The document provides an overview of basic image processing concepts and techniques using MATLAB, including:
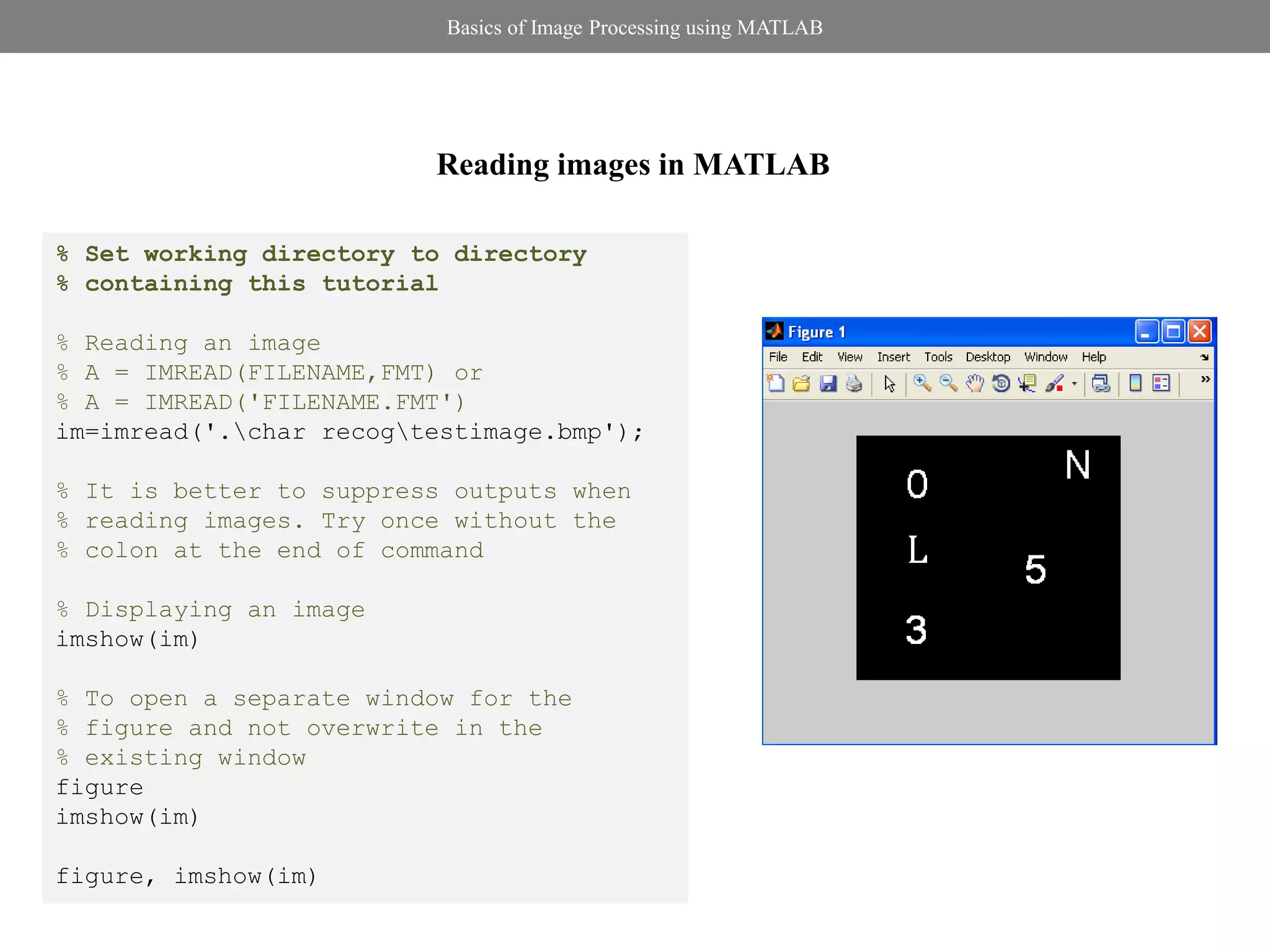
- Reading and displaying images
- Performing operations on image matrices like dilation, erosion, and thresholding
- Segmenting images using global and local thresholding methods
- Identifying and labeling connected components
- Extracting properties of connected components using regionprops
- Performing tasks like edge detection and noise removal
Code examples and explanations are provided for key functions like imread, imshow, imdilate, imerode, im2bw, regionprops, and edge.

![Basics of Image Processing using MATLAB
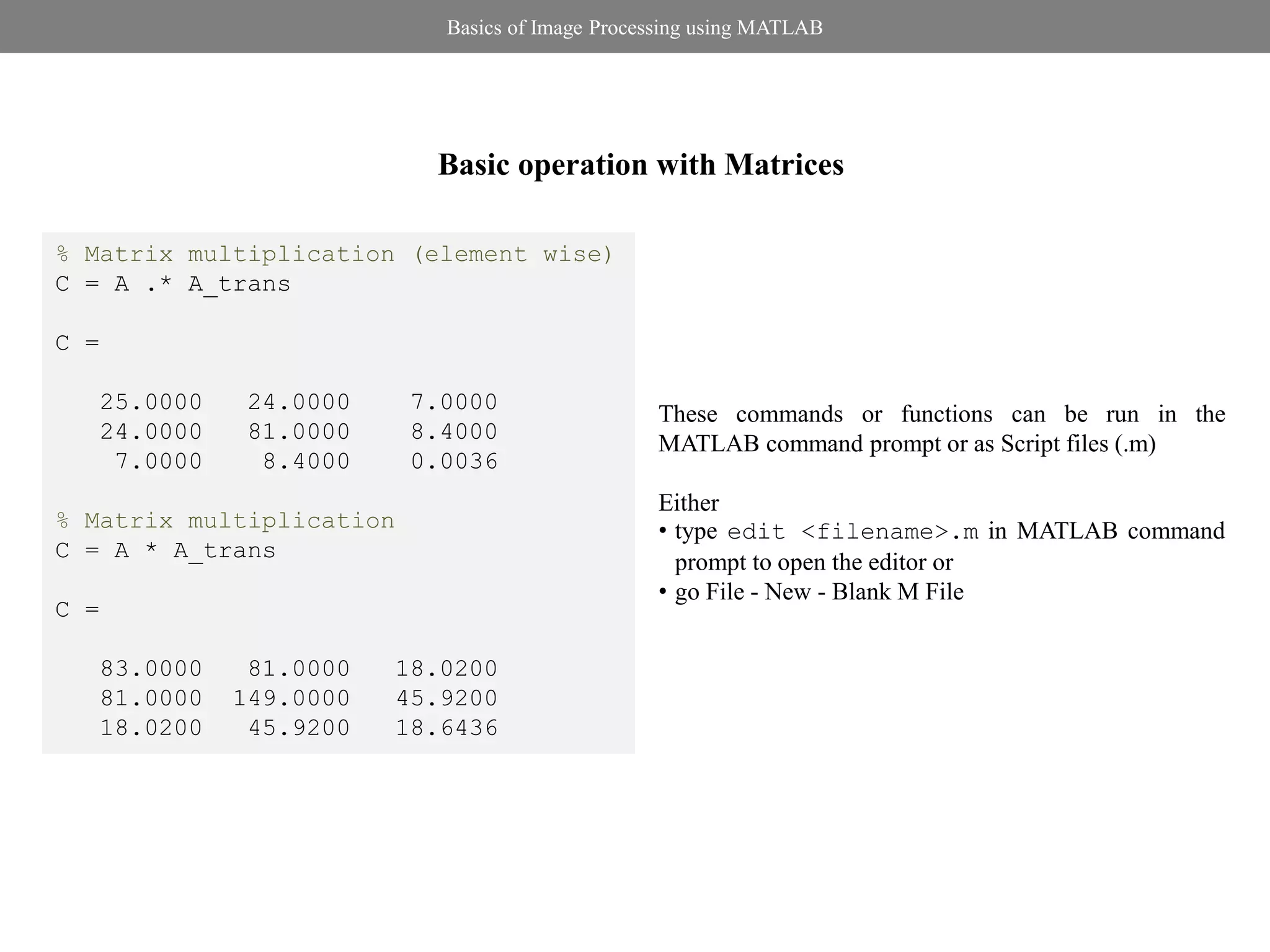
Basic operation with Matrices
% Use colon at the end to suppress % Transpose of a matrix
% output A_trans = A’
% To enter a matrix with real elements A_trans =
A = [5 3 7; 8 9 2; 1 4.2 6e-2]
5.0000 8.0000 1.0000
A = 3.0000 9.0000 4.2000
7.0000 2.0000 0.0600
5.0000 3.0000 7.0000
8.0000 9.0000 2.0000 % Matrix addition
1.0000 4.2000 0.0600 C = A + A_trans
% To enter a matrix with complex C =
% elements
X = [5+3*j 7+8j; 9+2j 1+4j;] 10.0000 11.0000 8.0000
11.0000 18.0000 6.2000
X = 8.0000 6.2000 0.1200
5.0000 + 3.0000i 7.0000 + 8.0000i
9.0000 + 2.0000i 1.0000 + 4.0000i](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdipusingmatlab-120618201616-phpapp02/75/Basics-of-Image-Processing-using-MATLAB-6-2048.jpg)
![Basics of Image Processing using MATLAB
Writing functions in MATLAB
Few examples of functions in MATLAB
% Function returning no output
function sample(ip1,ip2,ip3,…)
.
.
.
end
% Function with outputs
function [op1,op2,…]=sample(ip1,ip2,ip3,…)
.
.
.
End
% save the code as sample.m. Function name
% and m-file name should be the same](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdipusingmatlab-120618201616-phpapp02/75/Basics-of-Image-Processing-using-MATLAB-13-2048.jpg)

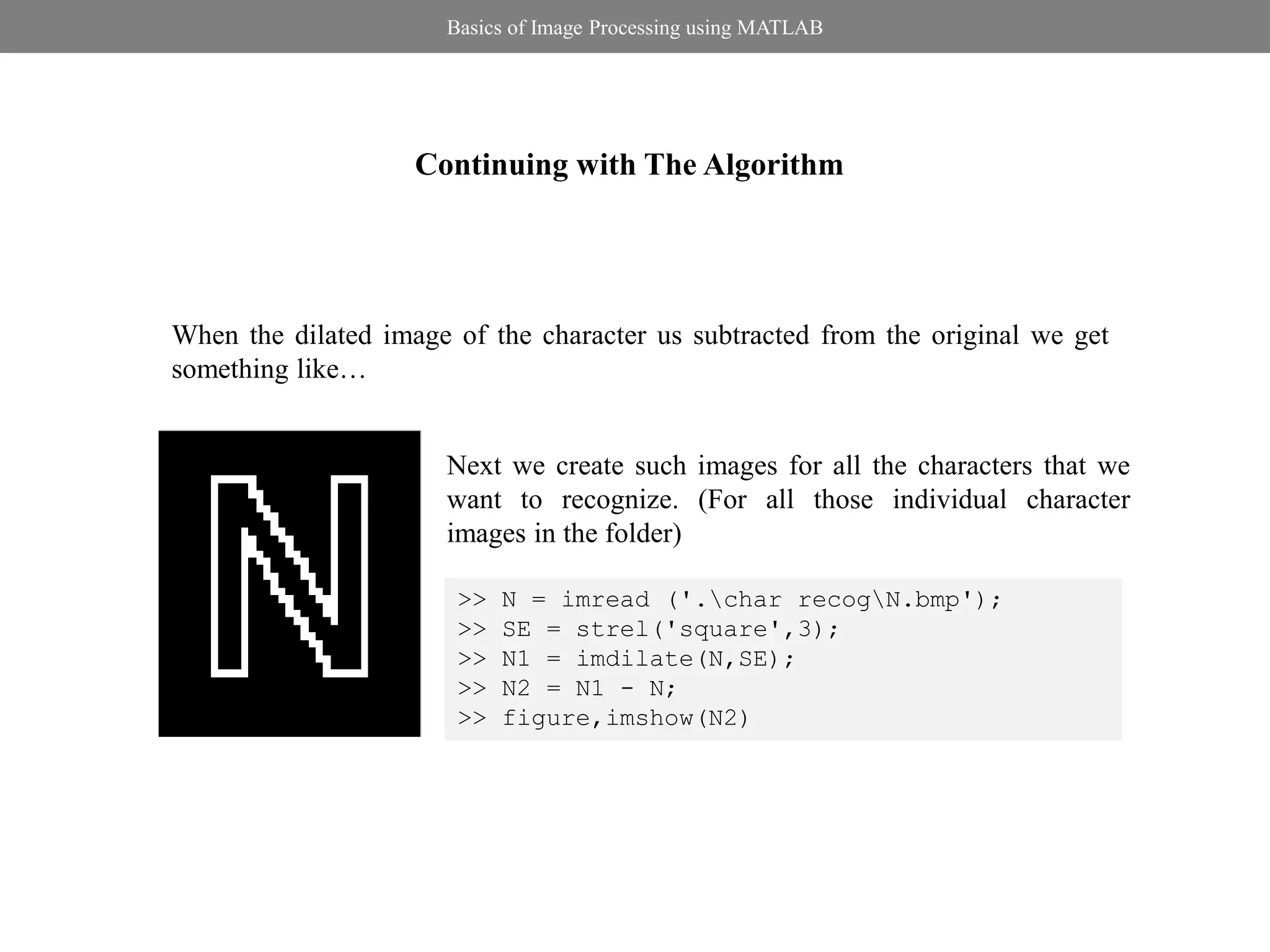

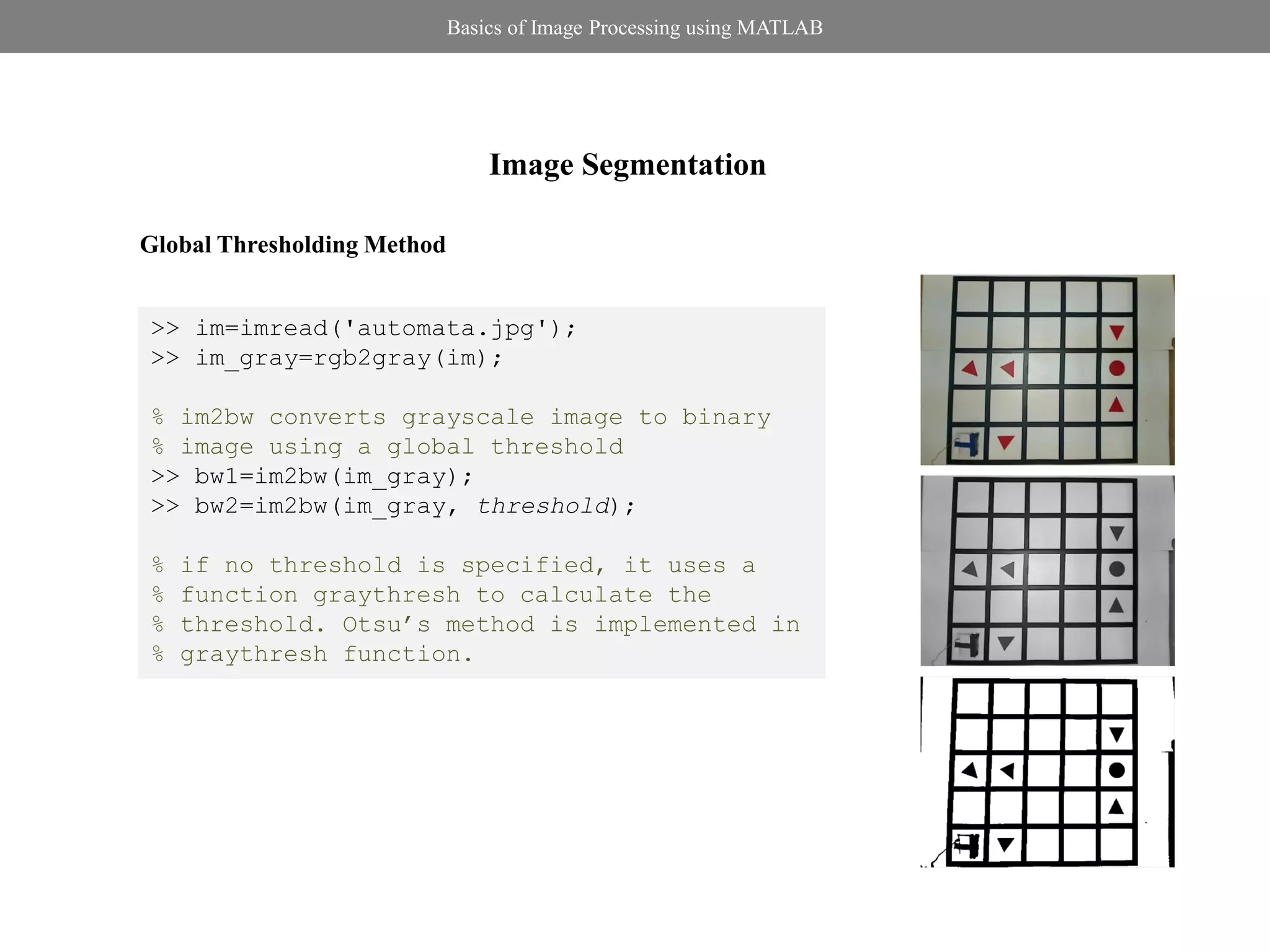
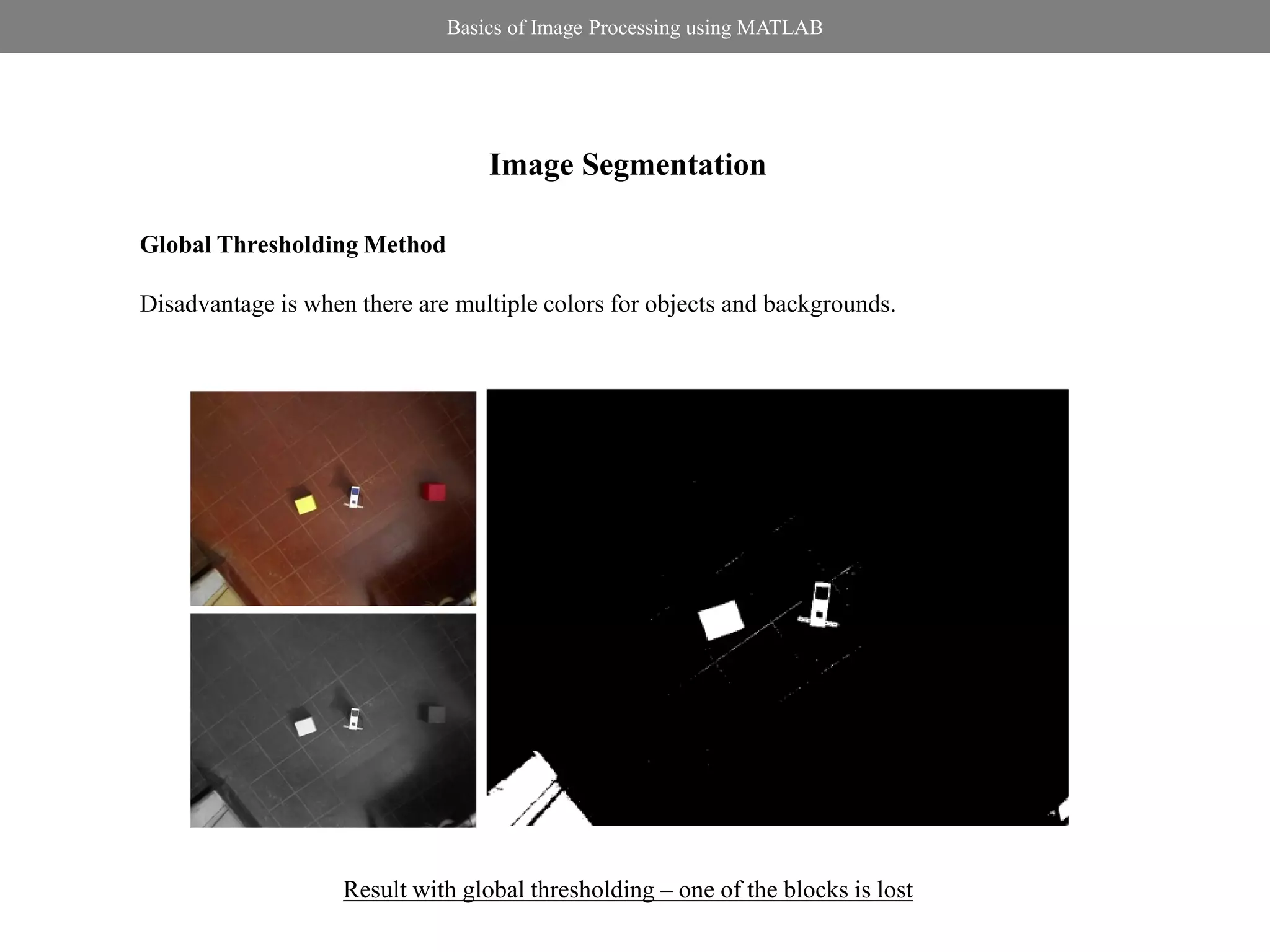
![Basics of Image Processing using MATLAB
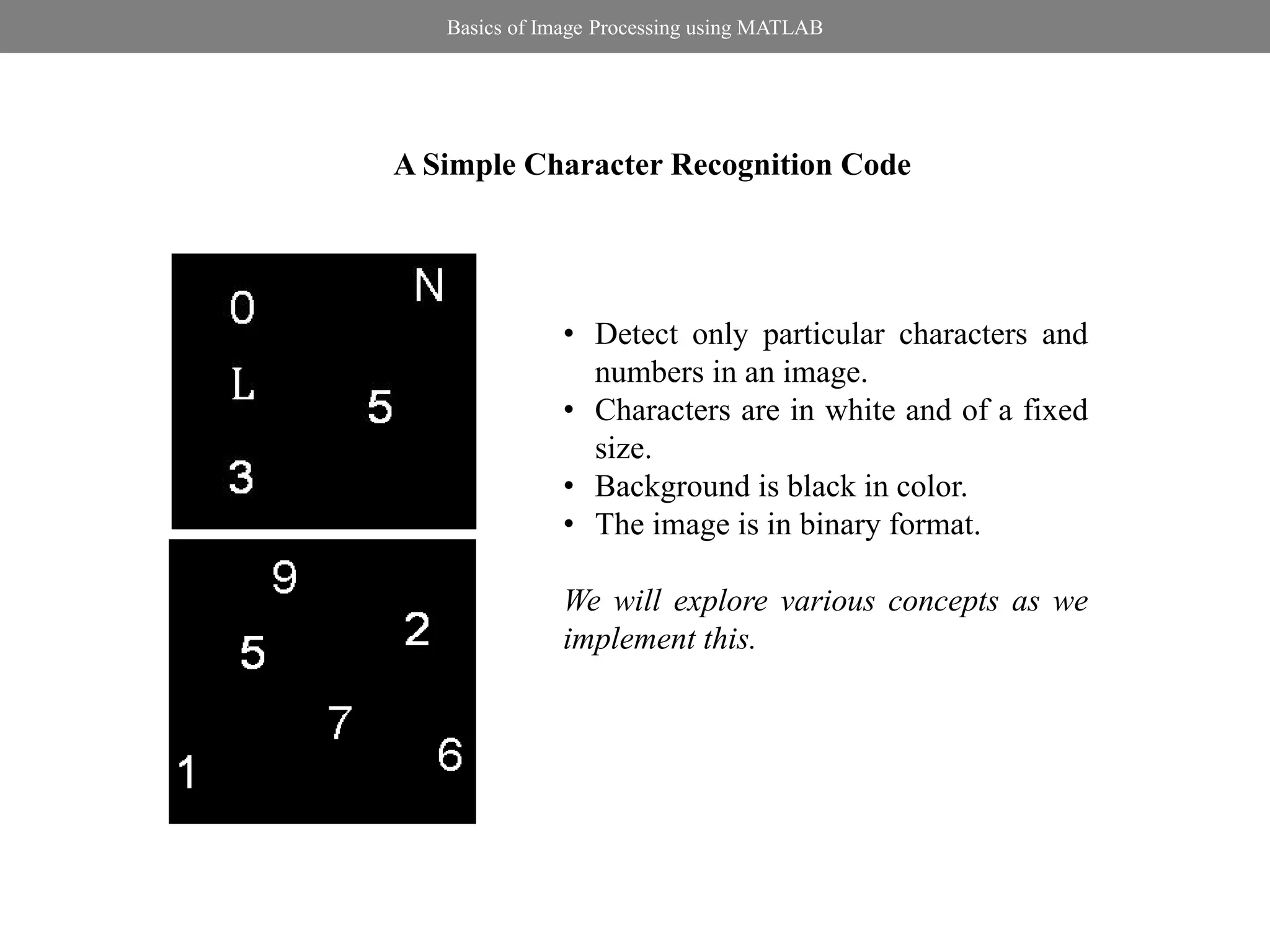
Image Segmentation
Local Thresholding Method: Niblack’s Method
>> im=imread('blocks.jpg');
255 if I( x, y ) T ( x, y ) >> im_gray=rgb2gray(im);
R( x, y ) 100 if I( x, y ) T ( x, y ) >> imt=niblack(im_gray,0.5,201);
>> figure,imshow(imt,[])
0
otherwise
% Here k=0.5 and N=201(preferably odd)
T ( x, y) N k N
% think about effects of values of N on
% processing time and k on thresholding
% level
k and N are to be empirically determined](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdipusingmatlab-120618201616-phpapp02/75/Basics-of-Image-Processing-using-MATLAB-21-2048.jpg)
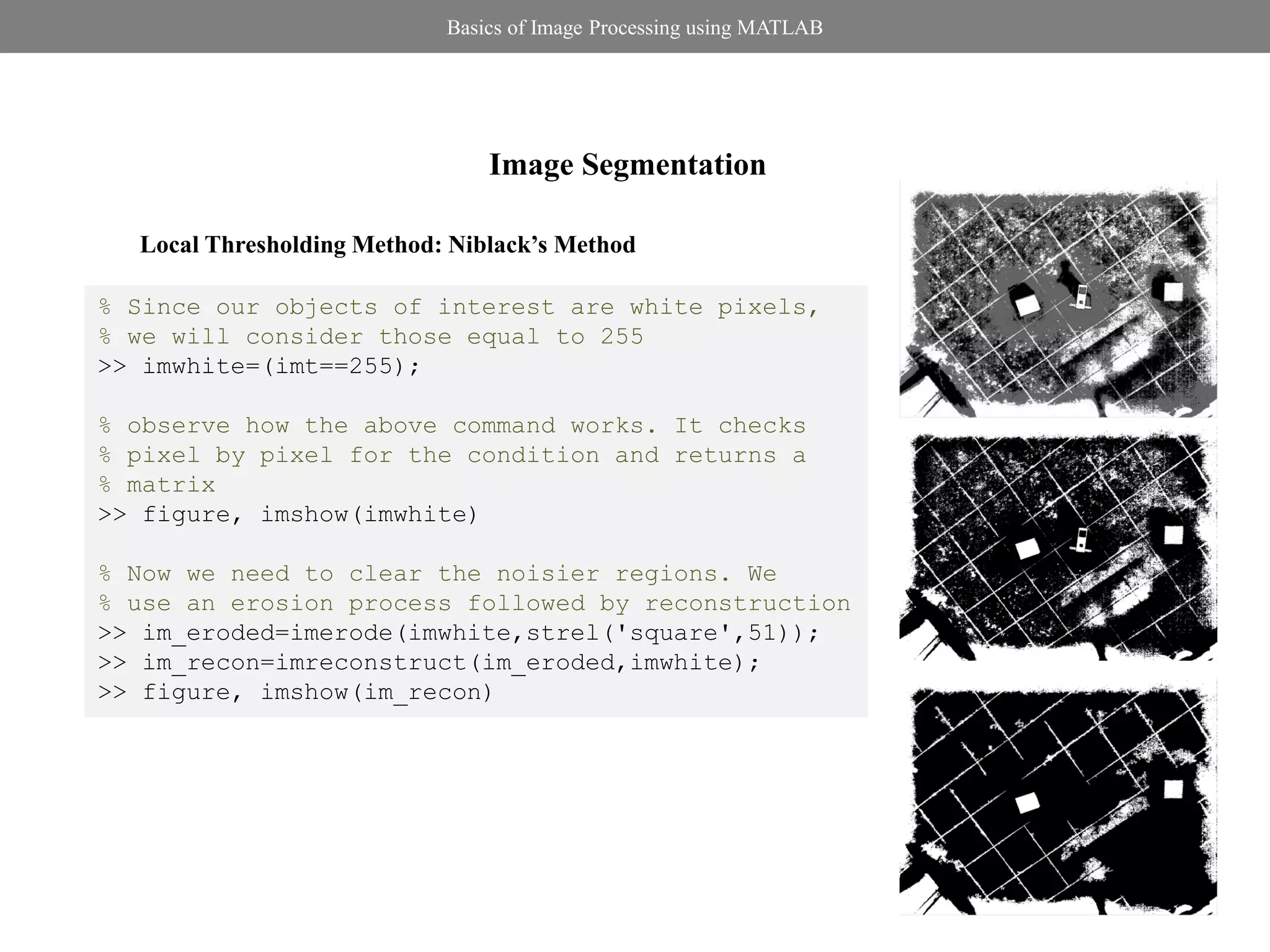
![Basics of Image Processing using MATLAB
Connected Components
% You can see pixels connected to each other
% form objects in the image. These are
% called connected components. Read more
% about 4-connectivity and 8-connectivity
% Label the connected components i.e. assign
% a particular number as pixel value to one CC
>> [bw_labelled num]=bwlabel(im_recon);
>> figure,imshow(bw_labelled,[])
% We can use regionprops() to extract some
% properties of the CCs
>> areas = regionprops(bw_labelled,'Area')
% Here areas is a struct variable
% Try experimenting with other properties and
% explore what property can be used to
% distinguish between CCs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdipusingmatlab-120618201616-phpapp02/75/Basics-of-Image-Processing-using-MATLAB-23-2048.jpg)
![Basics of Image Processing using MATLAB
% We will convert to struct to a normal array for easy operation
>> areas1=[];
>> for i=1:length(areas)
areas1=[areas1; areas(i,1).Area];
end
>> areas1
areas1 =
415711
26440
10350
8630
17971
8282
5243
% We are interested in objects (the squares) with area in range 8000-
% 9000
>> index=find(areas1>8000 & areas1<9000);
>> finalimg=zeros(size(bw_labelled));
>> for i=1:length(index)
finalimg=finalimg+(bw_labelled==index(i));
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdipusingmatlab-120618201616-phpapp02/75/Basics-of-Image-Processing-using-MATLAB-24-2048.jpg)
![Basics of Image Processing using MATLAB
>> figure,imshow(finalimg,[])
This was again a very crude way, since we are depending only on value of
area which might not remain constant if camera changes position.
Most of the times the standard features available with regionprops() is
not sufficient. We will have to write our own code to extract features.
Also we used hard thresholds for areas to classify CCs. Again most of the
times, this is not followed. Classifiers using Pattern Recognition techniques
are employed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdipusingmatlab-120618201616-phpapp02/75/Basics-of-Image-Processing-using-MATLAB-25-2048.jpg)
![Basics of Image Processing using MATLAB
Few Other Stuff
You can try
Edge detection
>> im=imread('ouch.jpg');
>> im_gray=rgb2gray(im);
>> imedge=edge(im_gray,'canny',[0.1 0.2]);
>> figure,imshow(imedge)
% Try different edge operators and
% threshold levels
and
Removing Noise By Median Filtering
(MATLAB Help)
There is more to learn in Image Processing. All the Best](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofdipusingmatlab-120618201616-phpapp02/75/Basics-of-Image-Processing-using-MATLAB-26-2048.jpg)
