The document discusses various methods for working with files in PHP, including opening and closing files, reading and writing file contents, splitting file paths and names, renaming/deleting files, and reading entire files. Specific functions covered include fopen(), fclose(), fread(), fwrite(), basename(), pathinfo(), rename(), unlink(), file(), fpassthrough(), and readfile().














![Writing with fwrite()-
fwrite($fp, String to write,[length of characters to write]);
It requires two arguments: a file handle ($fp) and a string (string of text to write to the file), and
writes the contents of string to the file referenced by fp, returning the number of bytes written
(or -1 on error).
$fp = fopen("data.txt","w");fwrite($fp, "ABCxyz");
This writes the character string "ABCxyz" to the beginning of the file data.txt.
If you specify an integer length as a third argument, it stops writing after length bytes (assuming
this is reached before the end of string). For example:
fwrite($fp, "abcdefghij", 4);
writes the first 4 bytes of "abcdefghij" (that is, "abcd") to the file referenced by $fp.
MONICA DESHMANE(H.V.DESAI COLLEGE,PUNE) 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap5phpfiles-part1-210313083113/75/Chap-5-php-files-part-1-16-2048.jpg)

![Splitting name and path from file:
method 2
$path=pathinfo(“/var/www/html/a.txt”);
echo $path[‘basename’];
echo $path[‘dirname’];
echo $path[‘extension’];
MONICA DESHMANE(H.V.DESAI COLLEGE,PUNE) 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap5phpfiles-part1-210313083113/75/Chap-5-php-files-part-1-18-2048.jpg)
![Rename and delete files
Rename-
Bool rename(old name,new name, [resource context])
Ex. Rename(“a.txt”,”b.txt”);
Copy-
Bool copy( source, destination)
Ex. copy(“a.txt”,”b.txt”);
MONICA DESHMANE(H.V.DESAI COLLEGE,PUNE) 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap5phpfiles-part1-210313083113/75/Chap-5-php-files-part-1-19-2048.jpg)
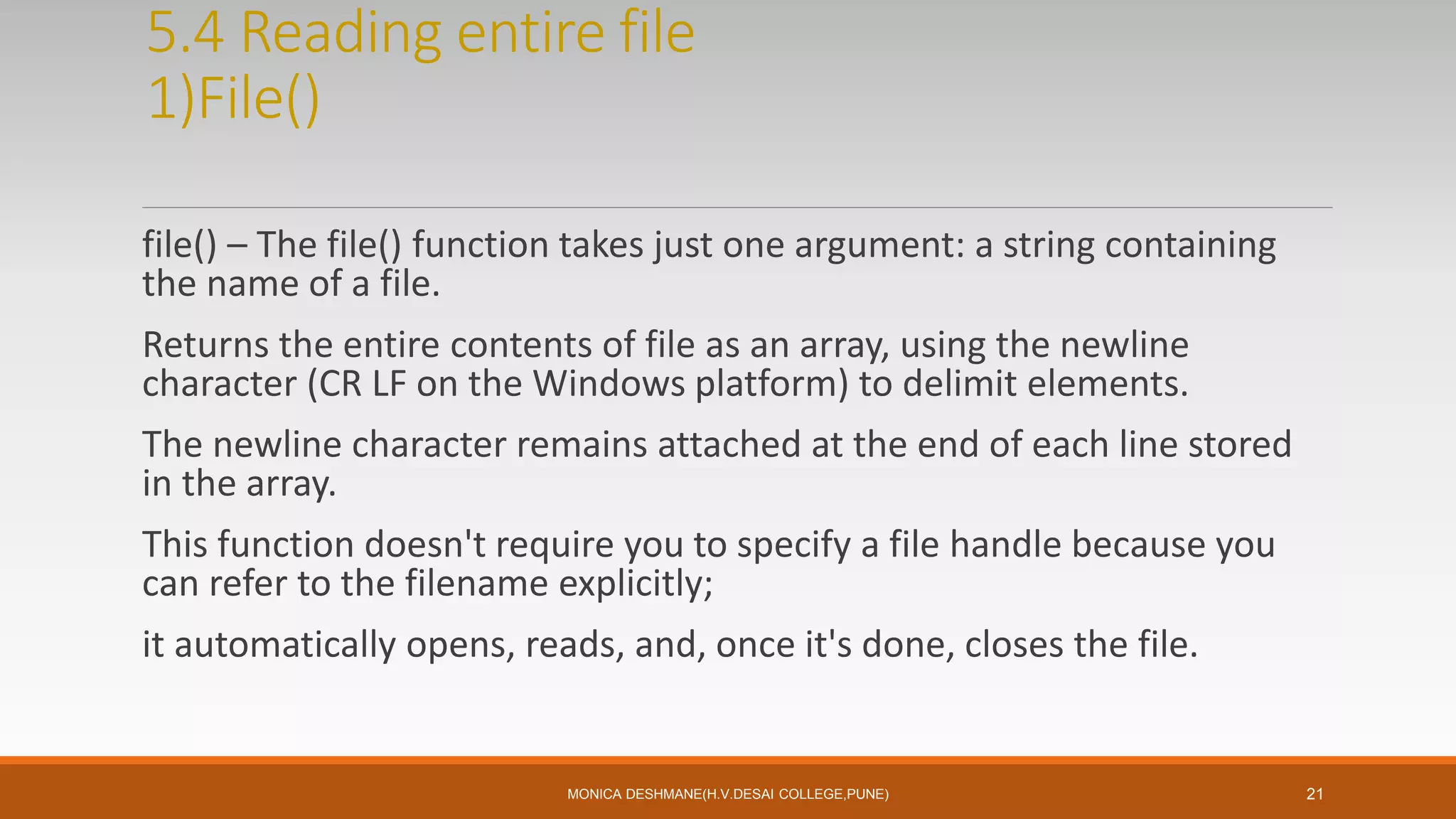
![Array file(file name, [int use_include_path, resource context])
Ex.
$data=file(“a.txt”);
Print_r($data);
MONICA DESHMANE(H.V.DESAI COLLEGE,PUNE) 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap5phpfiles-part1-210313083113/75/Chap-5-php-files-part-1-22-2048.jpg)

![3)readfile()
Readfile(filename,[include_path,context])
Ex.
echo readfile(“a.txt”);
MONICA DESHMANE(H.V.DESAI COLLEGE,PUNE) 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap5phpfiles-part1-210313083113/75/Chap-5-php-files-part-1-24-2048.jpg)