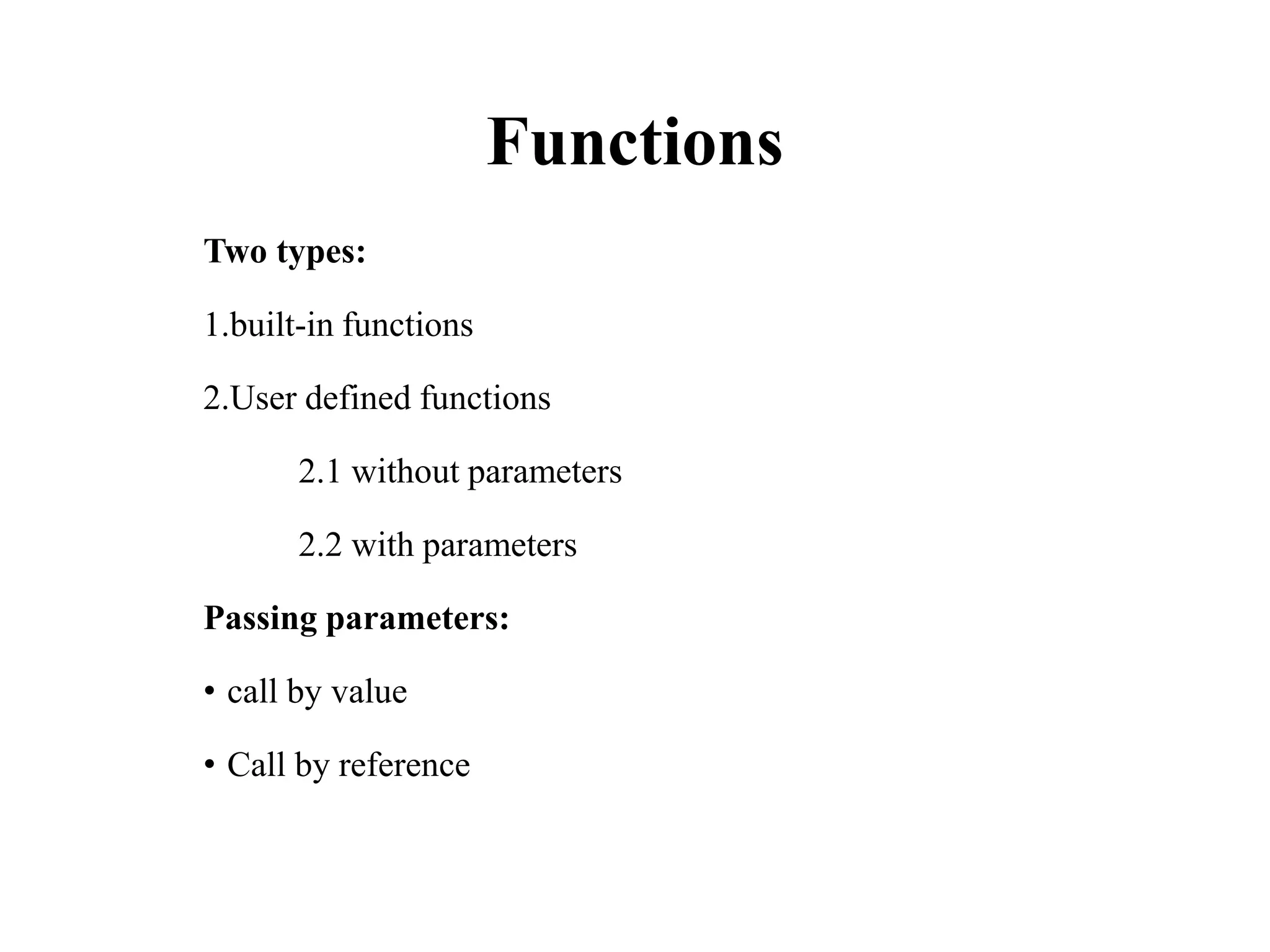
This document provides an introduction to the C programming language. It discusses the history and development of C, how C programs are structured, and the basic building blocks or tokens of C code like keywords, identifiers, constants, and operators. It also covers various data types in C, input and output functions, decision making and looping statements, functions, arrays, pointers, structures, unions, and file handling. The document is intended to give beginners an overview of the essential components of the C language.






![C Character set:
Any alphabet, digit or special
symbol can be termed as a character.
Below shows list of valid alphabets,
digits and symbols allowed in C.
Alphabets:
A, B, C, D, …, X, Y, Z
a, b, c, d, … ,x, y, z
Digits:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Special Symbols:
~ ‘ ! @ # % ^ & * ( ) _ - +
= | { }
[ ] : ; " ' < > , . ? /](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-introductionbythooyavan-160518102221/75/C-introduction-by-thooyavan-9-2048.jpg)









![Arrays
Collection of similar data
type
Syntax;
Datatype Arrayname[size];
Example: INTEGER
DATA TYPE
Int a[20];
for(i=0;i<=19;i++)
{
Scanf(“%d”,a[i]);
}
Example:char data type
Void main()
{
Char s[50];
Printf(“enter the name”);
Gets(s);
Puts(s);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-introductionbythooyavan-160518102221/75/C-introduction-by-thooyavan-26-2048.jpg)






