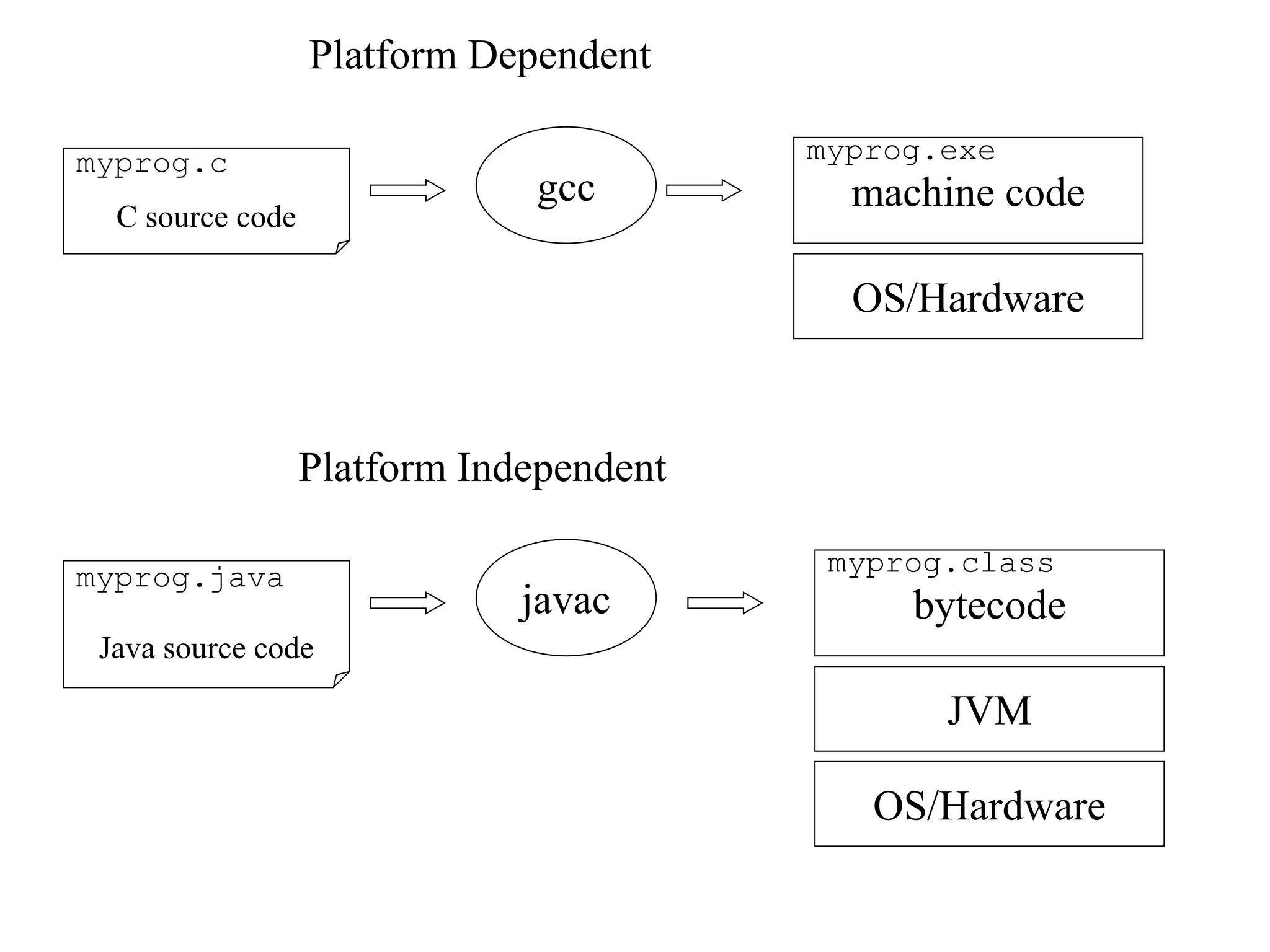
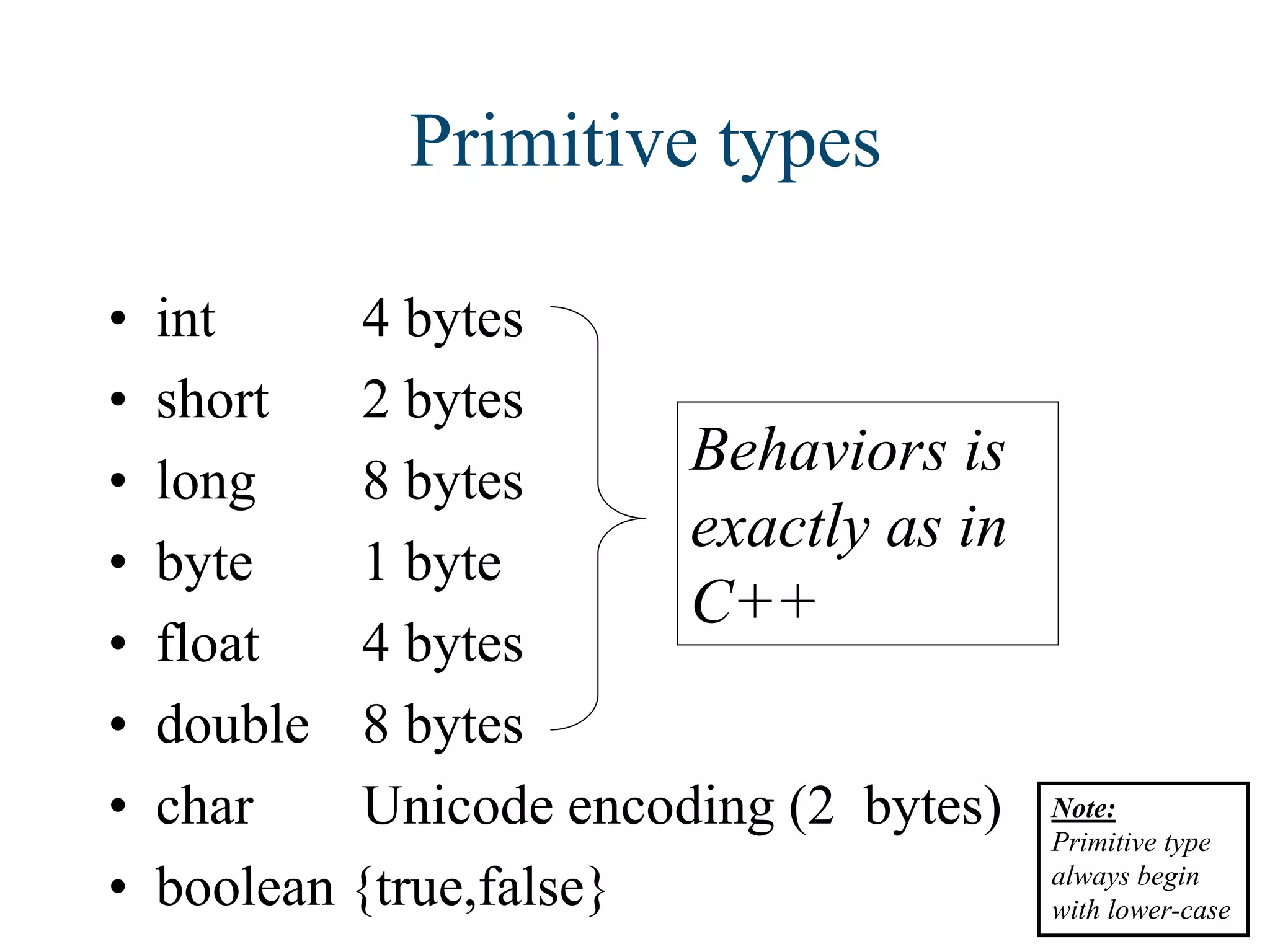
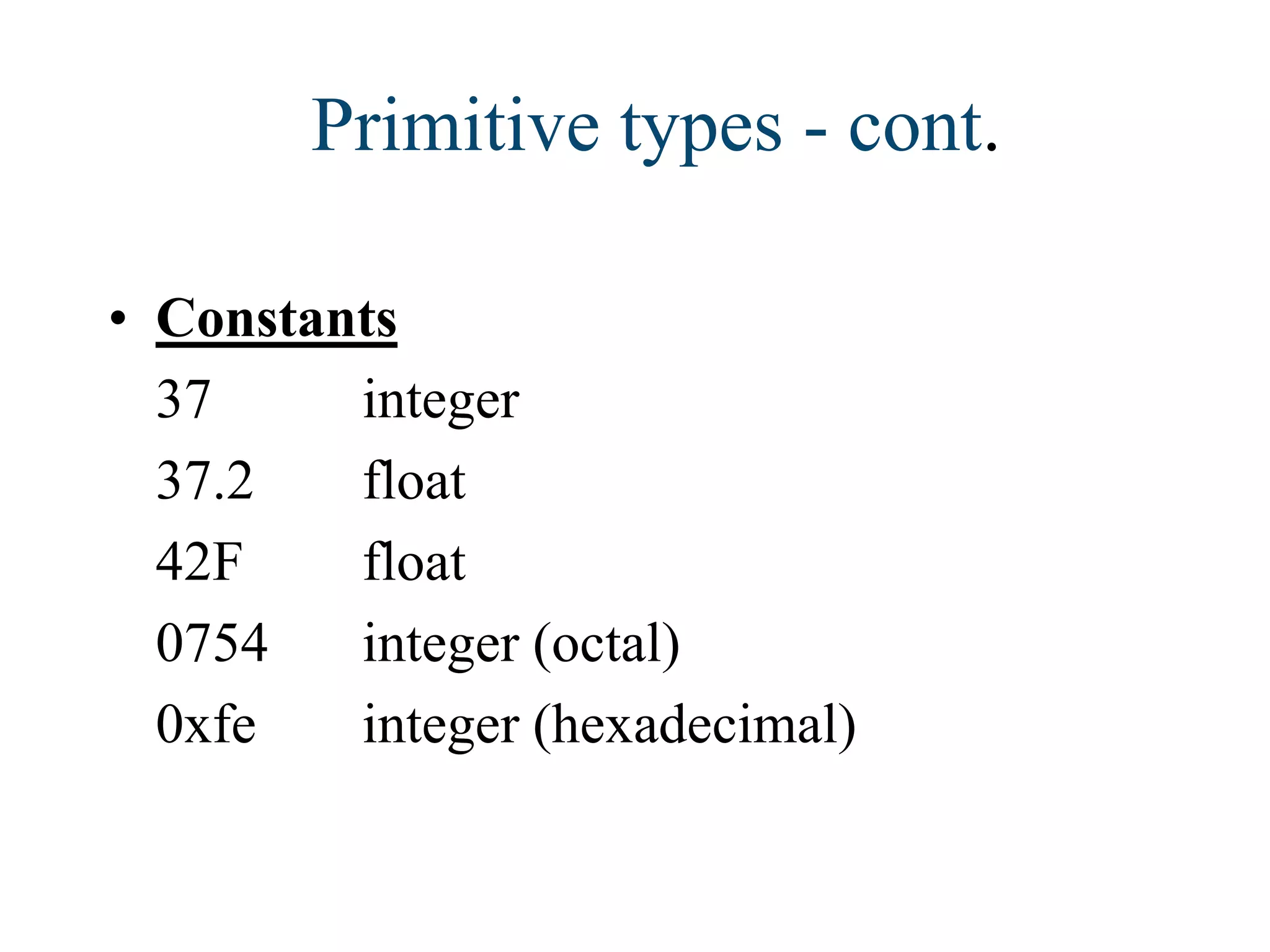
Java is a versatile programming language developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems, known for its simplicity, object-oriented approach, and platform independence. It supports various applications, including desktop, web, mobile, and embedded systems, and utilizes components like JVM, JRE, and JDK. Key concepts in Java include arrays, inheritance, polymorphism, abstract classes, interfaces, and a robust collection framework for managing data.



![Example program
class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(“Hello World !!!”);
}
}
Hello.java
C:javac Hello.java
C:java Hello
( compilation creates Hello.class )
(Execution on the local JVM)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-8-2048.jpg)
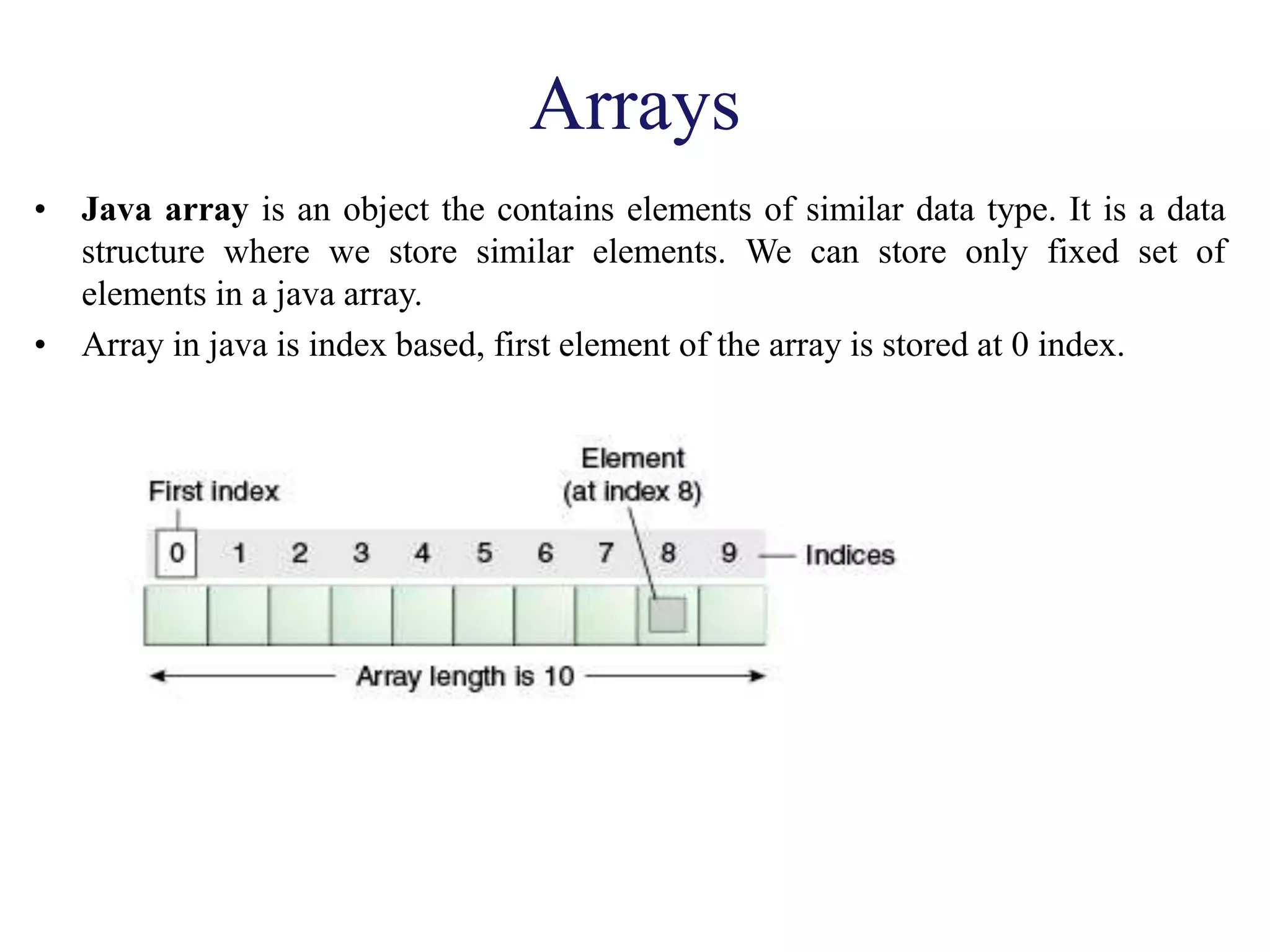

![Single-Dimension Array
Single-Dimension array in java
Syntax to Declare an Single-Dimension Array in java
dataType[] arr; (or)
dataType []arr; (or)
dataType arr[];
Output: 33
3
4
5
class Testarray1{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[]={33,3,4,5};//declaration, instantiation and initializ
ation
//printing array
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-11-2048.jpg)
![Multi-Dimension Array
Multidimensional array in java
In such case, data is stored in row and column based index (also known as
matrix form).
Syntax to Declare
Multidimensional Array in Java.
dataType[][] arrayRefVar; (or)
dataType [][]arrayRefVar; (or)
dataType arrayRefVar[][]; (or)
dataType []arrayRefVar[];
Output: 1 2 3
2 4 5
4 4 5
class Testarray3{
public static void main(String args[]){
//declaring and initializing 2D array
int arr[][]={{1,2,3},{2,4,5},{4,4,5}};
//printing 2D array
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-12-2048.jpg)
![Static - [1/4]
• Member data - Same data is used for all the instances (objects) of
some Class.
Class A {
public int y = 0;
public static int x_ = 1;
};
A a = new A();
A b = new A();
System.out.println(b.x_);
a.x_ = 5;
System.out.println(b.x_);
A.x_ = 10;
System.out.println(b.x_);
Assignment performed
on the first access to the
Class.
Only one instance of ‘x’
exists in memory
Output:
1
5
10
a b
y y
A.x_
0 0
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-13-2048.jpg)
![Static - [2/4]
• Member function
– Static member function can access only static members
– Static member function can be called without an instance.
Class TeaPot {
private static int numOfTP = 0;
private Color myColor_;
public TeaPot(Color c) {
myColor_ = c;
numOfTP++;
}
public static int howManyTeaPots()
{ return numOfTP; }
// error :
public static Color getColor()
{ return myColor_; }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-14-2048.jpg)
![Static - [2/4] cont.
Usage:
TeaPot tp1 = new TeaPot(Color.RED);
TeaPot tp2 = new TeaPot(Color.GREEN);
System.out.println(“We have “ +
TeaPot.howManyTeaPots()+ “Tea Pots”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-15-2048.jpg)
![Static - [3/4]
• Block
– Code that is executed in the first reference to the class.
– Several static blocks can exist in the same class
( Execution order is by the appearance order in the class definition
).
– Only static members can be accessed.
class RandomGenerator {
private static int seed_;
static {
int t = System.getTime() % 100;
seed_ = System.getTime();
while(t-- > 0)
seed_ = getNextNumber(seed_);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-16-2048.jpg)

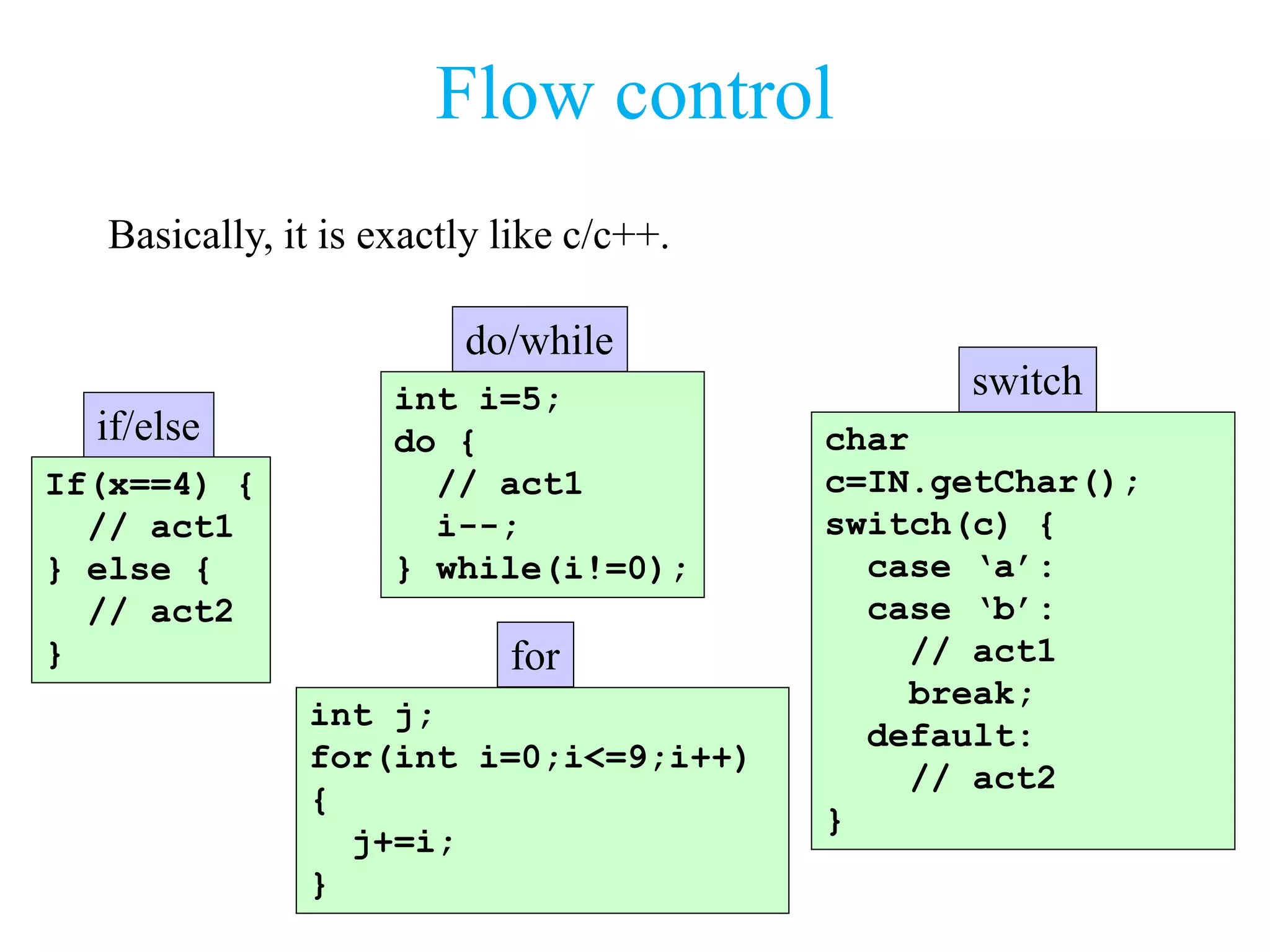

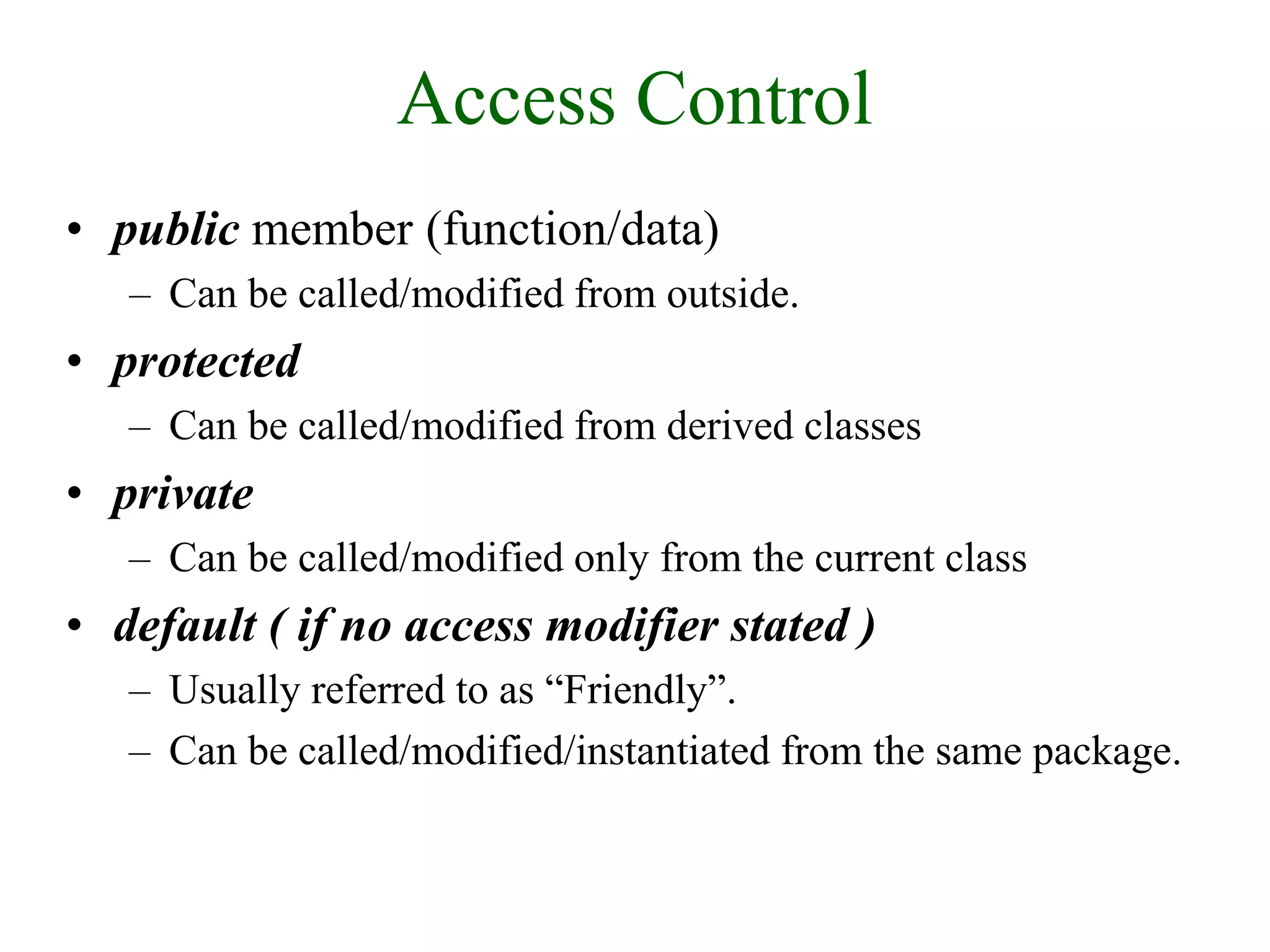
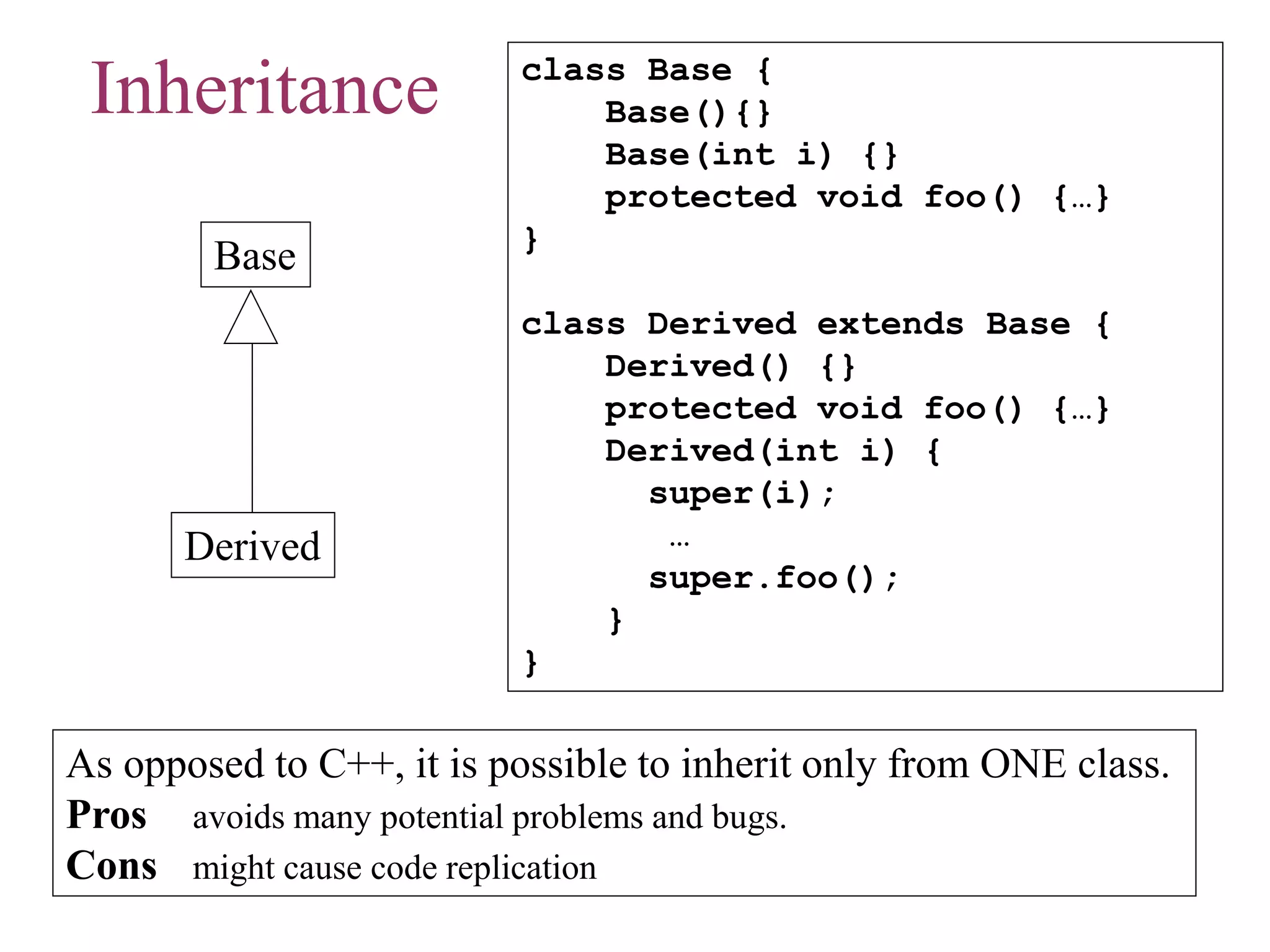

![Inheritance (2)
• In Java, all methods are virtual :
class Base {
void foo() {
System.out.println(“Base”);
}
}
class Derived extends Base {
void foo() {
System.out.println(“Derived”);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base b = new Derived();
b.foo(); // Derived.foo() will be activated
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-23-2048.jpg)


![Interface Example
interface printable{
void print();
}
class A6 implements printable{
public void print(){System.out.println("Hello");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
A6 obj = new A6();
obj.print();
}
}
Output: Hello](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-27-2048.jpg)

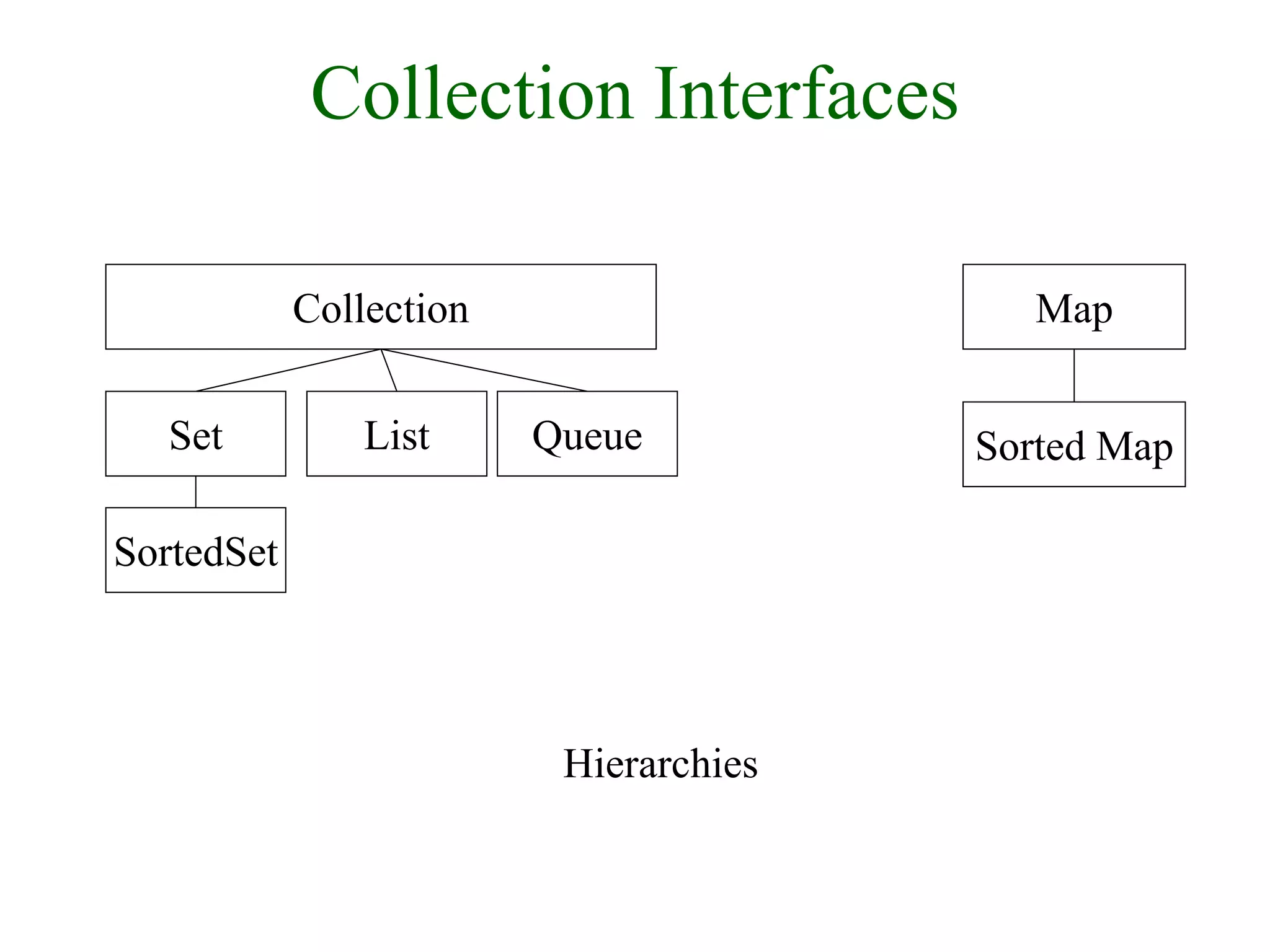
![Collection Interface
• Basic Operations
– int size();
– boolean isEmpty();
– boolean contains(Object element);
– boolean add(E element);
– boolean remove(Object element);
– Iterator iterator();
• Bulk Operations
– boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
– boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
– boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
– boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
– void clear();
• Array Operations
– Object[] toArray(); <T> T[] toArray(T[] a); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csejava-190826153137/75/Cse-java-31-2048.jpg)