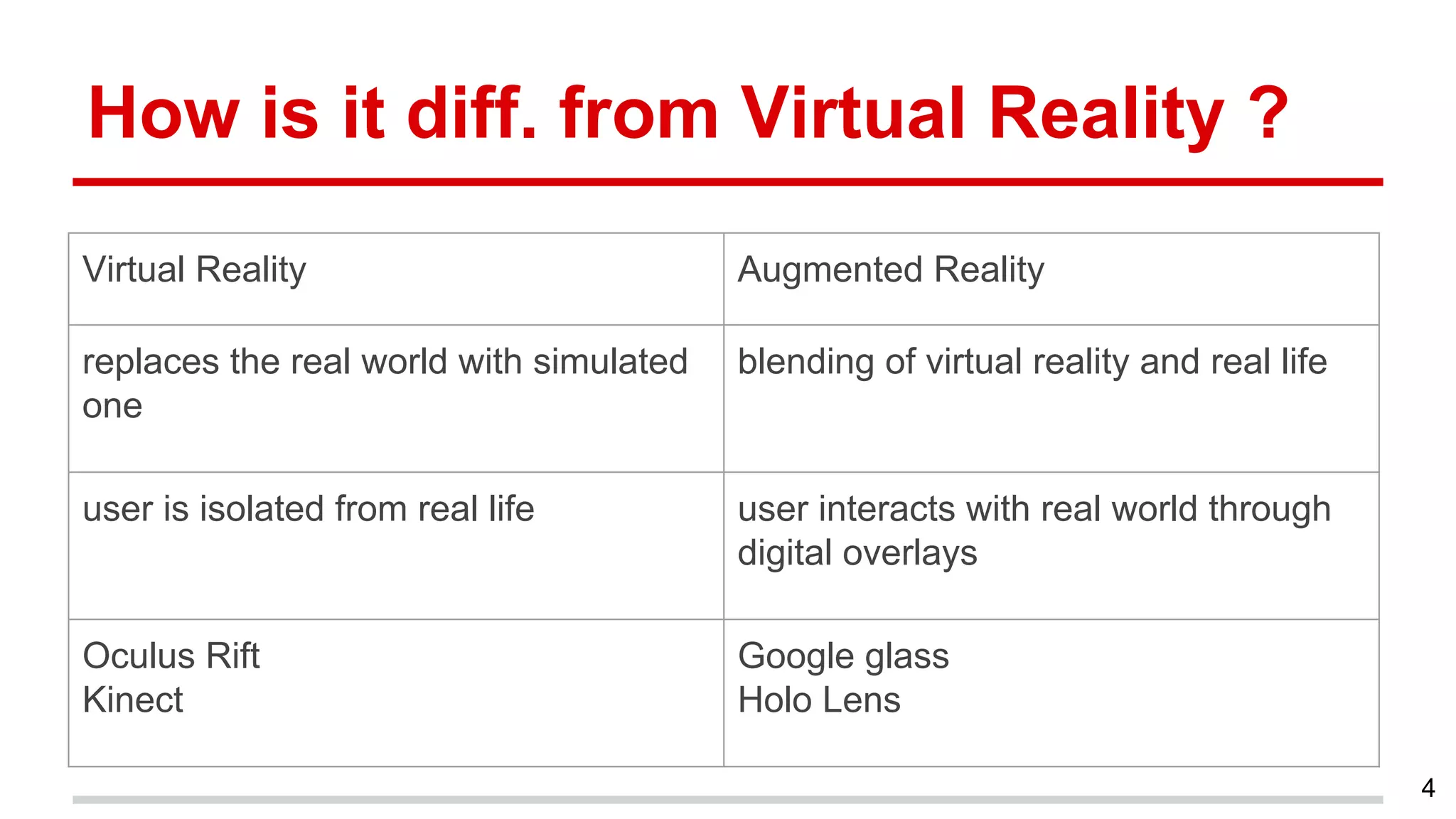
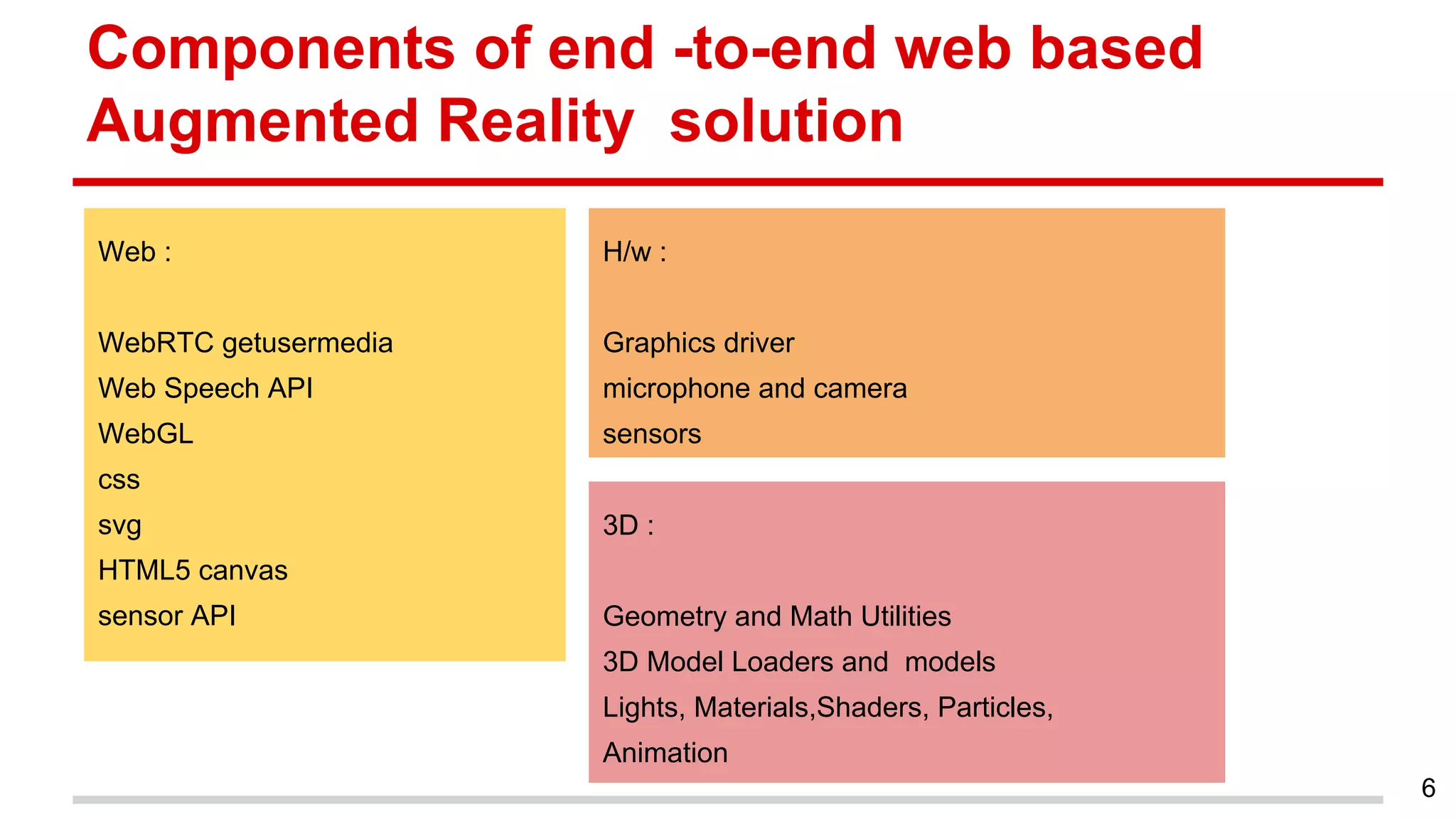
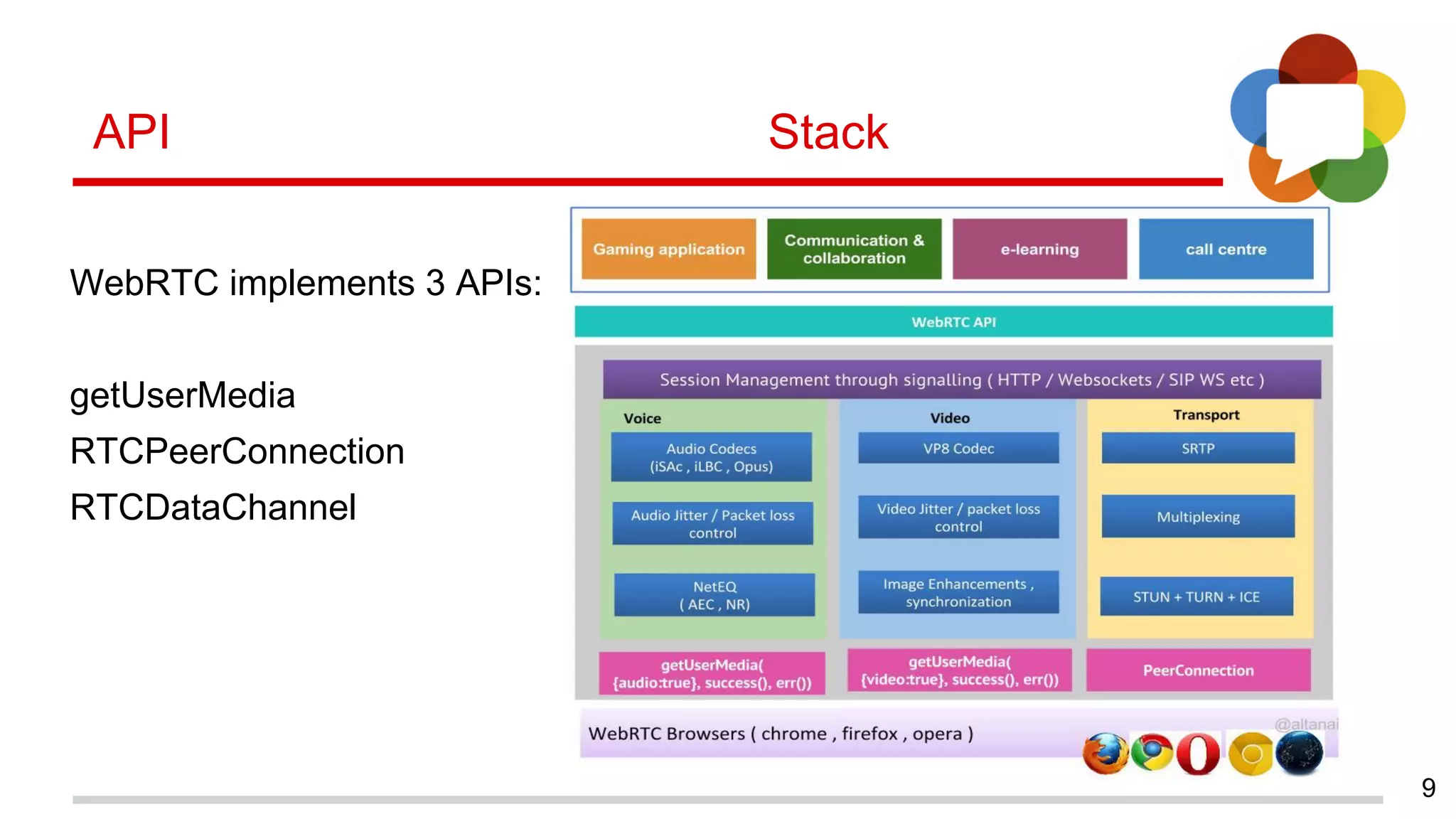
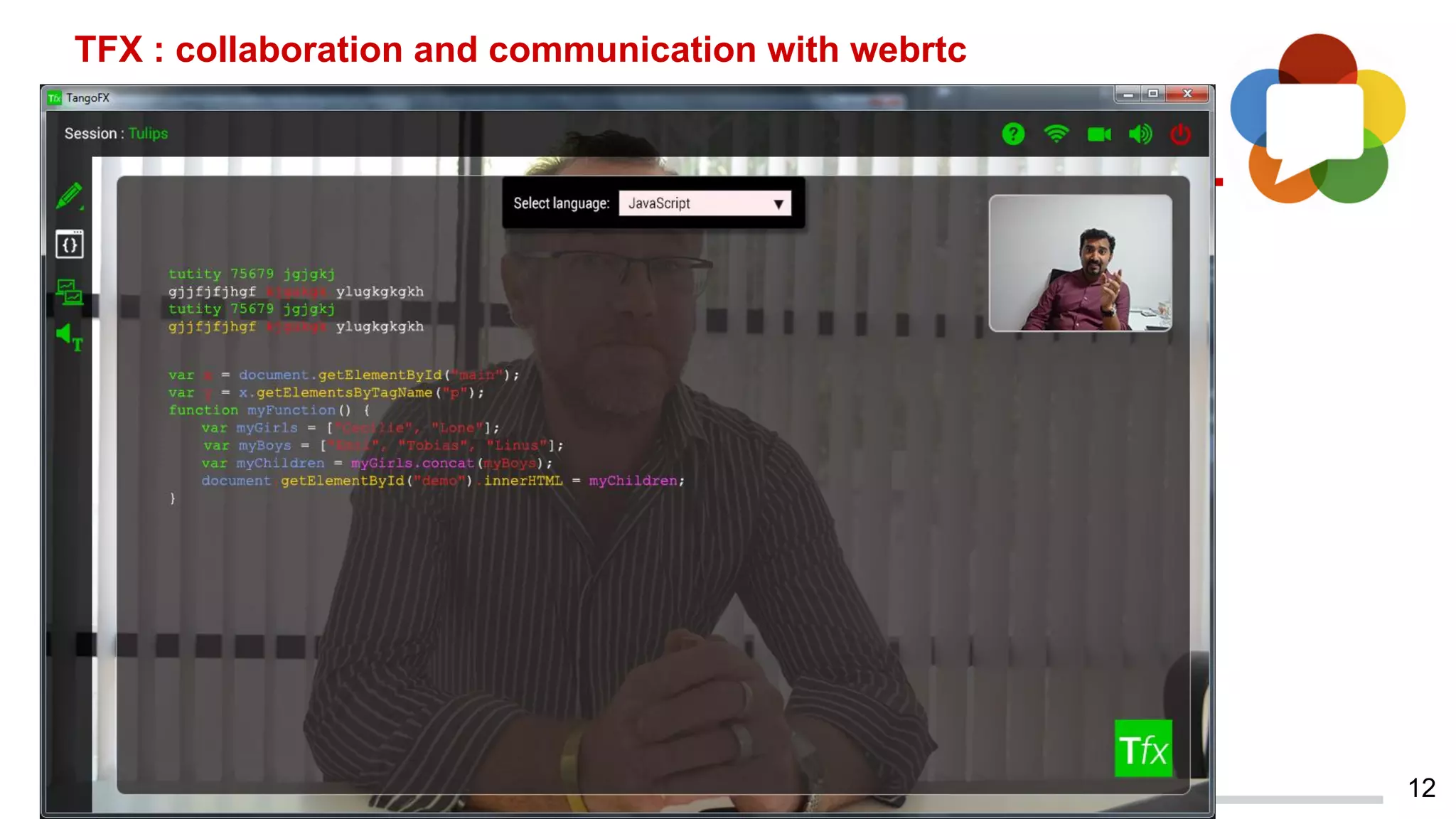
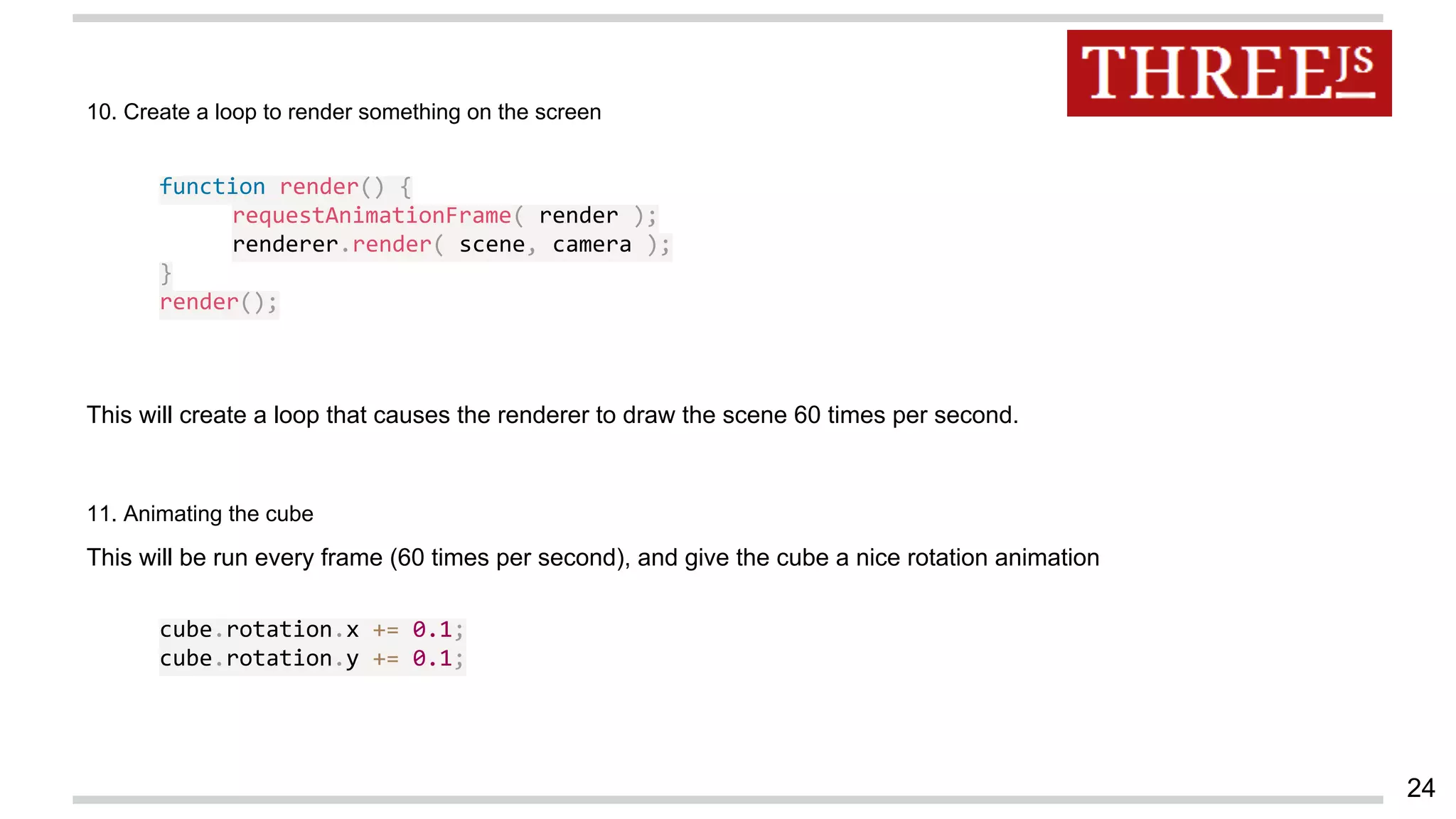
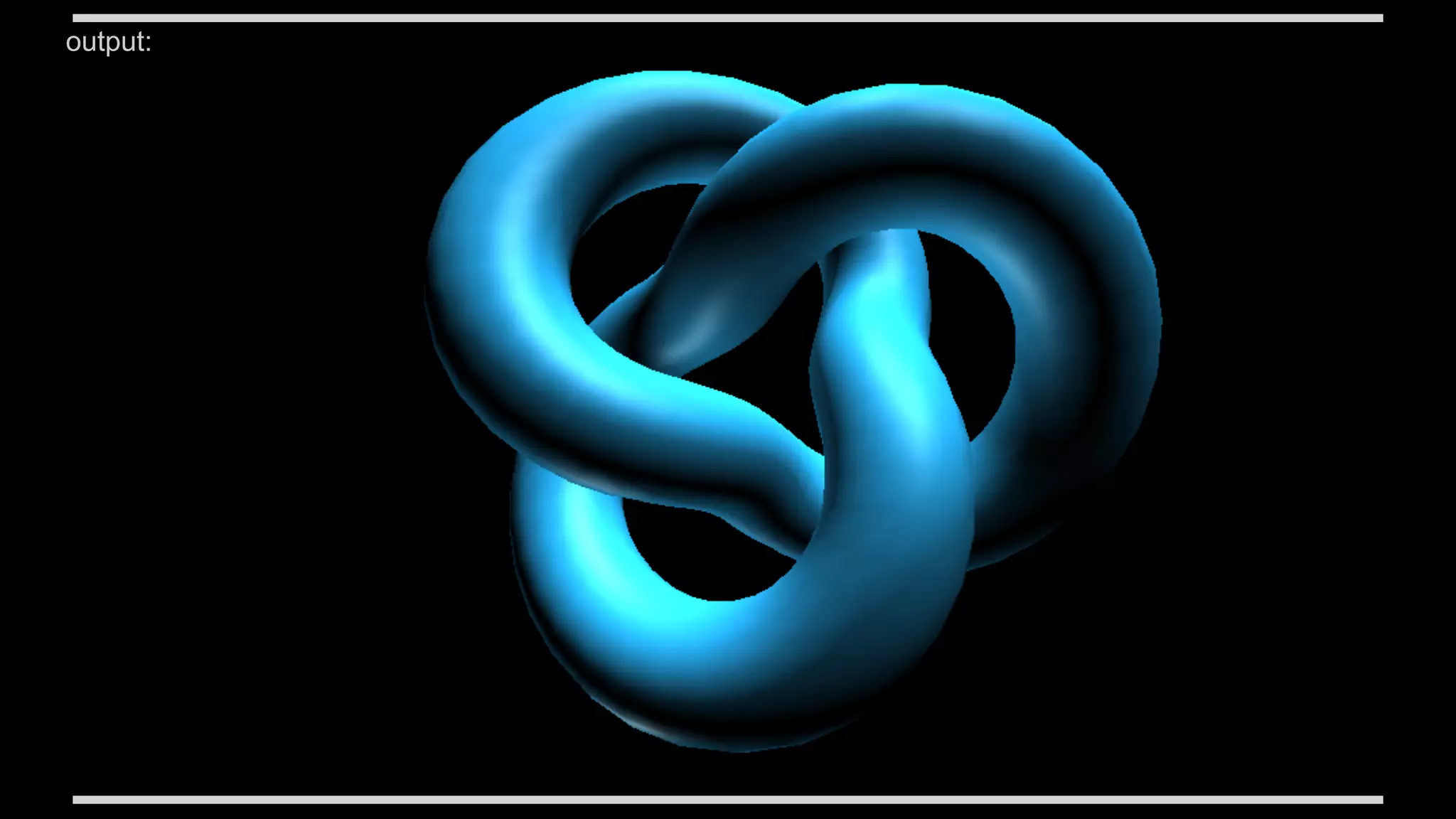
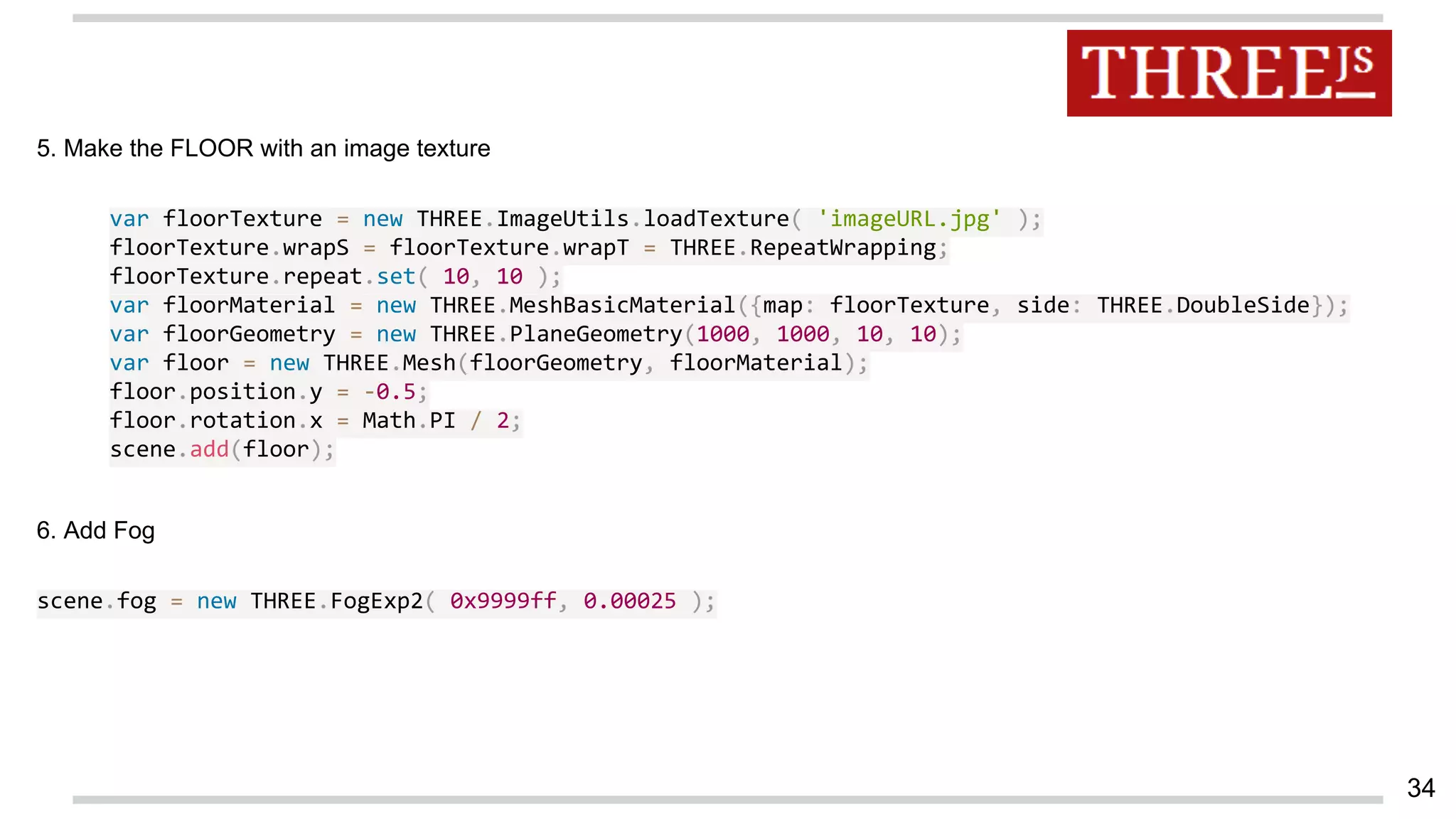
This document discusses augmented reality in a WebRTC browser. It begins with an introduction to augmented reality and how it differs from virtual reality by blending virtual elements with the real world. It then discusses various methods for rendering augmented reality using computer vision, object recognition, and other techniques. It also discusses the key components needed for a web-based augmented reality solution, including the getUserMedia API, WebGL, and WebRTC. The document provides an overview of WebRTC and examples of using it with APIs like getUserMedia and RTCPeerConnection to enable real-time communications in the browser. It concludes with discussing some JavaScript libraries that can be used to build 3D graphics like Three.js and examples of WebRTC and WebGL





![Code snippets for WebRTC
10
1.To begin with WebRTC we first need to validate that the browser has permission to access the webcam.
<video id="webcam" autoplay width="640" height="480"></video>
2. Find out if the user's browser can use the getUserMedia API.
function hasGetUserMedia() { return !!(navigator.webkitGetUserMedia); }
3. Get the stream from the user's webcam.
var video = $('#webcam')[0];
if (navigator.webkitGetUserMedia) {
navigator.webkitGetUserMedia(
{audio:true, video:true},
function(stream) { video.src = window.webkitURL.createObjectURL(stream); },
function(e) { alert('Webcam error!', e); }
);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/augmentedrealityinwebrtcbrowser-150509024601-lva1-app6892/75/Augmented-reality-in-web-rtc-browser-10-2048.jpg)




















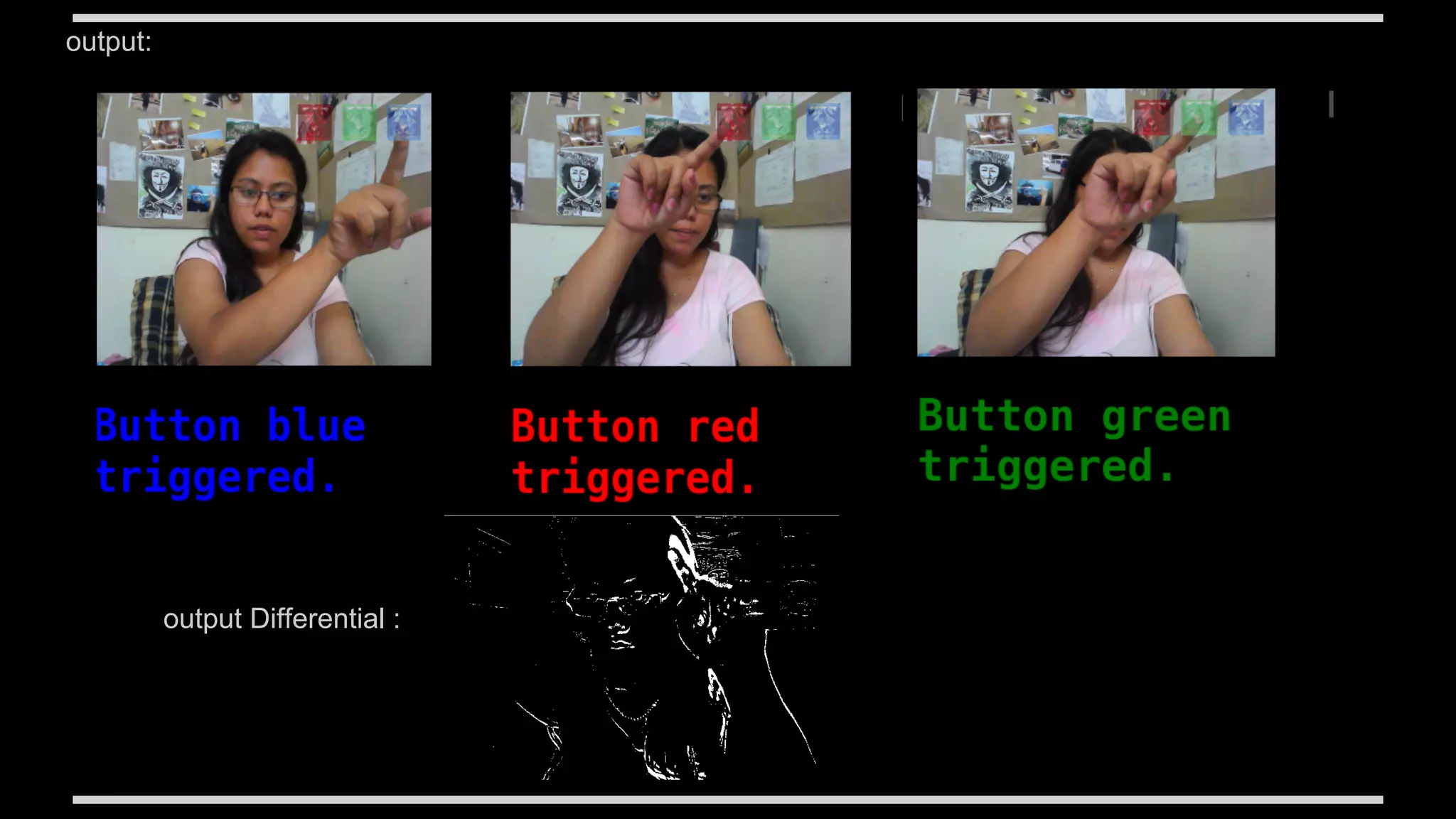
![4. Button touch detector
This example shows the process of triggering Web page activity by detecting motion using difference accuracy
1. Follow the same steps as in previous example
2. Define as many buttons
var buttons = [];
var button1 = new Image();
button1.src ="https://stemkoski.github.io/Three.js/images/SquareRed.png";
var buttonData1 = { name:"red", image:button1, x:320 - 96 - 30, y:10, w:32, h:32 };
buttons.push( buttonData1 );
3. make 3 layers of canvas for video , buttons and blended repectively .
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/augmentedrealityinwebrtcbrowser-150509024601-lva1-app6892/75/Augmented-reality-in-web-rtc-browser-38-2048.jpg)