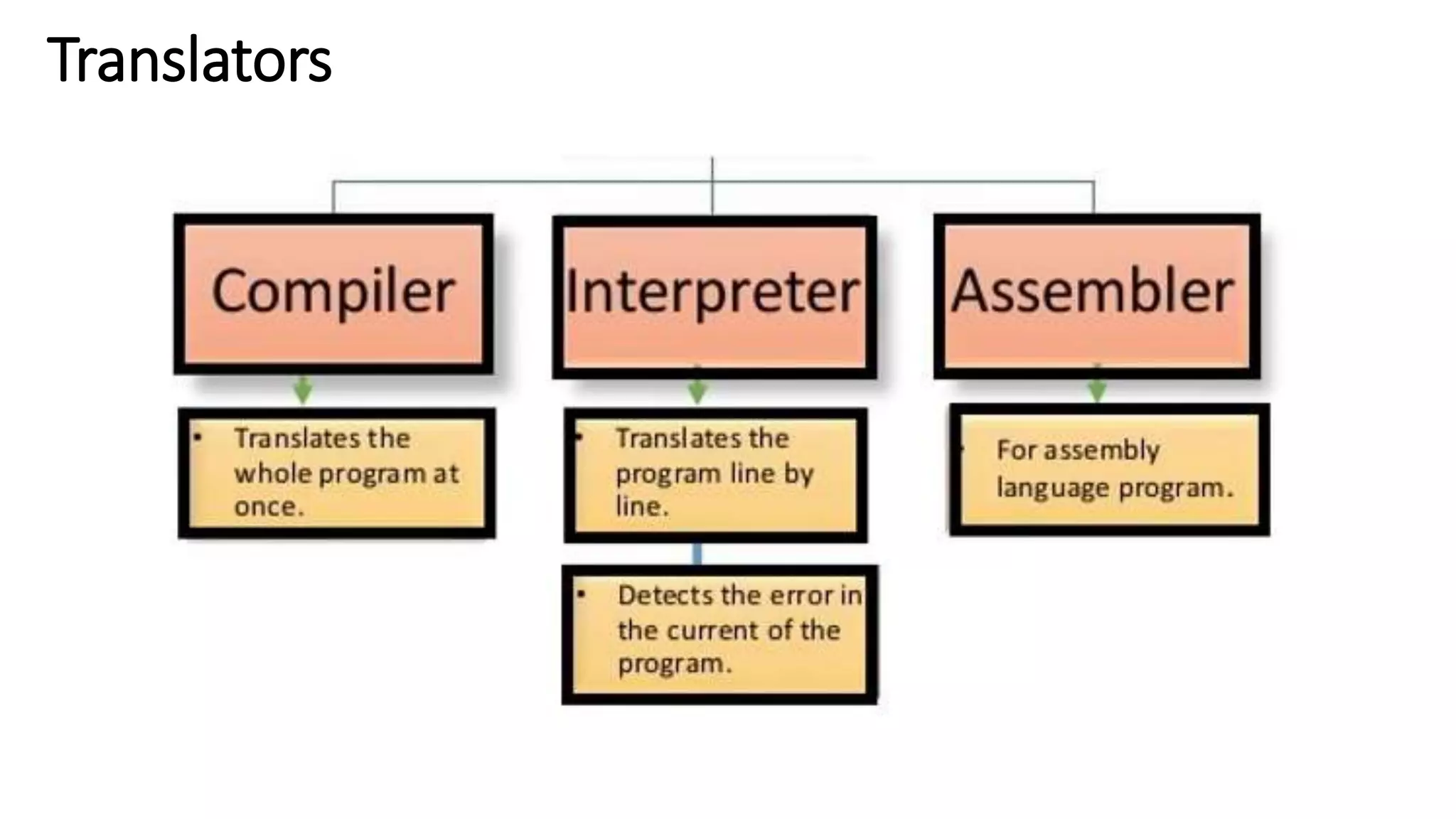
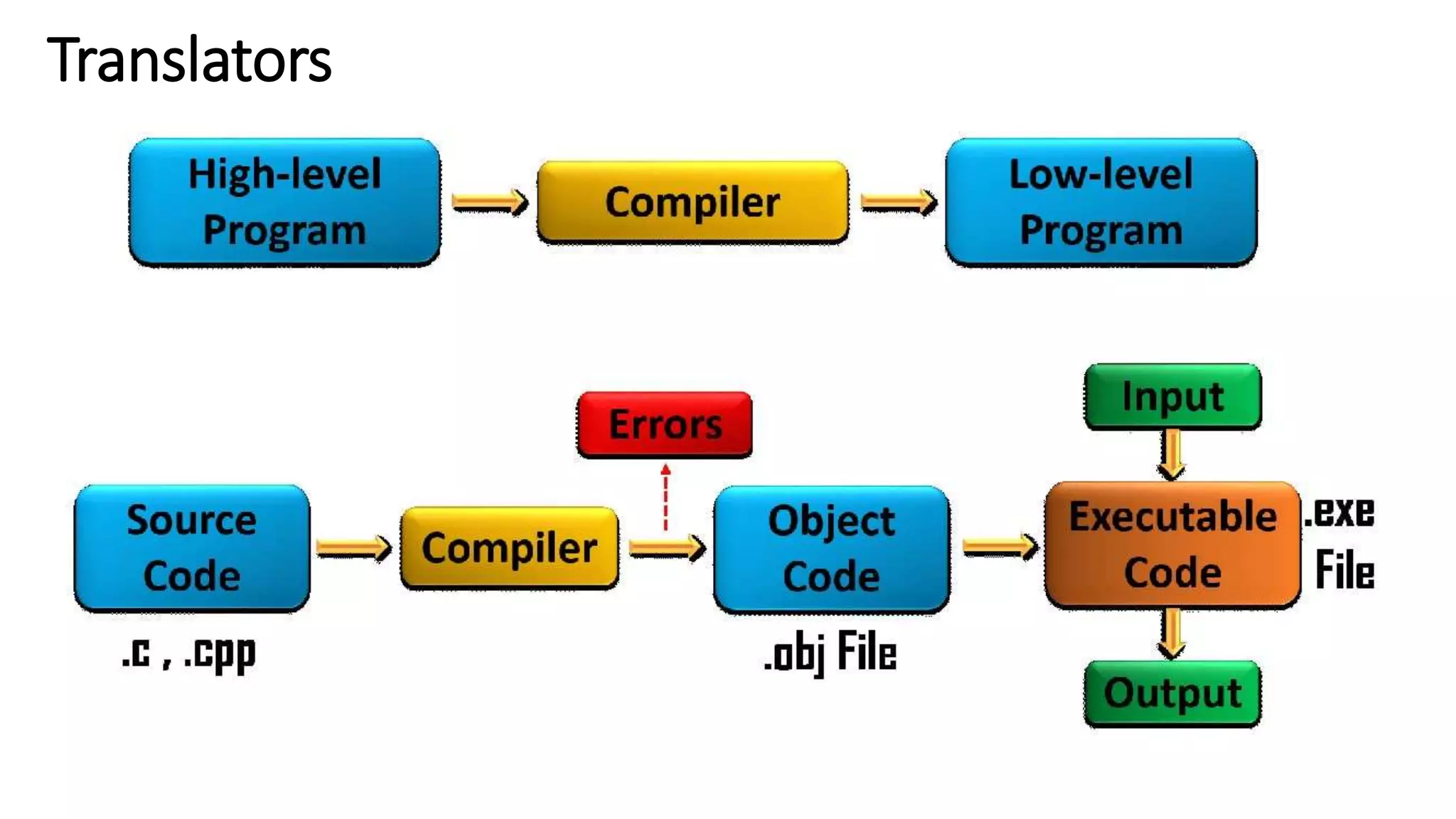
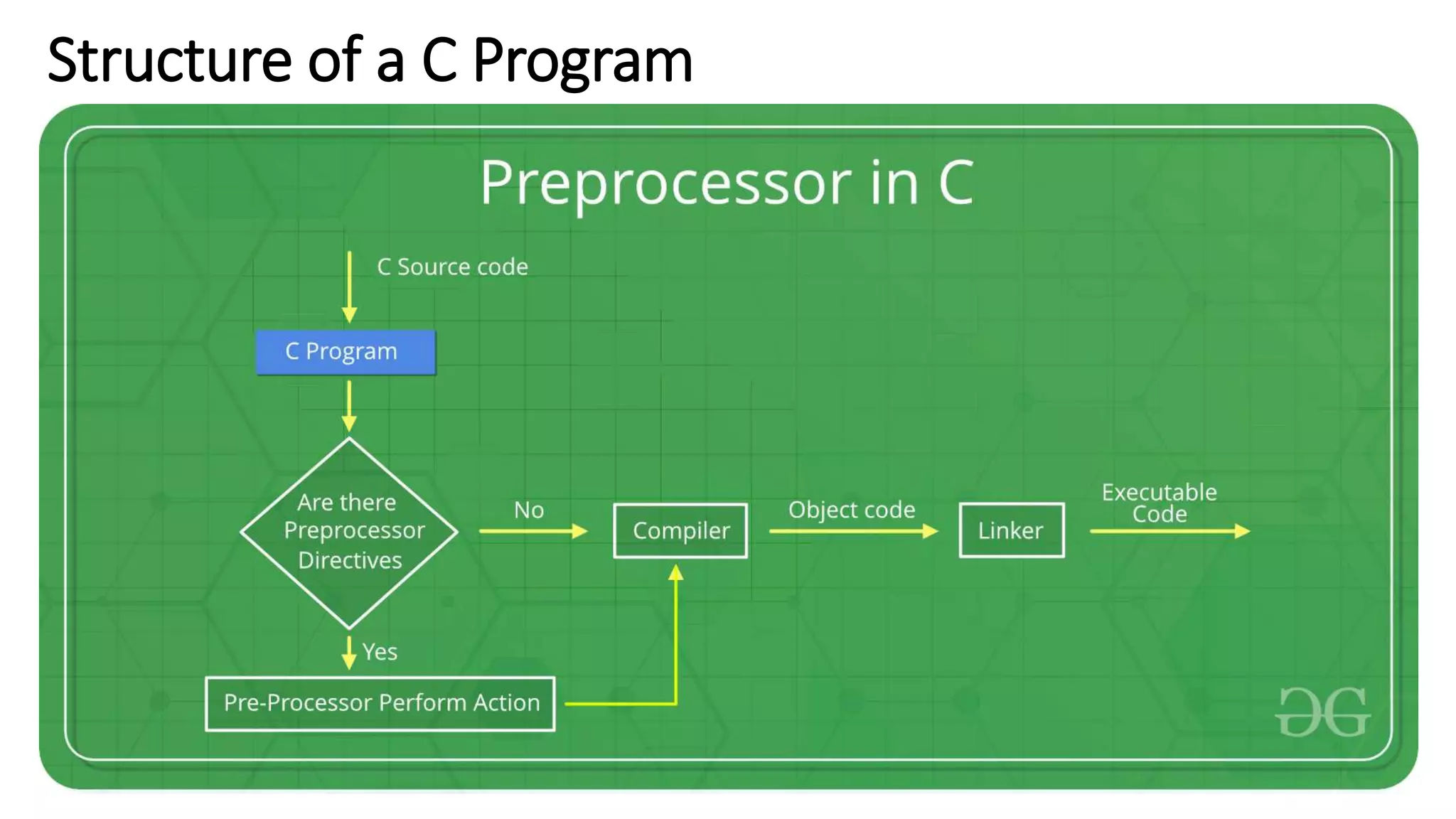
The document provides an overview of programming in C, highlighting its characteristics as a middle-level language with both high-level simplicity and low-level power. It discusses the structure of C programs, including functions, comments, preprocessor directives, and the execution environment for writing and compiling C programs. The document also details the process of creating, compiling, and executing C programs in Unix and Windows environments.