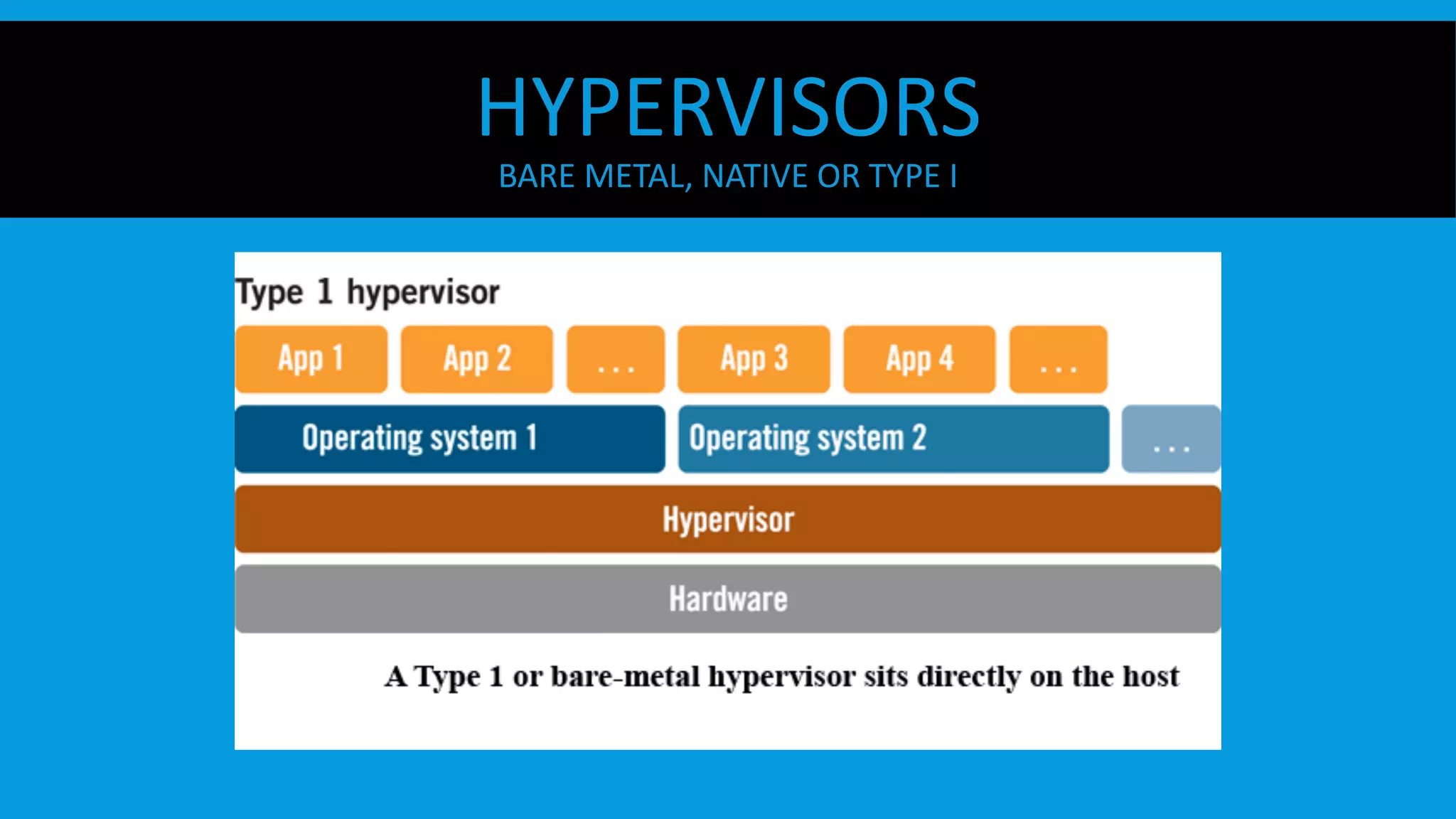
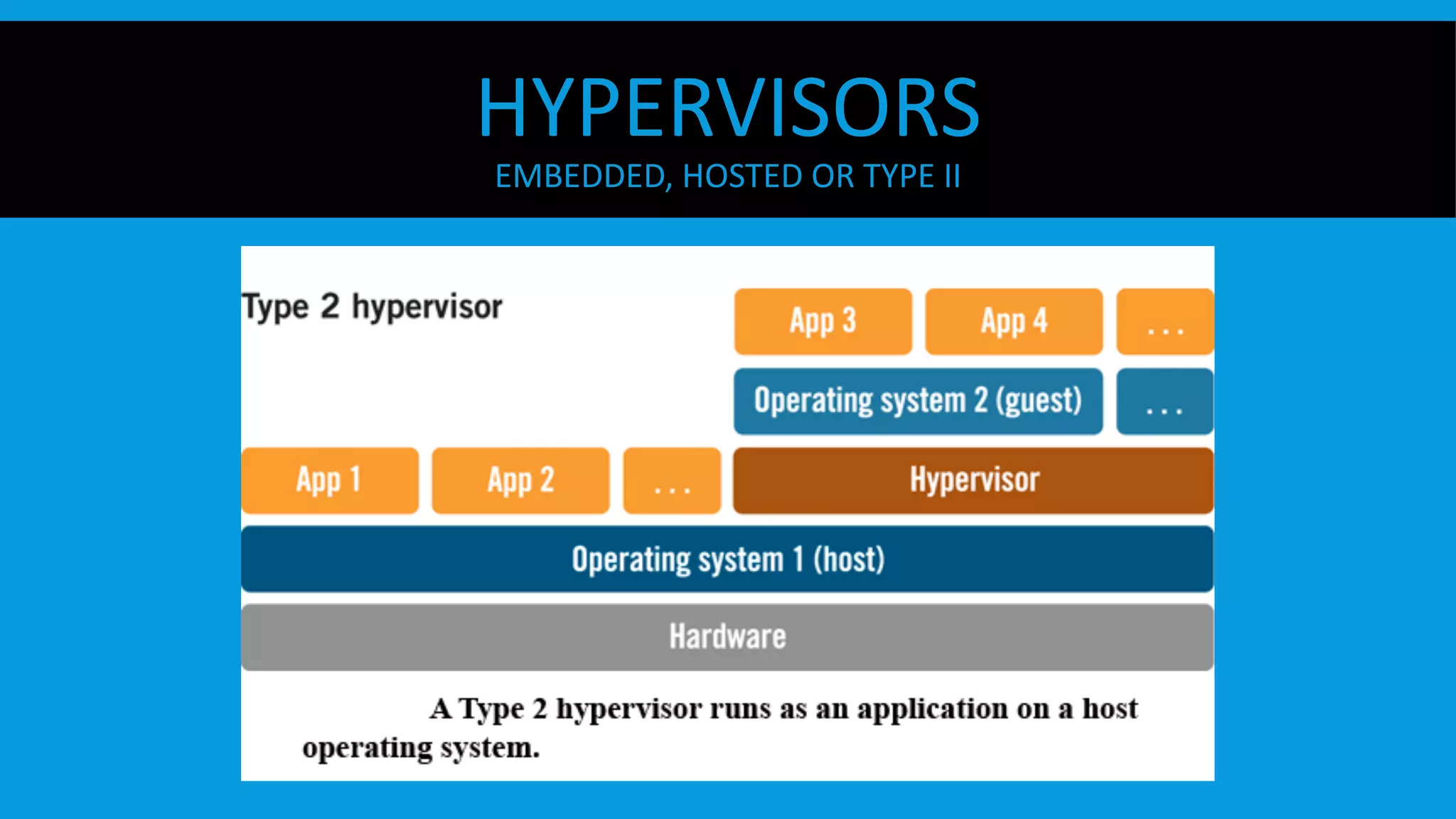
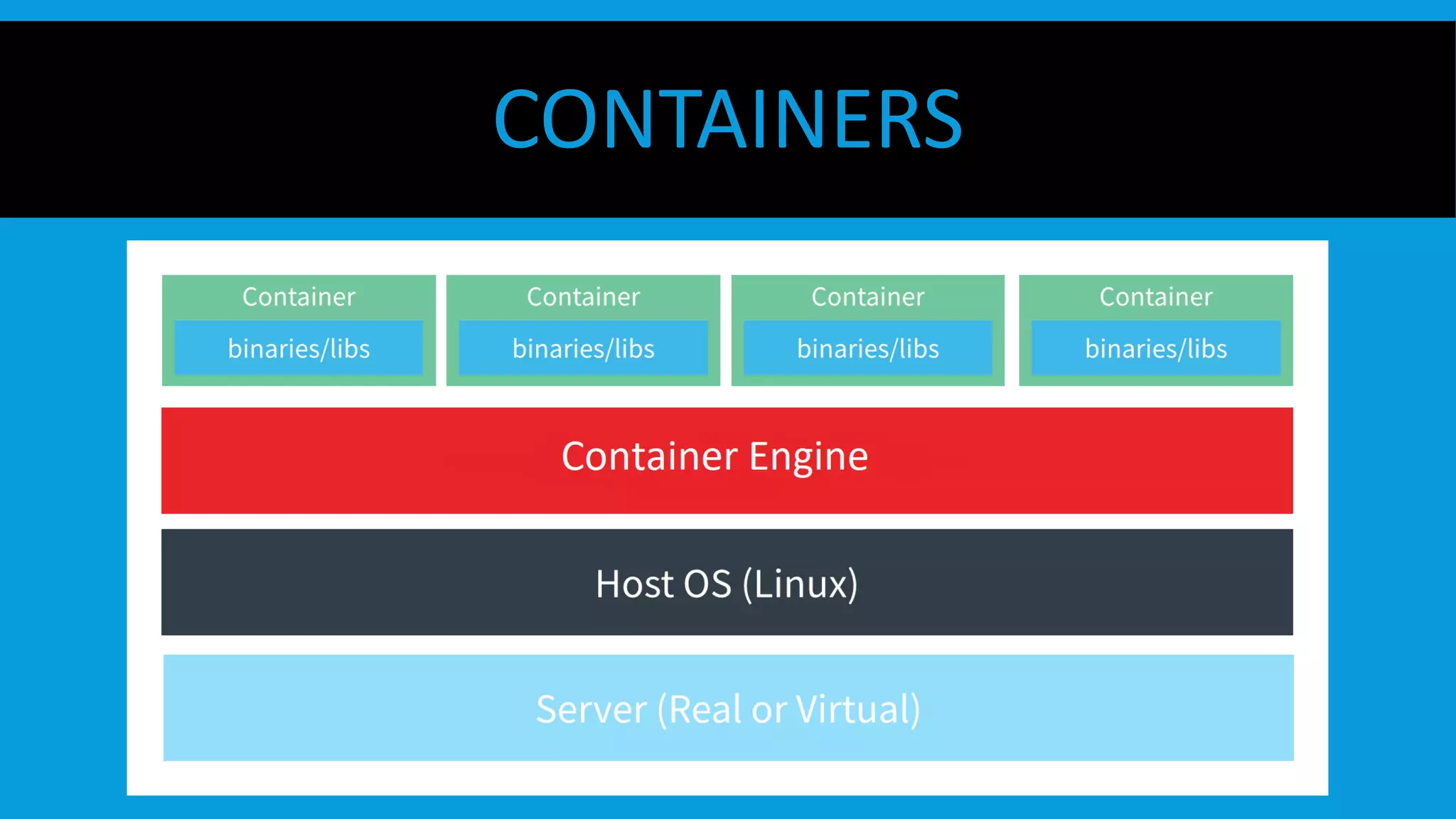
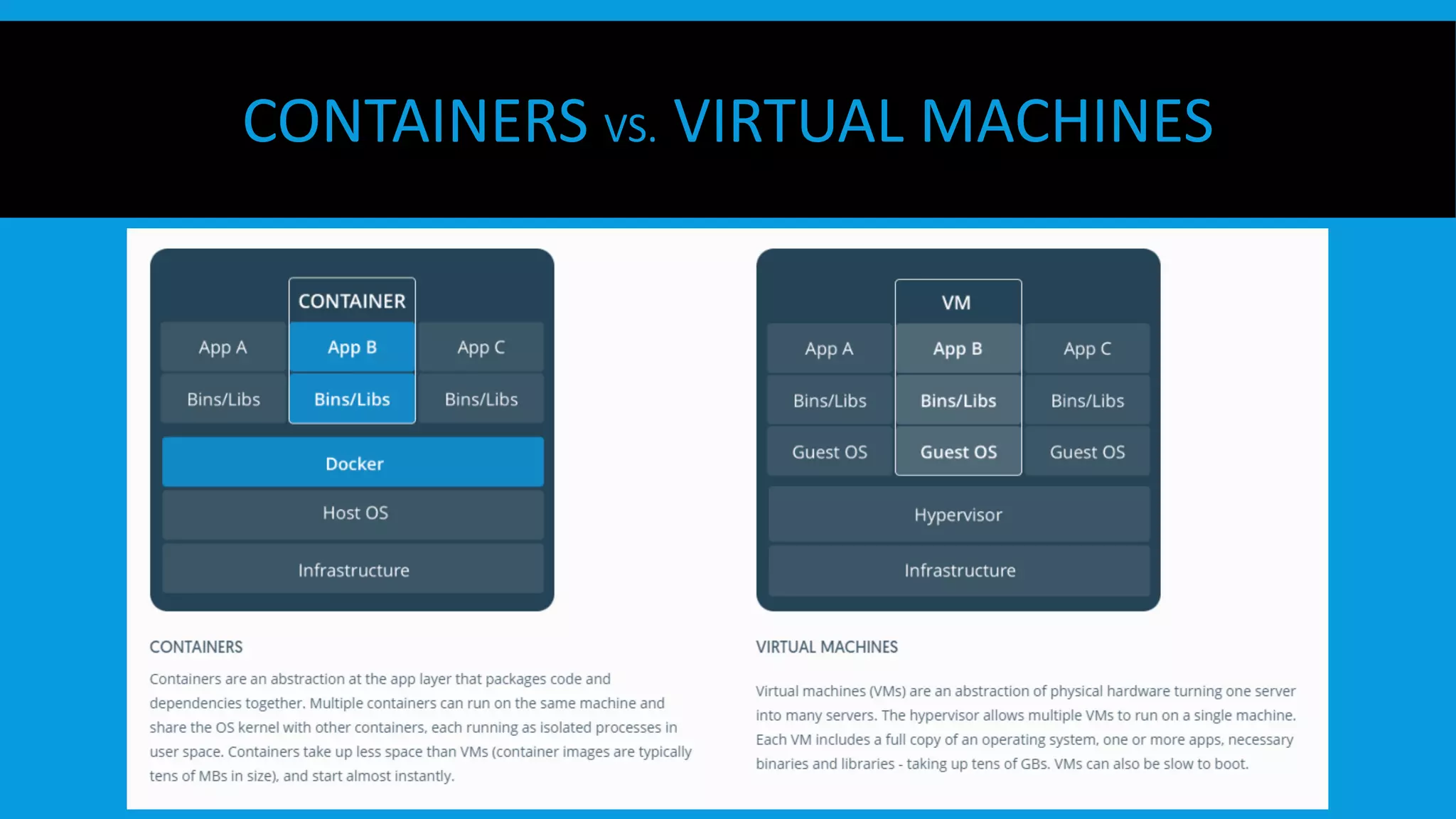
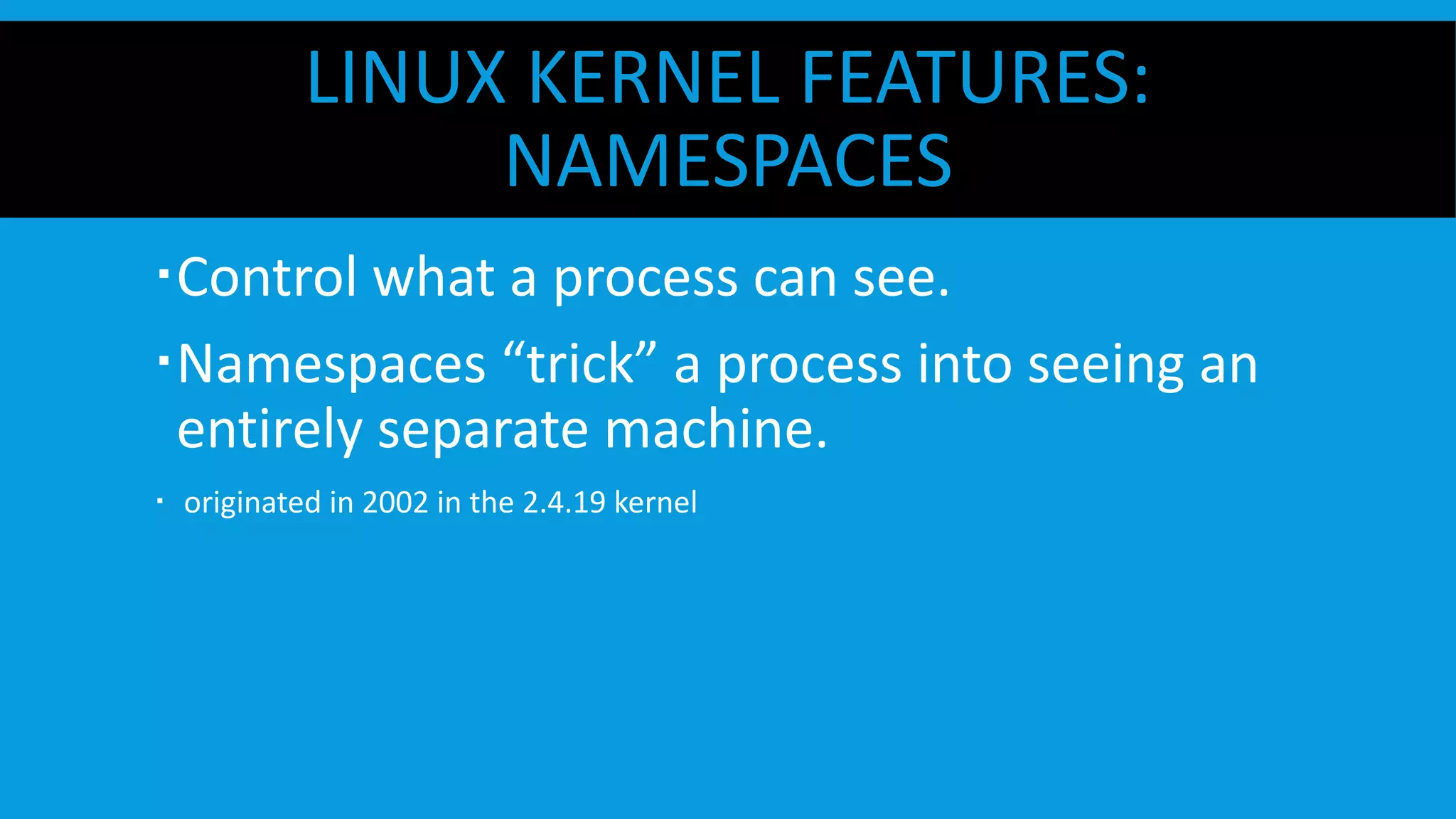
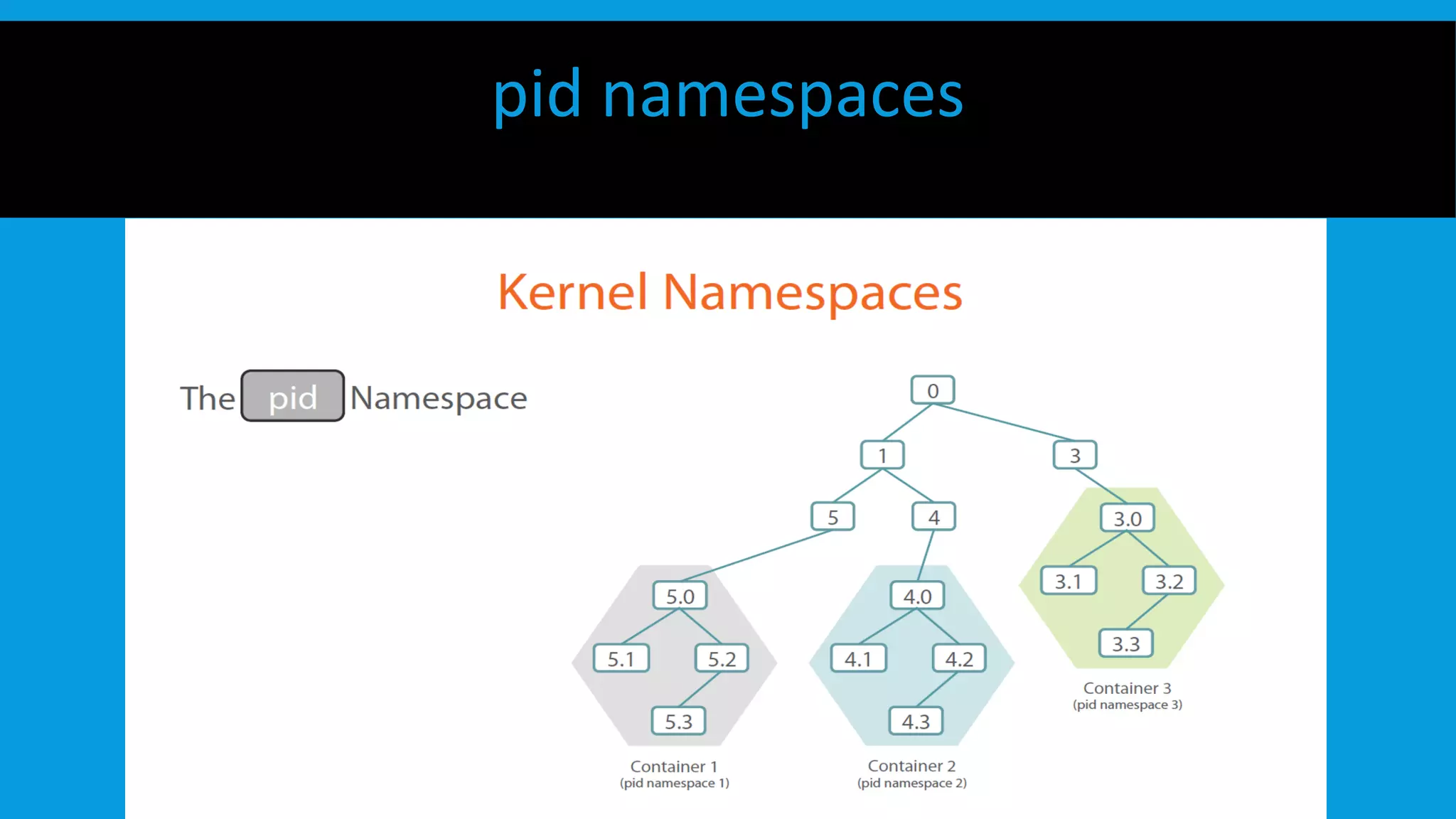
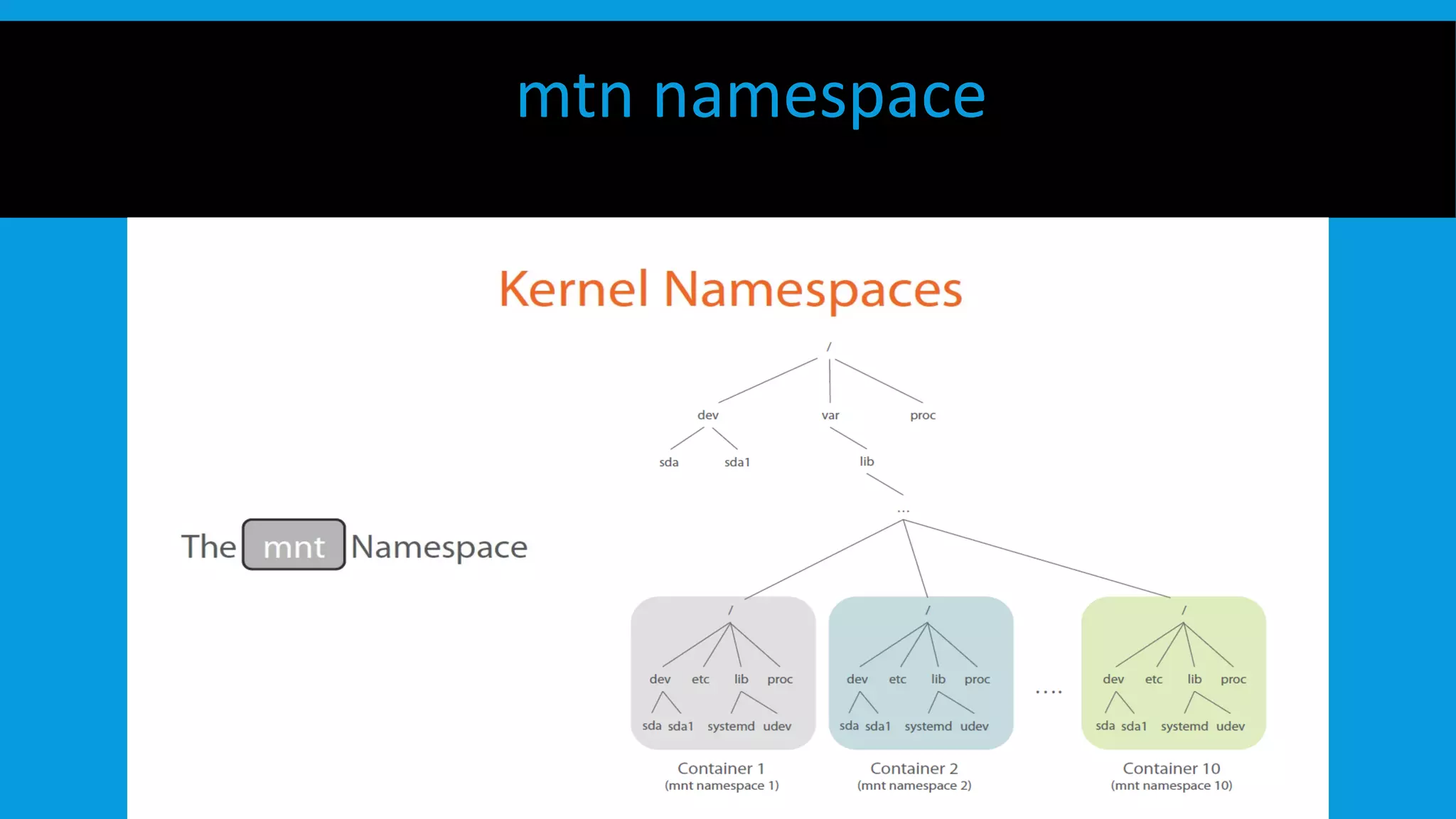
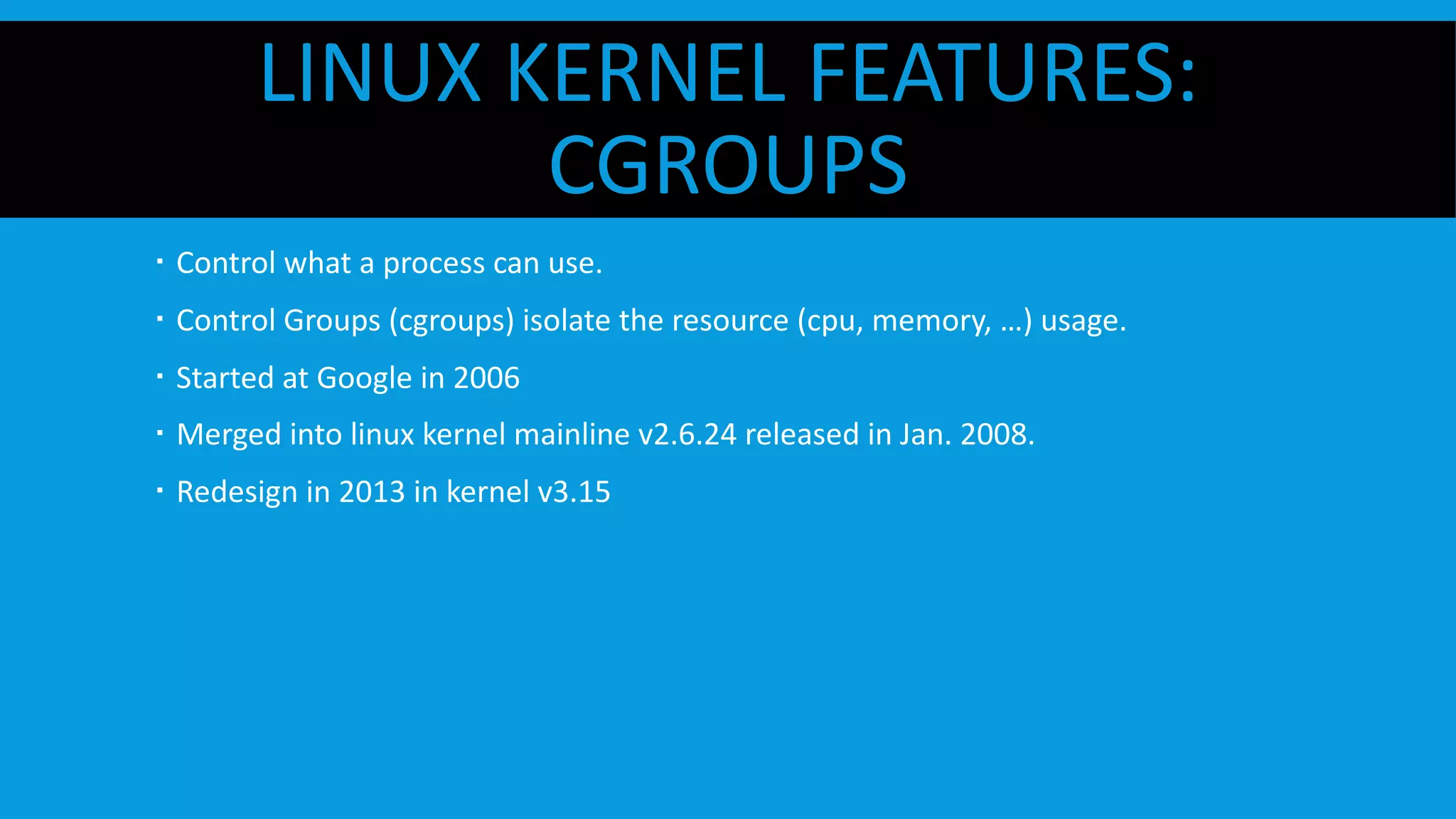
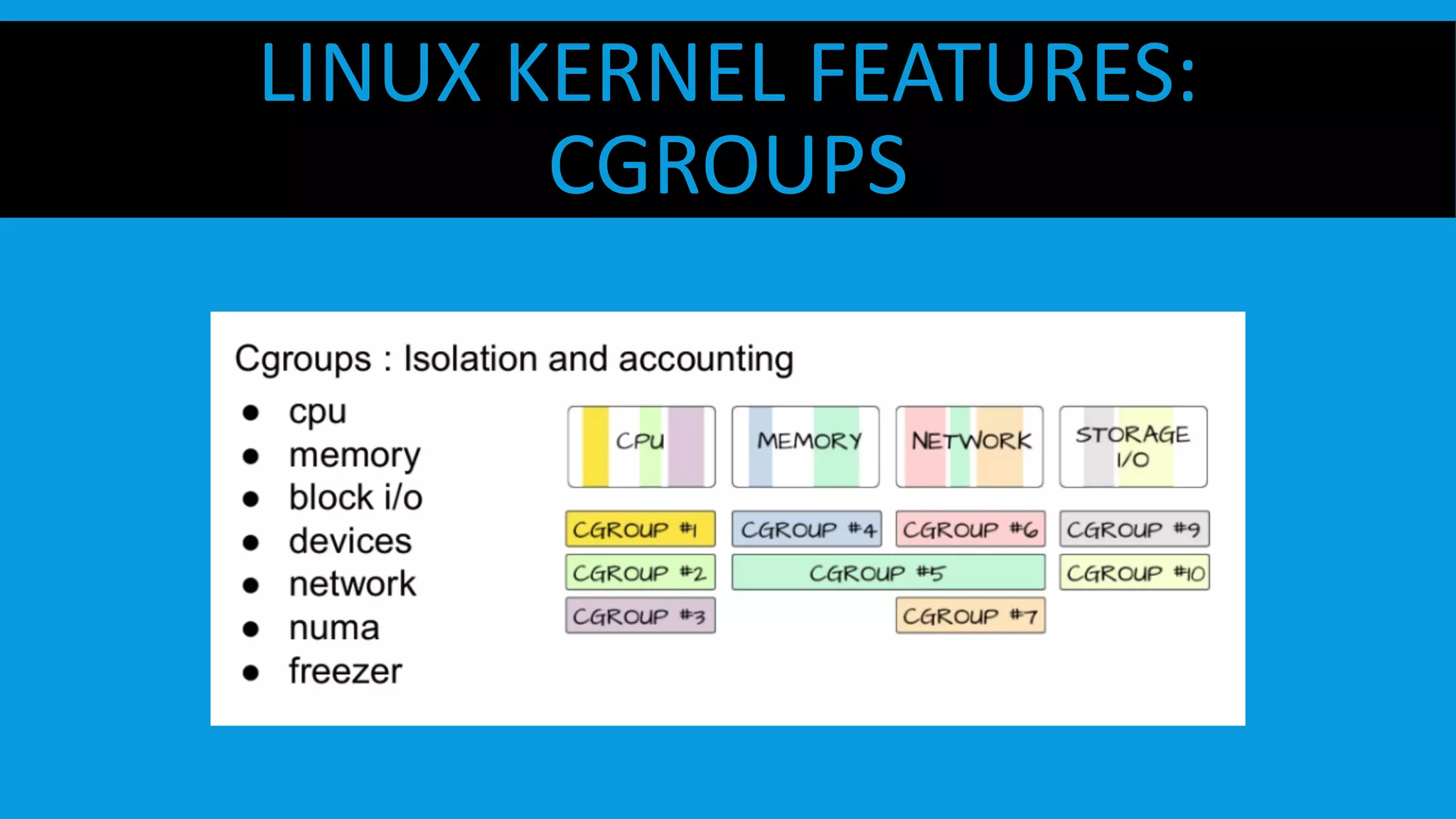
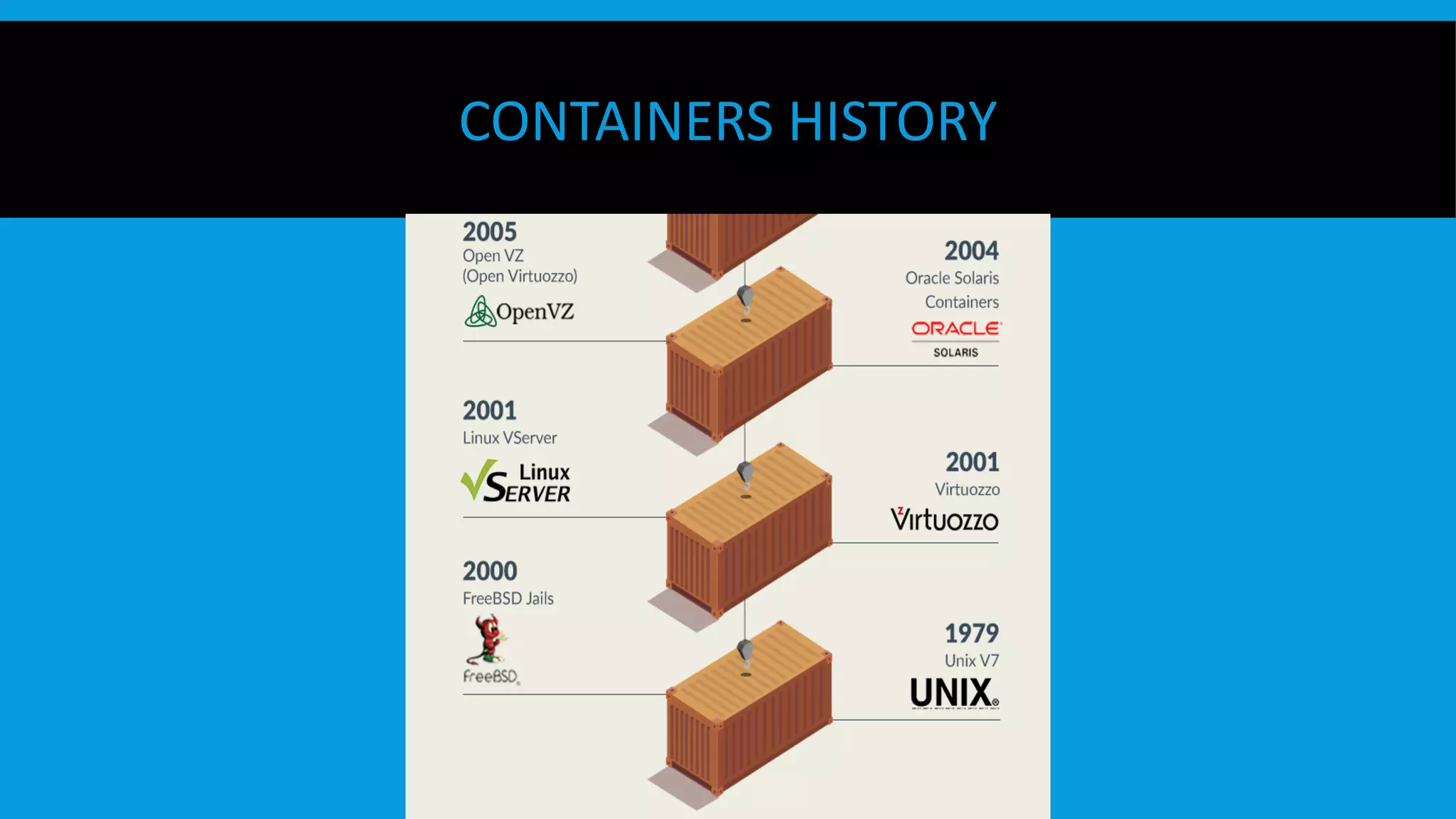
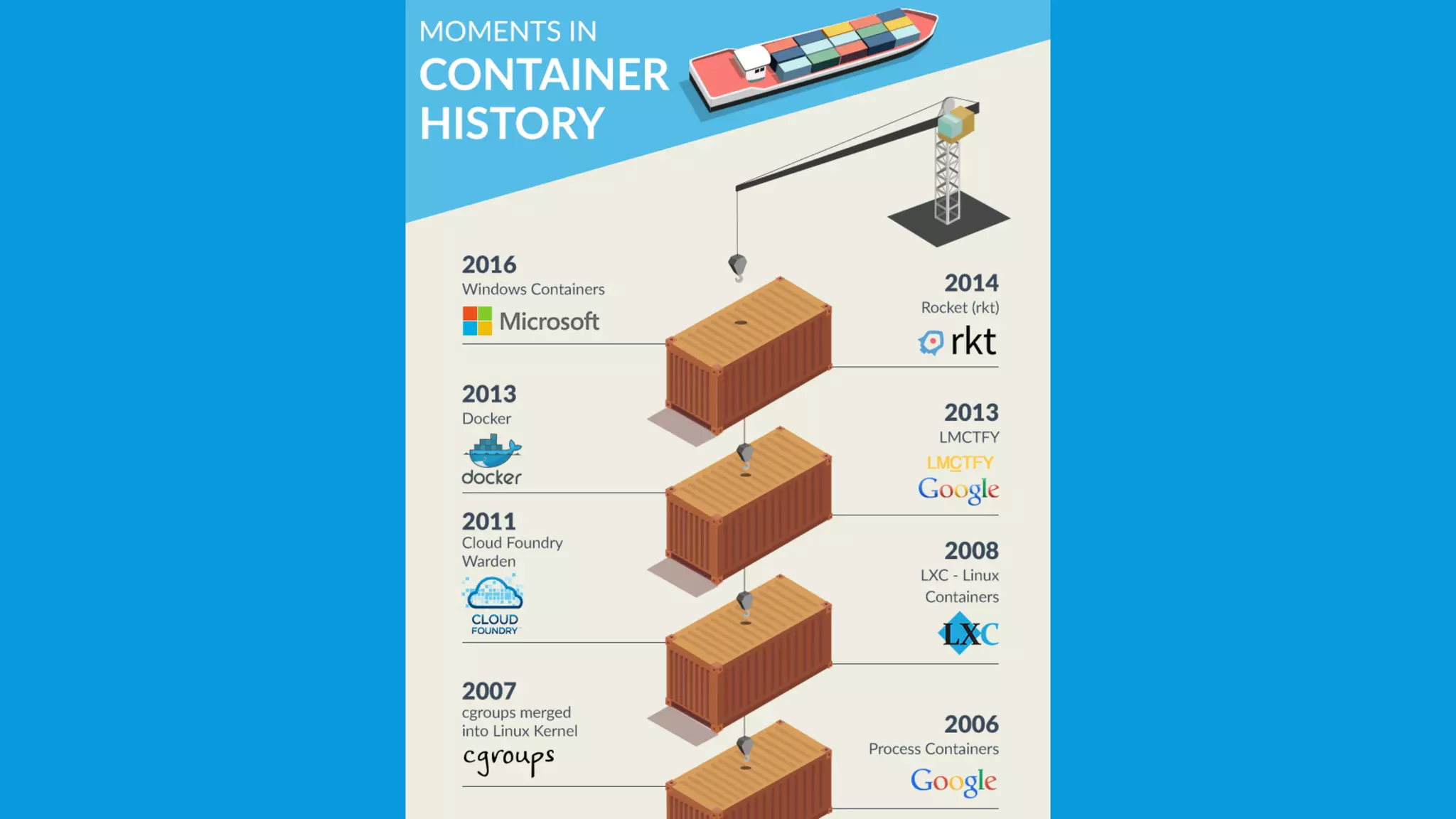
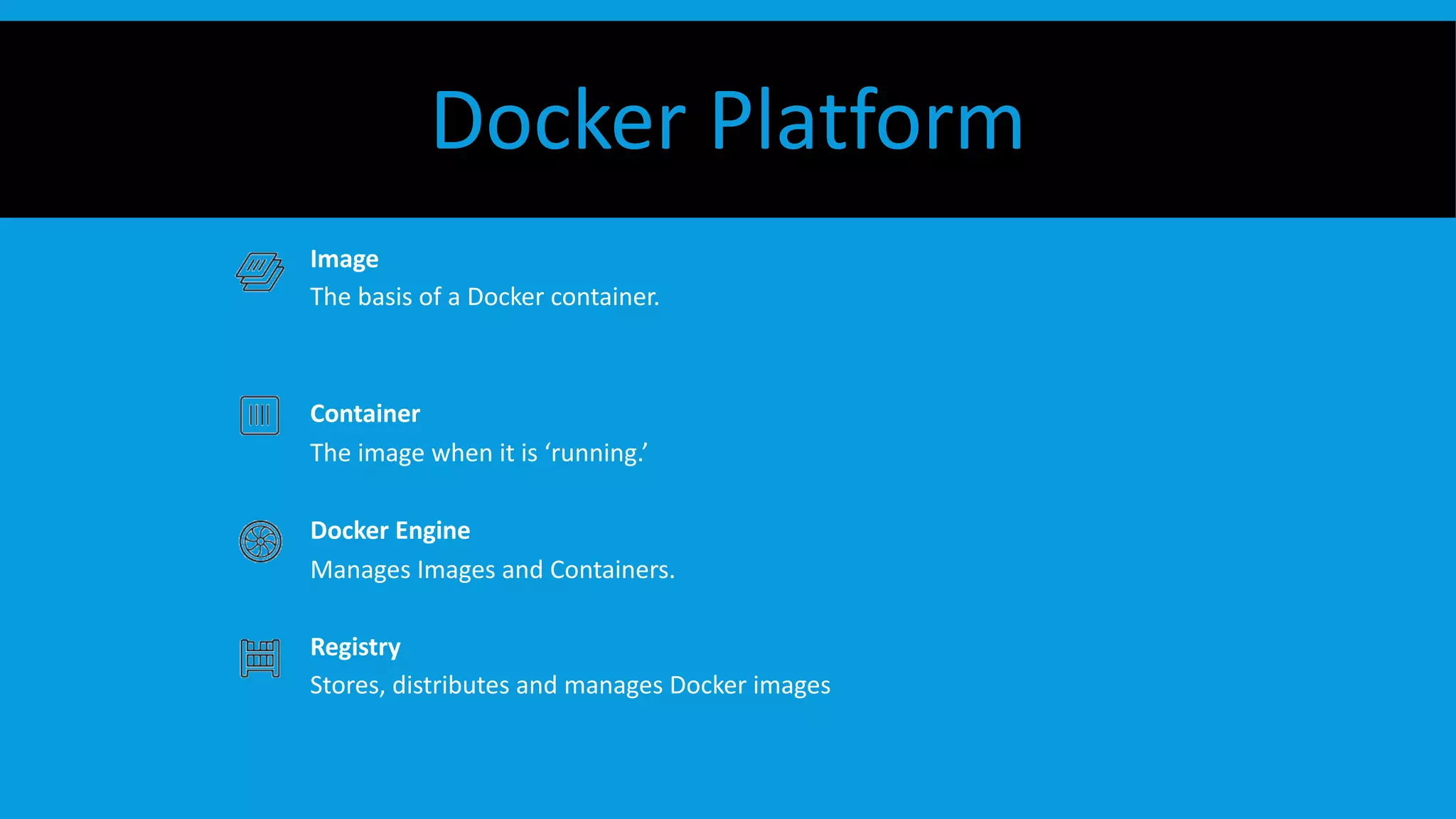
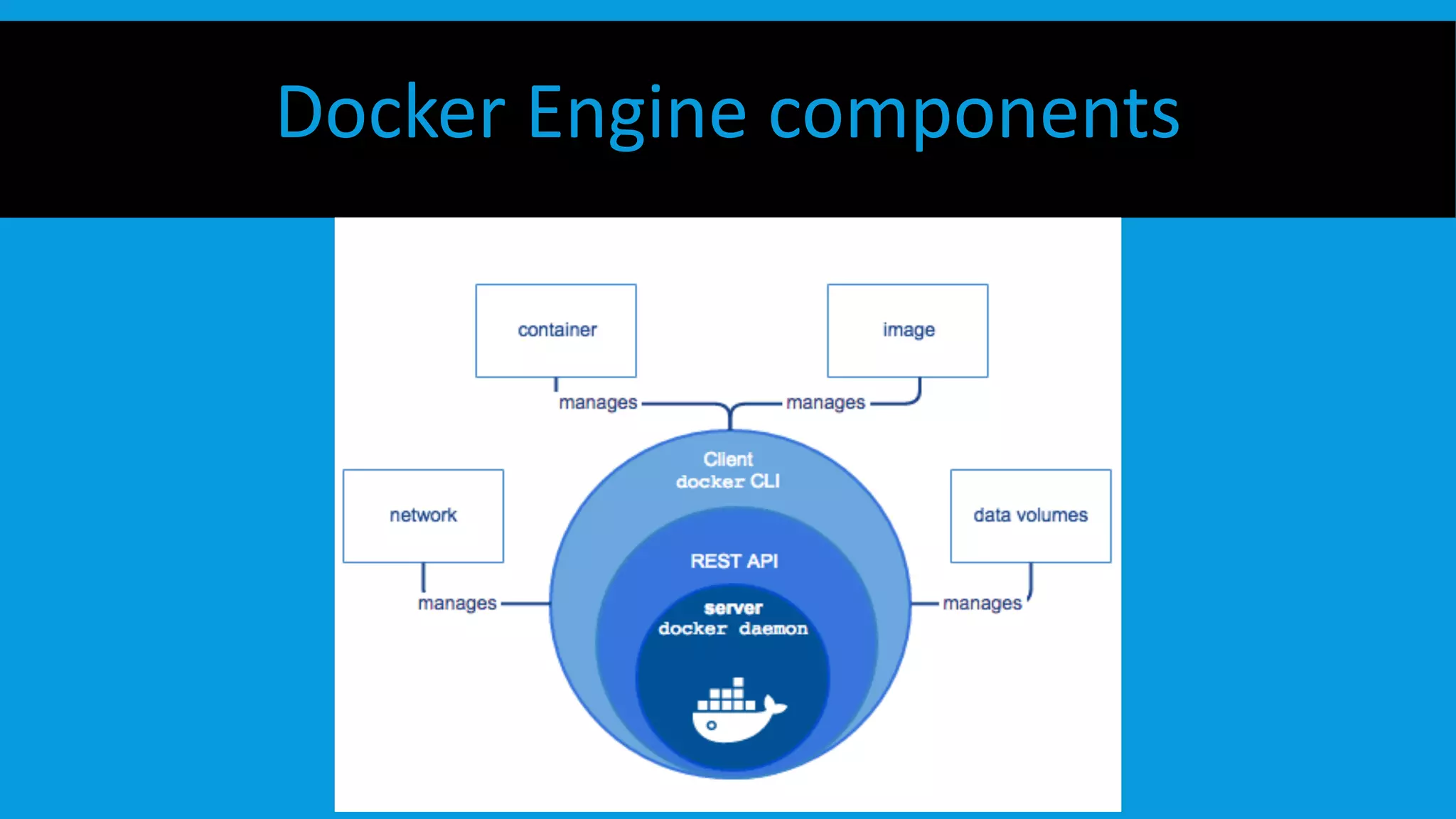
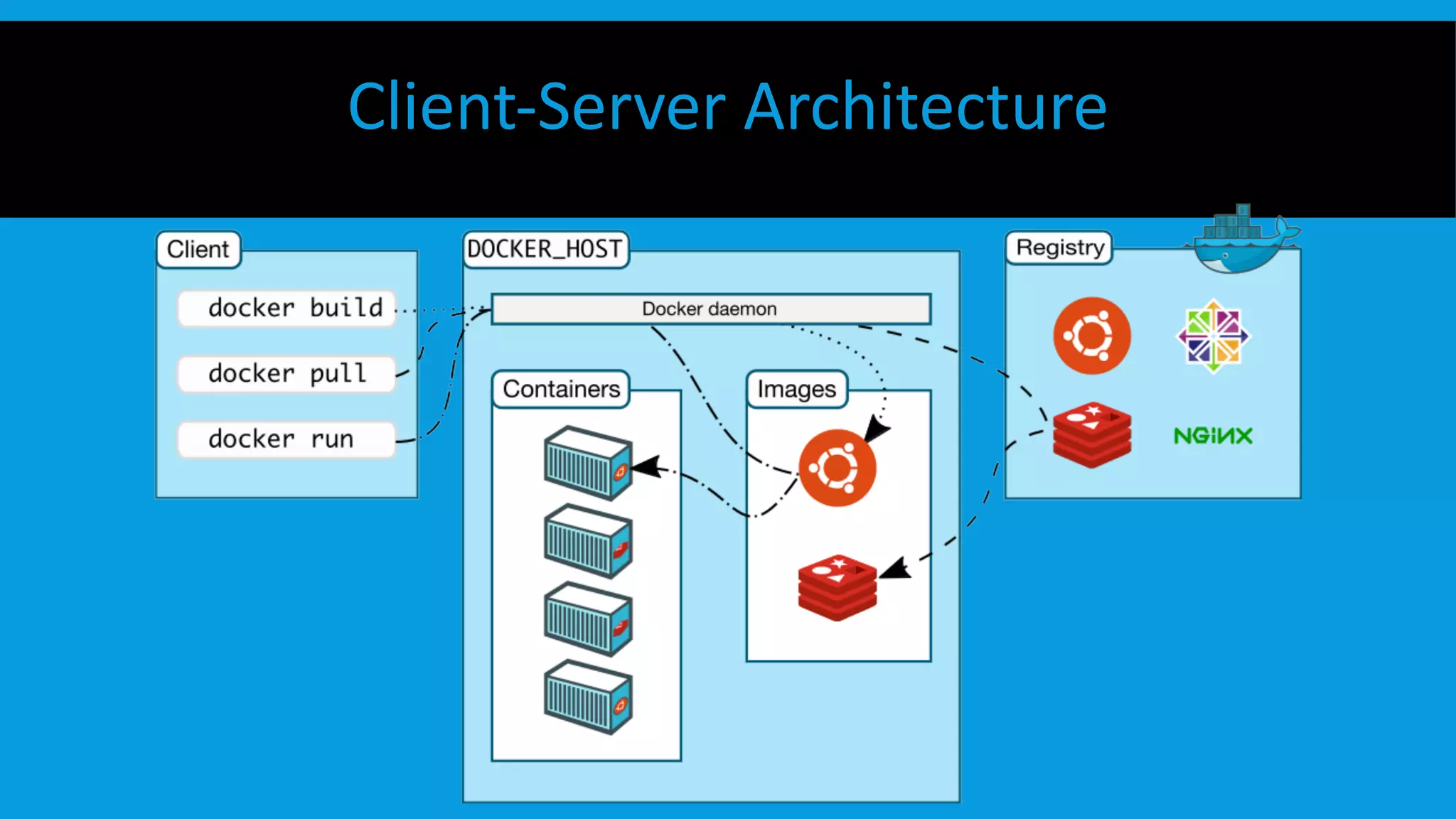
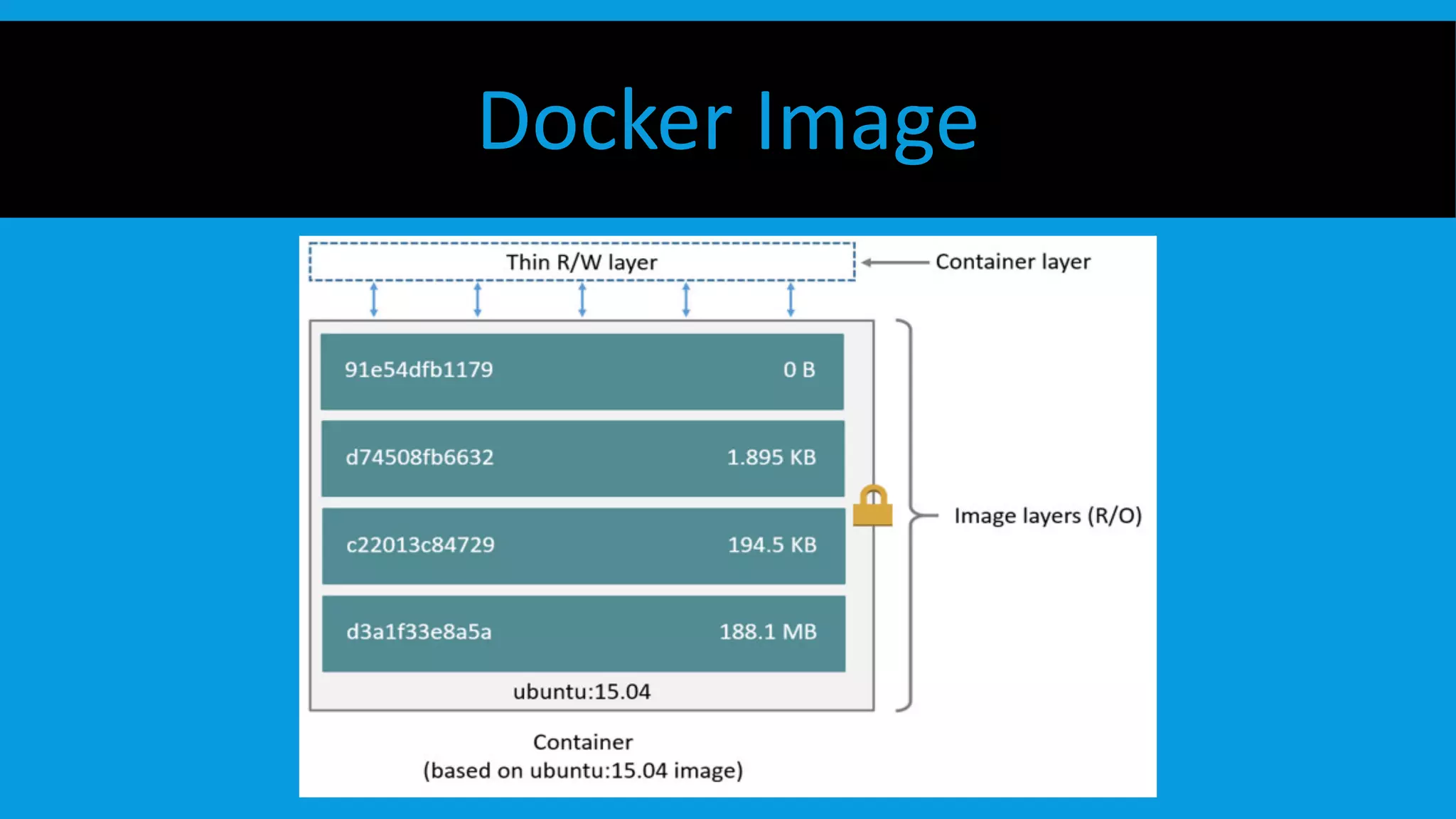
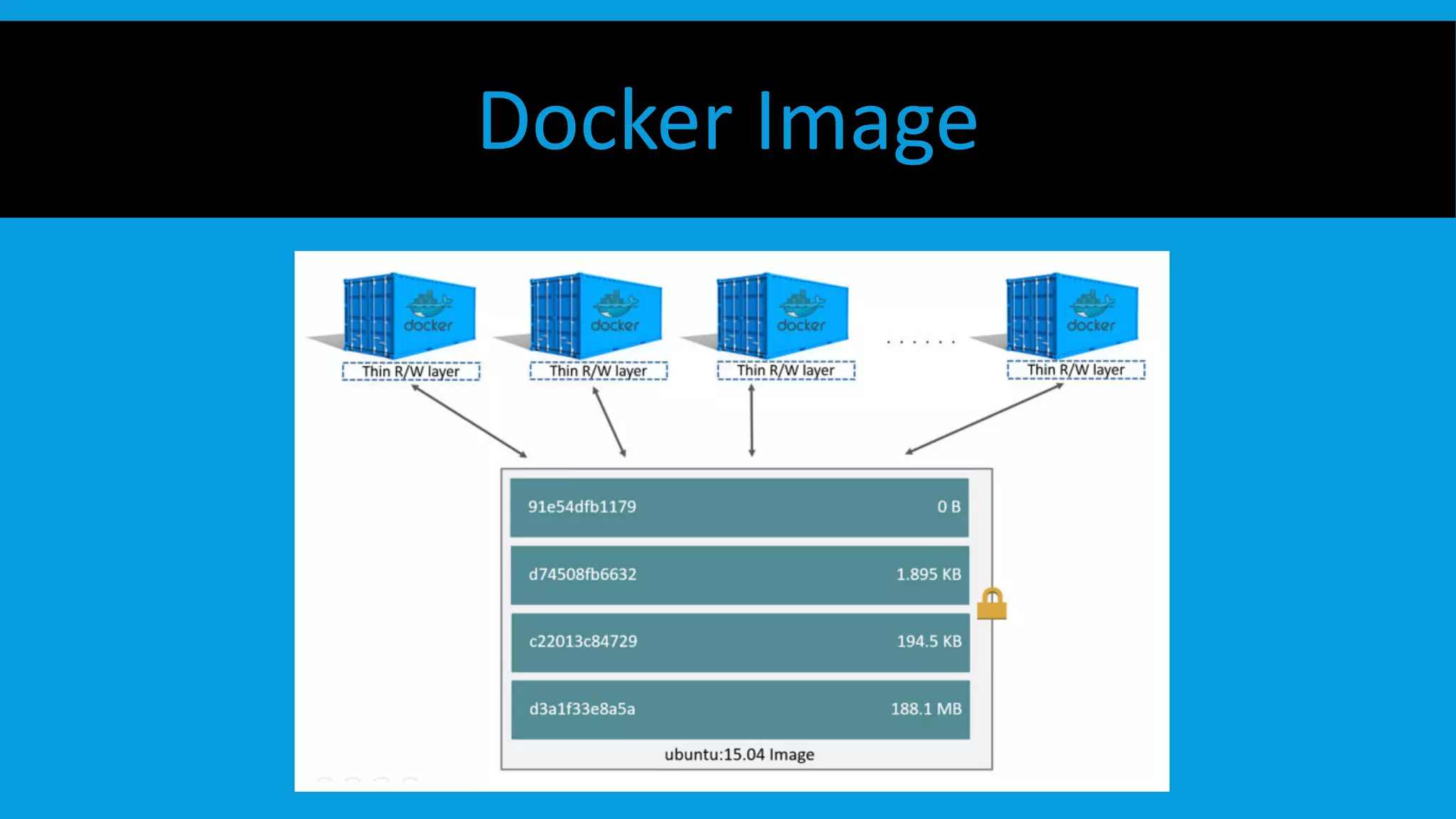
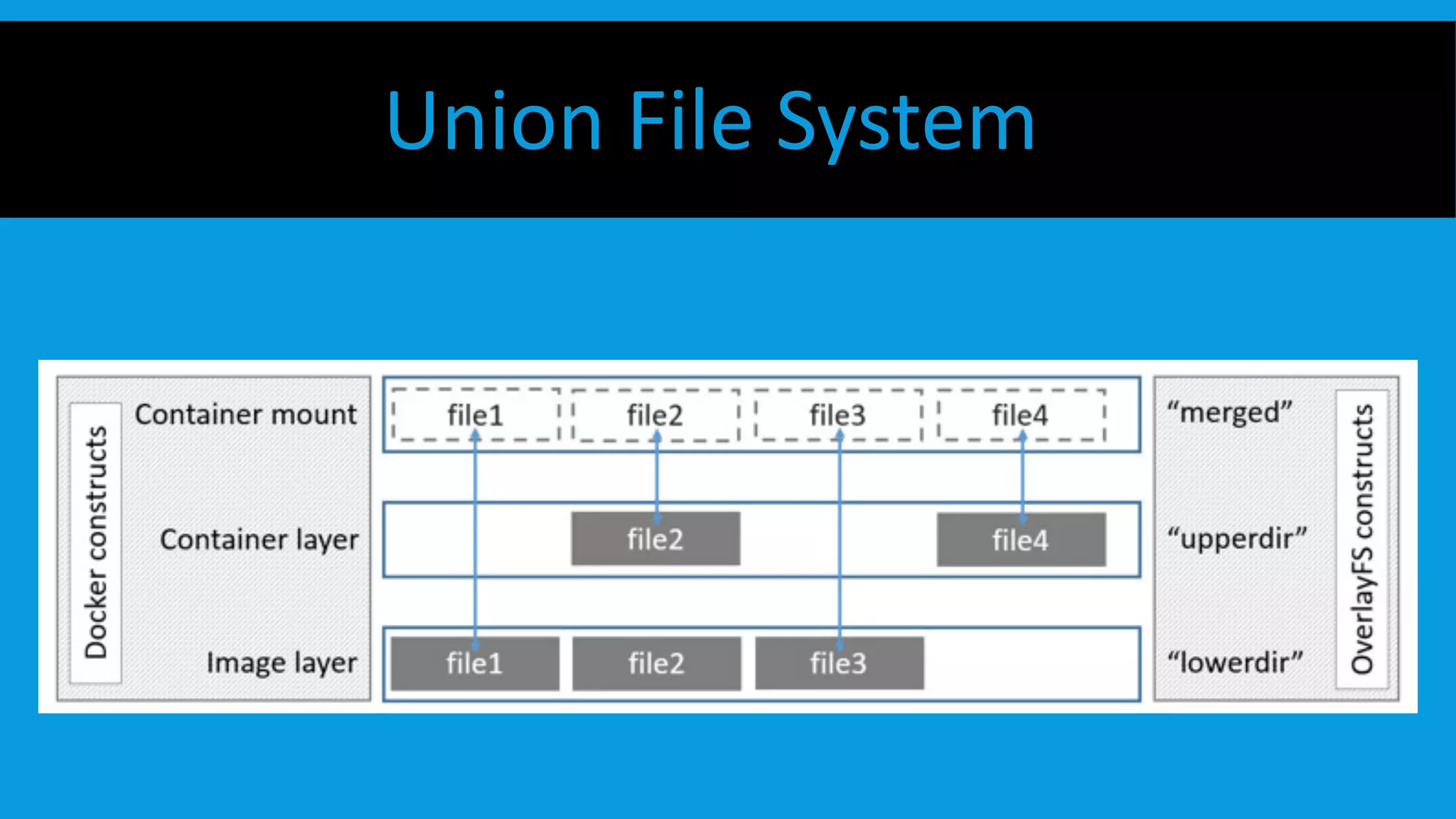
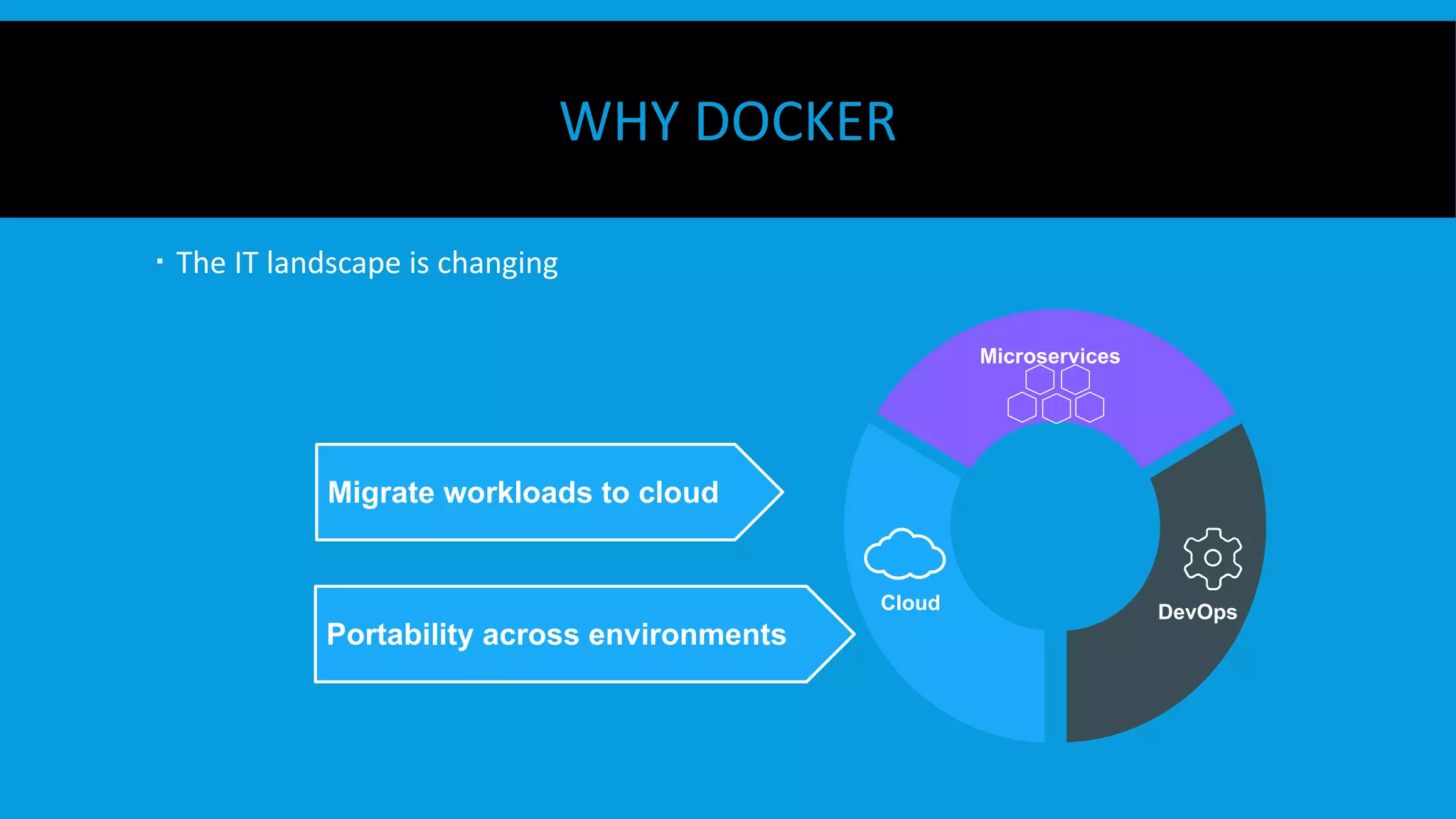
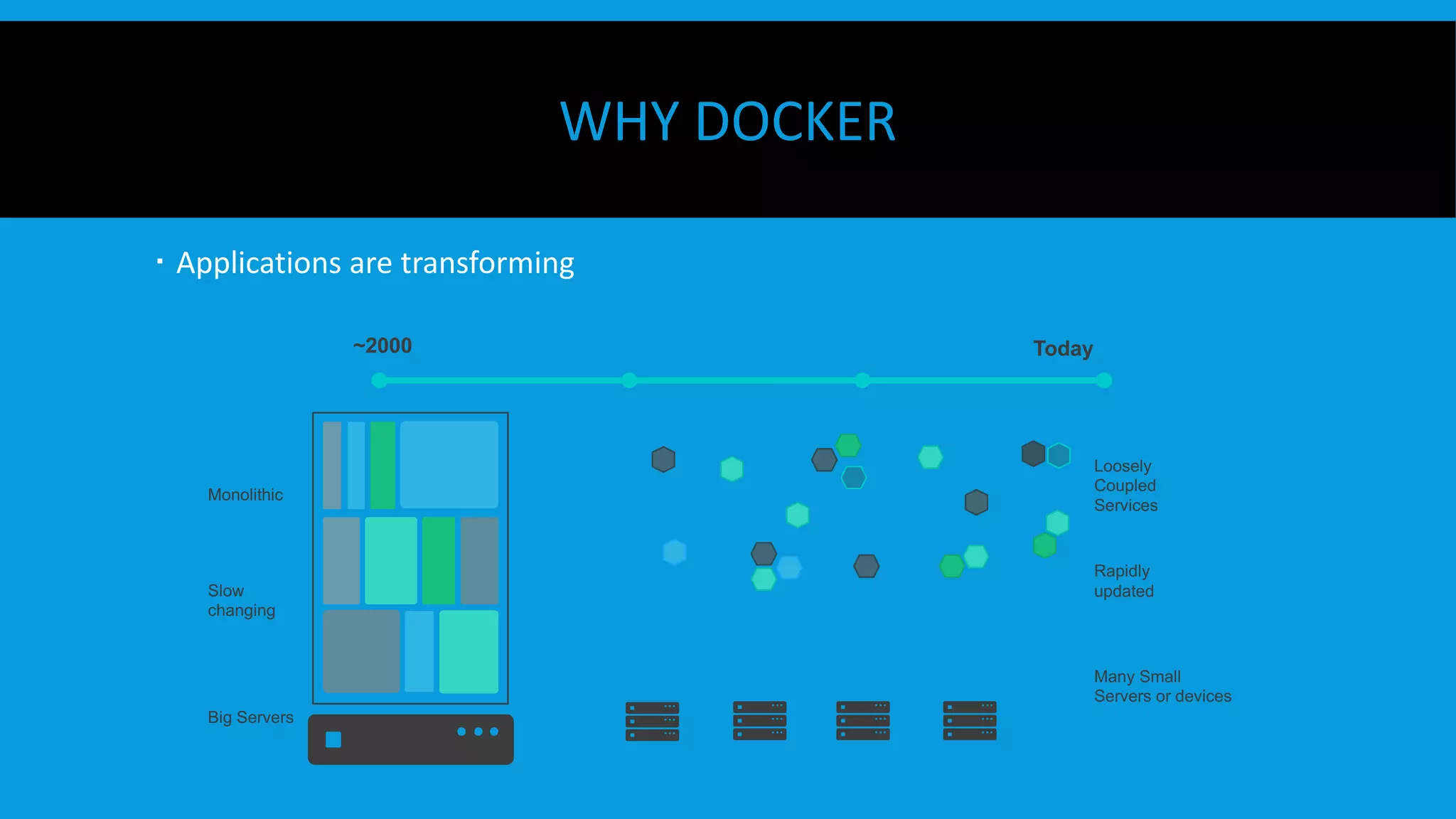
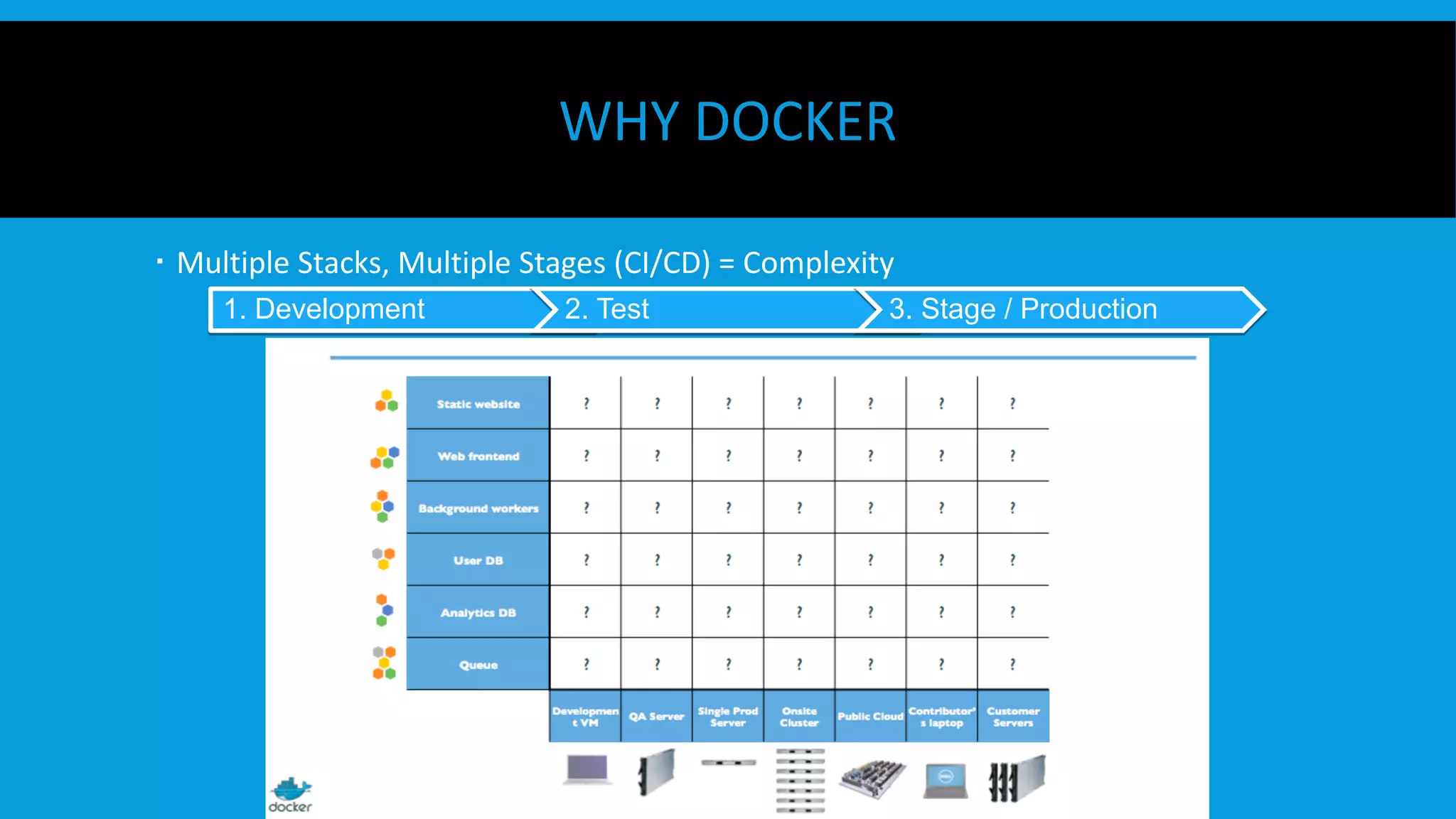
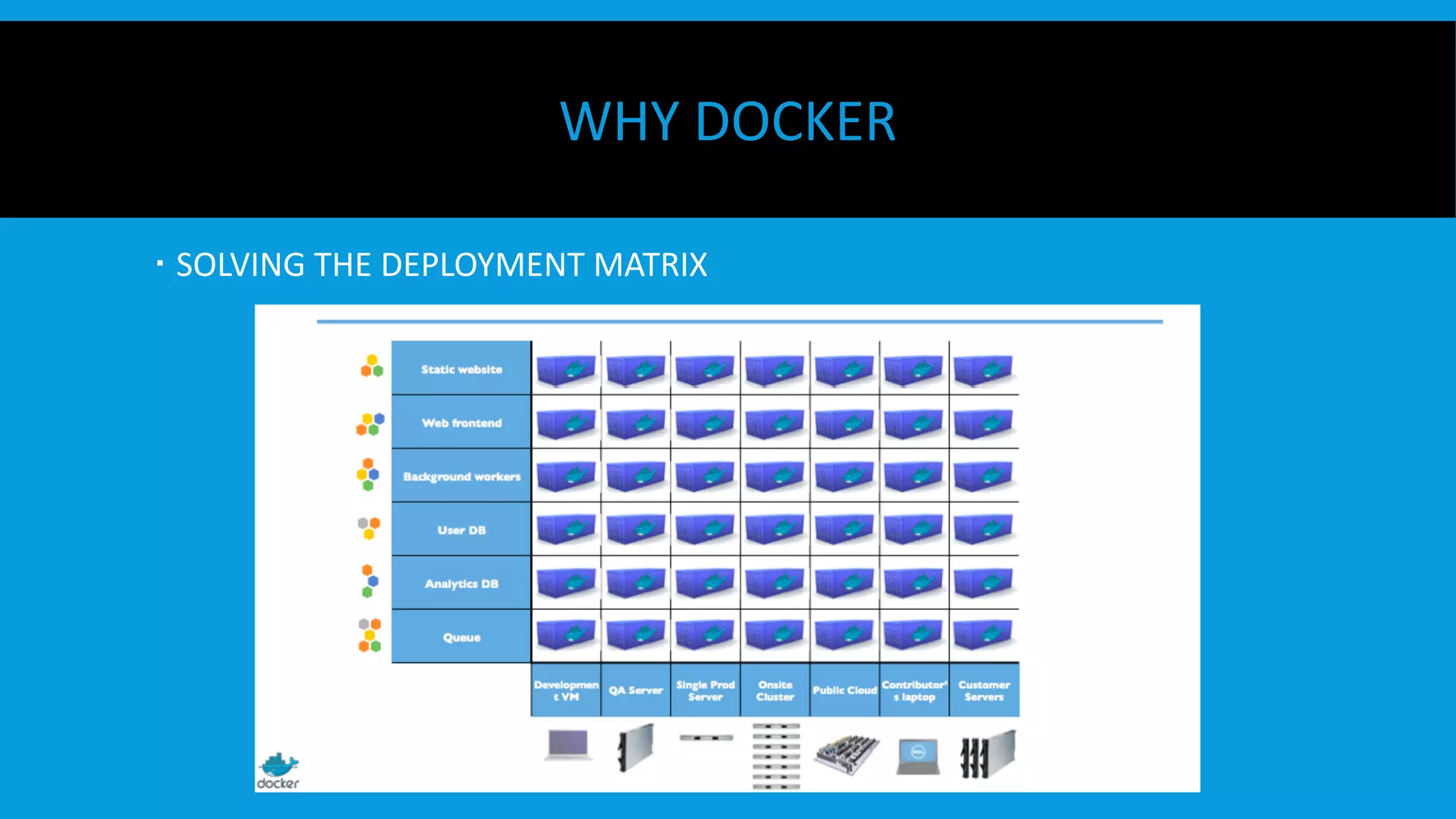
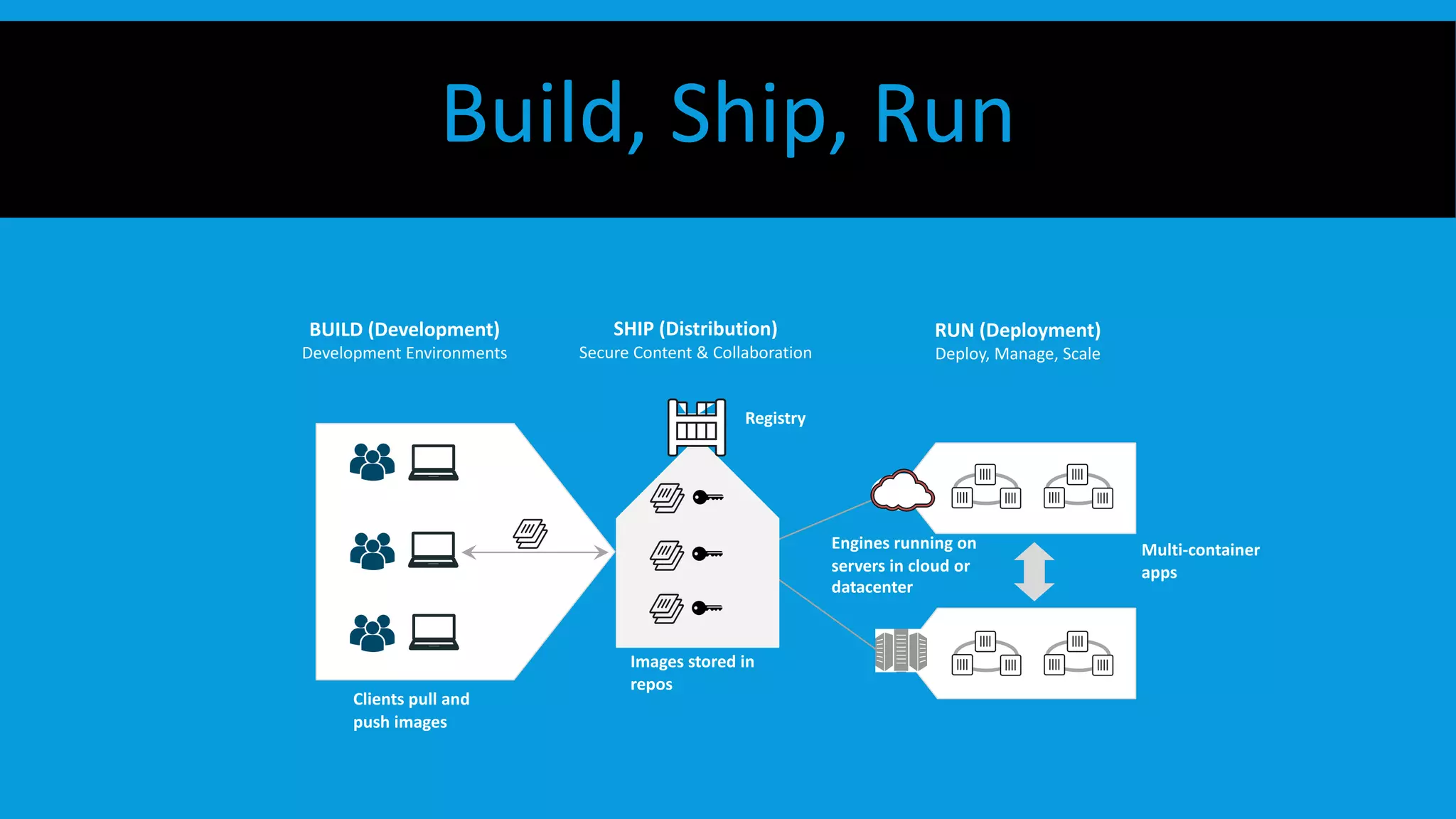
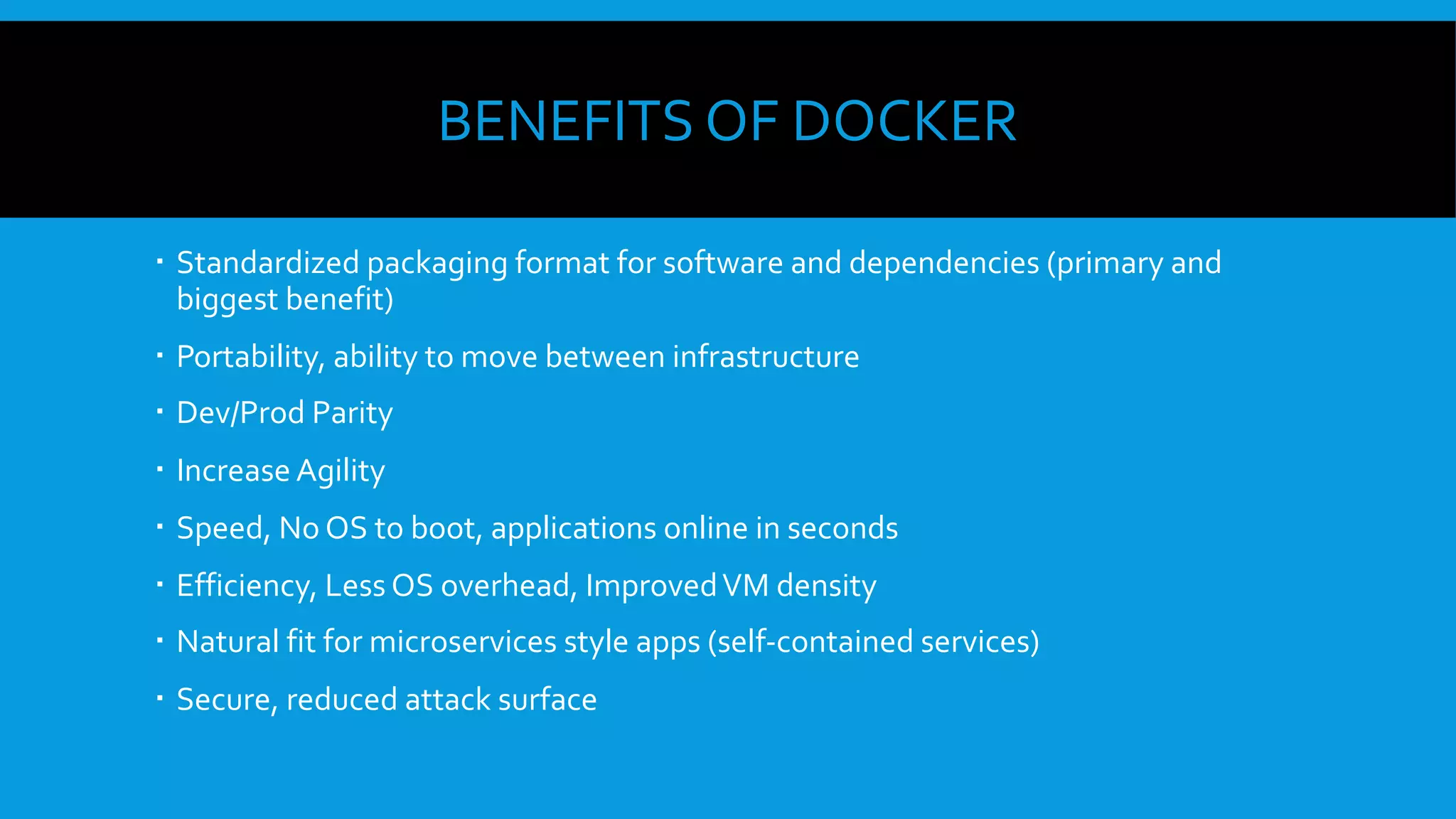
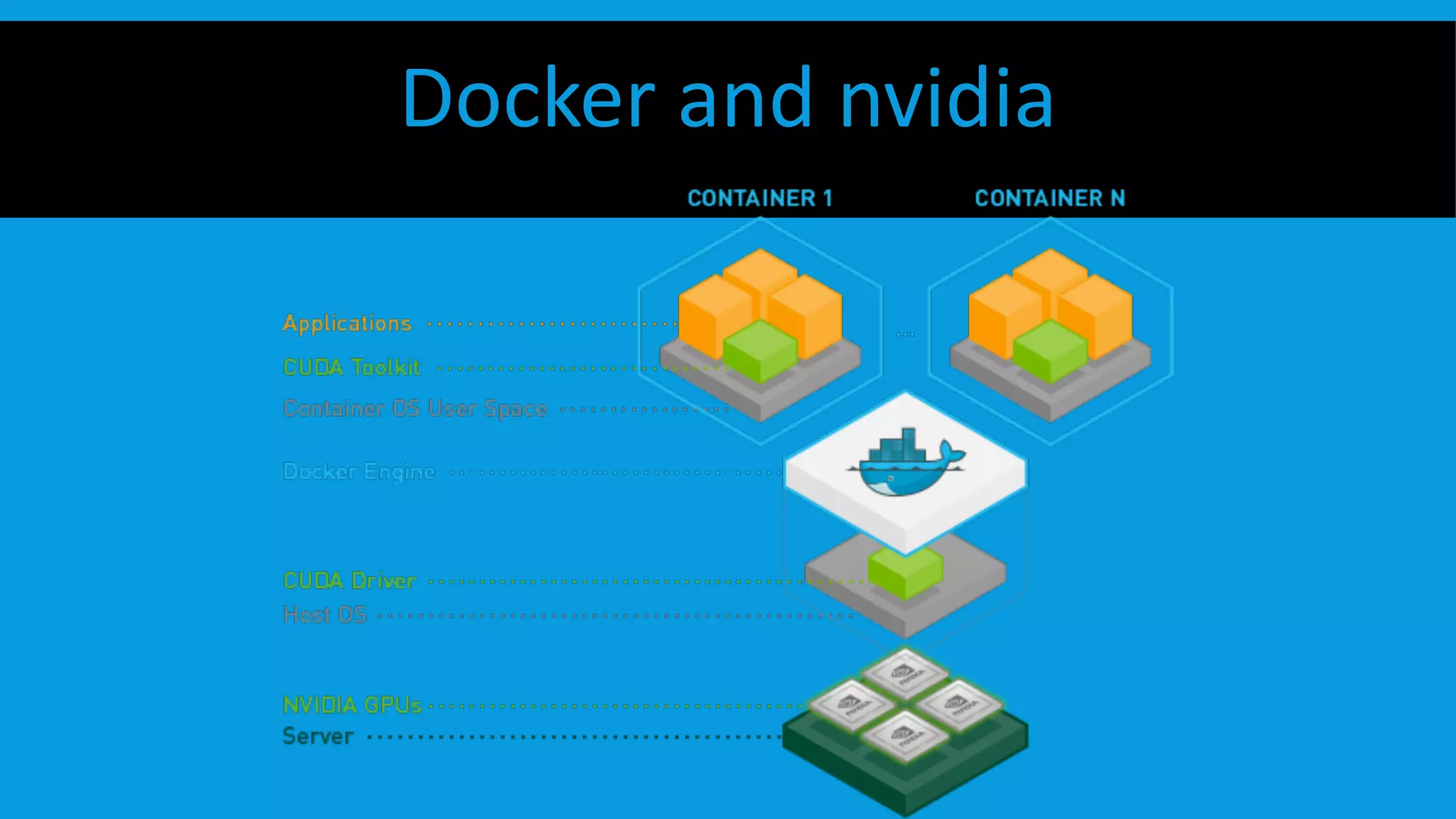
This document discusses containers and Docker. It provides an overview of containers compared to virtual machines and how they leverage features of the Linux kernel like namespaces and cgroups. It describes the history and components of Docker, including images, Dockerfile, registry, and engine. Benefits of Docker for development, deployment, and portability are outlined. Docker Compose is introduced for multi-container applications. Finally, using GPUs with Docker and Nvidia is briefly covered.