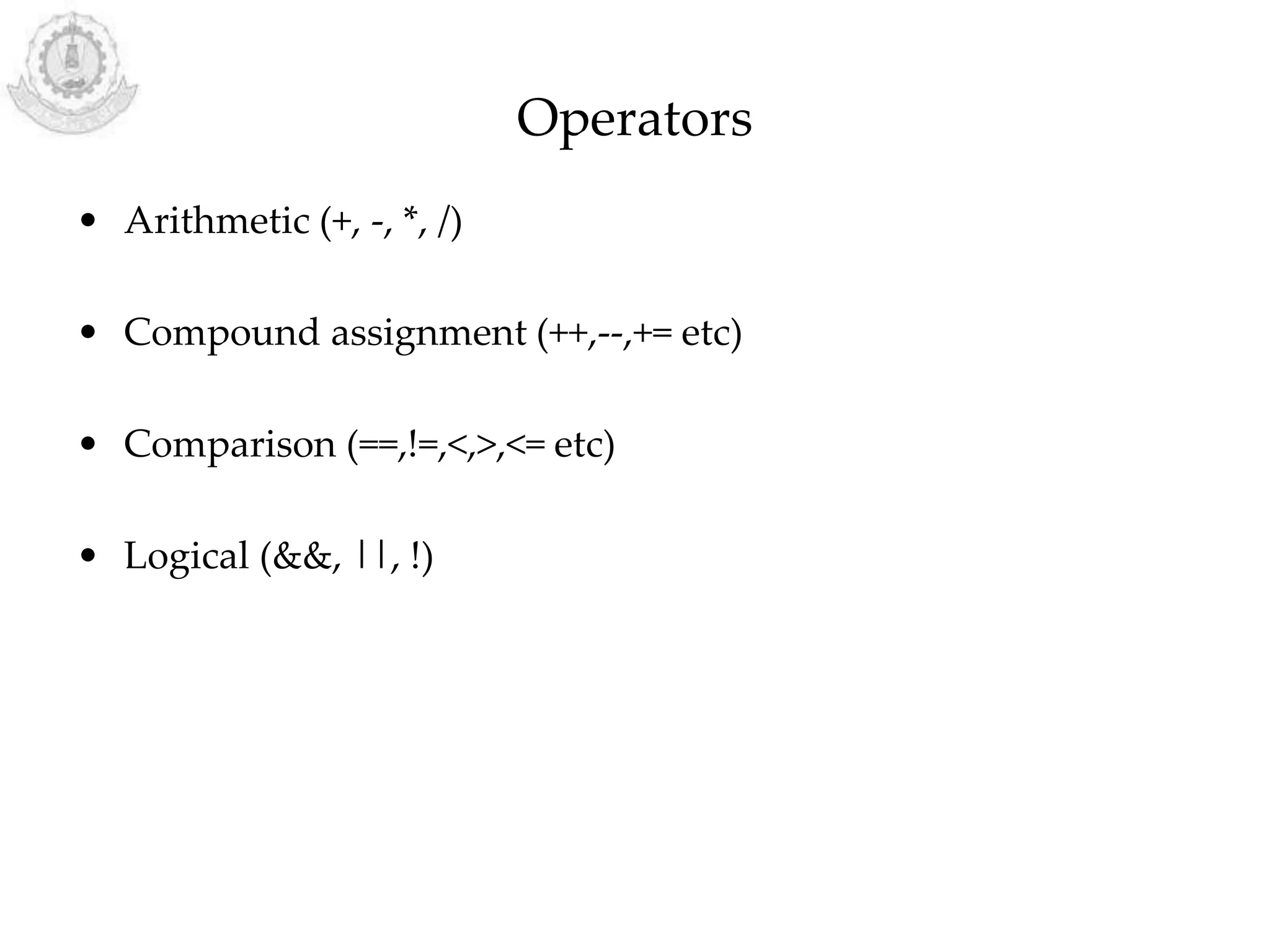
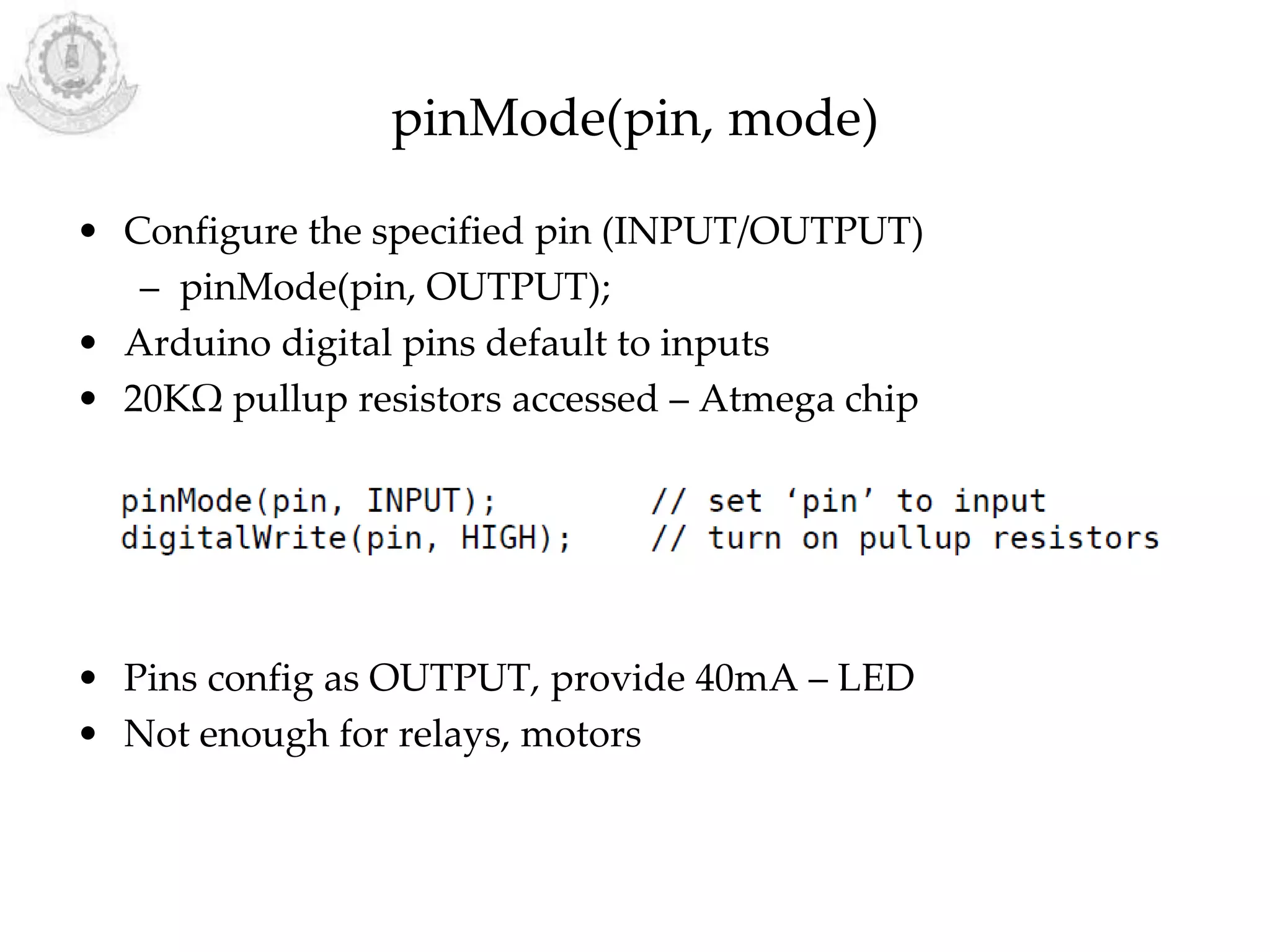
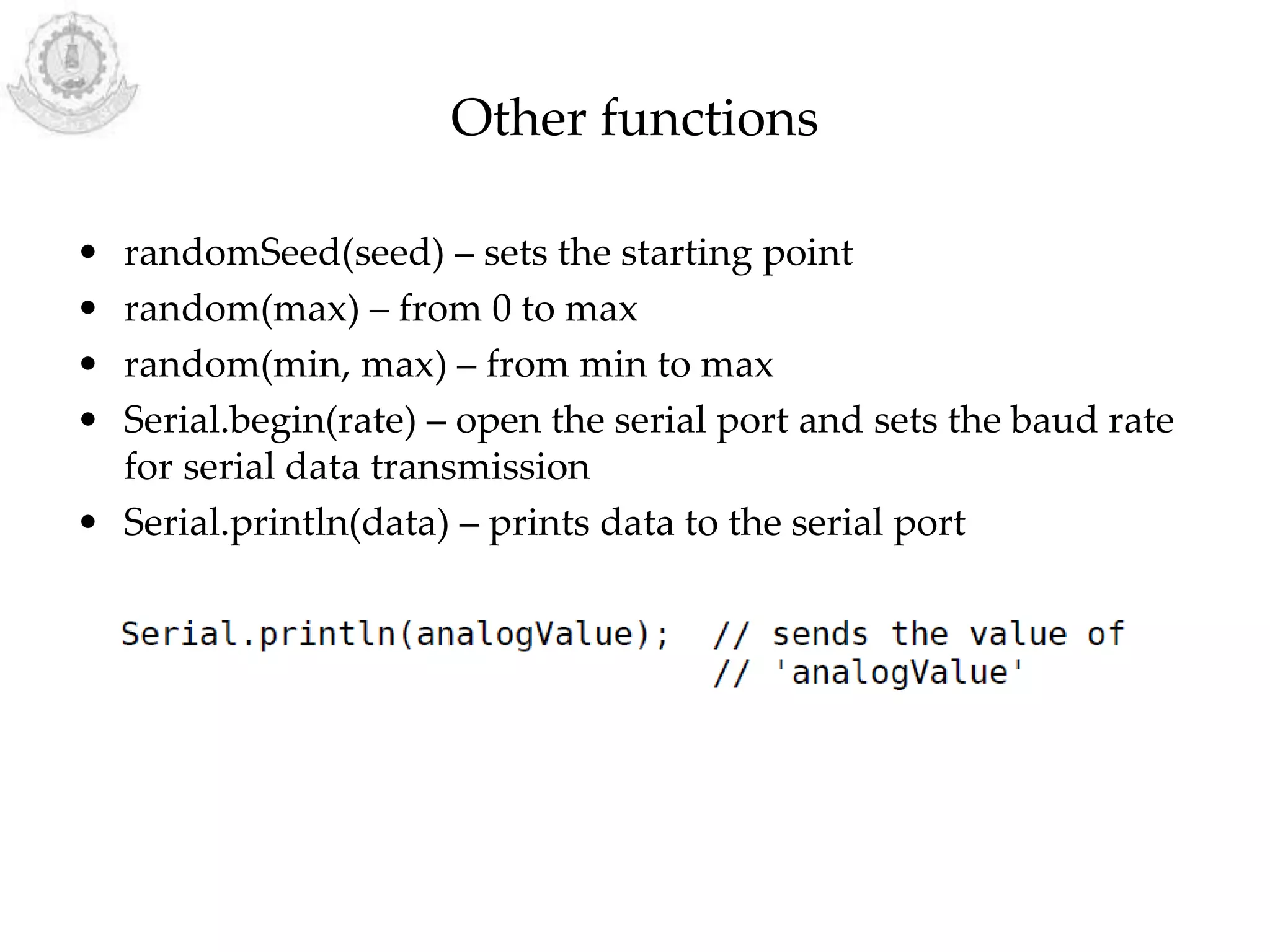
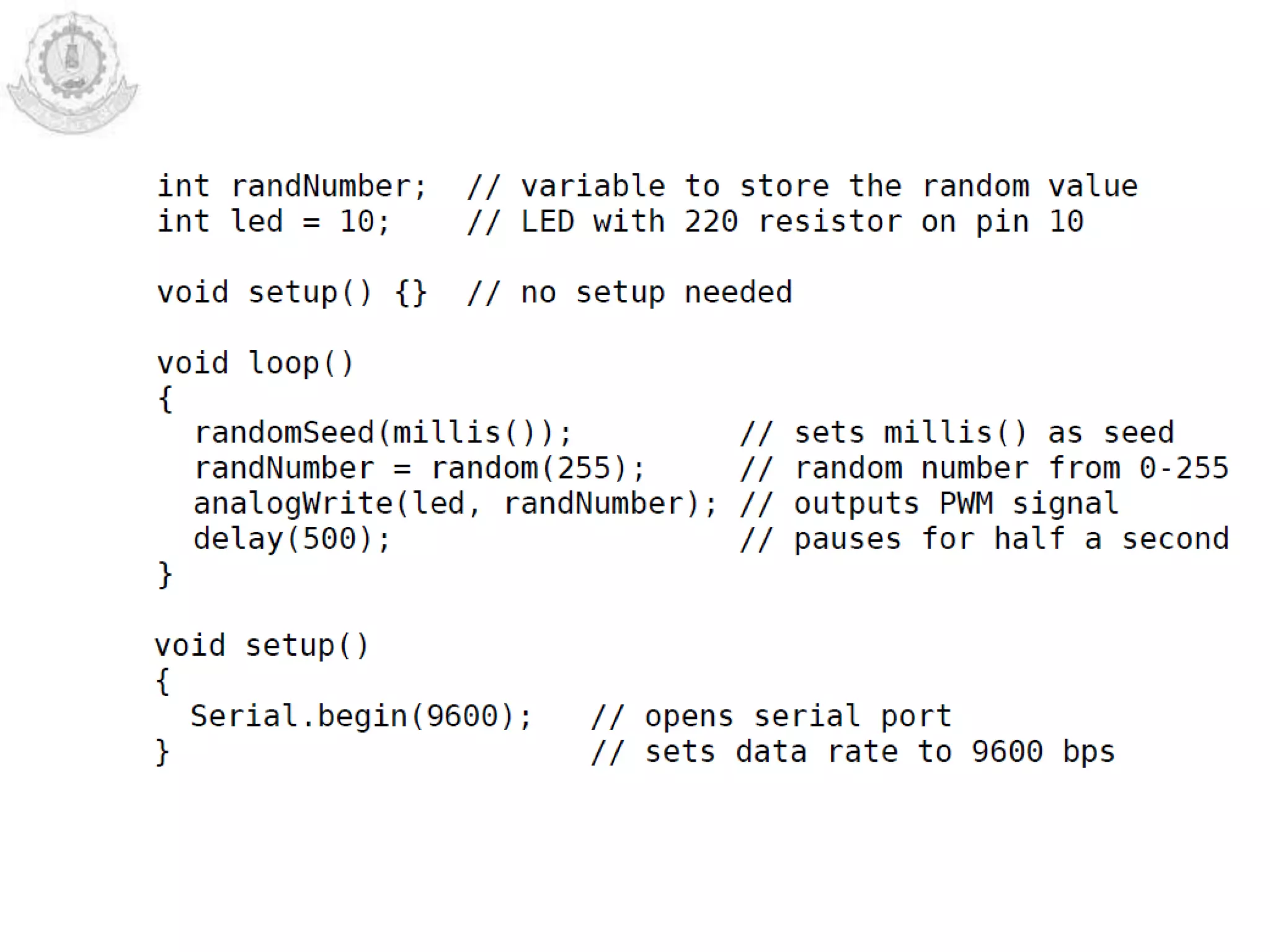
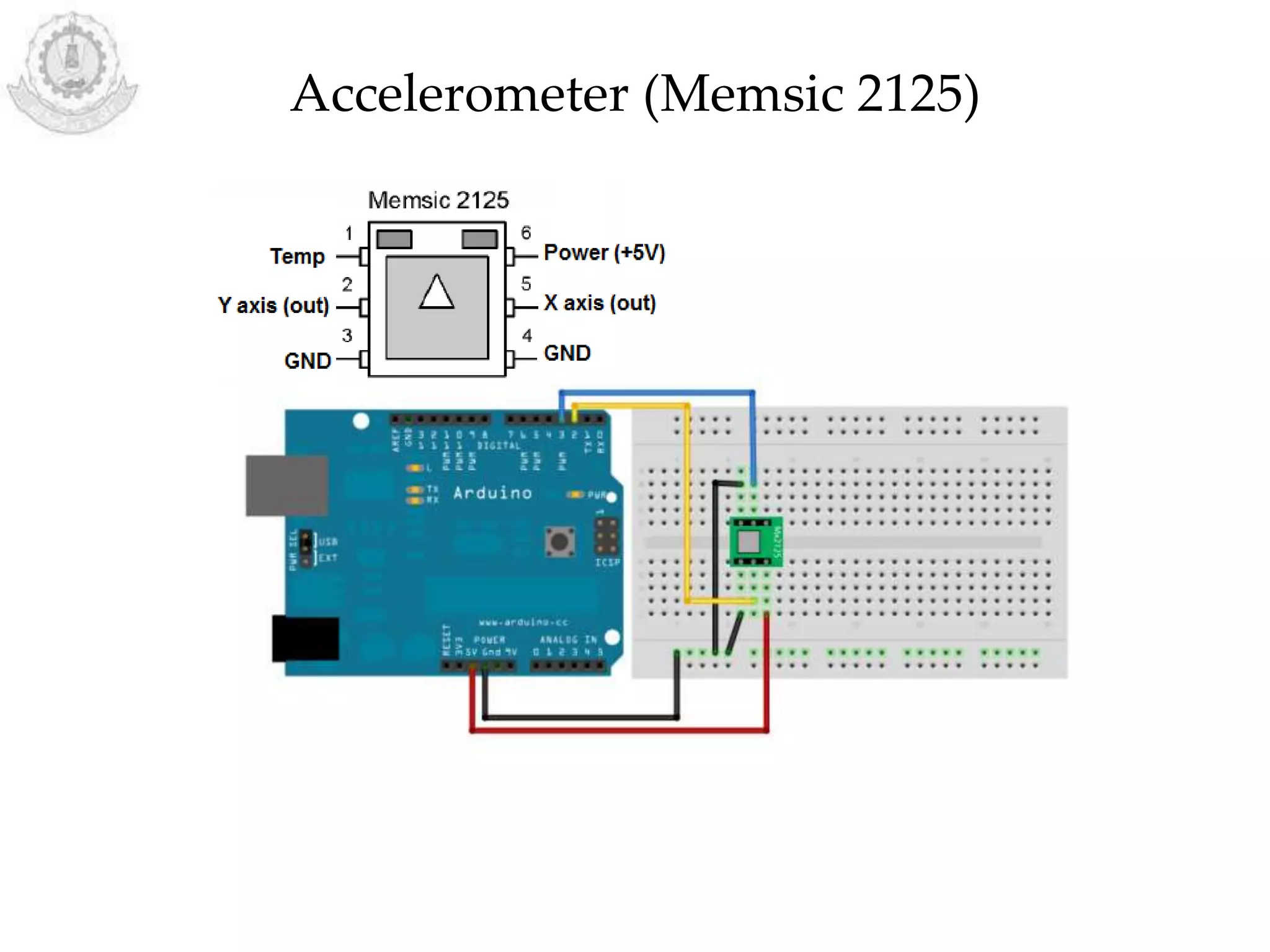
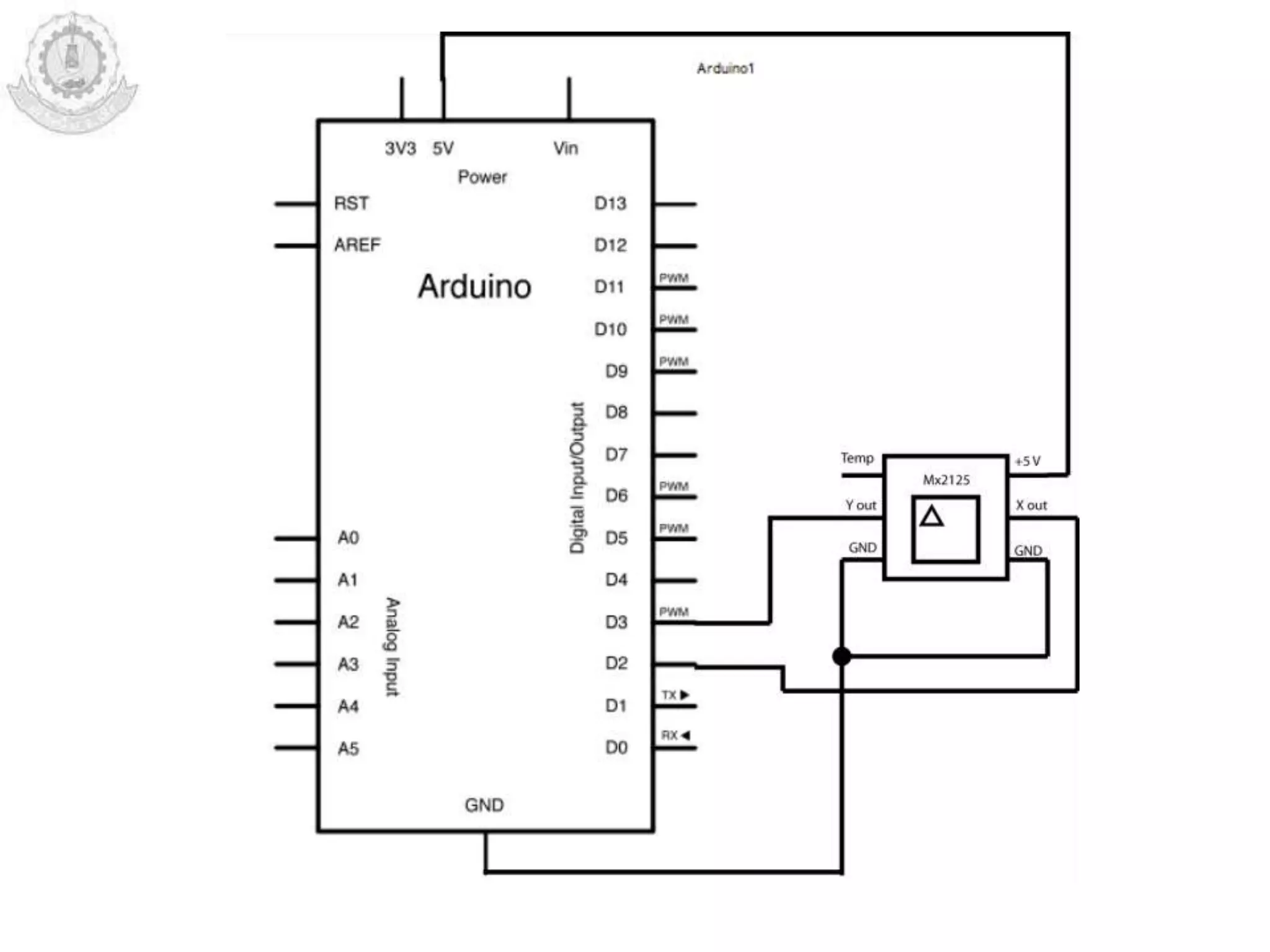
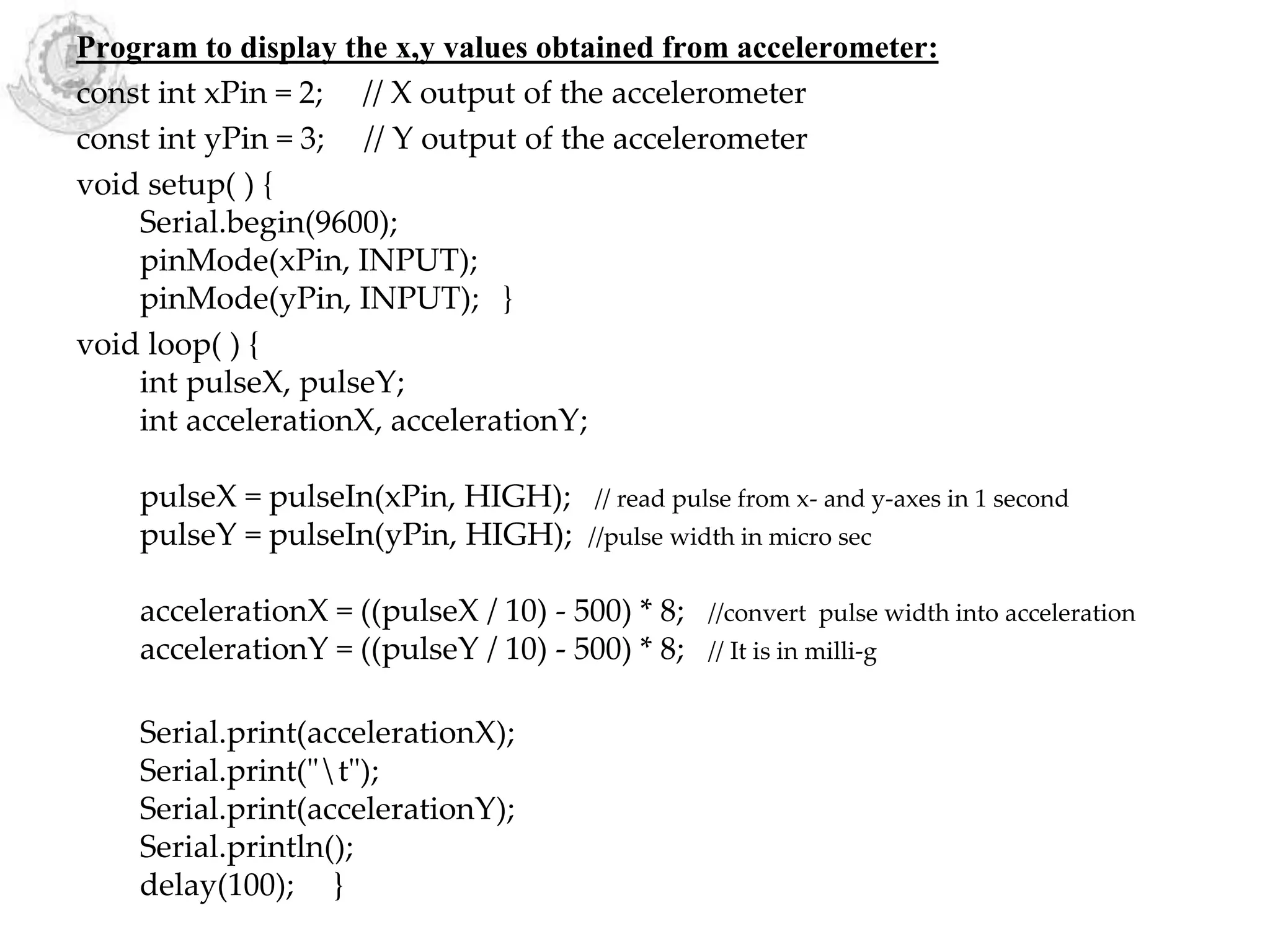
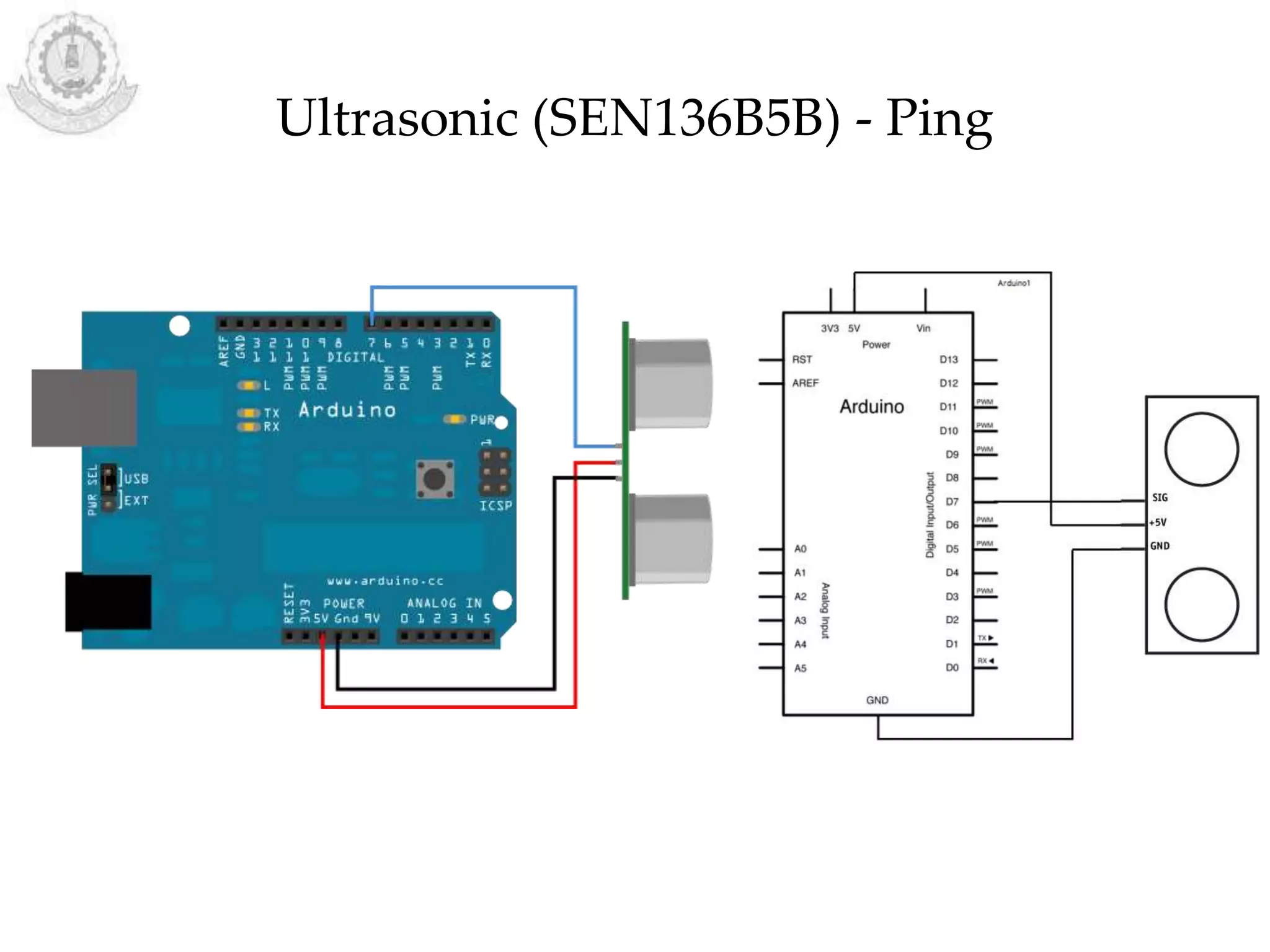
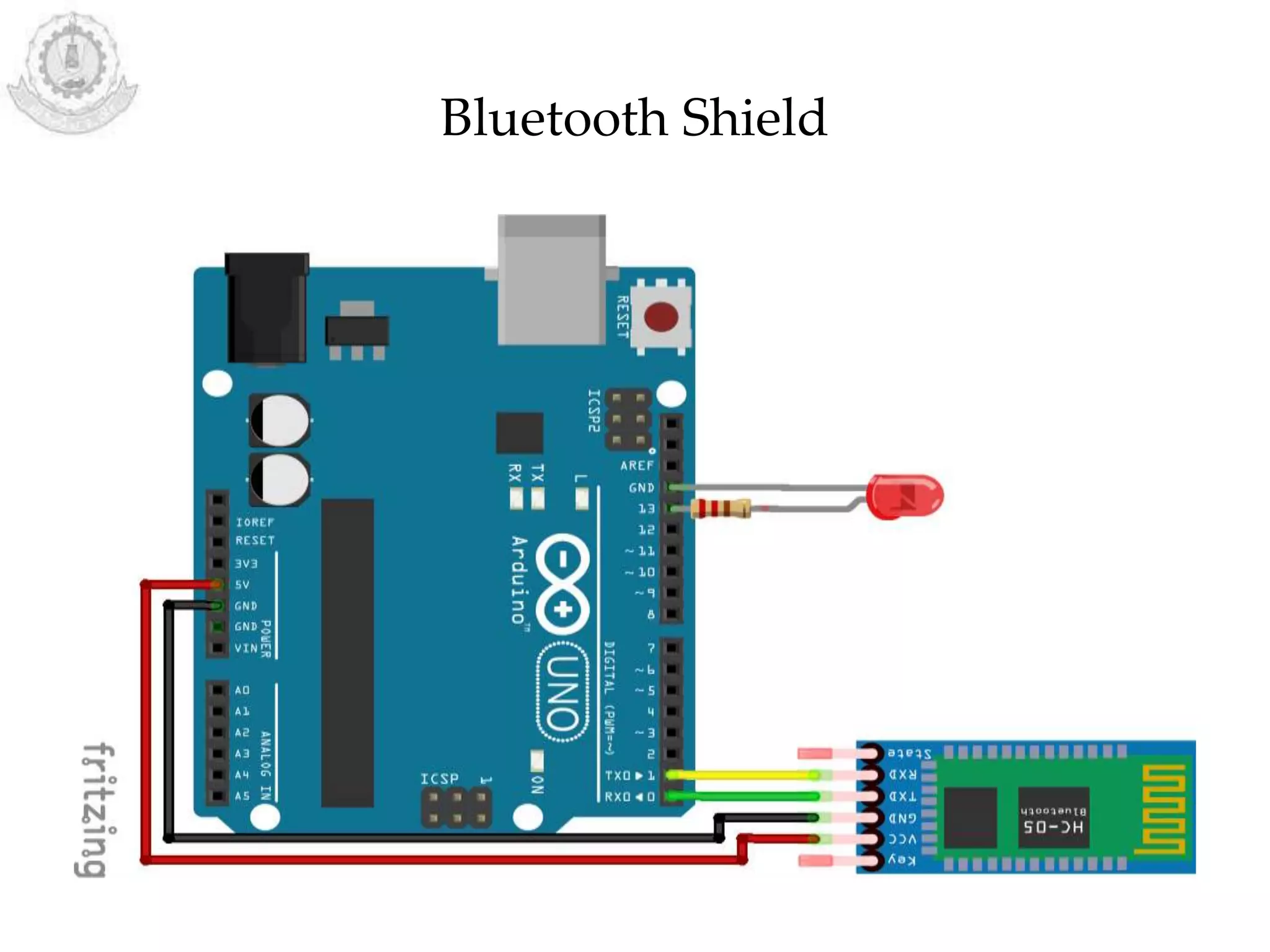
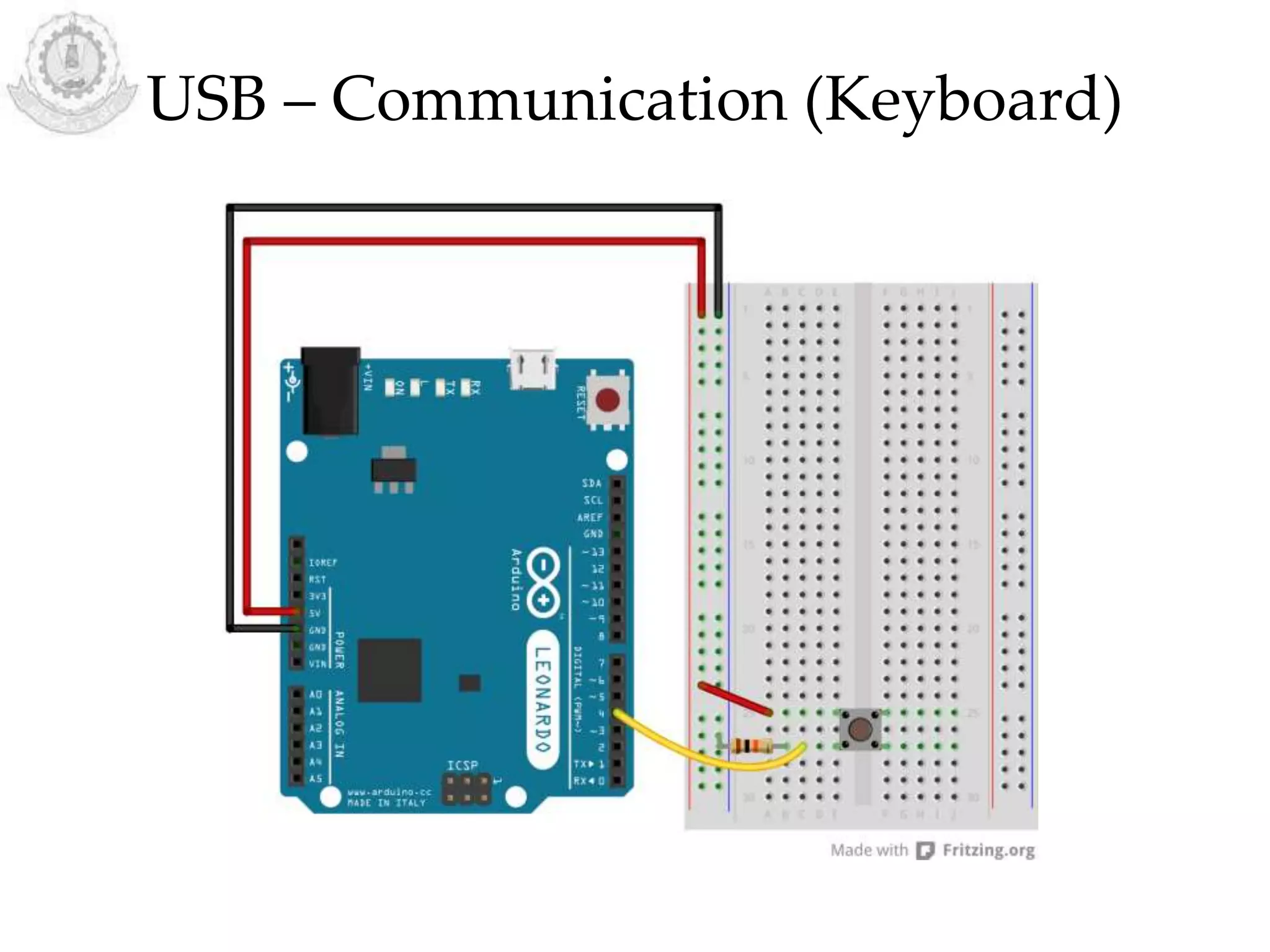
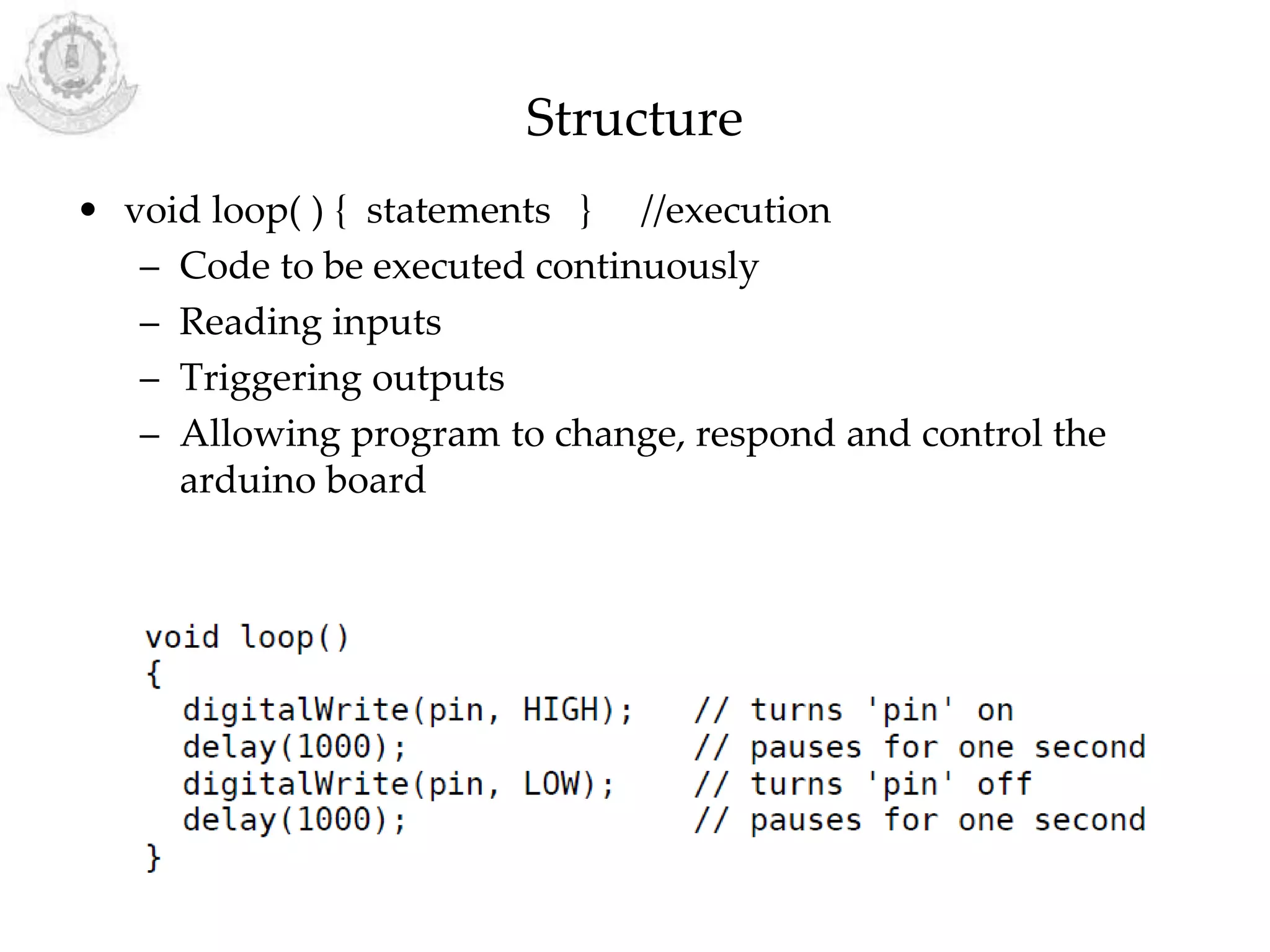
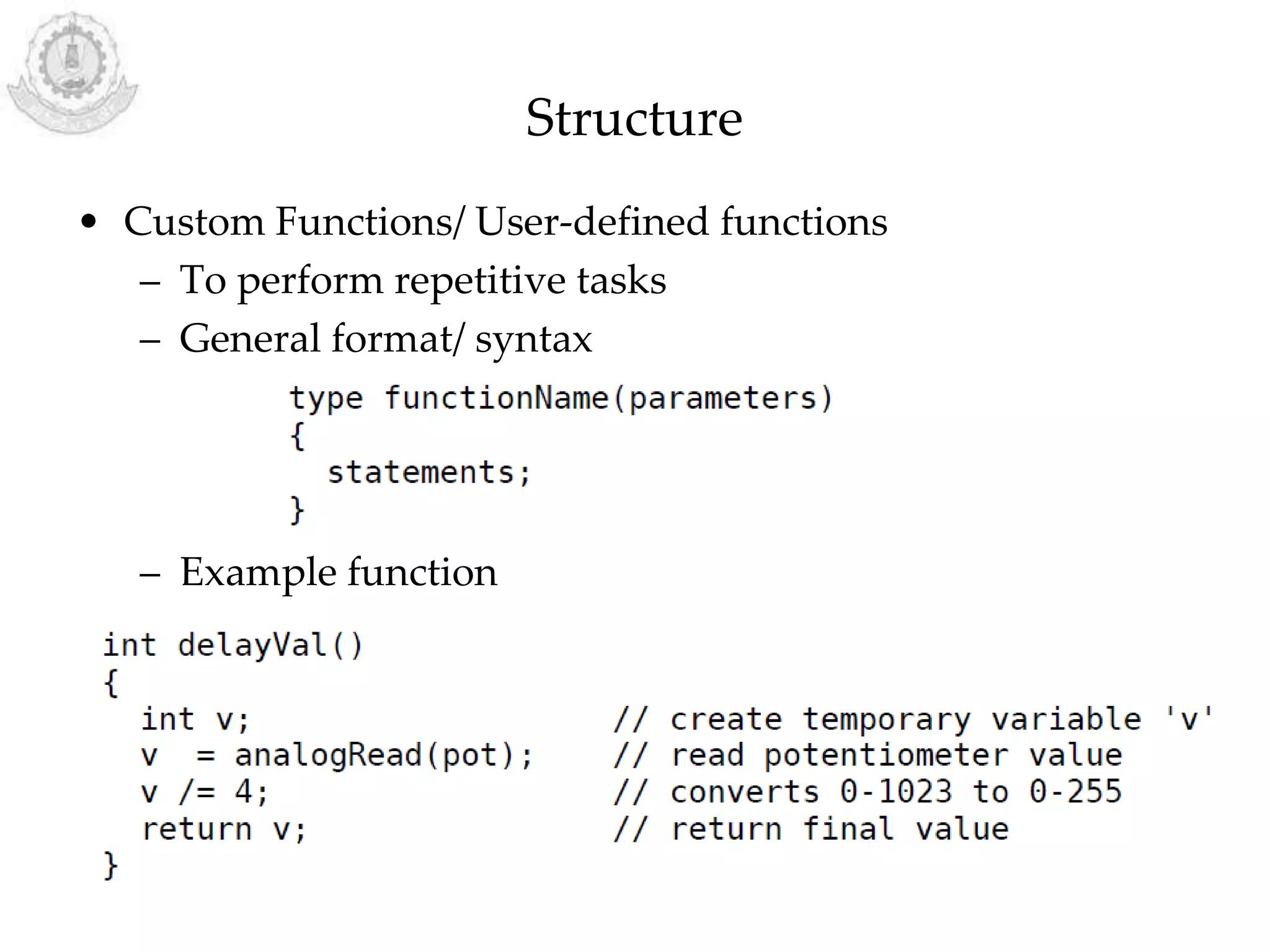
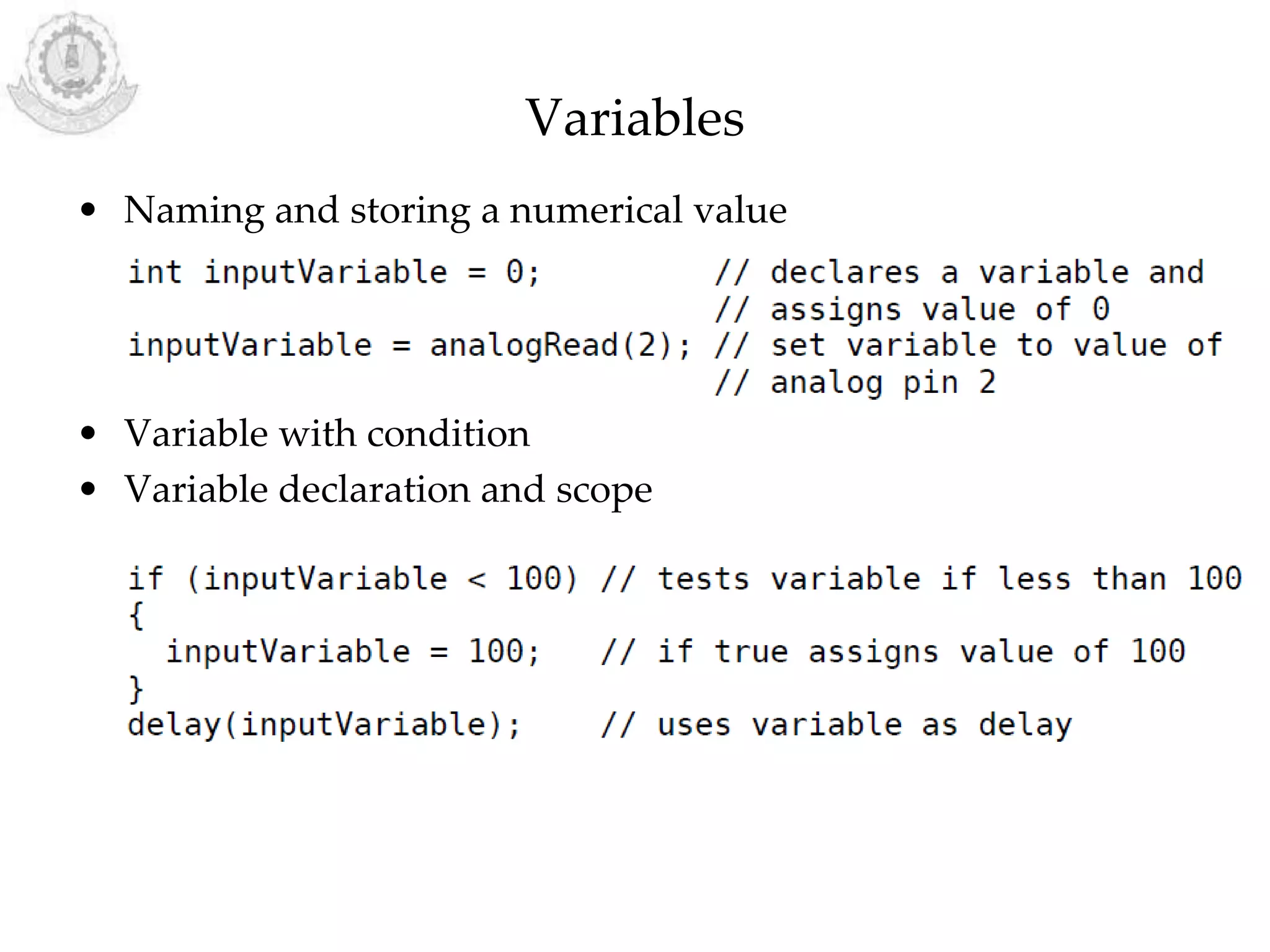
The document provides an overview of Arduino programming structures and concepts. It discusses the setup and loop functions, variables and data types, arrays, operators, constants, control structures, and input/output functions like pinMode, digitalRead, analogRead, and analogWrite. It also covers other functions for delay, random numbers, serial communication, and working with sensors like a vibration sensor, accelerometer, ultrasonic sensor, and Bluetooth shield. Example code is provided to read and display sensor values and control an LED.




![Arrays
• Collection of values
• Arrays are zero indexed (First pos – 0)
int myArray[ ]={value1, value2...};
int arr[3];
array[3]=10;
x=array[3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arduinoprogramming-190531083230/75/Arduino-Programming-8-2048.jpg)