customers[‘makar’];
- this will display all columns for key ‘makar’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-32-2048.jpg)
![33 www.ExigenServices.com
Reading data
To list a range of rows use list command:
list Customers;
list Customers[a:];
list Customers[a:c] limit 40;
- you can specify limit of rows that will be displayed (default - 100)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-33-2048.jpg)
![34 www.ExigenServices.com
Reading data
To get columns number use count command:
count Customers[‘ivan’]
- this will display number of columns for key ‘ivan’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-34-2048.jpg)
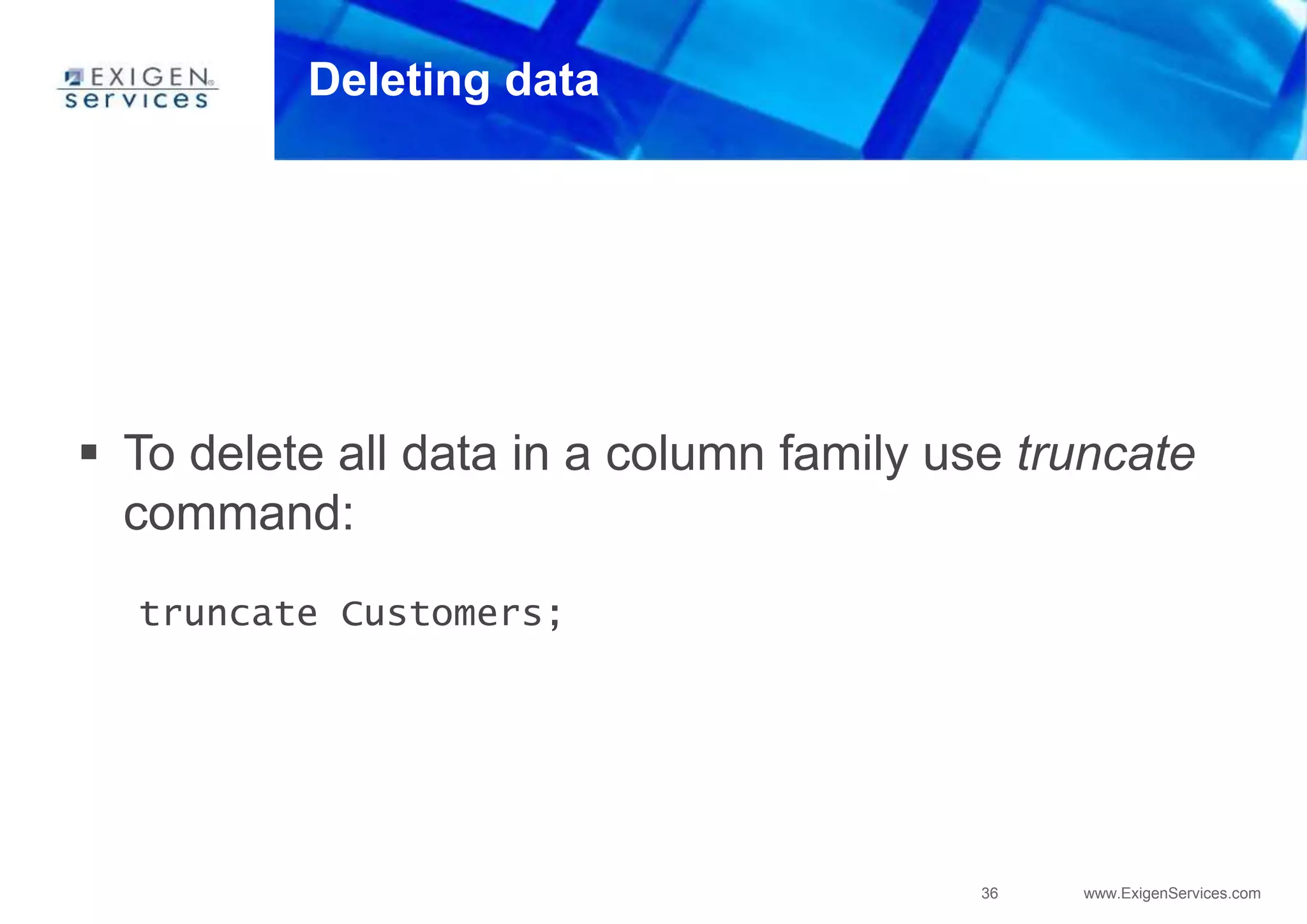
![35 www.ExigenServices.com
Deleting data
To delete a row, a column or a subcolumn use del
command:
del Customers[‘ivan’];
- this will delete all columns for key ‘ivan’
del Customers[‘ivan’][‘name’];
- this will delete column name for key ‘ivan’
del Customers[‘ivan’][‘accounts’][‘2312784829312343’];
- this will delete a subcolumn with an account number from ‘accounts’
column for key ‘ivan’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-35-2048.jpg)



![41 www.ExigenServices.com
Column metadata
You can define validators for each known column in the
family
create column family User
with column_metadata = [
{column_name: name, validation_class: UTF8Type},
{column_name: age, validation_class: IntegerType},
{column_name: birth, validation_class: UTF8Type}
];
Columns not listed in this section are validated with
default_validation_class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-41-2048.jpg)

![43 www.ExigenServices.com
Creating index
Define it in column metadata
For example in cassandra-cli:
create column family users with
comparator=UTF8Type and column_metadata=[{
column_name: birth_date,
validation_class: LongType,
index_type: KEYS
}];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecassandra-futurewithoutboundariespart3-150806104545-lva1-app6892/75/Apache-cassandra-future-without-boundaries-part3-43-2048.jpg)




