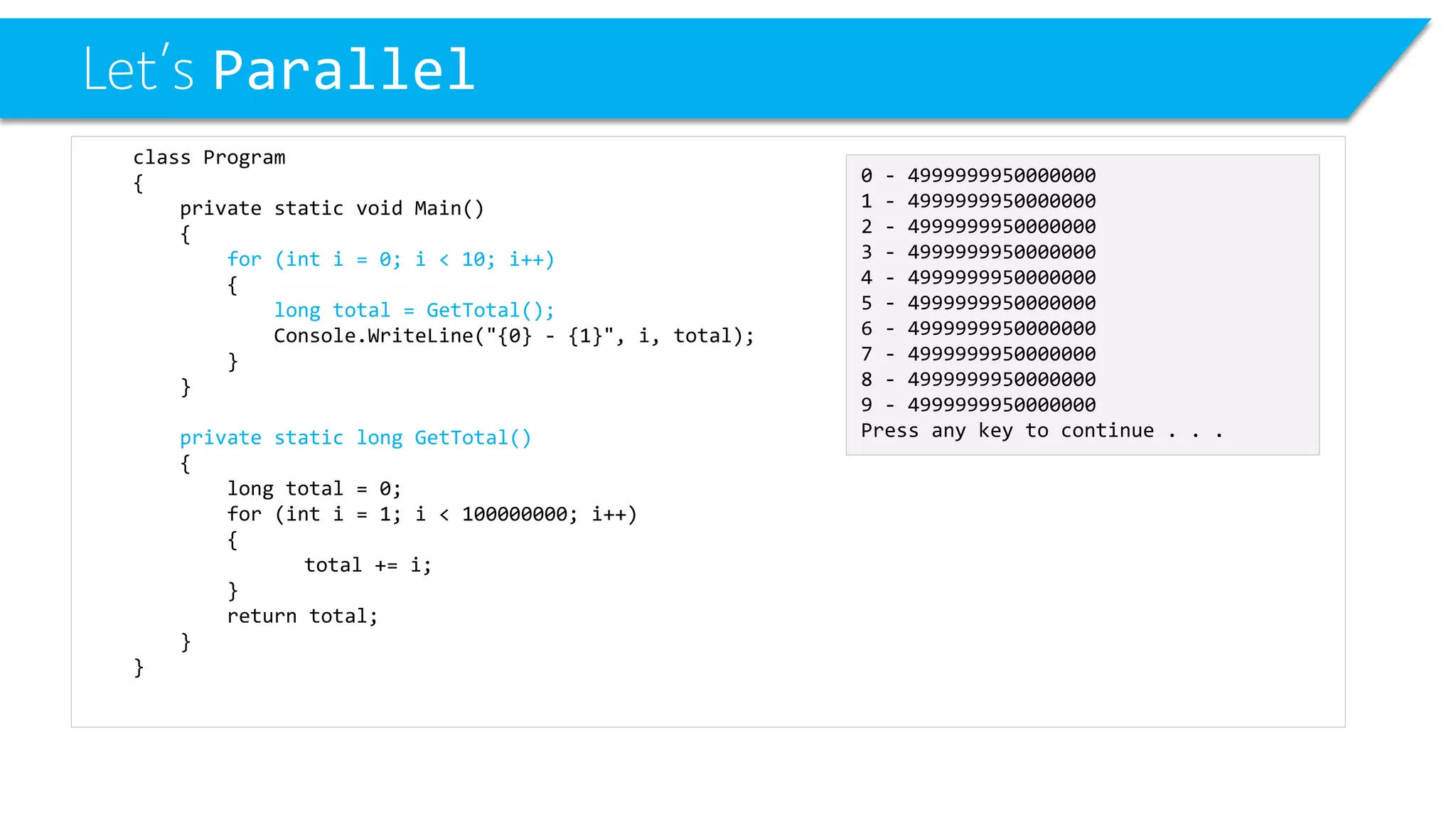
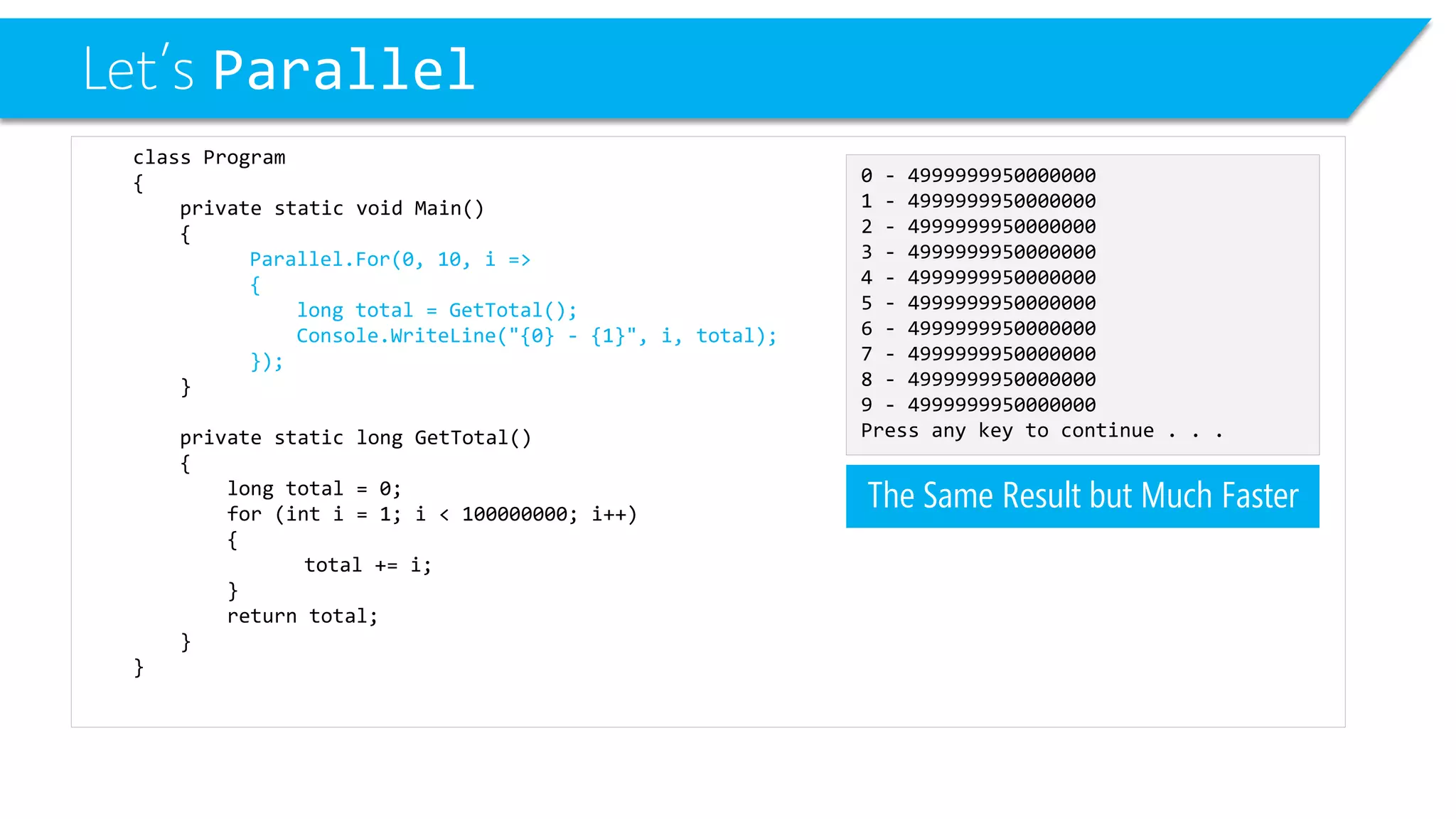
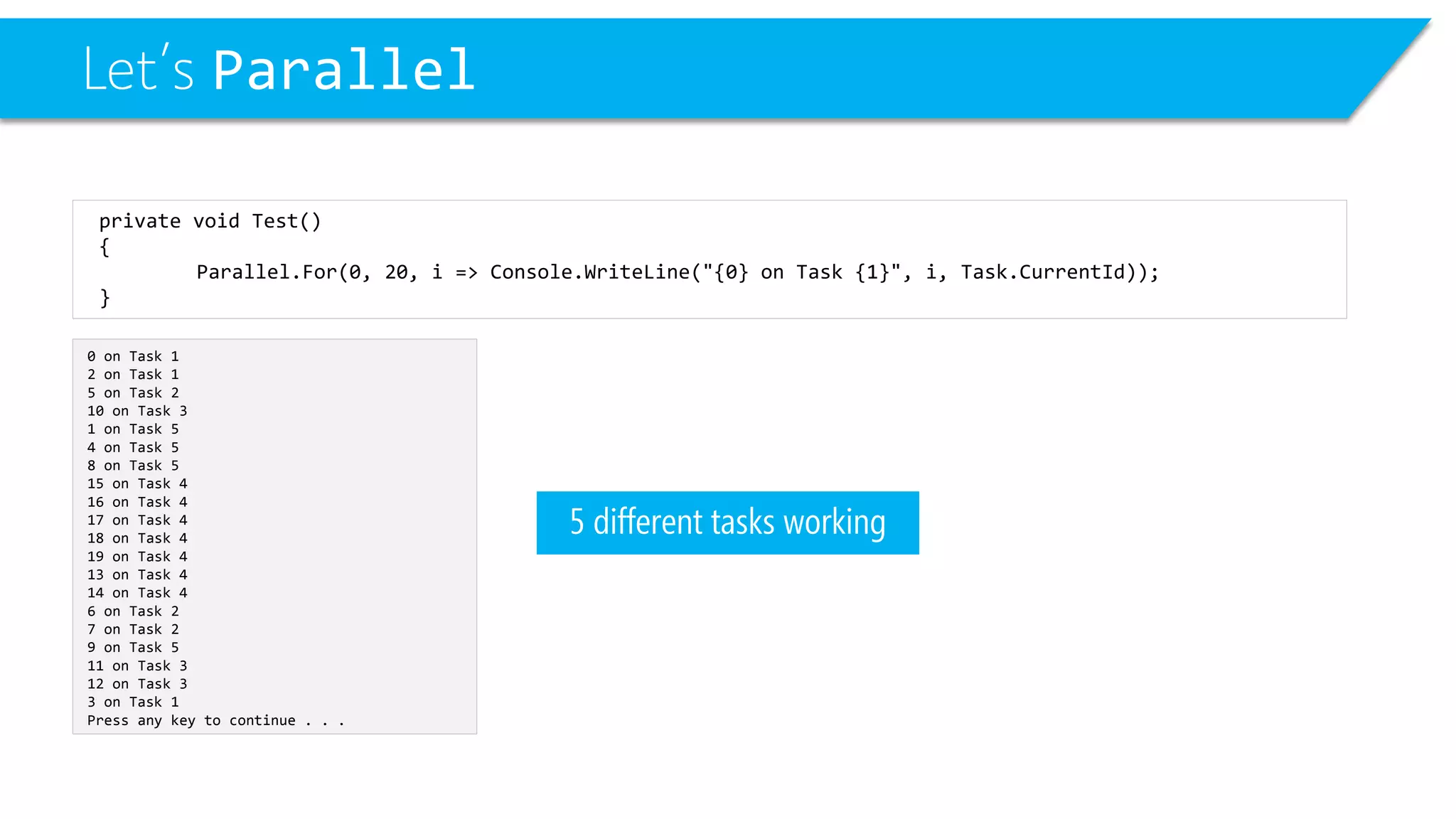
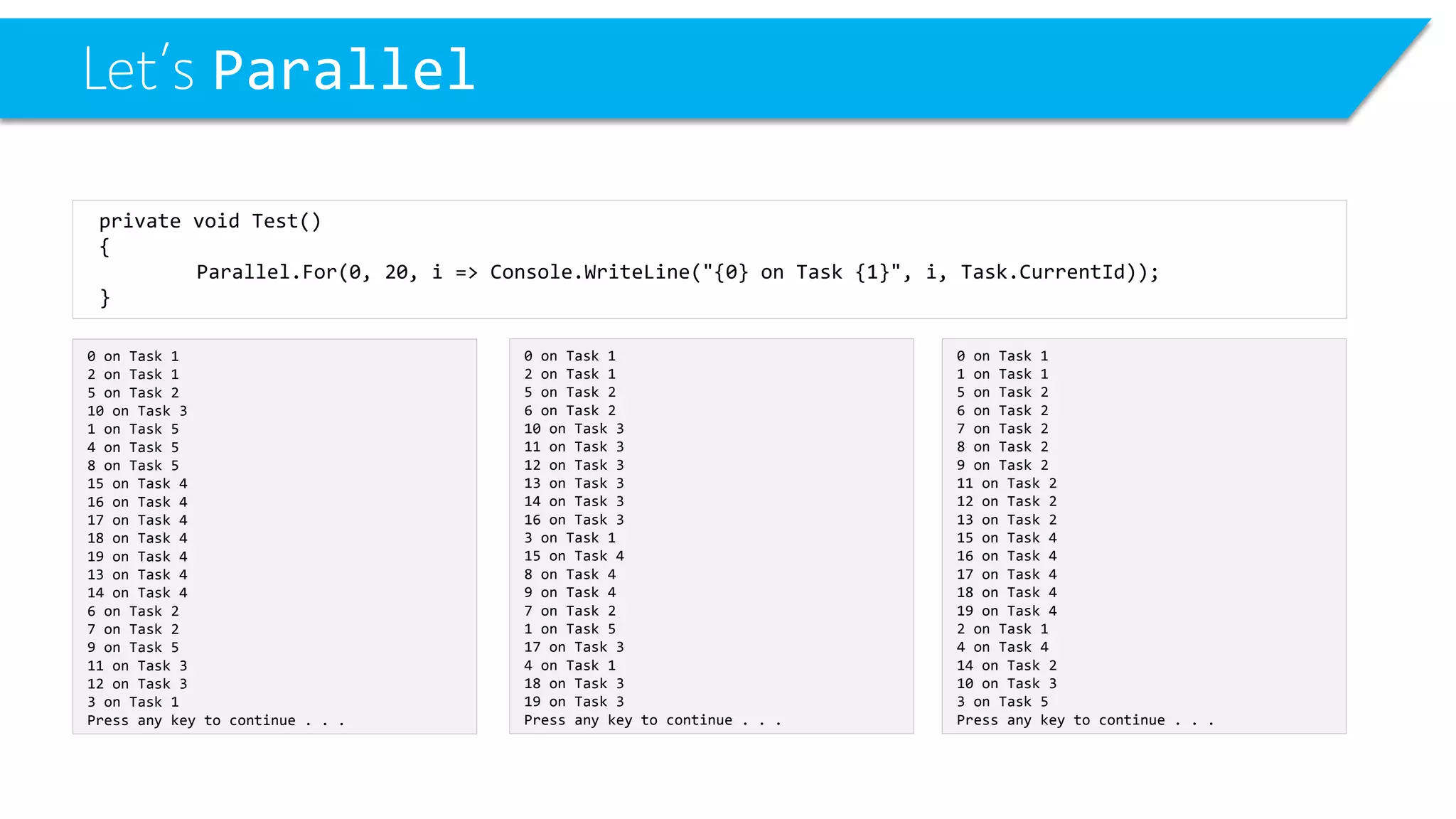
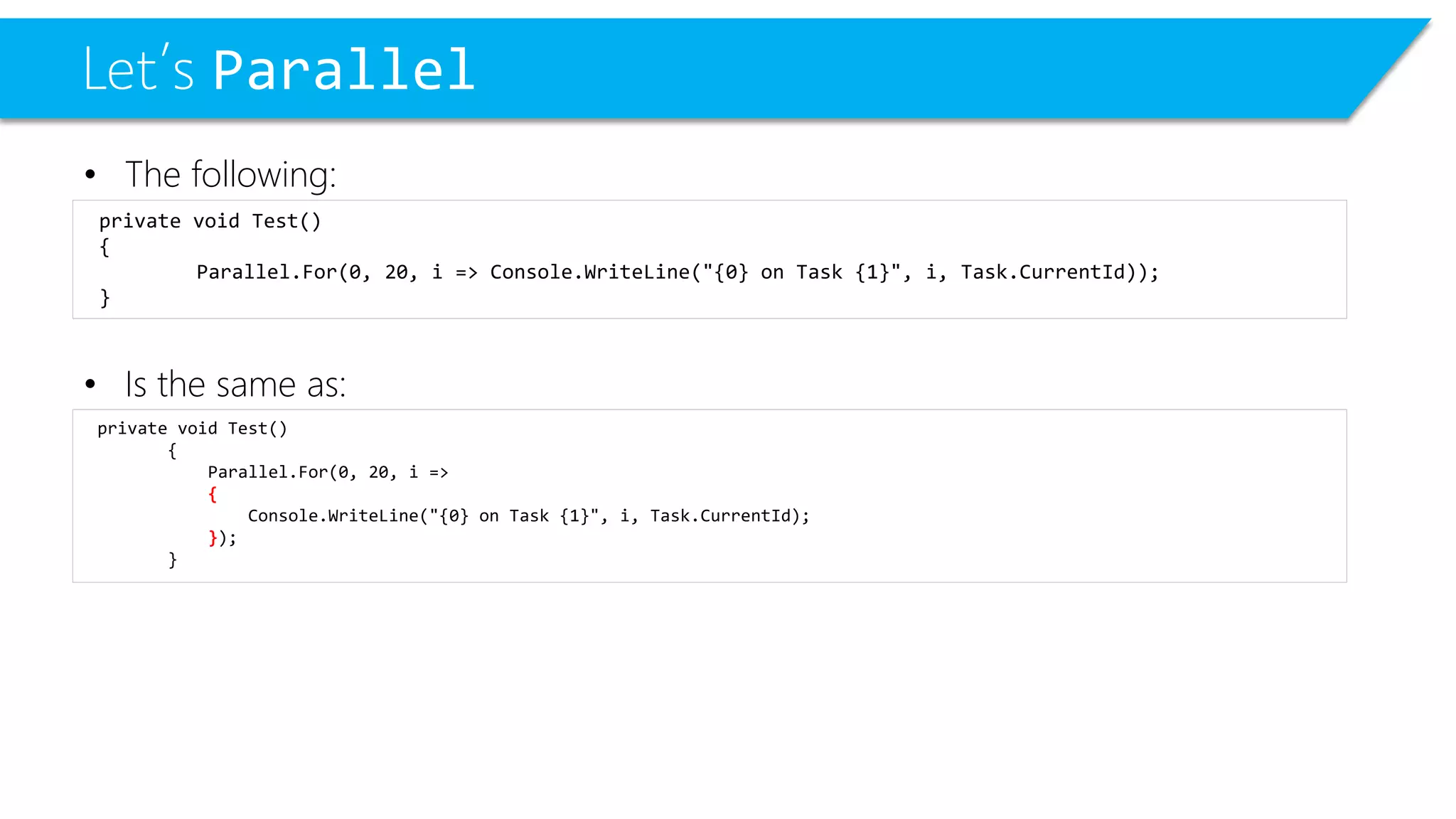
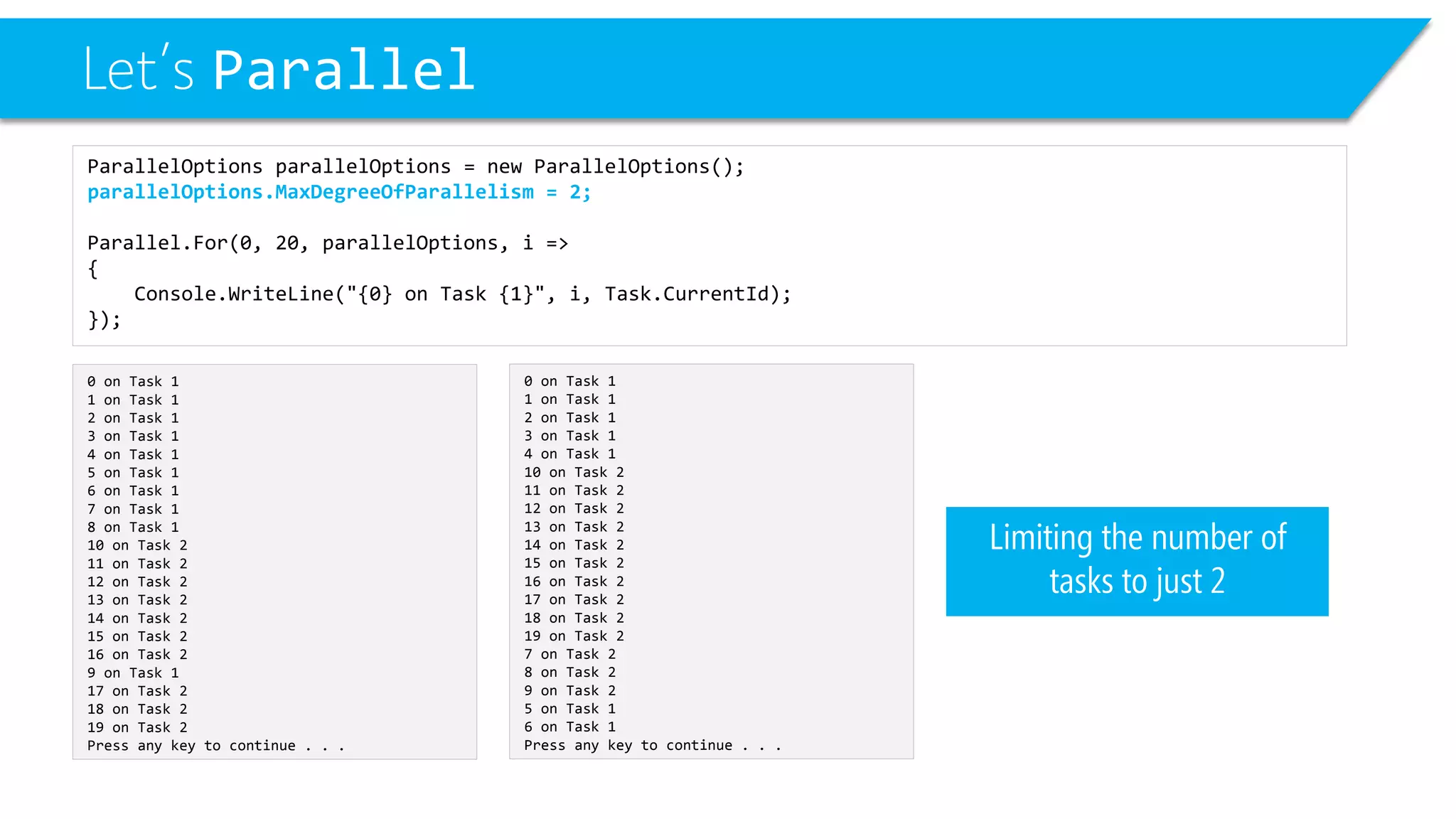
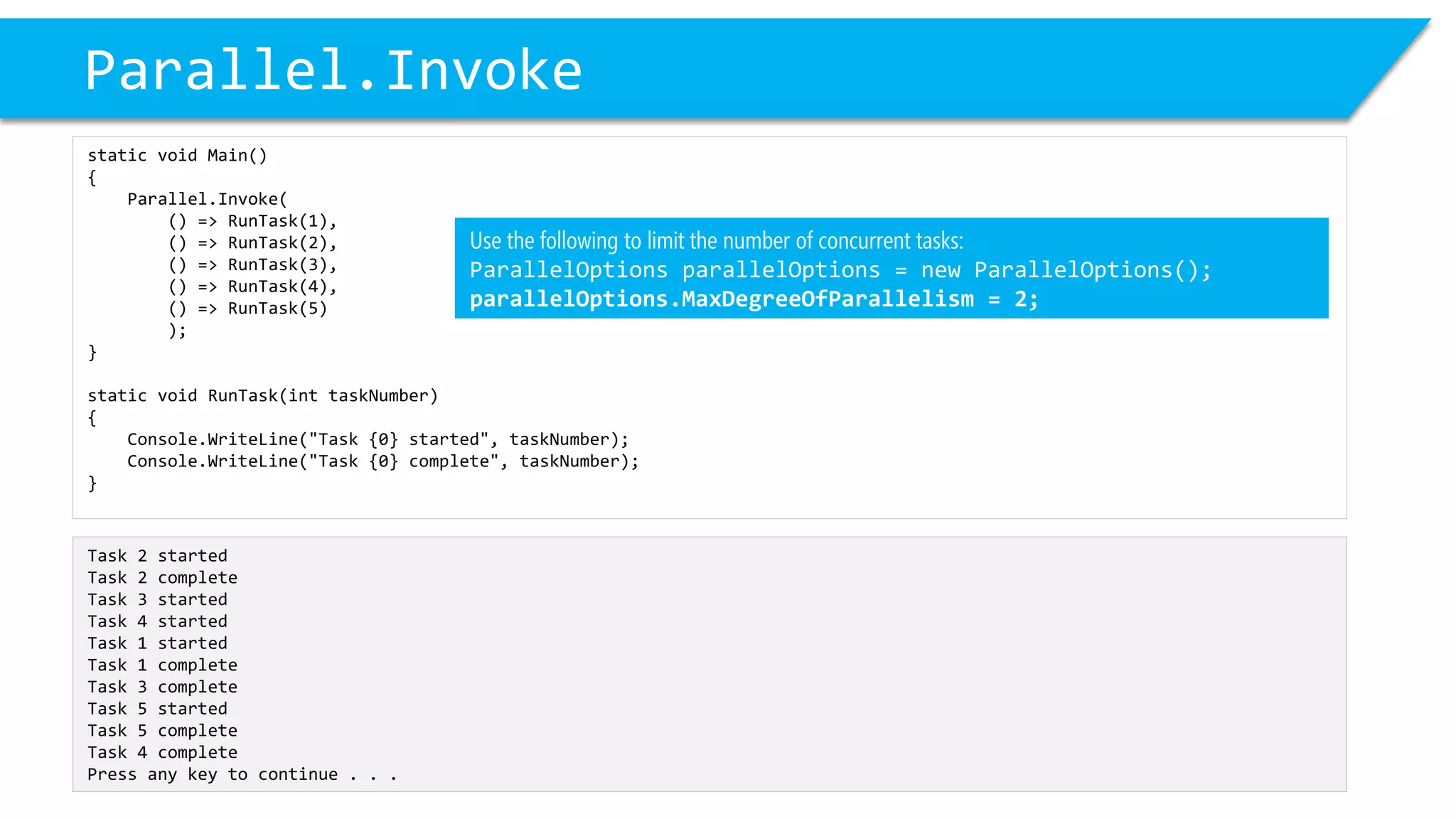
This document discusses threading and parallel programming in C#. It demonstrates how to use Parallel.For to execute a loop in parallel threads to improve performance. It also shows examples of potential threading issues like race conditions that can occur when accessing shared resources from multiple threads simultaneously without synchronization. The document presents solutions for race conditions using locks to synchronize access to shared resources.












![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-20-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
Incremented counter to 1.
Decremented counter to -1.
Final counter value is -1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-21-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
Incremented counter to 1.
Decremented counter to -1.
Final counter value is -1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-22-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
Incremented counter to 1.
Decremented counter to -1.
Final counter value is -1.
Race Conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-23-2048.jpg)

![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
}
Race Conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-25-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
}
Race Conditions
New](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-26-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
}
Race Conditions
Shared object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-27-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
}
Race Conditions
Locking the shared object for each thread](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-28-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
}
The right output
Incremented counter to 1.
Decremented counter to 0.
Final counter value is 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-29-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
}
Not good, don’t do this, or lock a string or etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-31-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Parallel.Invoke(AddOne,
SubtractOne);
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp++;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
lock (_lock)
{
inttemp = _counter;
temp--;
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", temp);
_counter = temp;
}
}
}
The best choice for a locking object is a private or protected object defined within the class that controls the shared state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-32-2048.jpg)

![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
constintsleepAmount= 500;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread tAdd= new Thread(AddOne);
Thread tSub= new Thread(SubtractOne);
tAdd.Start();
tSub.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter++;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter--;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-34-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
constintsleepAmount= 500;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread tAdd= new Thread(AddOne);
Thread tSub= new Thread(SubtractOne);
tAdd.Start();
tSub.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter++;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter--;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
}
}
Monitor Lock](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-35-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
constintsleepAmount= 500;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread tAdd= new Thread(AddOne);
Thread tSub= new Thread(SubtractOne);
tAdd.Start();
tSub.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter++;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter--;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
}
}
Acquire Lock](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-36-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
constintsleepAmount= 500;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread tAdd= new Thread(AddOne);
Thread tSub= new Thread(SubtractOne);
tAdd.Start();
tSub.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter++;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter--;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
}
}
Release Lock](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-37-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
constintsleepAmount= 500;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread tAdd= new Thread(AddOne);
Thread tSub= new Thread(SubtractOne);
tAdd.Start();
tSub.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter++;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter--;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
}
}
Final counter value is 0.
Incremented counter to 1.
Decremented counter to 0.
Press any key to continue . . .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-38-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
constintsleepAmount= 500;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread tAdd= new Thread(AddOne);
Thread tSub= new Thread(SubtractOne);
tAdd.Start();
tSub.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter++;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter--;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
}
}
Final counter value is 0.
Incremented counter to 1.
Decremented counter to 0.
Press any key to continue . . .
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-39-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
constintsleepAmount= 500;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread tAdd= new Thread(AddOne);
Thread tSub= new Thread(SubtractOne);
tAdd.Start();
tSub.Start();
tAdd.Join();
tSub.Join();
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter++;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter--;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
}
}
Blocks the calling thread until the thread terminates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-40-2048.jpg)
![Threading Problems
class Program
{
static int_counter = 0;
static object _lock = new object();
constintsleepAmount= 500;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread tAdd= new Thread(AddOne);
Thread tSub= new Thread(SubtractOne);
tAdd.Start();
tSub.Start();
tAdd.Join();
tSub.Join();
Console.WriteLine("Final counter value is {0}.", _counter);
}
static void AddOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter++;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Incremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
static void SubtractOne()
{
Monitor.Enter(_lock);
try
{
_counter--;
Thread.Sleep(sleepAmount);
Console.WriteLine("Decremented counter to {0}.", _counter);
}
finally { Monitor.Exit(_lock); }
}
}
}
Incremented counter to 1.
Decremented counter to 0.
Final counter value is 0.
Press any key to continue . . .
Blocks the calling thread until the thread terminates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-41-2048.jpg)


![Wait
int[] values = null;
Task loadDataTask= new Task(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data...");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
values = Enumerable.Range(1,10).ToArray();
});
loadDataTask.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Data total = {0}", values.Sum());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-44-2048.jpg)
![Wait
int[] values = null;
Task loadDataTask= new Task(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data...");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
values = Enumerable.Range(1,10).ToArray();
});
loadDataTask.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Data total = {0}", values.Sum());
Will throw ArgumentNullExceptionbecause we are trying to use the array before it has been populated by the parallel task.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-45-2048.jpg)
![Wait
int[] values = null;
Task loadDataTask= new Task(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data...");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
values = Enumerable.Range(1,10).ToArray();
});
loadDataTask.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Data total = {0}", values.Sum());
Will throw ArgumentNullExceptionbecause we are trying to use the array before it has been populated by the parallel task.
int[] values = null;
Task loadDataTask= new Task(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data...");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
values = Enumerable.Range(1,10).ToArray();
});
loadDataTask.Start();
loadDataTask.Wait();
loadDataTask.Dispose();
Console.WriteLine("Data total = {0}", values.Sum()); // Data total = 55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-46-2048.jpg)
![int[] values = null;
Task loadDataTask= new Task(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data...");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
values = Enumerable.Range(1,10).ToArray();
});
loadDataTask.Start();
loadDataTask.Wait();
loadDataTask.Dispose();
Console.WriteLine("Data total = {0}", values.Sum()); // Data total = 55
Wait
int[] values = null;
Task loadDataTask= new Task(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data...");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
values = Enumerable.Range(1,10).ToArray();
});
loadDataTask.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Data total = {0}", values.Sum());
To fix it, we will now waitfor the task to be done](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-47-2048.jpg)
![int[] values = null;
Task loadDataTask= new Task(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data...");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
values = Enumerable.Range(1,10).ToArray();
});
loadDataTask.Start();
loadDataTask.Wait();
loadDataTask.Dispose();
Console.WriteLine("Data total = {0}", values.Sum());
Wait
int[] values = null;
Task loadDataTask= new Task(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading data...");
Thread.Sleep(5000);
values = Enumerable.Range(1,10).ToArray();
});
loadDataTask.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Data total = {0}", values.Sum());
The output will be Data total = 55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpadvancedl04-threading-140825093242-phpapp02/75/C-Advanced-L04-Threading-48-2048.jpg)
