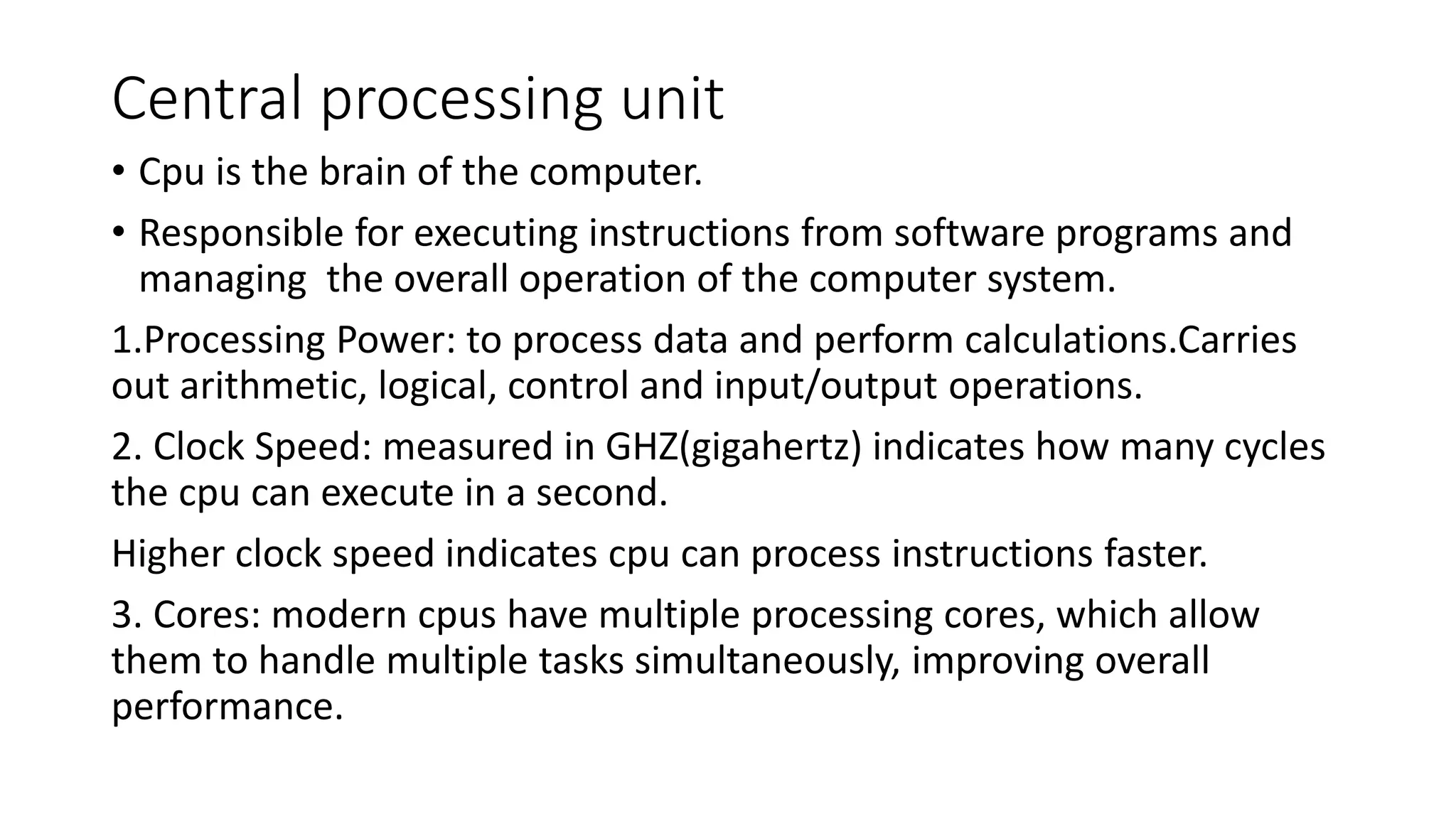
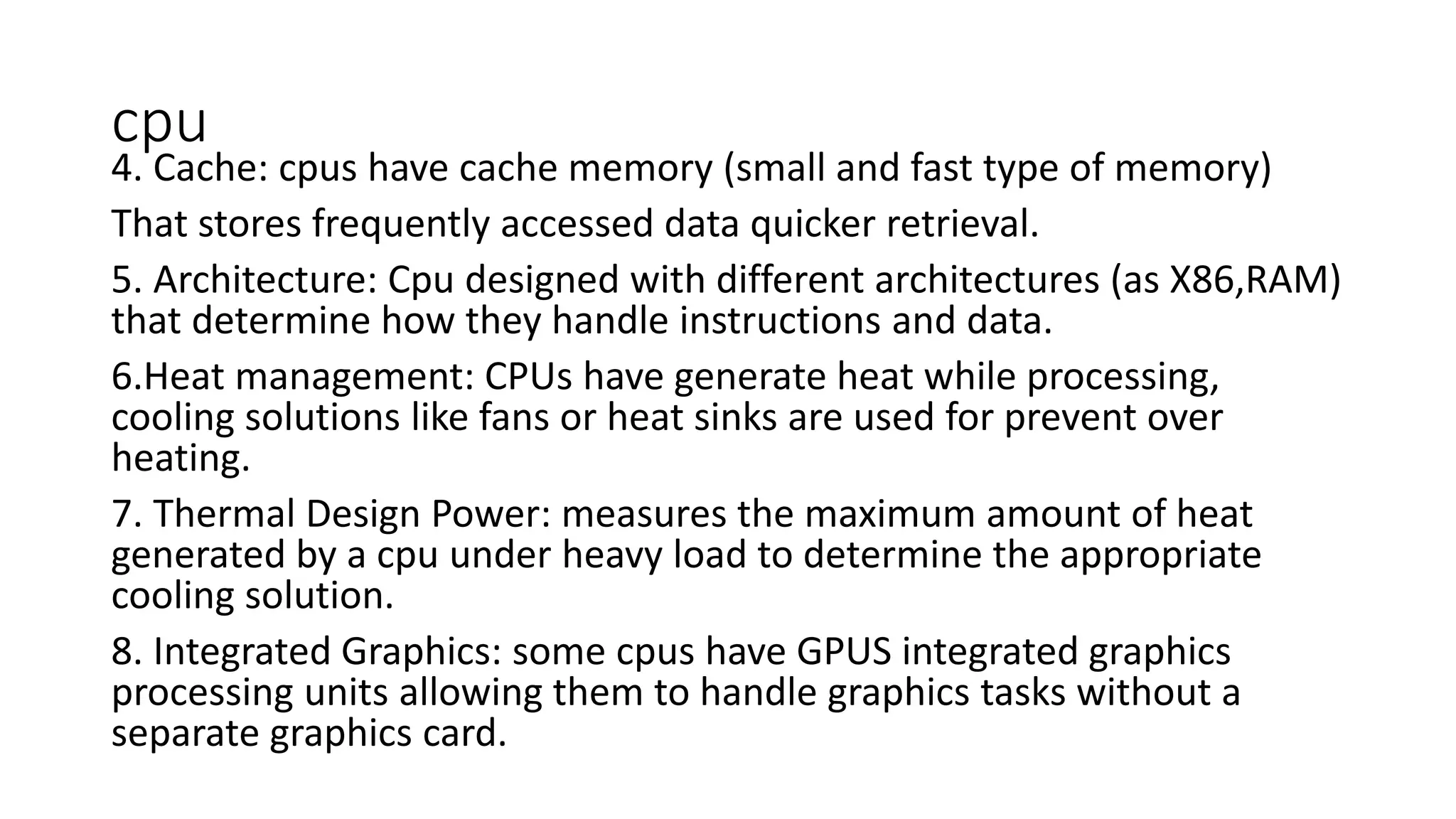
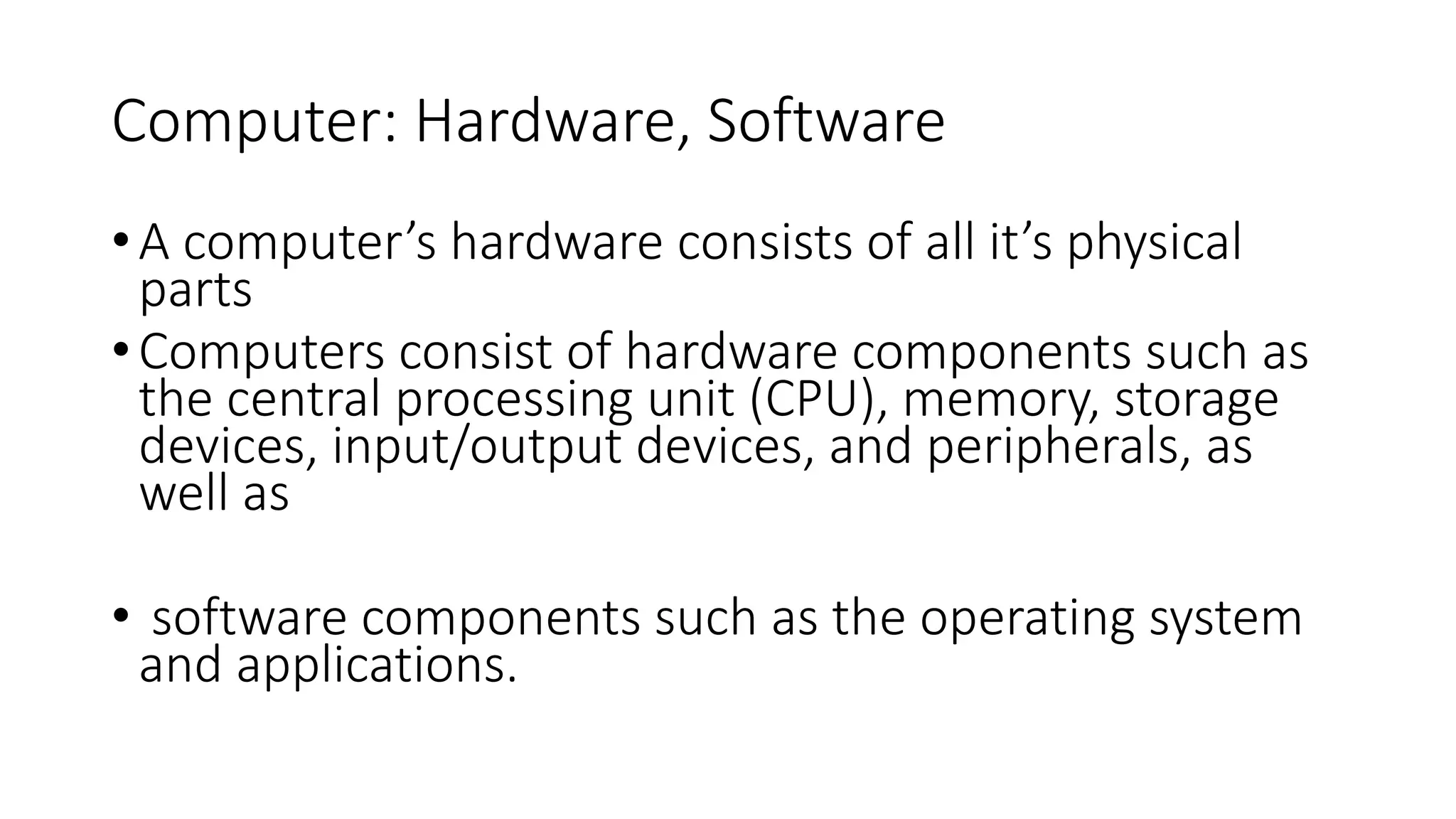
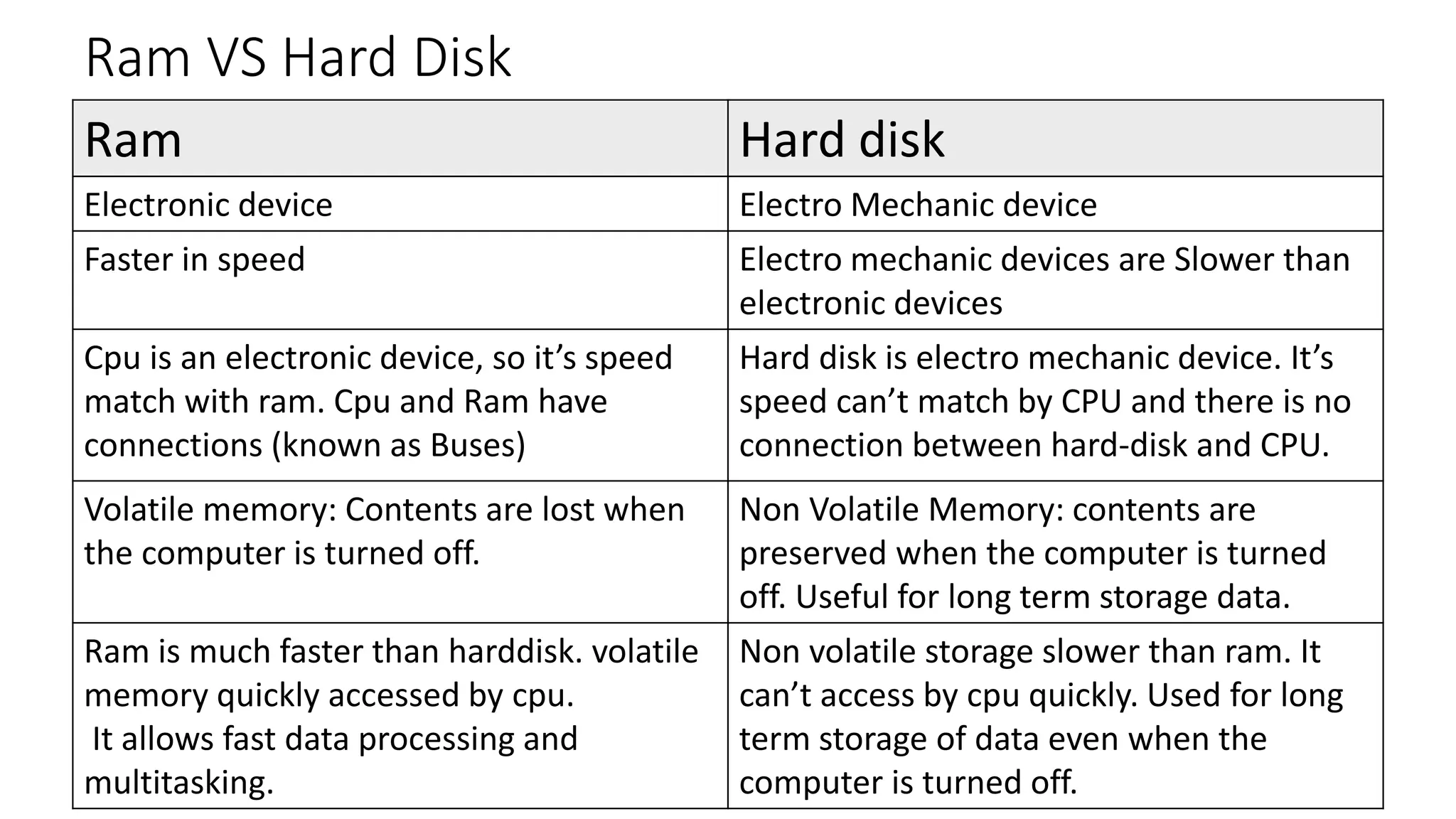
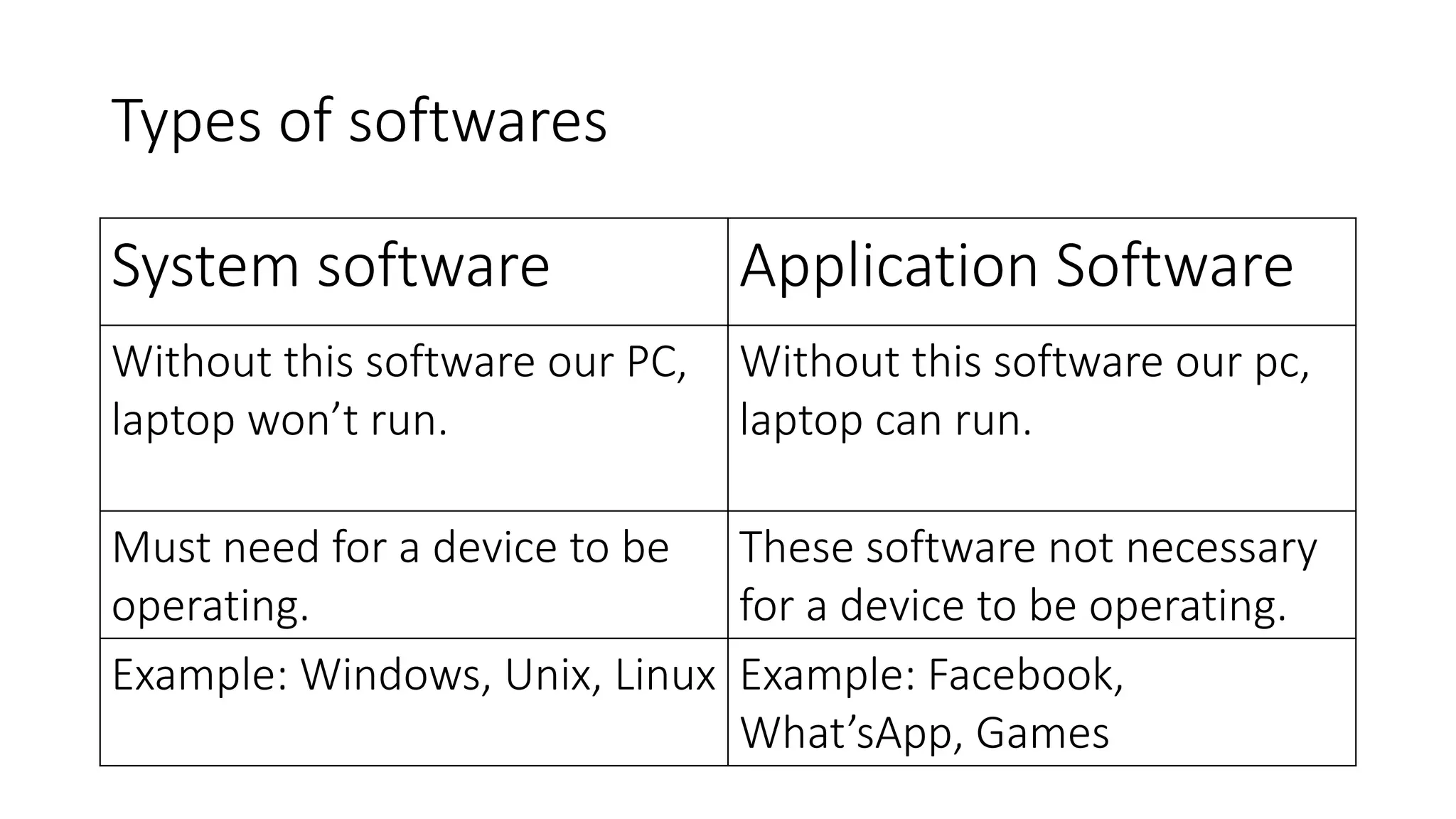
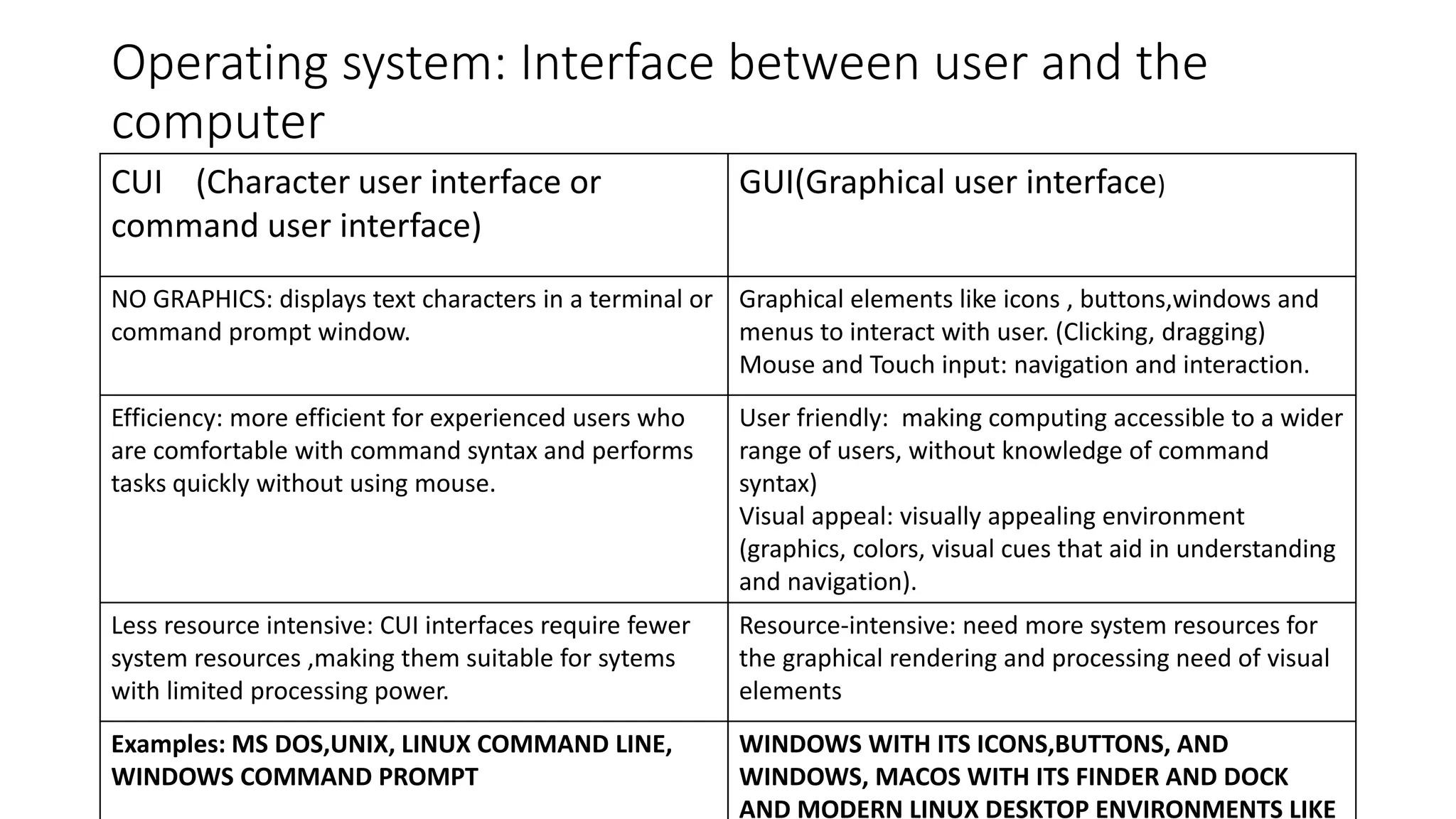
This document provides information about computers and their components. It discusses that a computer is an electronic device that can receive, store, process and output data. It then describes the basic functions of a computer like accepting, storing, processing and retrieving data. It also lists common uses of computers in areas like communication, education, business and science. The document further explains concepts like data, information, central processing unit and its functions. It discusses computer hardware and software components. It also describes various input and output devices of a computer. Finally, it covers types of operating systems and software.