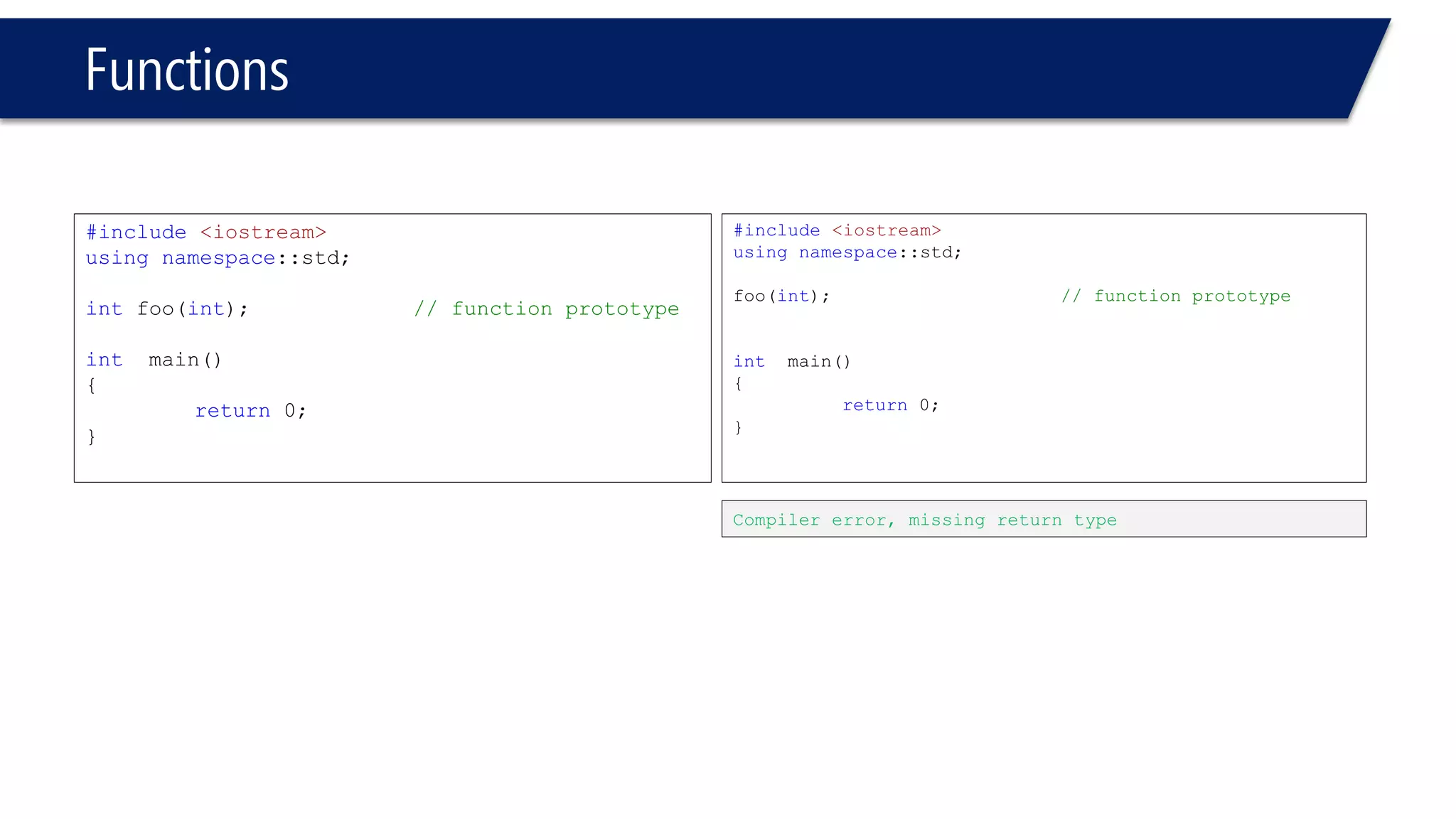
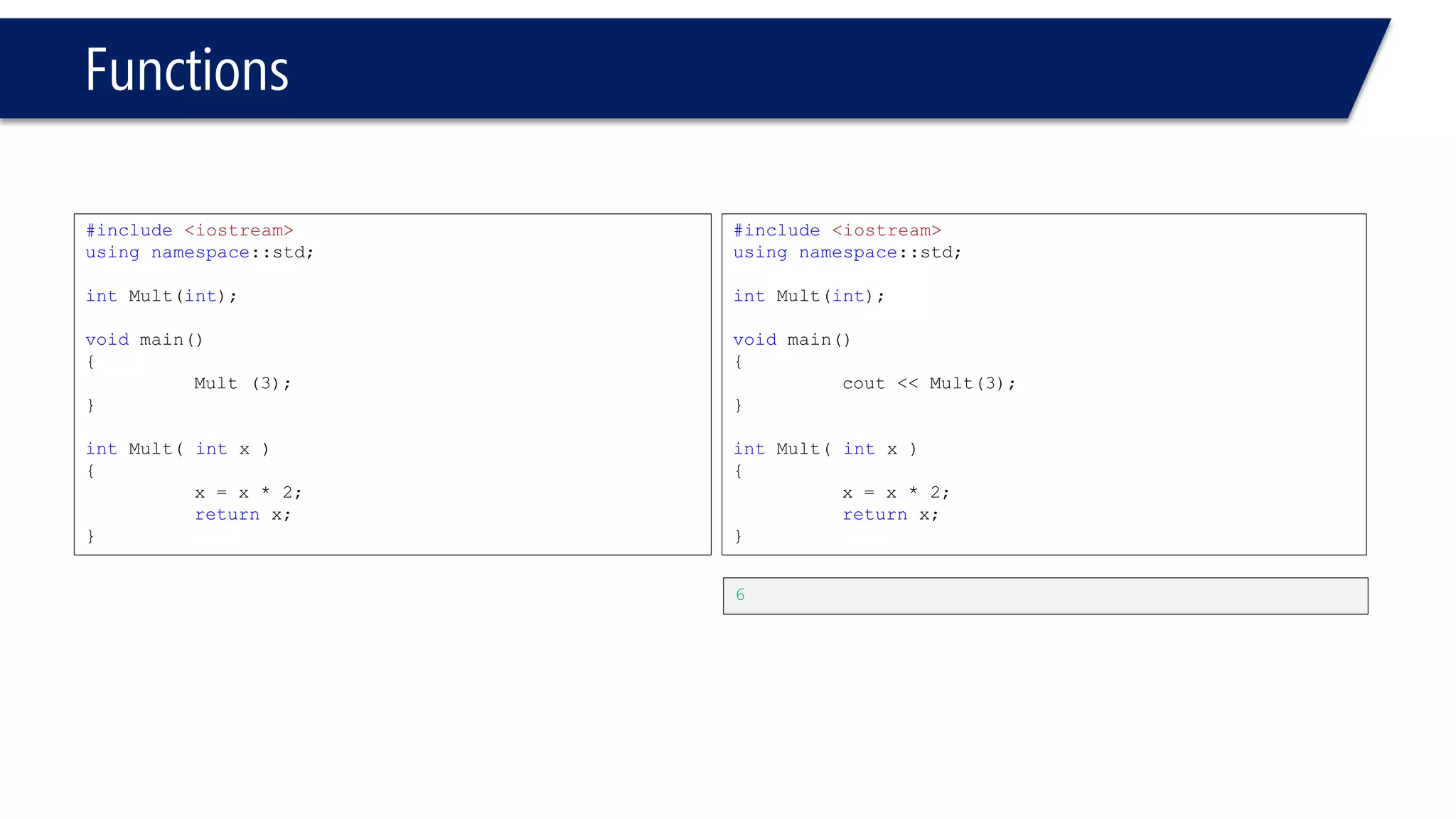
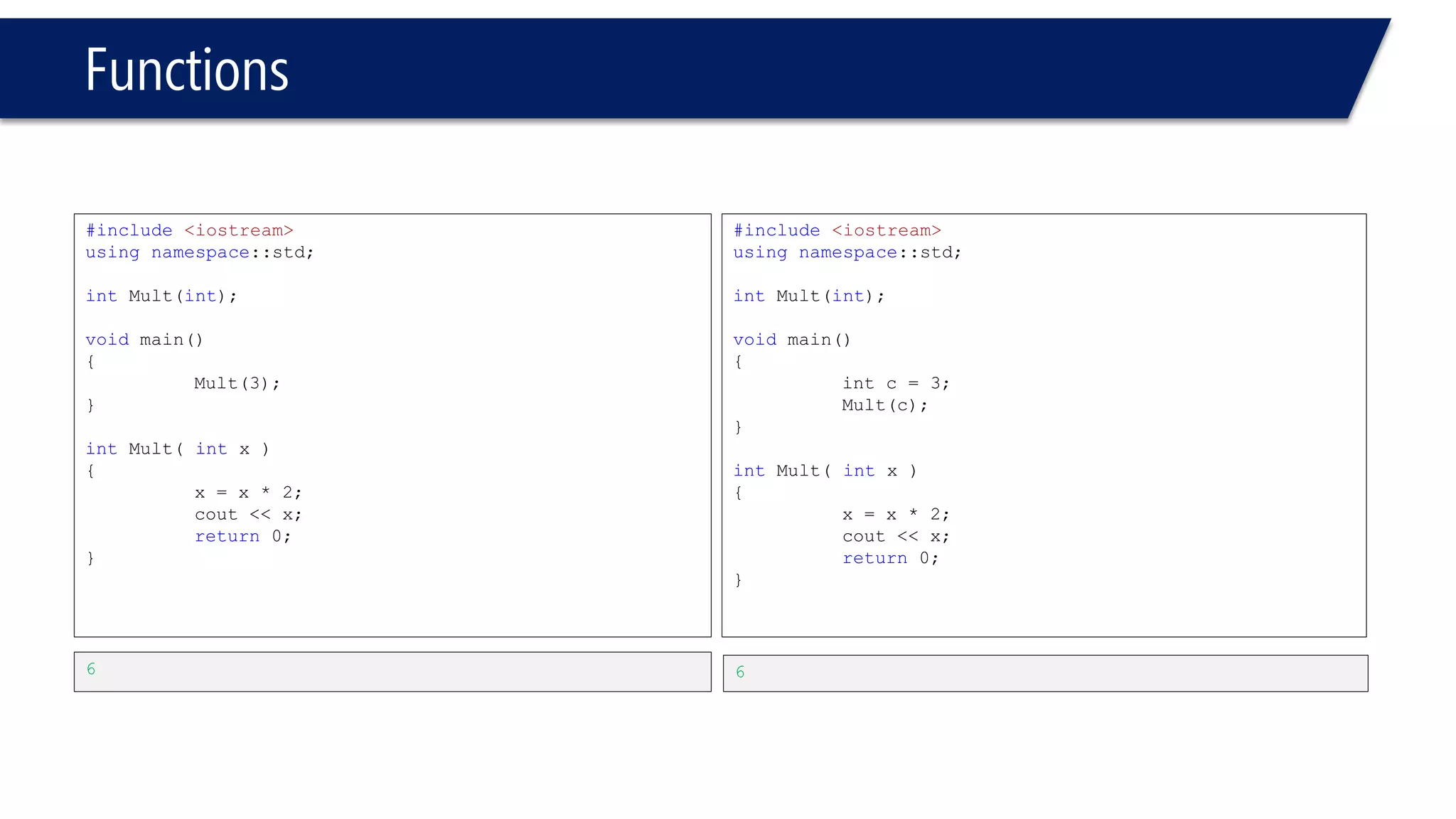
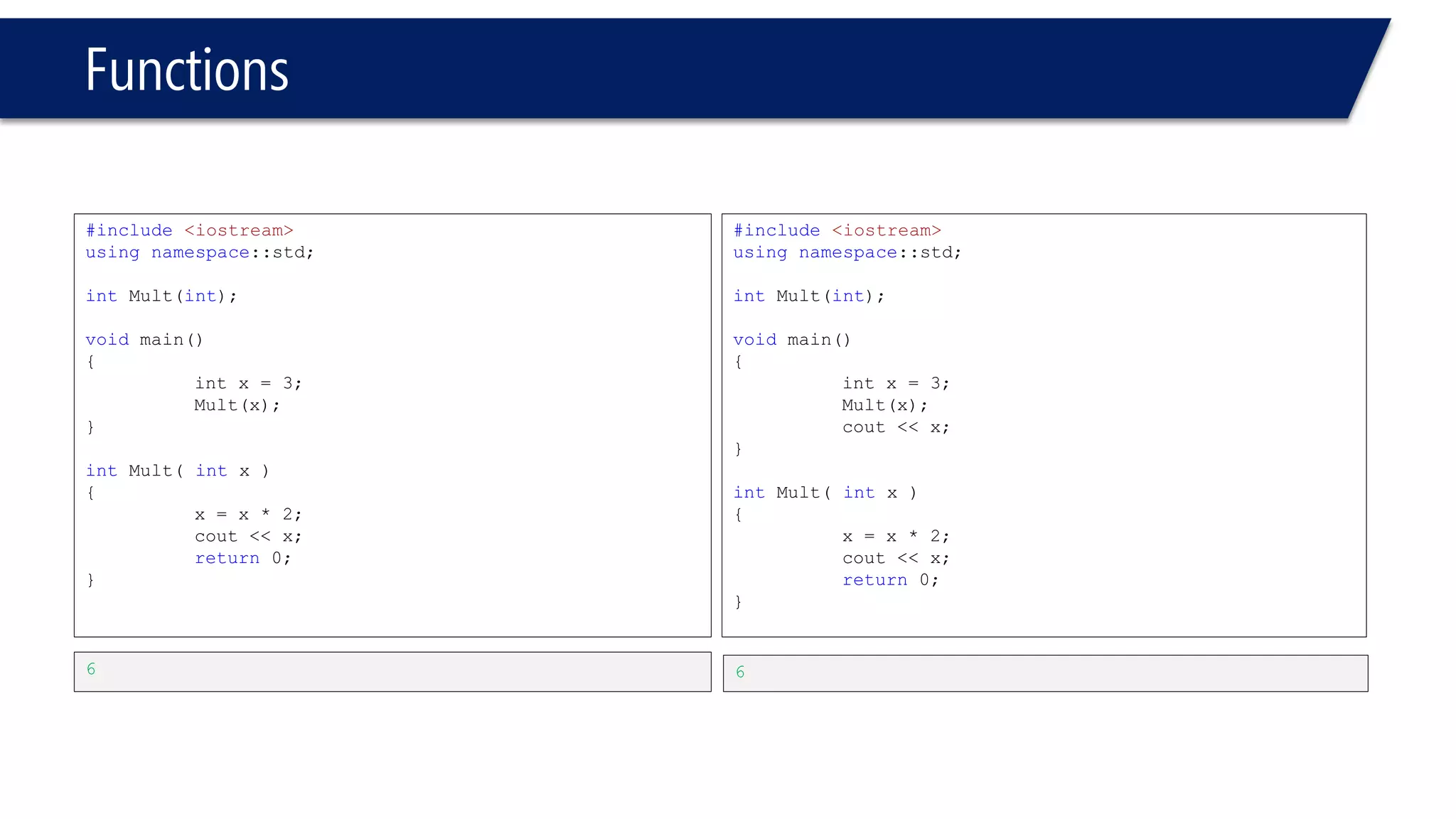
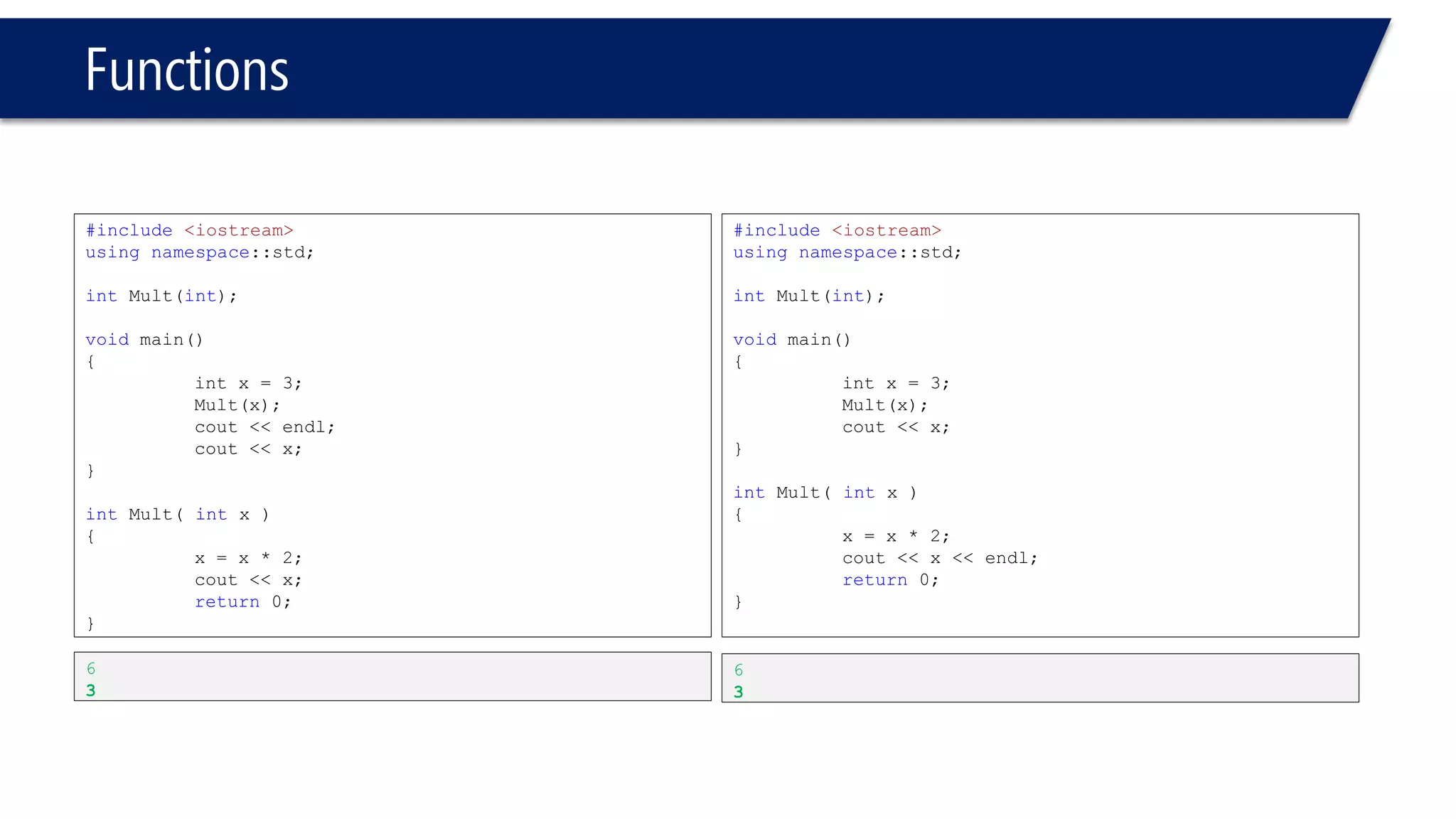
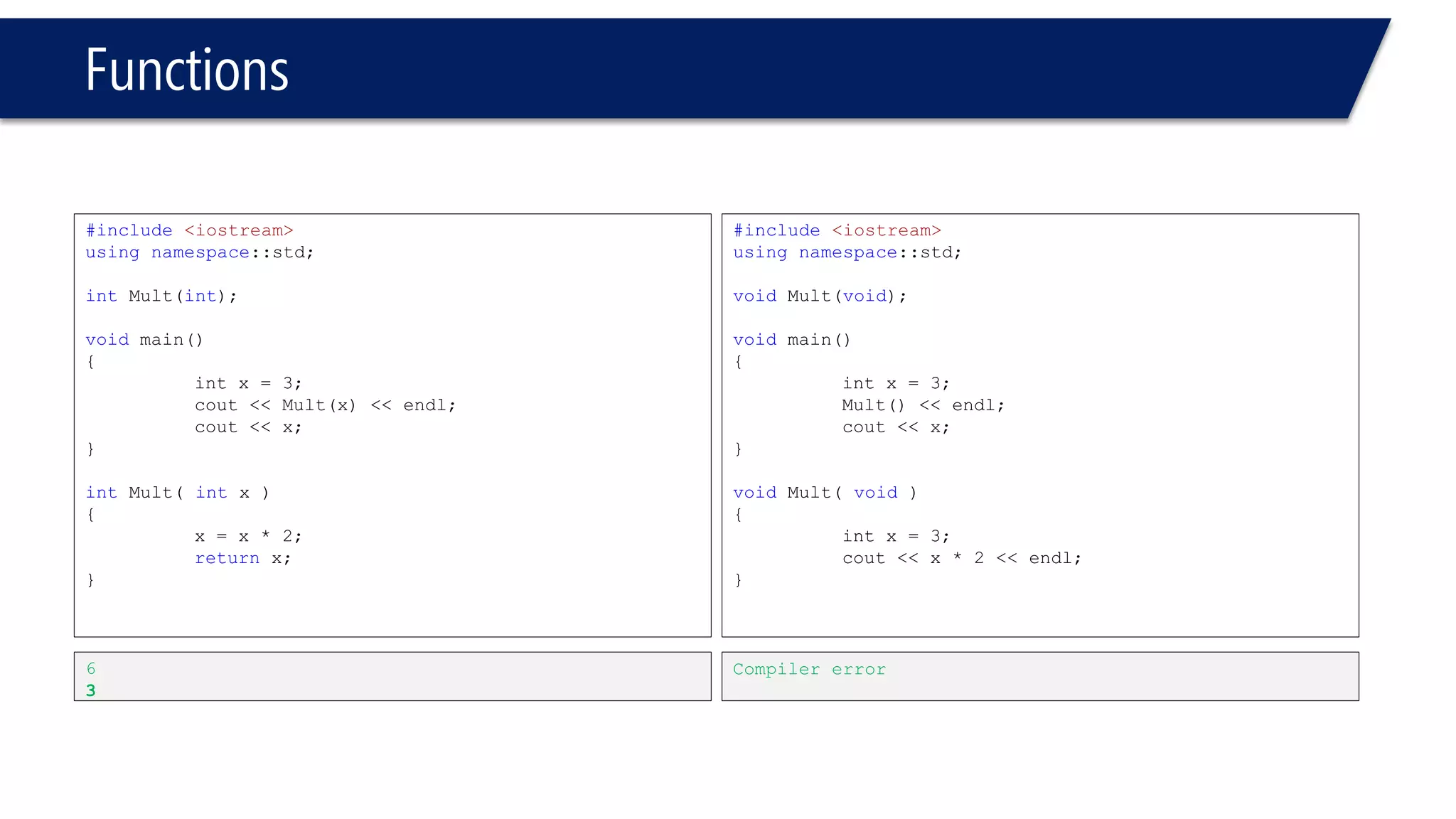
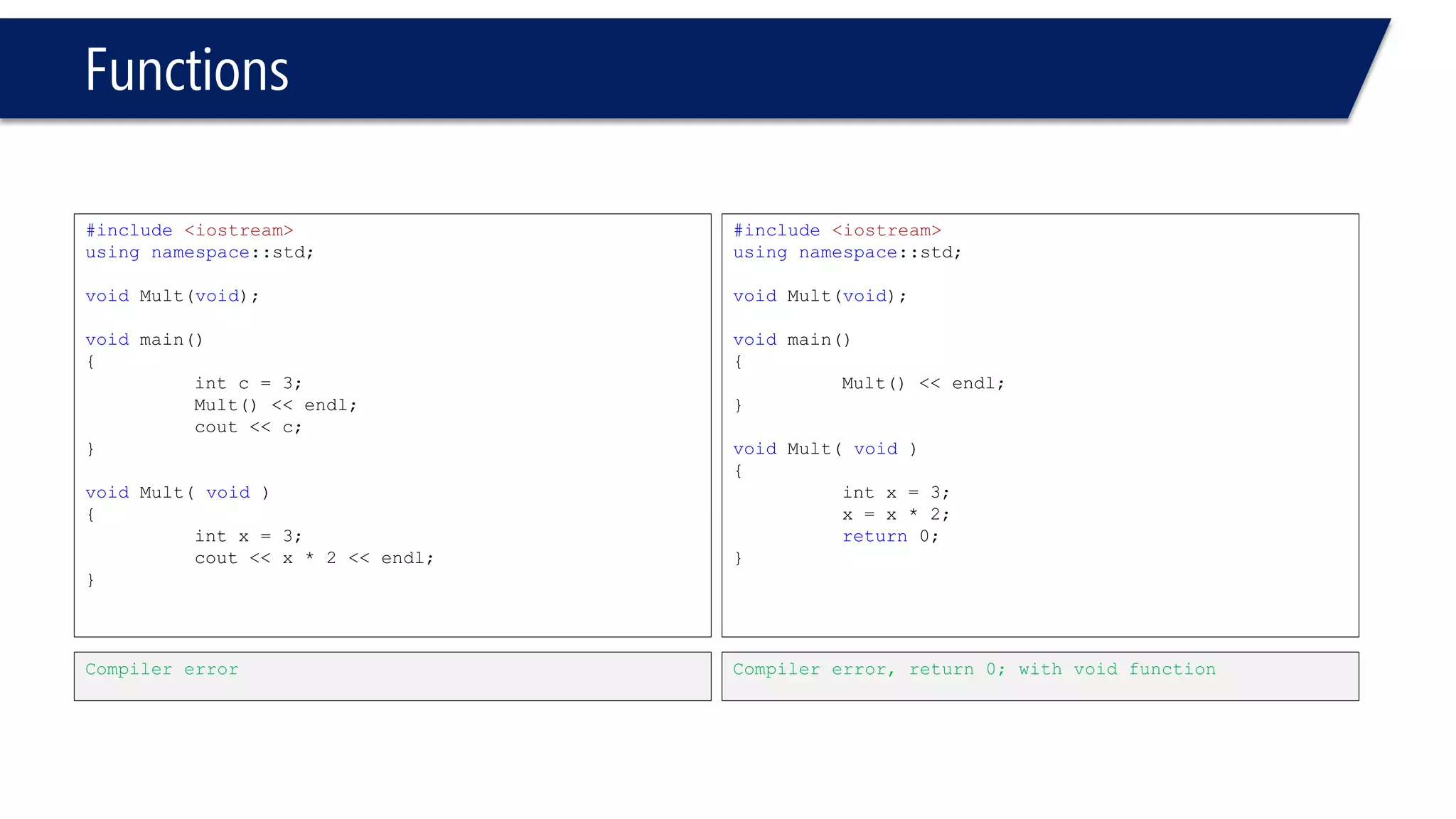
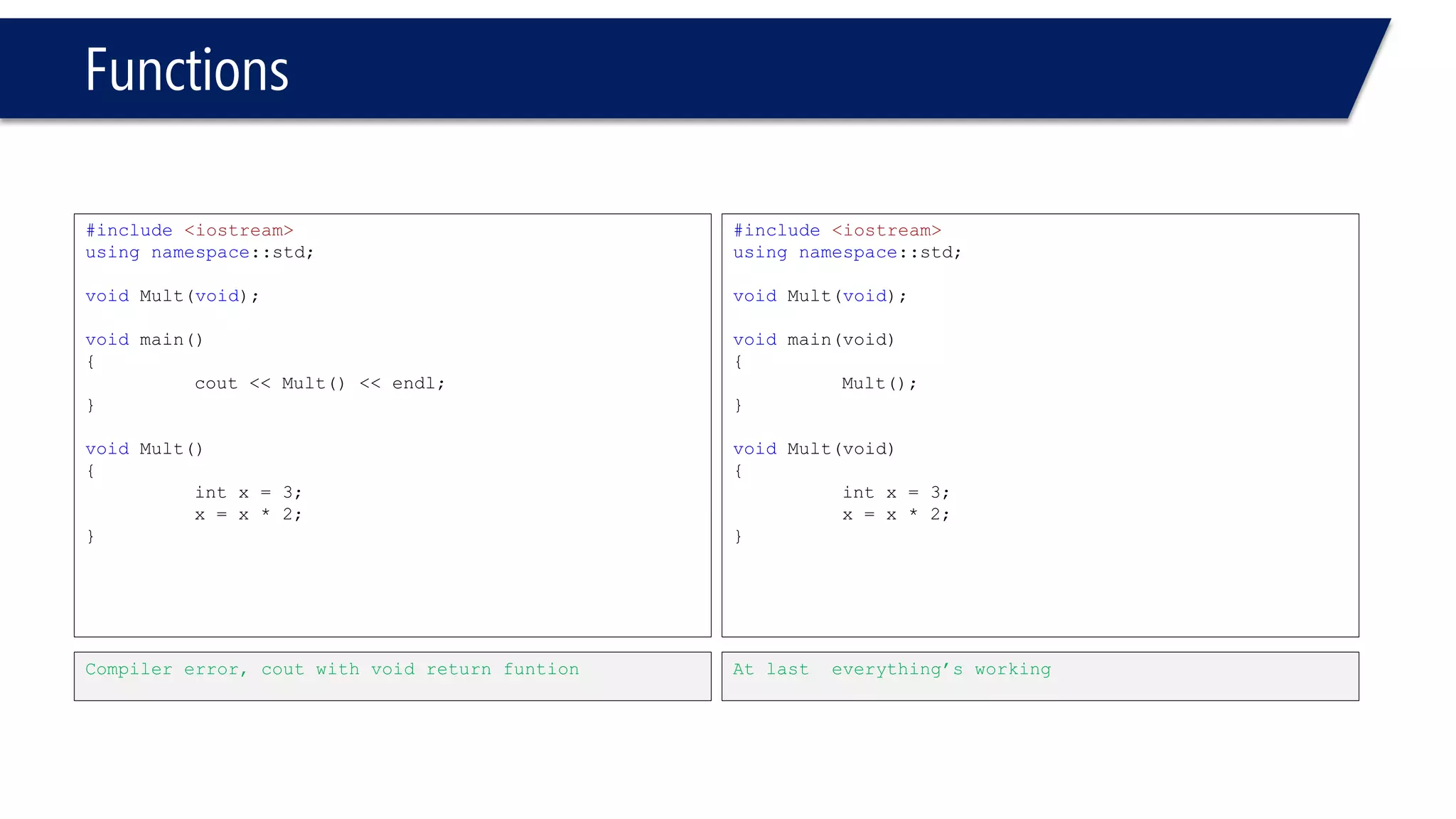
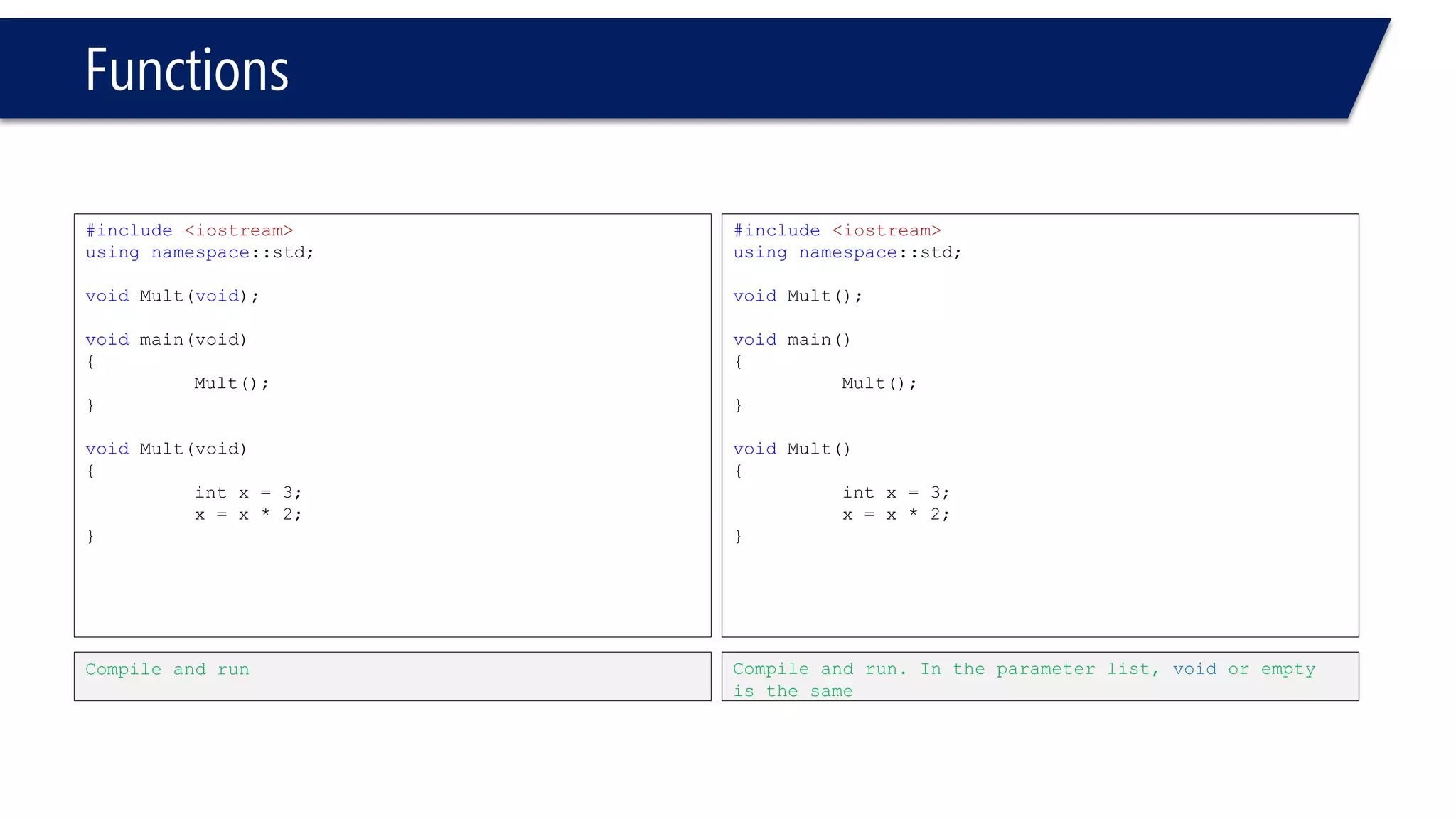
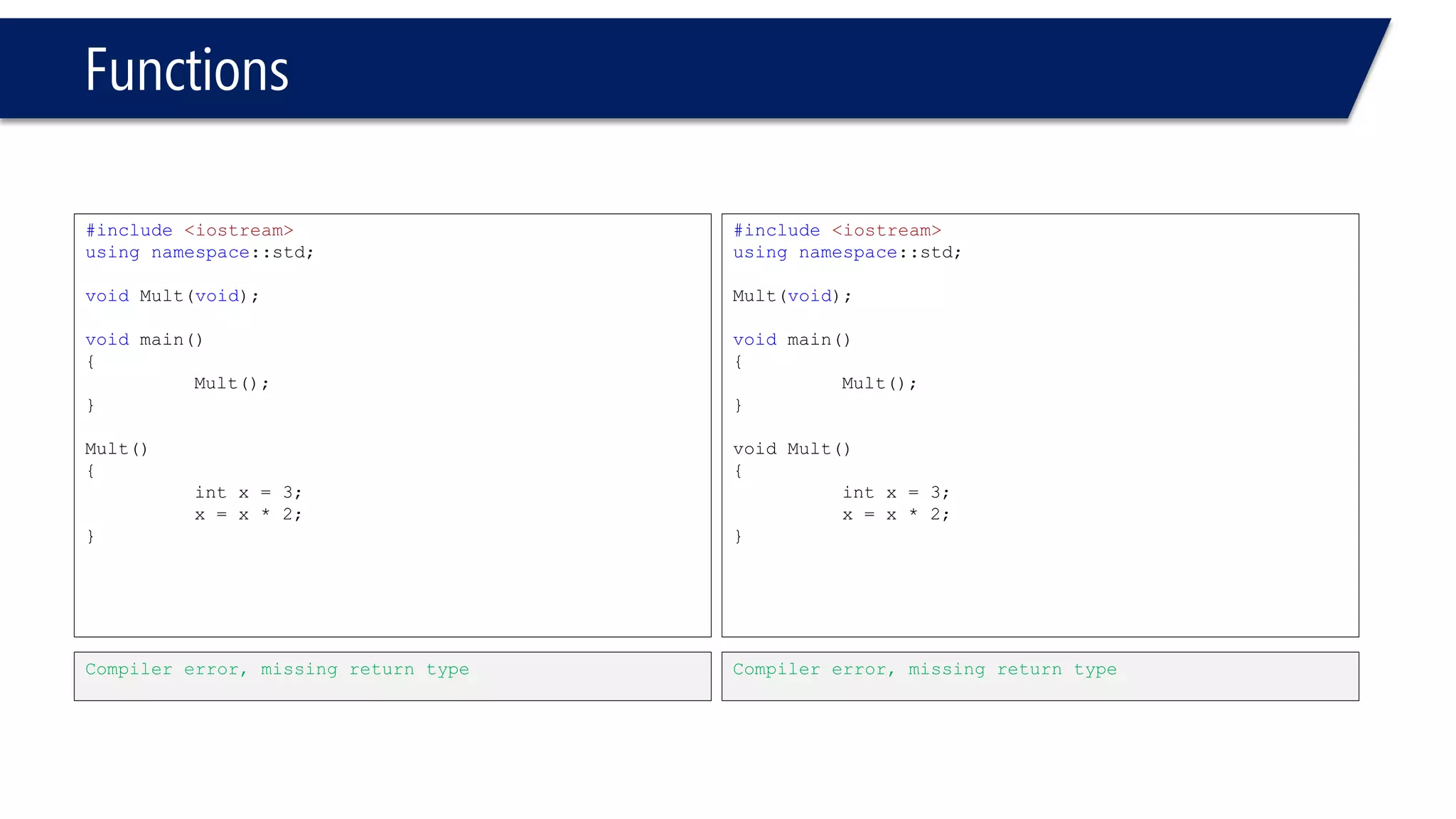
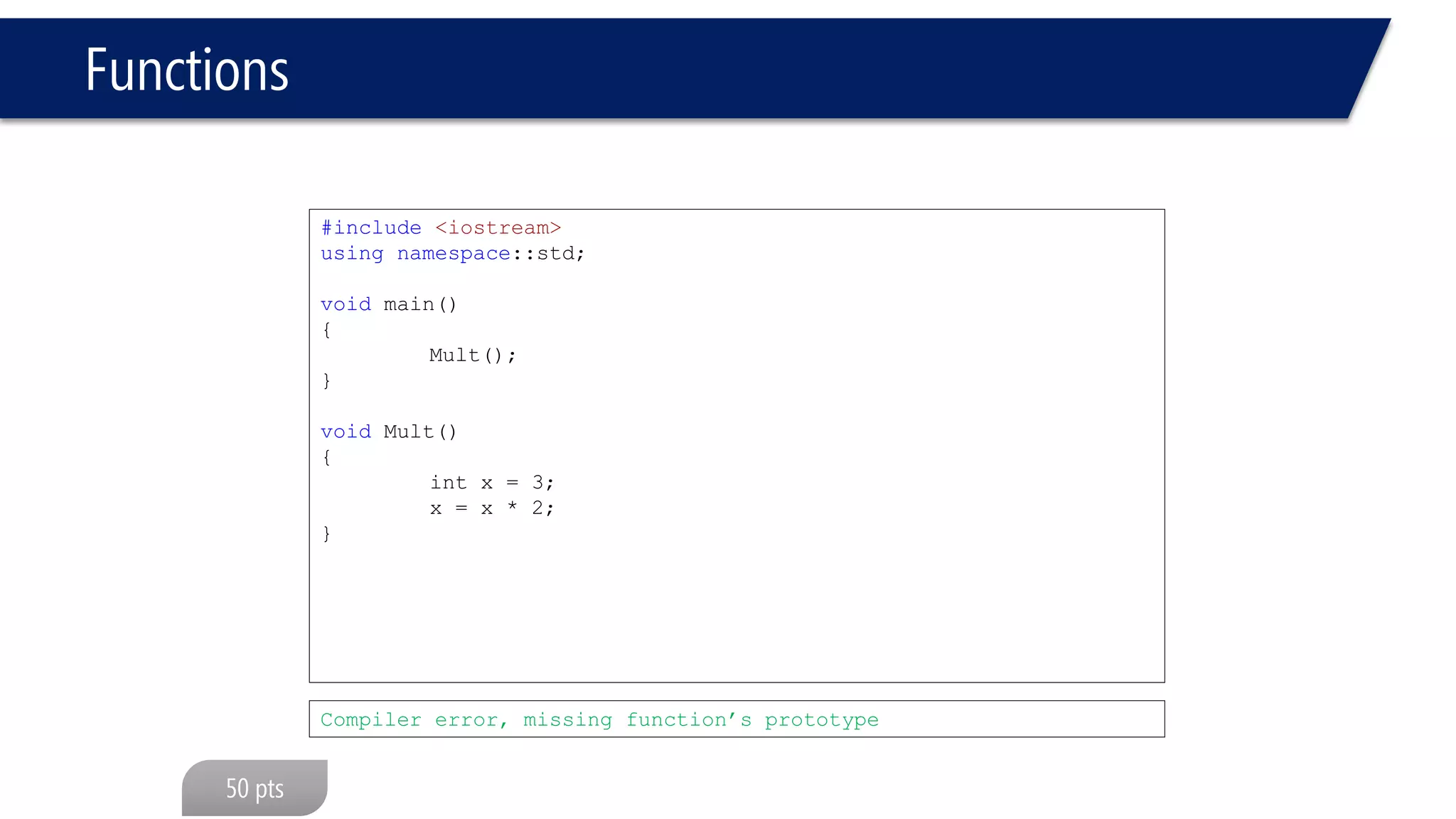
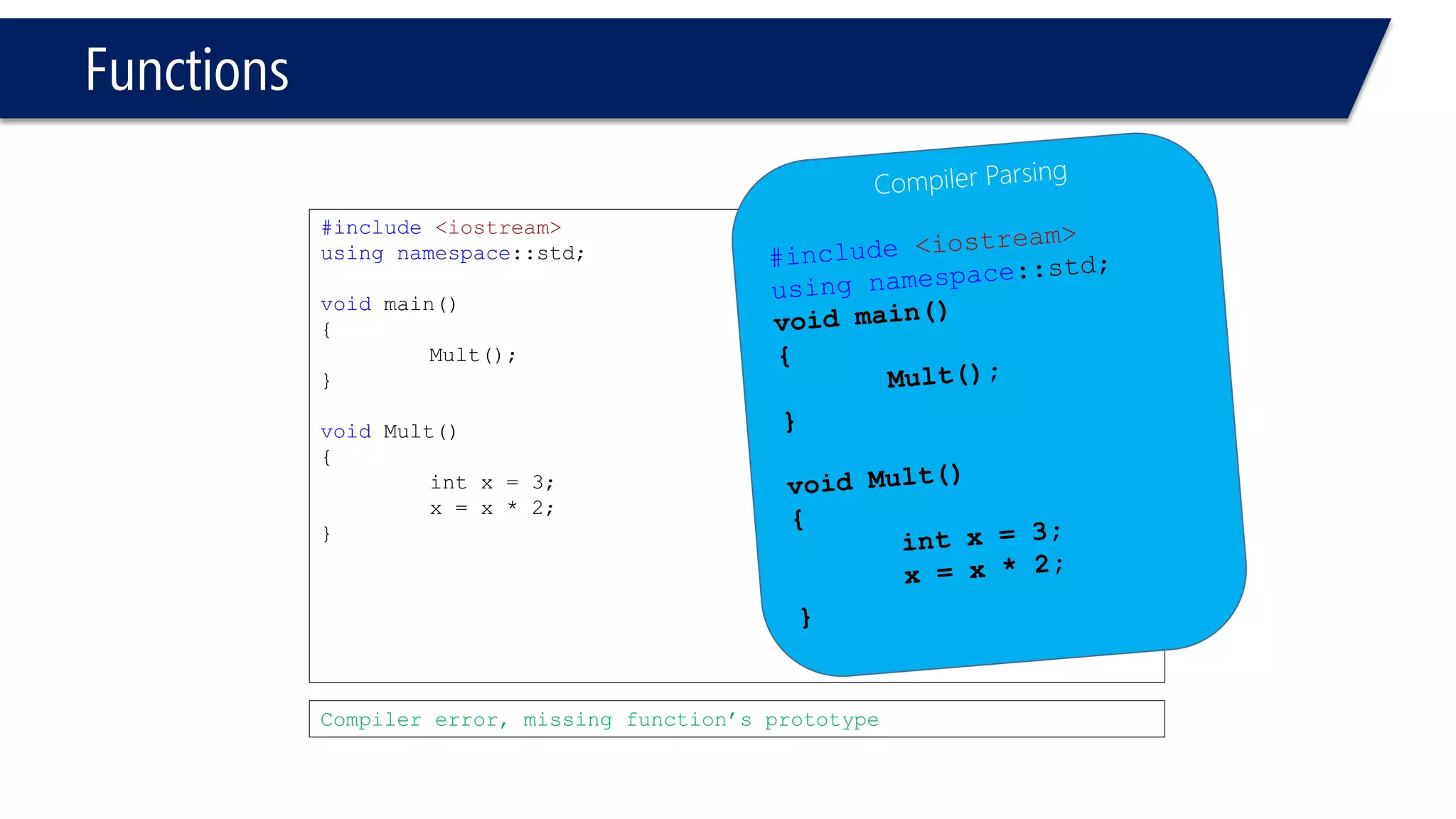
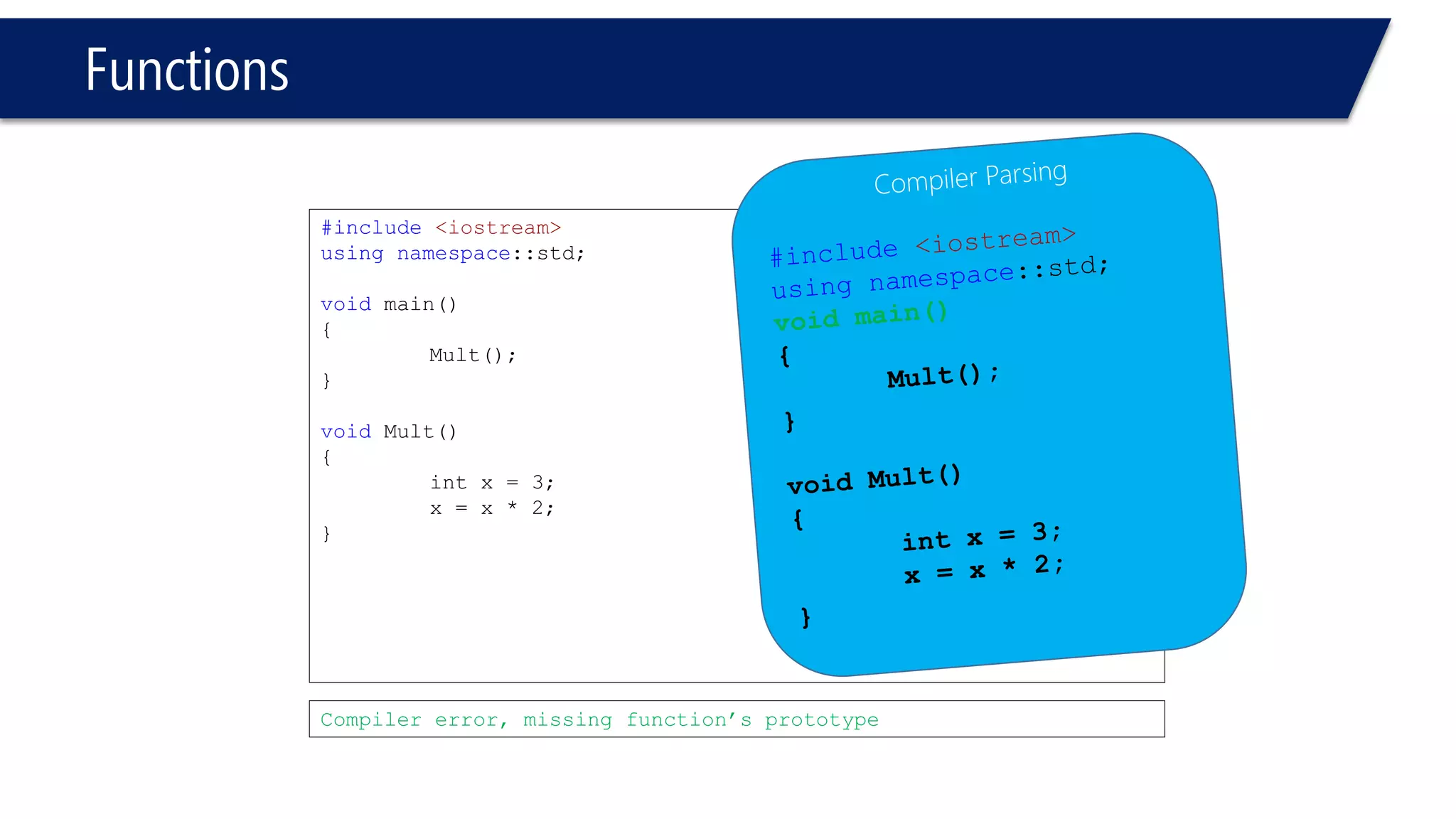
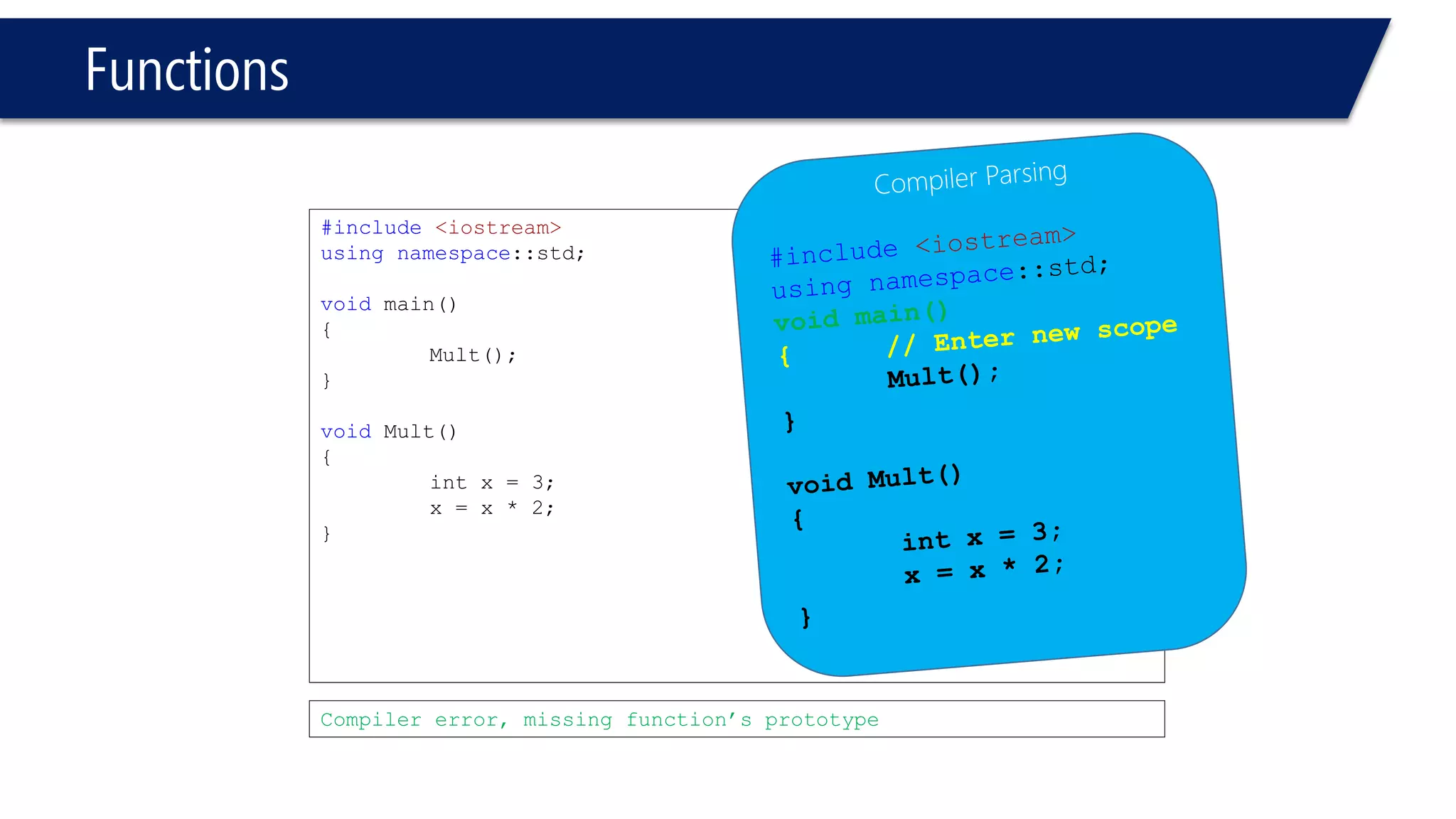
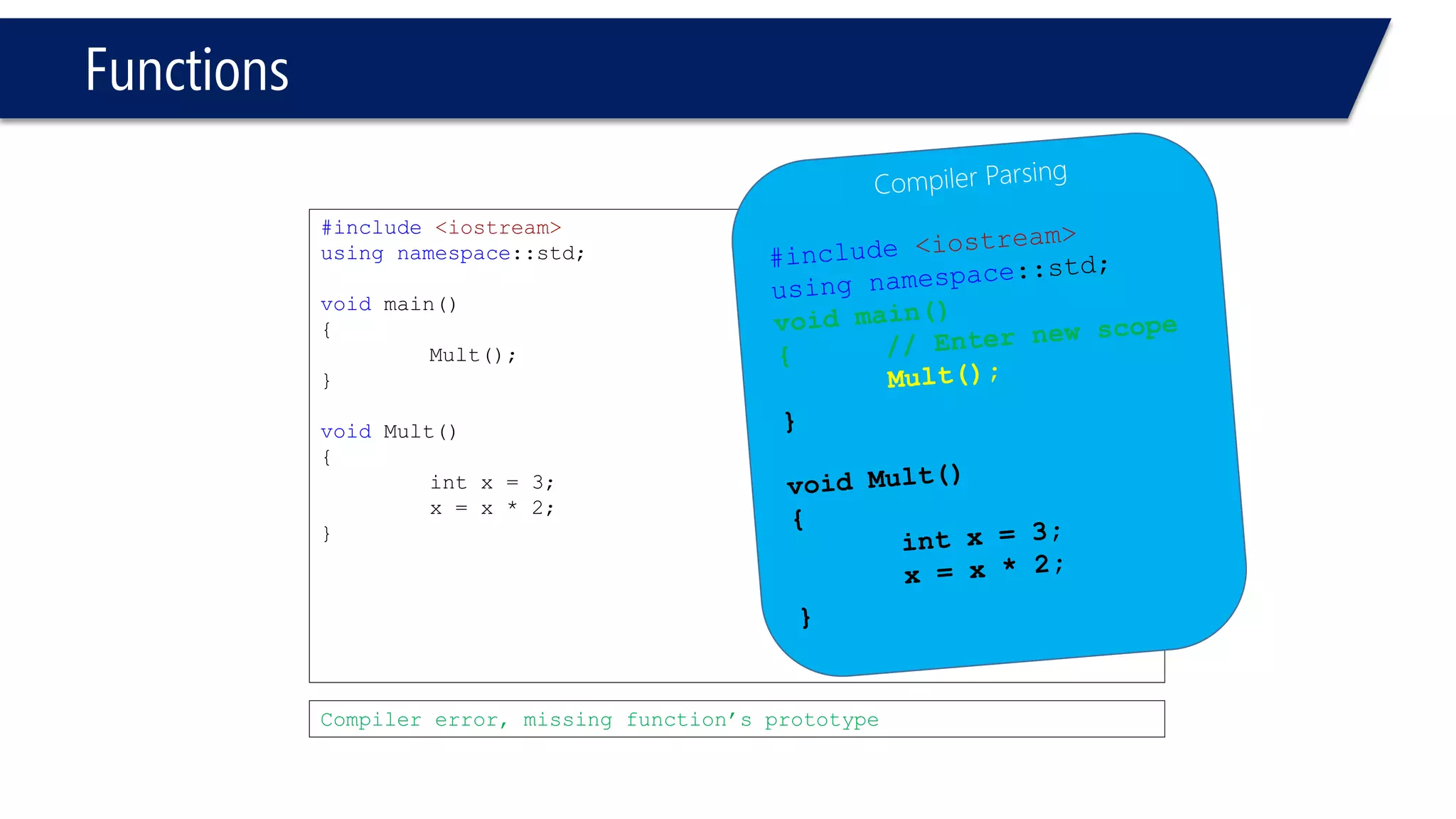
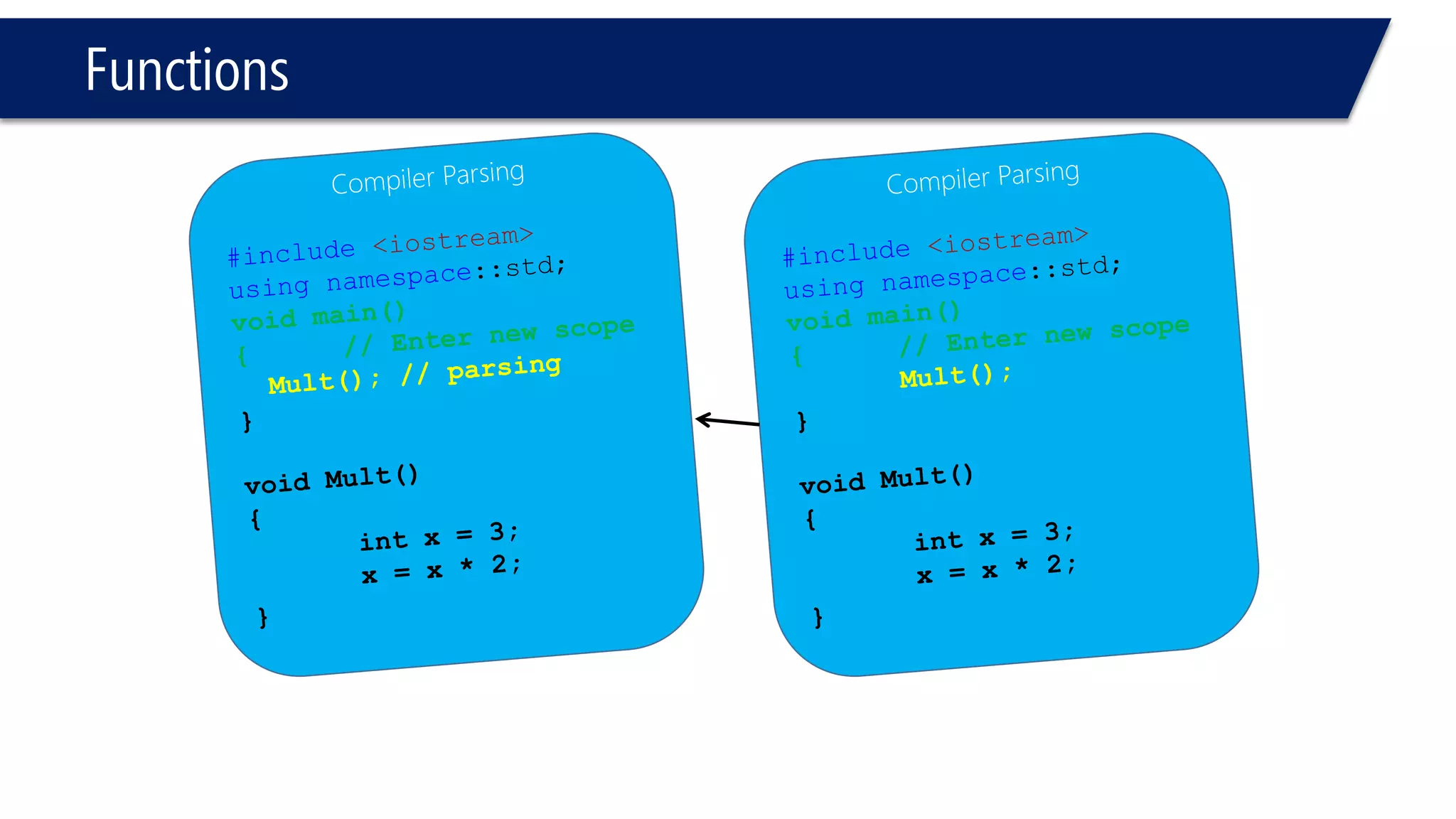
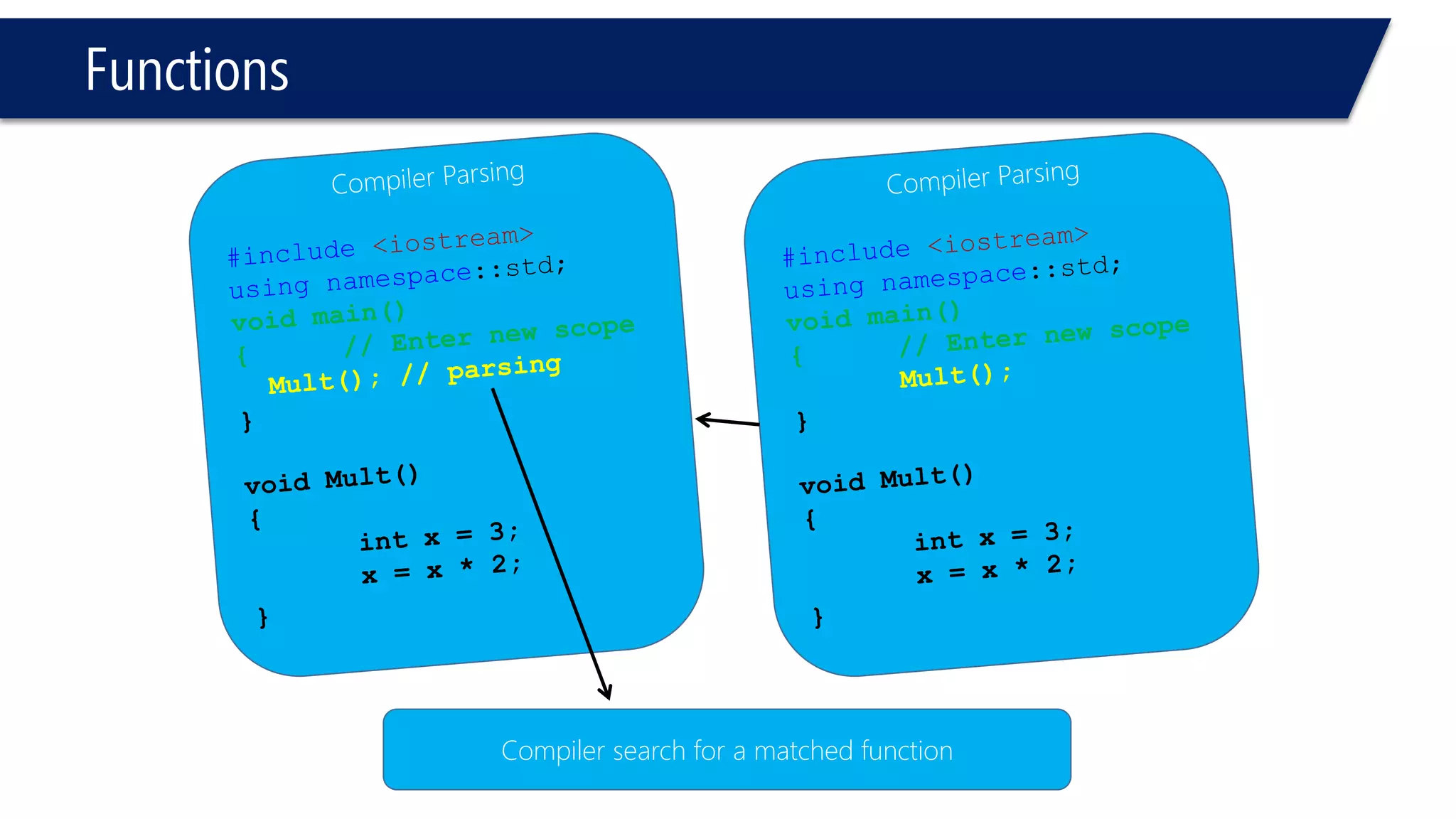
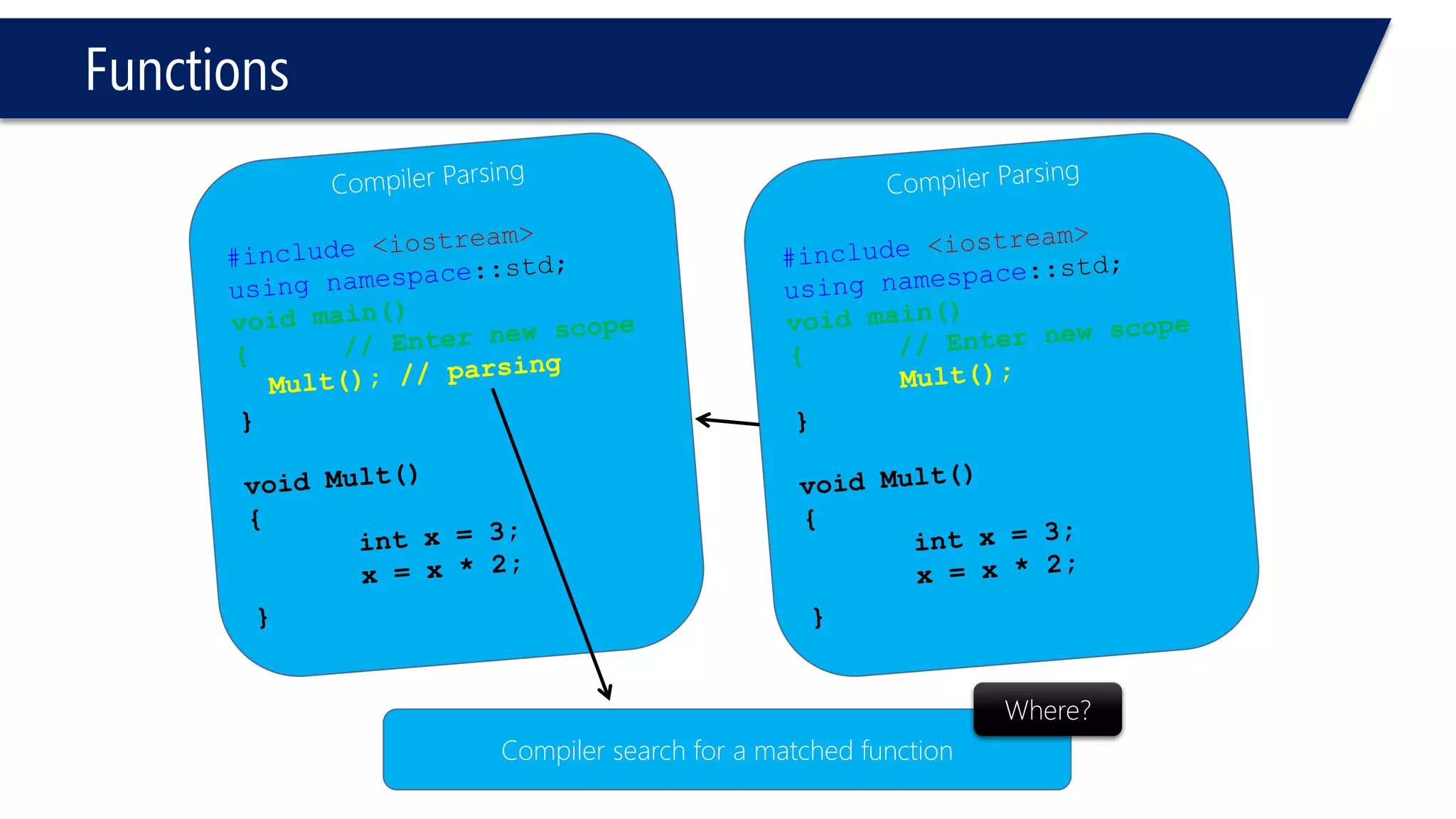
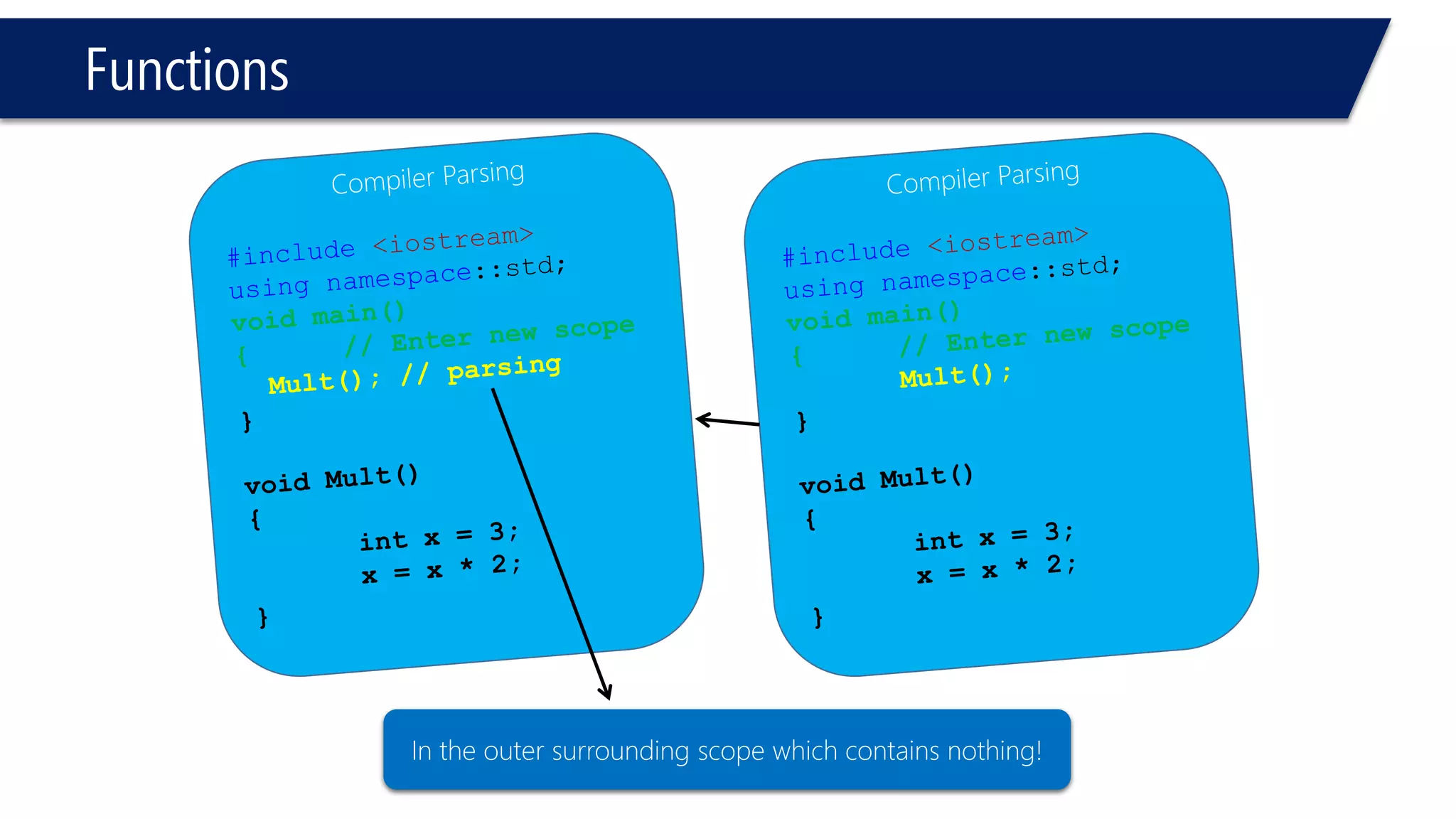
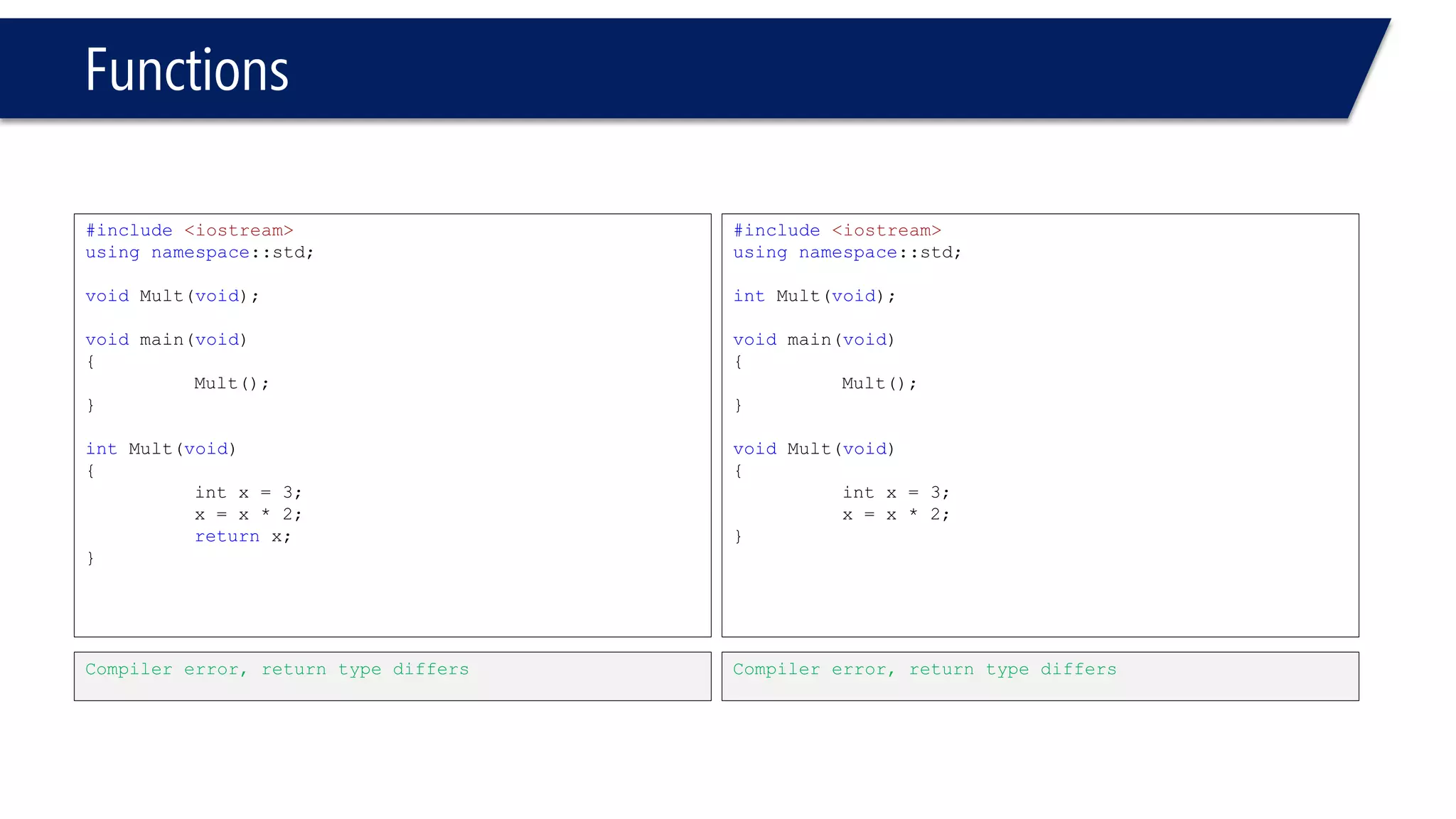
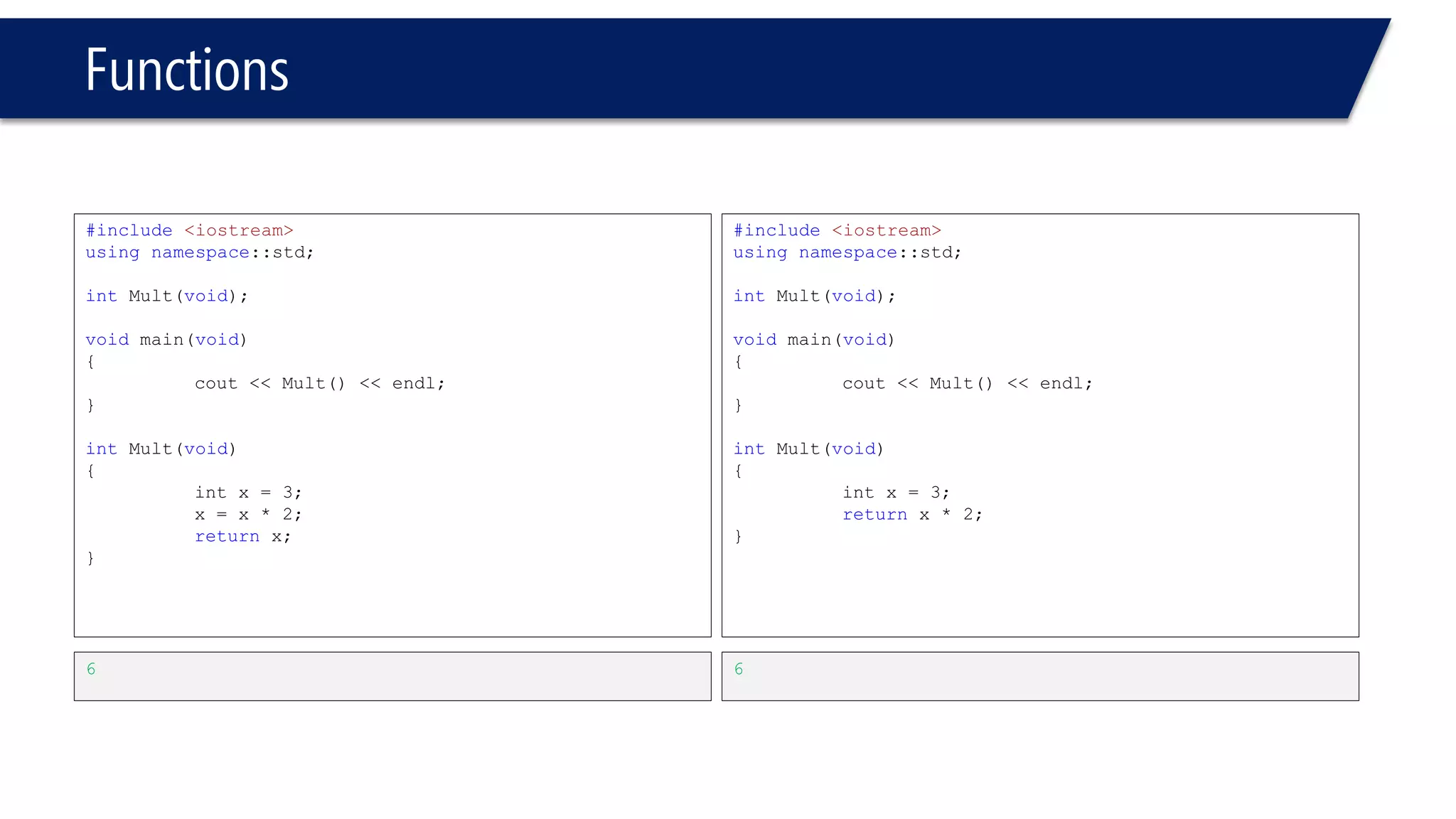
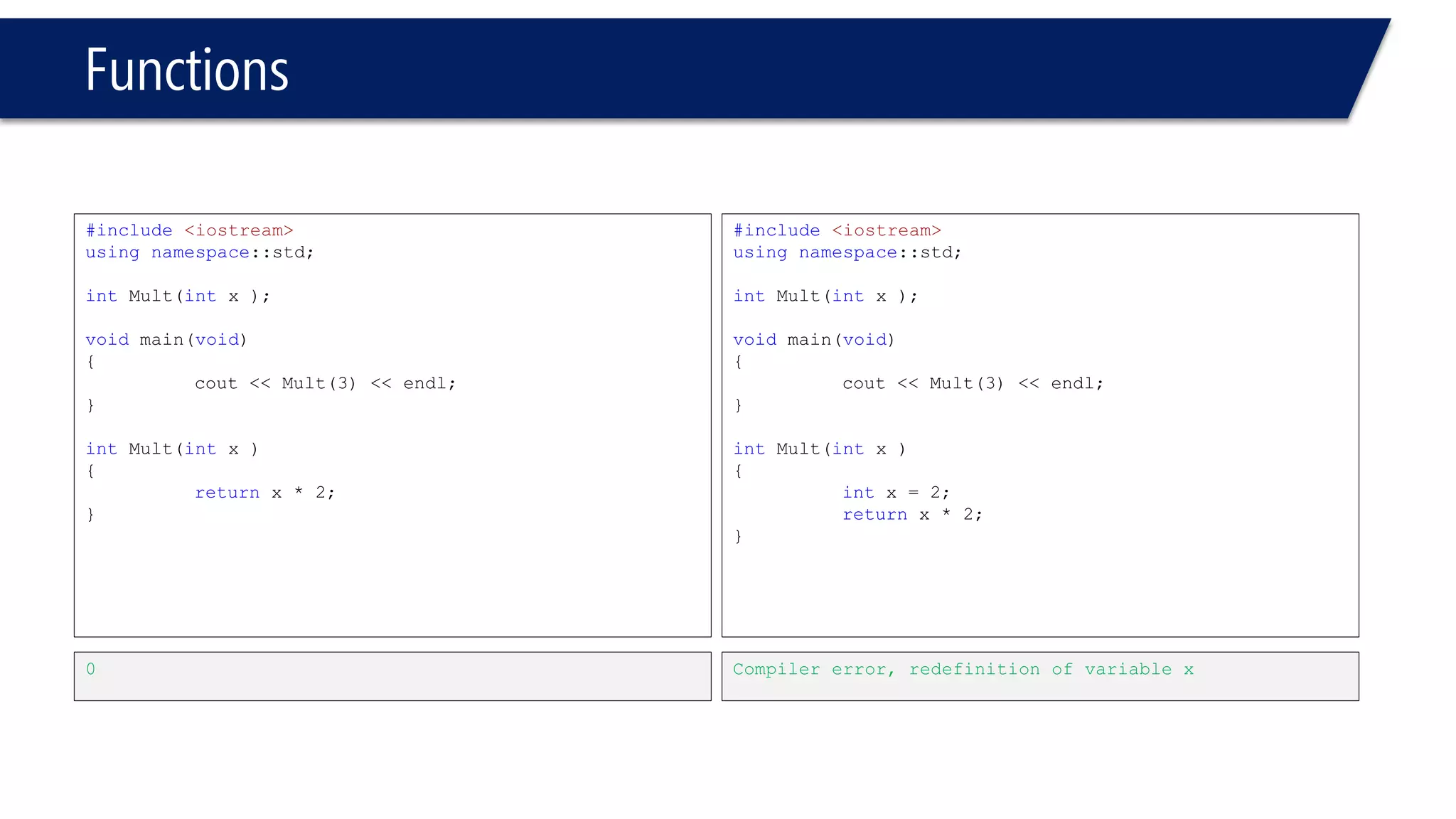
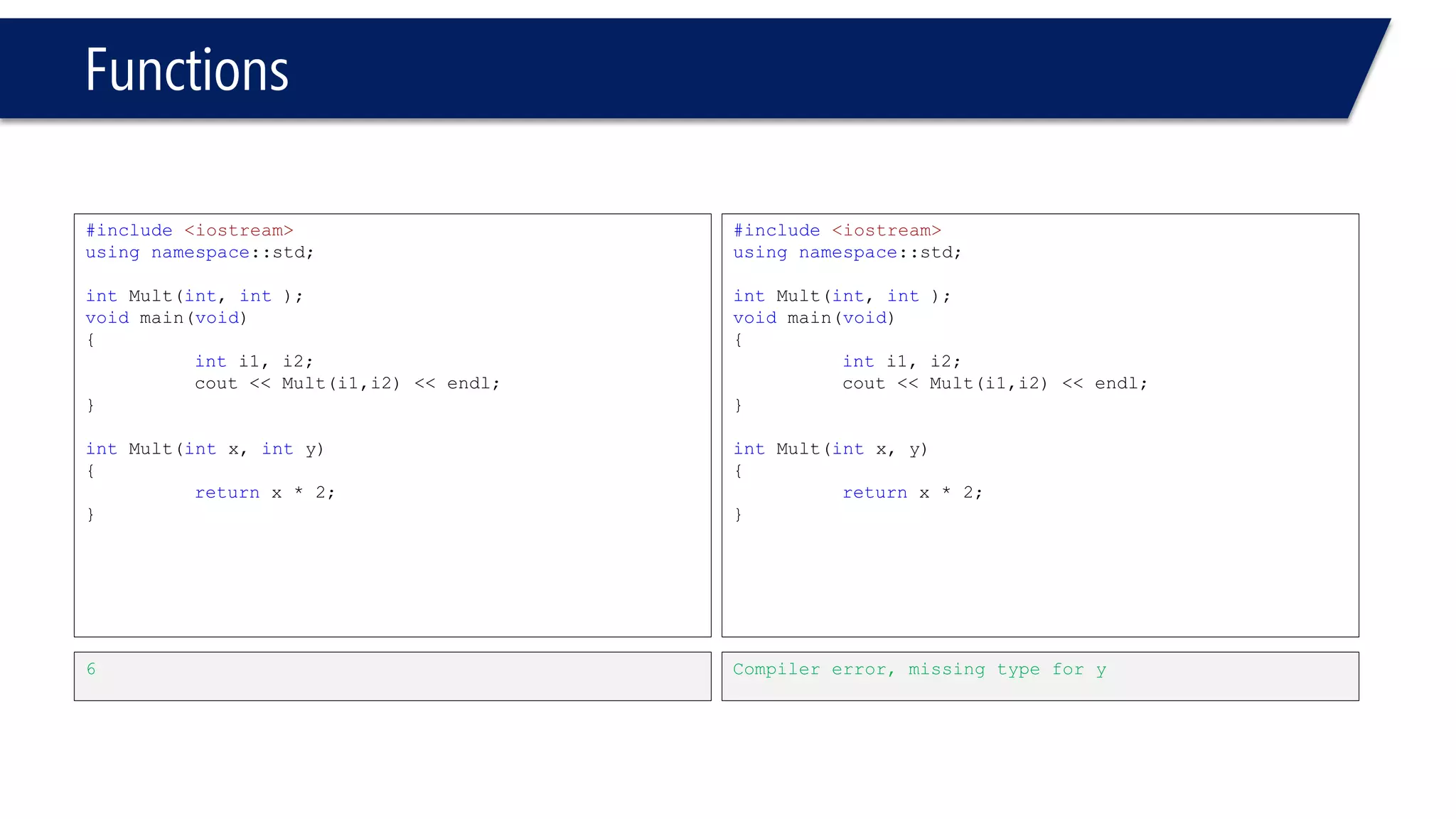
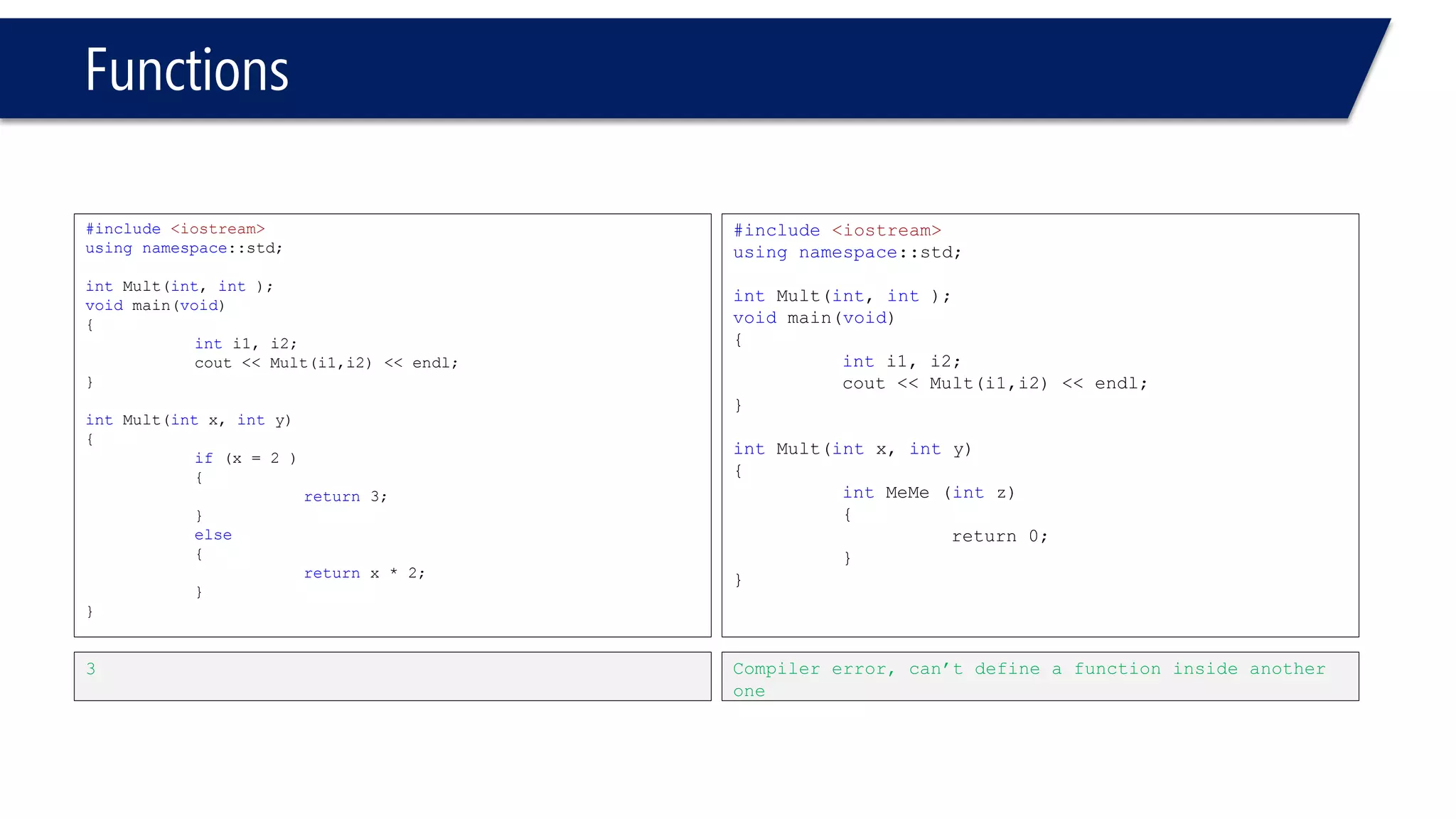
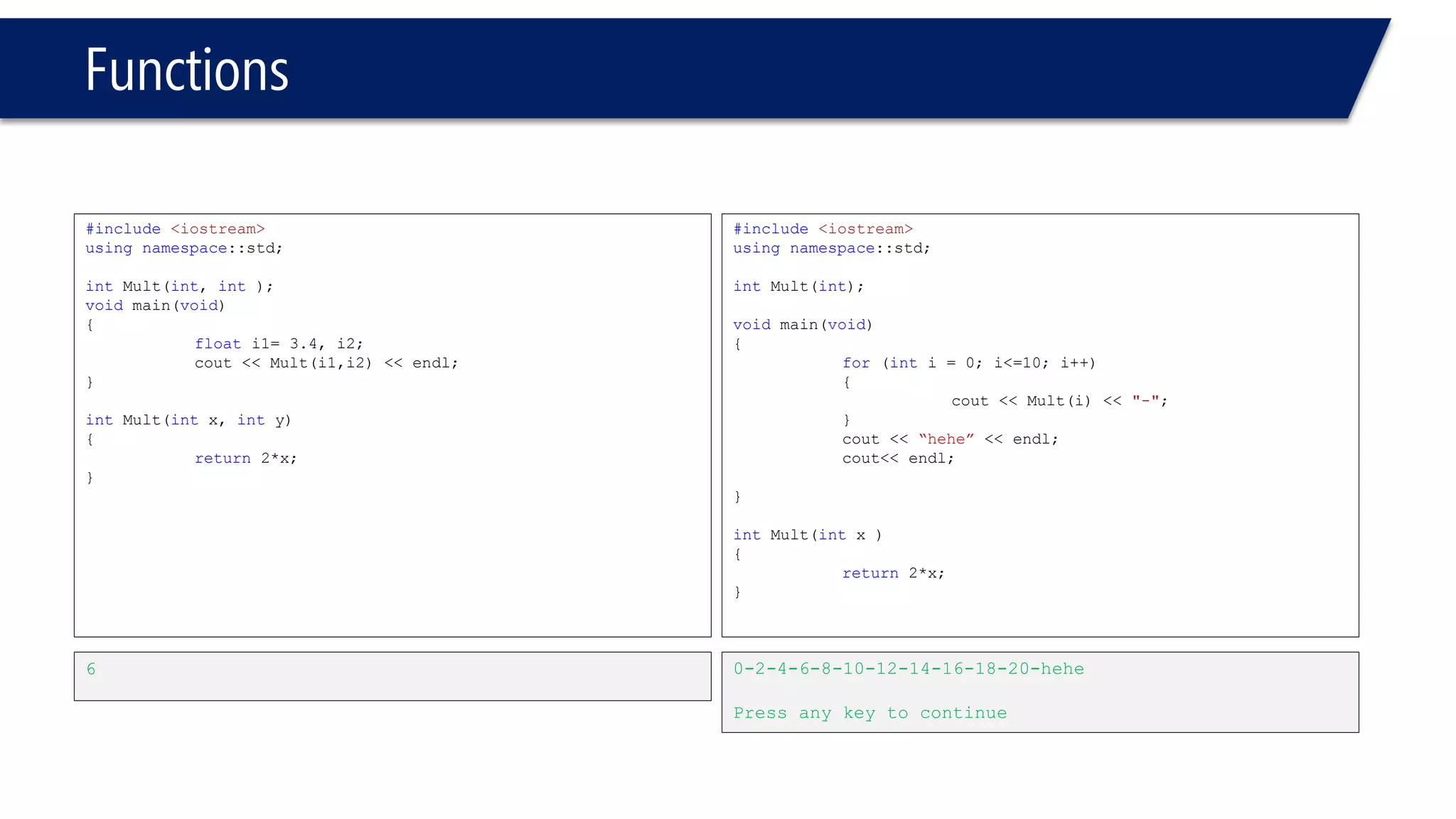
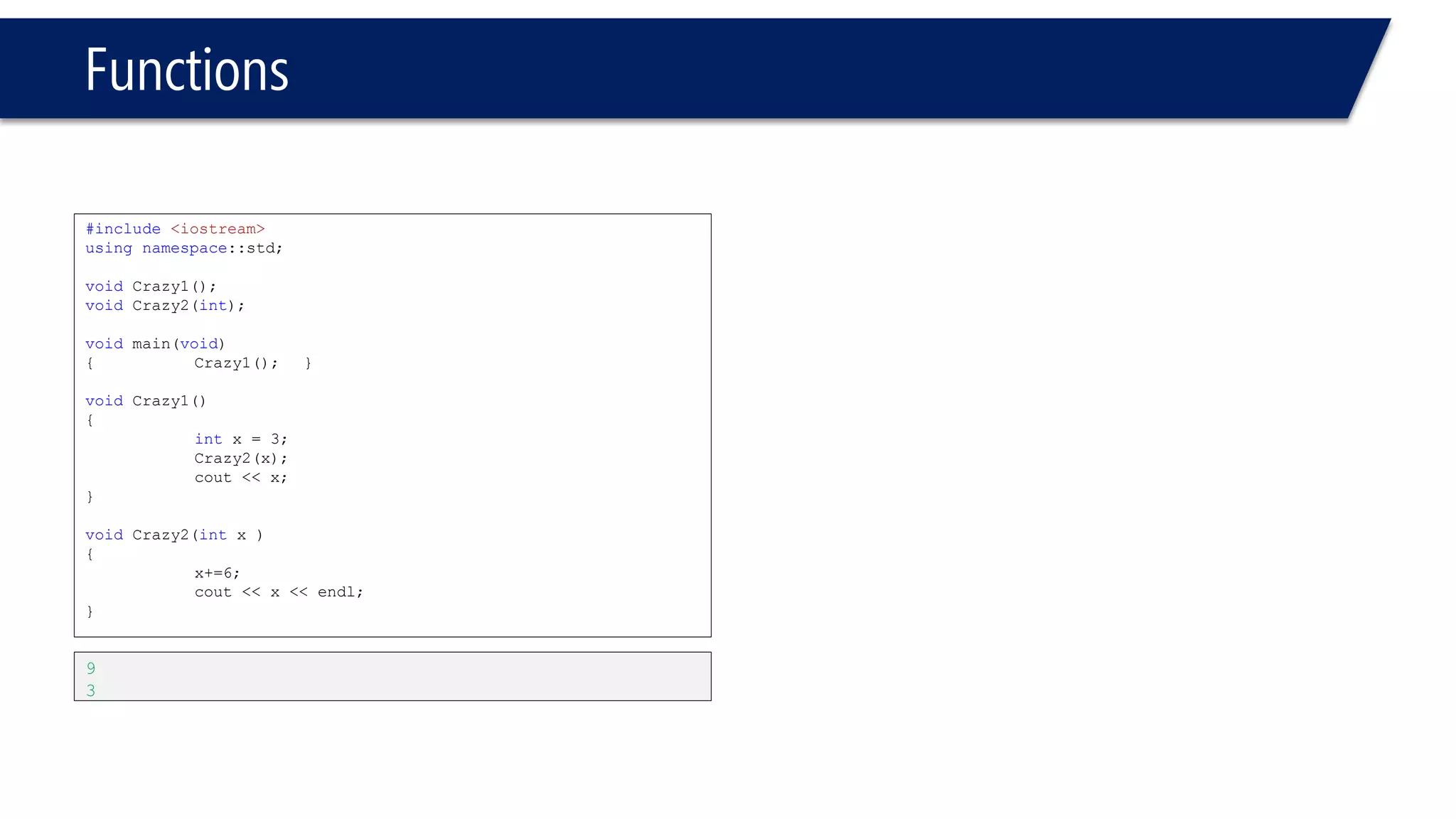
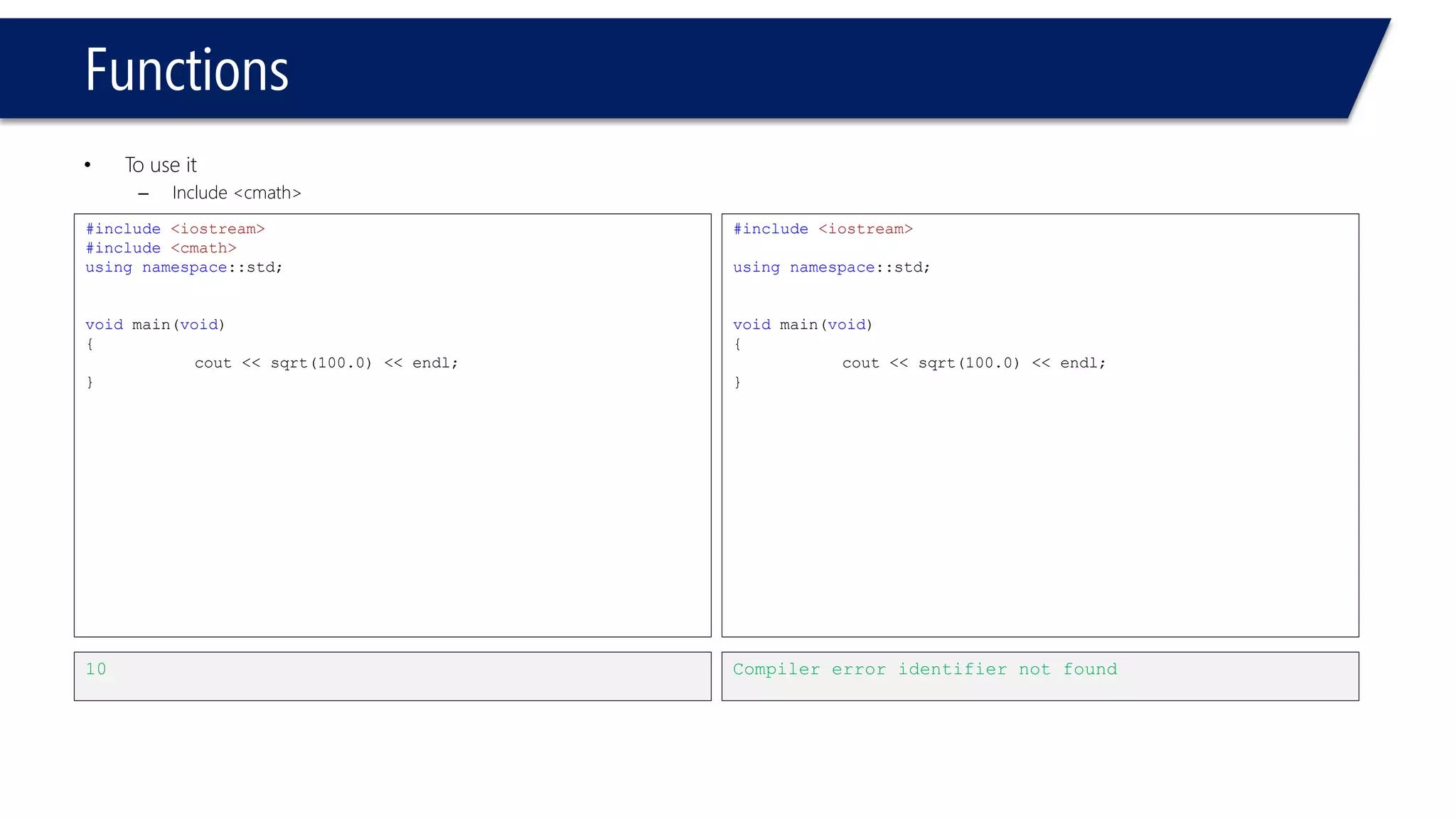
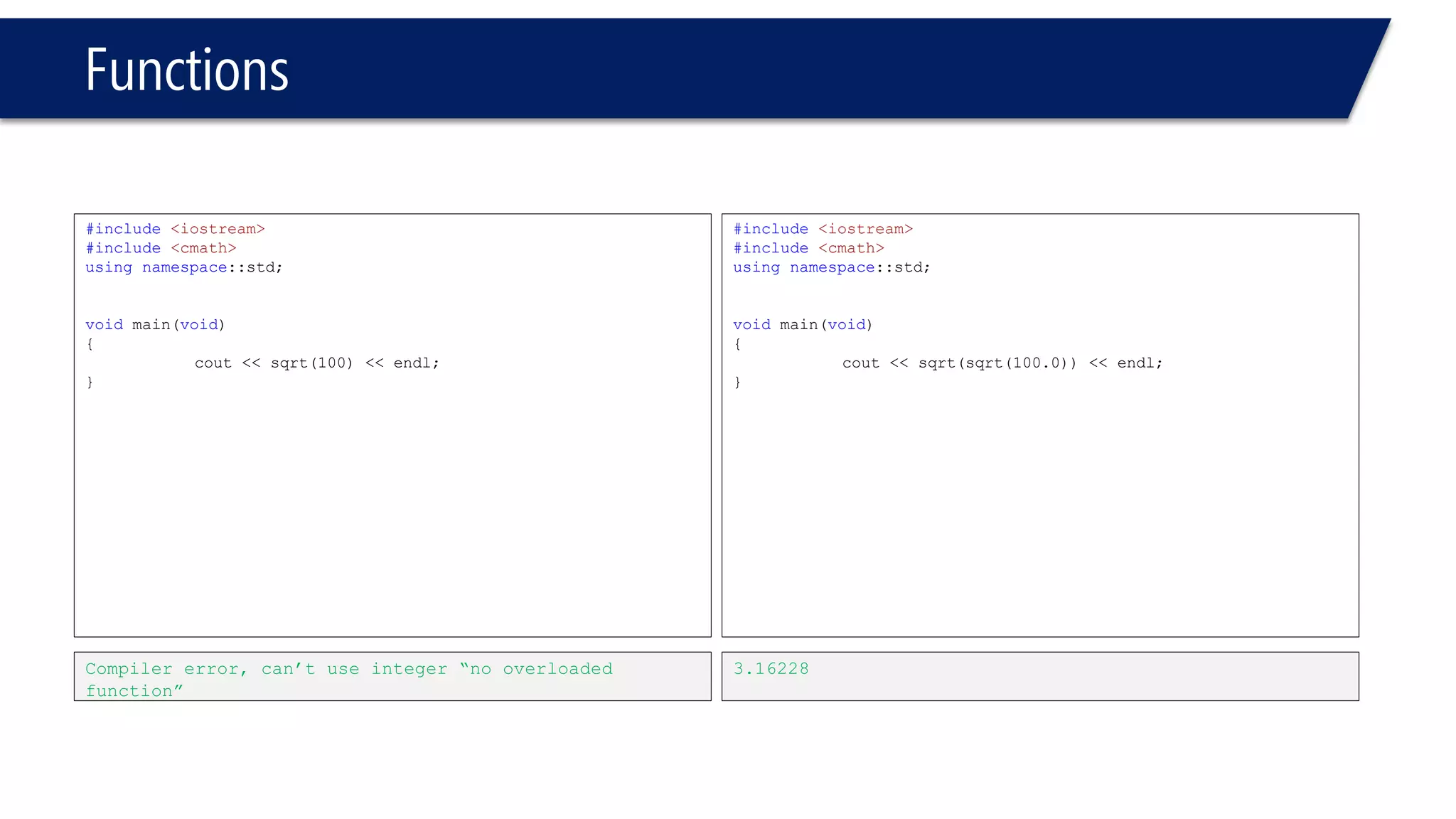
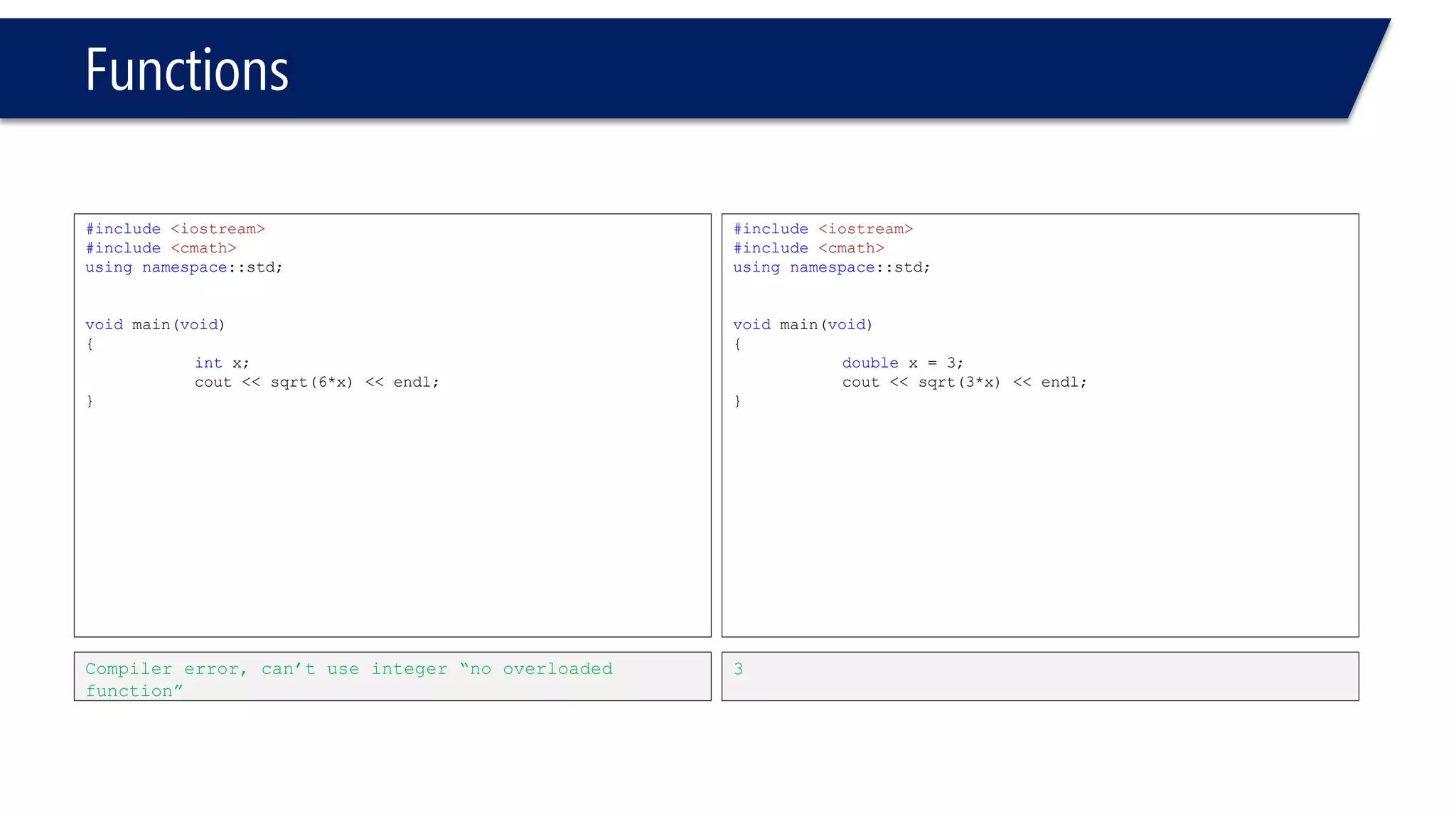
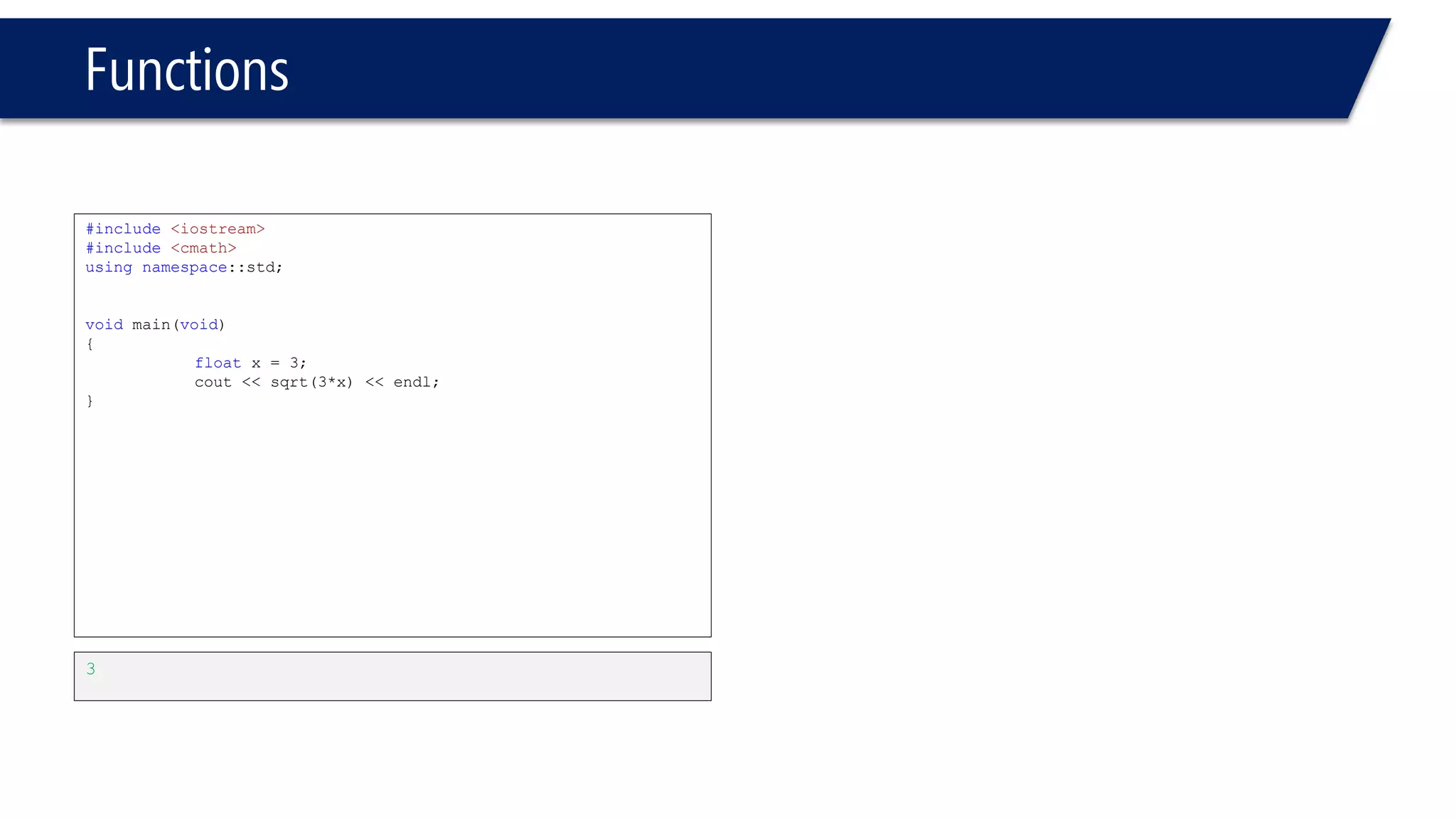
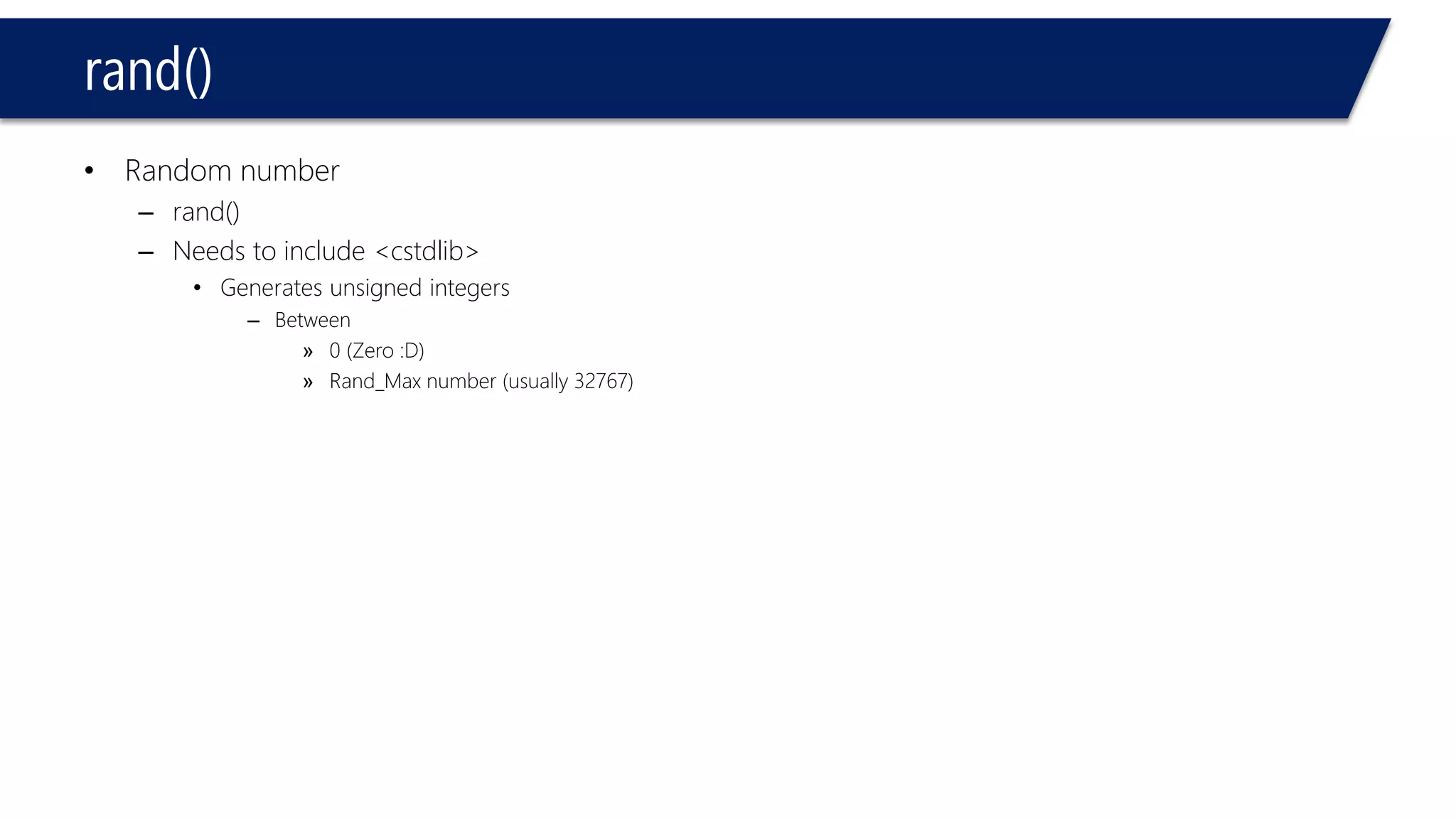
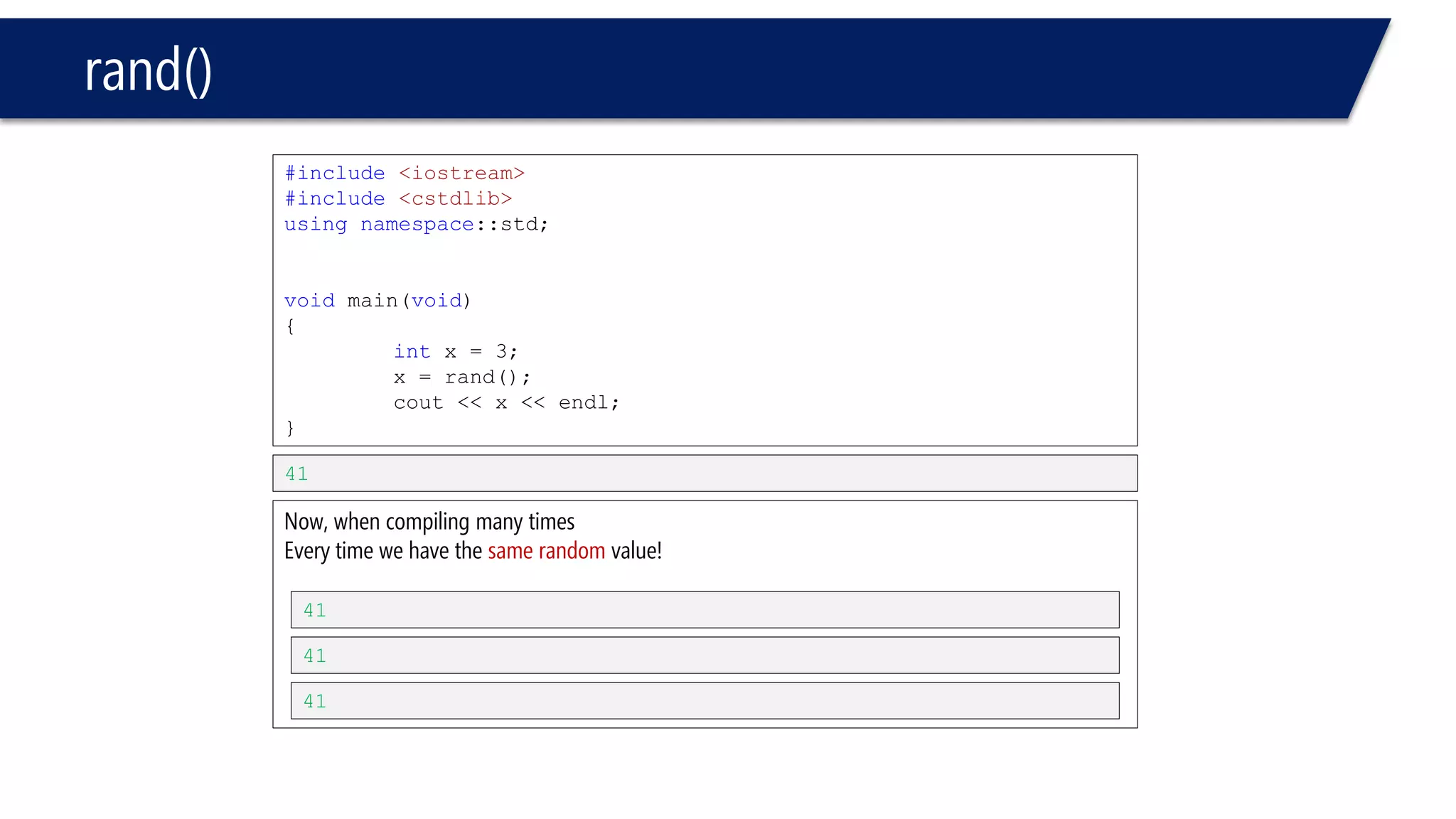
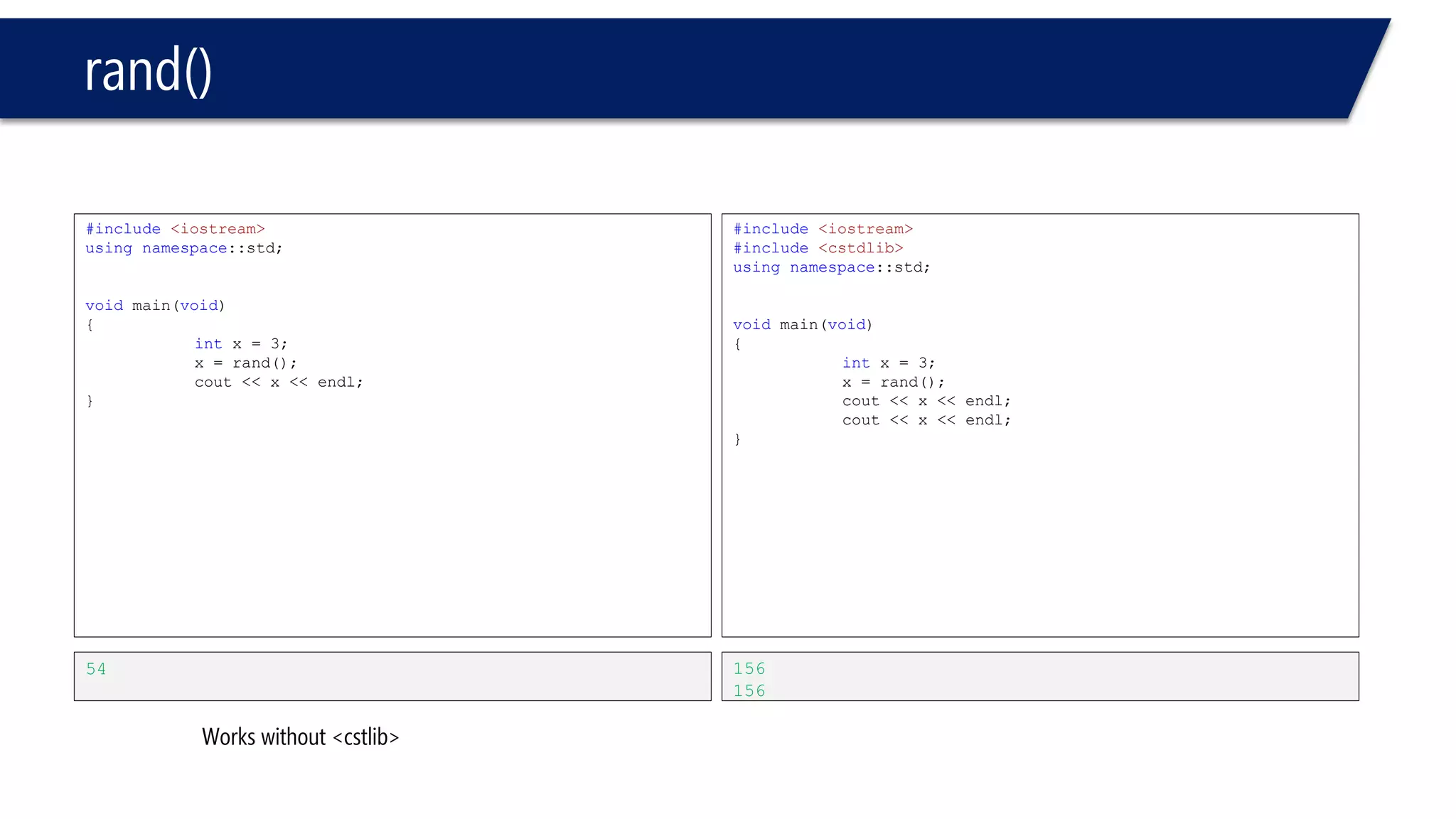
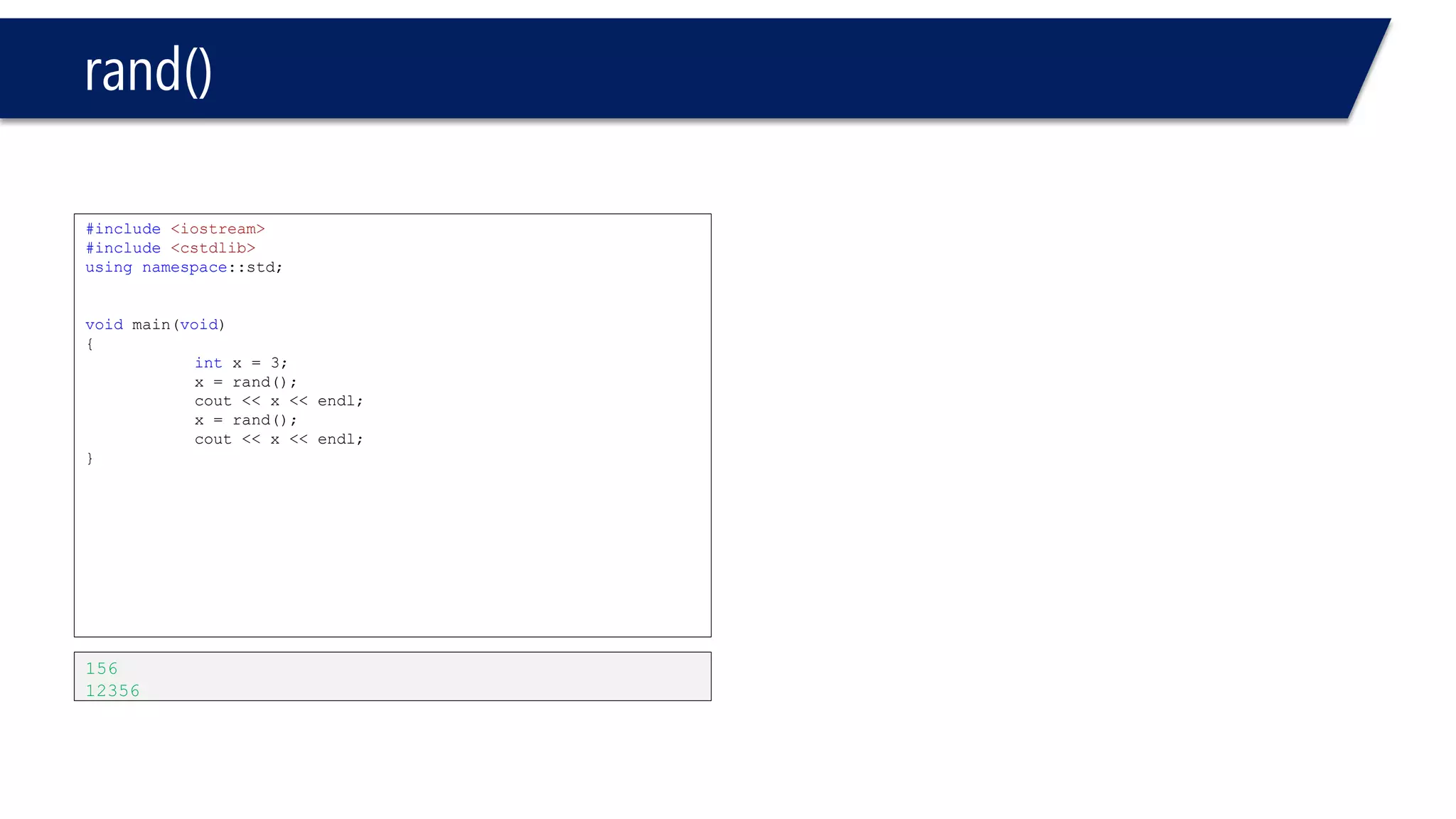
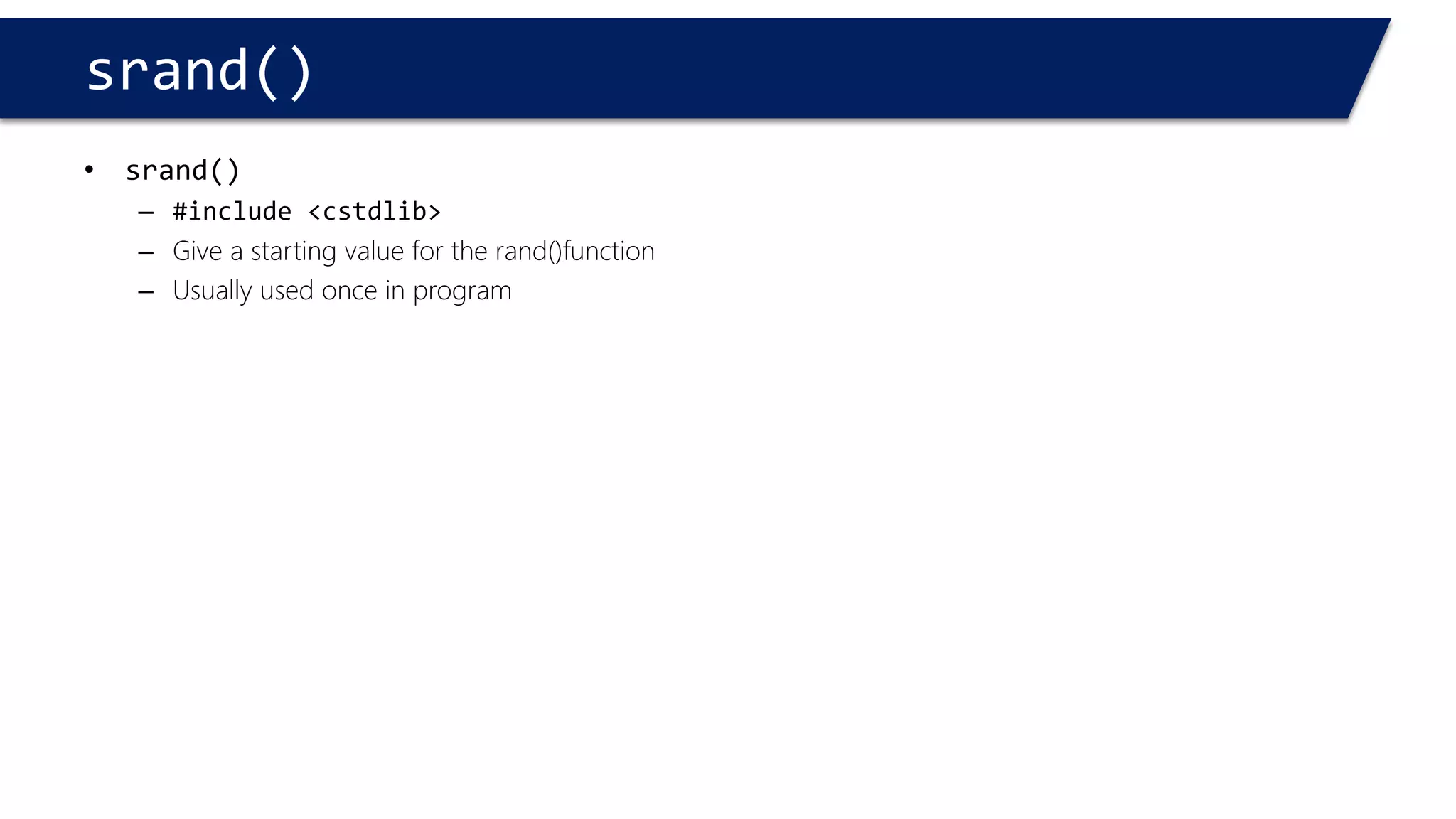
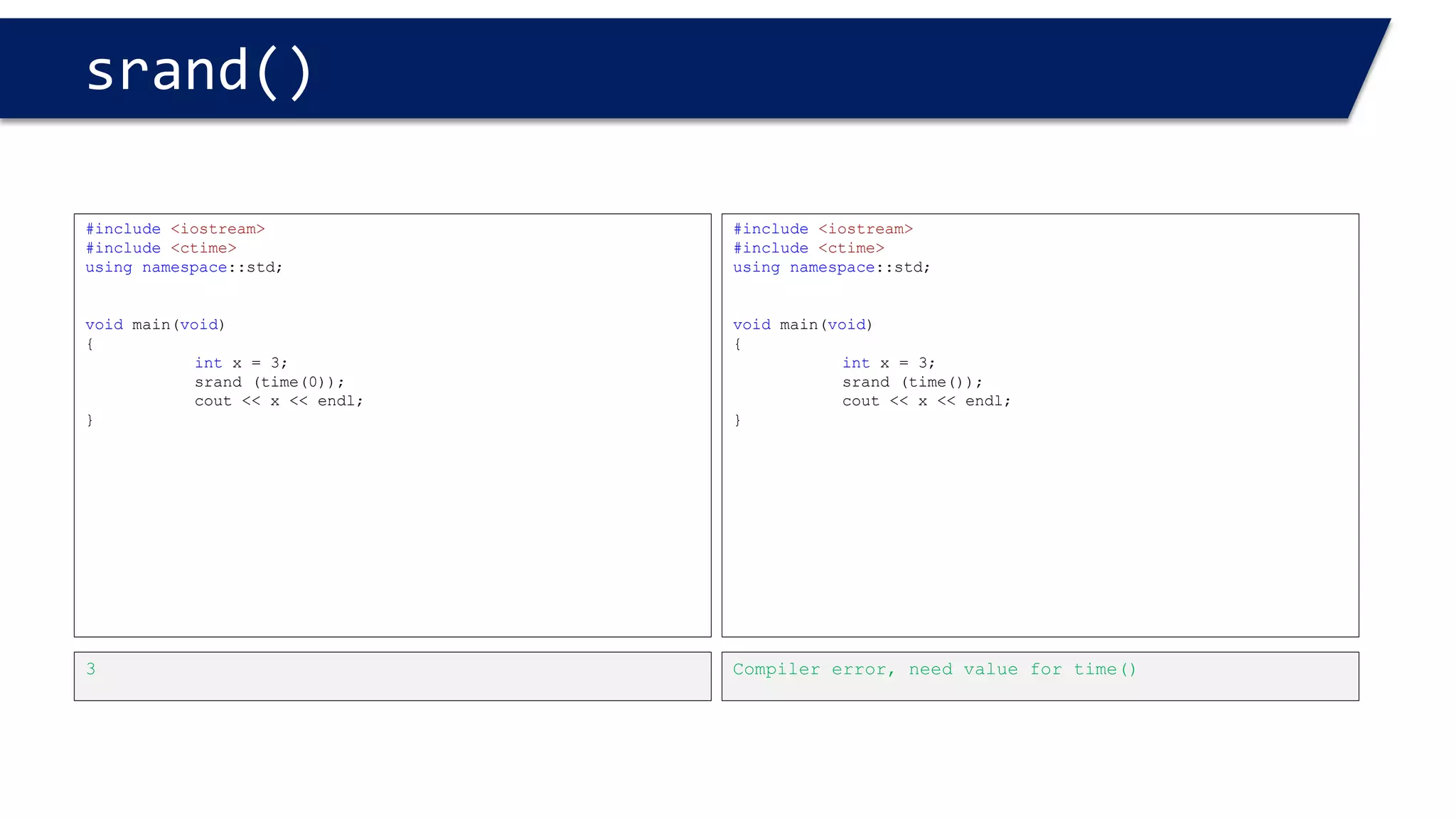
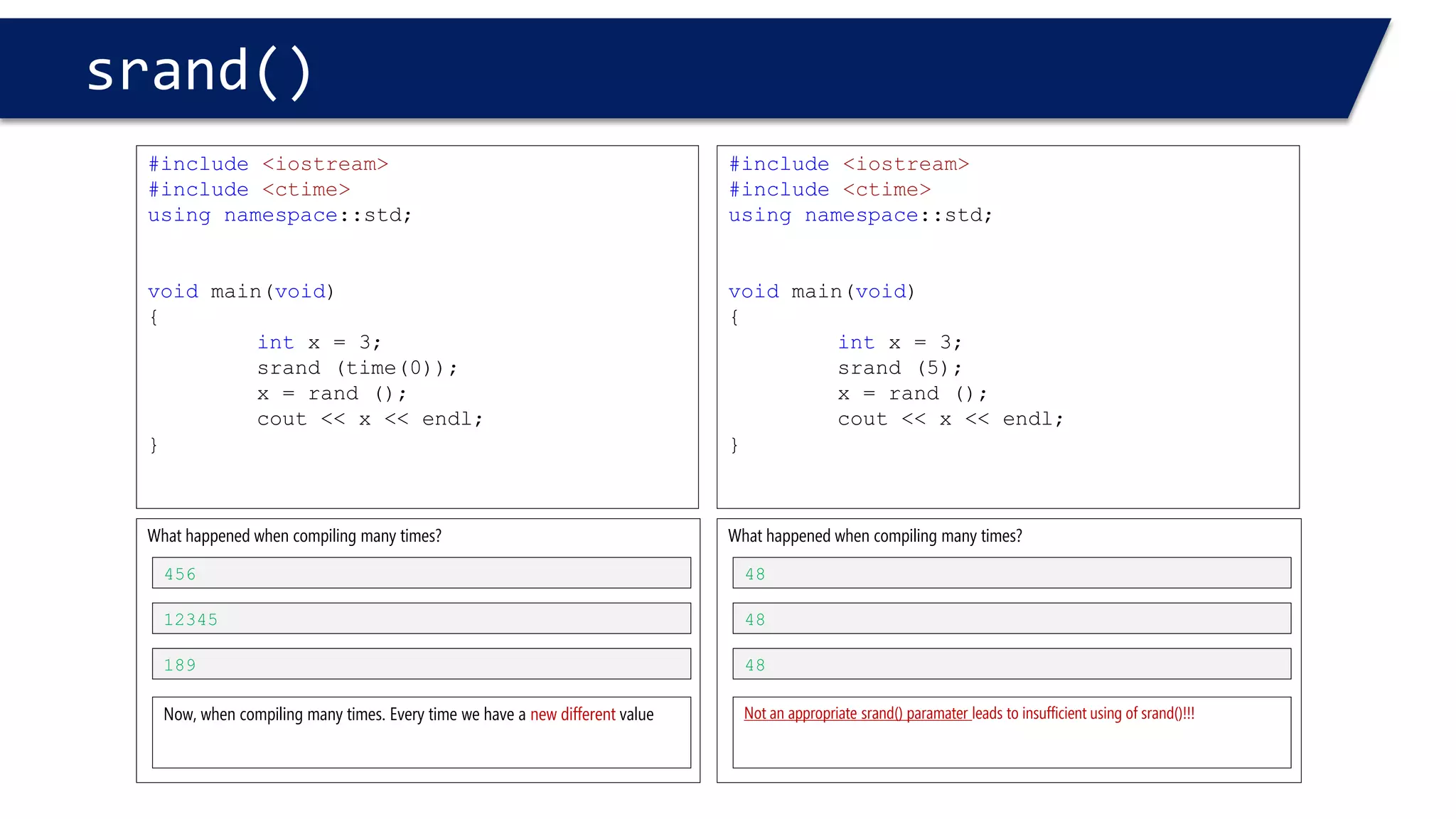
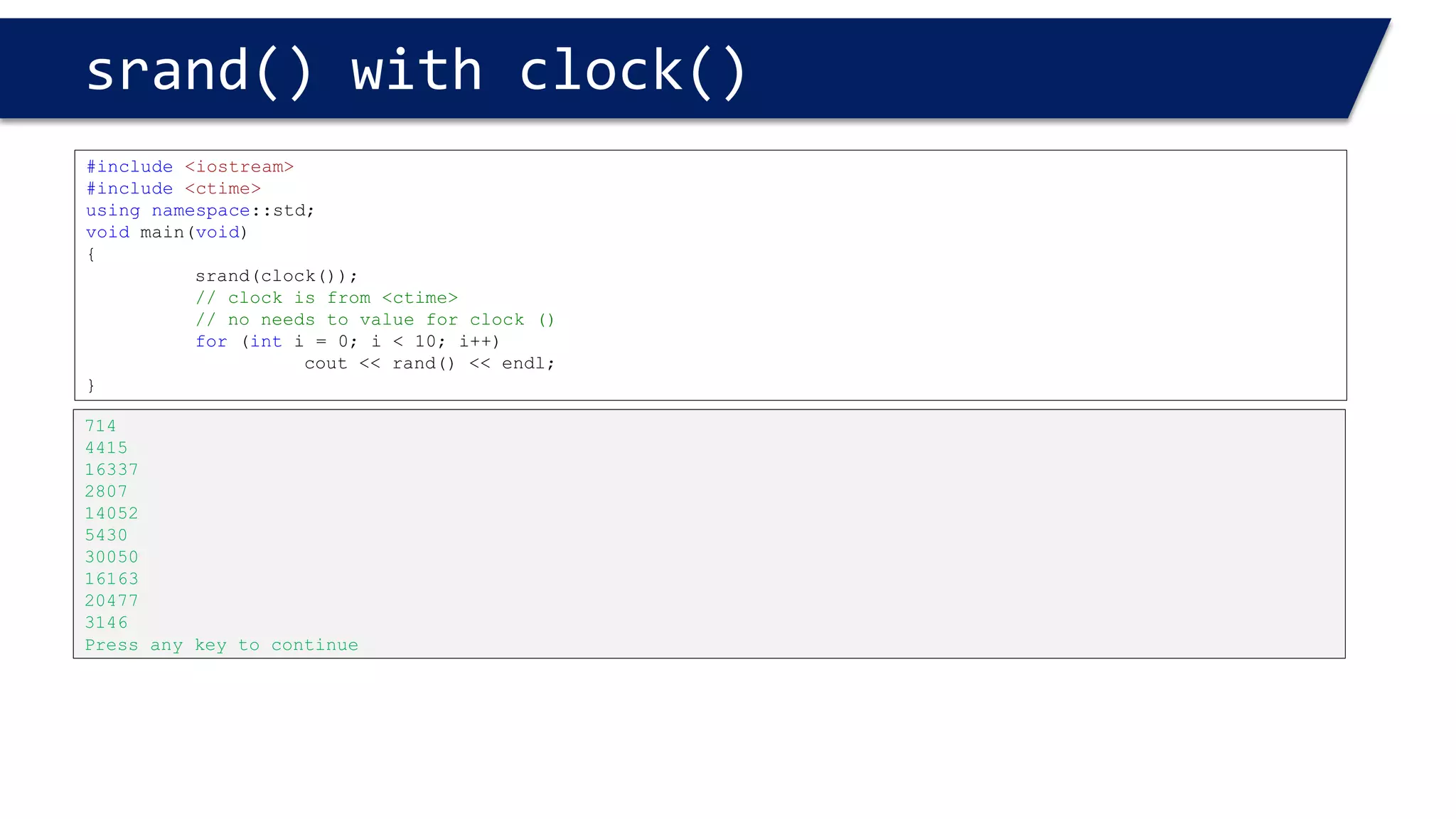
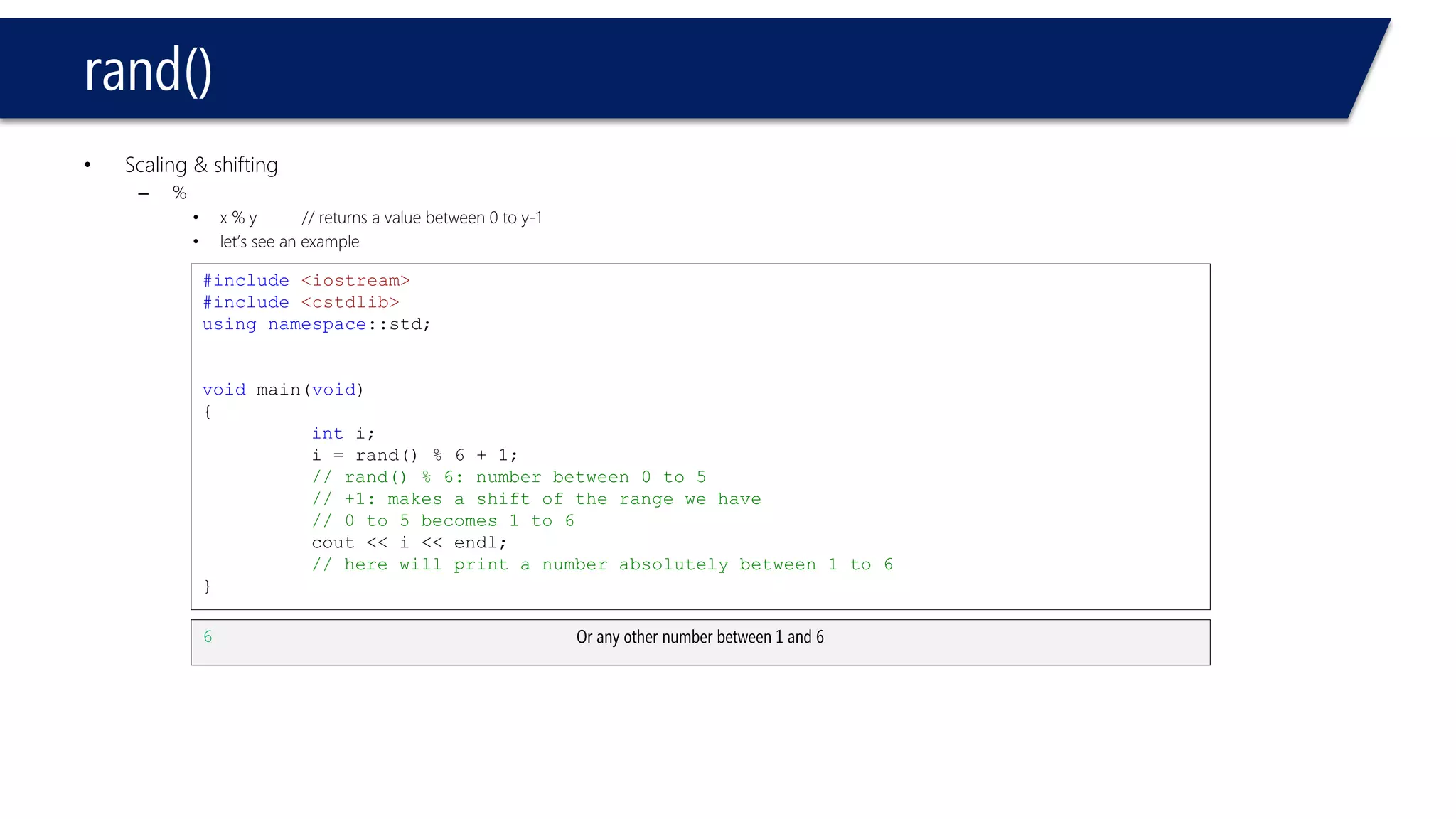
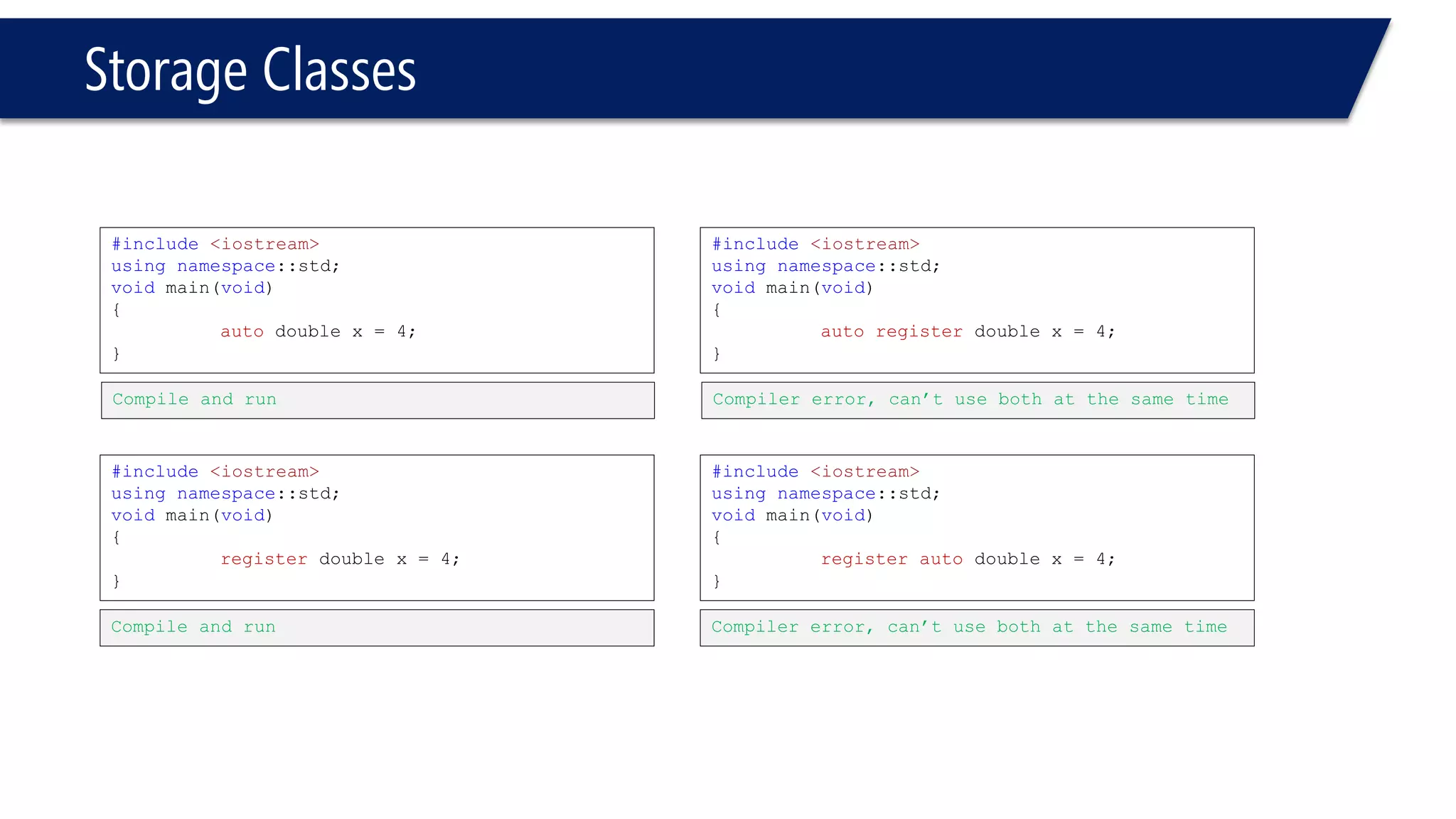
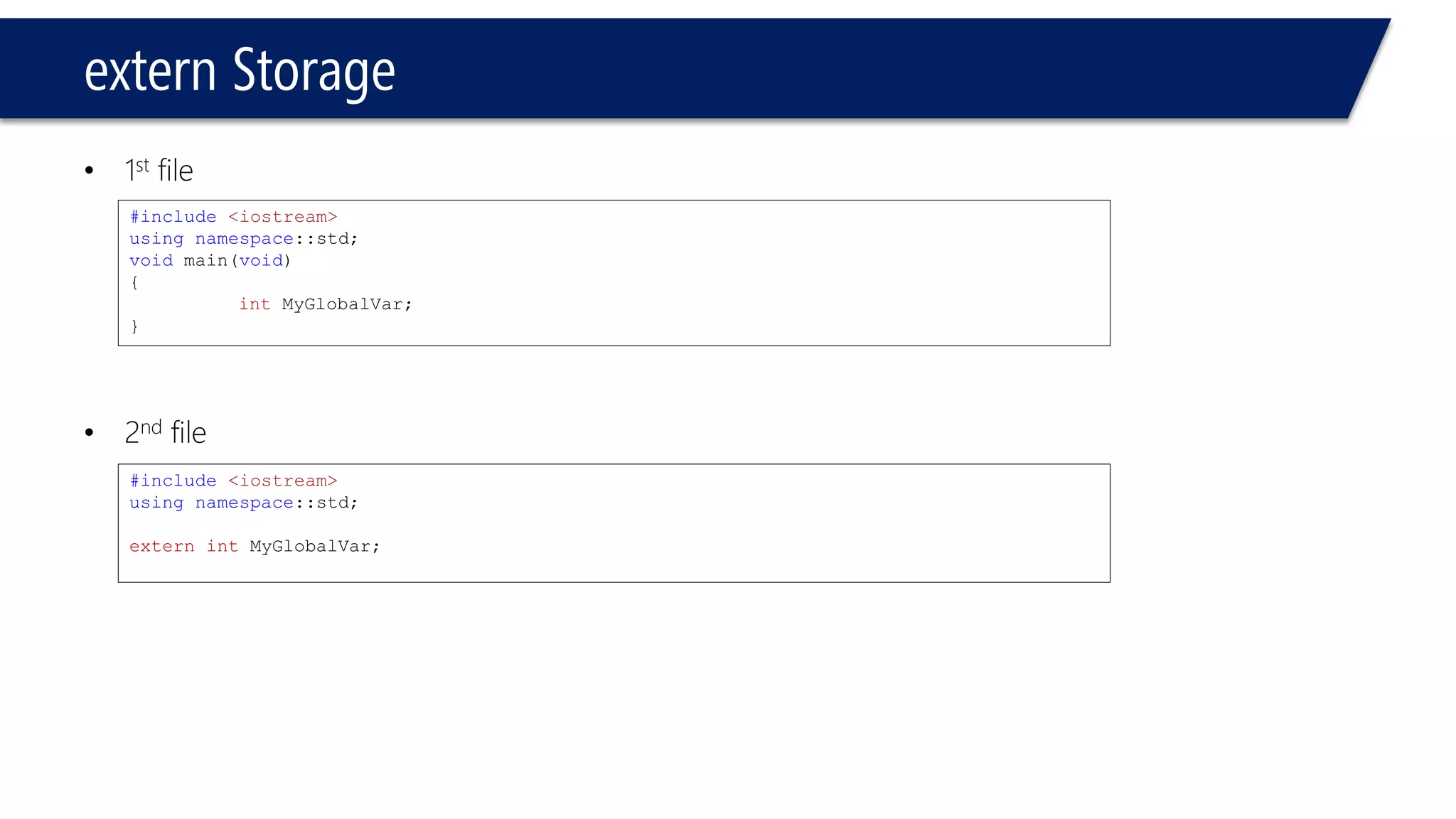
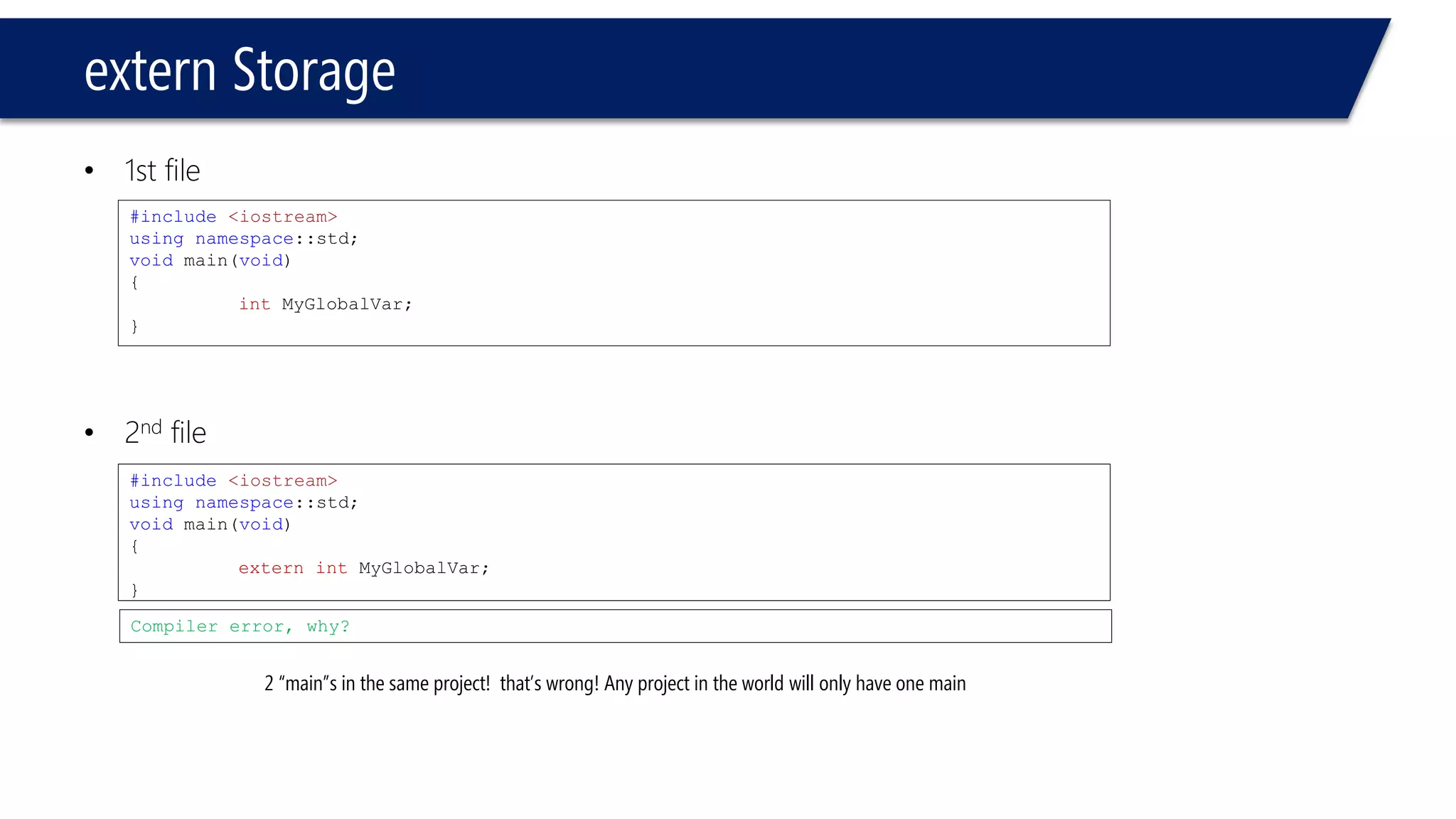
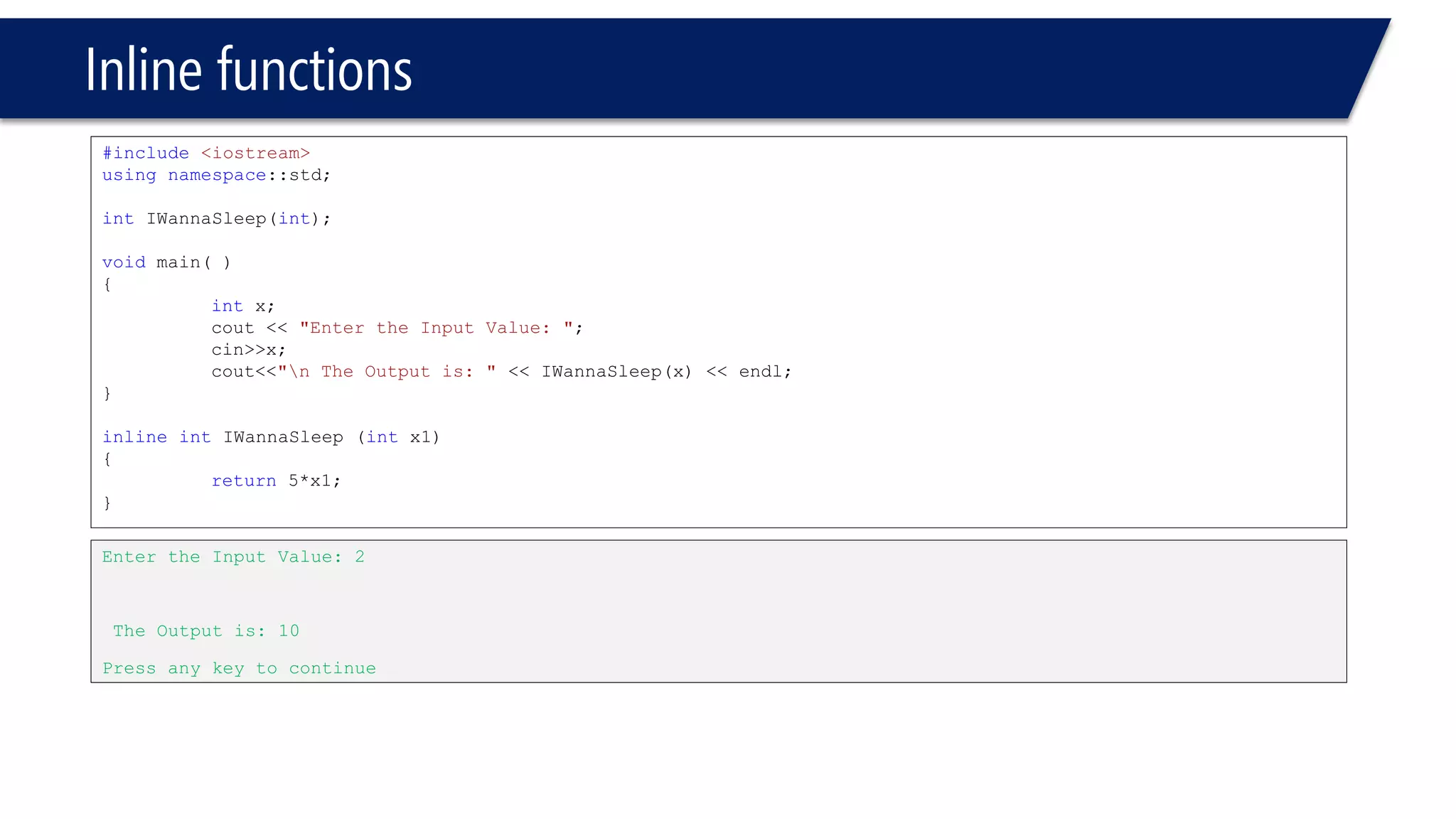
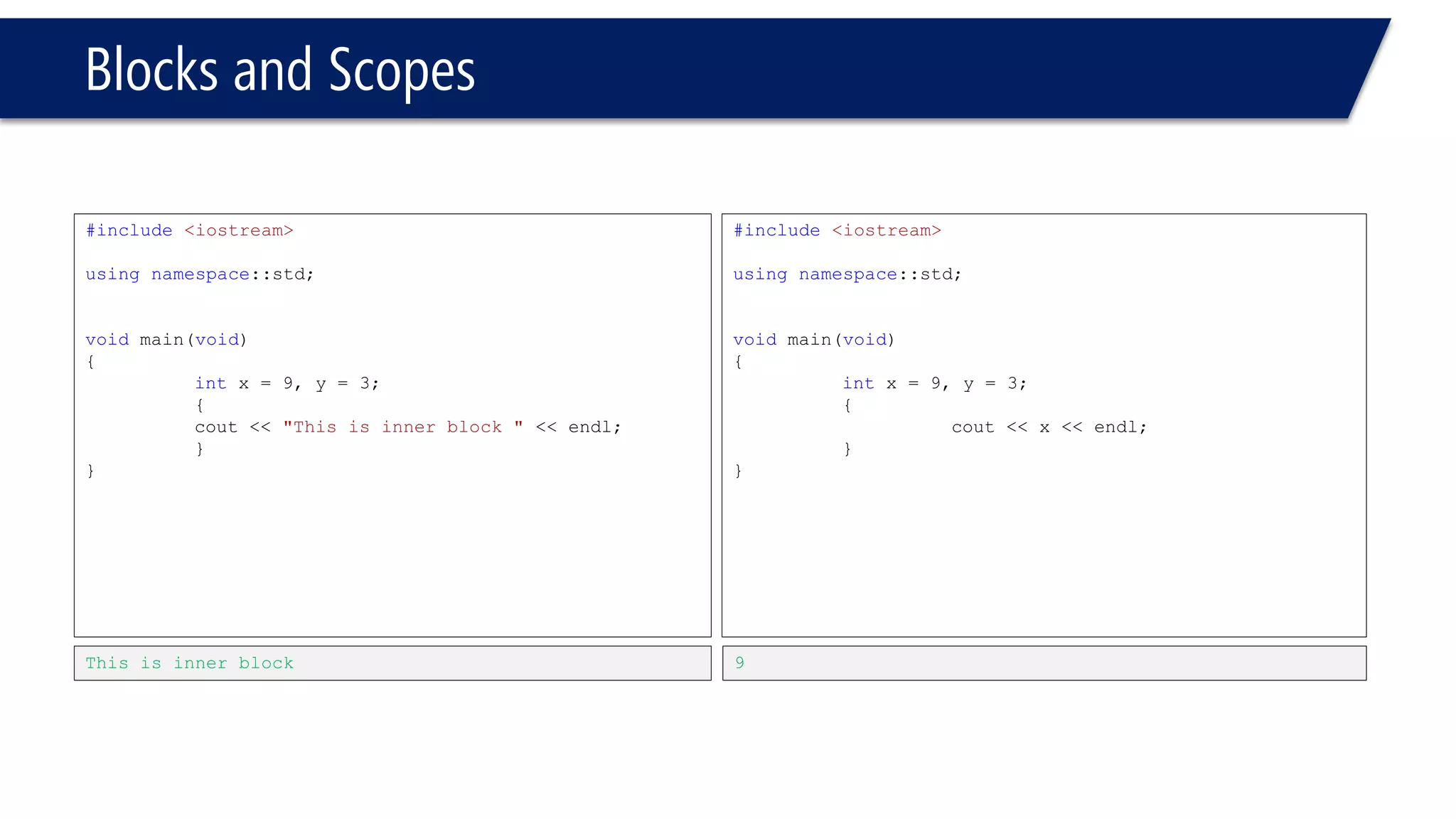
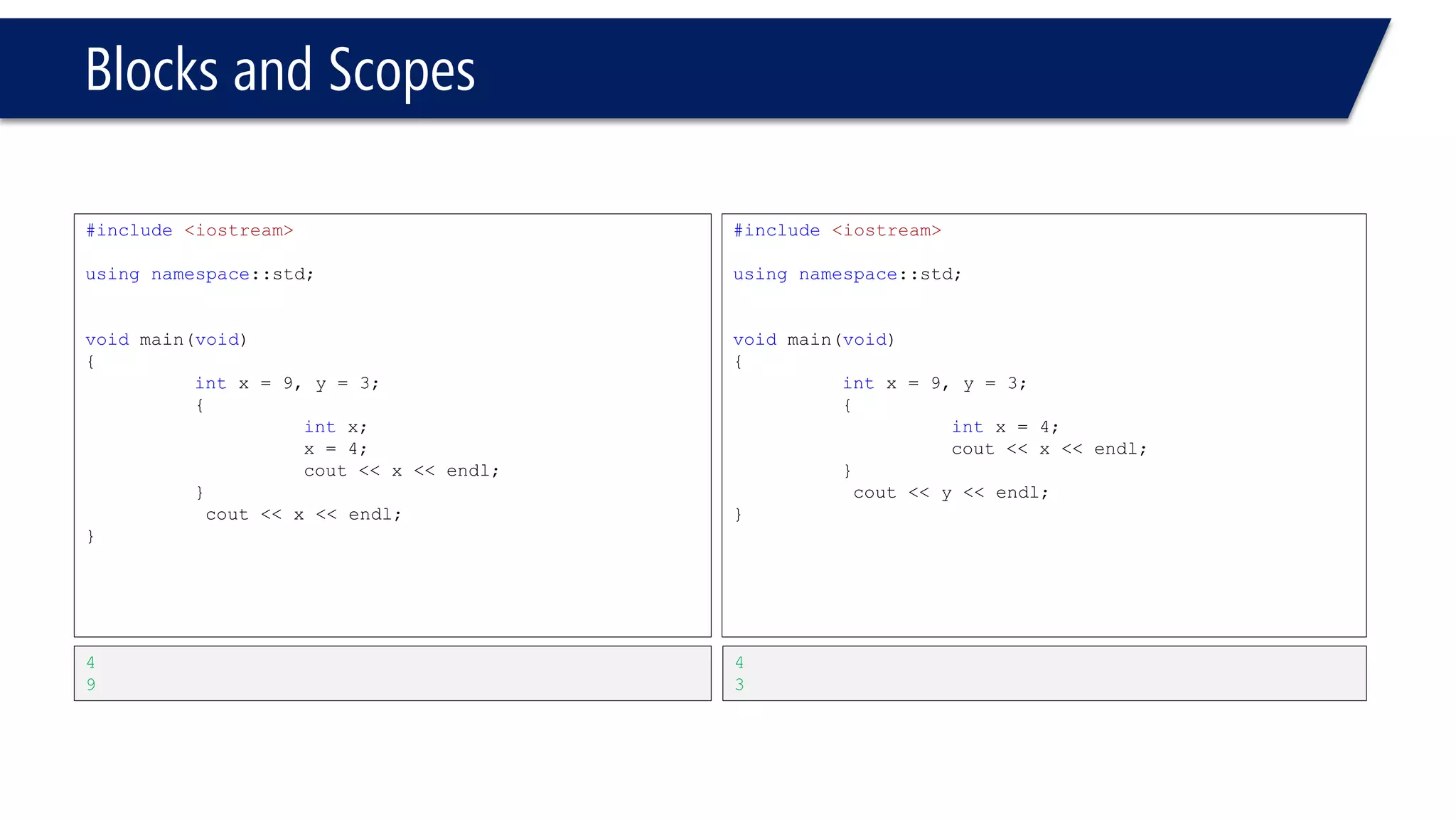
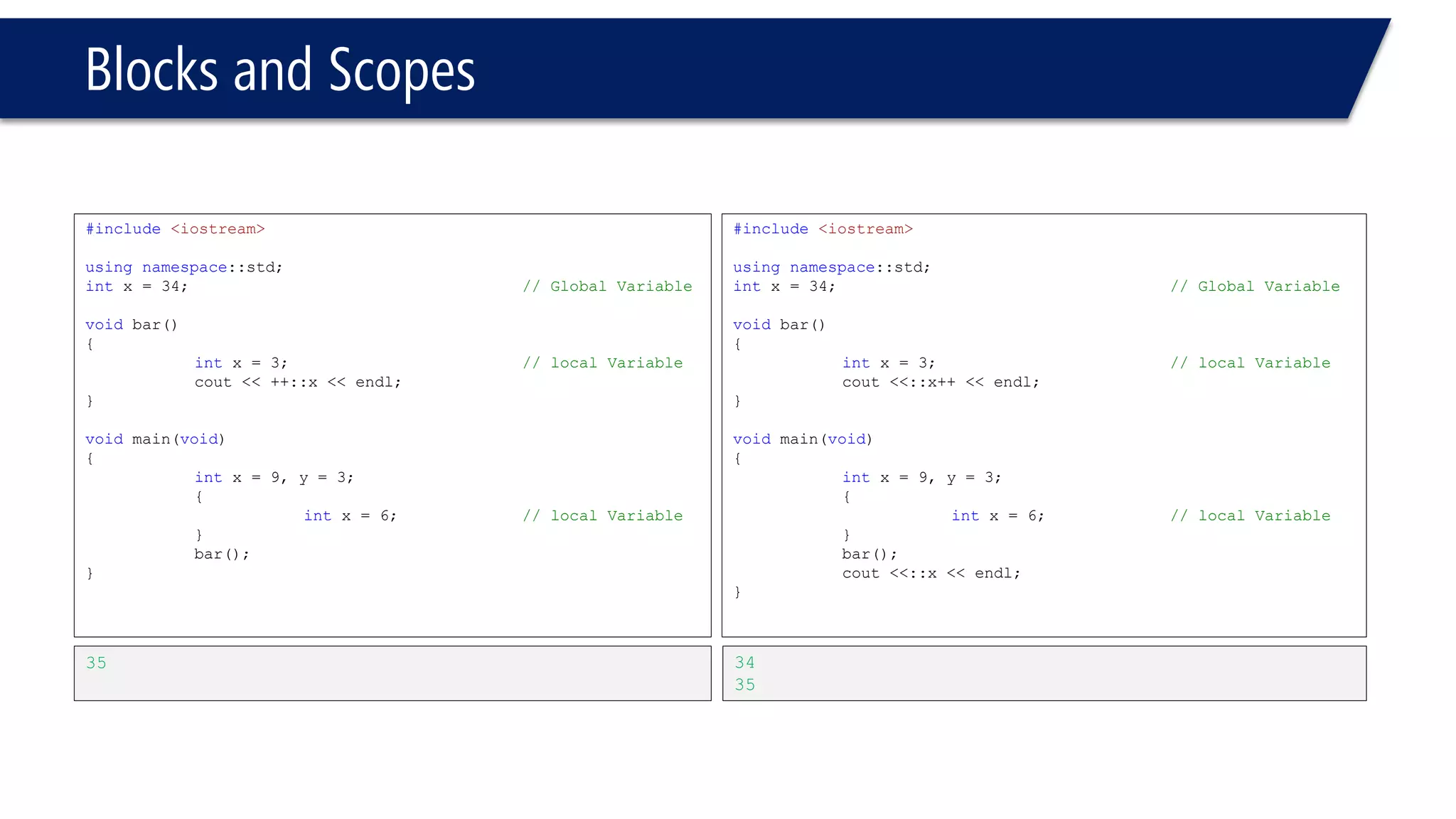
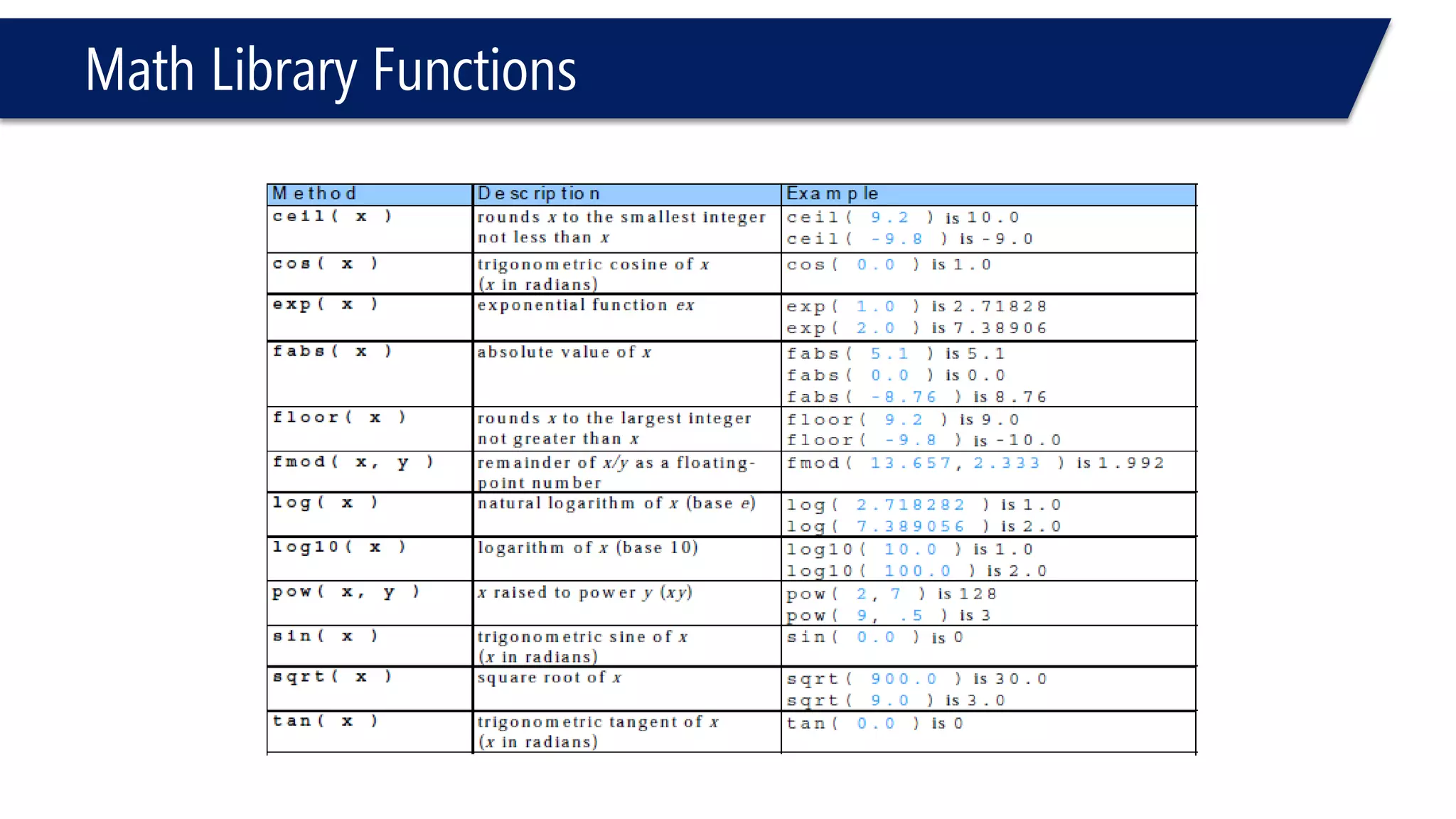
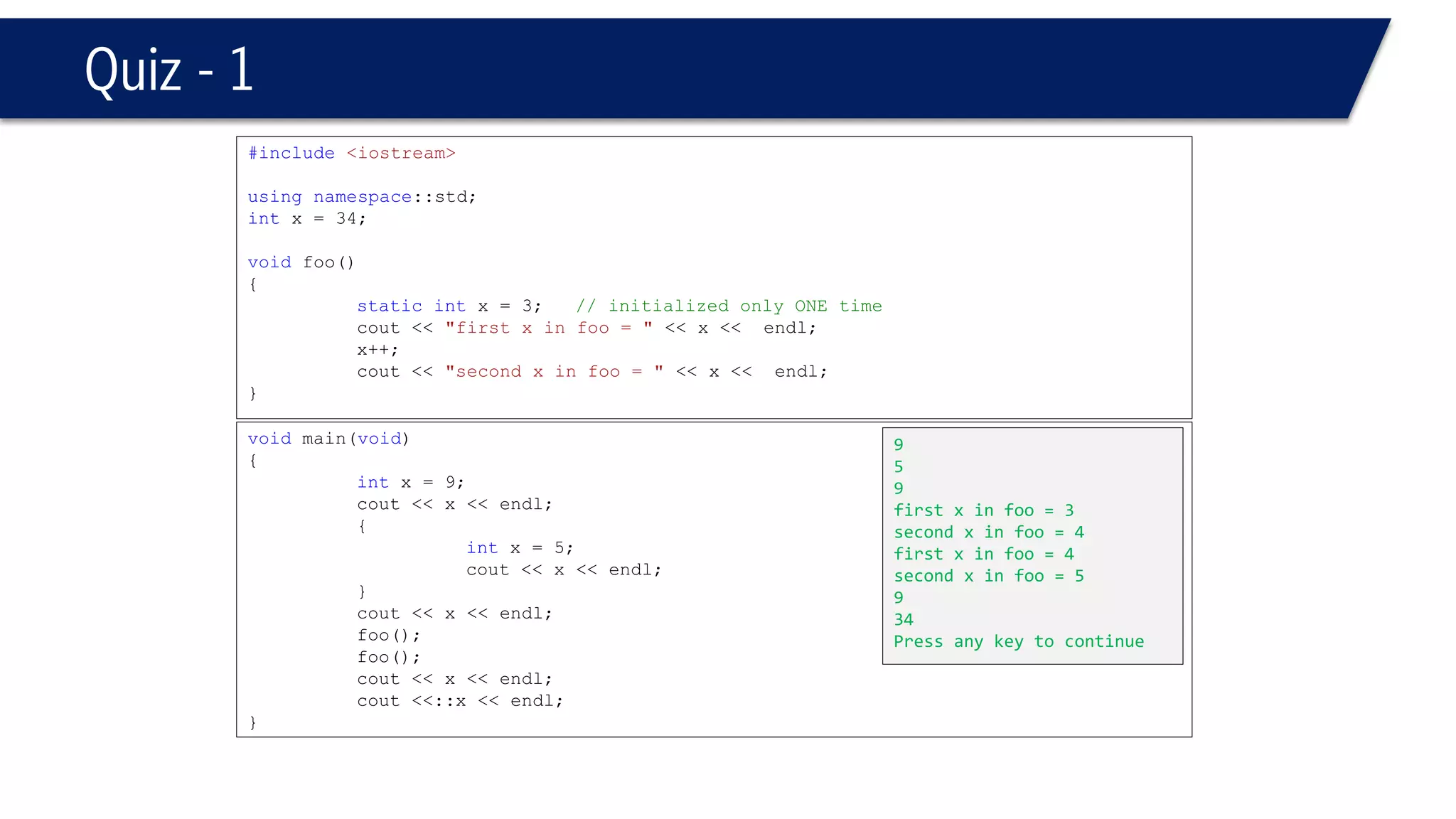
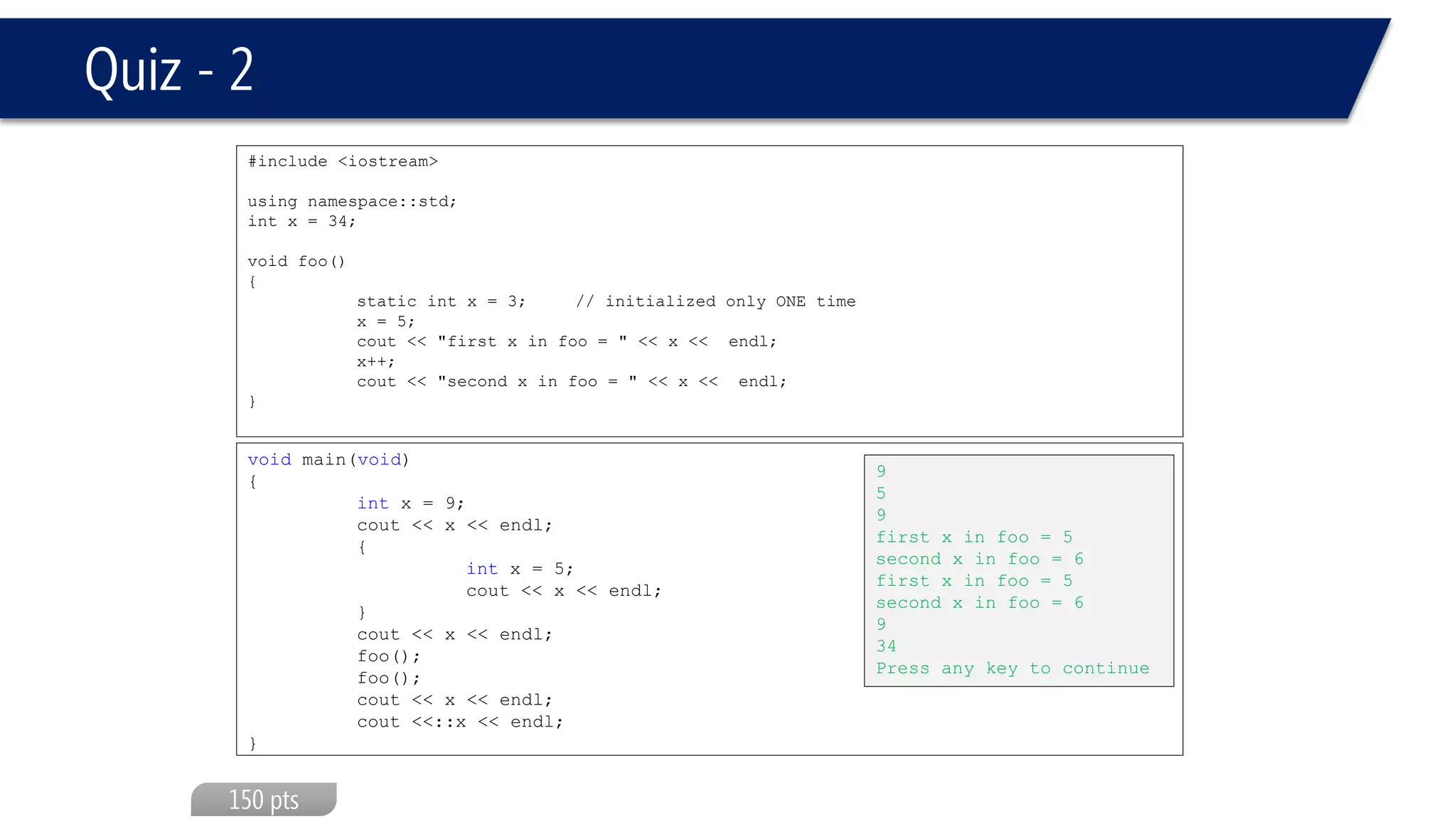
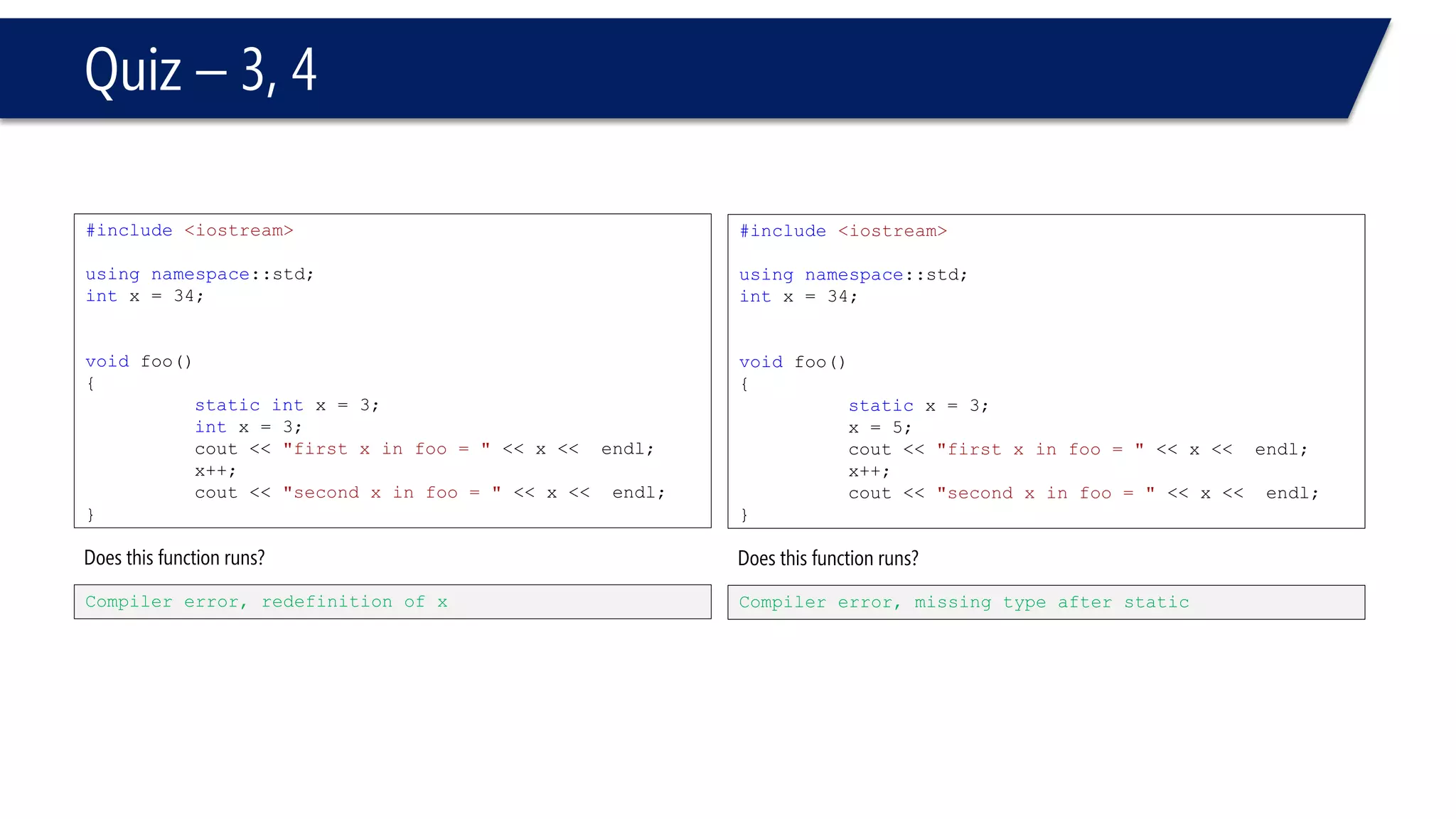
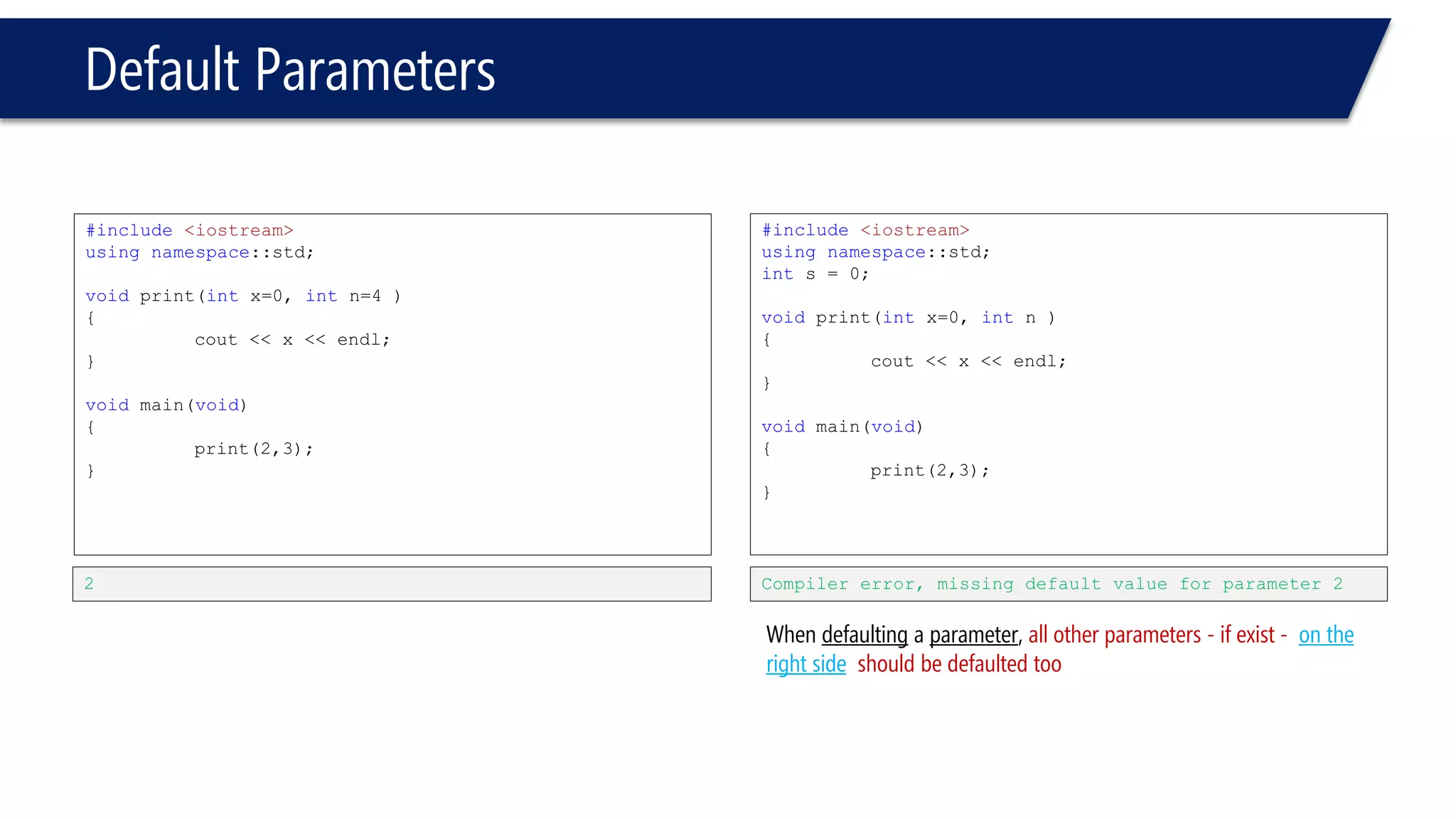
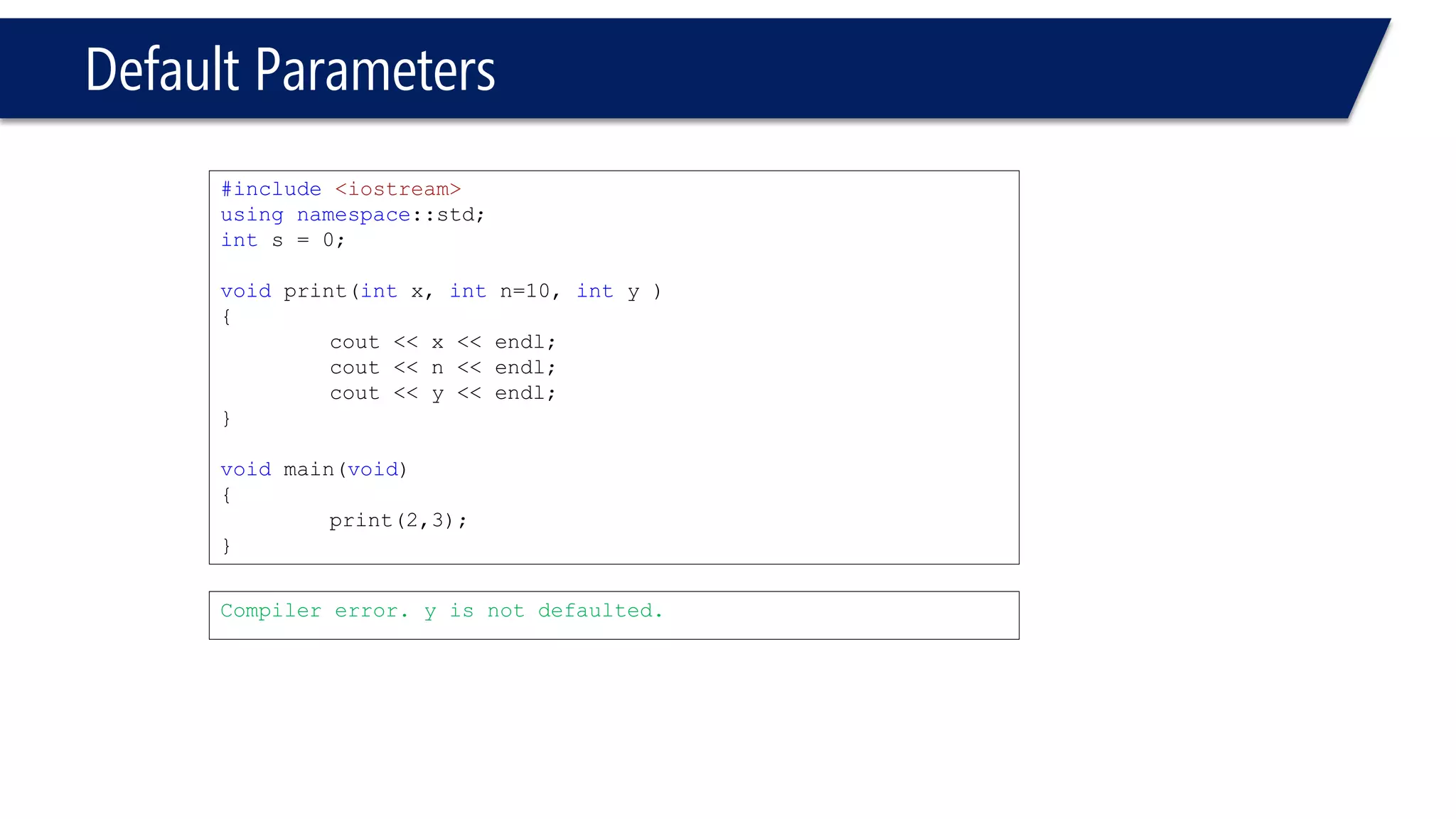
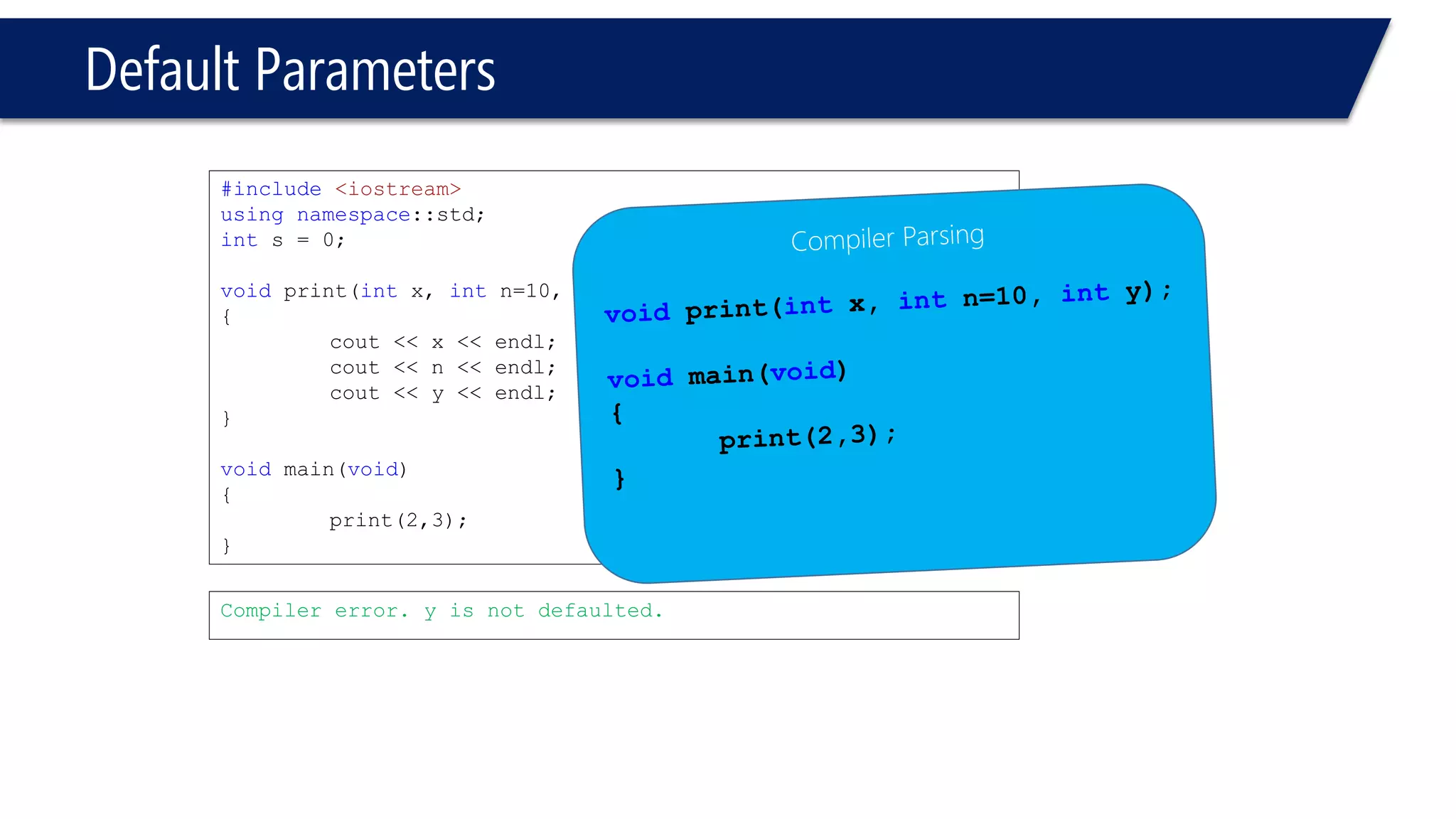
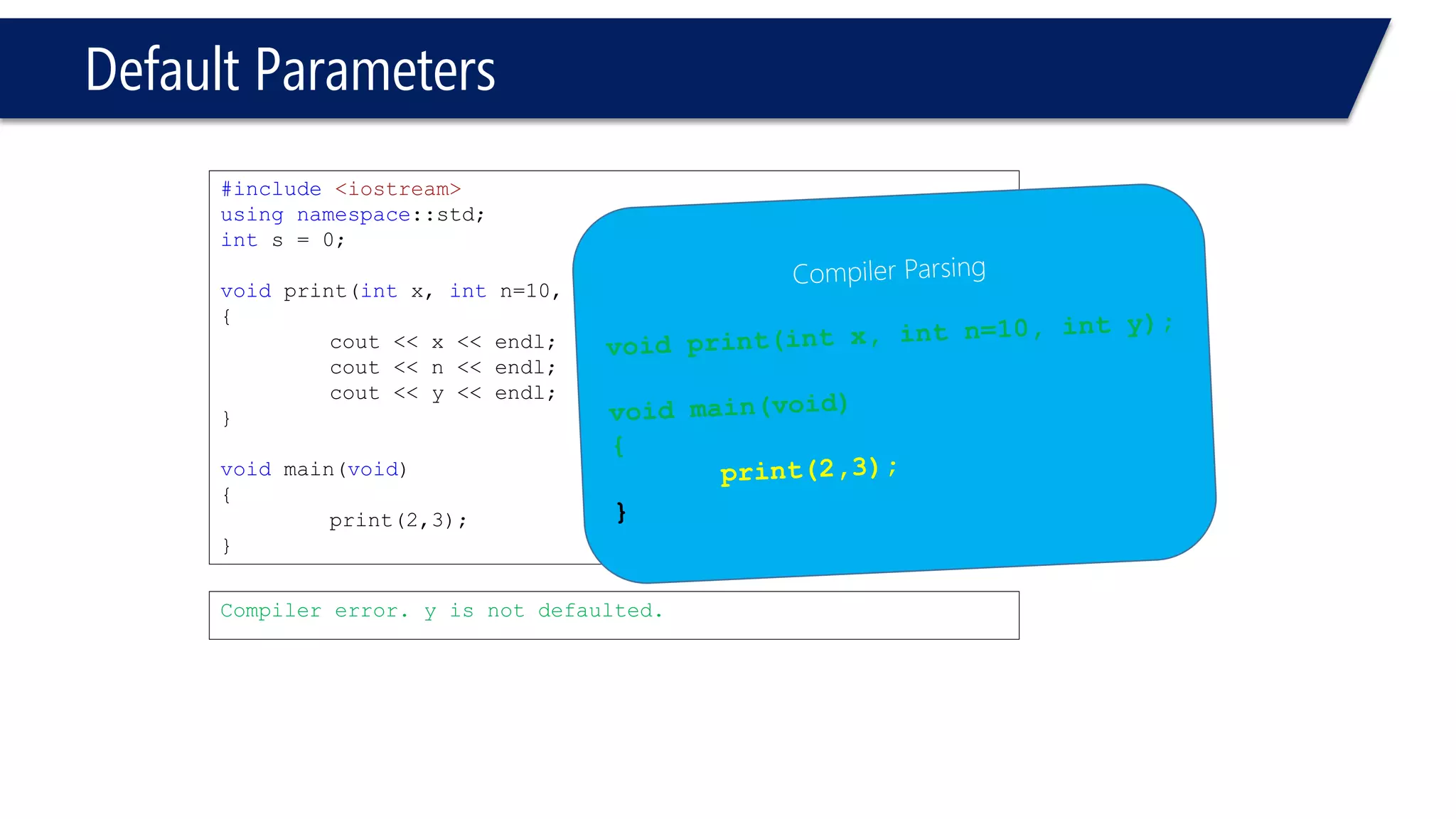
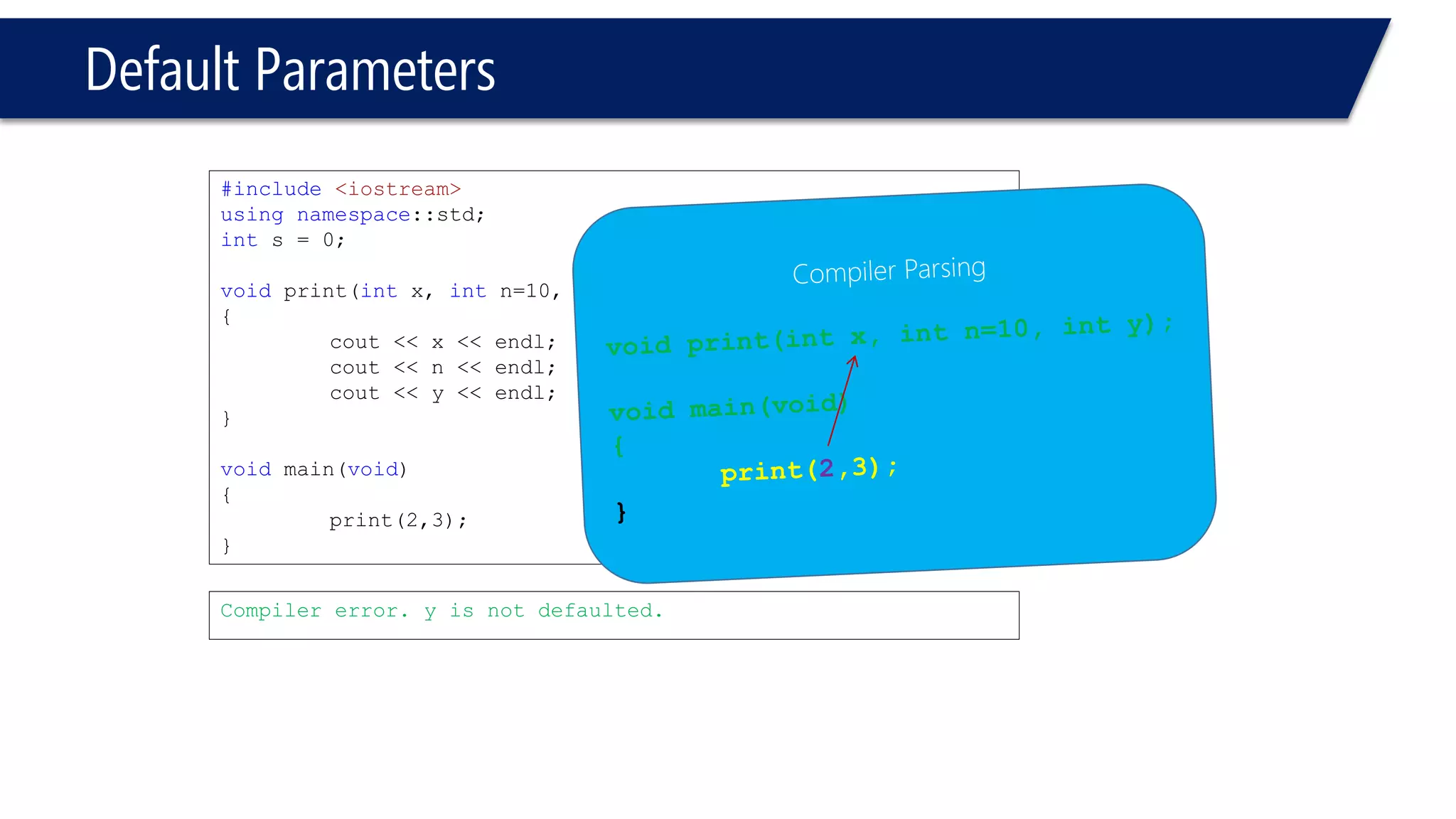
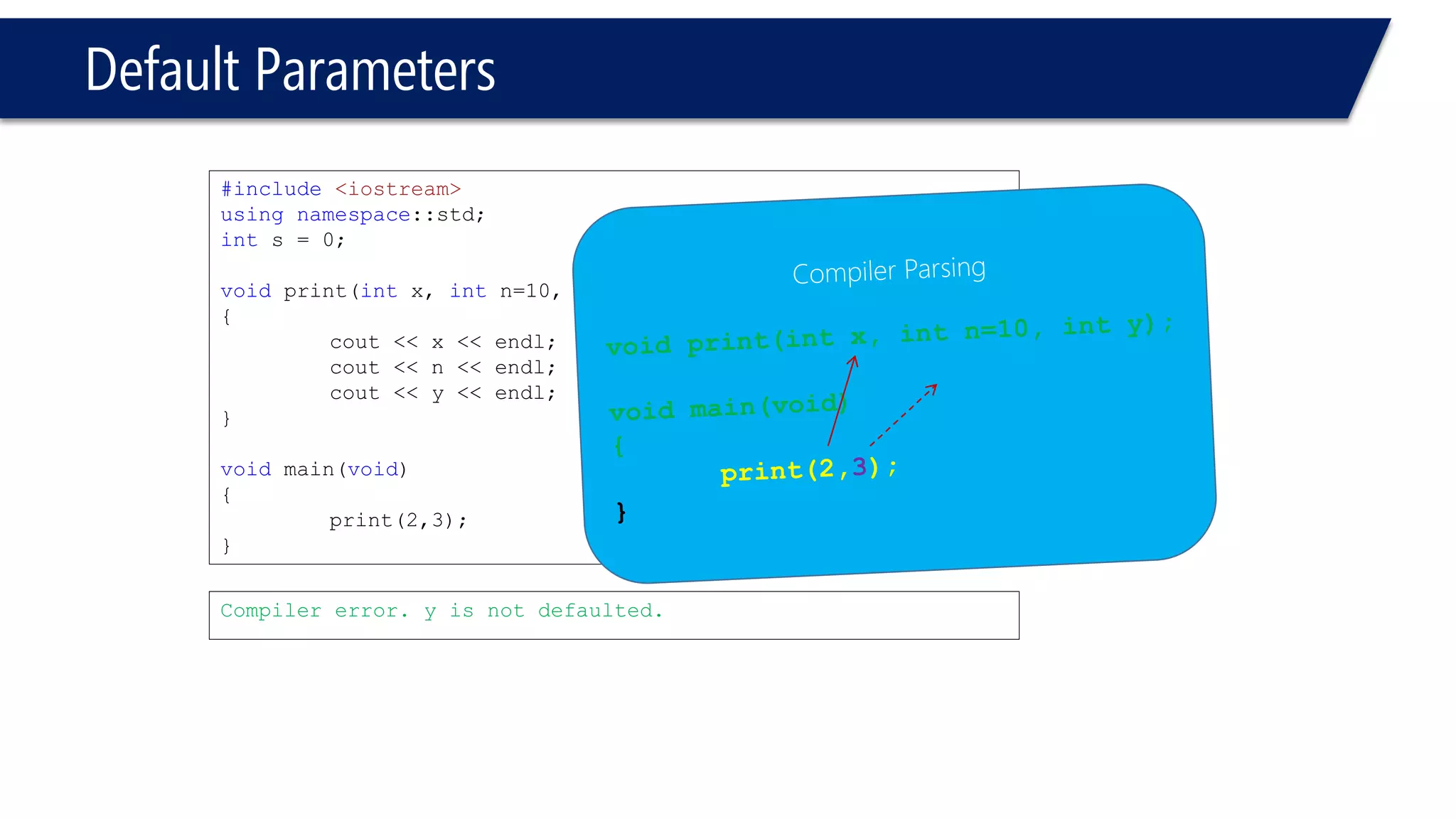
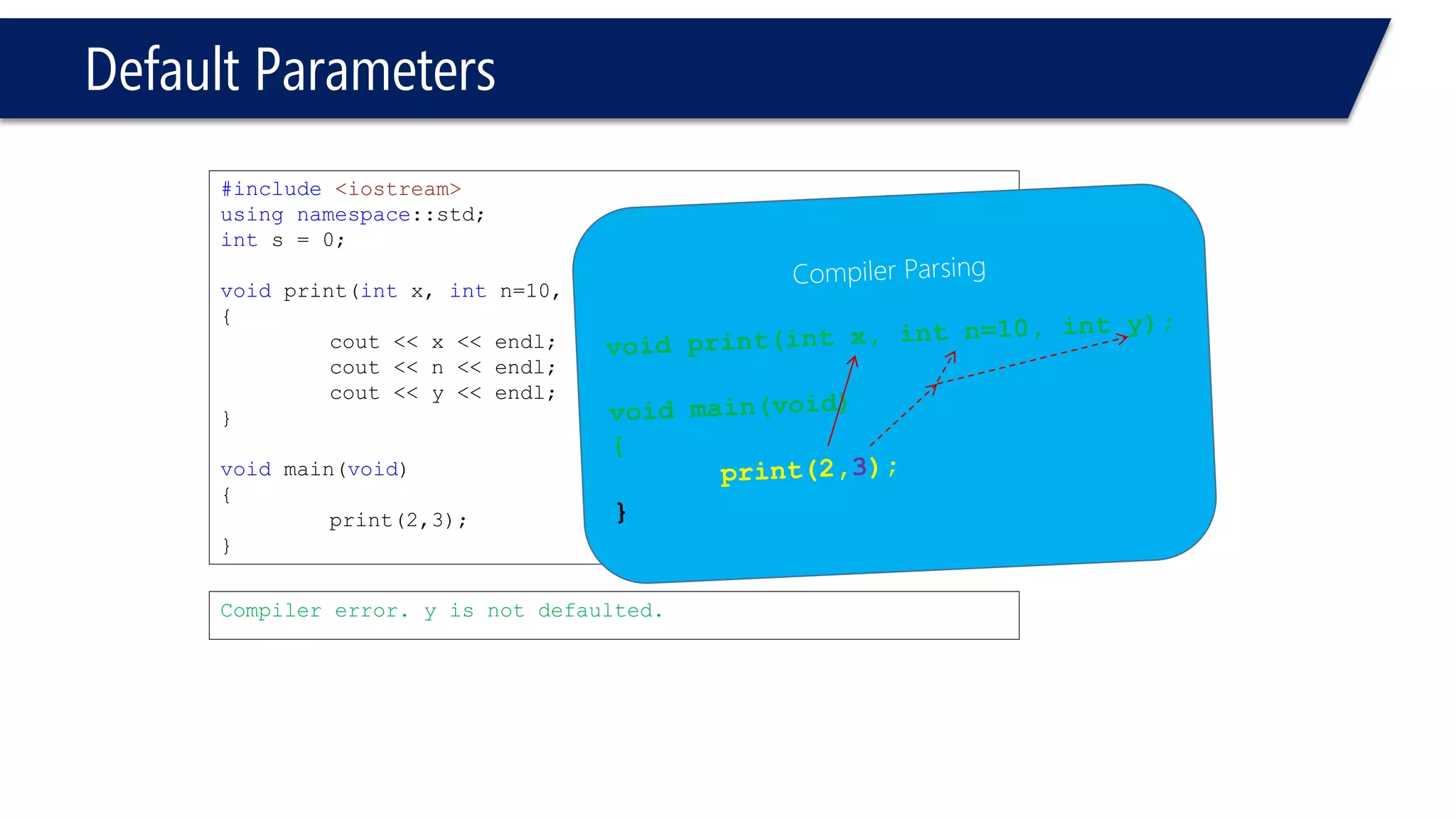
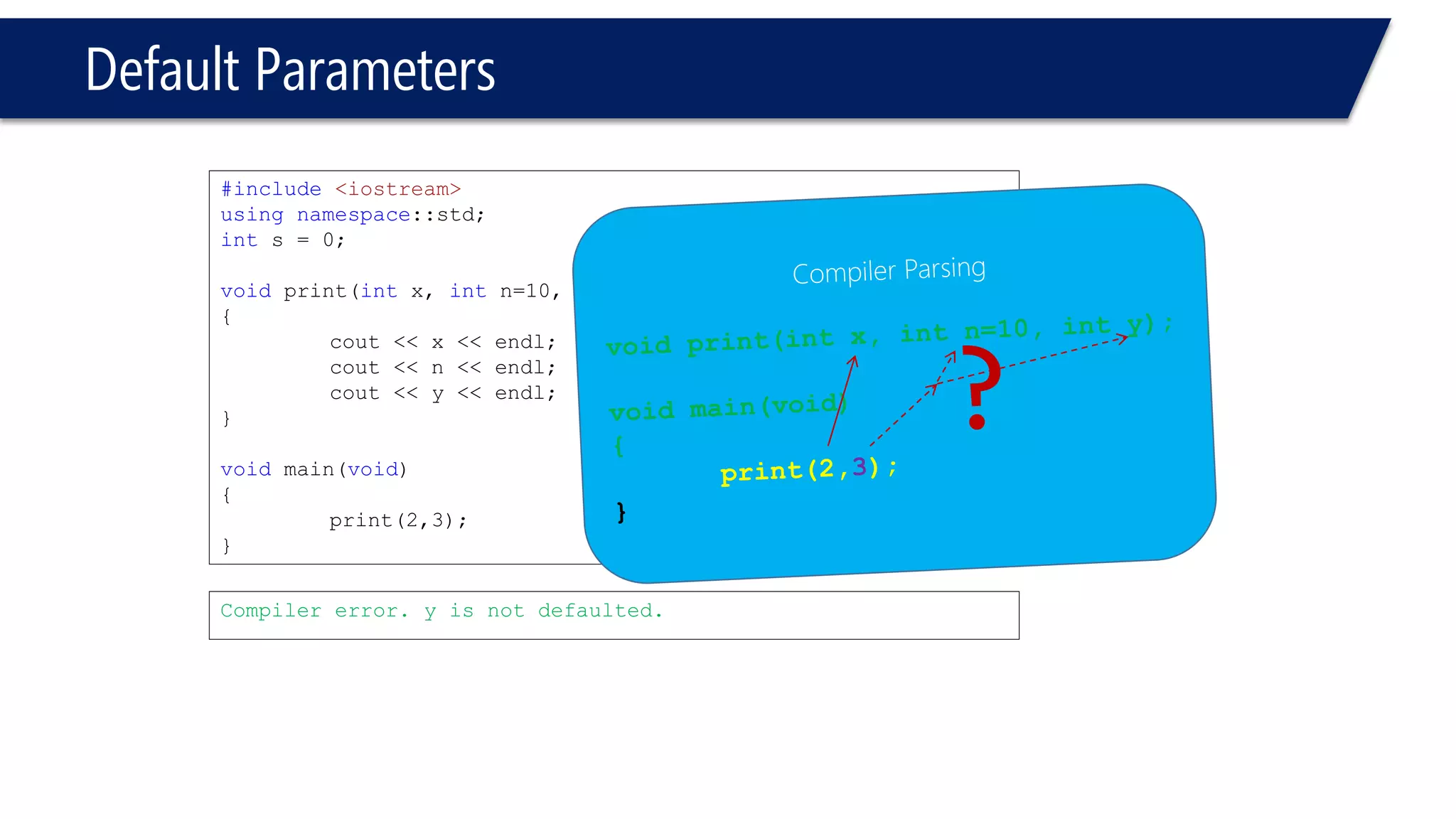
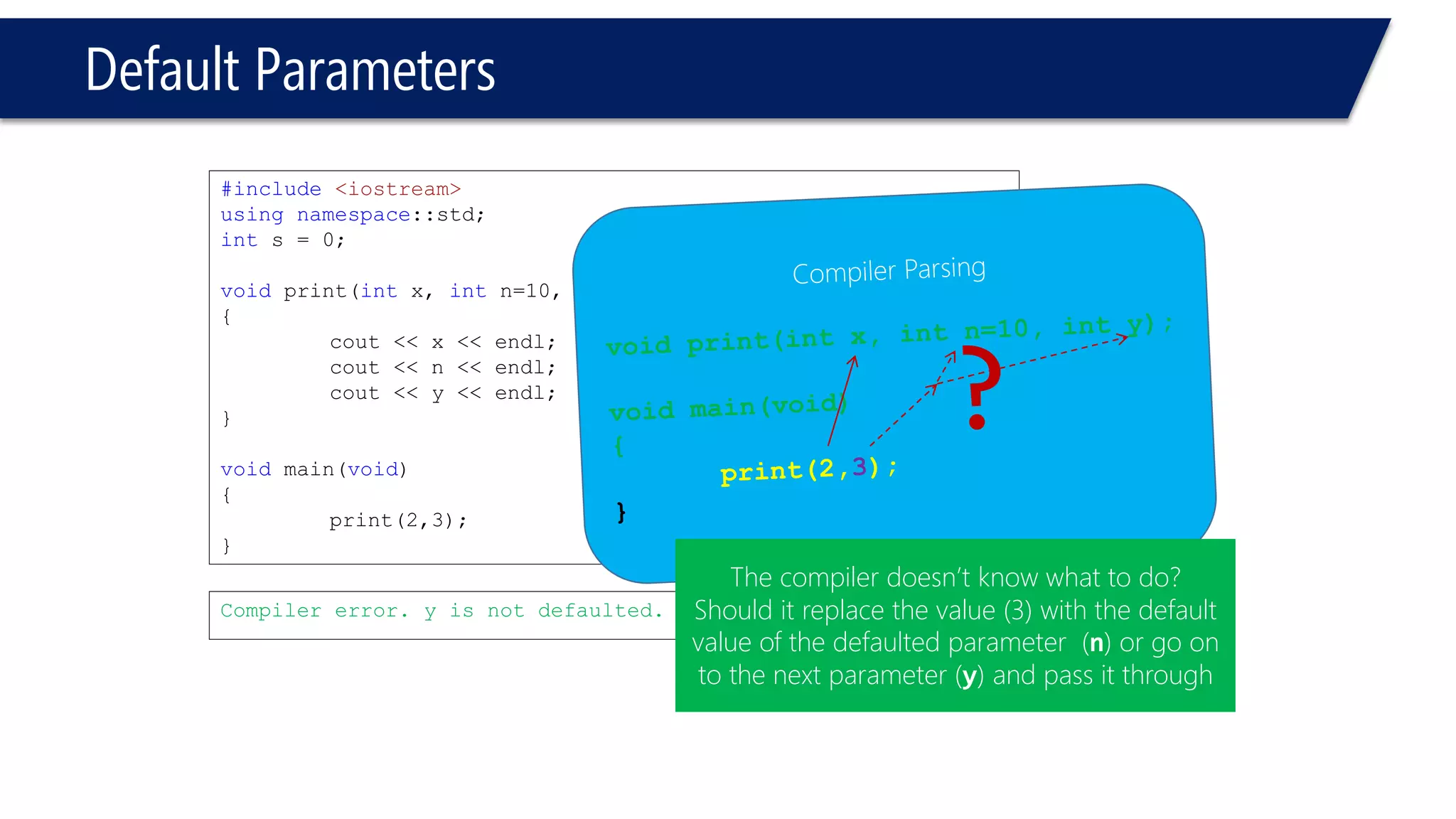
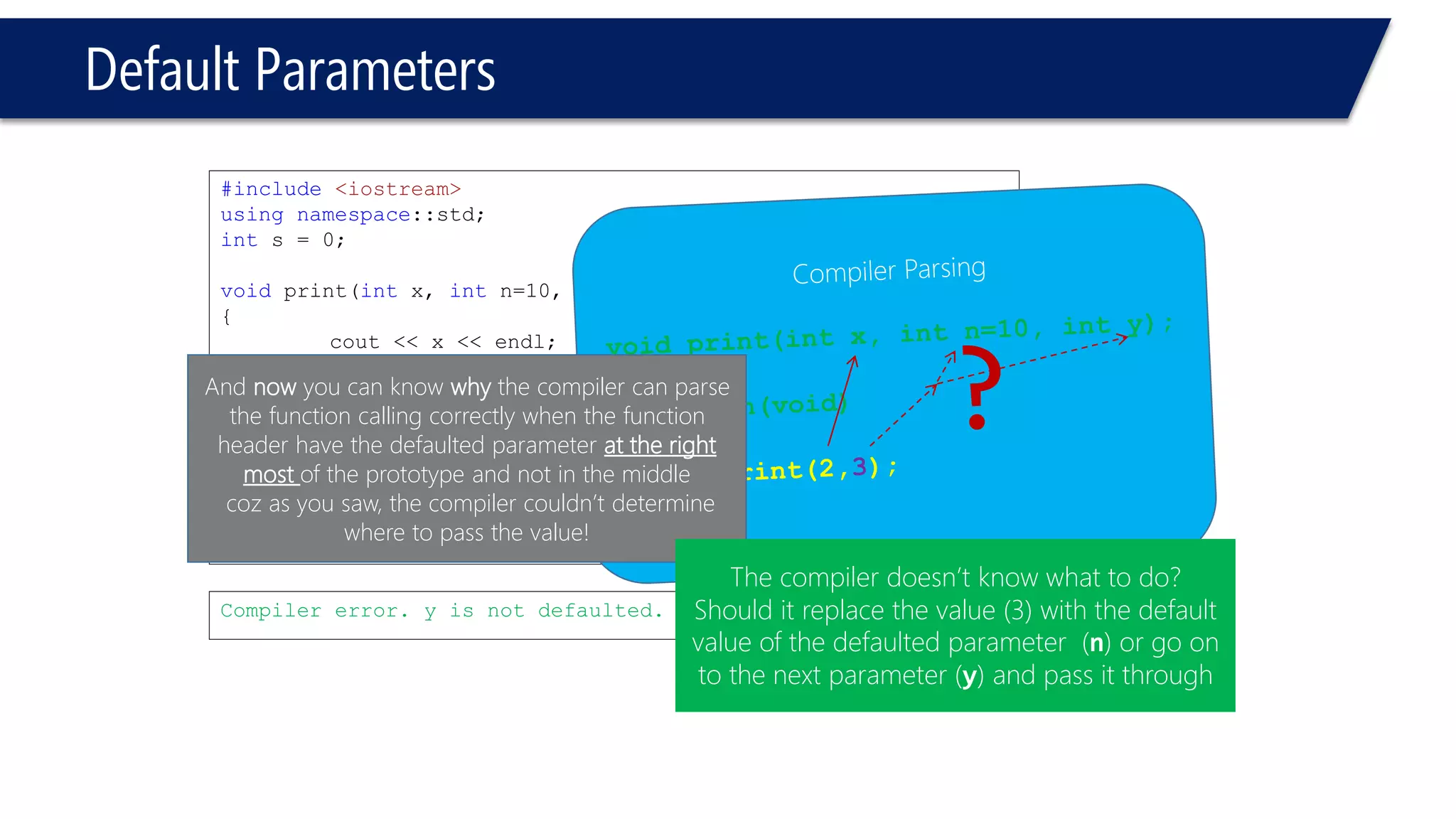
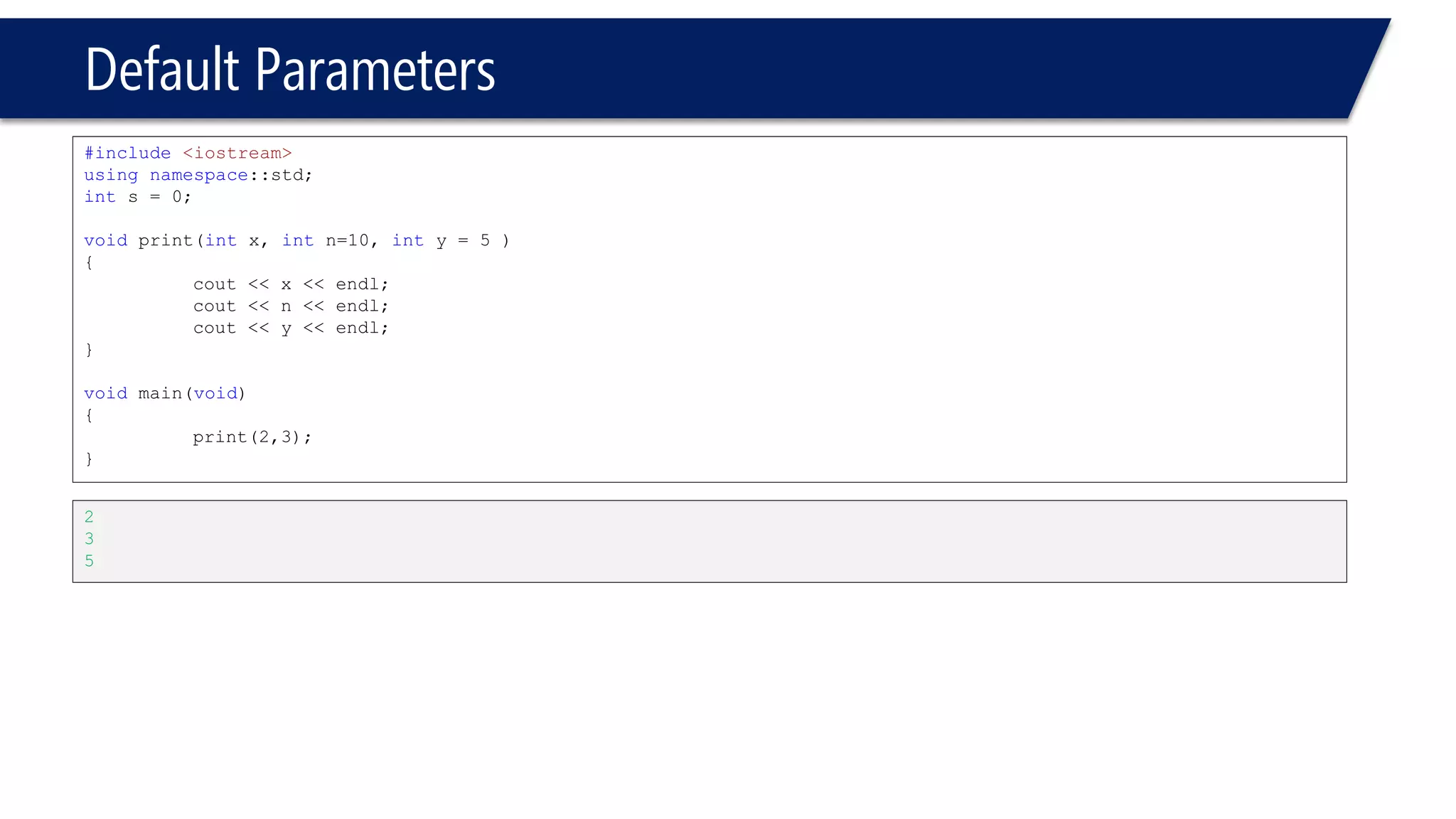
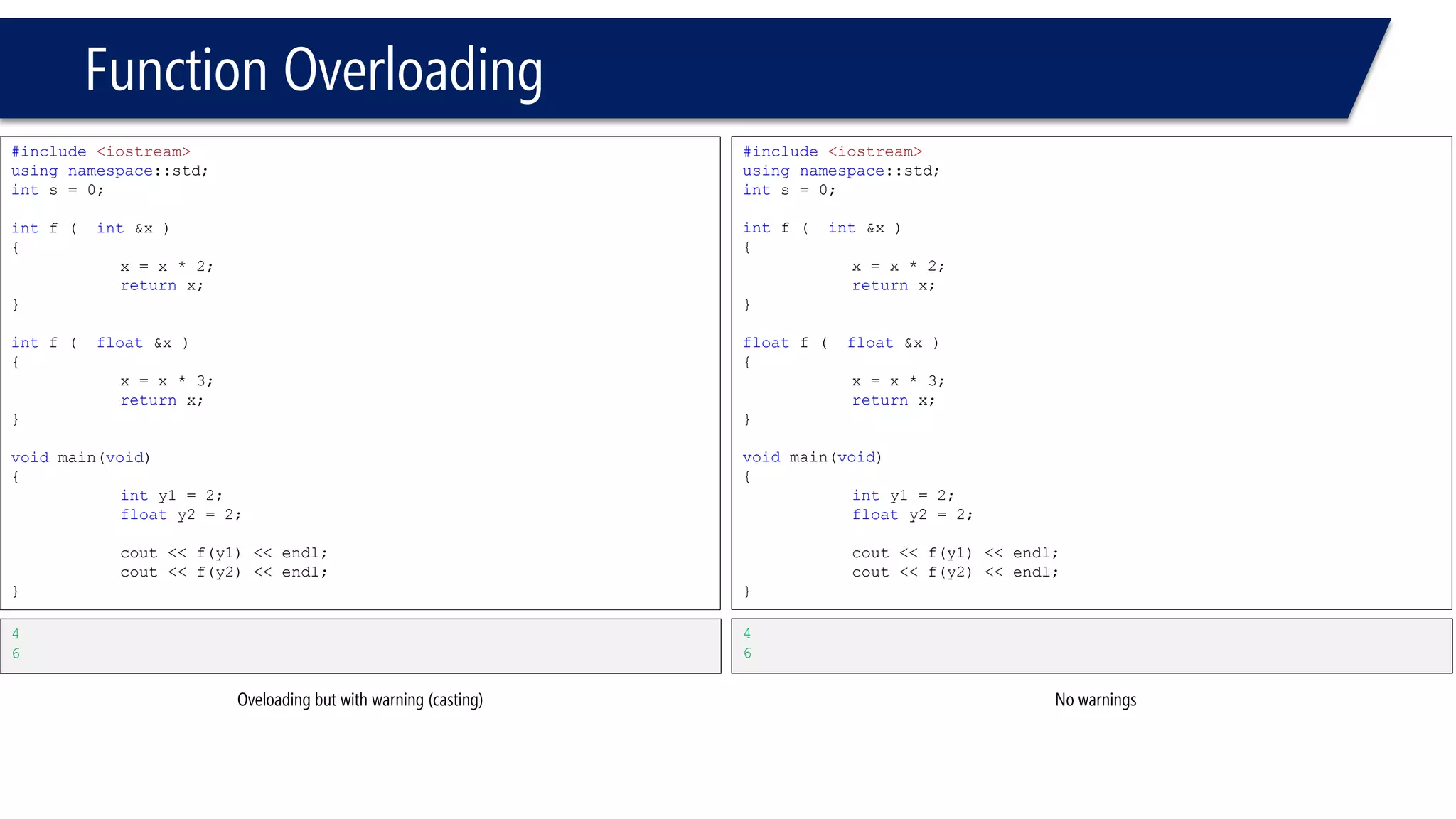
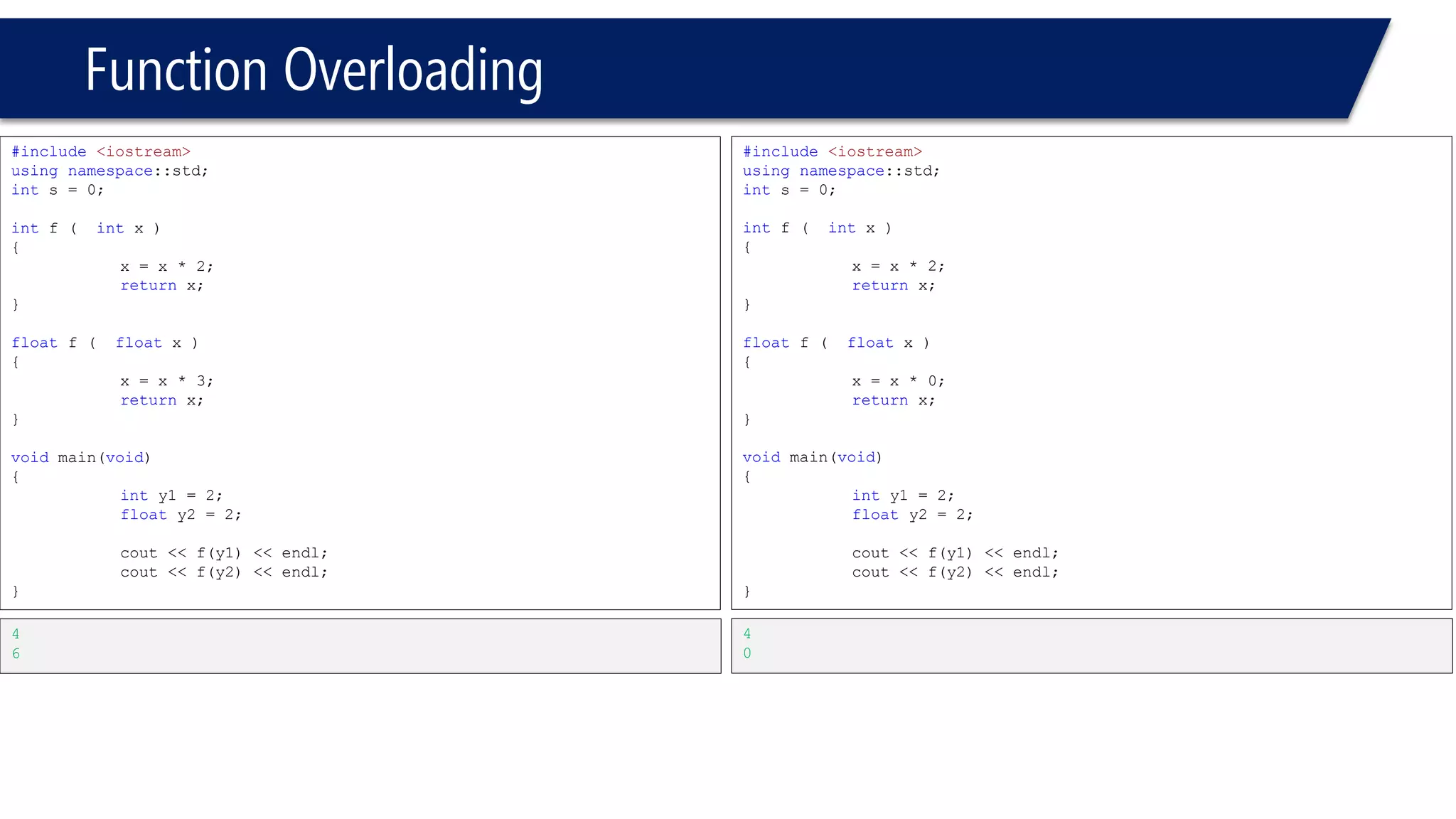
The document discusses functions in C++. It covers function prototypes, definitions, parameters, return types, and passing arguments to functions. Examples are provided of defining, declaring, calling functions, and common errors like missing return types or incorrect parameter types. Predefined functions from headers like sqrt() from cmath and rand() from cstdlib are also demonstrated.