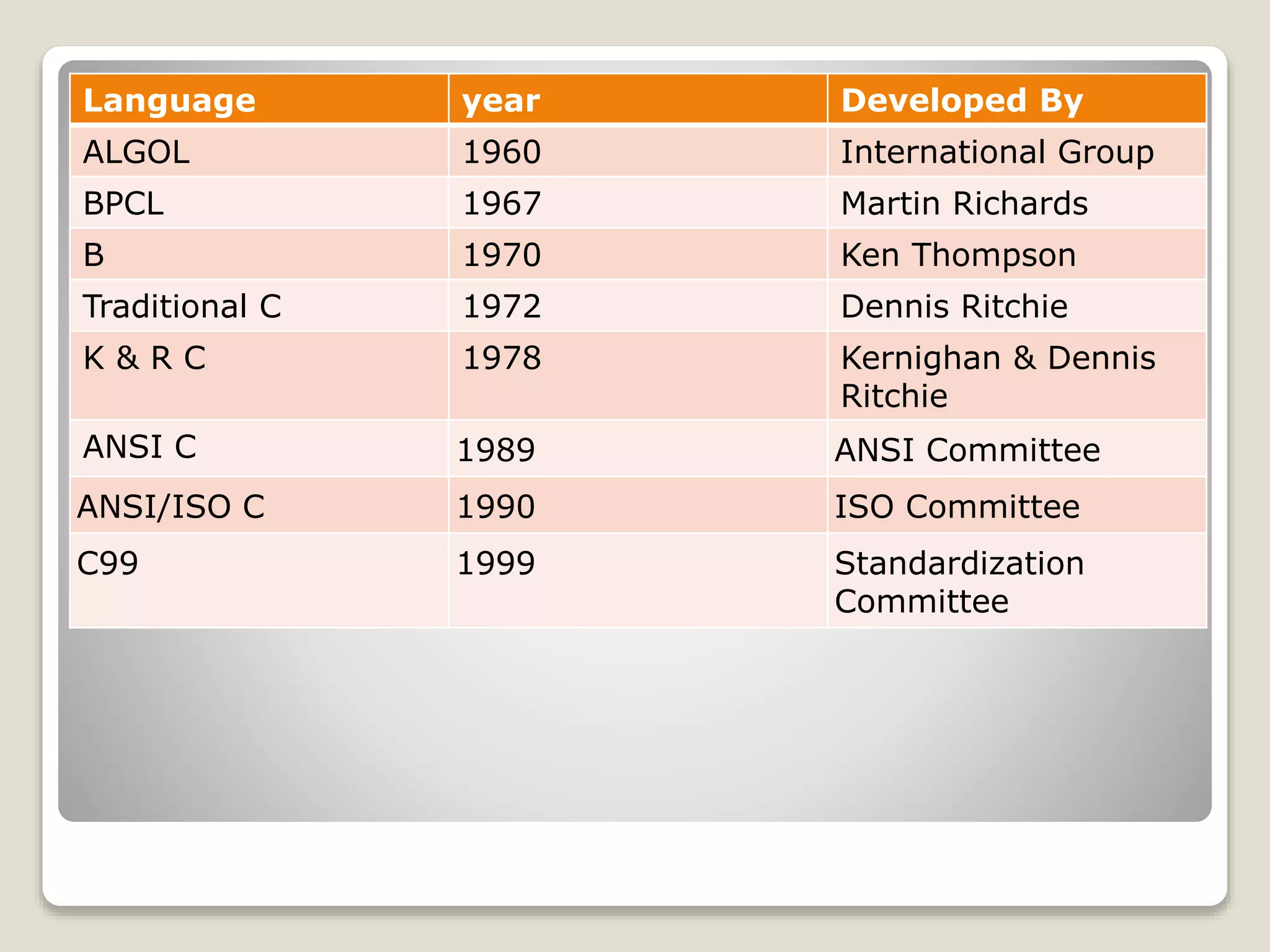
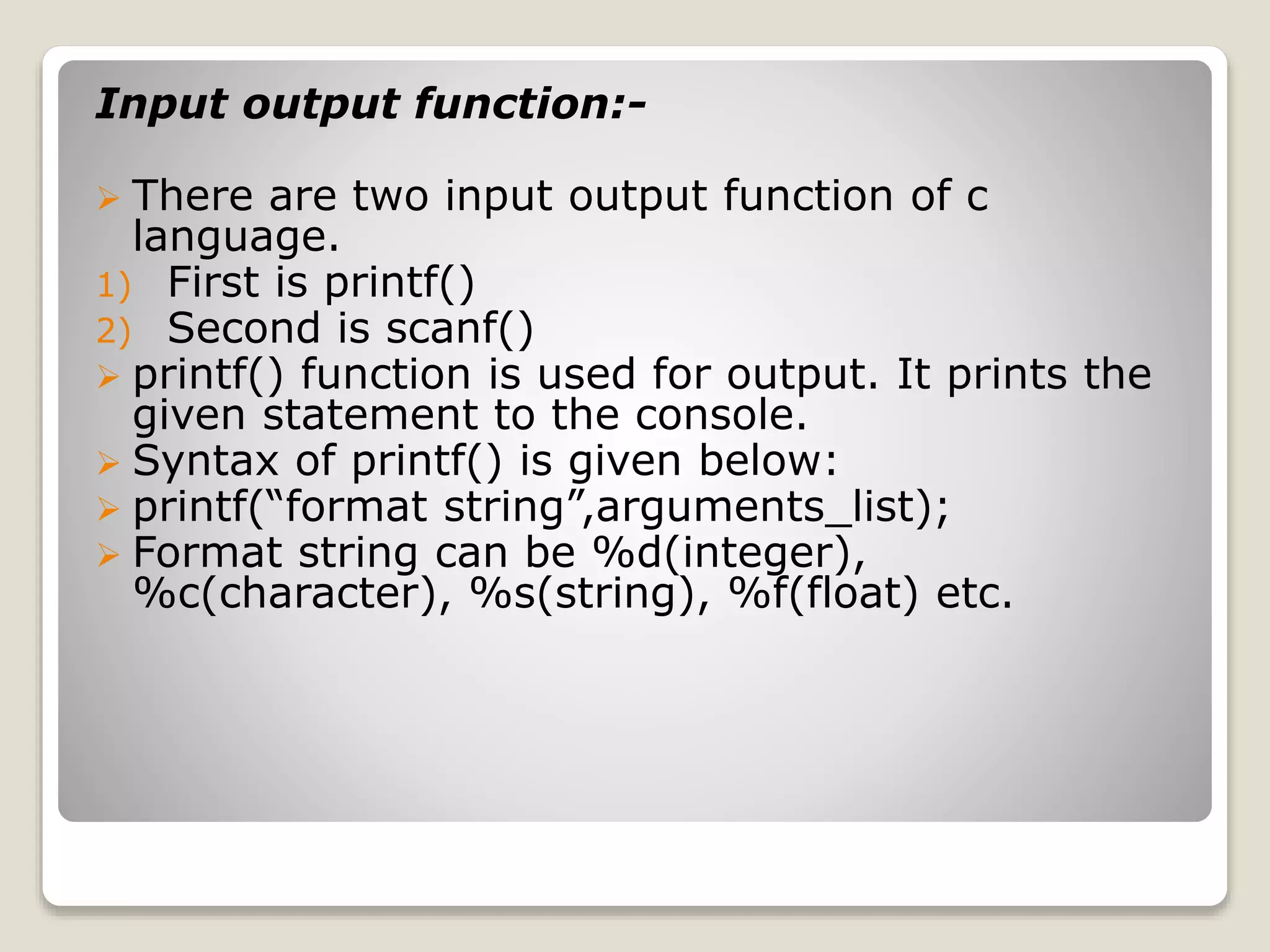
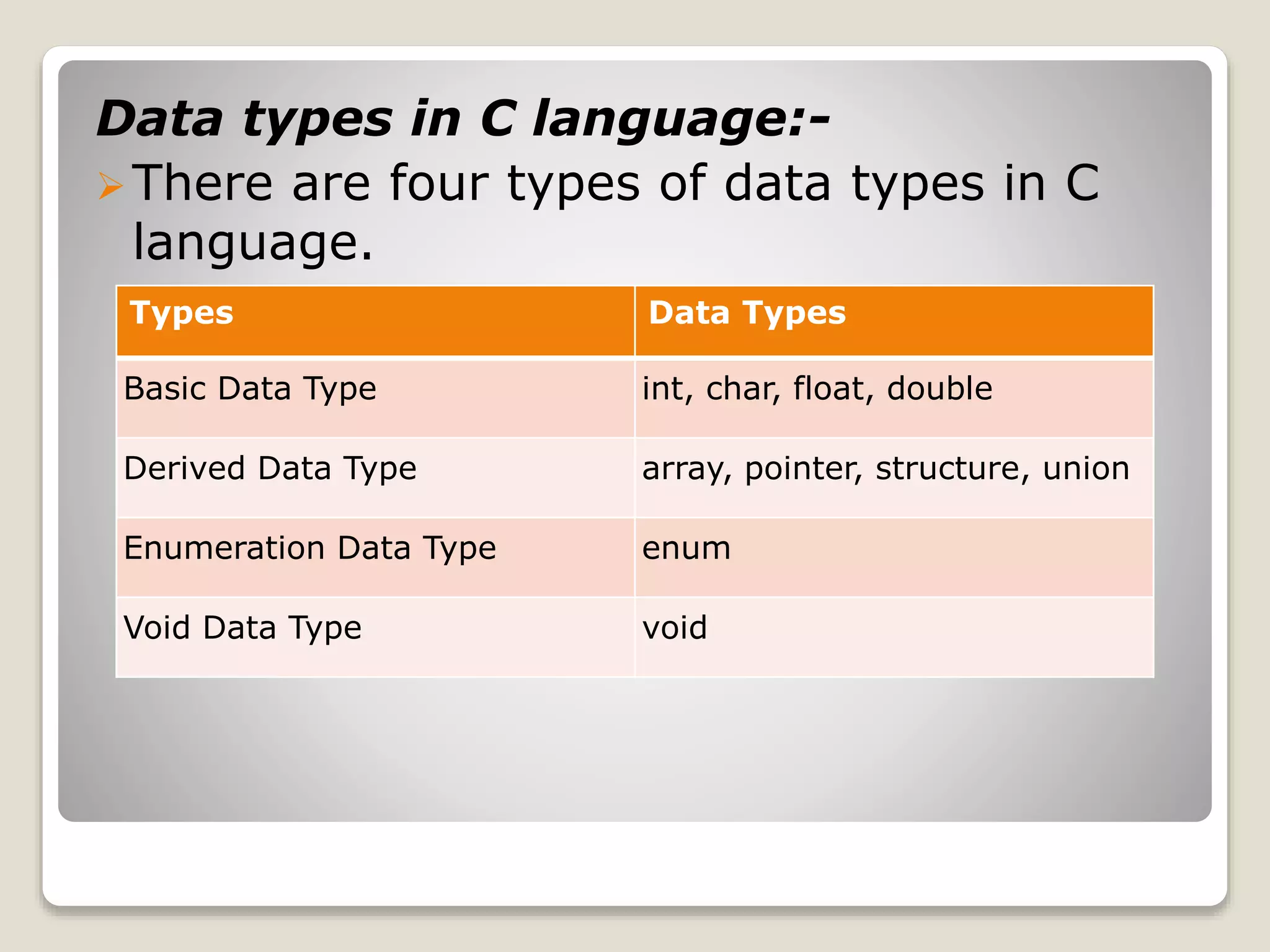
The document is a comprehensive tutorial on the C programming language covering its history, features, data types, keywords, operators, control statements, functions, and arrays. It highlights the language's development by Dennis Ritchie in 1972 and includes sample code for basic operations, input/output functions, and control statements. Additionally, it explains concepts like call by value and call by reference, recursion, and the organization of arrays.
































![Array in C:-
Array in C language is a collection or group of
elements (data). All the elements of array
are homogeneous(similar). It has contiguous memory
location.
Declaration of array:-
data_type array_name[array_size];
Eg:-
int marks[7];
Types of array:-
1) 1-D Array
2) 2-D Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramminglanguagetutorial-140626075213-phpapp01/75/C-Programming-Language-Tutorial-for-beginners-JavaTpoint-36-2048.jpg)

![2-D Array in C:-
2-d Array is represented in the form of
rows and columns, also known as matrix.
It is also known as array of arrays or list
of arrays.
Declaration of 2-d array:-
data_type array_name[size1][size2];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramminglanguagetutorial-140626075213-phpapp01/75/C-Programming-Language-Tutorial-for-beginners-JavaTpoint-38-2048.jpg)
![Initialization of 2-d array:-
int arr[3][4]={{1,2,3,4},{2,3,4,5},{3,4,
5,6}};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramminglanguagetutorial-140626075213-phpapp01/75/C-Programming-Language-Tutorial-for-beginners-JavaTpoint-39-2048.jpg)