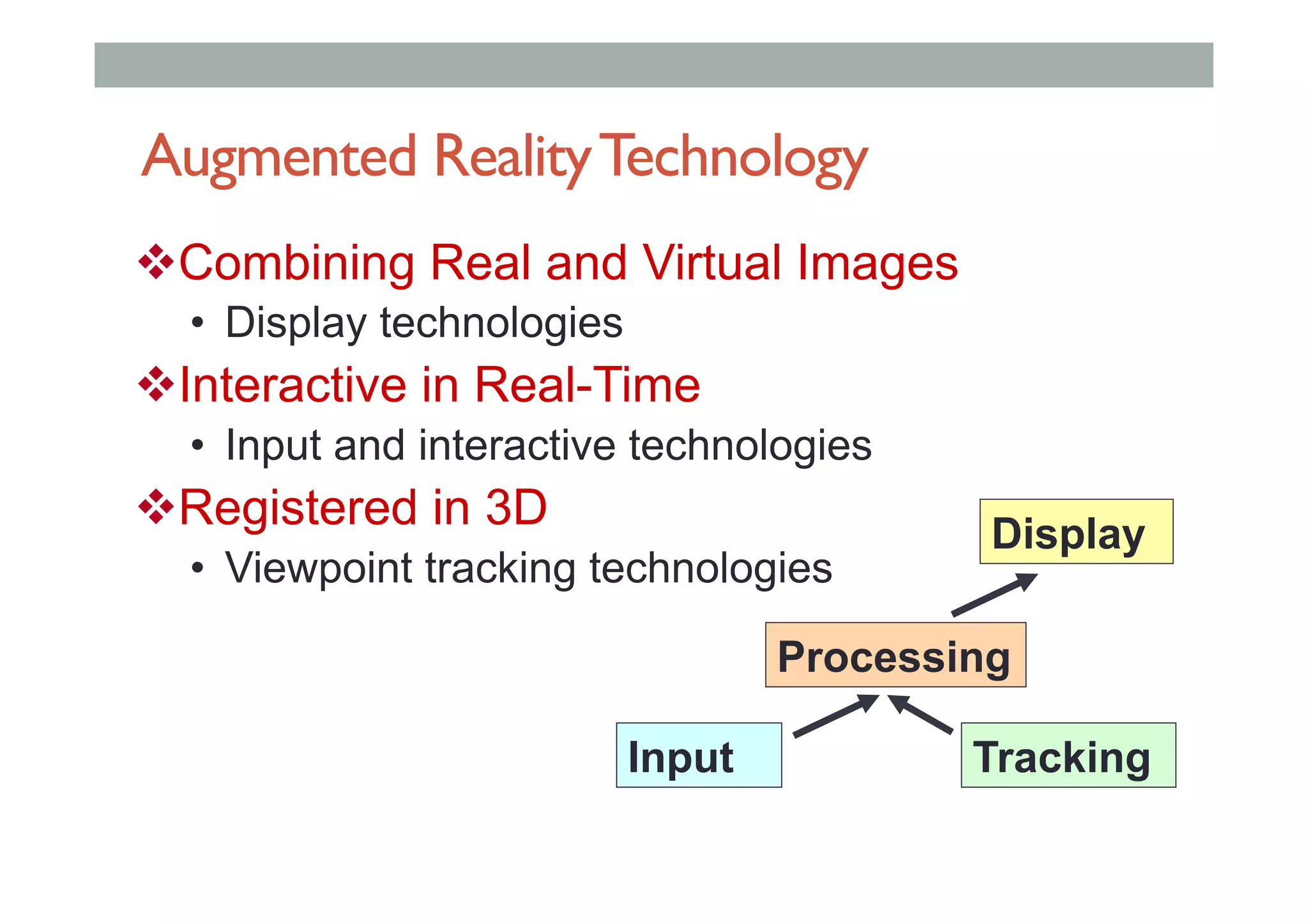
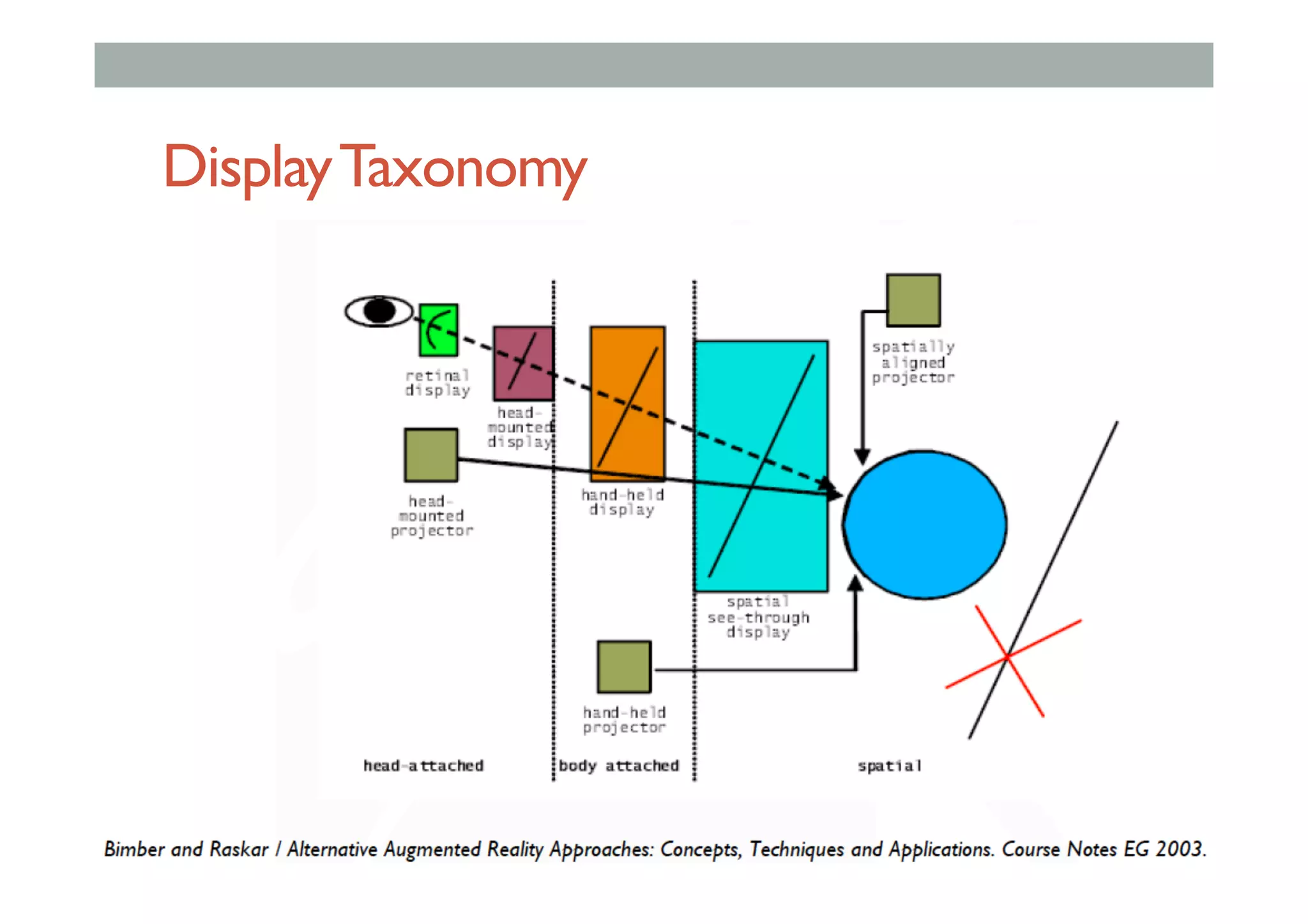
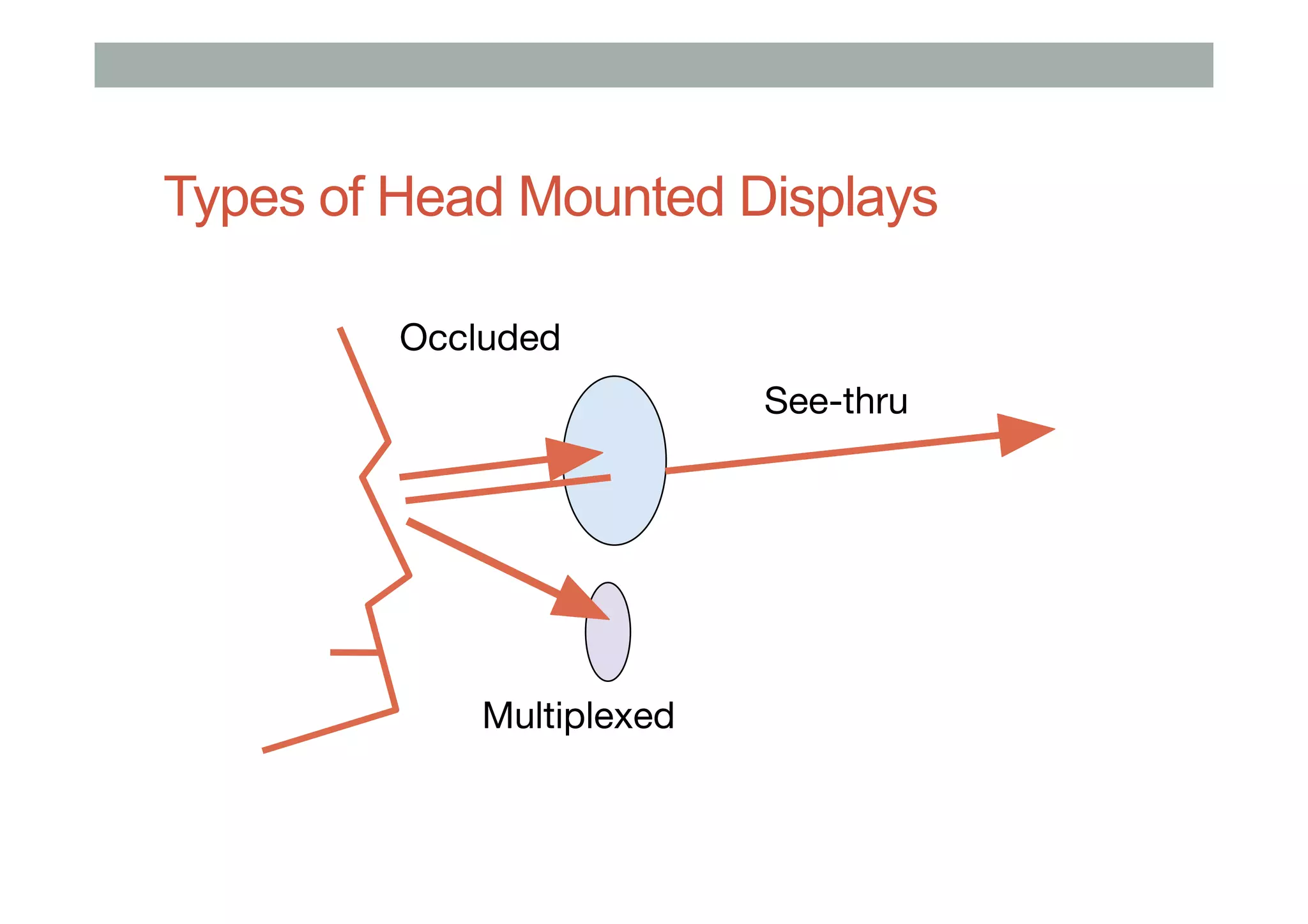
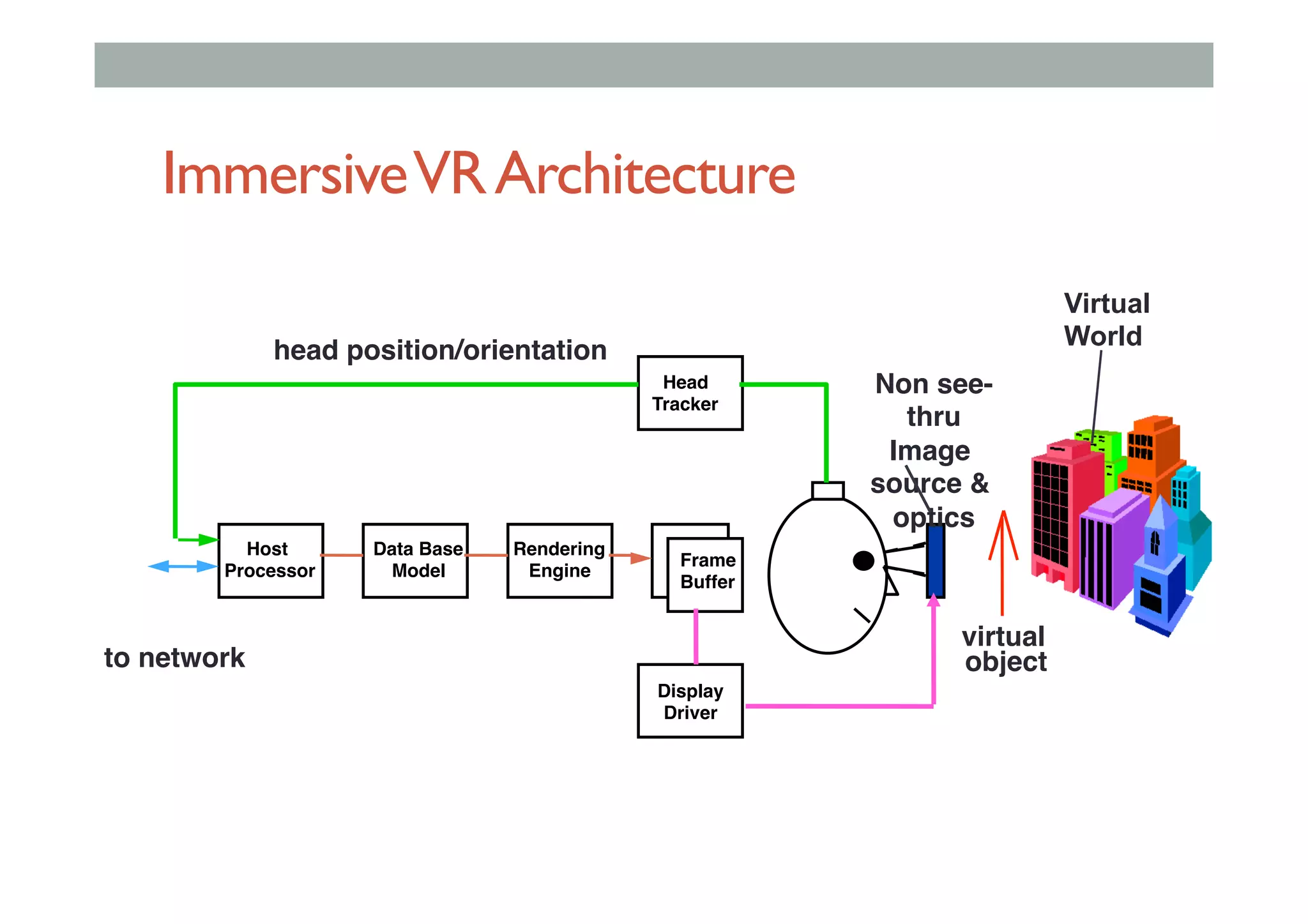
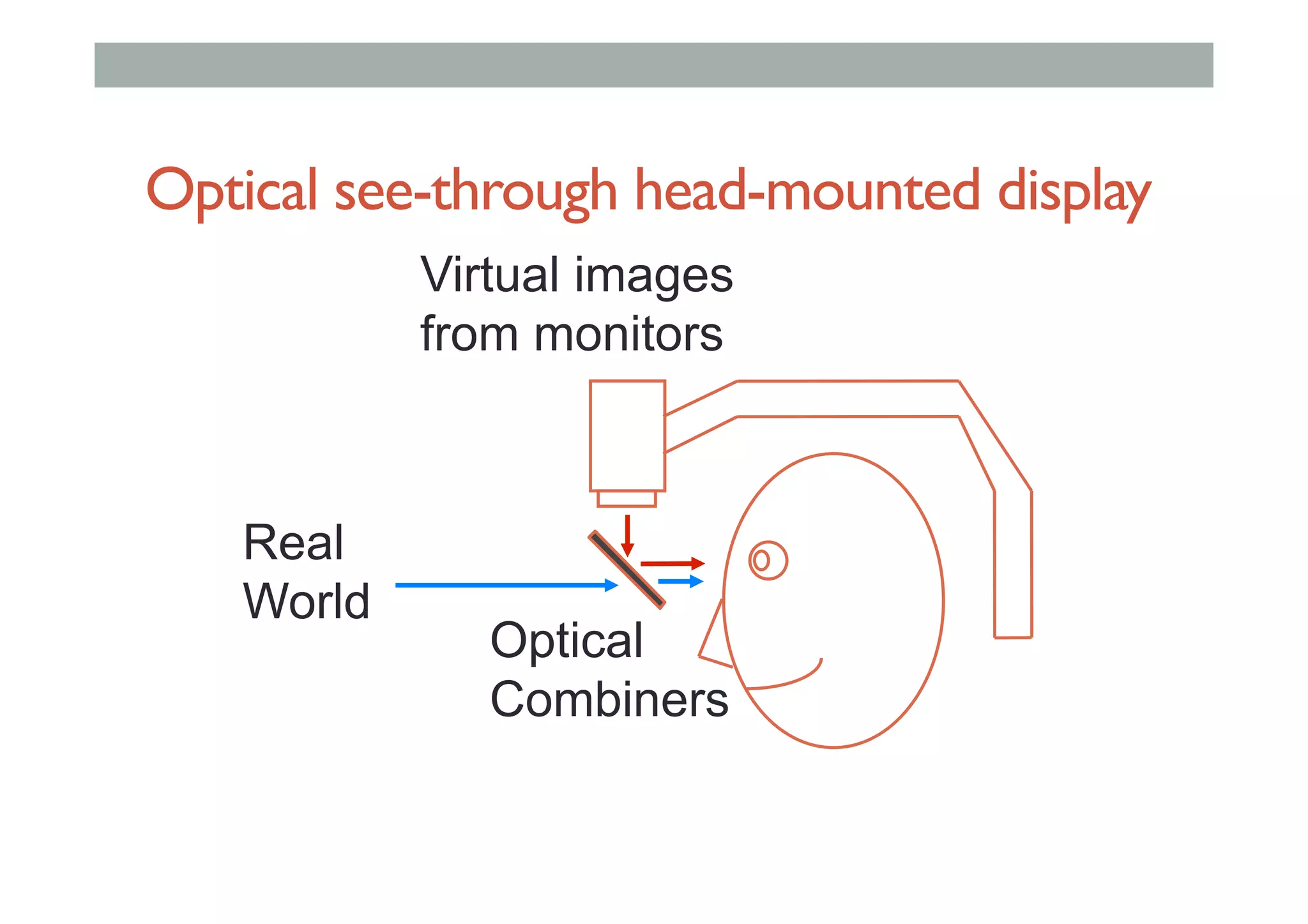
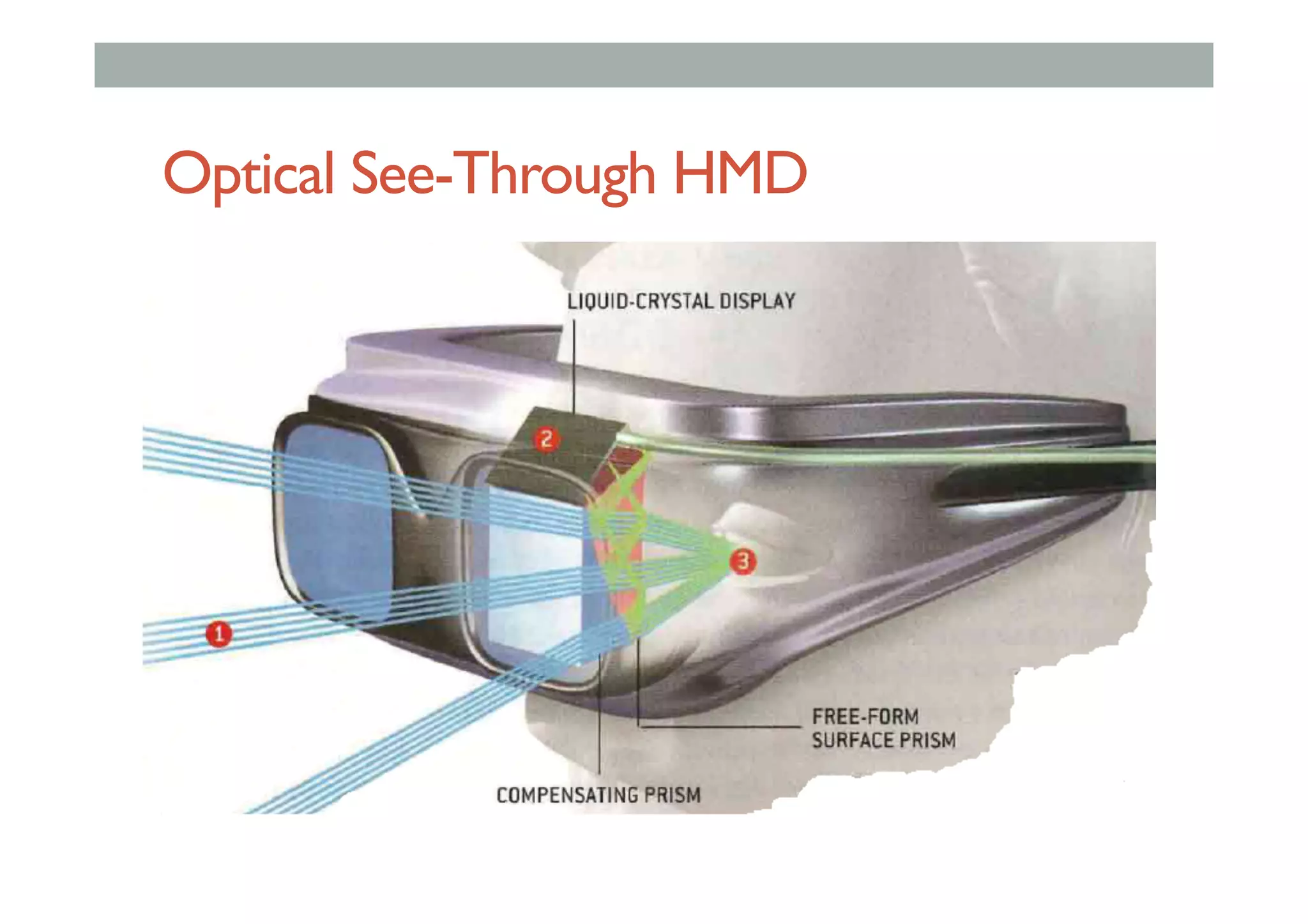
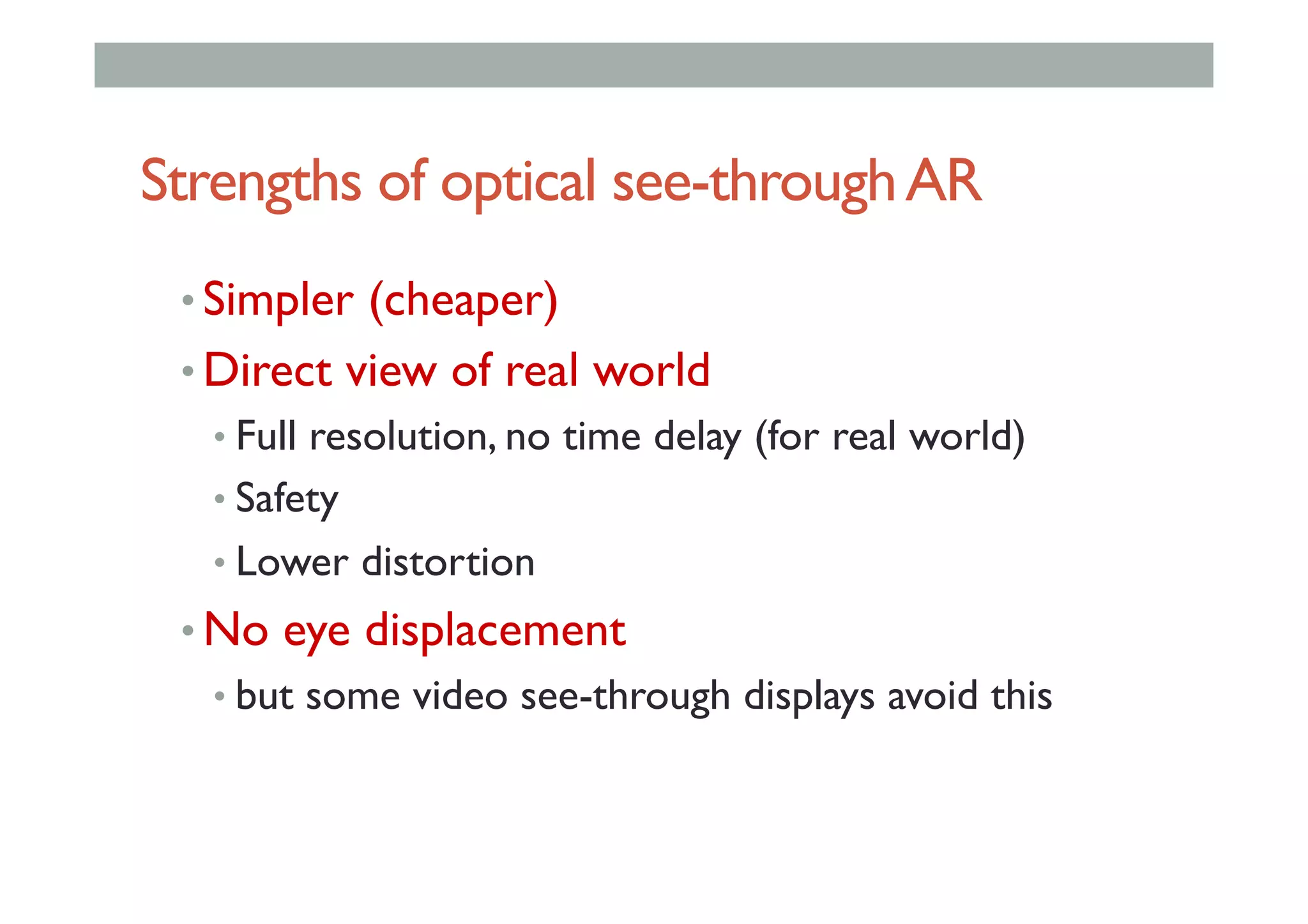
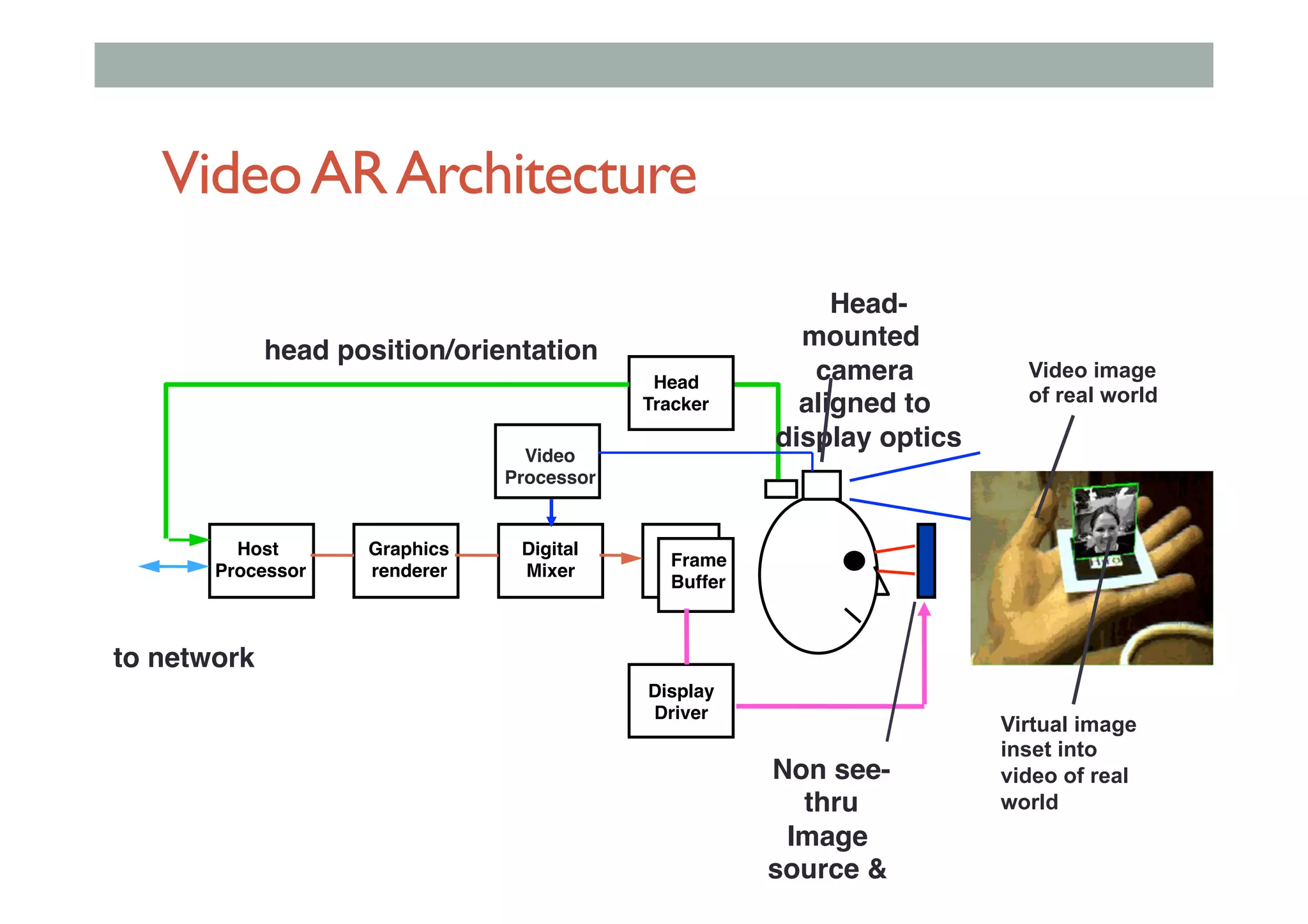
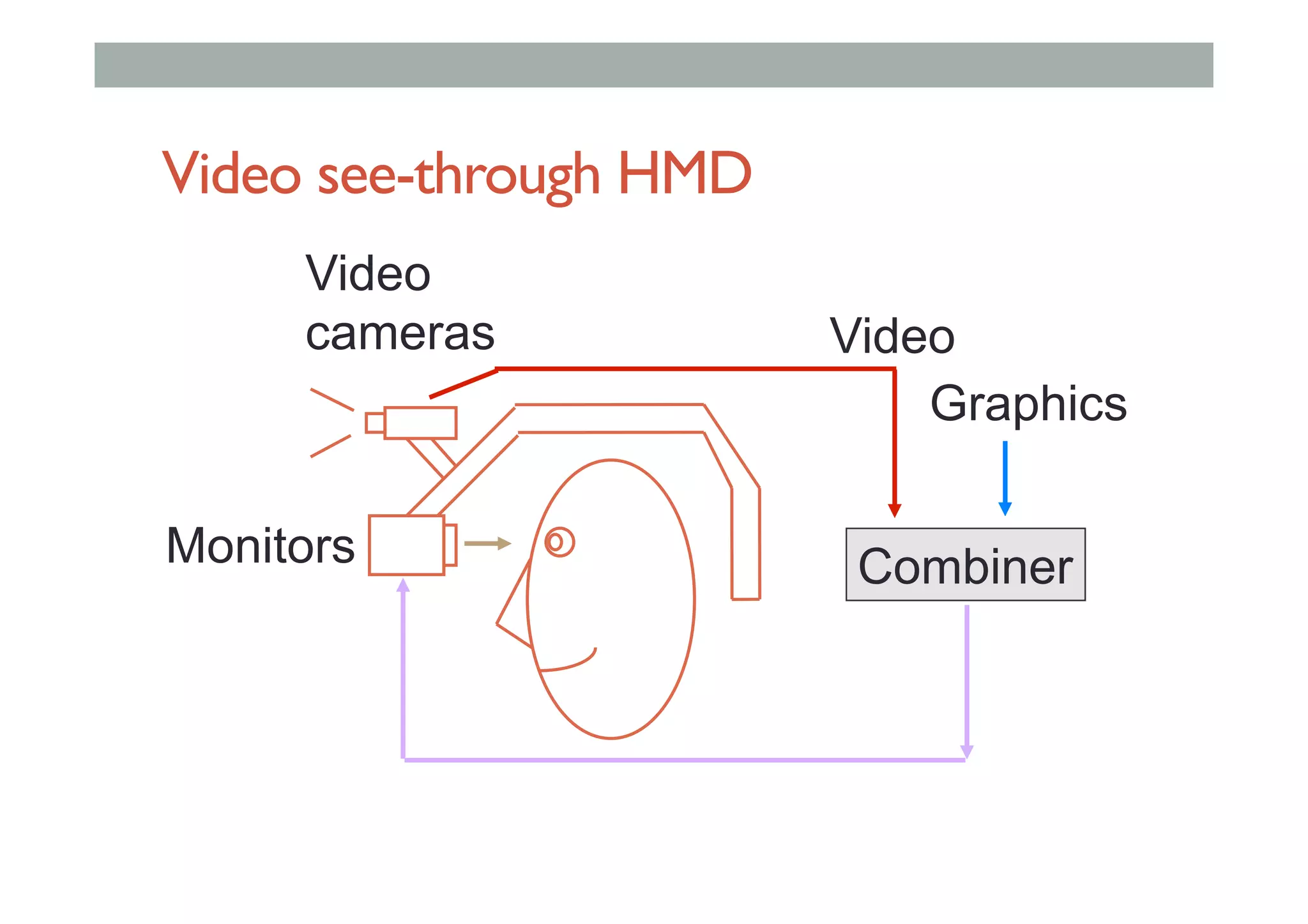
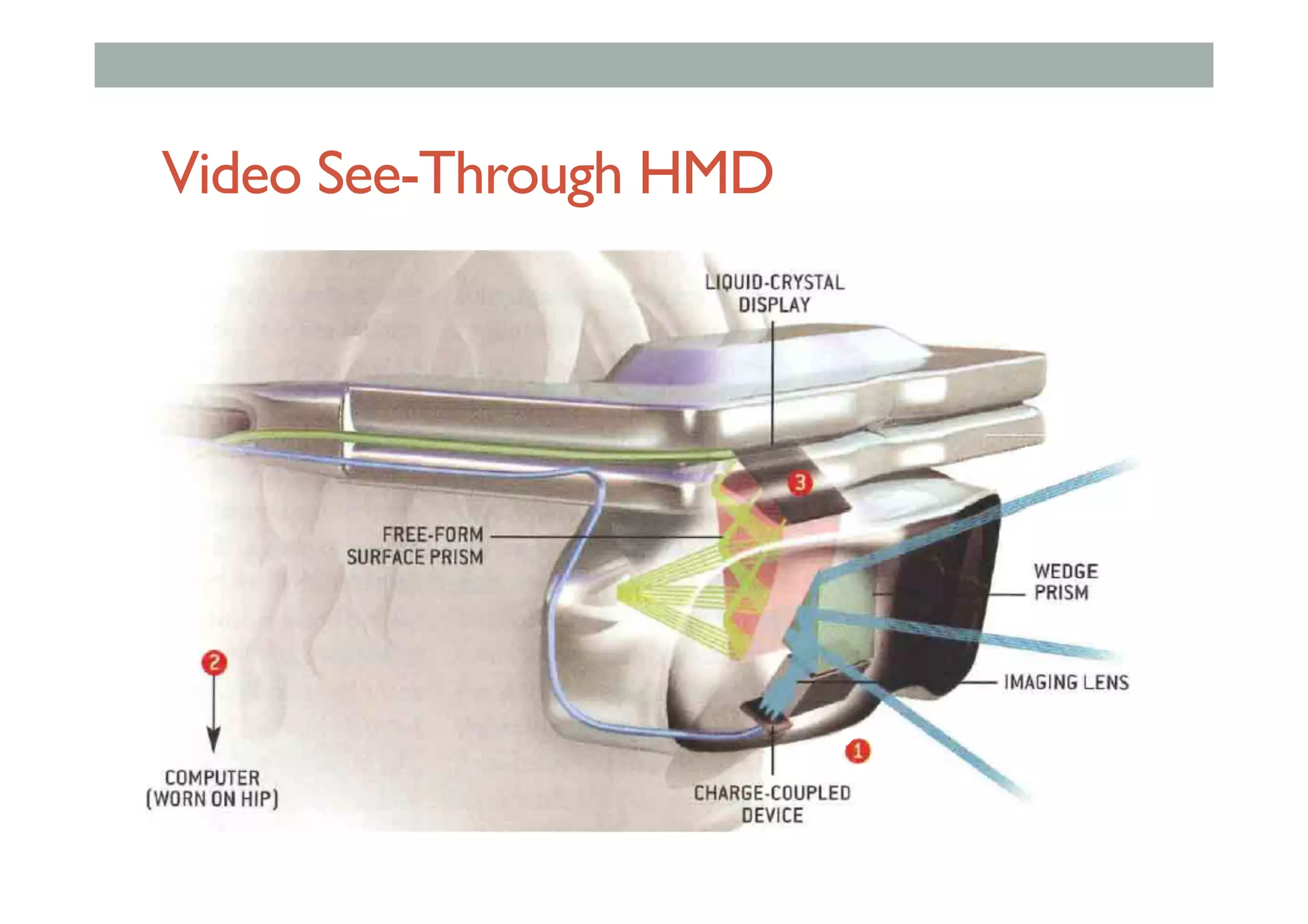
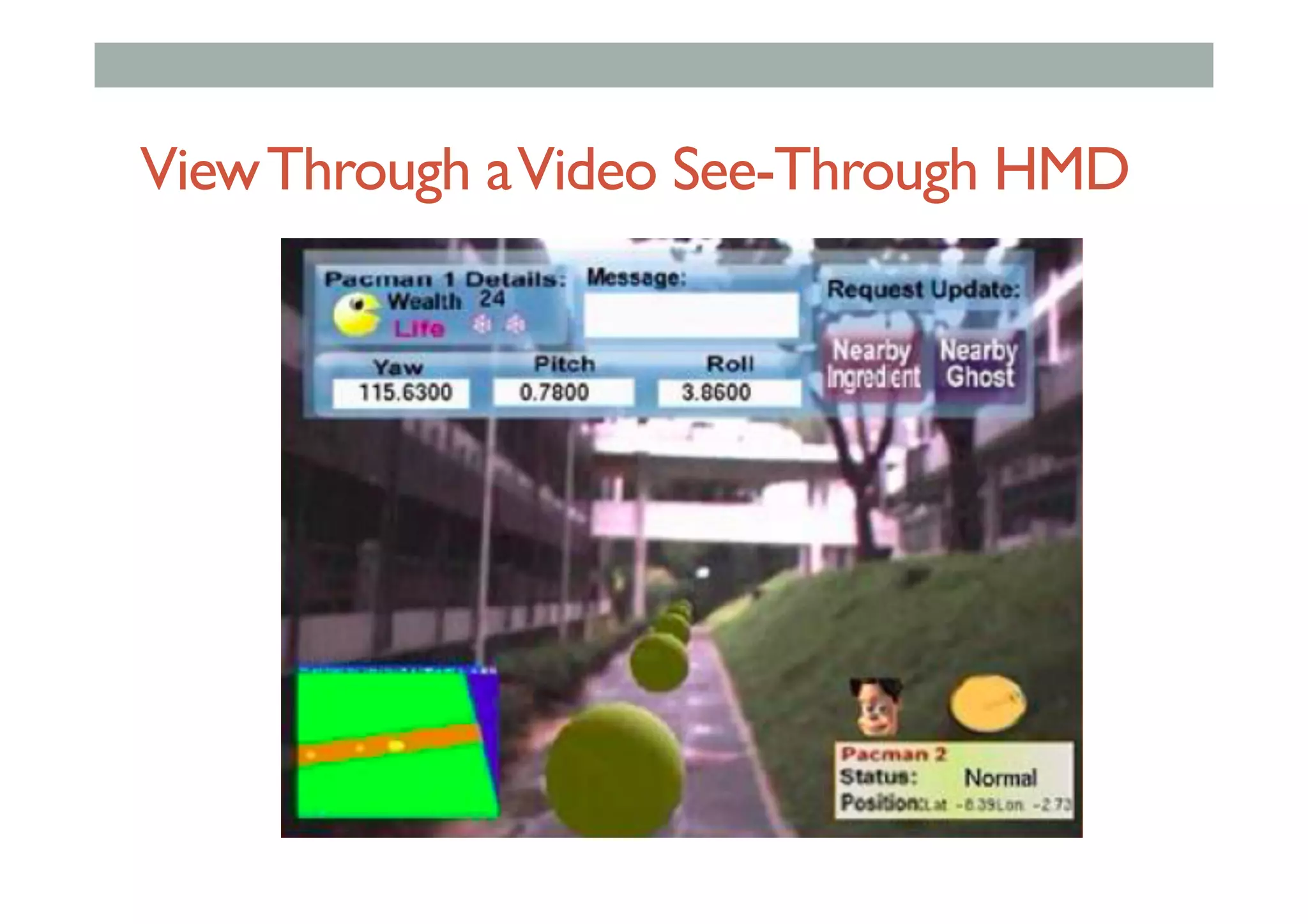
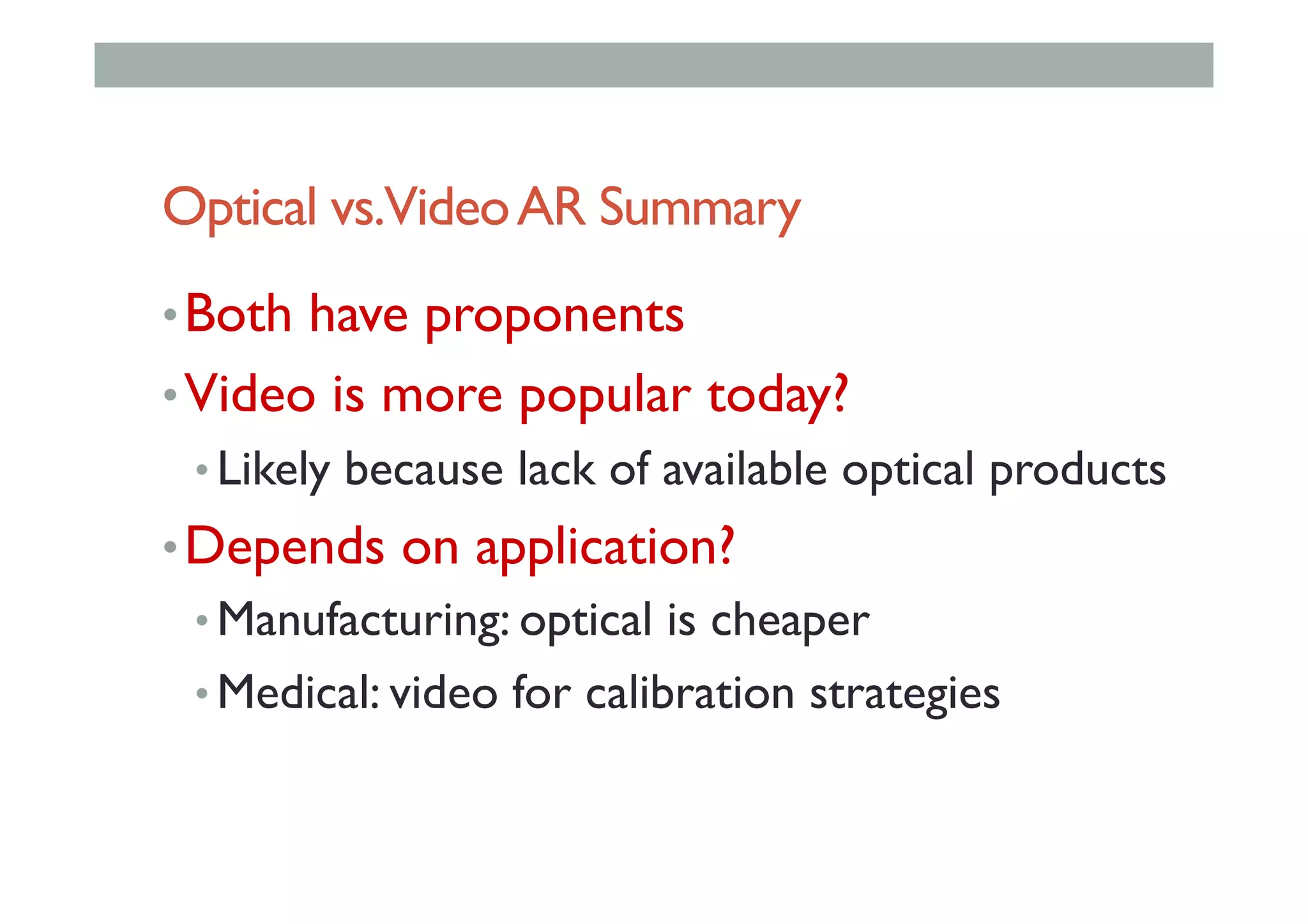
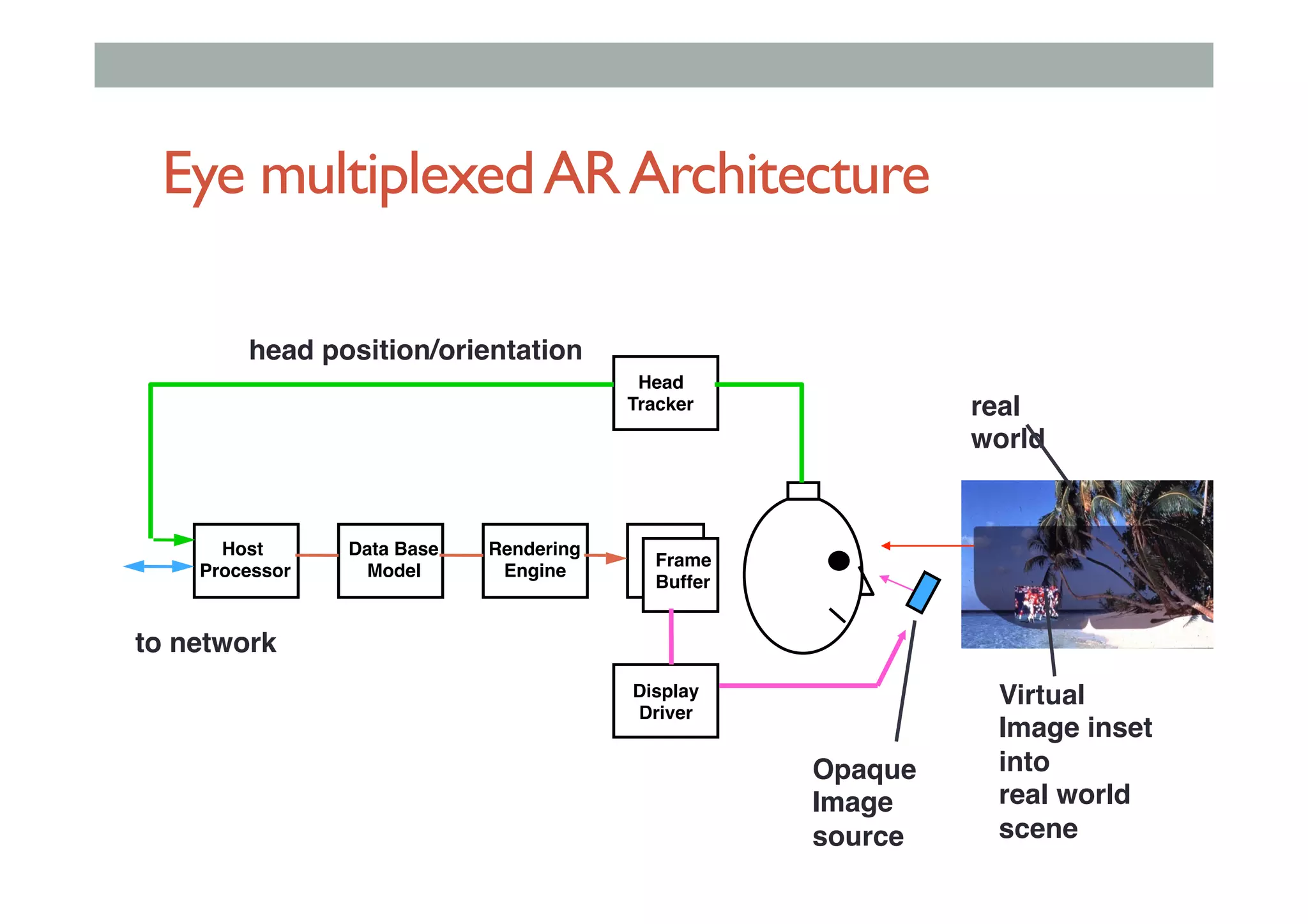
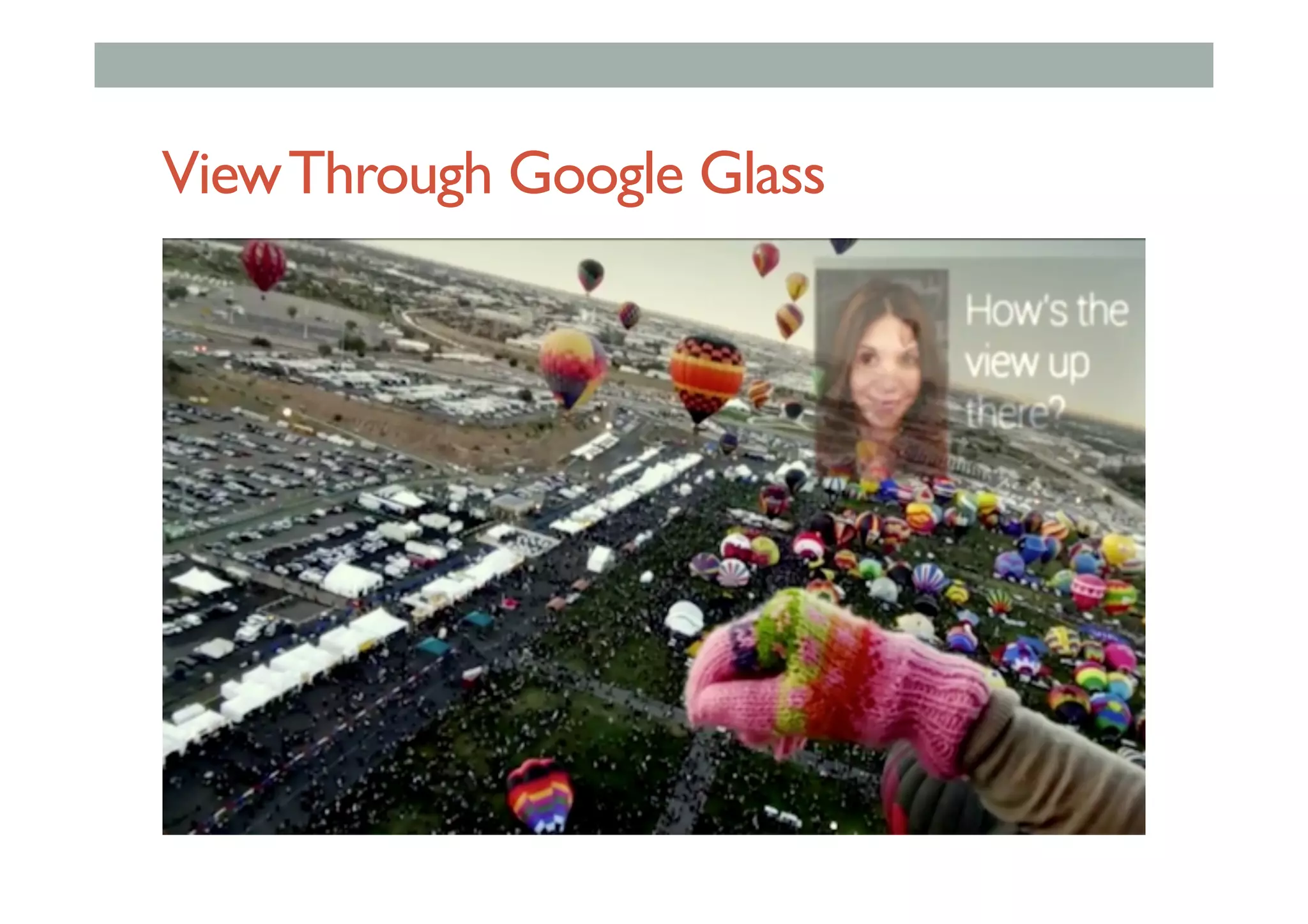
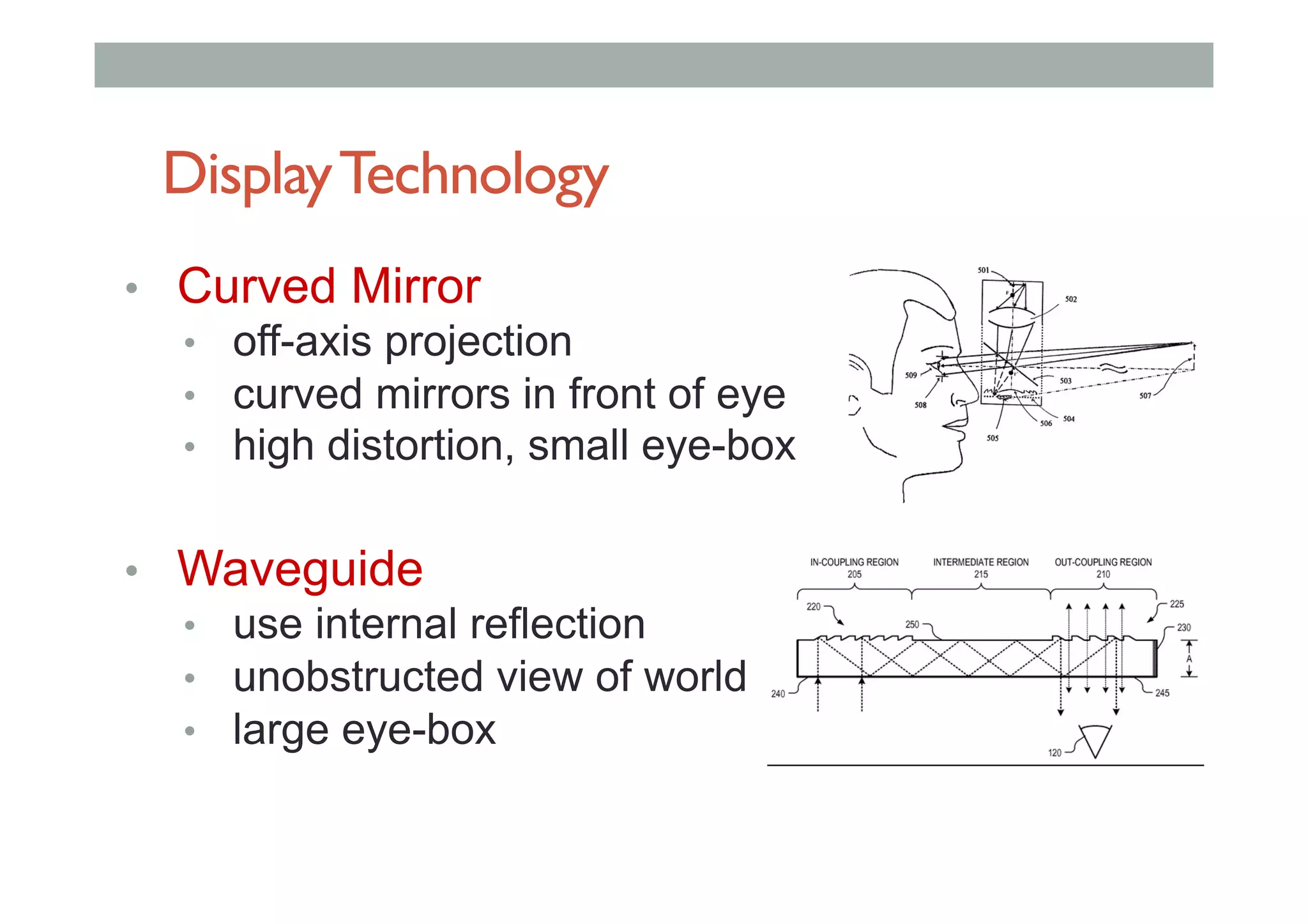
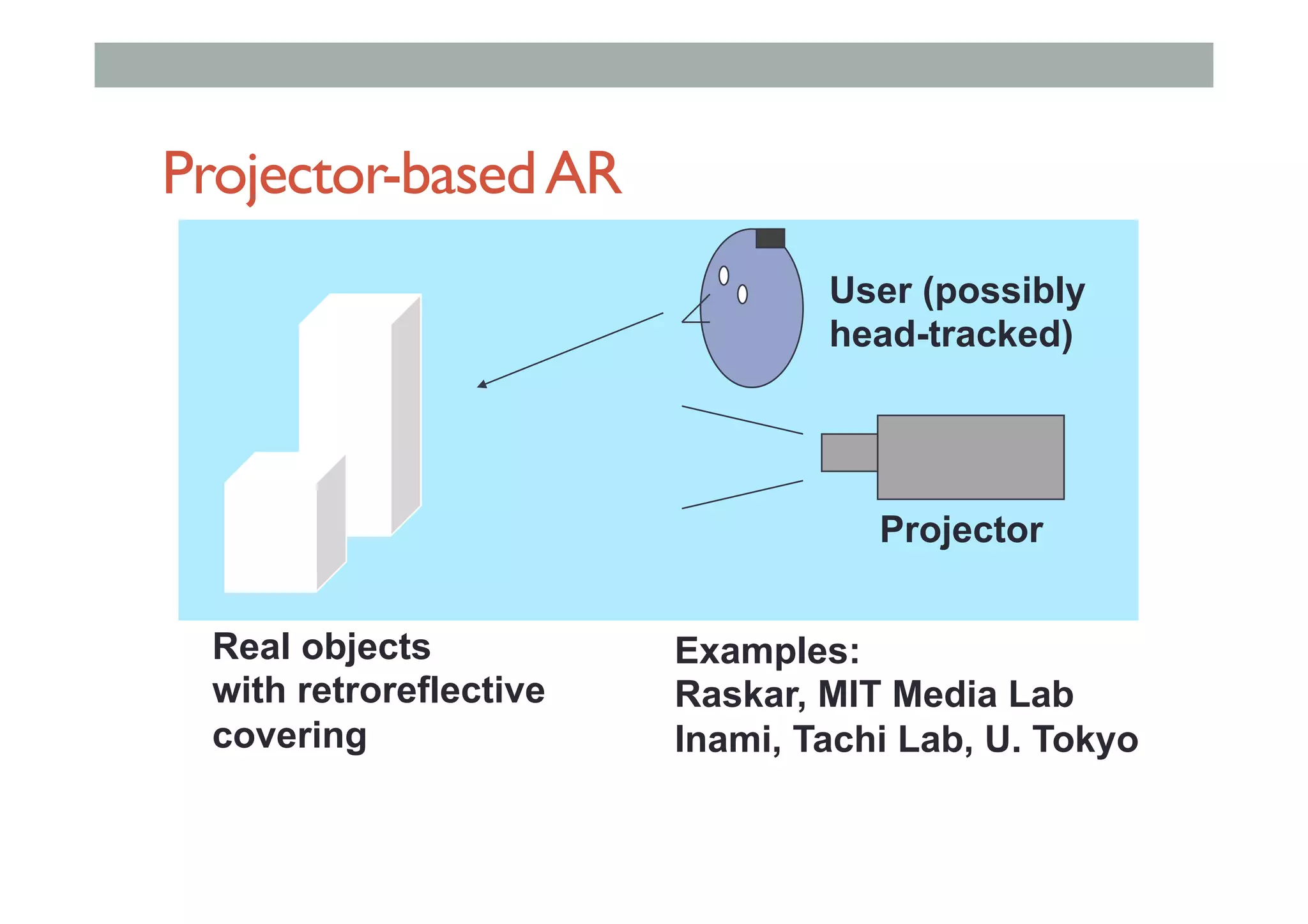
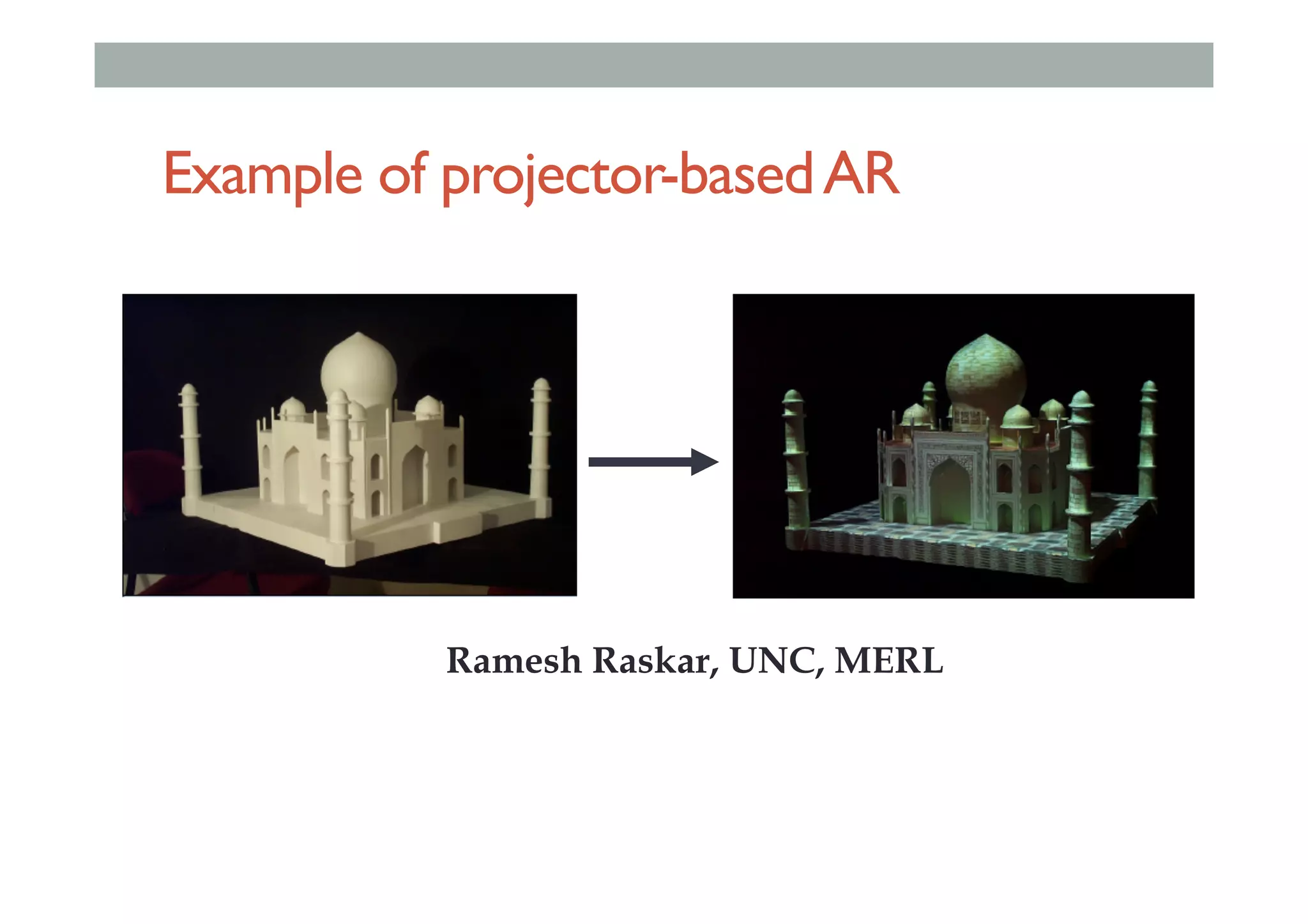
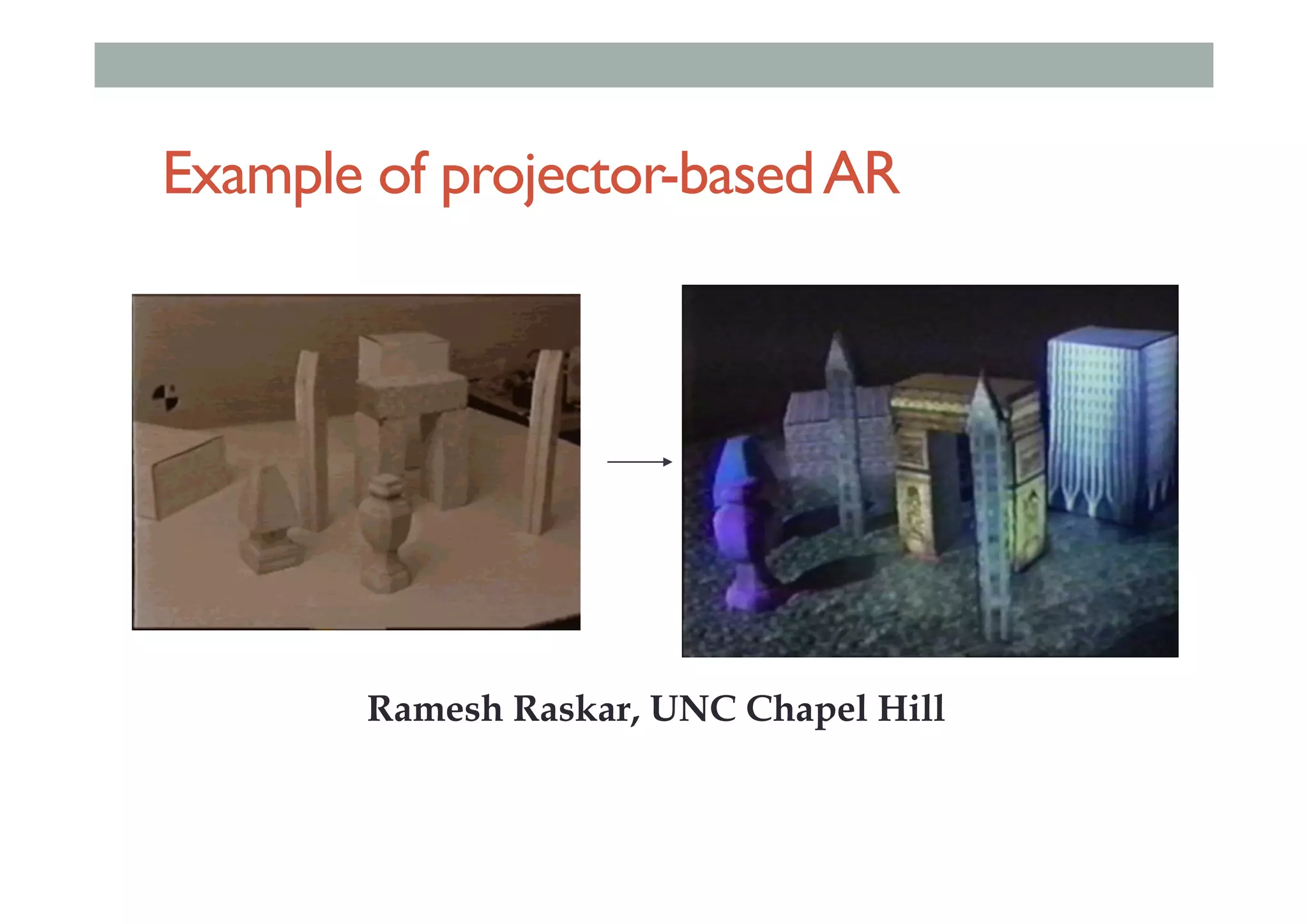
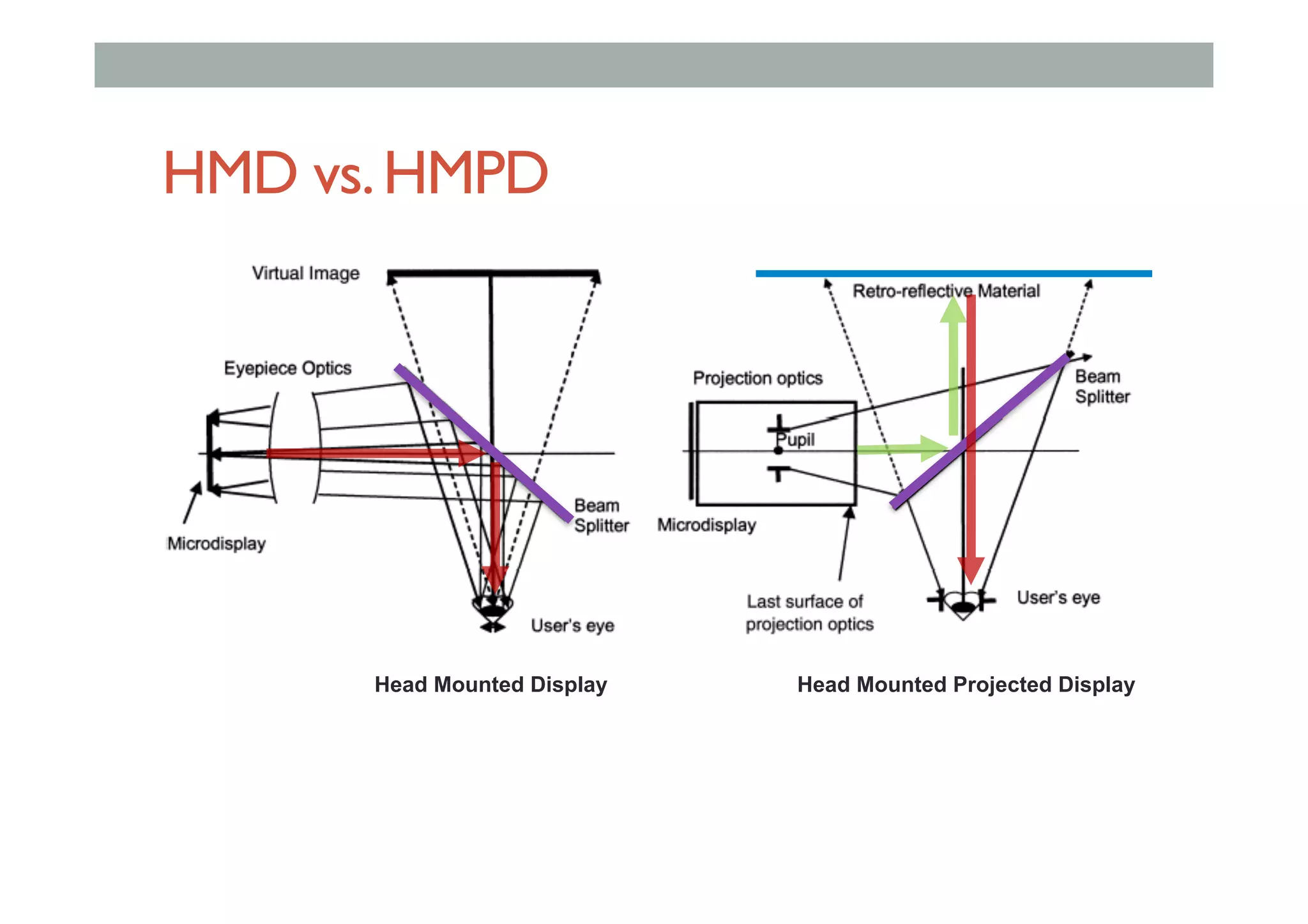
The document details augment reality (AR) technology, focusing on its definition, interactive characteristics, and various display technologies. It compares head-mounted displays (HMDs), optical and video see-through systems, and introduces spatial augmented reality with examples and advancements in AR displays. The discussion also includes various applications and considerations for different display methods and their implications in fields such as manufacturing and medicine.

![Augmented Reality Definition
• Defining Characteristics [Azuma 97]
• Combines Real andVirtual Images
• Both can be seen at the same time
• Interactive in real-time
• The virtual content can be interacted with
• Registered in 3D
• Virtual objects appear fixed in space
Azuma, R. T. (1997). A survey of augmented reality. Presence, 6(4), 355-385.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture9-artechnologynovideo2-161012194551/75/COMP-4010-Lecture9-AR-Displays-2-2048.jpg)