This document discusses C# threads and threading concepts in 3 paragraphs:
C# threads are managed by the System.Threading.Thread class and are passed a function using a ThreadStart delegate. Threads can be started and have properties like IsBackground that indicate their state.
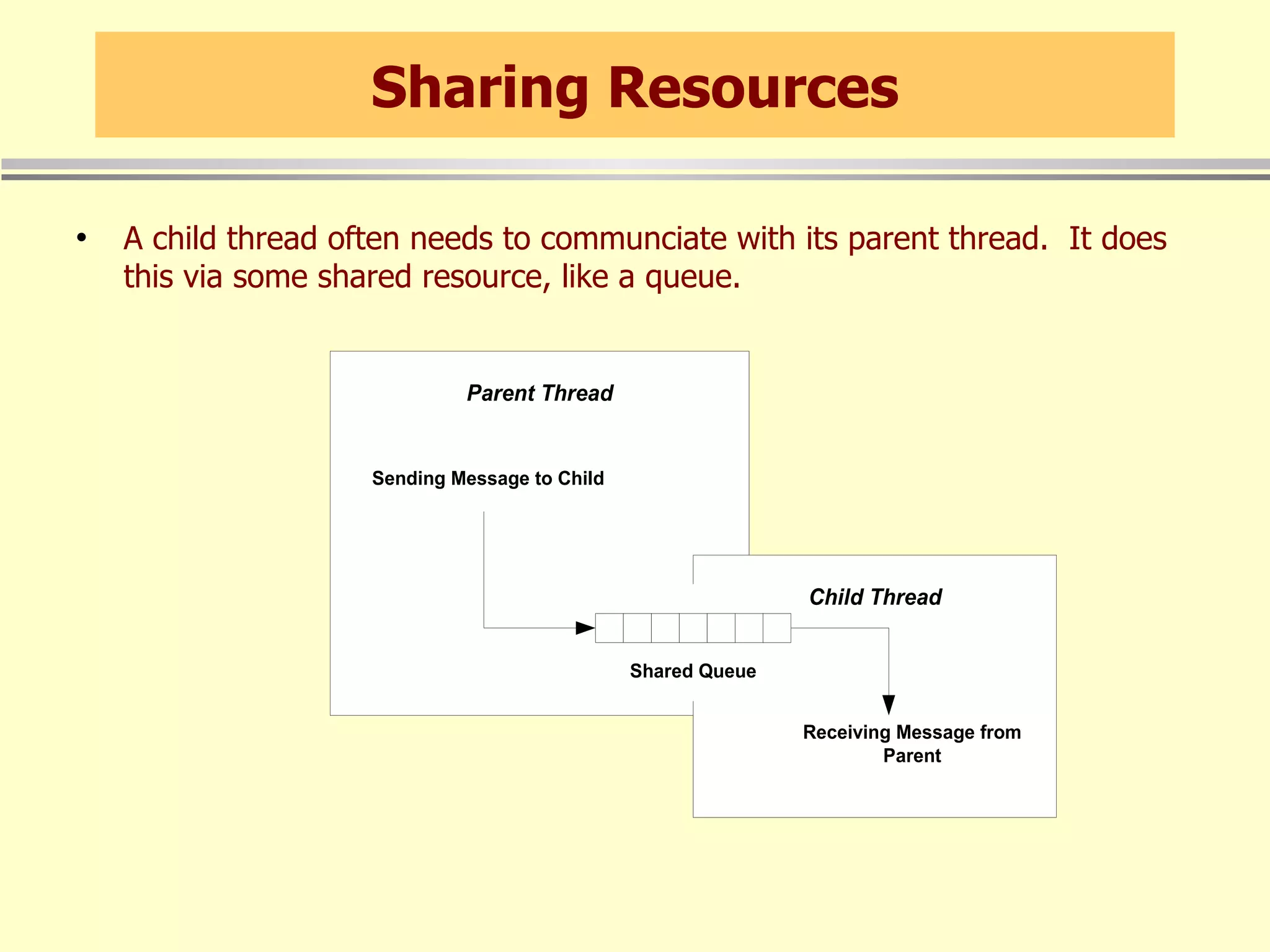
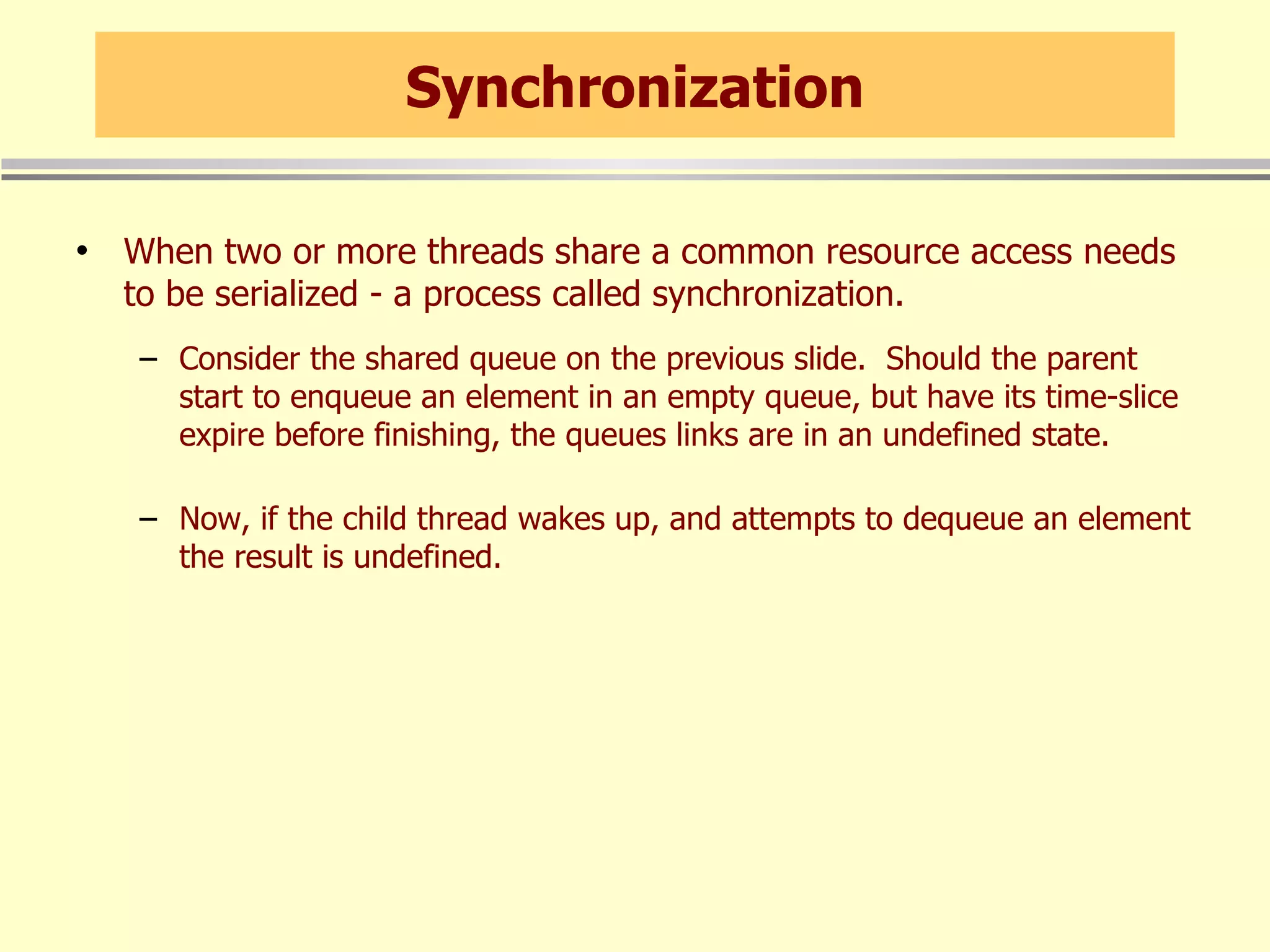
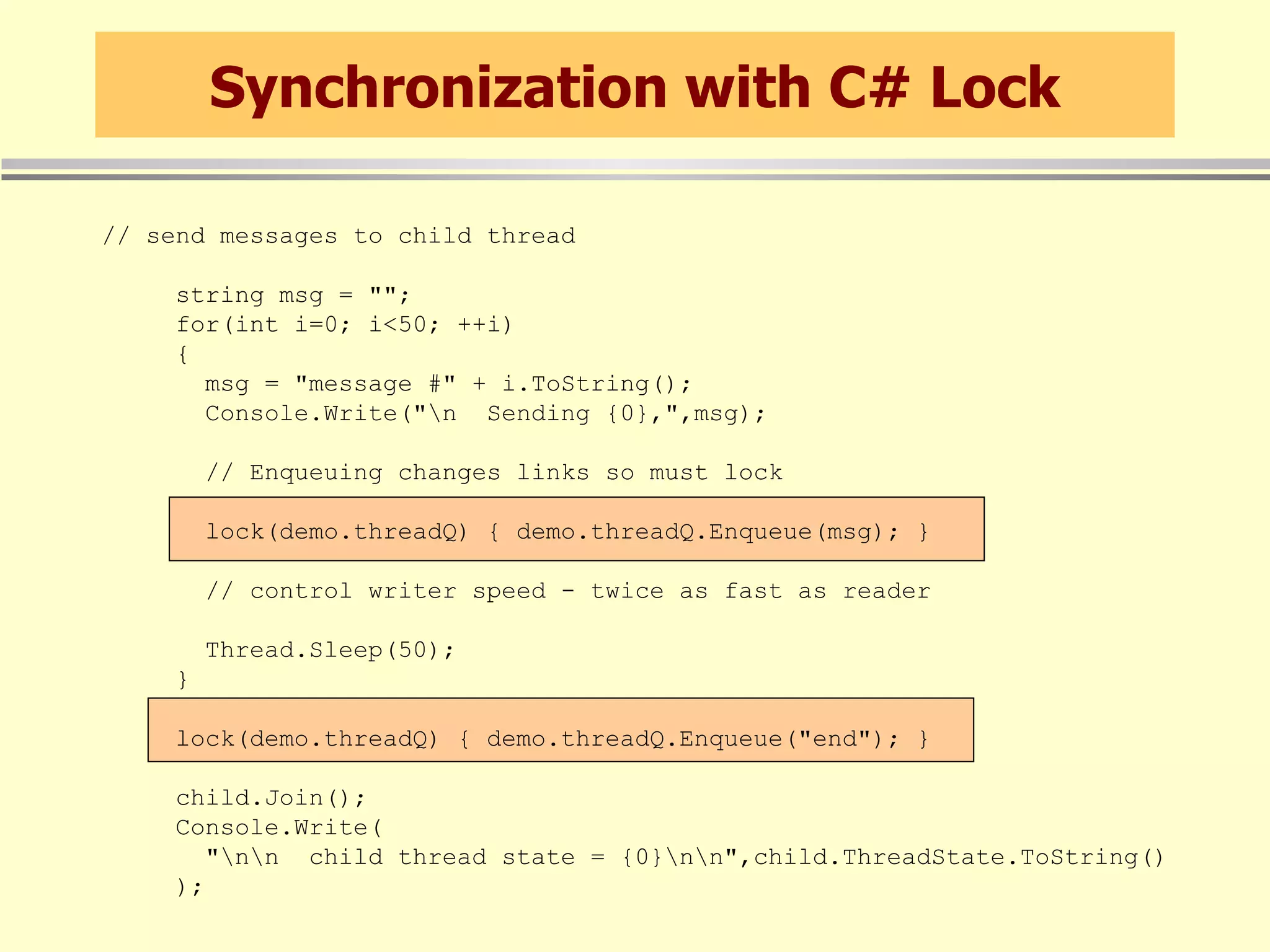
When threads share resources, synchronization is needed to serialize access. The C# lock statement can be used to synchronize access to shared resources like queues. Other synchronization primitives like Monitor, Interlocked, and ReaderWriterLock are also available.
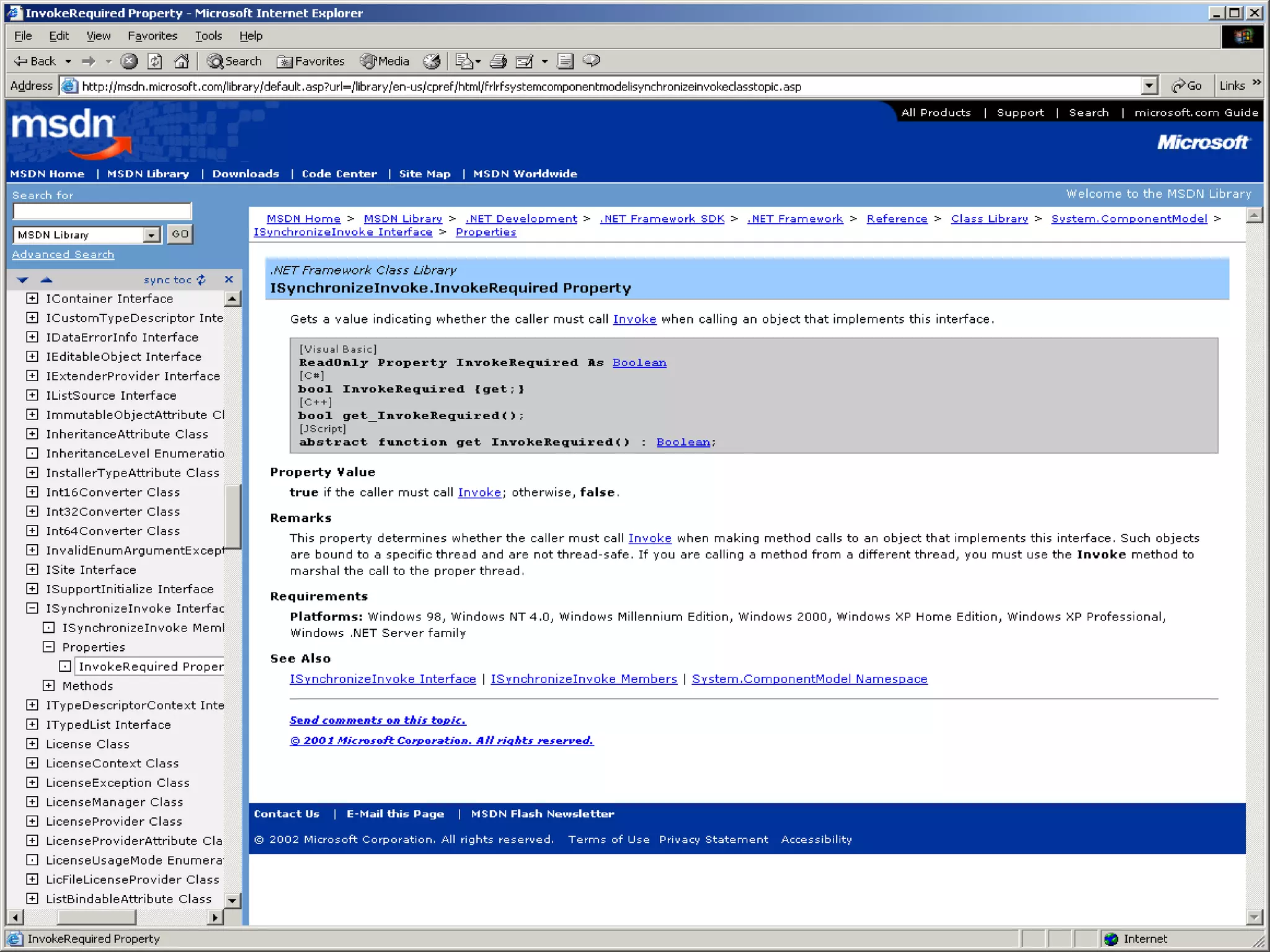
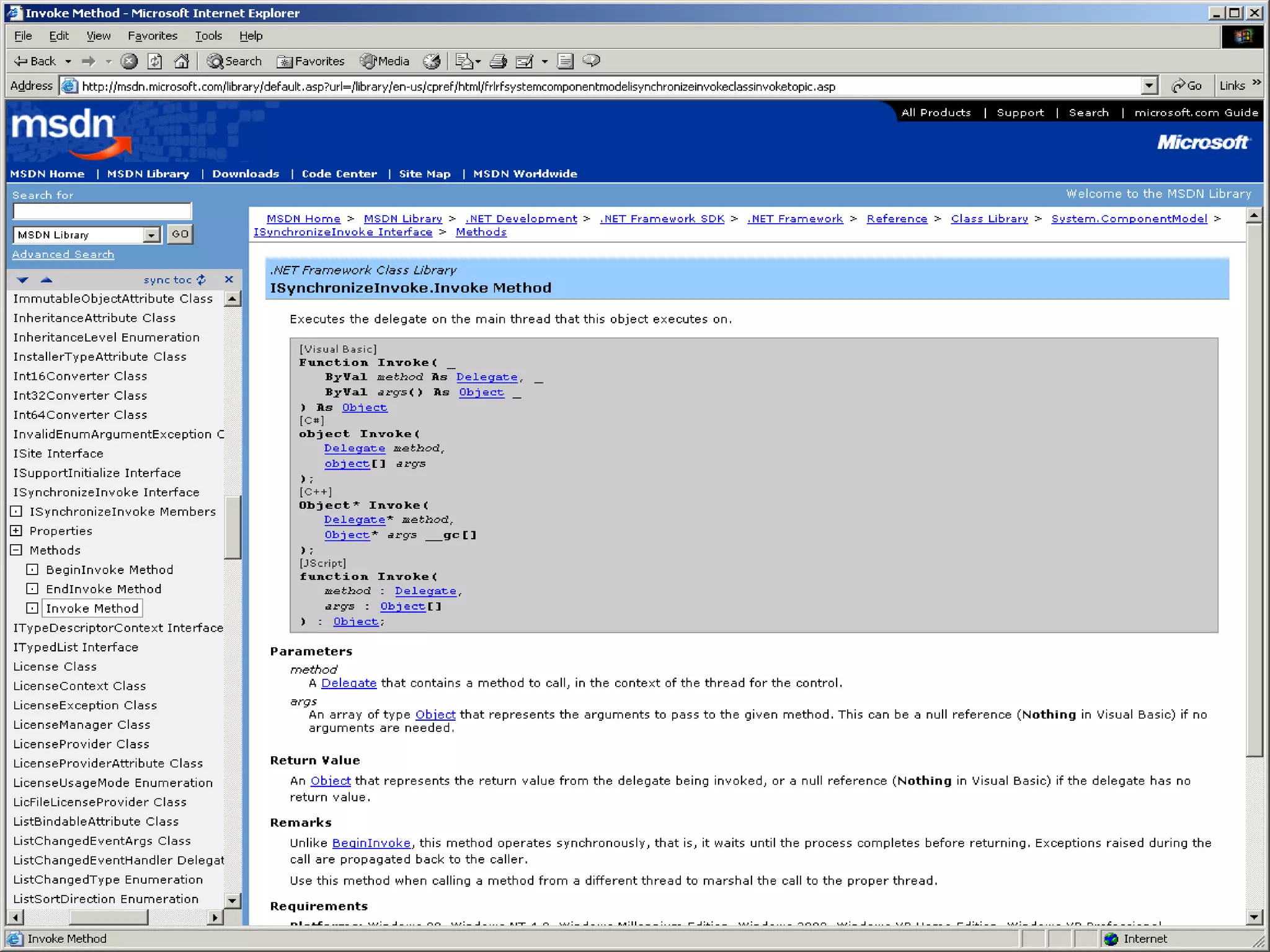
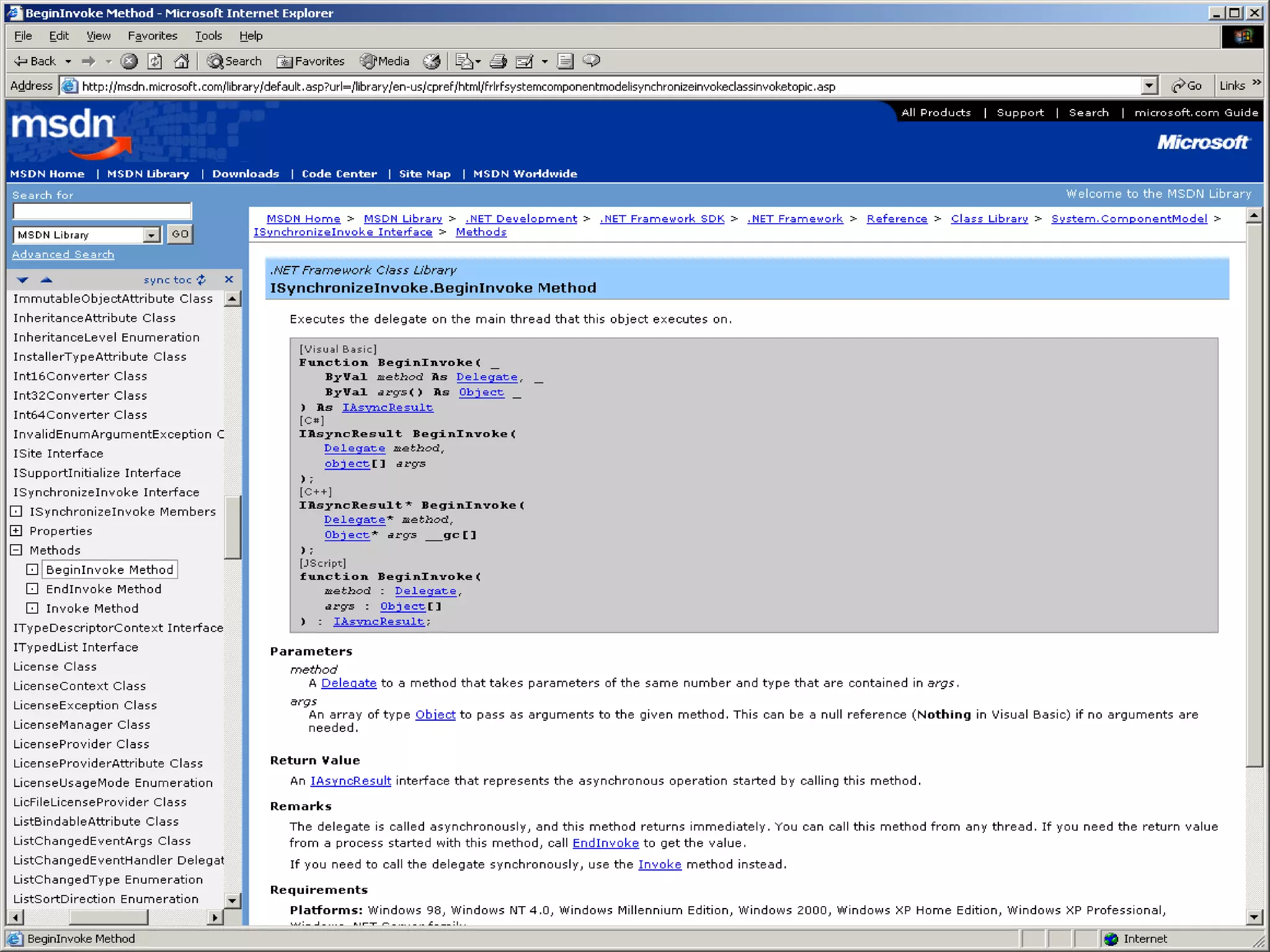
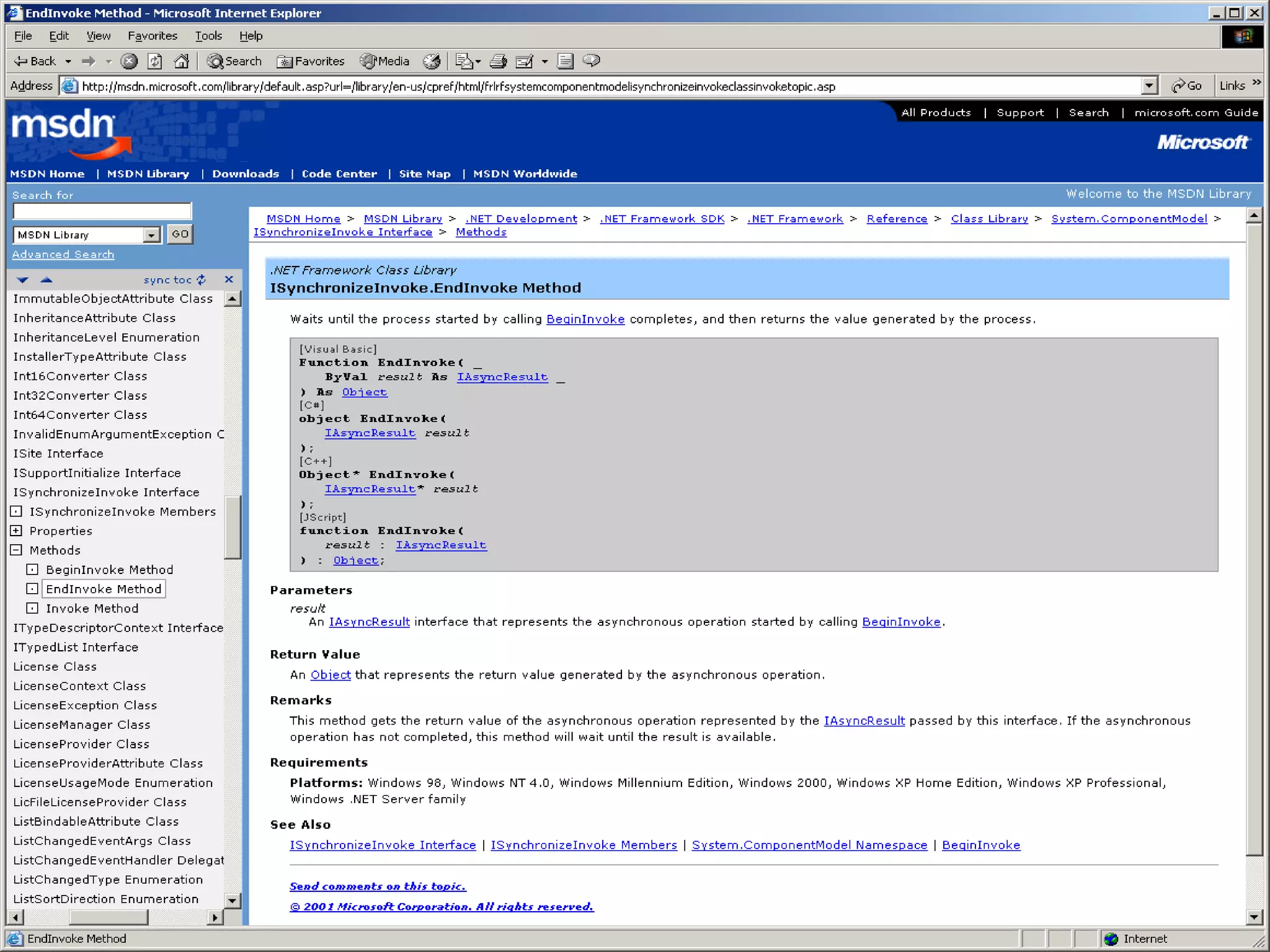
User interface threads in Windows Forms are separate from worker threads that do background processing. Worker threads must communicate with UI threads using Form methods like Invoke, BeginInvoke, and EndInvoke
![C# Threads GUIDED BY, G.SURESH.,DEPT.OF MCA PRESENTED BY, S.KARTHICK[MCA969] P.MUTHU KUMAR[MCA976] P.MURUGESAN[MCA977] A.SENTHIL KUMAR[MCA999]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threads-csharp-111218044150-phpapp01/75/Threads-c-sharp-1-2048.jpg)





![Method Decoration Methods can be decorated with a MethodImpl attribute, synchronizing access much like a Win32 critical section. [MethodImpl (MethodImplOptions.Synchronized)] string myMethod(string input) { … } Note that this synchronizes a region of code, while lock and Monitor synchronize objects.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threads-csharp-111218044150-phpapp01/75/Threads-c-sharp-12-2048.jpg)

![BeginInvoke Example for (i = 1; i <= 25; i++) { s = "Step number " + i.ToString() + " executed"; Thread.Sleep(400); // Make asynchronous call to main form. // MainForm.AddString function runs in main thread // because we activated the delegate through form's // Invoke (synchronous) or BeginInvoke (asynchronous) functions. // To make synchronous call use Invoke. m_form.BeginInvoke(m_form.m_DelegateAddString, new Object[] {s}); // check if thread is cancelled if ( m_EventStop.WaitOne(0, true) ) { // clean-up operations may be placed here // ... // inform main thread that this thread stopped m_EventStopped.Set(); return; } } Delegate arguments passed as an array of objects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/threads-csharp-111218044150-phpapp01/75/Threads-c-sharp-14-2048.jpg)