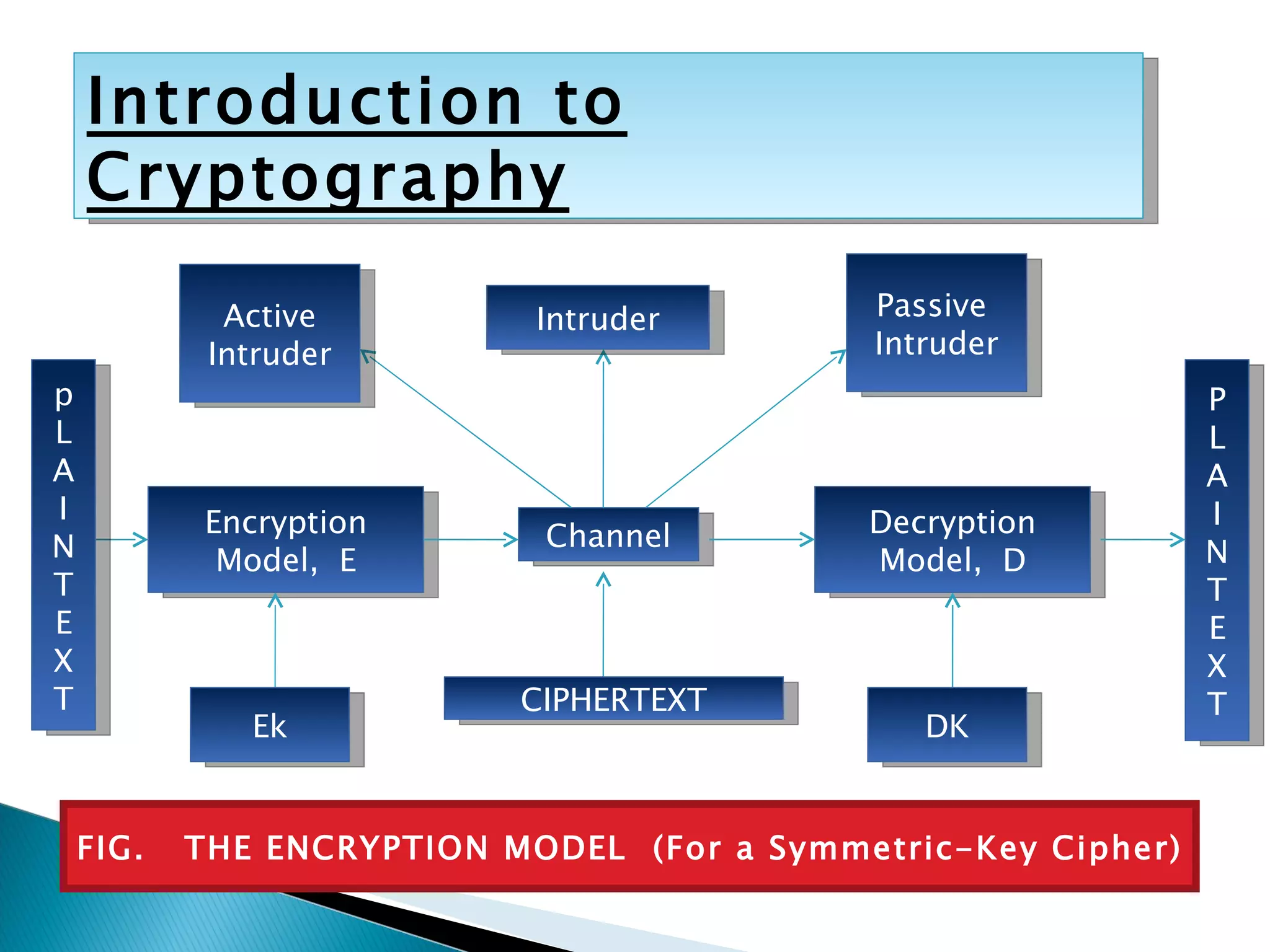
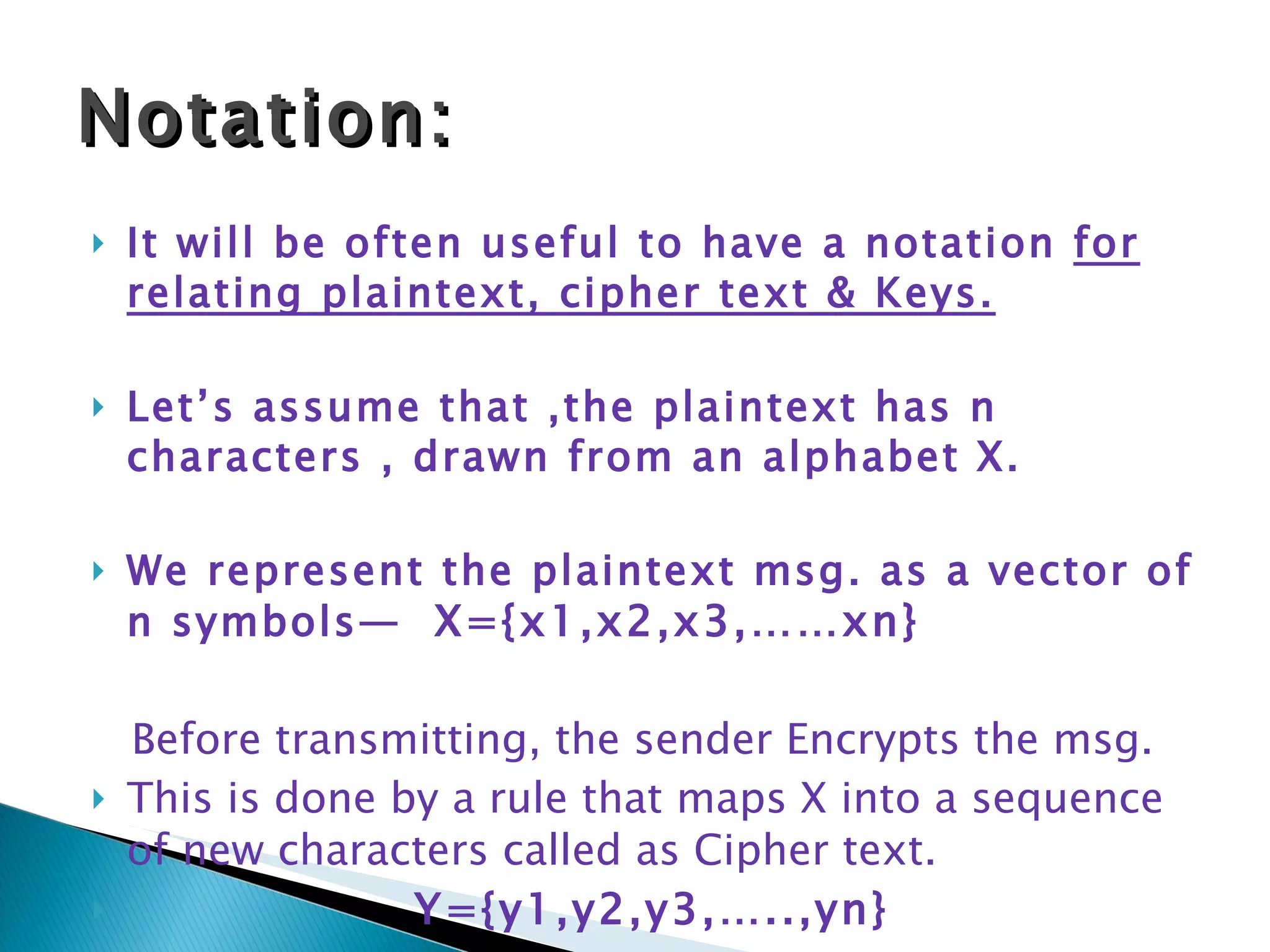
Cryptography involves secret writing and encrypting messages so that only authorized parties can read them. It uses algorithms and keys to encrypt plaintext into ciphertext. Cryptanalysis involves breaking ciphers, while cryptography is designing ciphers. Cryptology encompasses both cryptography and cryptanalysis. Common encryption models involve plaintext being encrypted into ciphertext using a key, which is then transmitted and decrypted by the intended receiver using the same key.