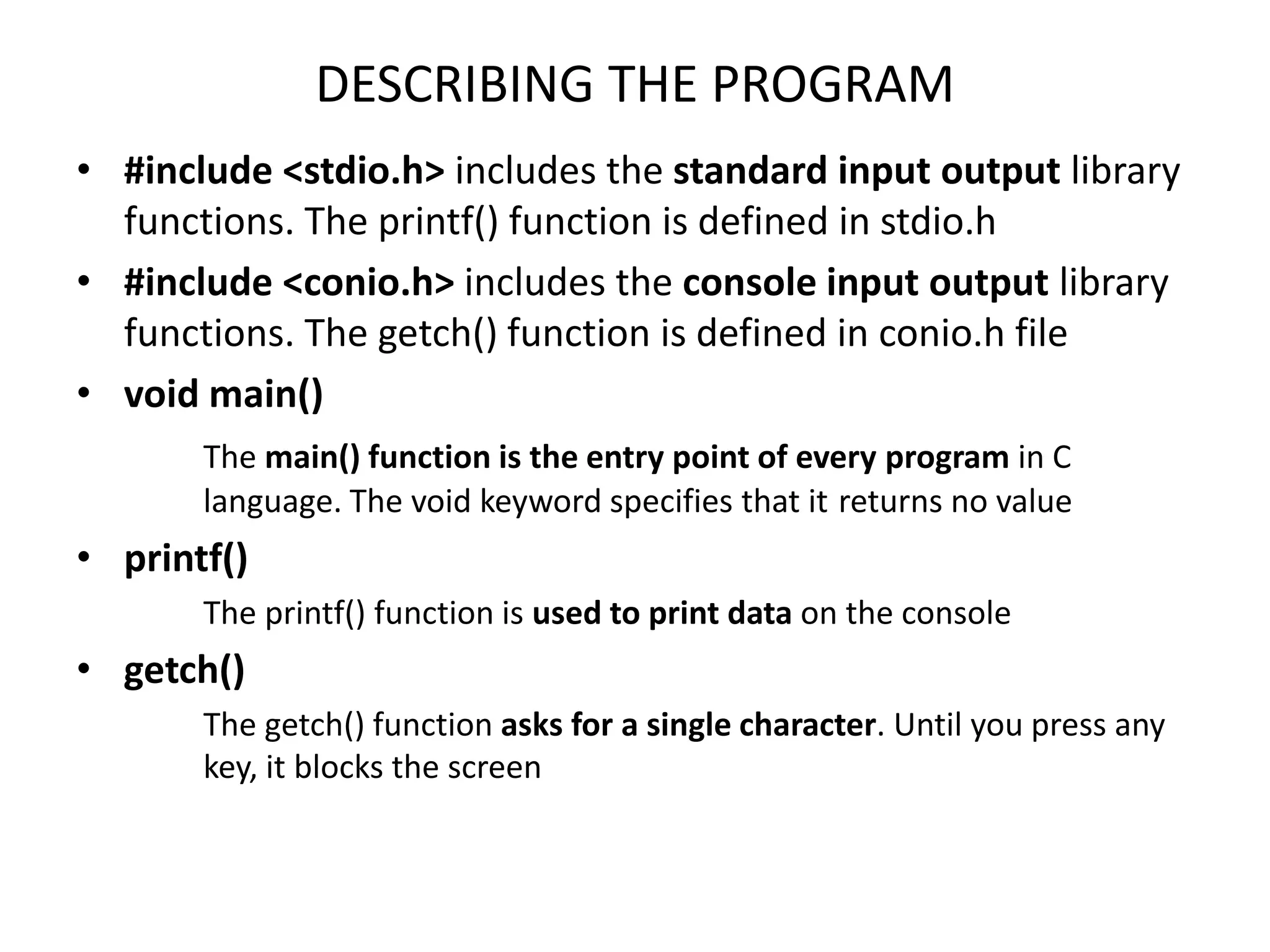
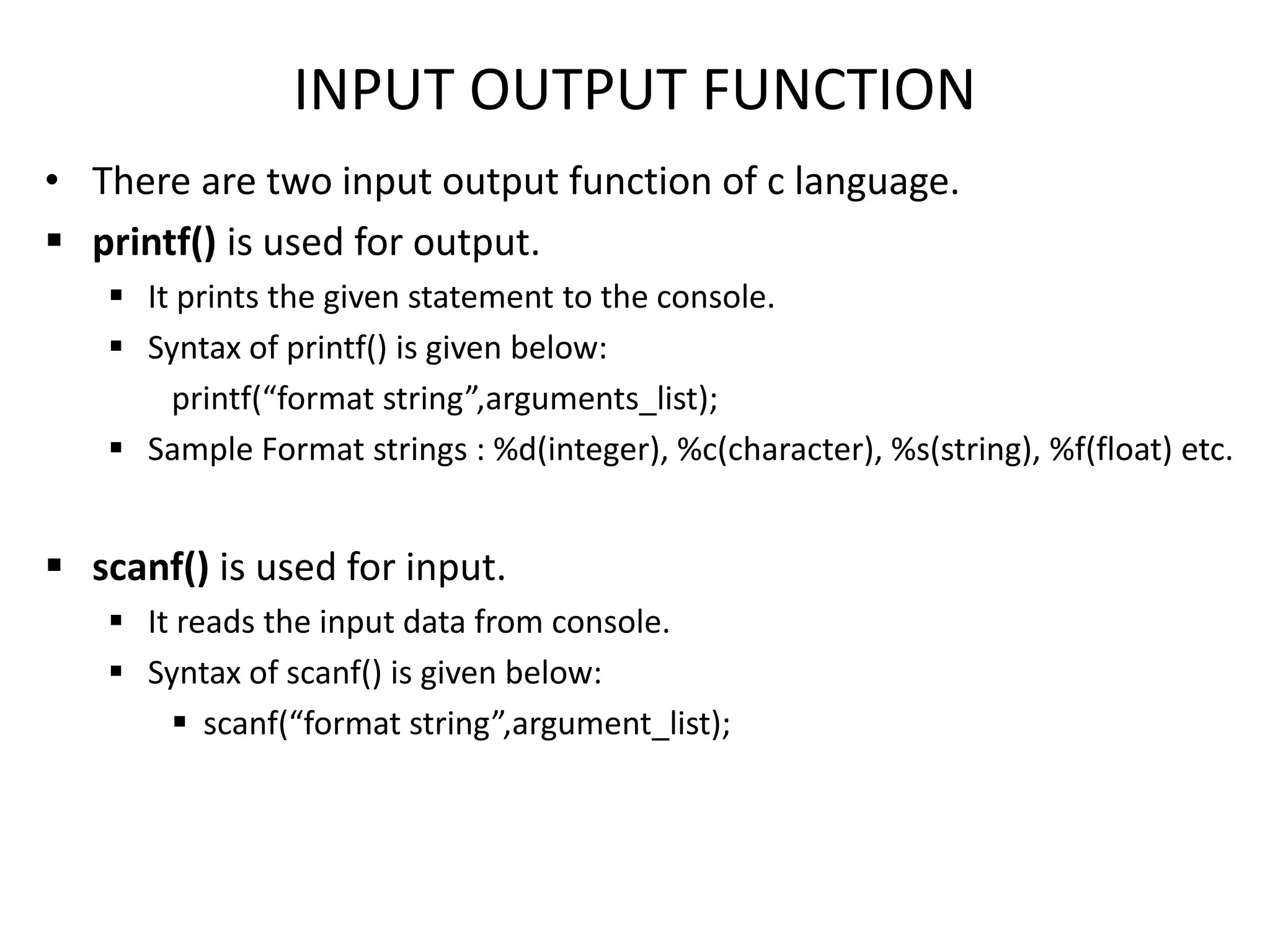
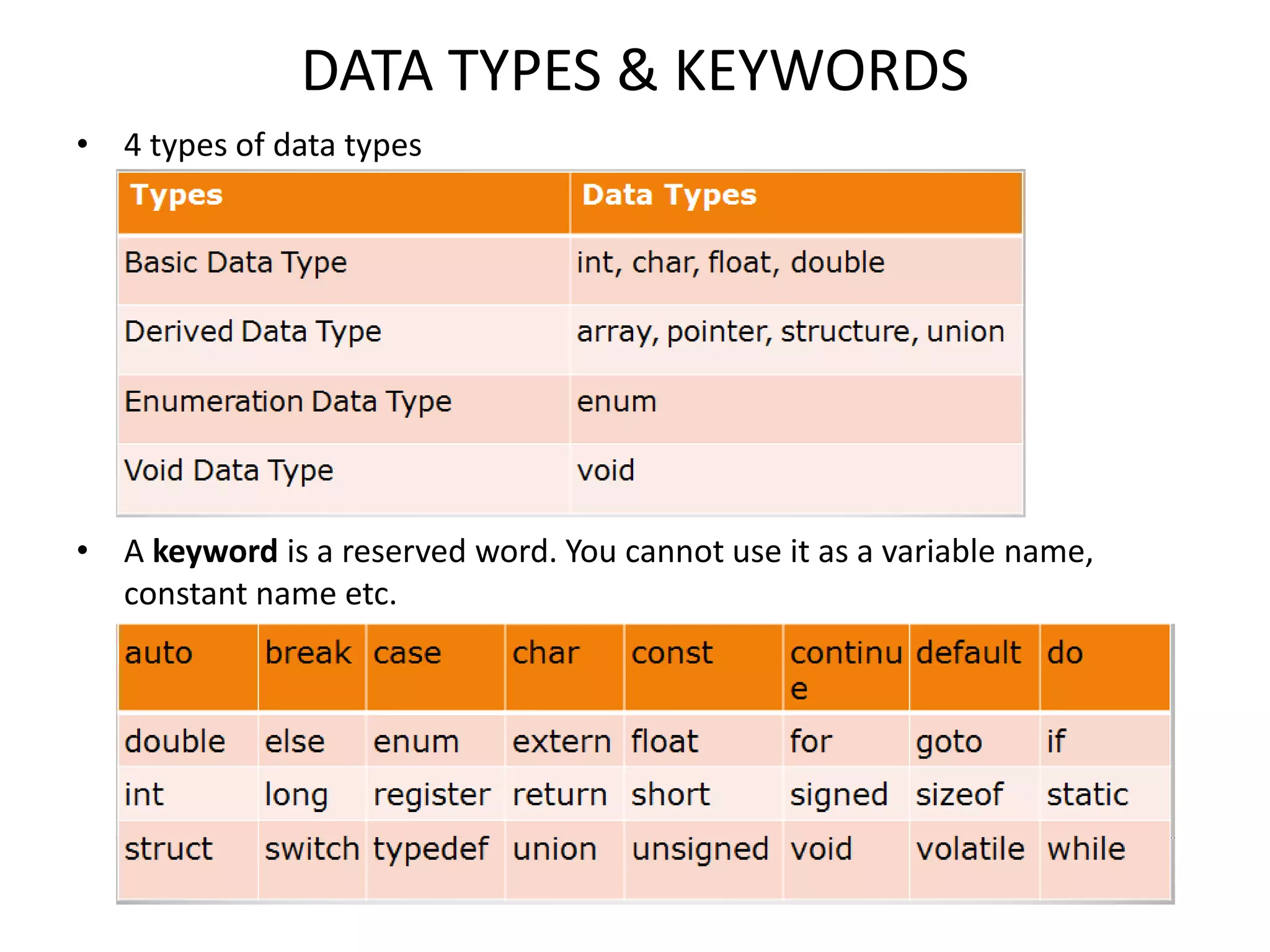
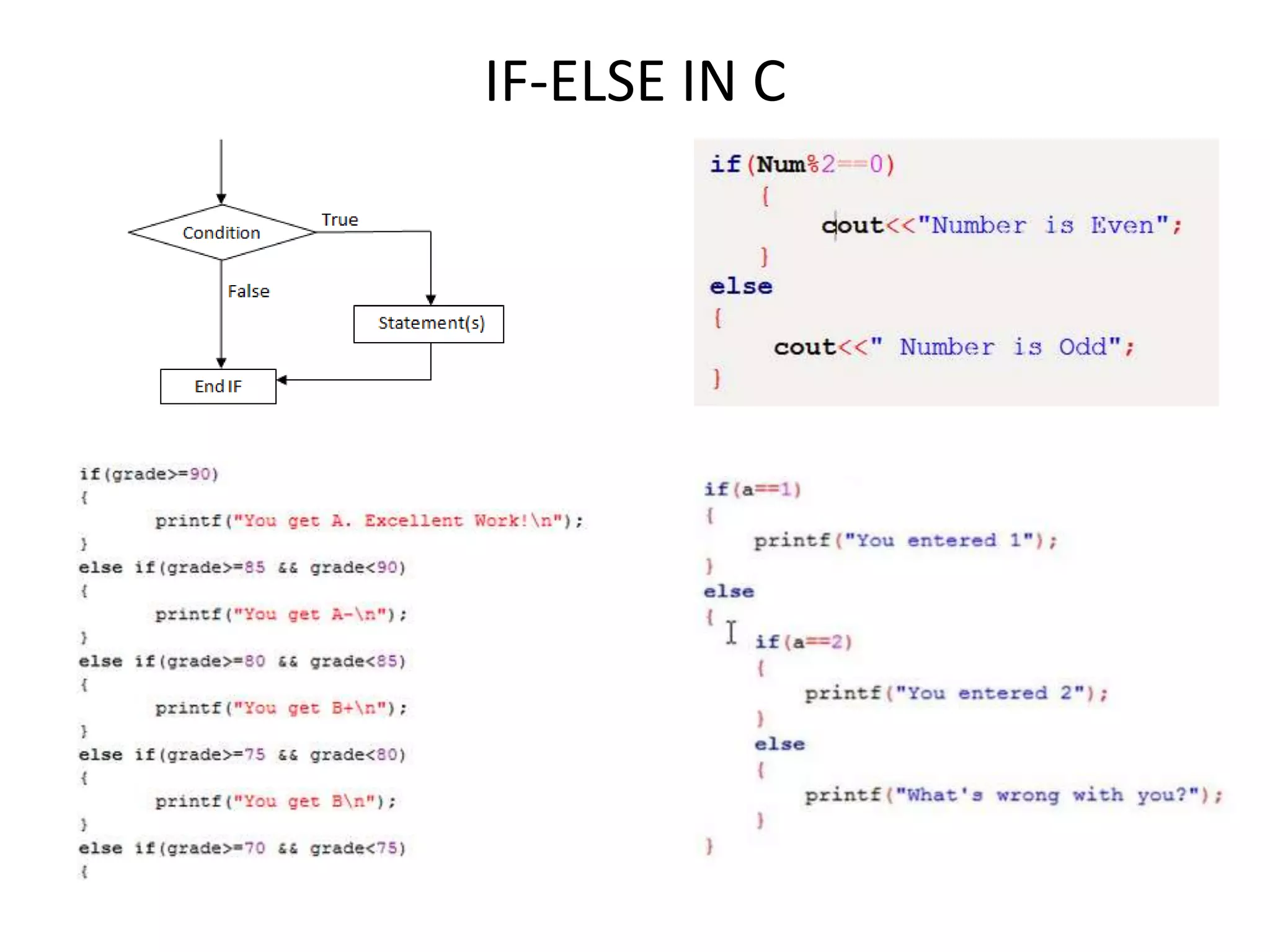
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, including its features and basic syntax. It describes fundamental concepts such as data types, control statements, functions, and arrays, with examples of input/output functions and program structure. The information highlights both the procedural nature and modularity of C, alongside its operators and loop mechanisms.









![ARRAY IN C
• Array in C language is a collection or group of elements (data). All
the elements of array are homogeneous(similar). It has
contiguous memory location.
• Declaration of array :
data_type array_name[array_size];
• Types of array:-
1-D Array
2-D Array
• Advantage of array :
Code Optimization
Easy to traverse data
Easy to sort data
Random Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clanguage-161220160936/75/Introduction-to-C-programming-17-2048.jpg)