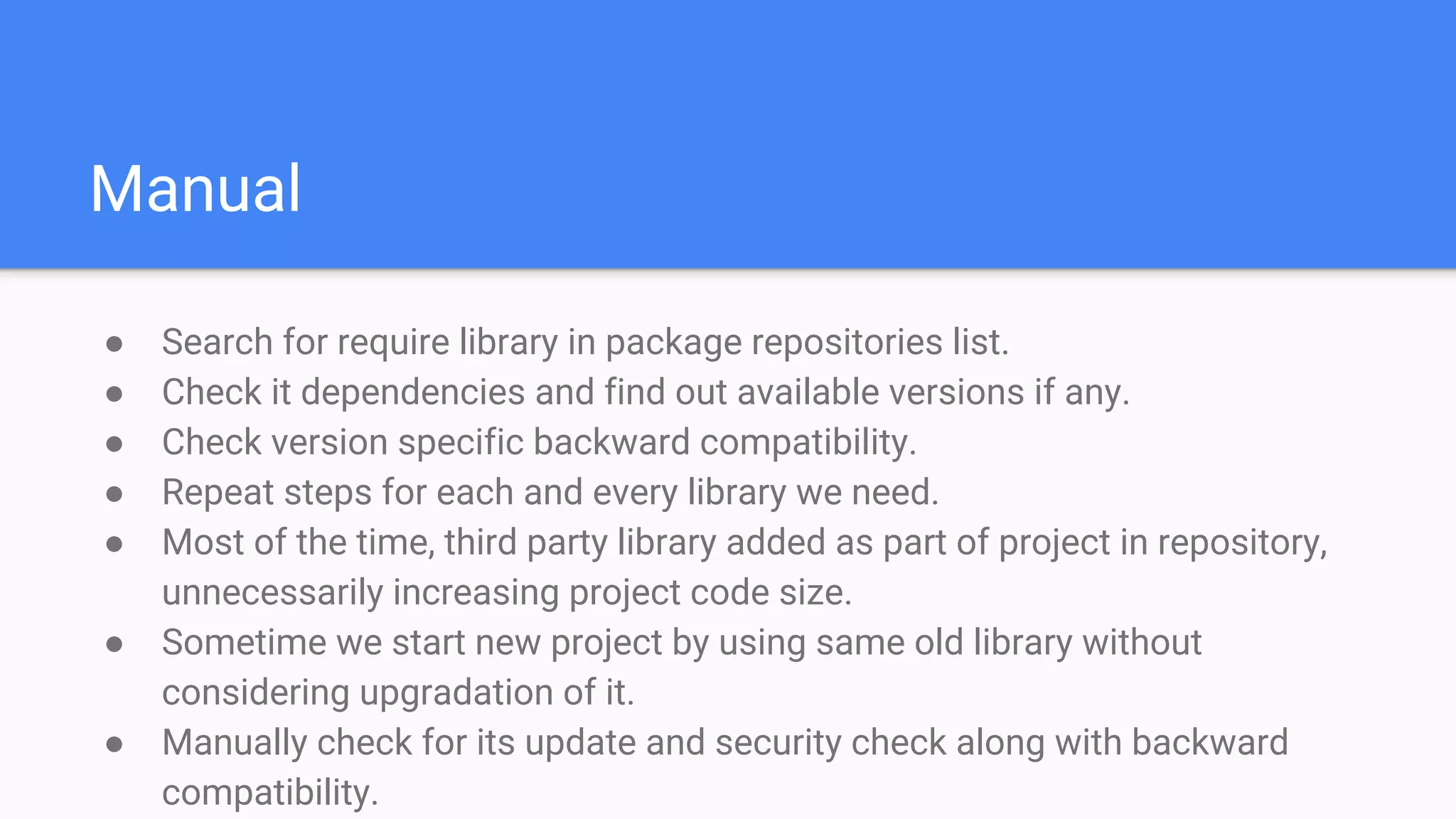
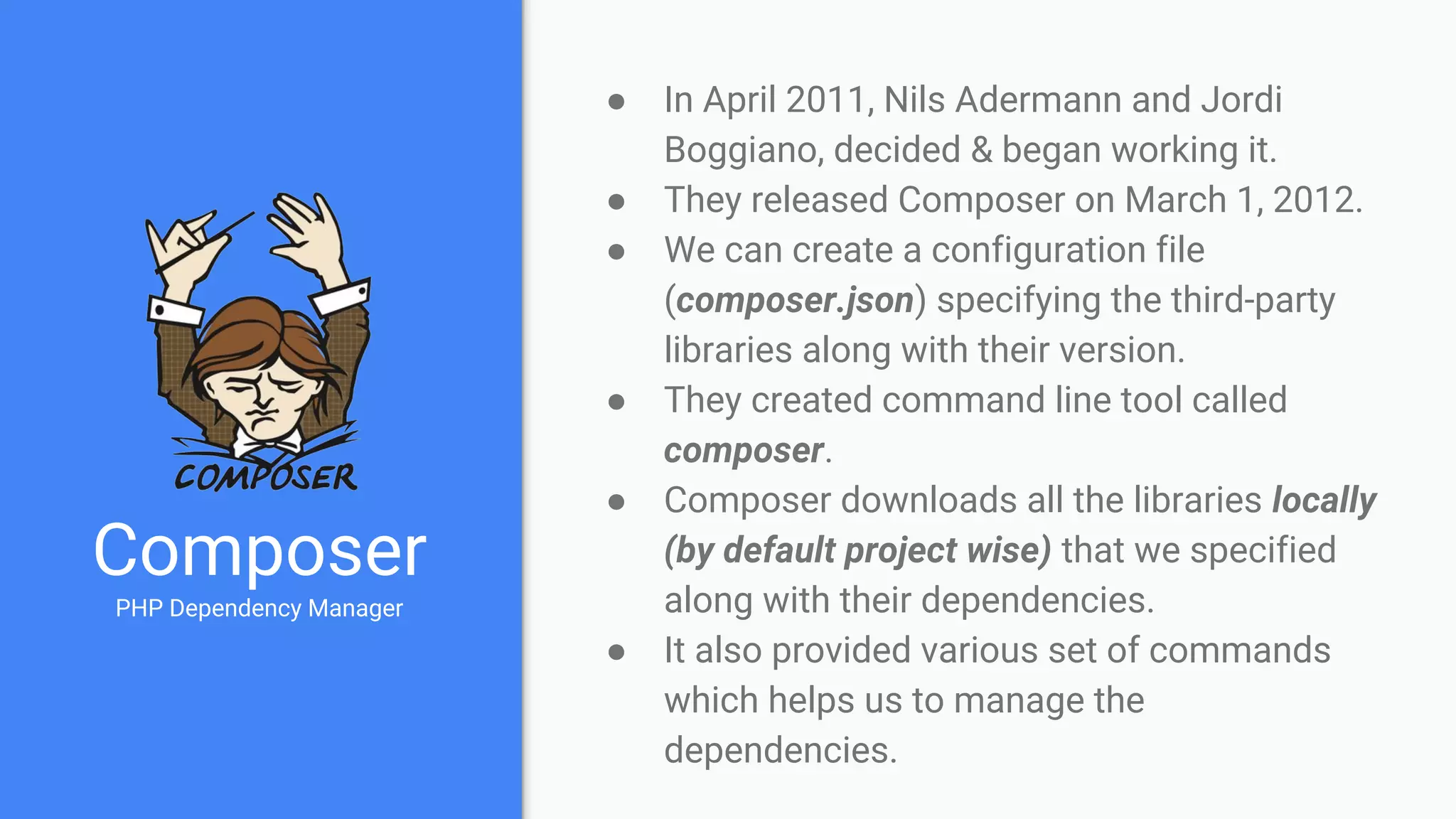
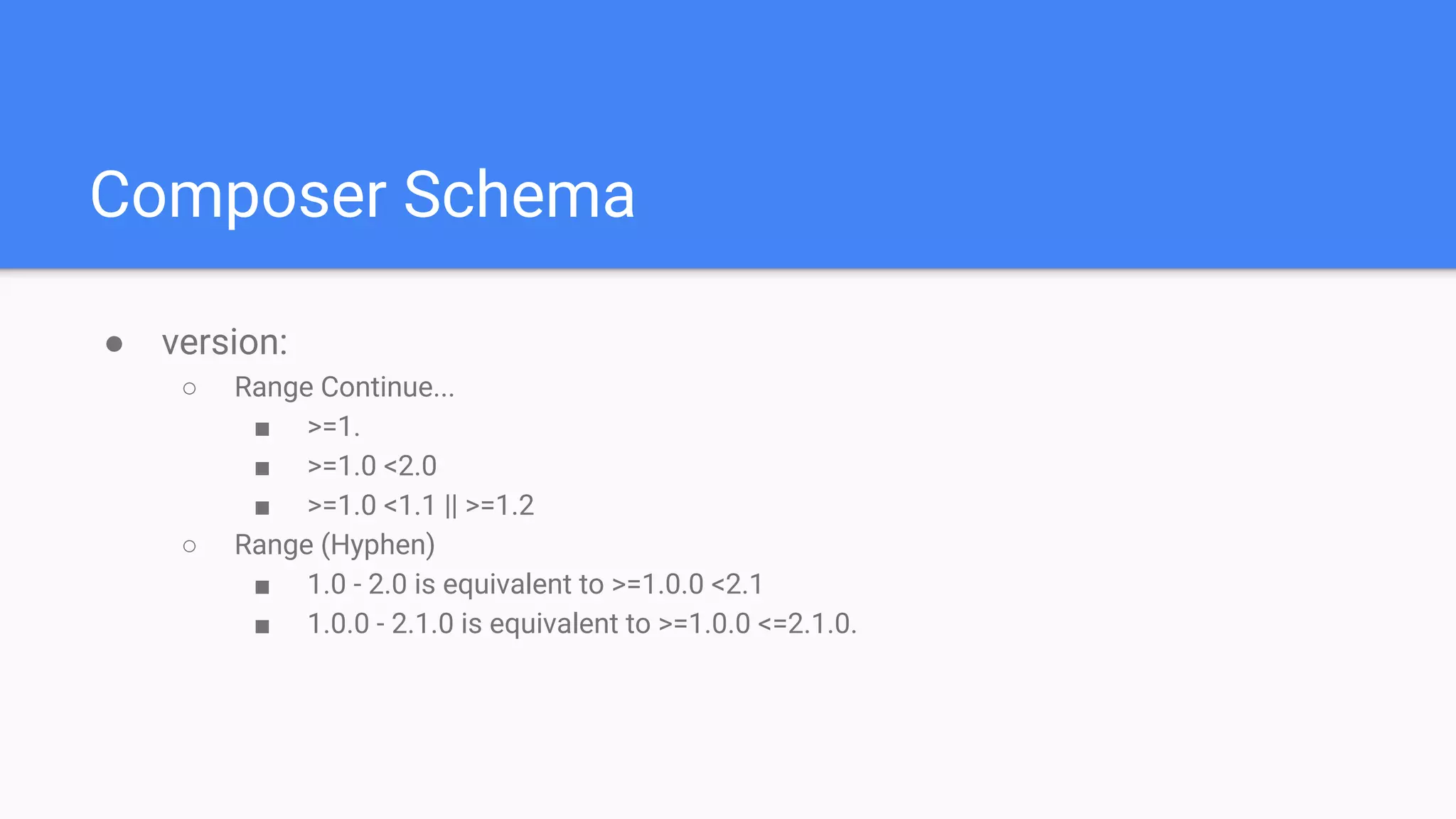
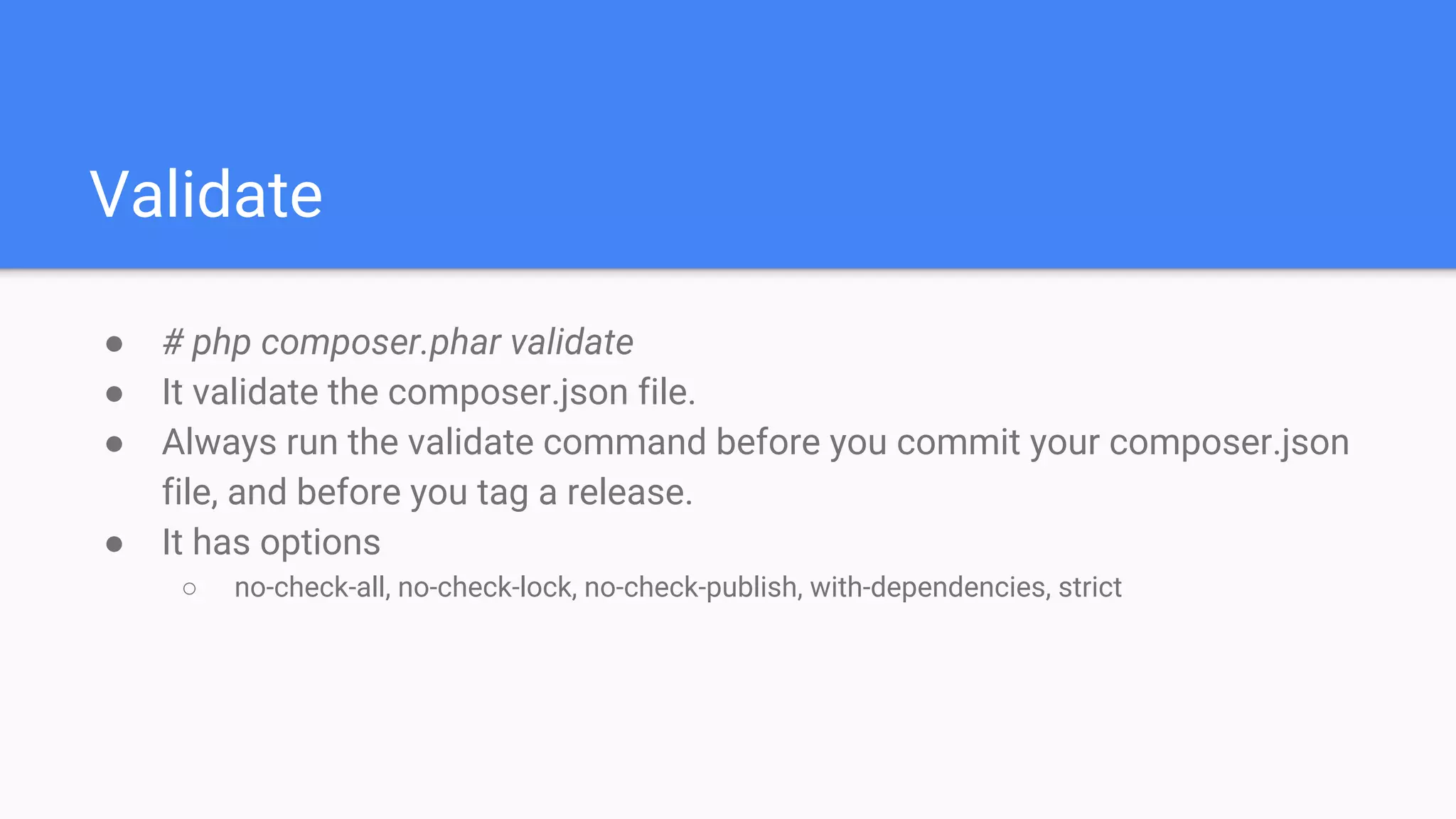
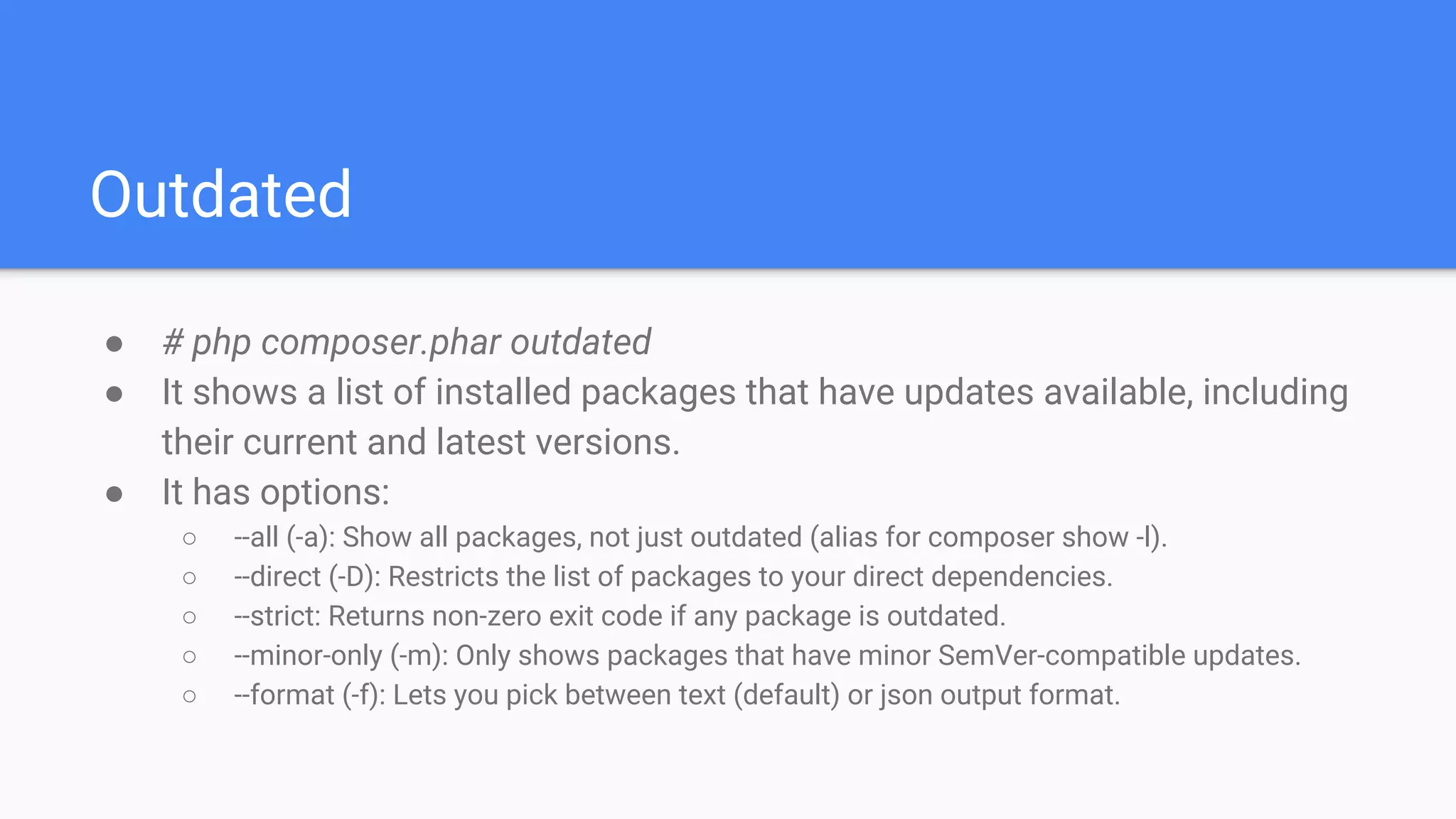
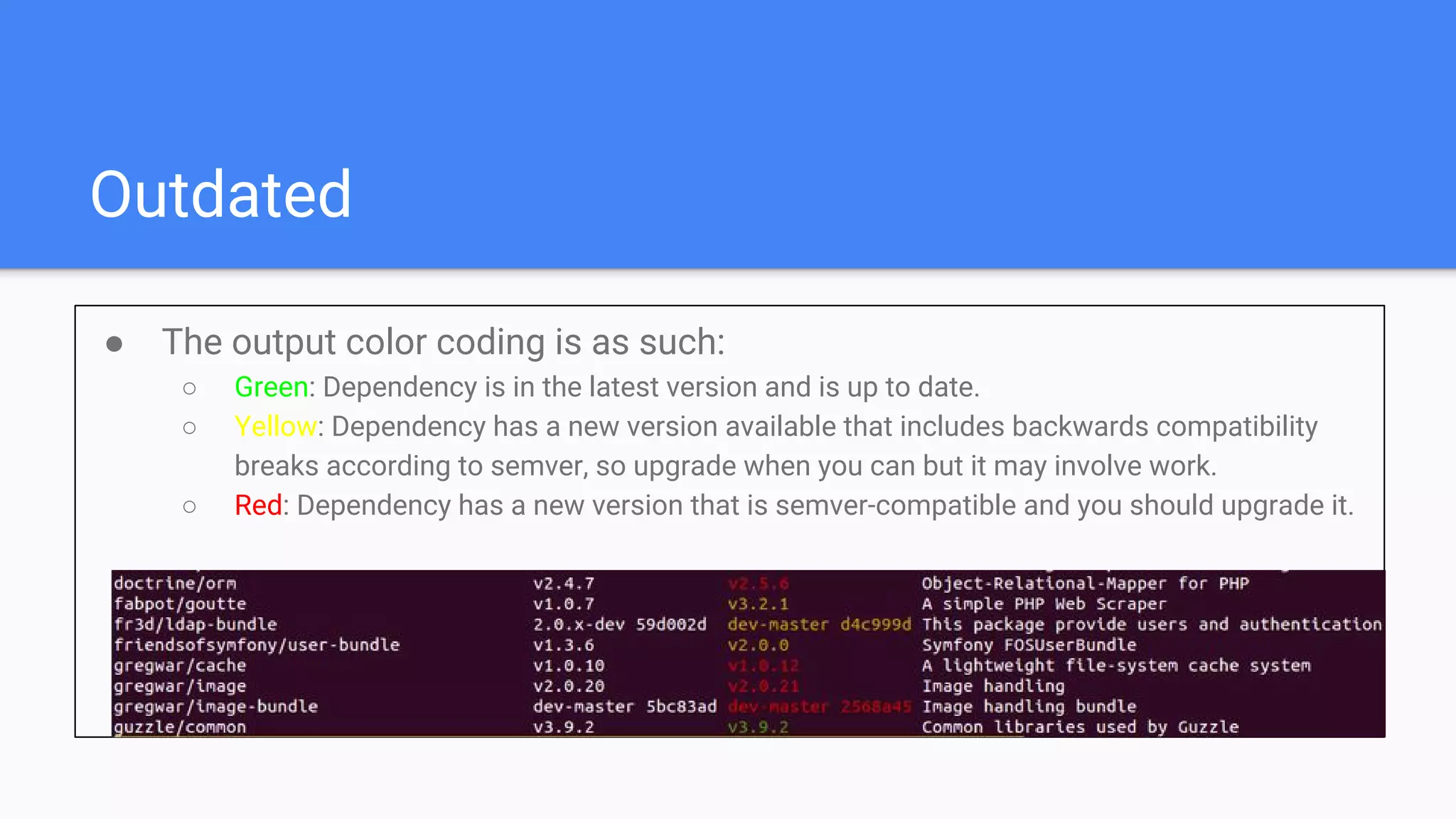
Tool for dependency management in PHP. Composer is a dependency manager for PHP which allows you to declare and install dependencies for PHP applications. It provides a composer.json file to define dependencies and versions, and a command line interface to install, update, and manage dependencies. Key features include automated installation of dependencies and their transitive dependencies, semantic versioning support, and tools to validate configurations and check for outdated packages.