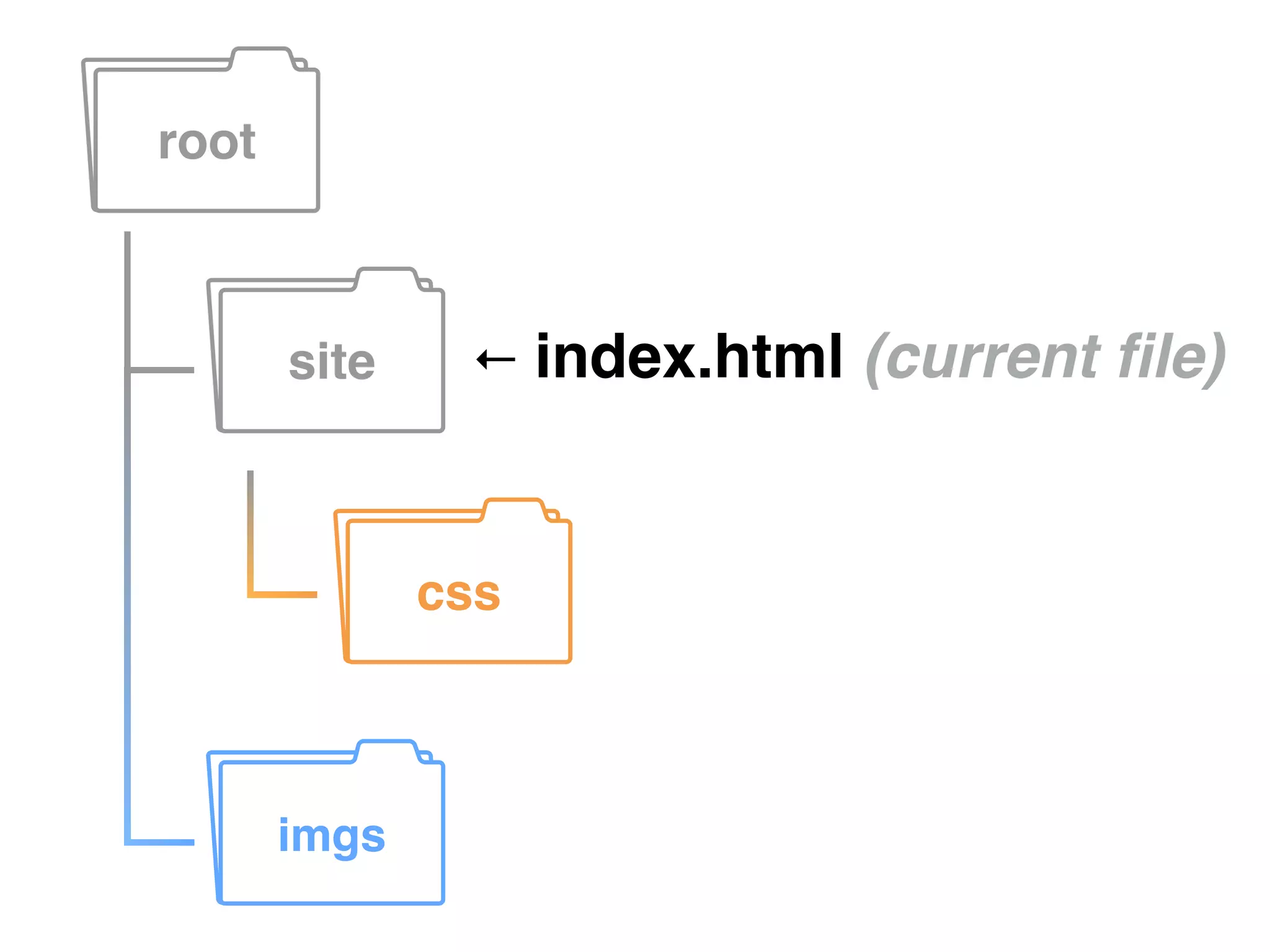
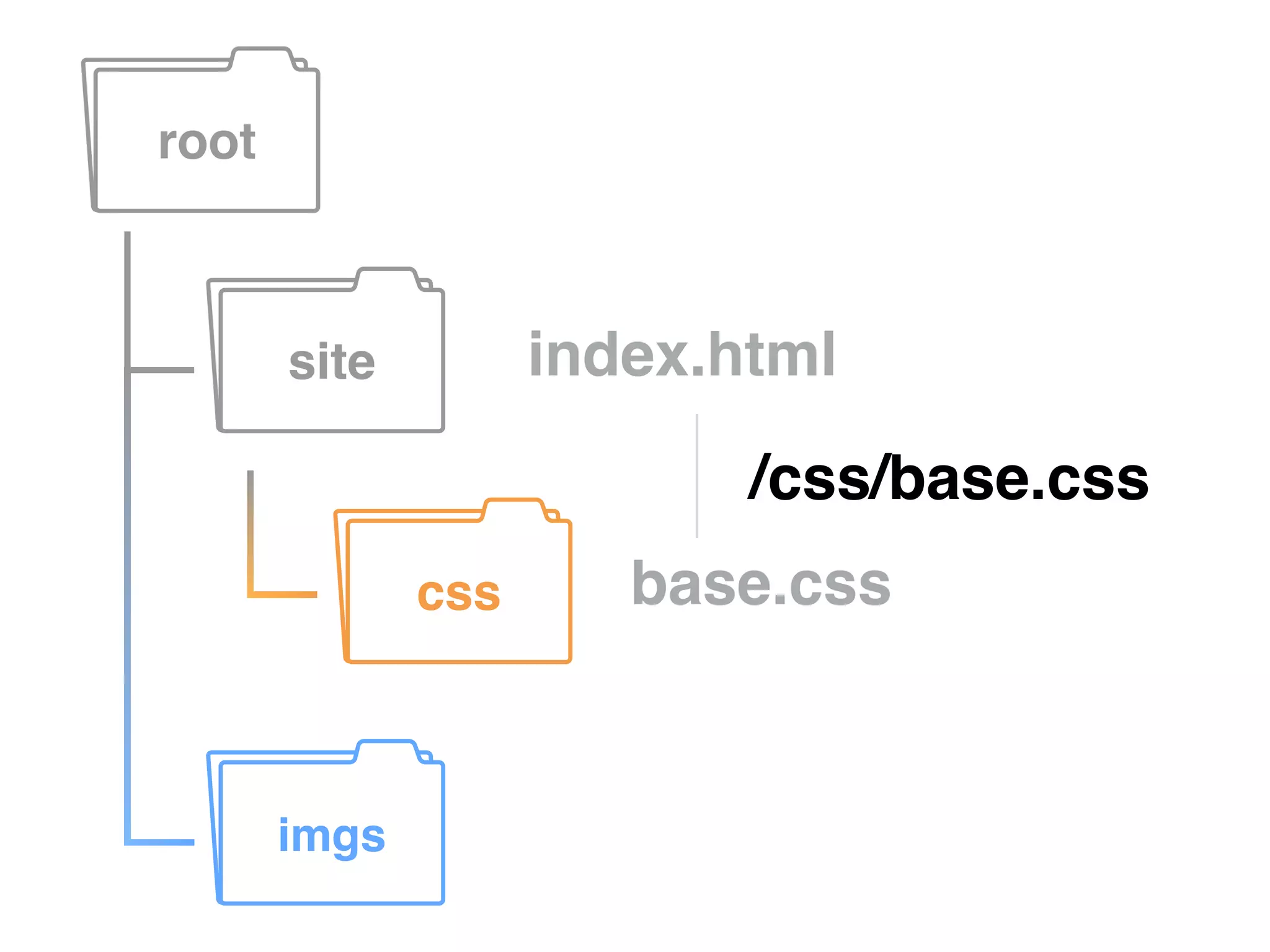
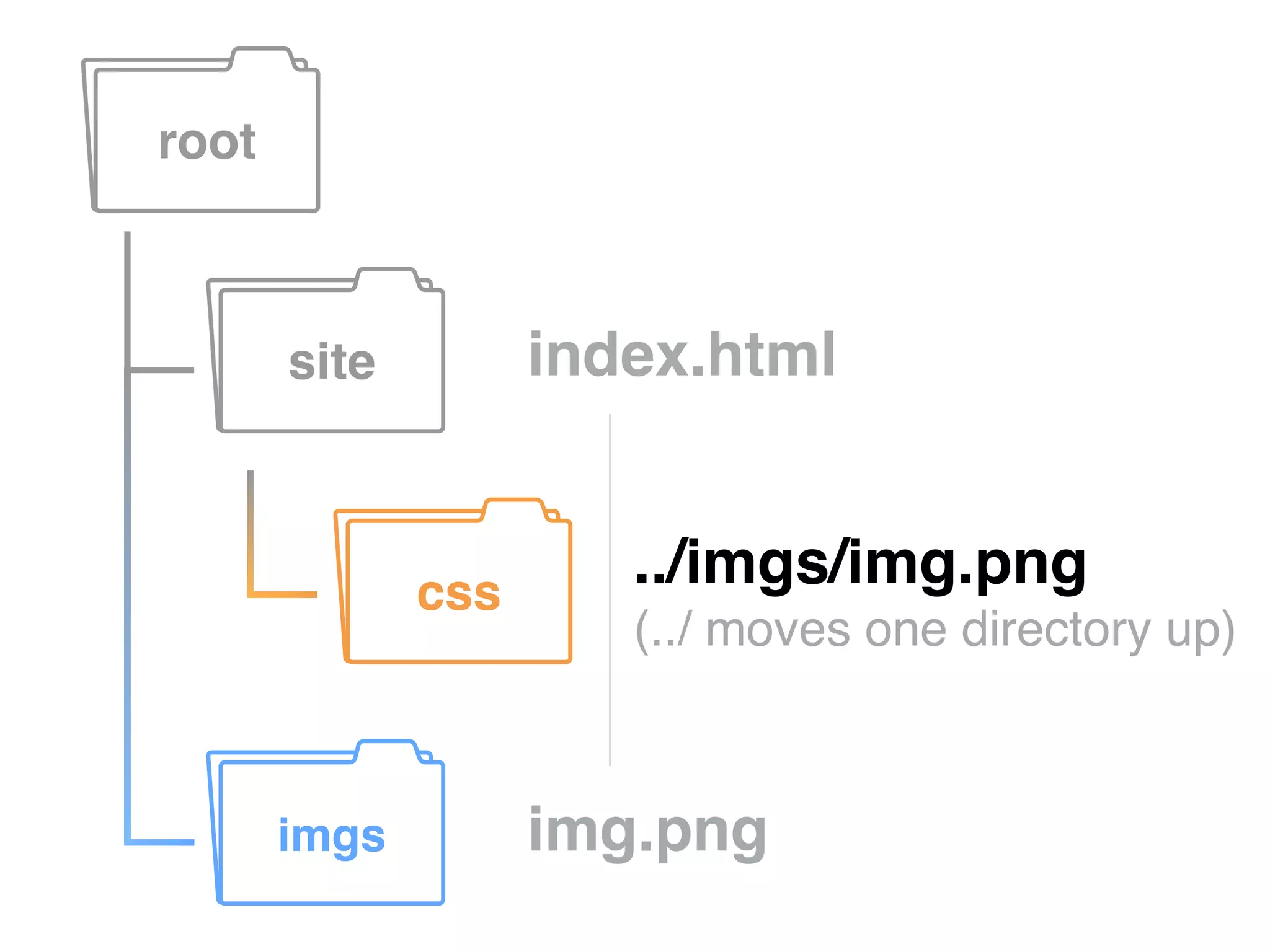
This document provides information on various web development topics such as linking files, paths, CSS, JavaScript, and patterns. It discusses absolute vs relative paths and examples of each. CSS topics covered include linking external style sheets, CSS selectors like ID, class, and element selectors, and CSS specificity. JavaScript topics include linking JavaScript files and writing JavaScript code. Patterns discussed include building navigations from lists. Assignments are provided to create HTML pages with navigation and styling, link a JavaScript file with an alert, read about JSON, and learn about handlebars.js templating.