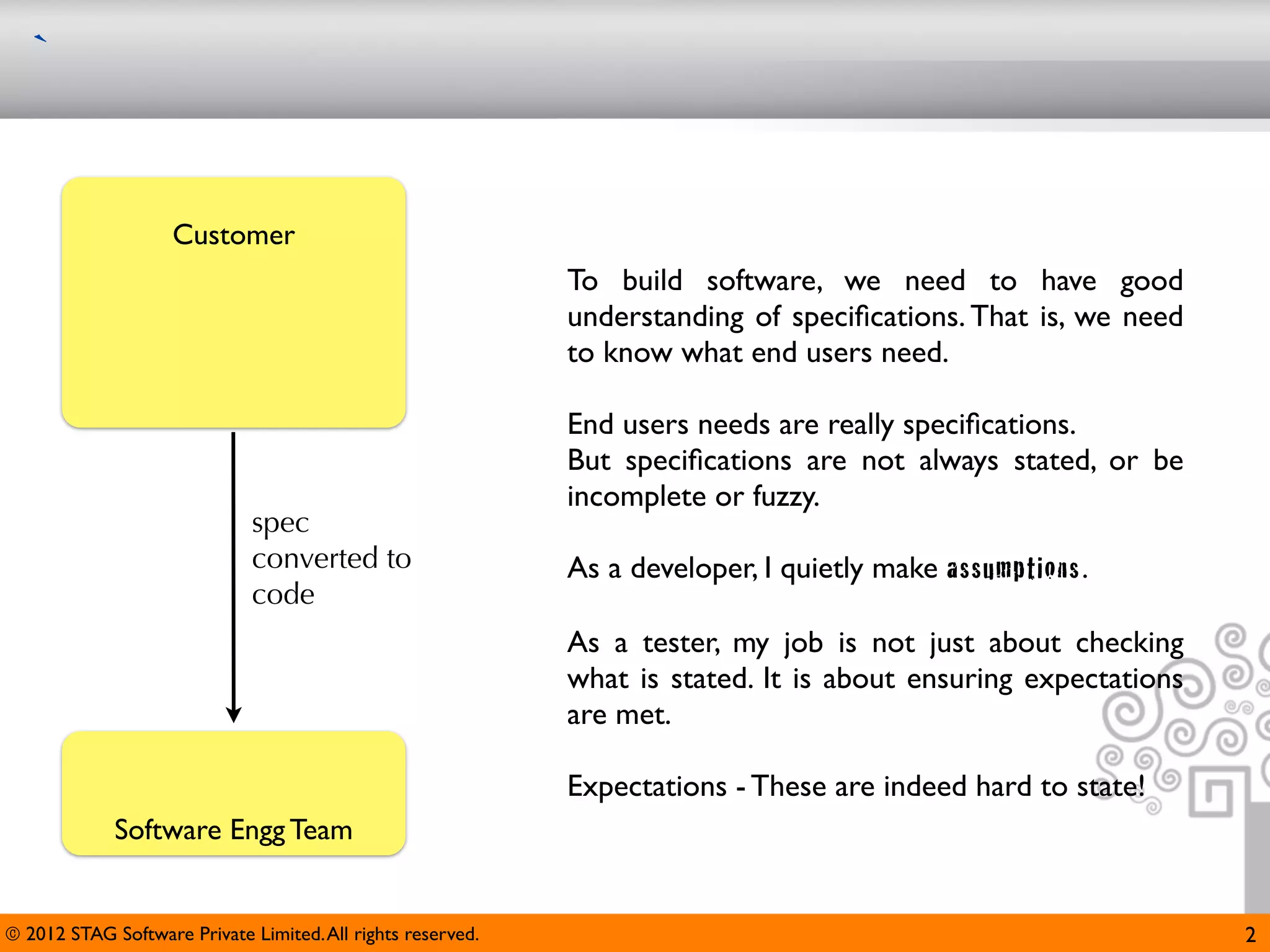
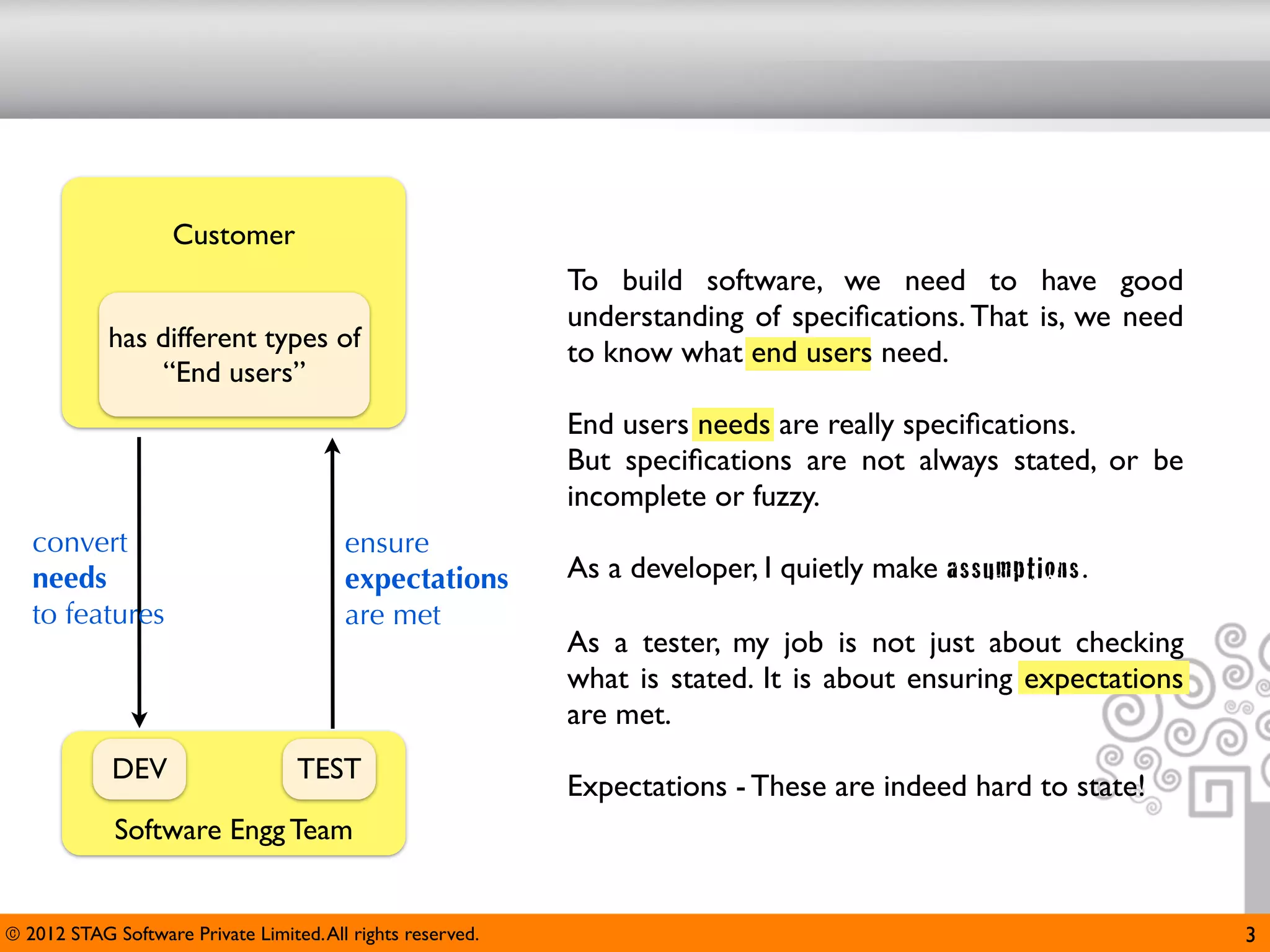
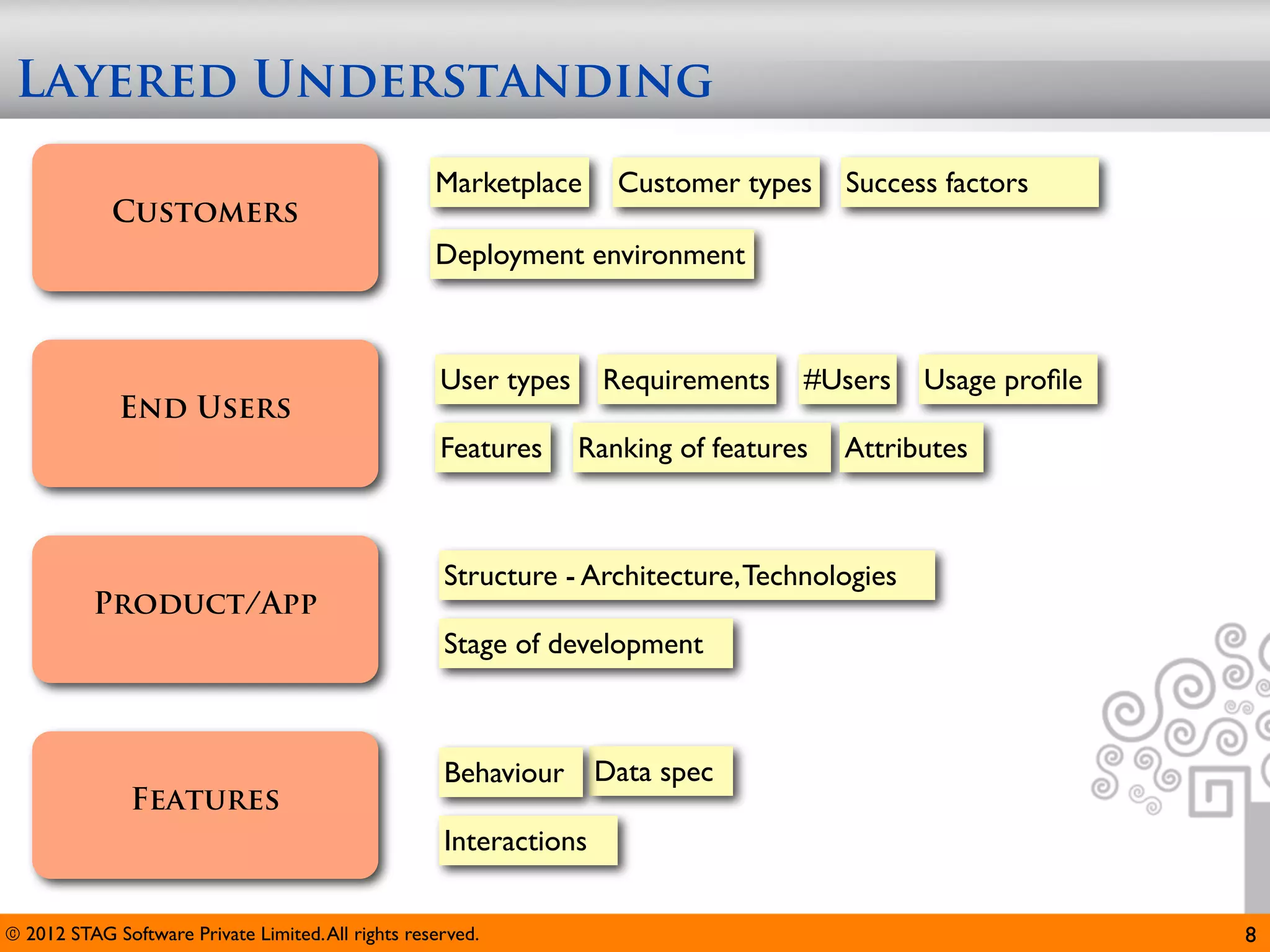
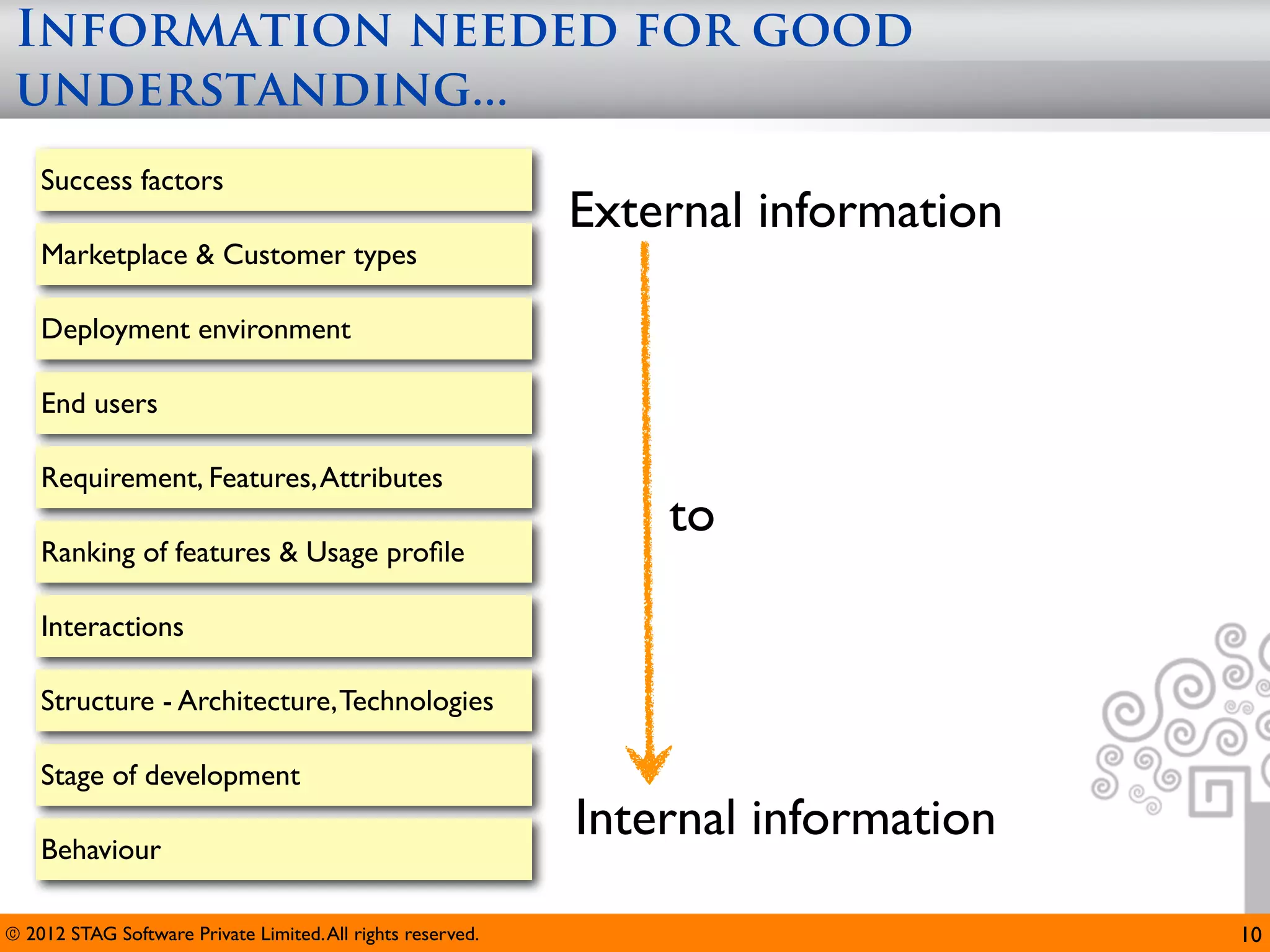
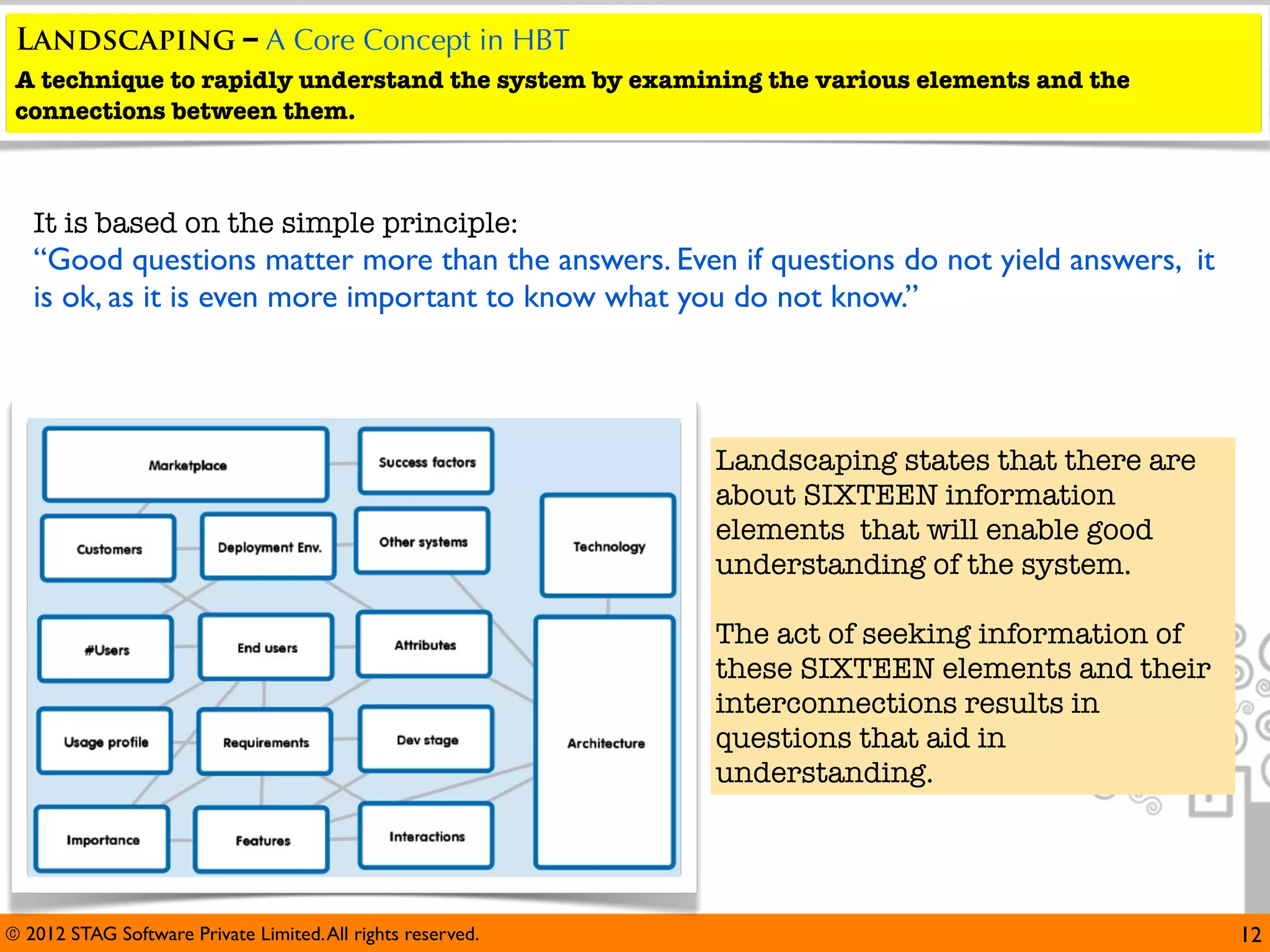
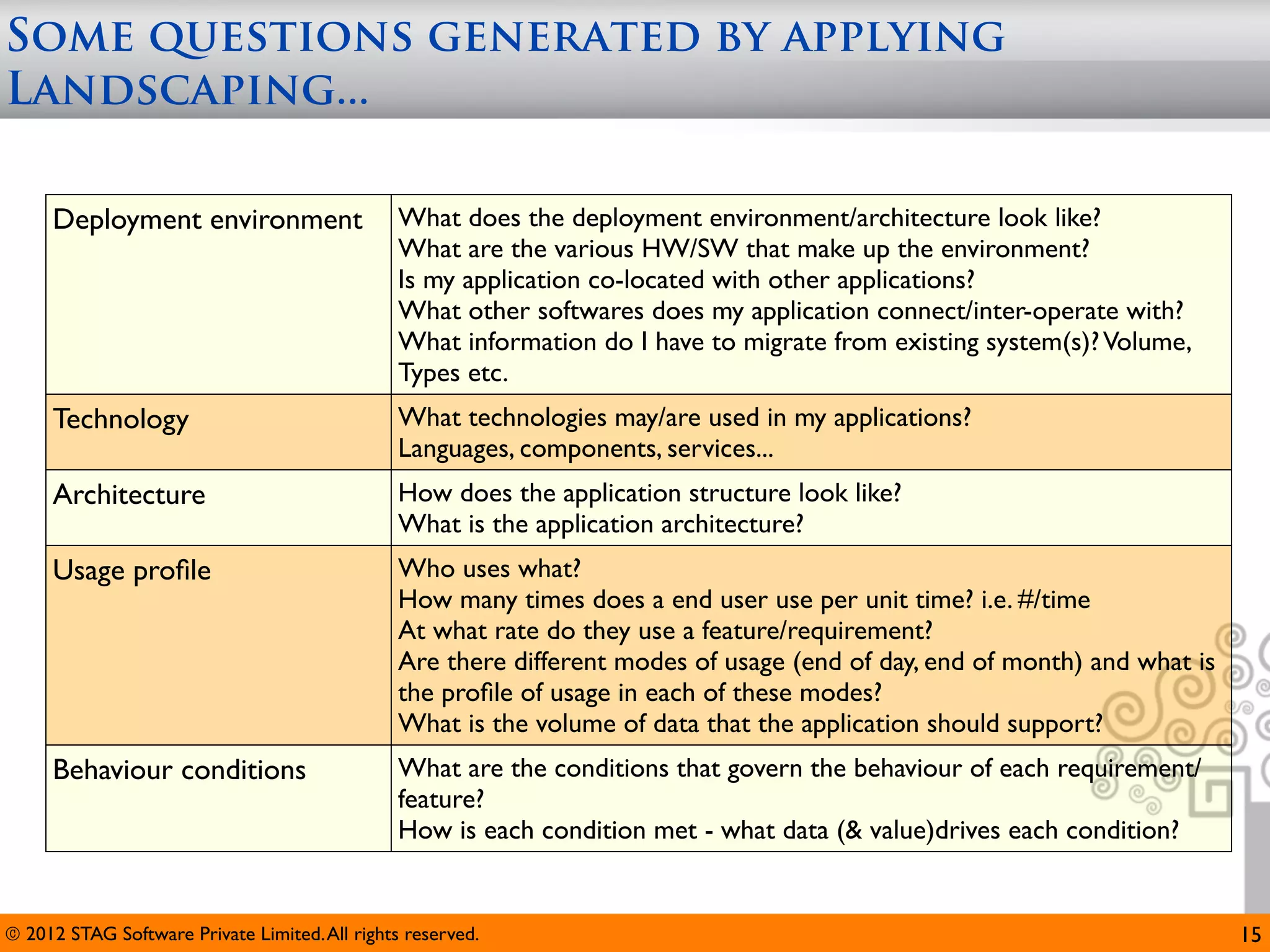
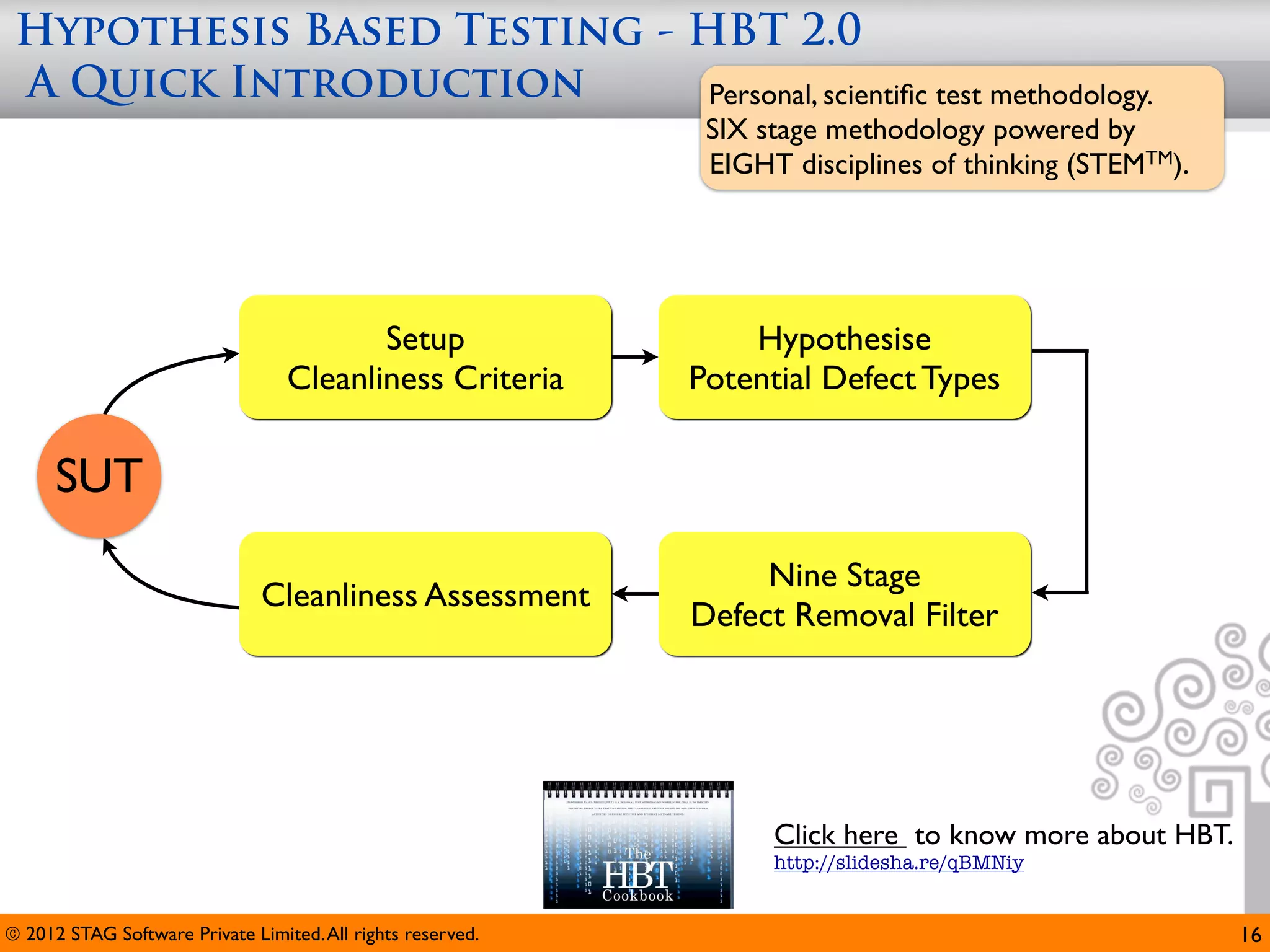
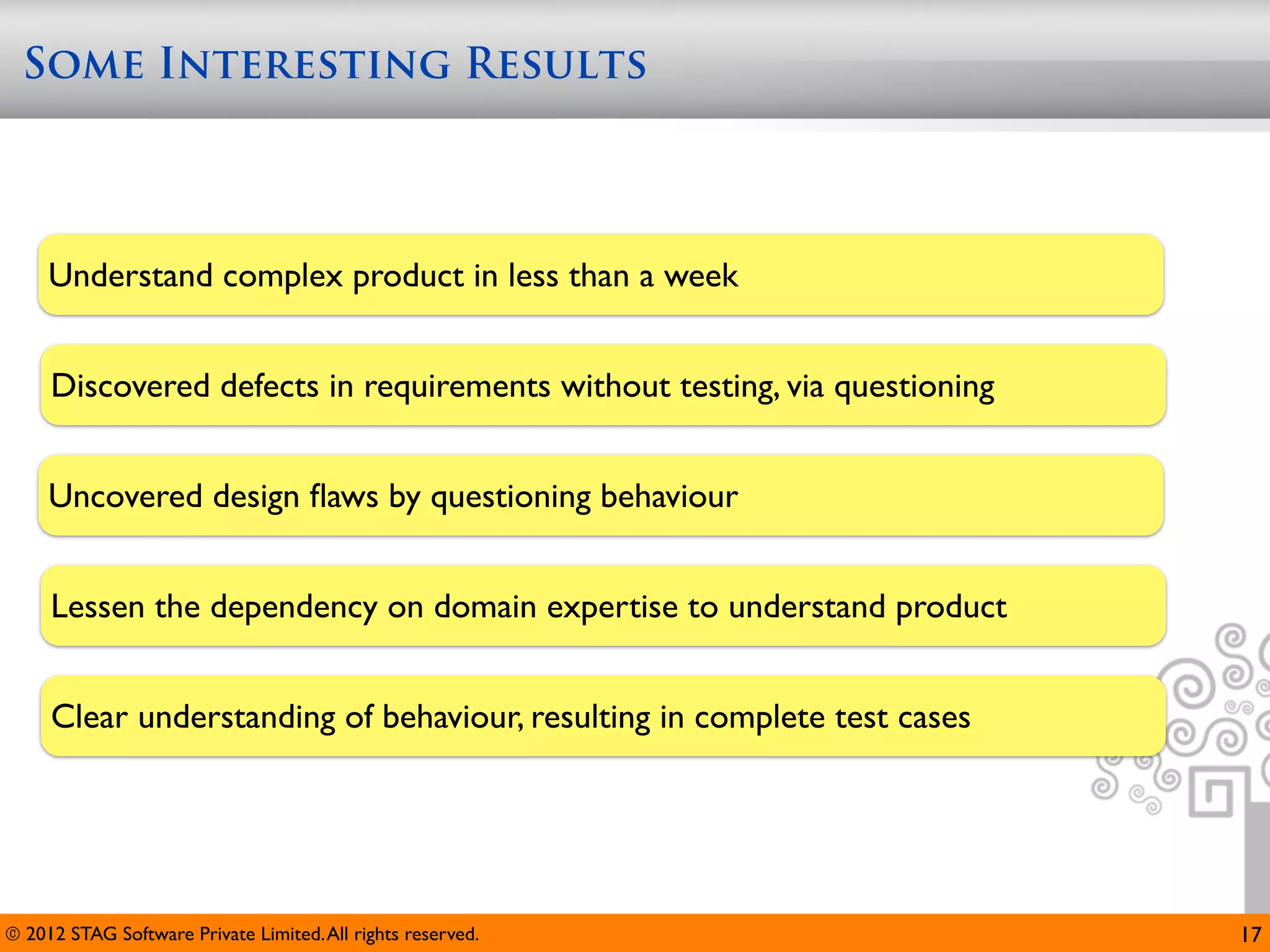
The document emphasizes the importance of effective questioning in software development to accurately understand end users' needs and specifications, which are often vague or unspecified. It discusses a systematic approach, termed 'science of questioning', to decompose problems and connect various elements like marketplace, customer types, and deployment environment to generate insightful questions. Techniques such as 'landscaping' and 'viewpoints' are introduced to aid testers in grasping user expectations and improving understanding of complex applications.