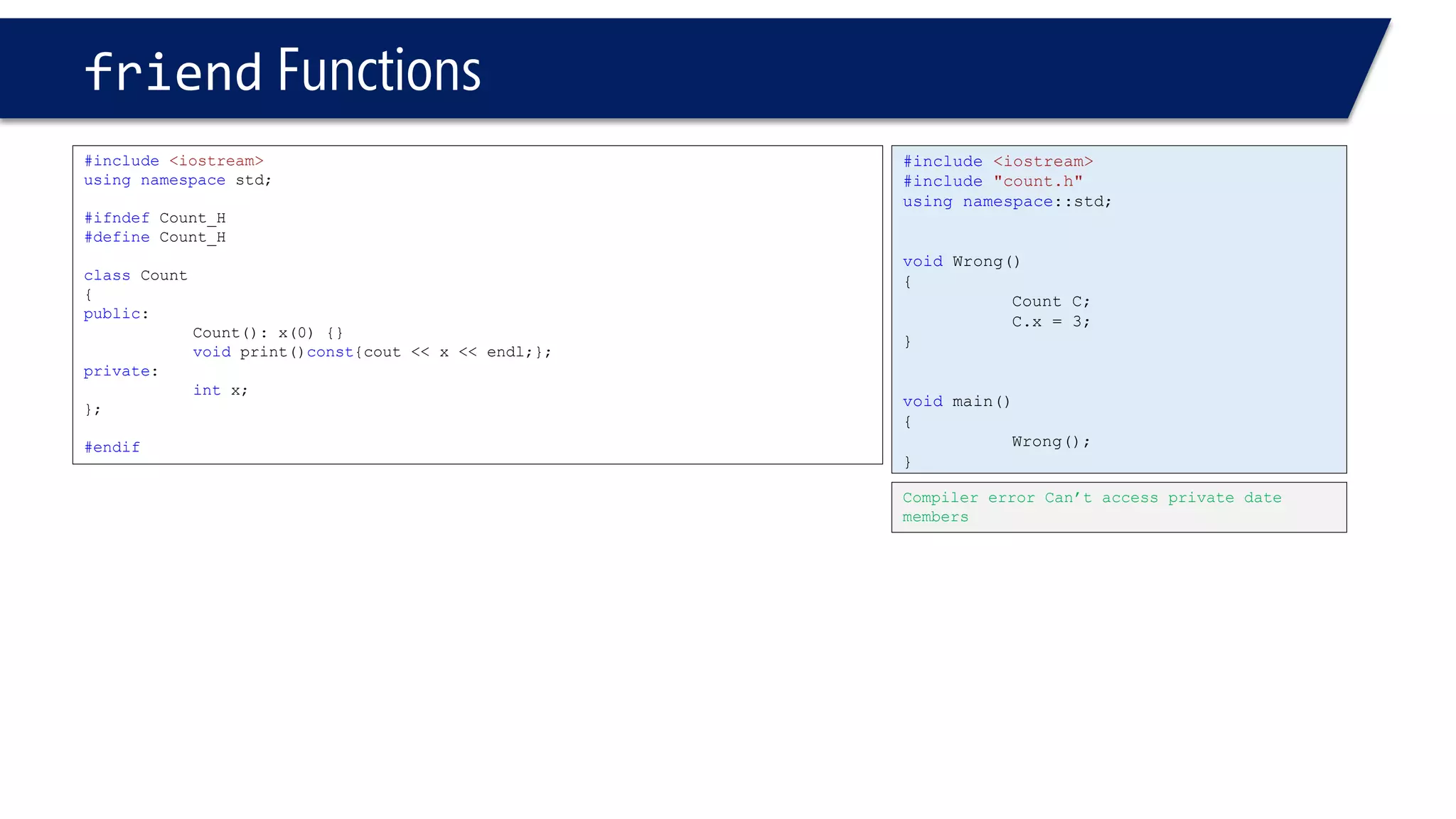
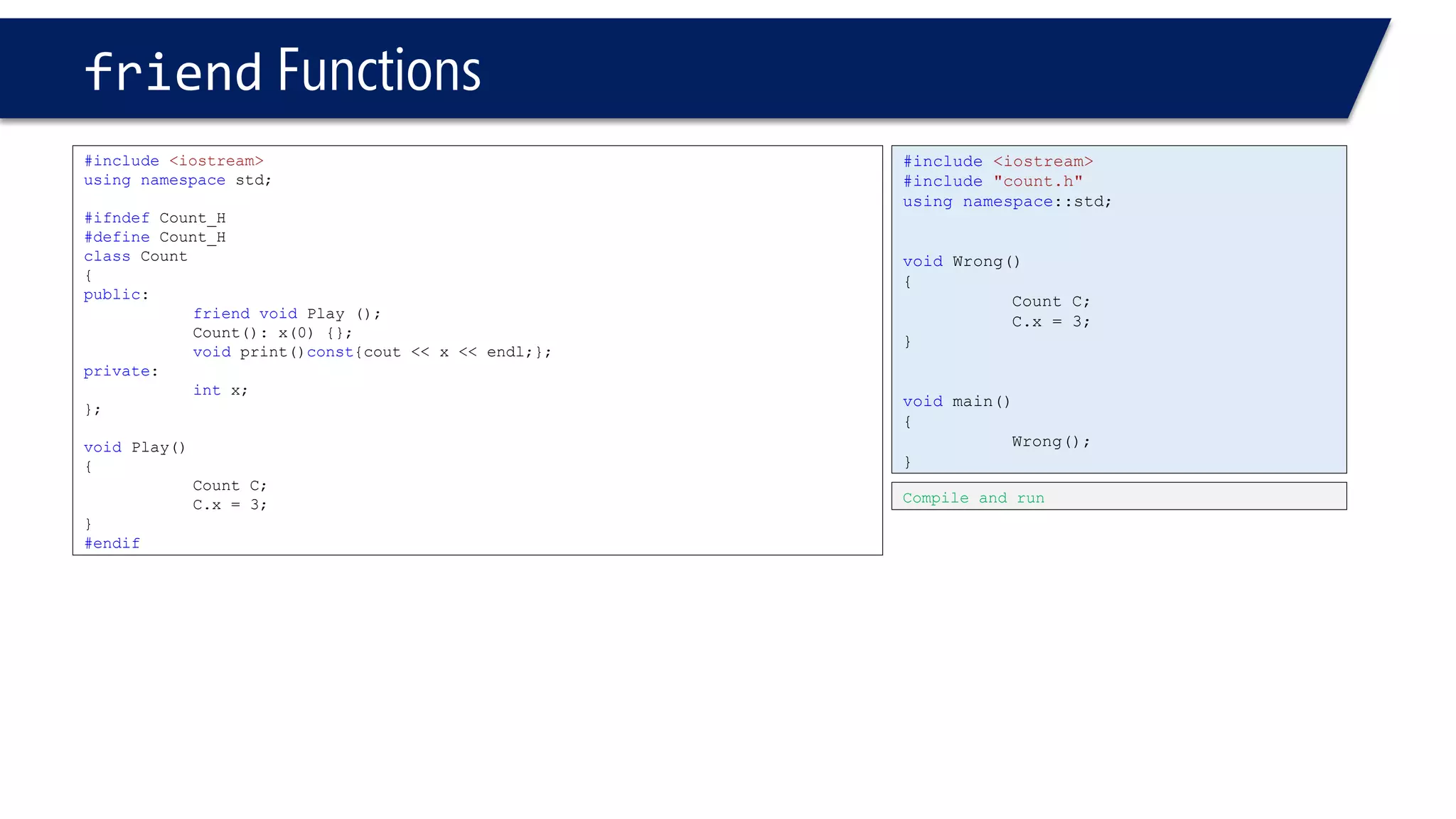
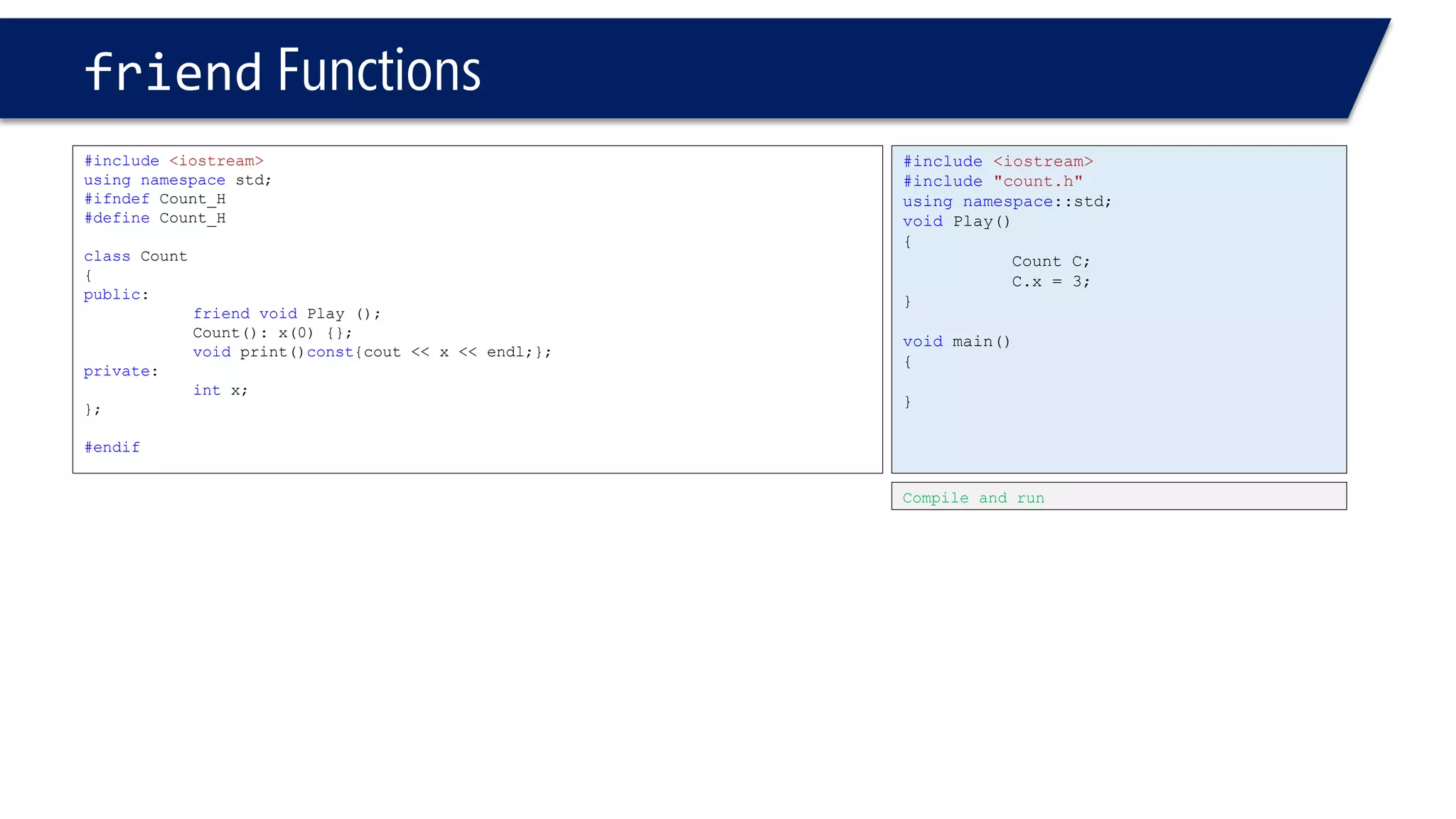
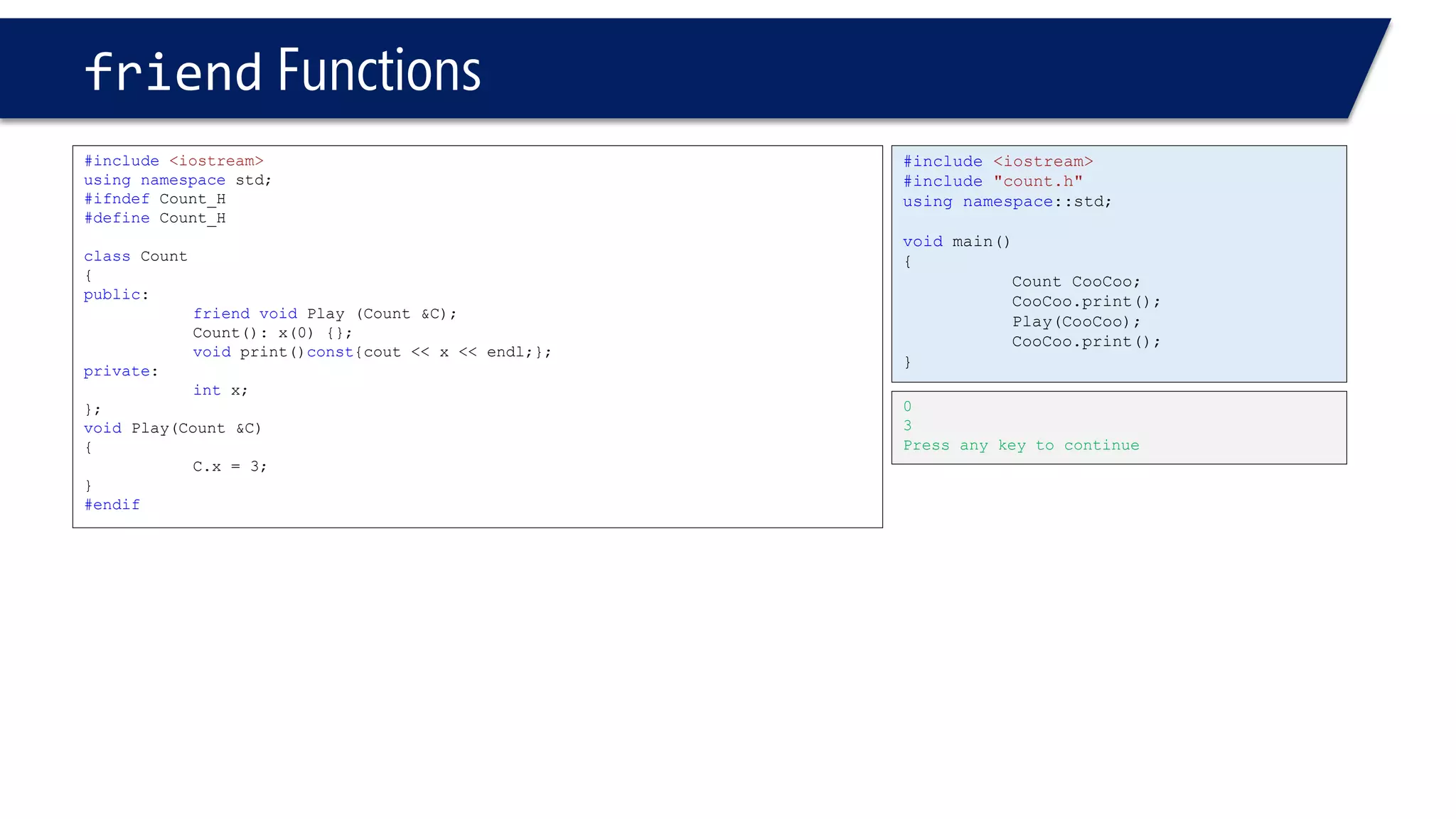
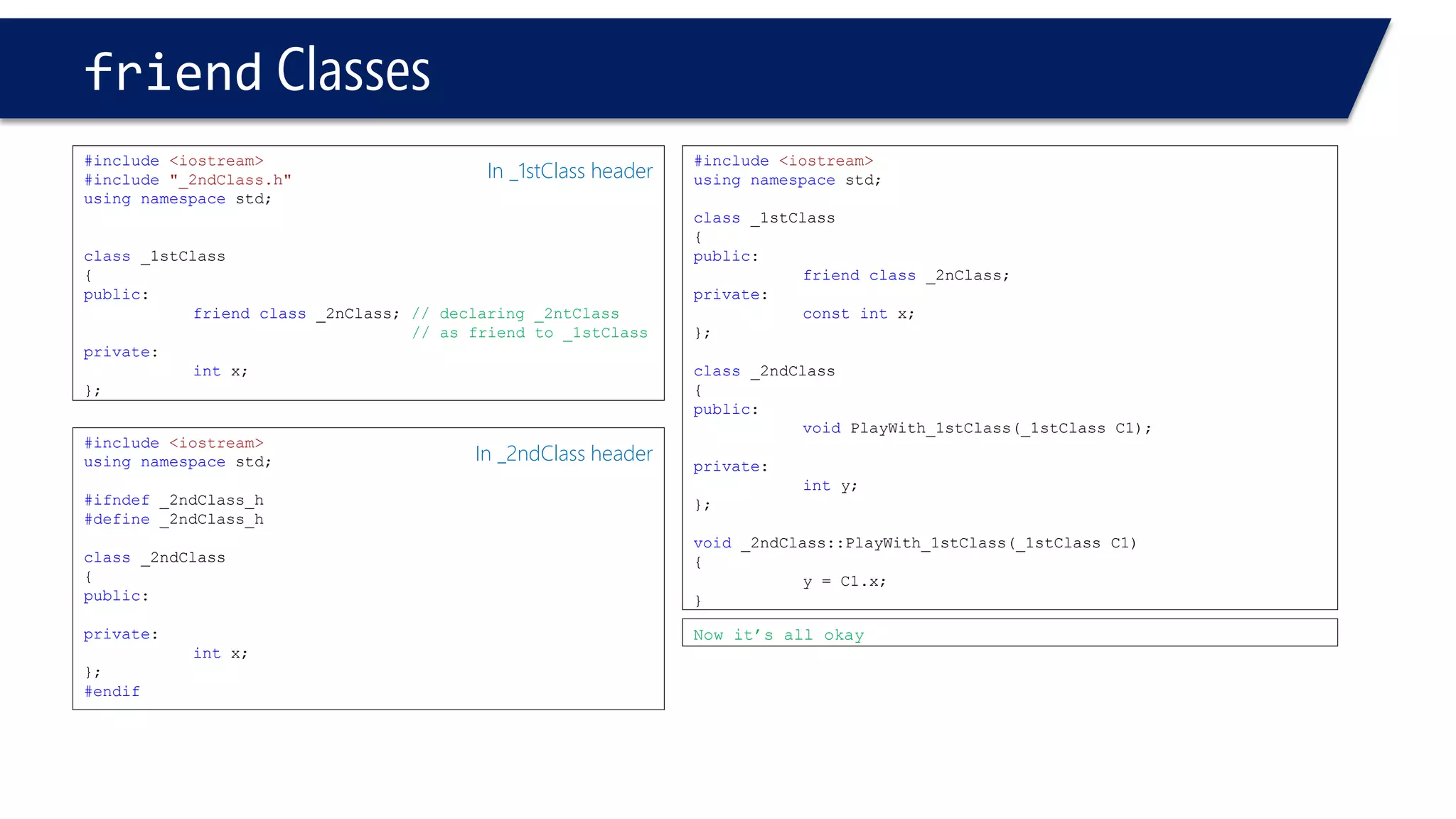
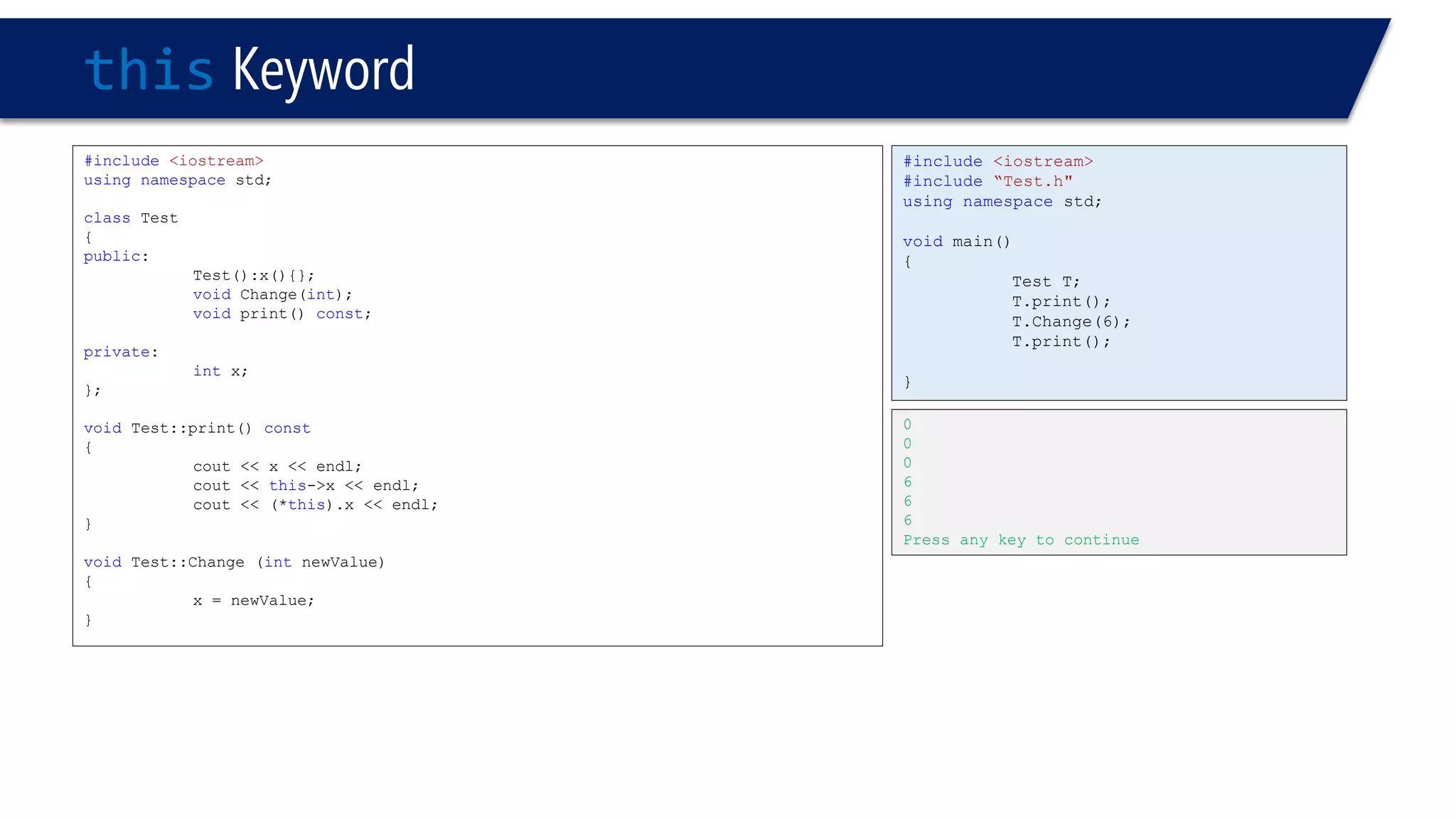
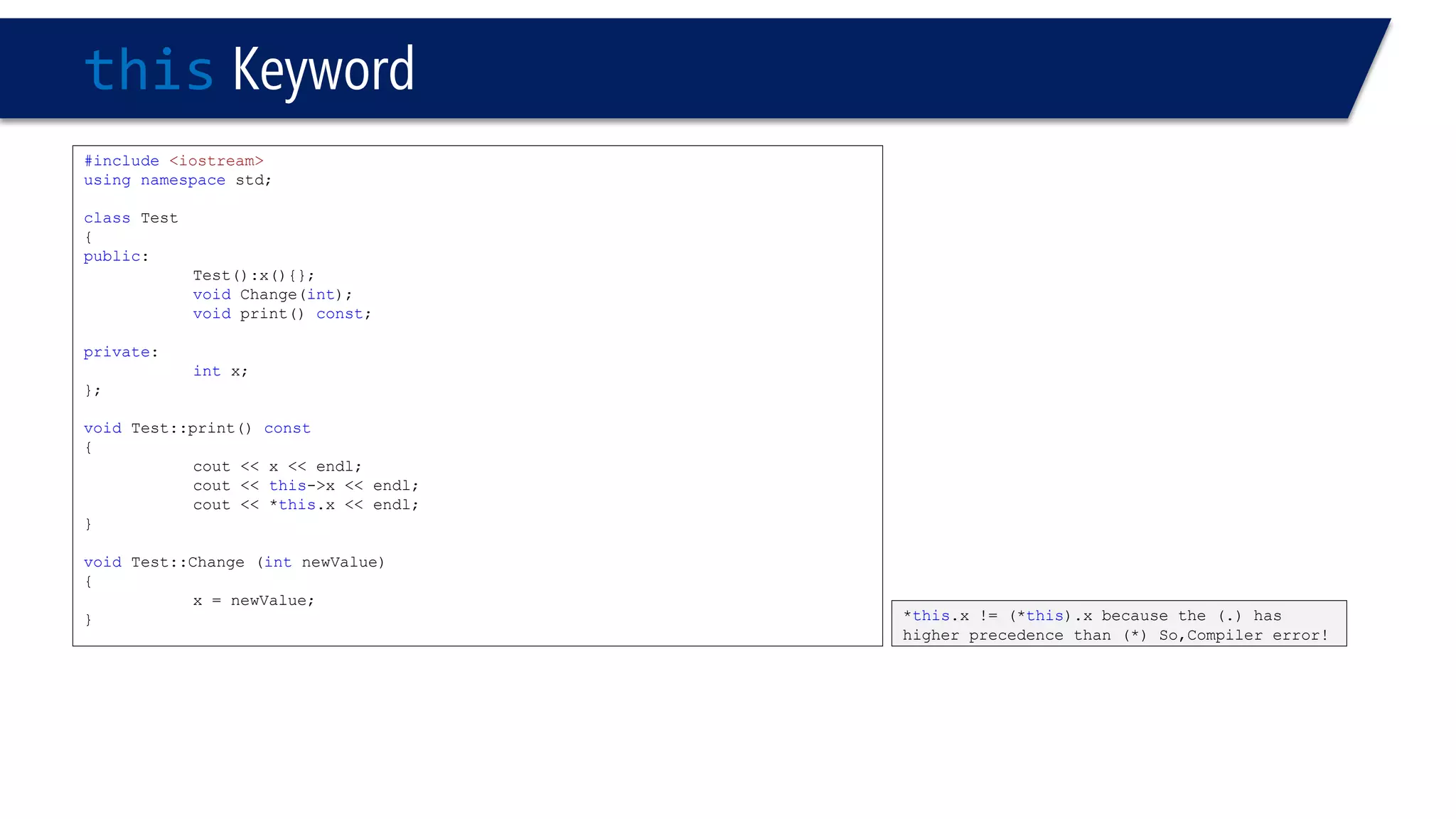
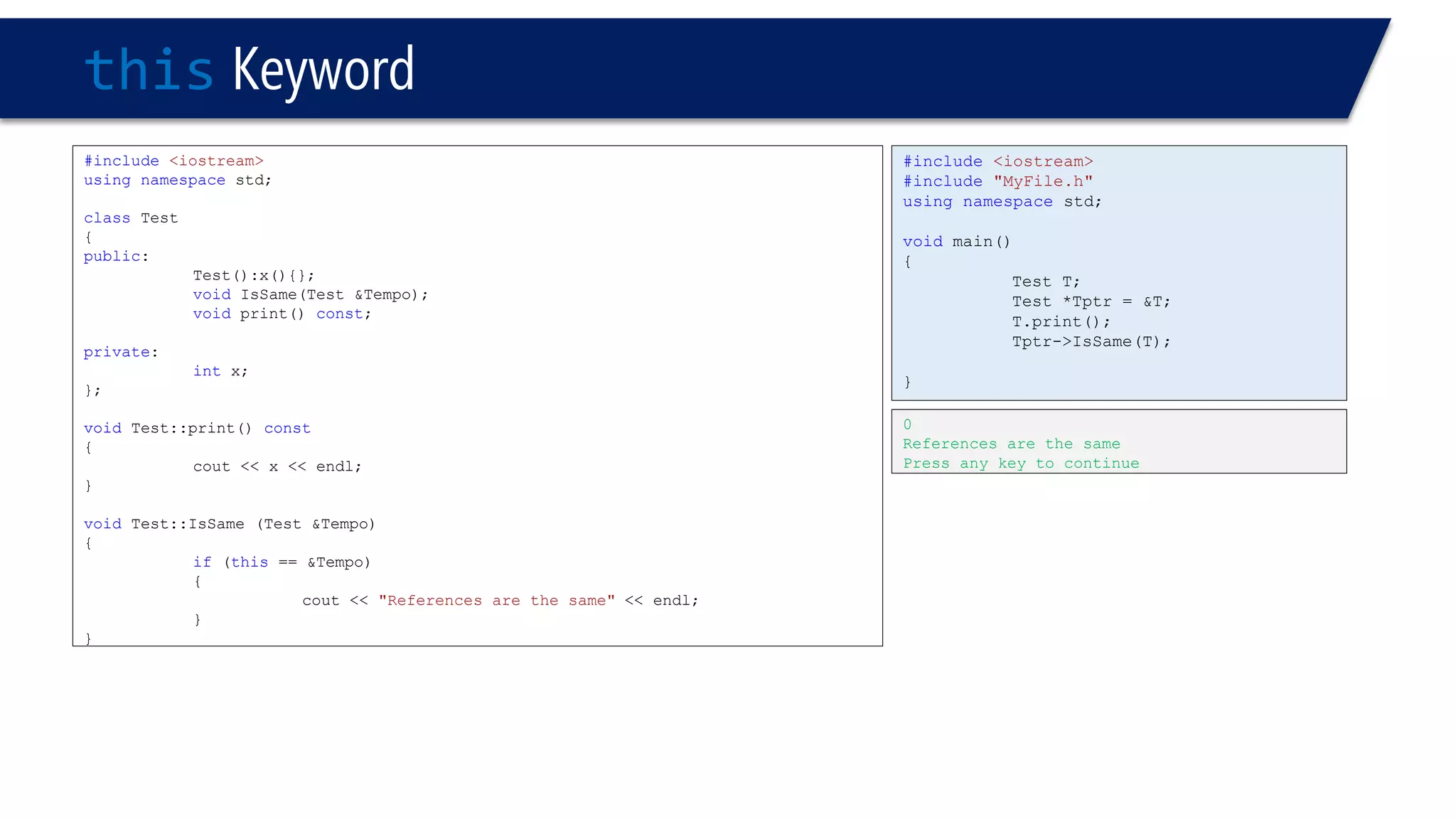
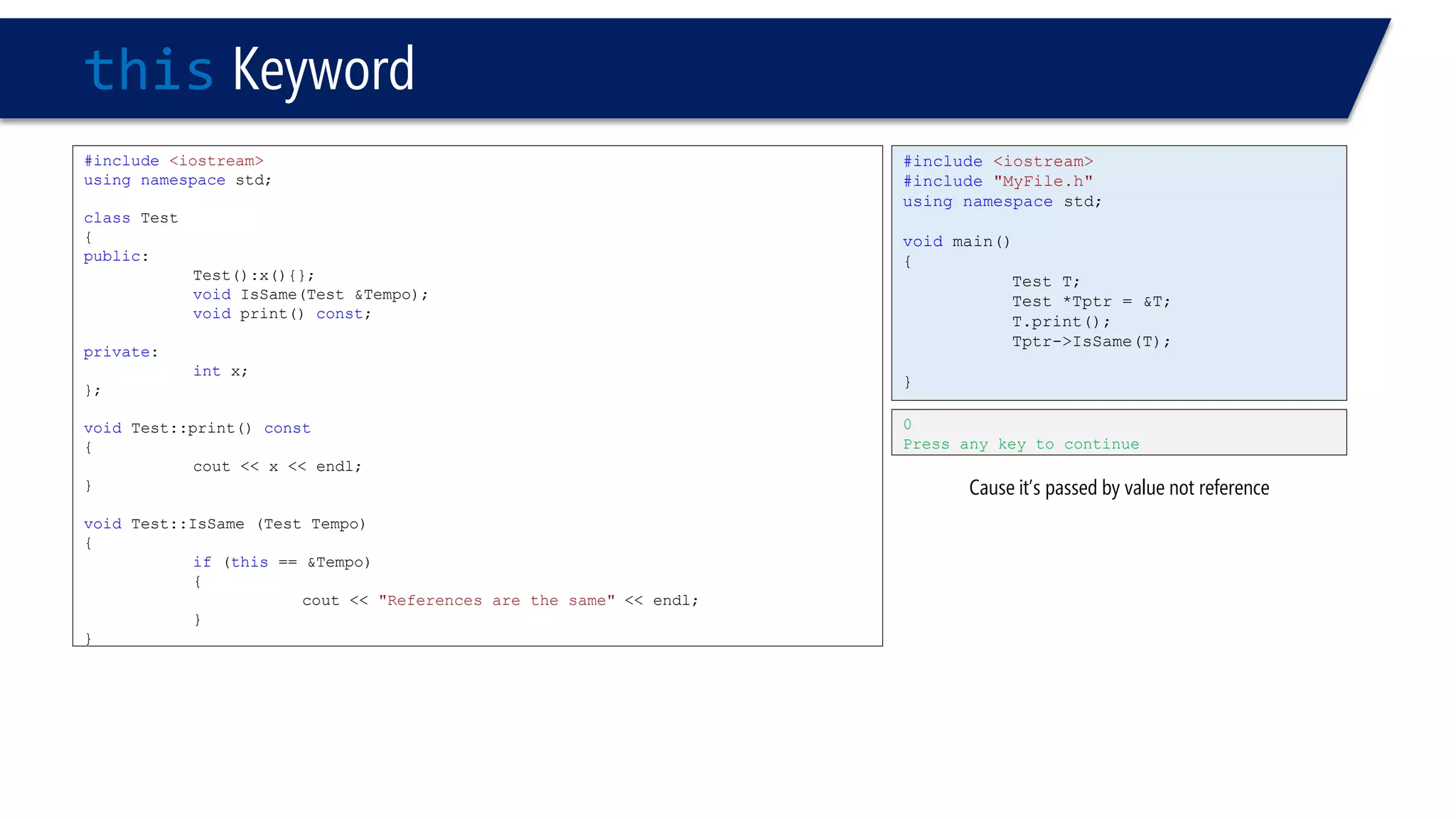
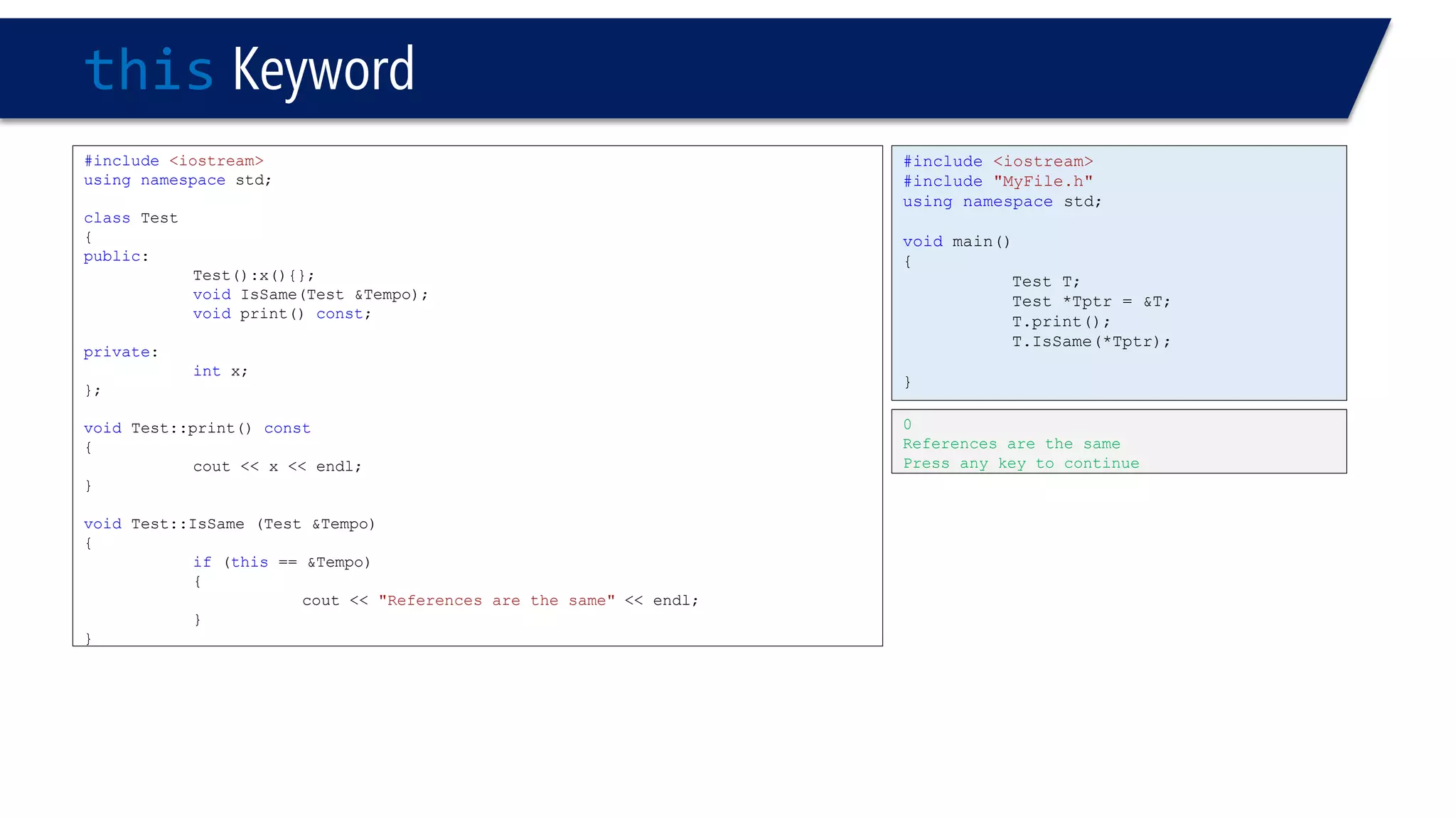
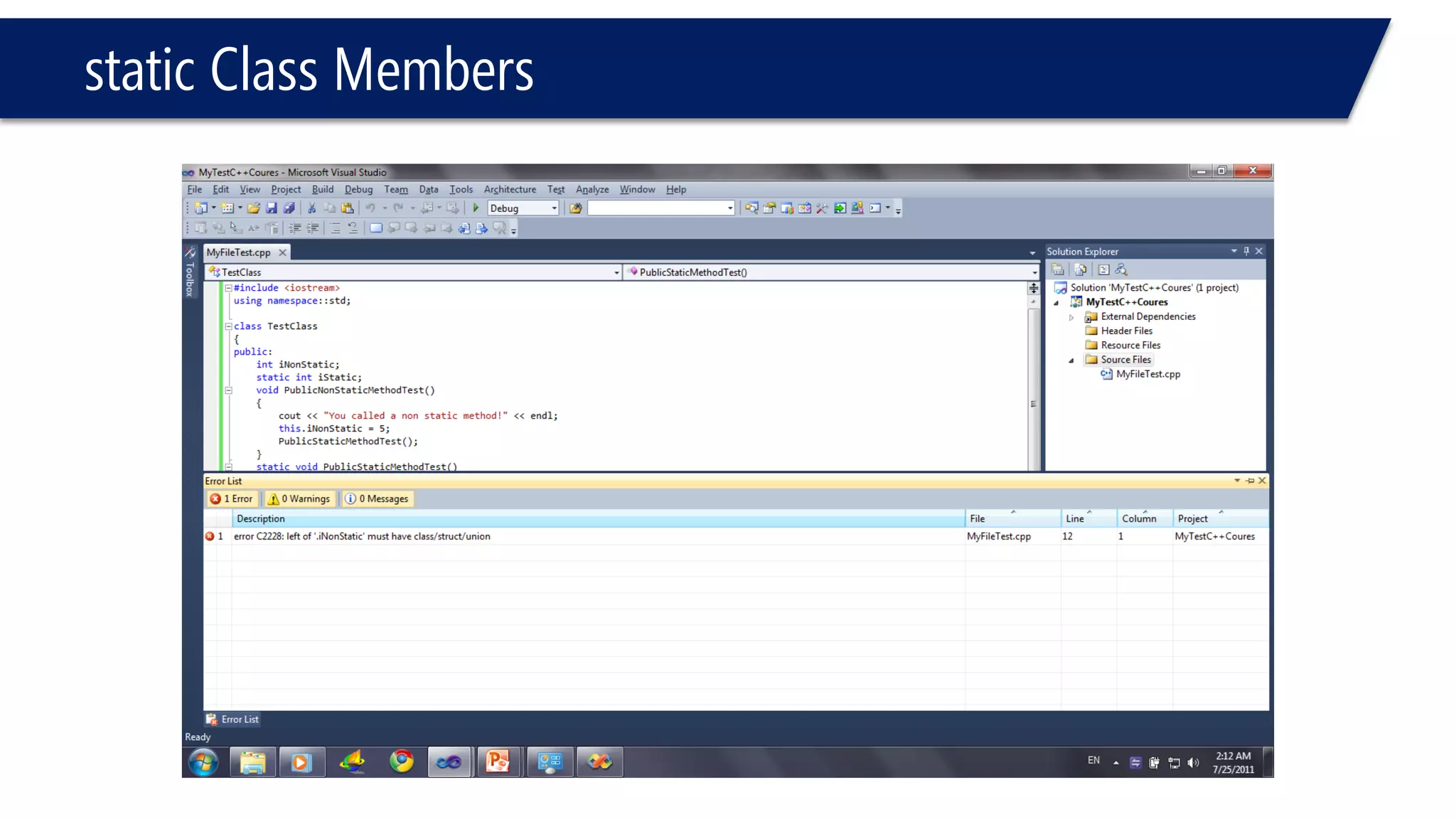
The document discusses the use of the this keyword in C++ classes. It explains that this represents the address of the object and can be used explicitly or implicitly. It demonstrates using this to check if a parameter passed to a member function is the object itself, and to access data members. It shows that this->, (*this). and just x are equivalent ways to access data members from within member functions. It also provides an example of using this to check if two references are referring to the same object.


![Composition
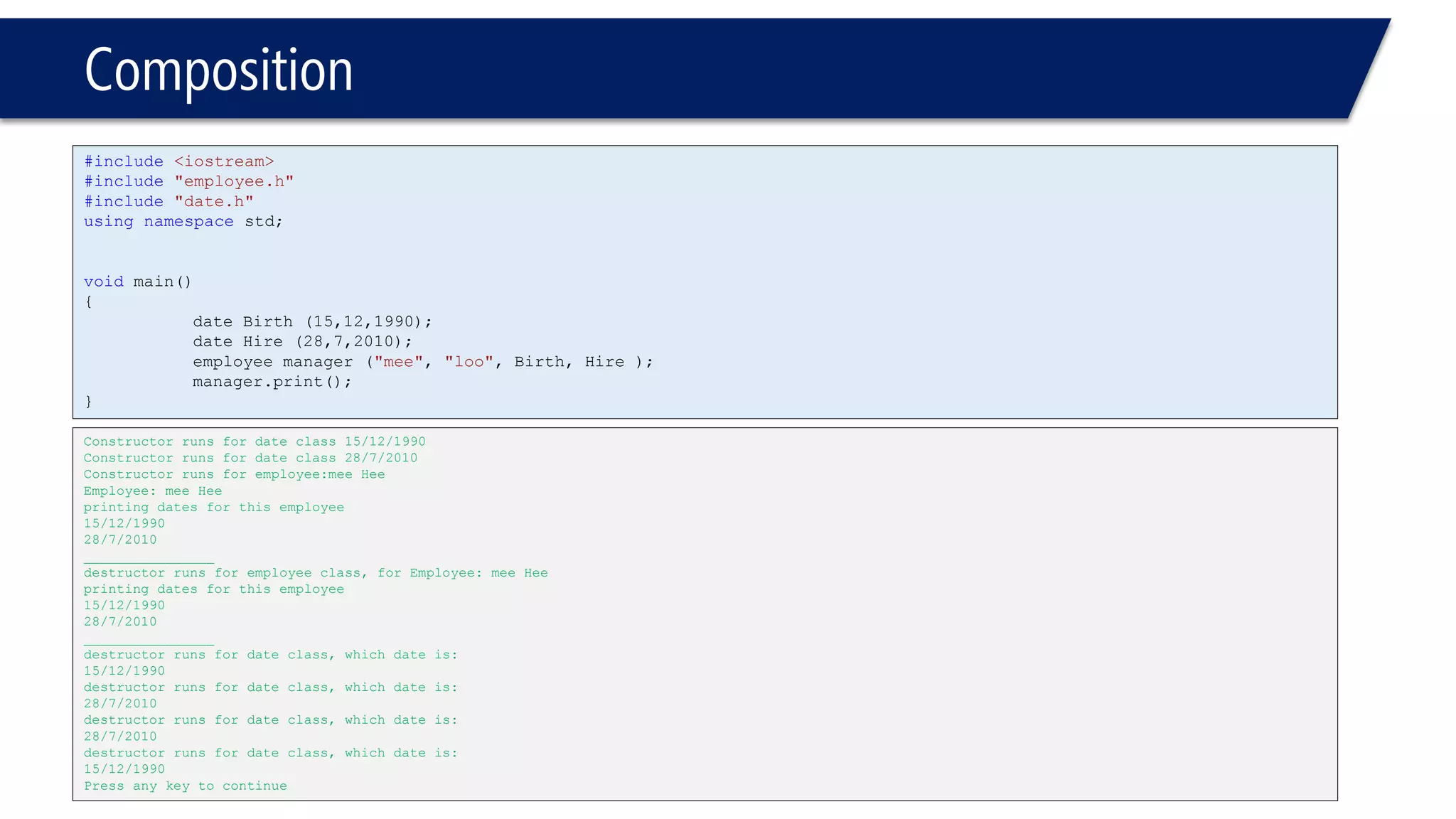
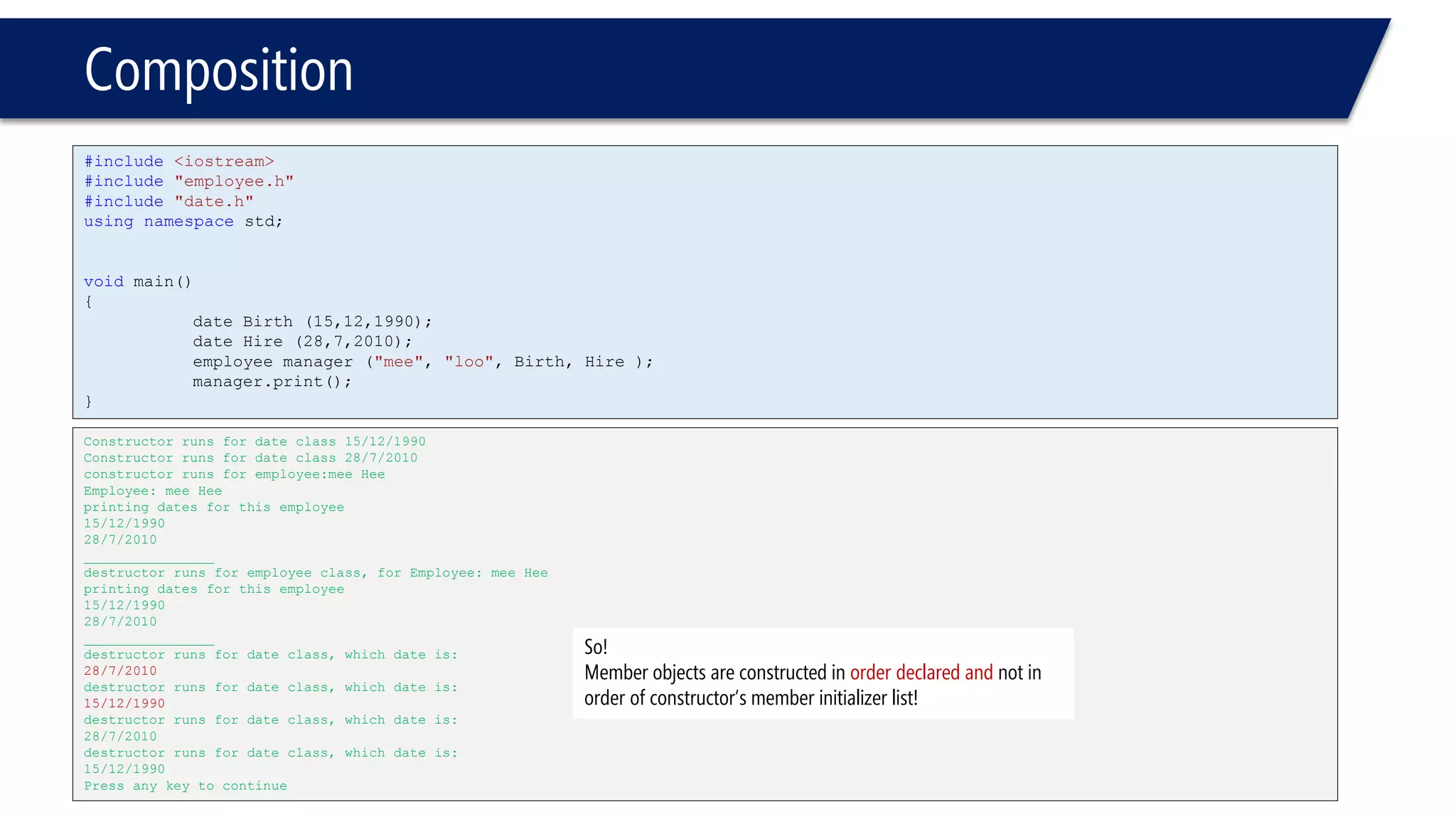
#include<iostream>
#include"date.h"
usingnamespacestd;
#ifndefemployee_h
#defineemployee_h
classemployee
{
public:
employee();
employee(char*First,
char*Last,
constdate& d1,
constdate& d2);
voidprint()const;
~employee();
private:
charFirstName [20];
charLastName [20];
constdate hiredate;
constdate birthdate;
};
employee::employee(char*First, char*Last,constdate& d1, constdate& d2):birthdate(d1), hiredate(d2)
{
intLength = strlen(First);
strncpy(FirstName,First,20);
FirstName[Length]='0';
strncpy(LastName,Last,20);
LastName[Length]='0';
cout<<“Constructor runs for employee:"<<FirstName<<' '<< LastName<<endl;
// ' ' space char;)
}
voidemployee::print() const
{
cout << "Employee: "<< FirstName << ' '<< LastName << endl;
cout << "printing dates for this employee"<< endl;
birthdate.print();
hiredate.print();
cout << "________________"<< endl;
}
employee::~employee()
{
cout << "destructor runs for employee class, for ";
print();
}
#endif](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-5-2048.jpg)
![Composition
classemployee
{
public:
employee();
employee(char*First,
char*Last,
constdate& d1,
constdate& d2);
voidprint()const;
~employee();
private:
charFirstName [20];
charLastName [20];
constdate hiredate;
constdate birthdate;
};
classemployee
{
public:
employee();
employee(char*First,
char*Last,
constdate& d1,
constdate& d2);
voidprint()const;
~employee();
private:
charFirstName [20];
charLastName [20];
const date birthdate;// we change this
const date hiredate;// we change this
};
Change this to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-7-2048.jpg)










![static Class Members
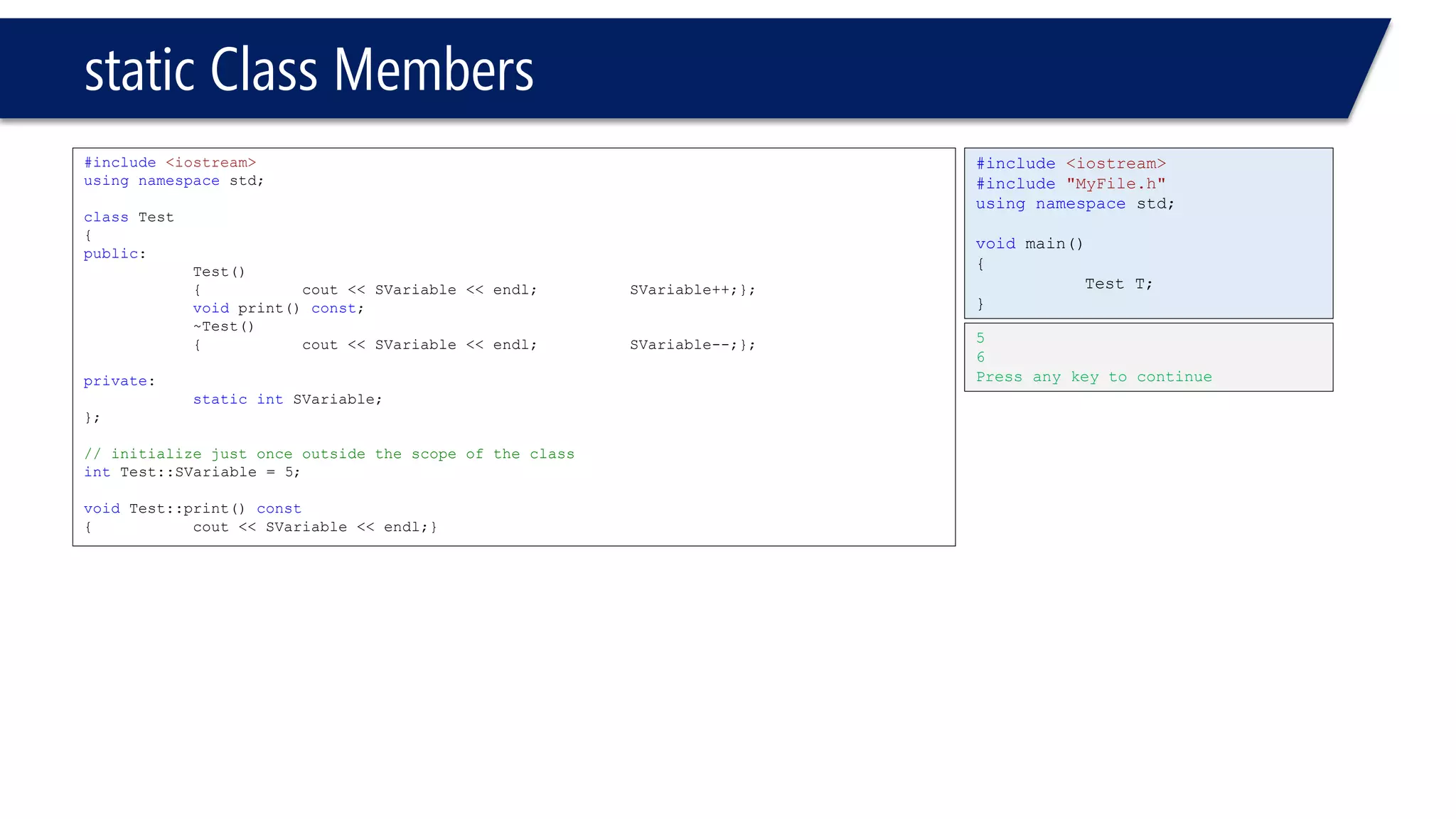
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
classTest
{
public:
Test()
{cout << "const "<< SVariable << endl; SVariable++;};
voidprint() const;
~Test()
{cout << "dest "<< SVariable << endl;SVariable- -;};
staticintSVariable;
private:
};
intTest::SVariable = 5;// initialize just once outside the scope of the class
voidTest::print() const
{cout << SVariable << endl;}
#include<iostream>
#include"MyFile.h"
usingnamespacestd;
voidmain()
{
{
Test T[5];
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
}
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
}
const 5
const 6
const 7
const 8
const 9
10
dest 10
dest 9
dest 8
dest 7
dest 6
5
Press any key to continue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-34-2048.jpg)
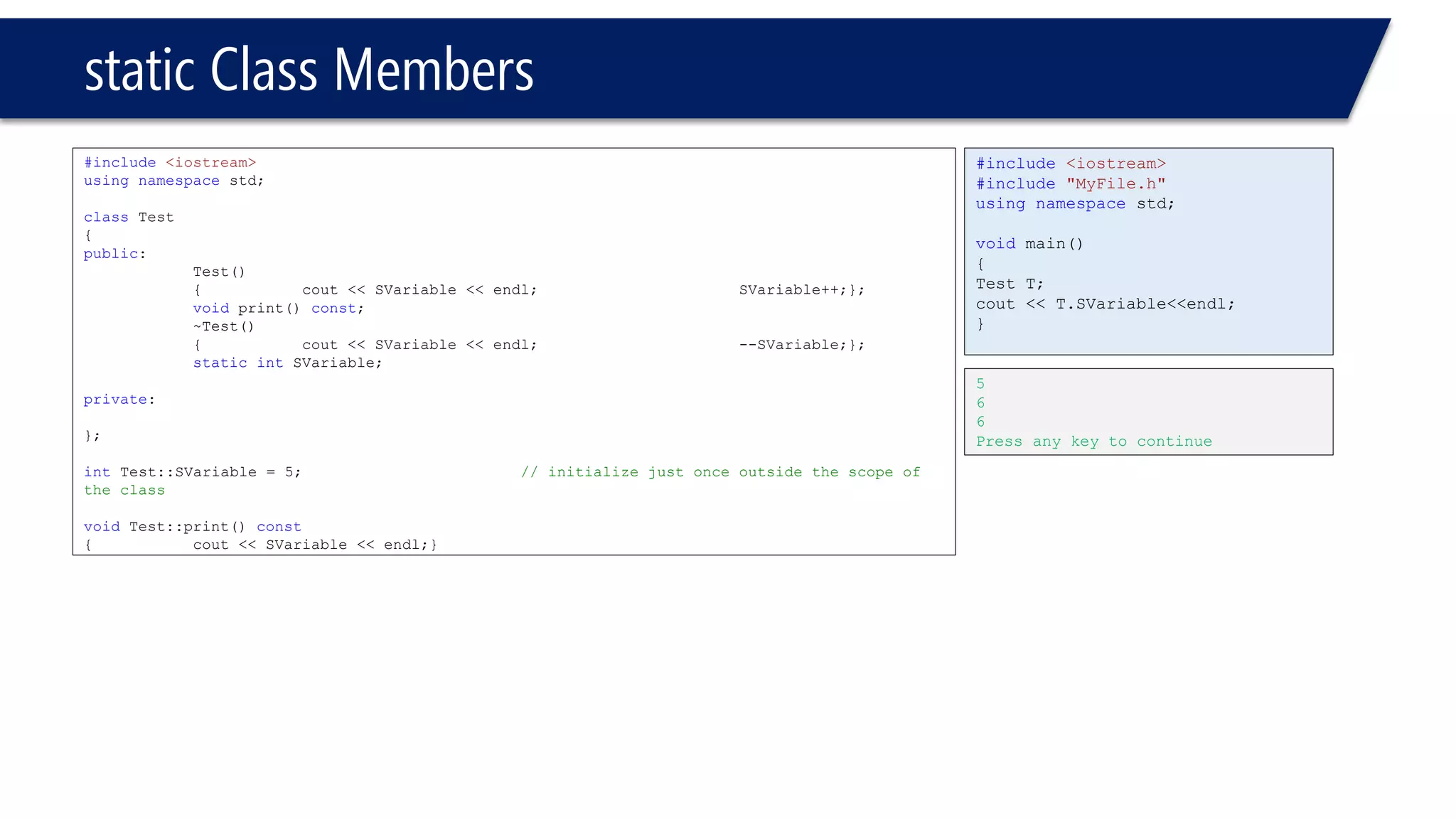
![static Class Members
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
classTest
{
public:
Test()
{cout << "const "<< SVariable << endl; SVariable++;};
voidprint() const;
~Test()
{cout << "dest "<< SVariable << endl;SVariable- -;};
staticintSVariable;
private:
};
intTest::SVariable = 5;// initialize just once outside the scope of the class
voidTest::print() const
{cout << SVariable << endl;}
#include<iostream>
#include"MyFile.h"
usingnamespacestd;
voidmain()
{
{
Test *T = newTest[5];
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
}
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
}
const 5
const 6
const 7
const 8
const 9
10
10
Press any key to continue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-35-2048.jpg)
![static Class Members
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
classTest
{
public:
Test()
{cout << "const "<< SVariable << endl; SVariable++;};
voidprint() const;
~Test()
{cout << "dest "<< SVariable << endl;SVariable- -;};
staticintSVariable;
private:
};
intTest::SVariable = 5;// initialize just once outside the scope of the class
voidTest::print() const
{cout << SVariable << endl;}
#include<iostream>
#include"MyFile.h"
usingnamespacestd;
voidmain()
{
{
Test *T = newTest[5];
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
delete[] T;
}
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
}
const 5
const 6
const 7
const 8
const 9
10
dest 10
dest 9
dest 8
dest 7
dest 6
5
5
Press any key to continue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-36-2048.jpg)
![static Class Members
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
classTest
{
public:
Test()
{cout << "const "<< SVariable << endl; SVariable++;};
voidprint() const;
~Test()
{cout << "dest "<< SVariable << endl;SVariable- -;};
staticintSVariable;
private:
};
intTest::SVariable = 5;// initialize just once outside the scope of the class
voidTest::print() const
{cout << SVariable << endl;}
#include<iostream>
#include"MyFile.h"
usingnamespacestd;
voidmain()
{
{
Test *T = newTest[5];
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
}
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
delete[] T;
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
}
Compile error. Undeclared identifier T
We did allocate memory and we have never been de-allocated it!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-37-2048.jpg)









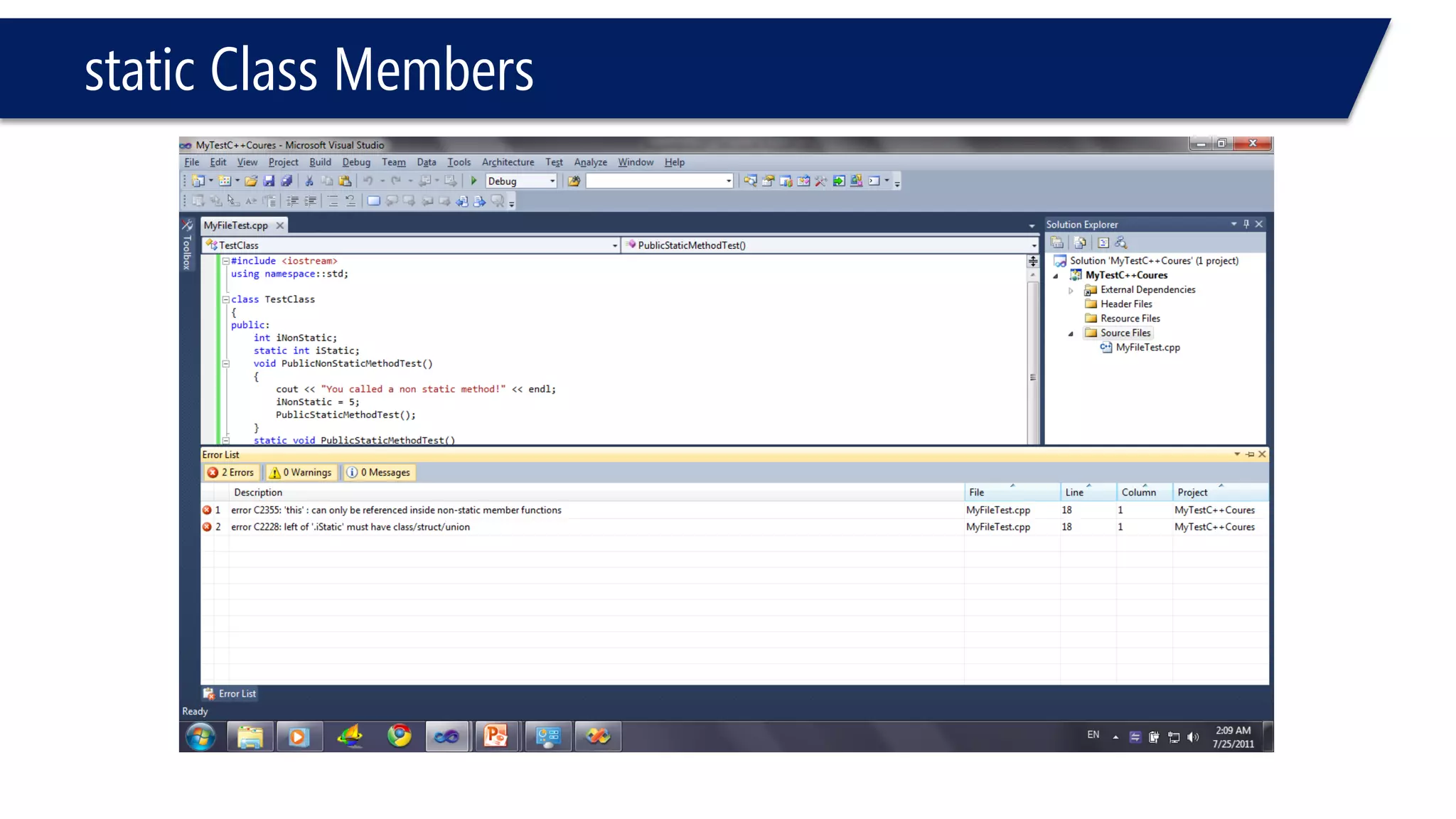
![static Class Members
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
classTest
{
public:
Test()
{++SVariable;
cout << "const "<< SVariable << endl;
};
voidprint() const;
~Test()
{--SVariable;
cout << "dest "<< SVariable << endl;
};
staticintSGet();// static member function
private:
staticintSVariable;// static date member
};
intTest::SVariable = 0;// initialize just once outside the scope of the class
voidTest::print() const
{cout << SVariable << endl;}
intTest::SGet()
{
returnSVariable;
}
#include<iostream>
#include"MyFile.h"
usingnamespacestd;
voidmain()
{
Test TSource;
Test *T1 = newTest;
Test *T2;
delete[]T1;
cout << T1->SGet() << endl;
}
Runtime error coz of [] not compiler error for sure!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-47-2048.jpg)









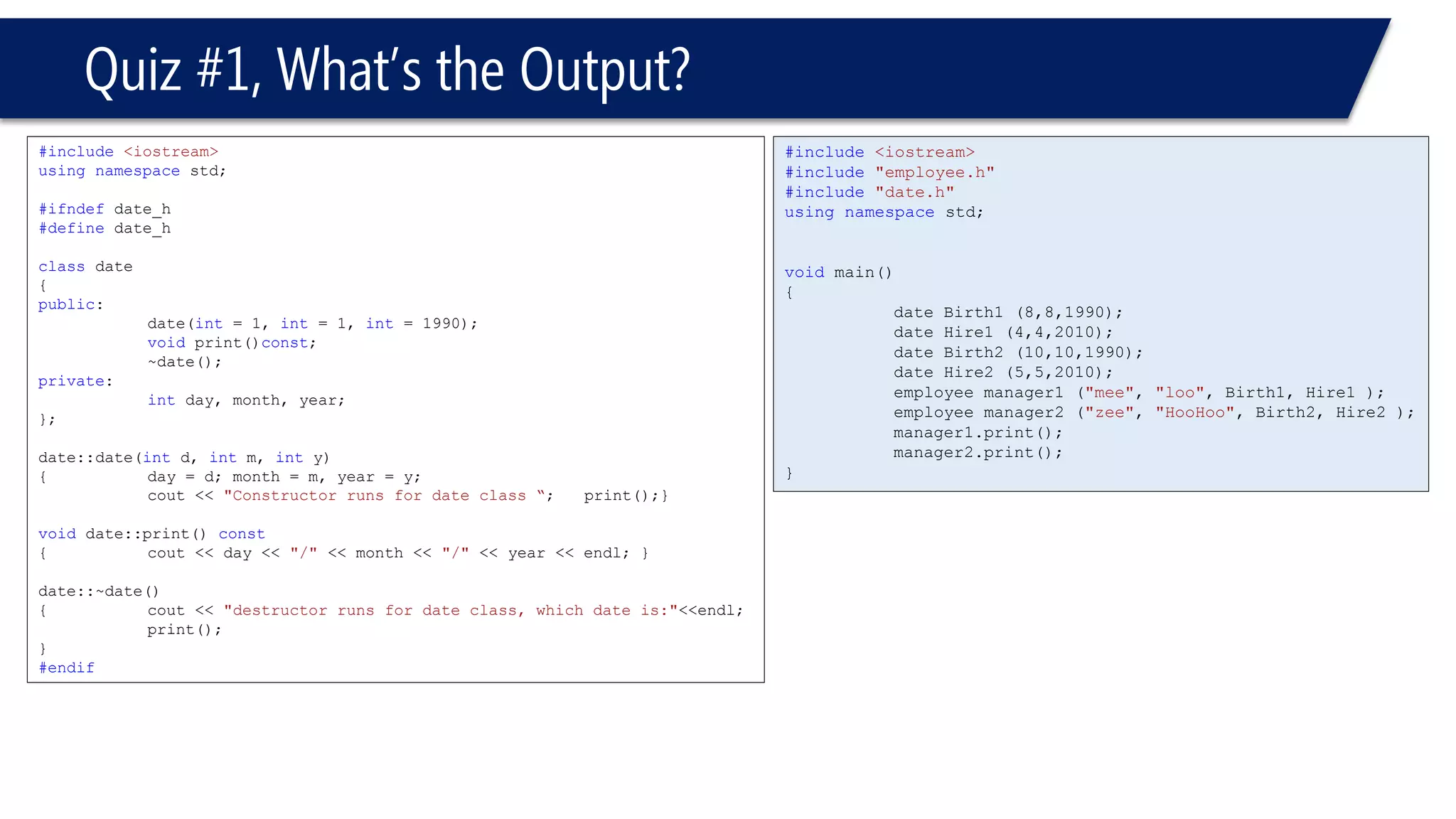
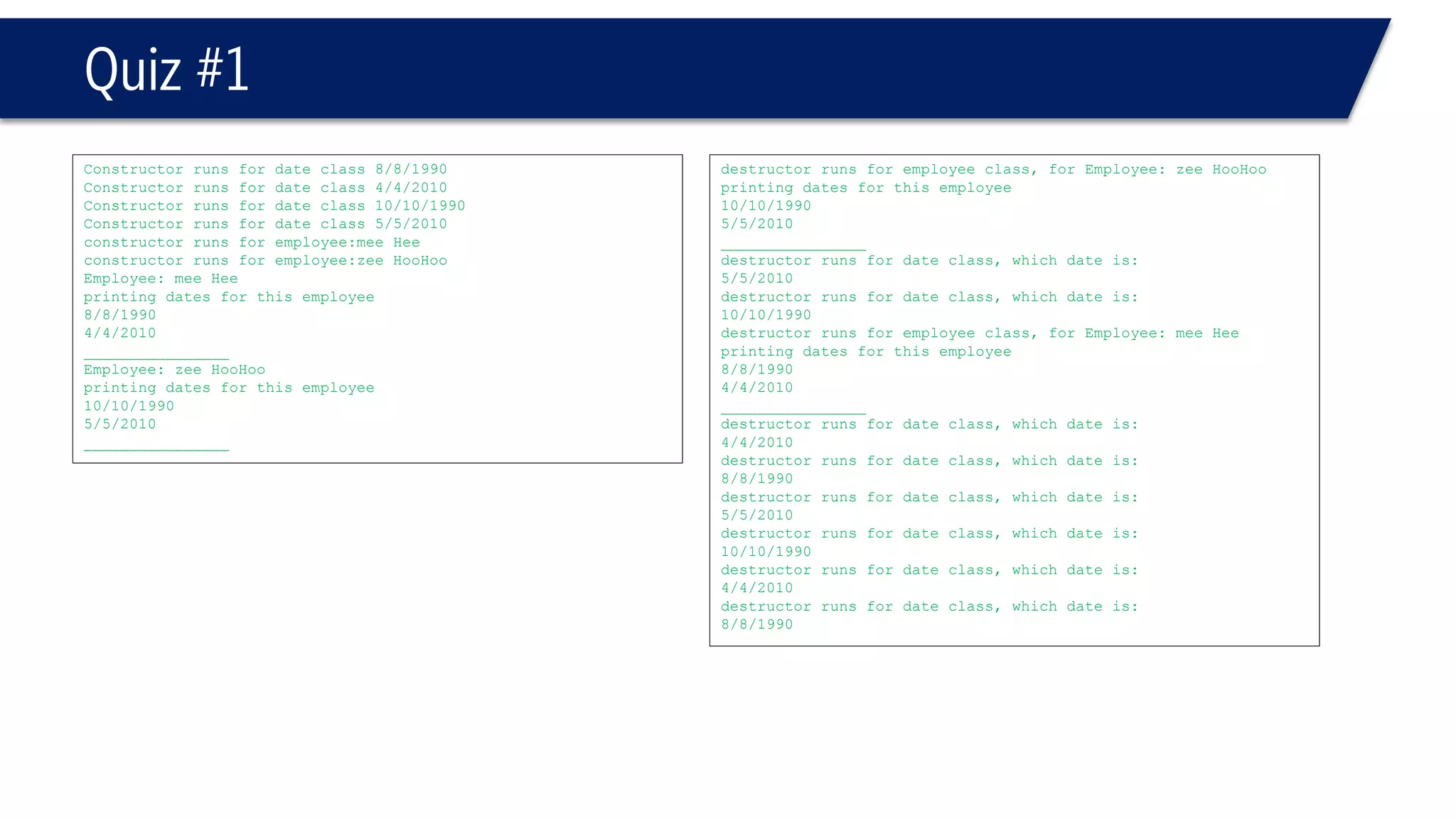
![Quiz #1
#include<iostream>
#include"date.h"
usingnamespacestd;
#ifndefemployee_h
#defineemployee_h
classemployee
{
public:
employee();
employee(char*First,
char*Last,
constdate& d1,
constdate& d2);
voidprint()const;
~employee();
private:
charFirstName [20];
charLastName [20];
constdate hiredate;
constdate birthdate;
};
employee::employee(char*First, char*Last,constdate& d1, constdate& d2):birthdate(d1), hiredate(d2)
{
intLength = strlen(First);
strncpy(FirstName,First,20);
FirstName[Length]='0';
strncpy(LastName,Last,20);
LastName[Length]='0';
cout<<"constructor runs for employee:"<<FirstName<<' '<< LastName<<endl;
// ' ' space char;)
}
voidemployee::print() const
{
cout << "Employee: "<< FirstName << ' '<< LastName << endl;
cout << "printing dates for this employee"<< endl;
birthdate.print();
hiredate.print();
cout << "________________"<< endl;
}
employee::~employee()
{
cout << "destructor runs for employee class, for ";
print();
}
#endif](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-60-2048.jpg)
![Quiz #2, What’s the Output?
#include<iostream>
usingnamespacestd;
classTest
{
public:
Test()
{
cout << "const "<< SVariable << endl;
SVariable++;
};
voidprint() const;
~Test()
{cout << "dest "<< SVariable << endl;
SVariable--;
};
staticintSVariable;
private:
};
intTest::SVariable = 5;
voidTest::print() const
{
cout << SVariable << endl;
}
#include<iostream>
#include"MyFile.h"
usingnamespacestd;
voidmain()
{
Test T1;
{
Test T2[5];
Test TTemp;
cout << TTemp.SVariable << endl;
}
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
Test *T3 = &T1;
staticTest T4;
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
Test* &T5 = T3;
cout << Test::SVariable << endl;
}
const 5
const 6
const 7
const 8
const 9
const 10
const 11
12
dest 12
dest 11
dest 10
dest 9
dest 8
dest 7
6
const 6
7
7
dest 7
dest 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppl09-classesp2-140831021526-phpapp01/75/C-L09-Classes-Part2-63-2048.jpg)