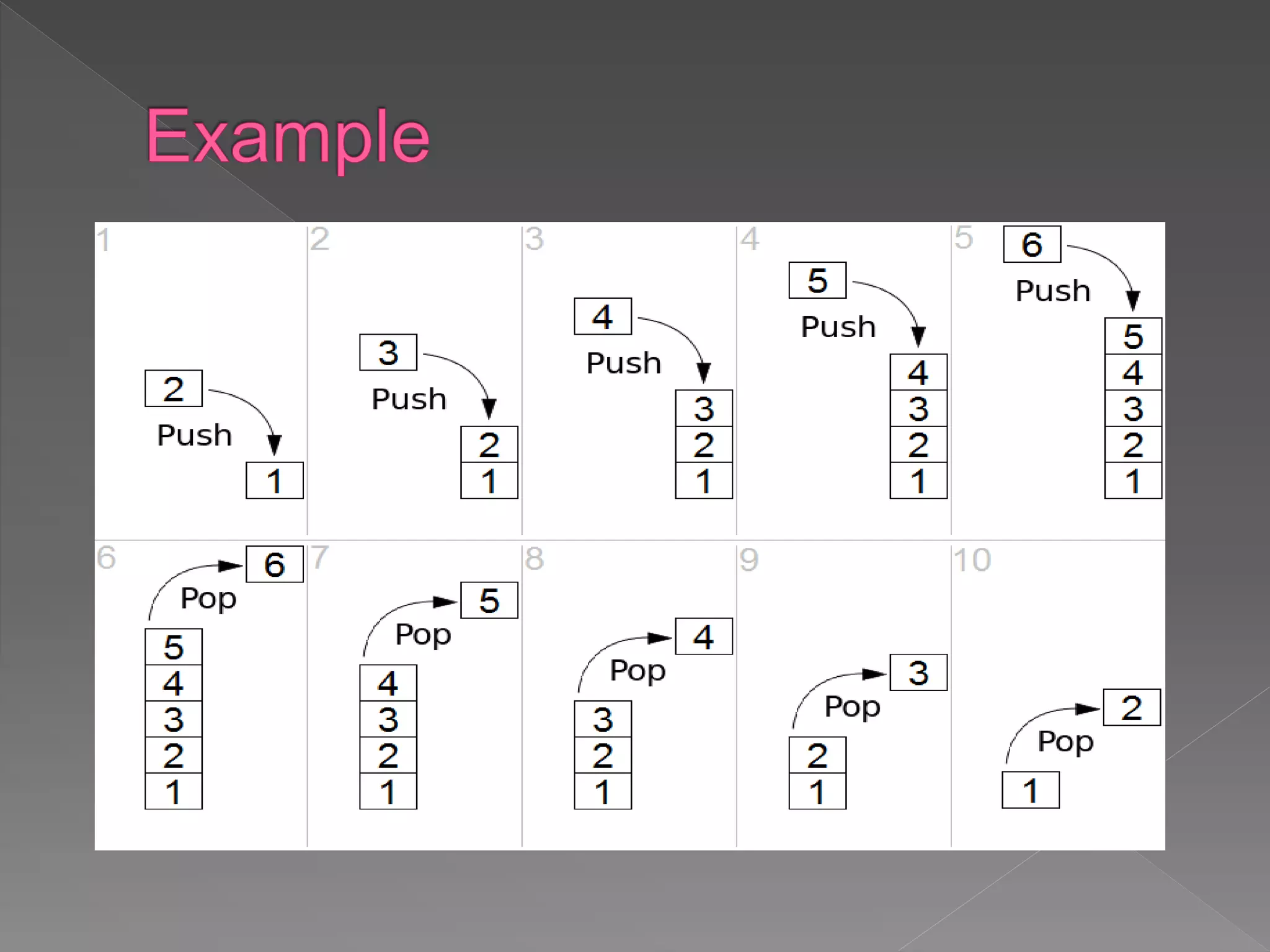
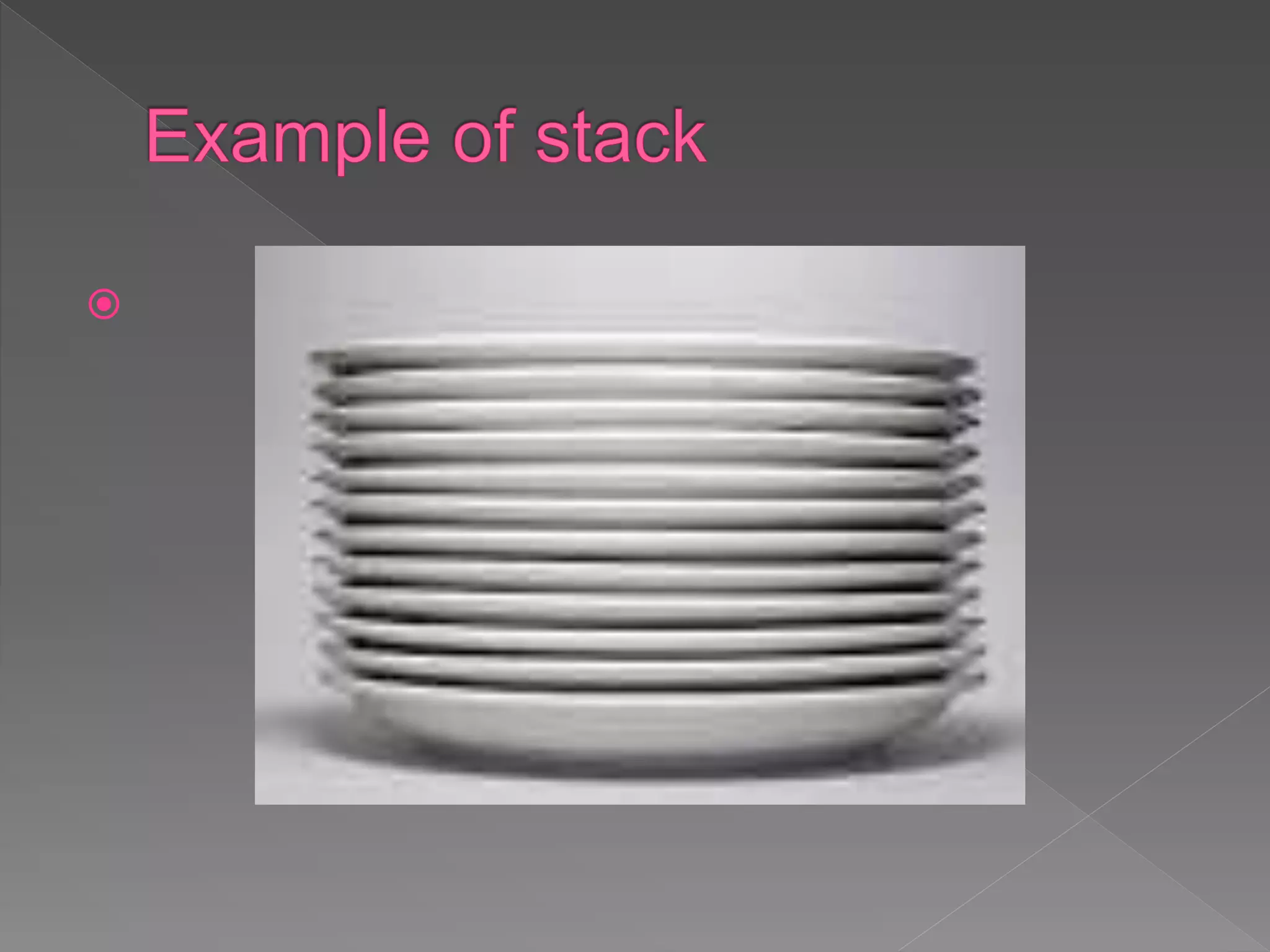
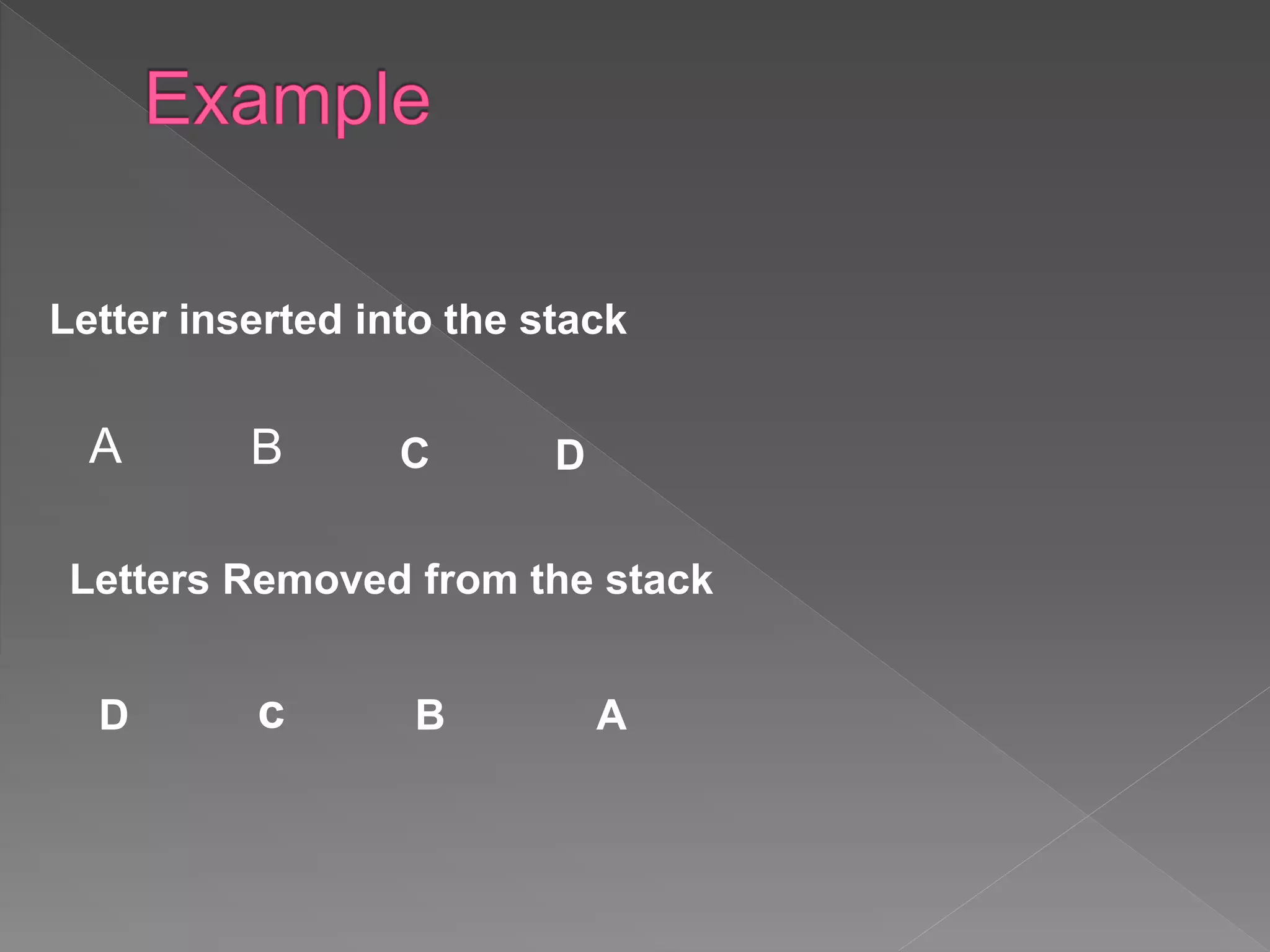
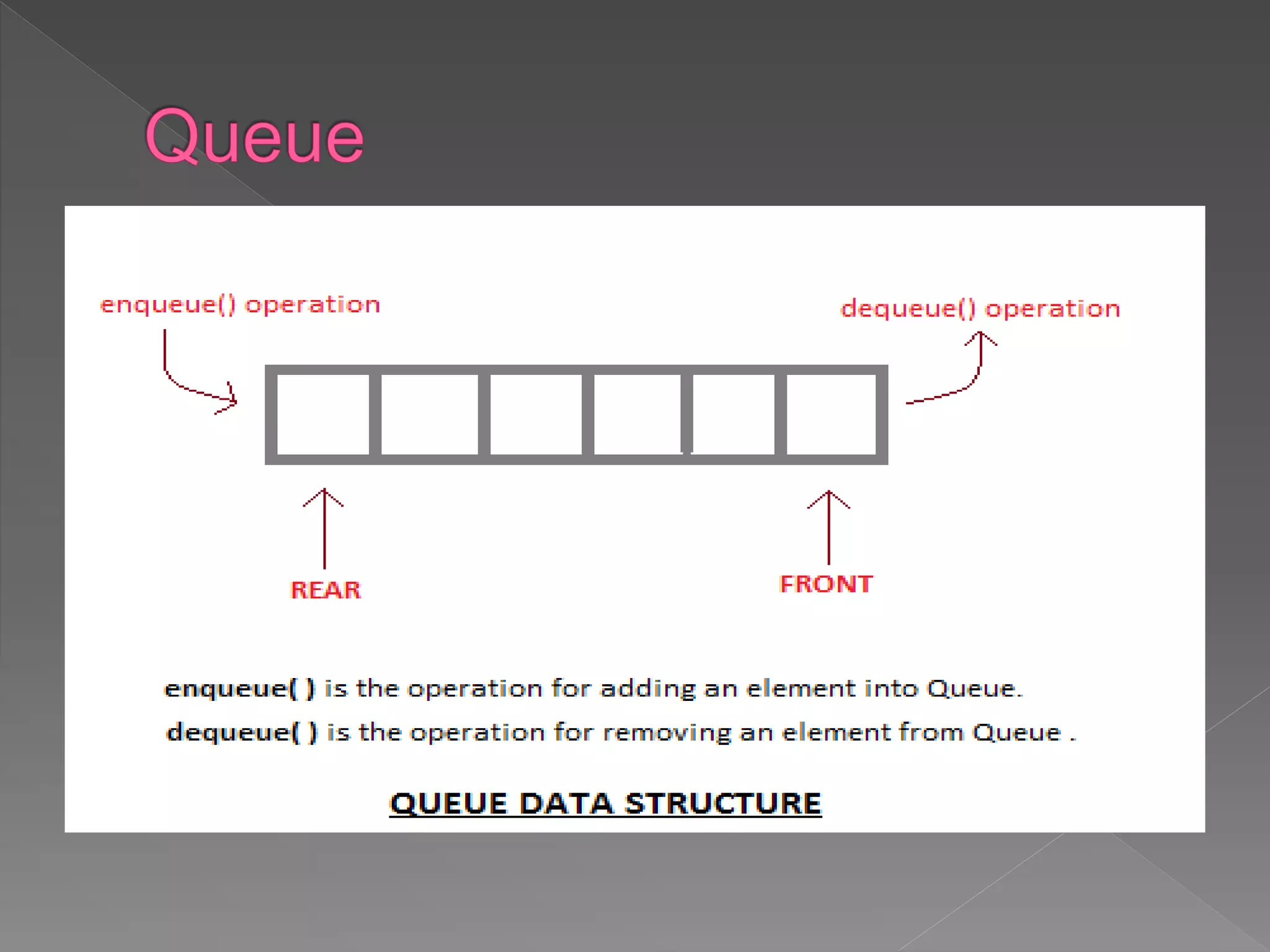
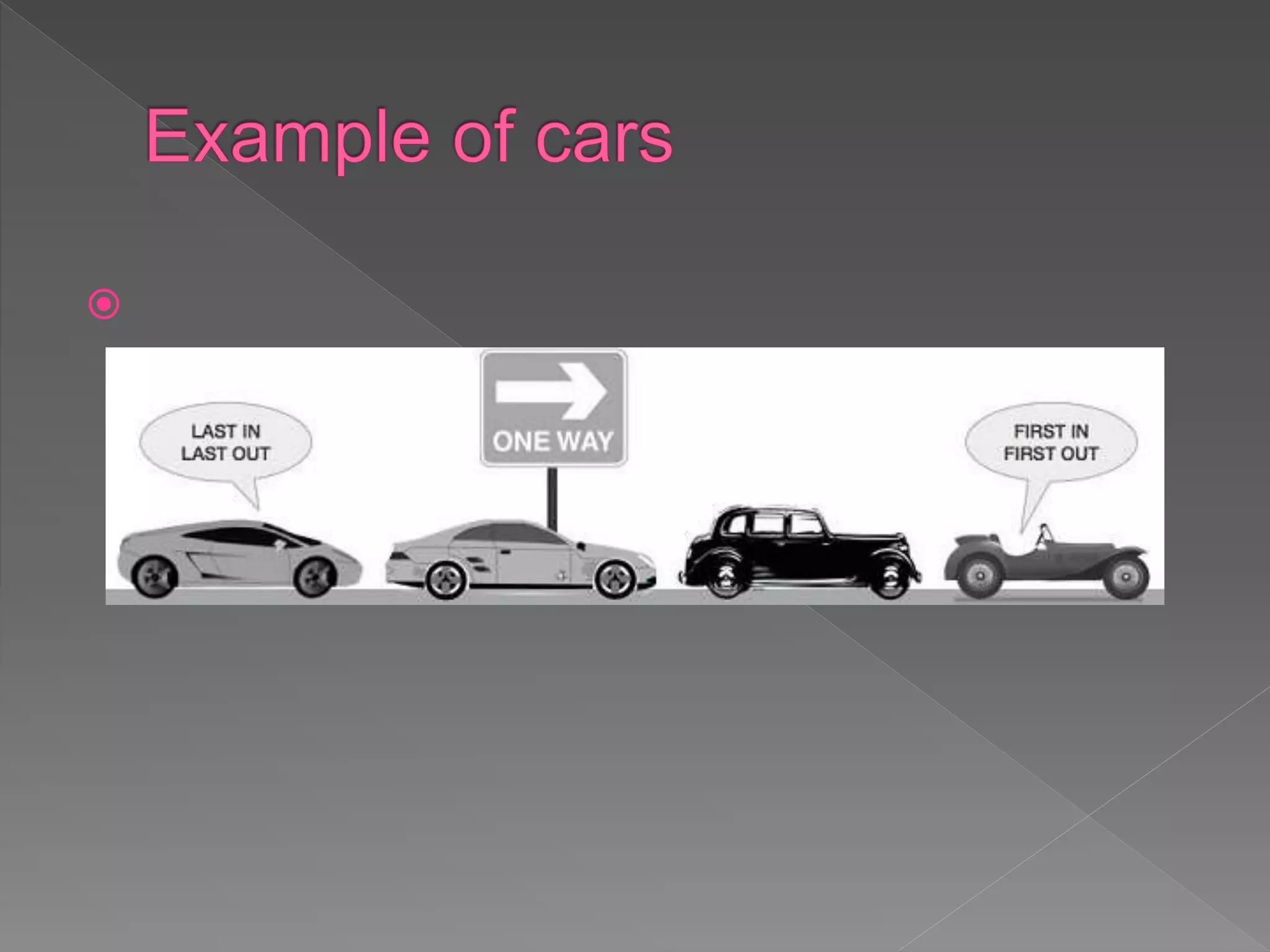
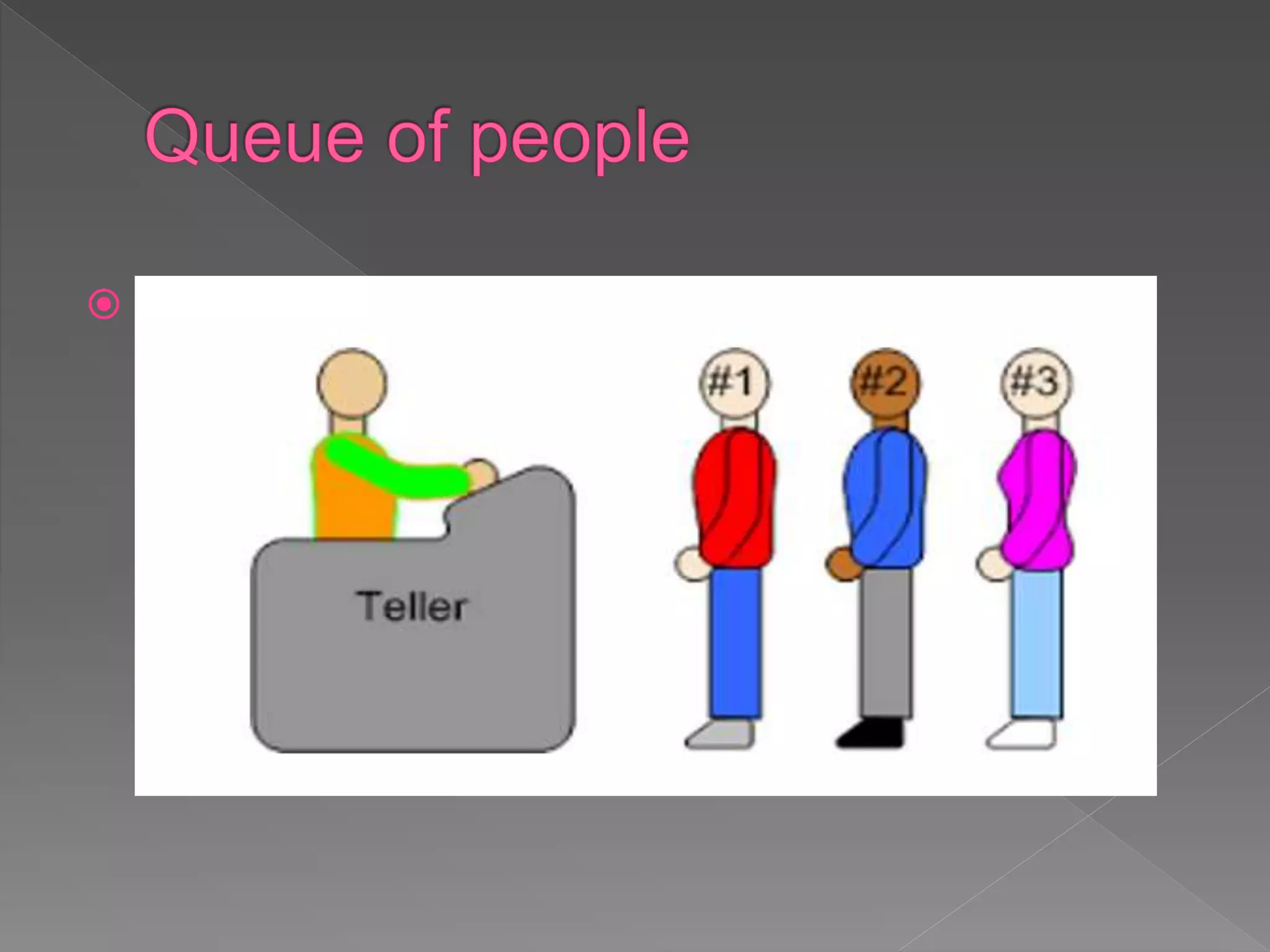
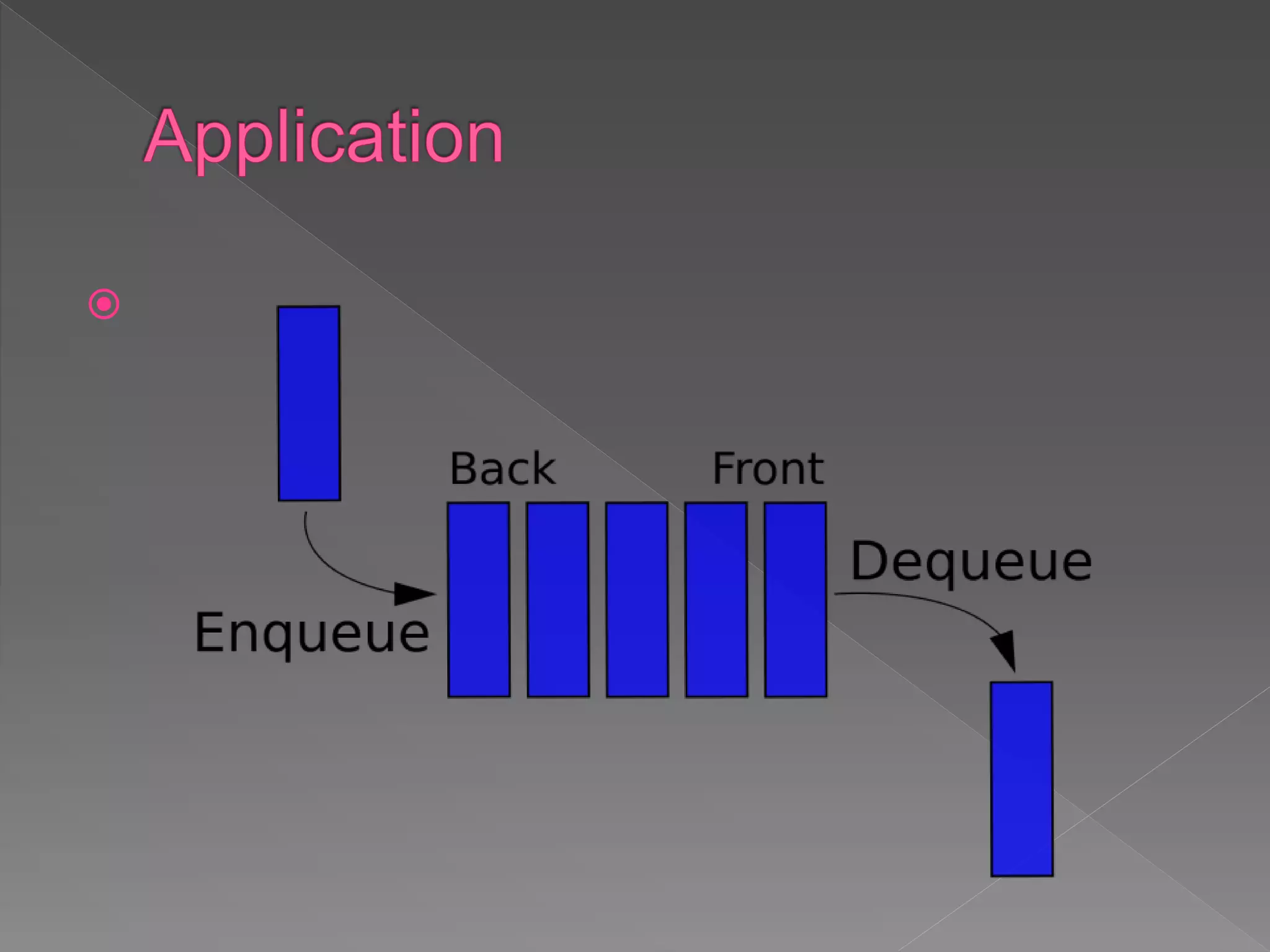
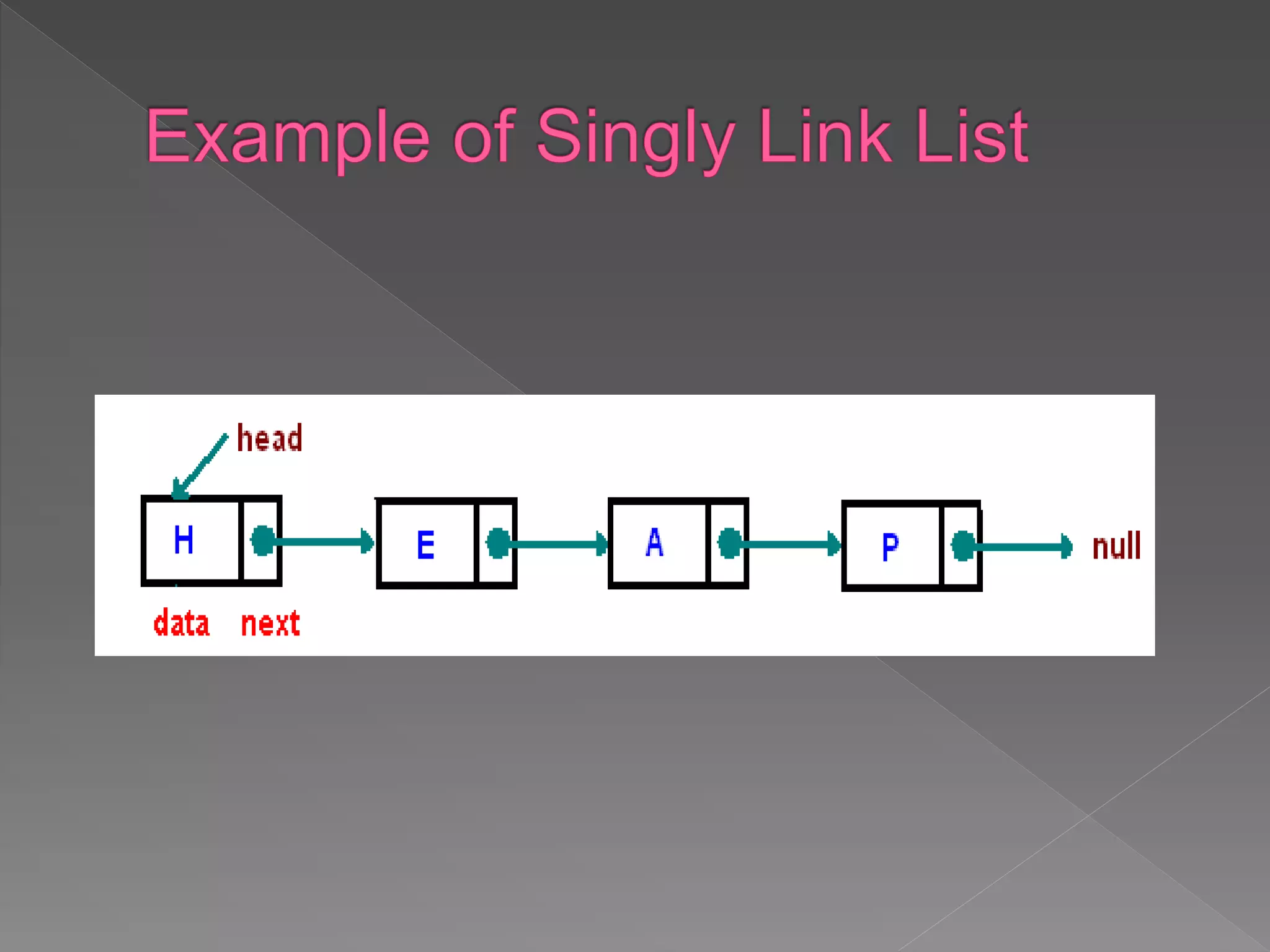
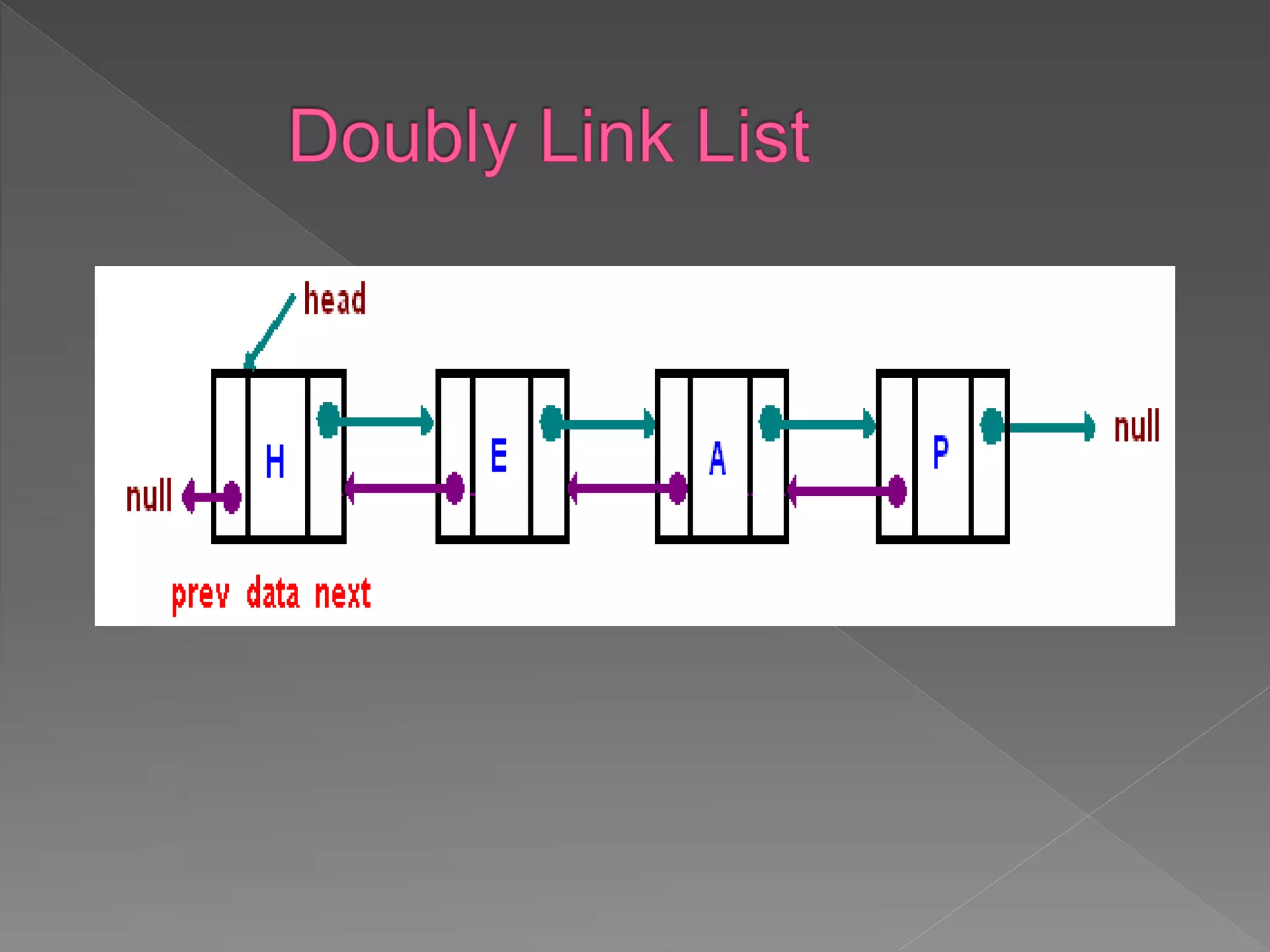
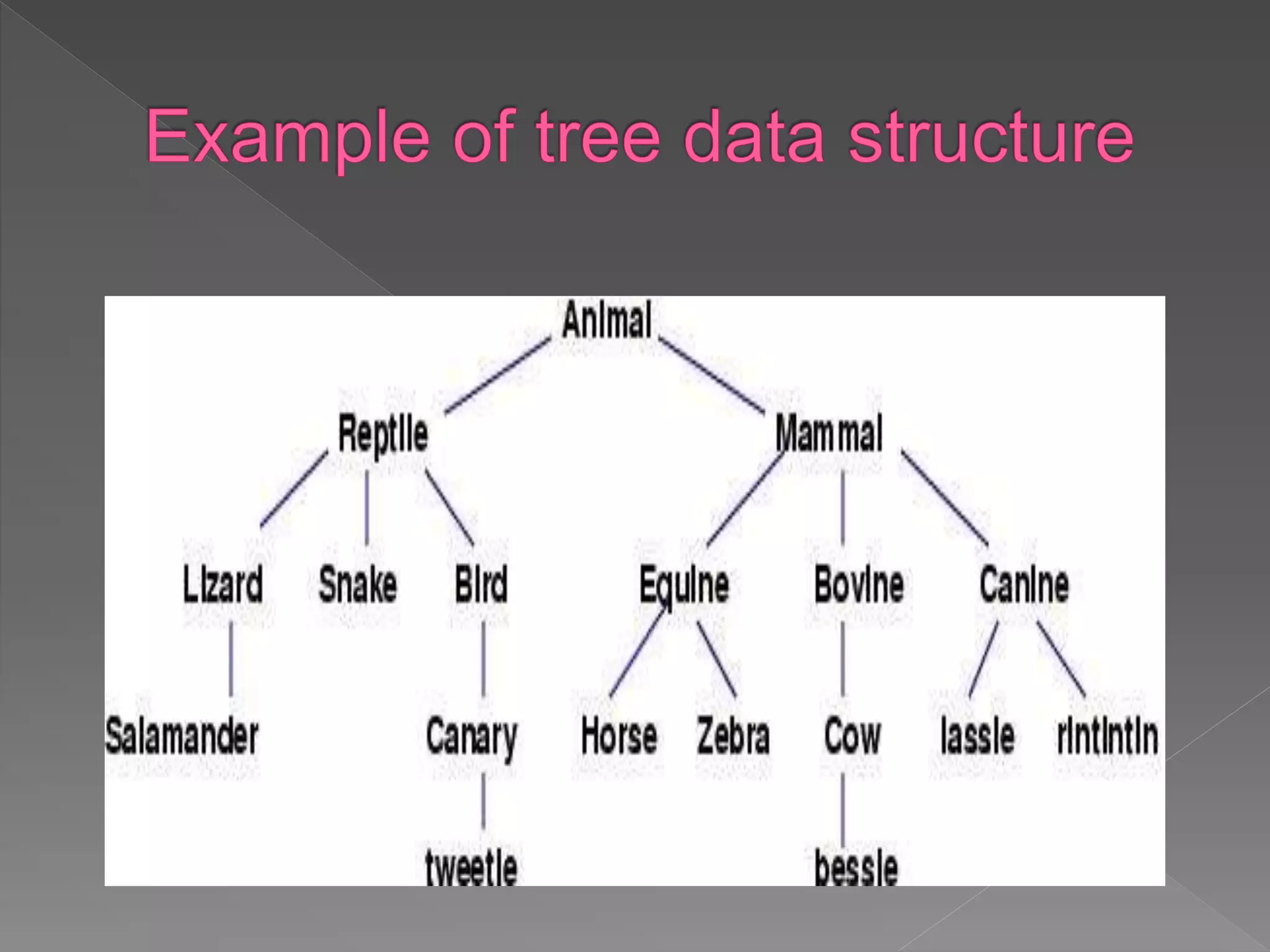
The document discusses different data structures used to organize and store data in a computer including arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, trees, and graphs. It provides examples of each data structure and how they are used, such as stacks being used for undo functions in text editors and queues being used for processes in operating systems and packets in data communication. Trees and graphs are described as tools for organizing hierarchical relationships and mapping relationships between data objects.