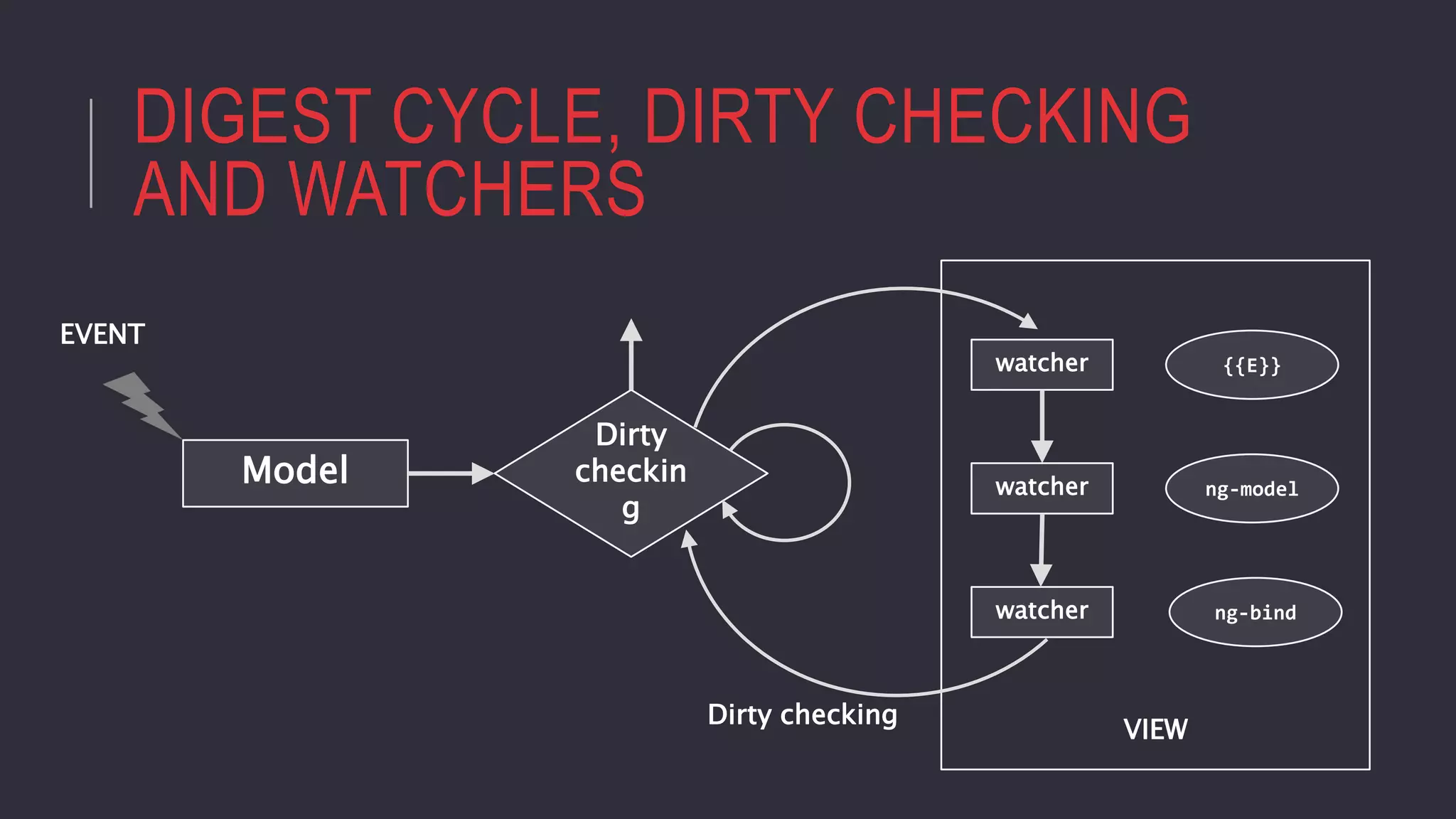
AngularJS is a JavaScript framework that allows developers to create single-page applications. It provides features like two-way data binding, dependency injection, templating, directives and services. The document defines AngularJS, describes its key features and provides examples of how to use controllers, scopes, expressions, services, factories, directives and more to build Angular applications. It also includes exercises for readers to practice creating an Angular movie app that displays now playing movies, actors and allows loading more movies.






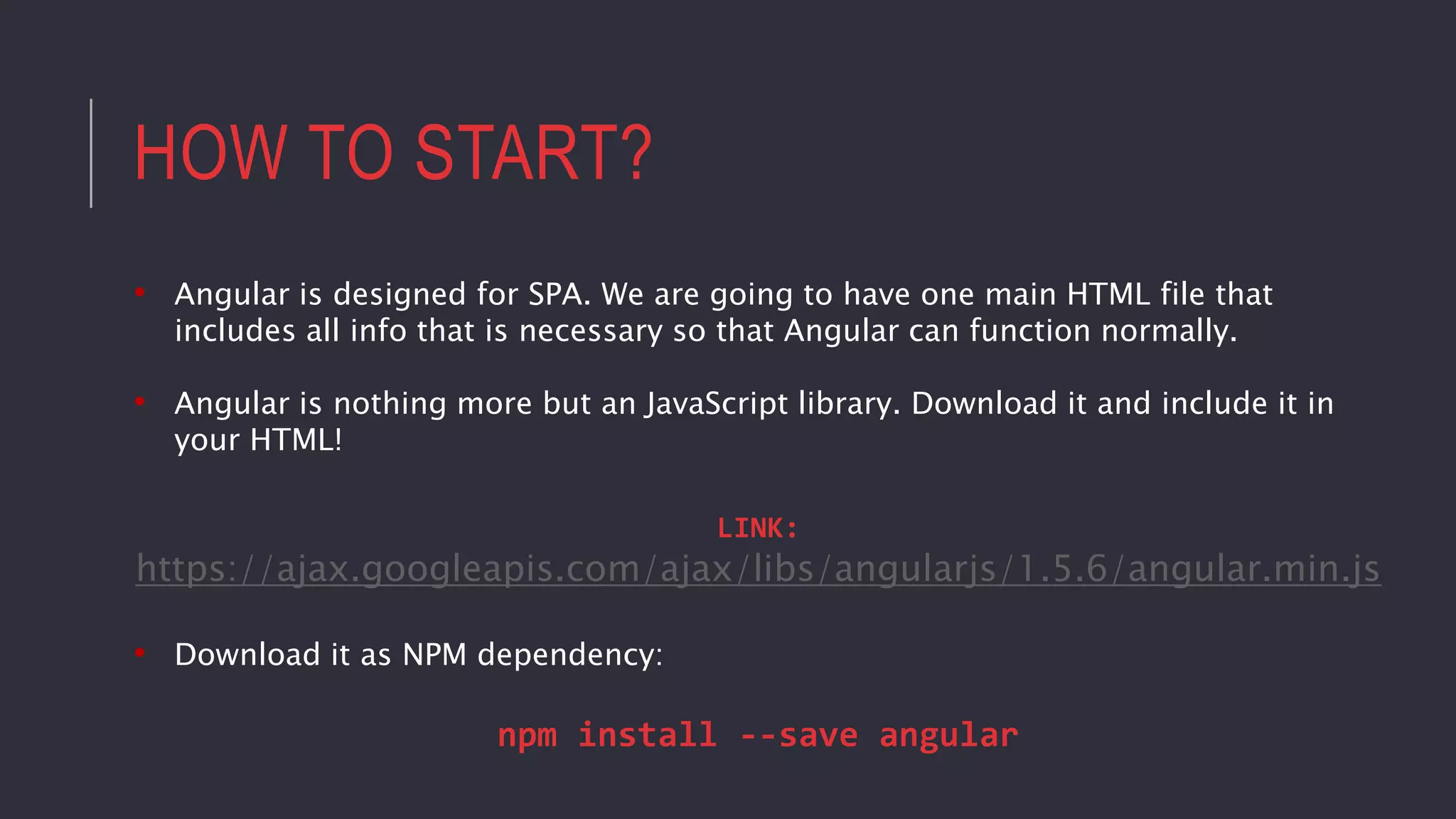
![HOW TO START?
• The Angular application starts from the DOM element where the ng-
app is declared
• ng-app holds the name of the Angular application
<div ng-app="myApp"></div>
• Declare the name of the application in separate JS file and include it in the main HTML
file
const app = angular.module('myApp', []);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoangularjs-161128214513/75/Basics-of-AngularJS-11-2048.jpg)
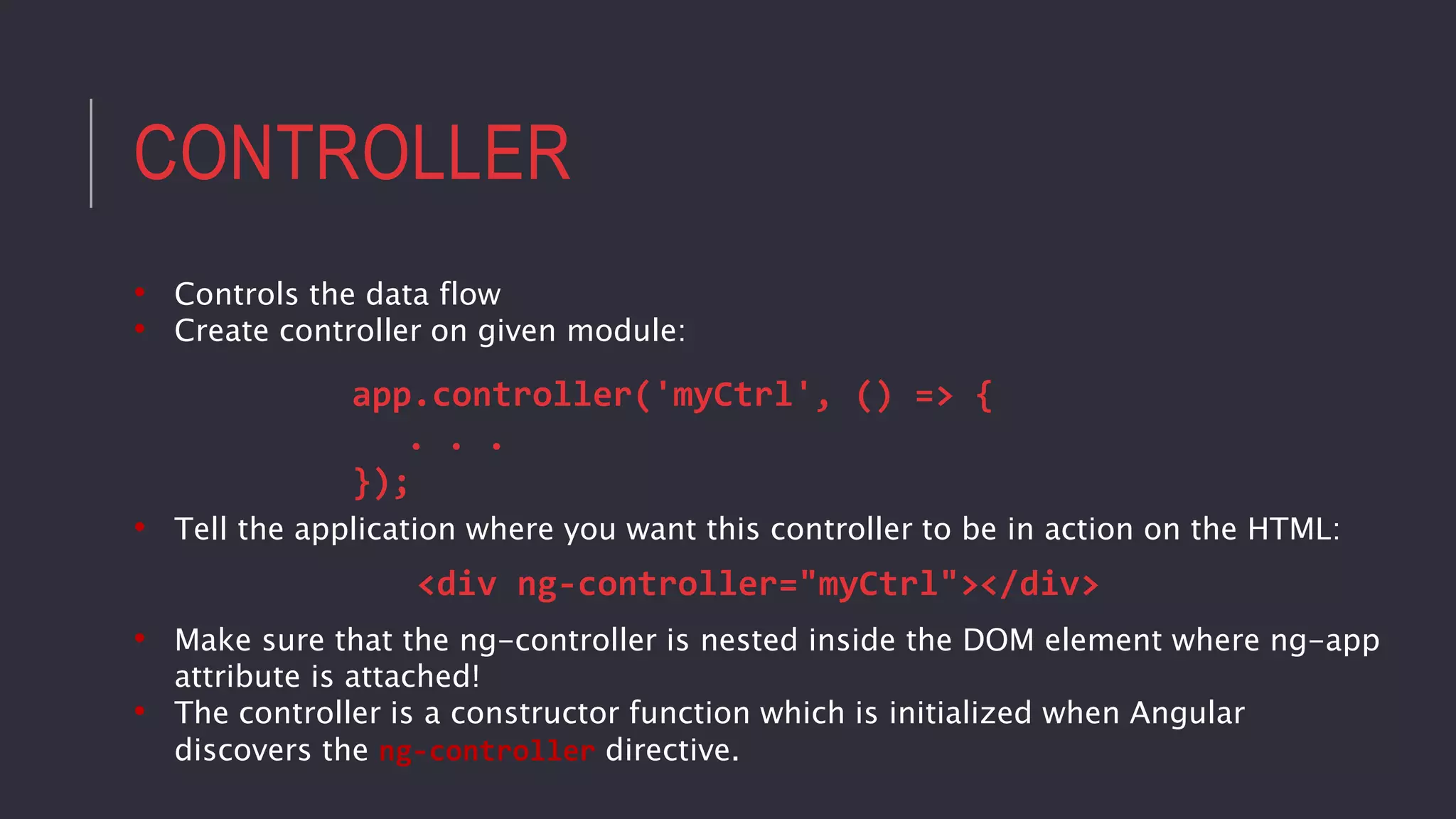
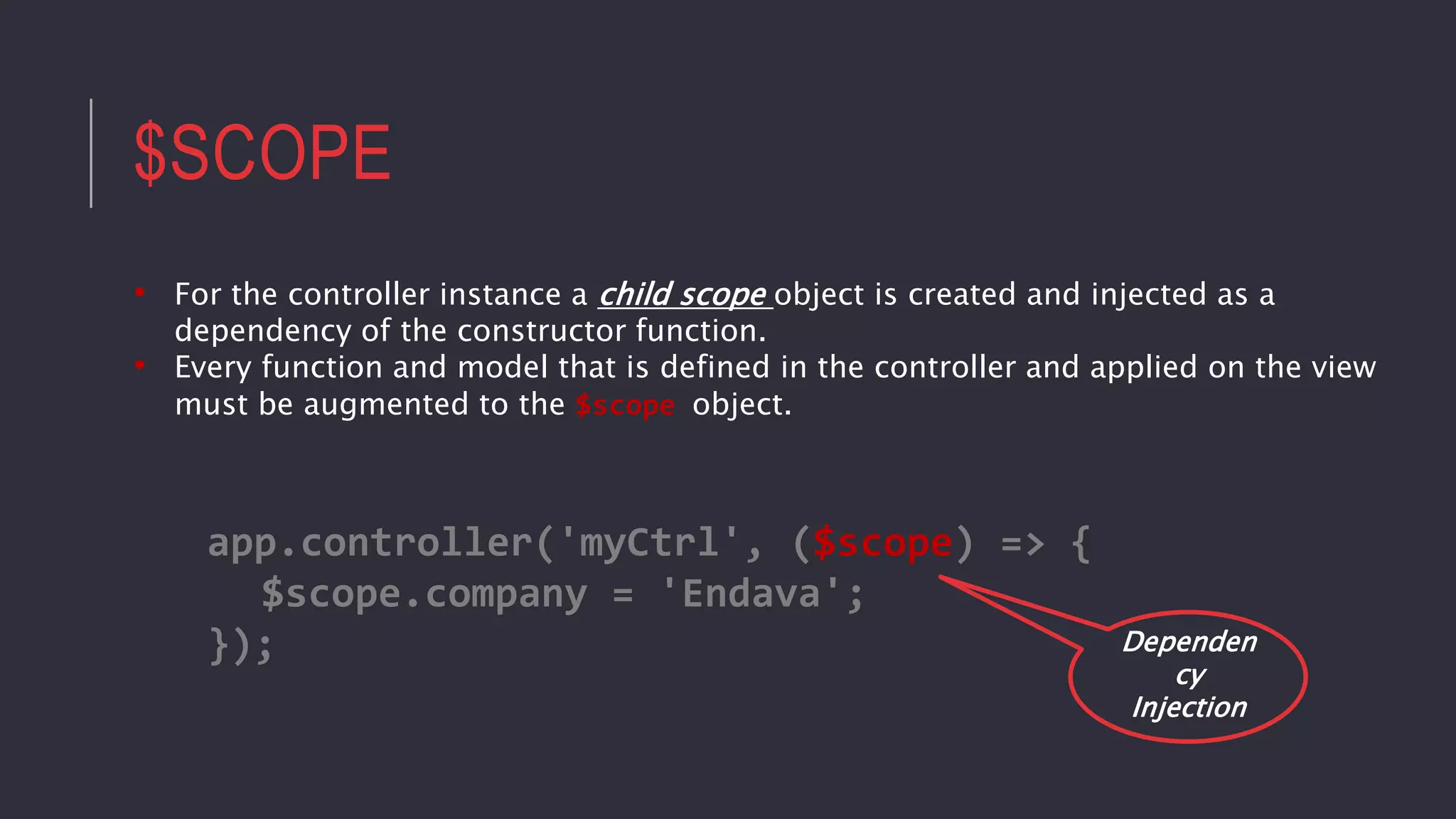

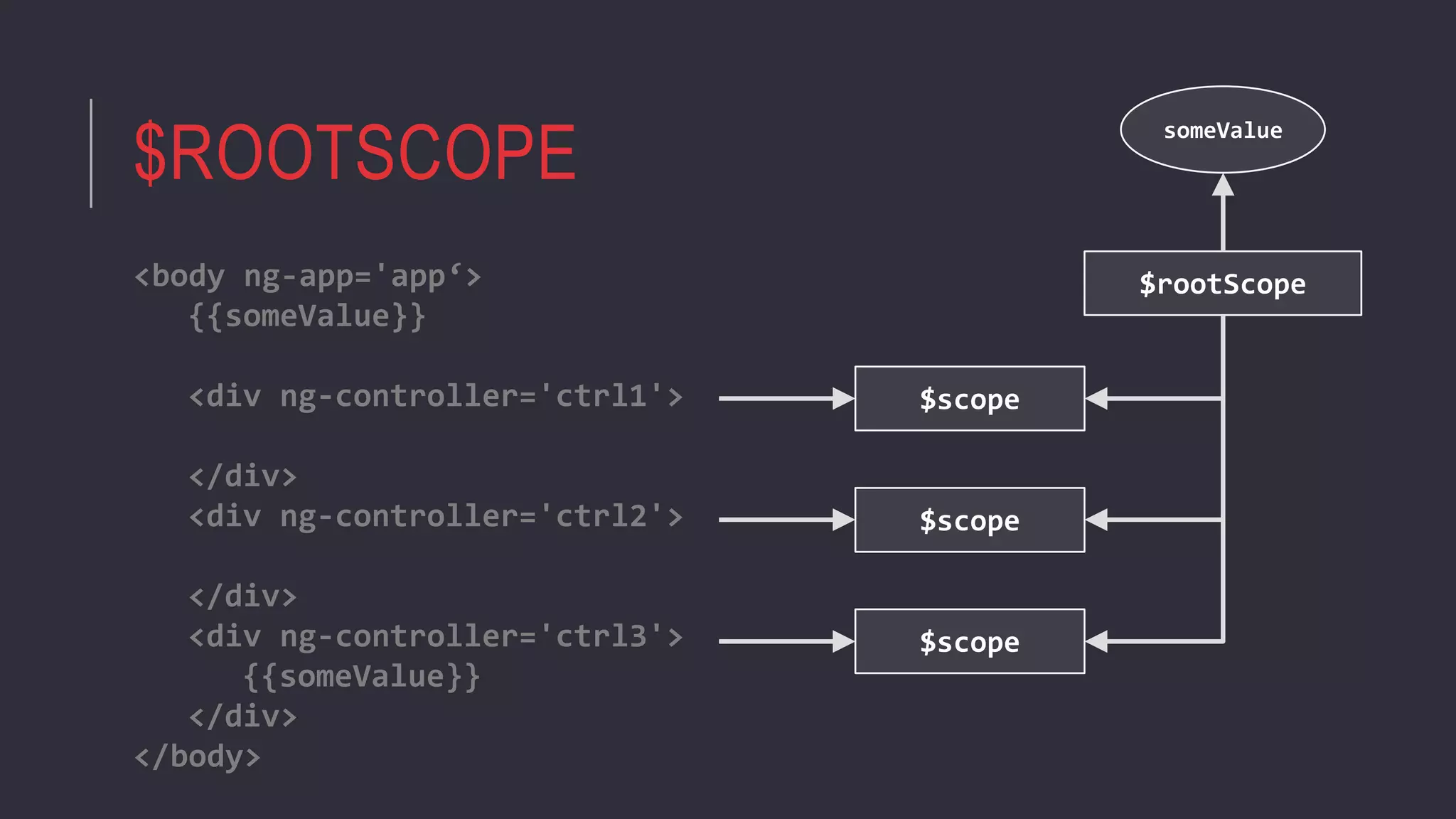








![DIRECTIVE
Examples:
$scope.cities = [
{name: 'Skopje', country: 'MKD'},
{name: 'Washington', country: 'US'},
{name: 'Moscow', country: 'RU'},
];
<tr ng-repeat=“city in cities track by $index”>
<td>{{city.name}}</td>
<td>{{city.country}}</td>
</tr>
<option ng-options=“city.name for city in cities track by $index”></option>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoangularjs-161128214513/75/Basics-of-AngularJS-24-2048.jpg)