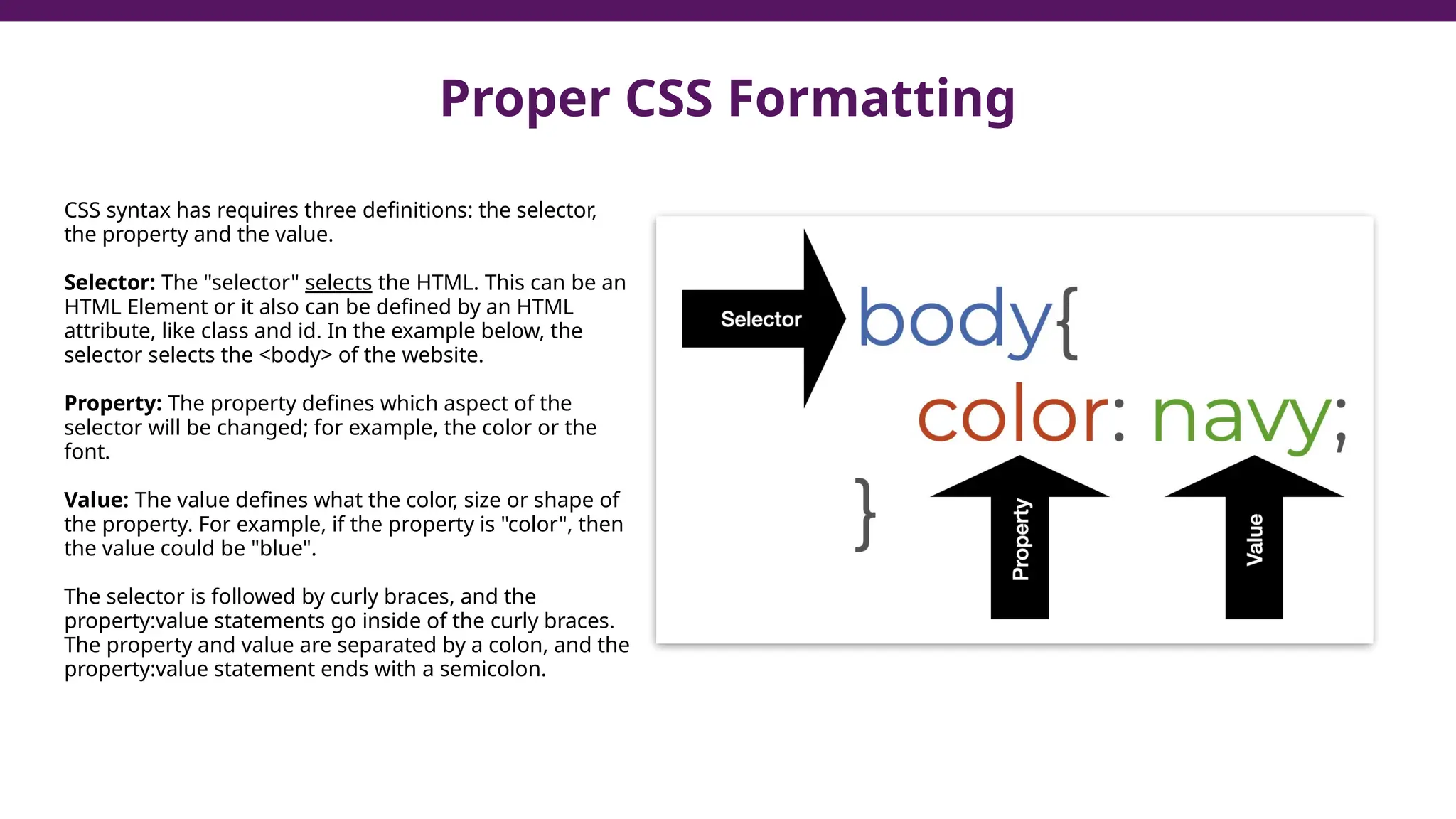
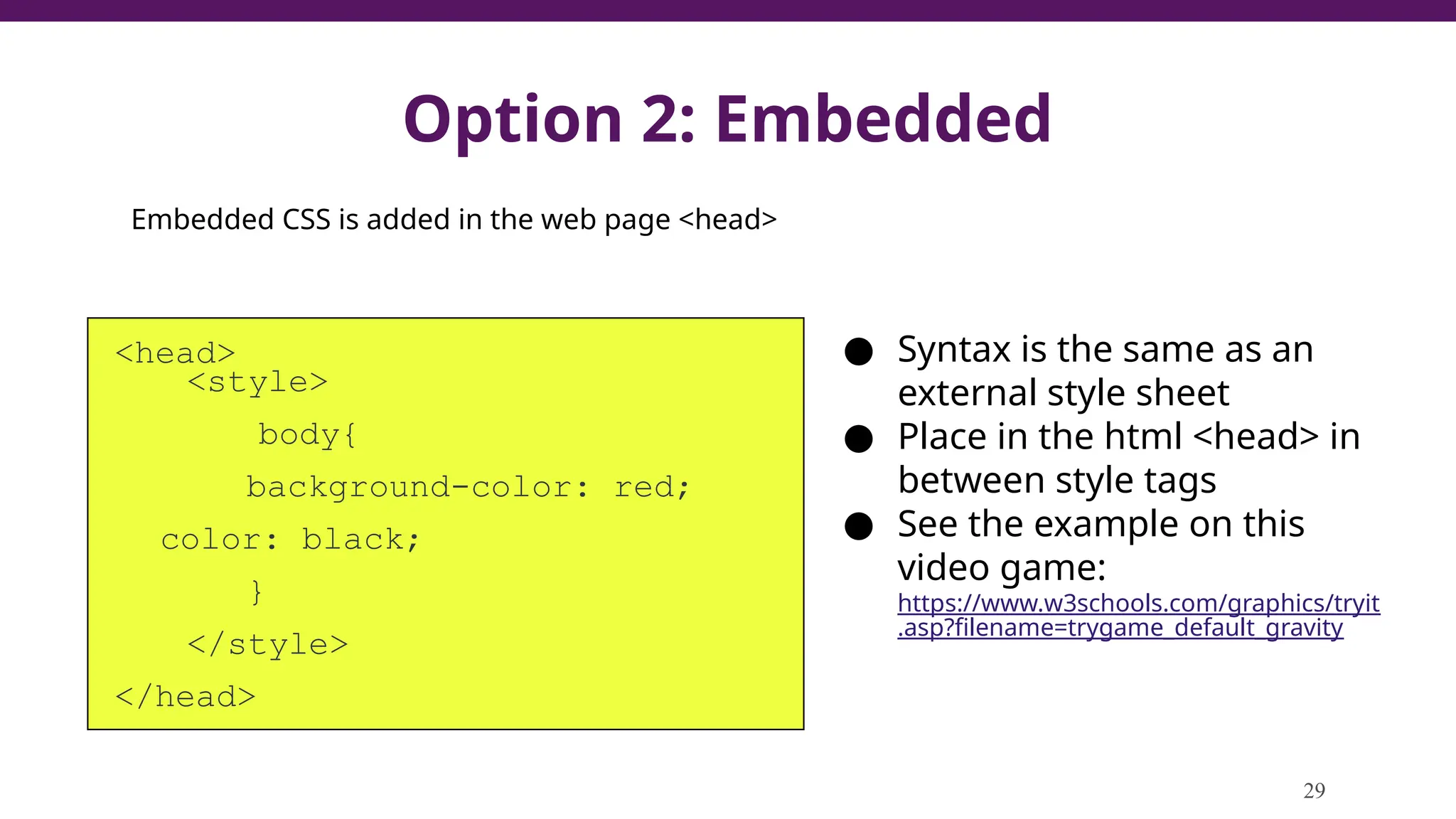
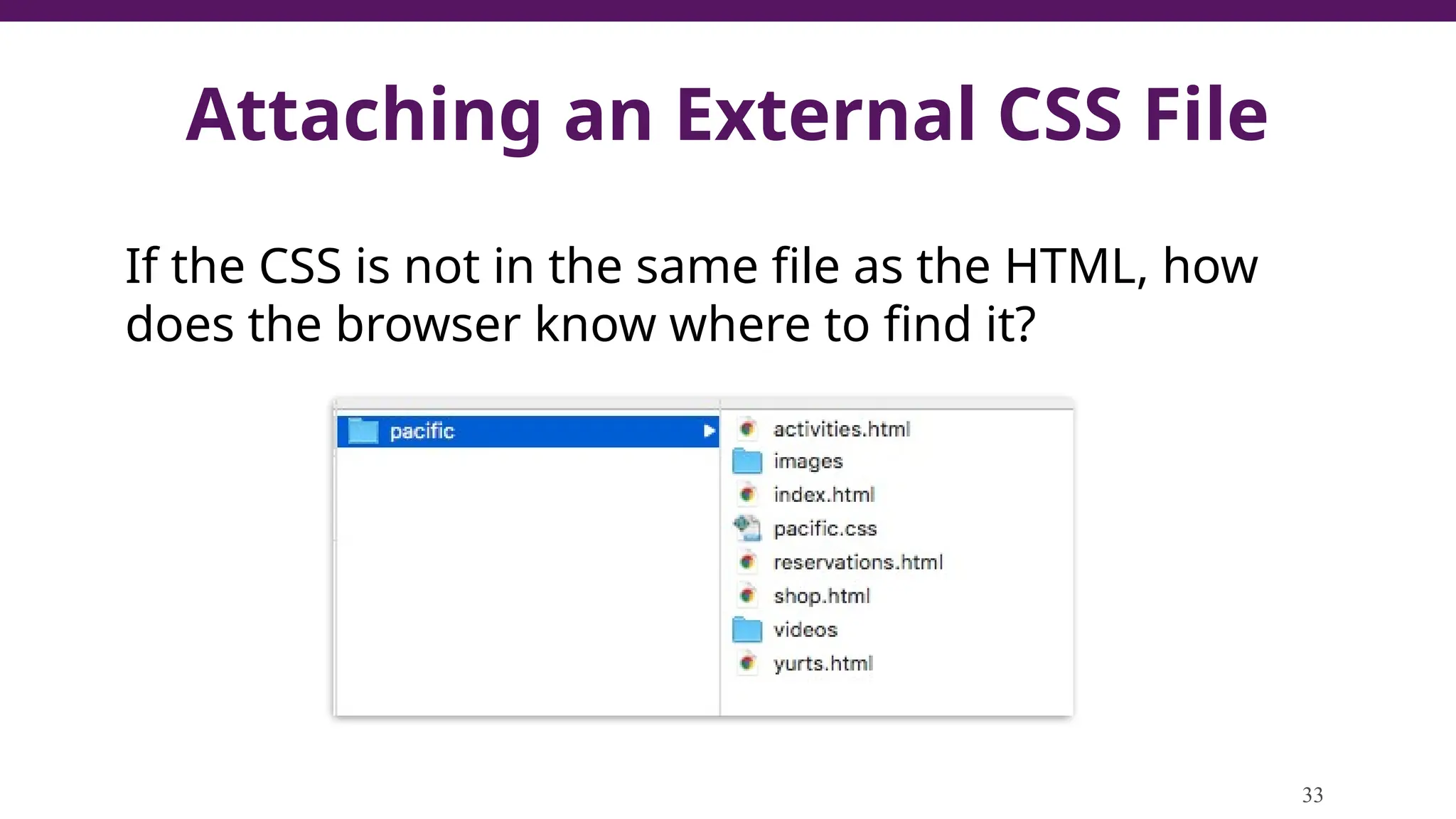
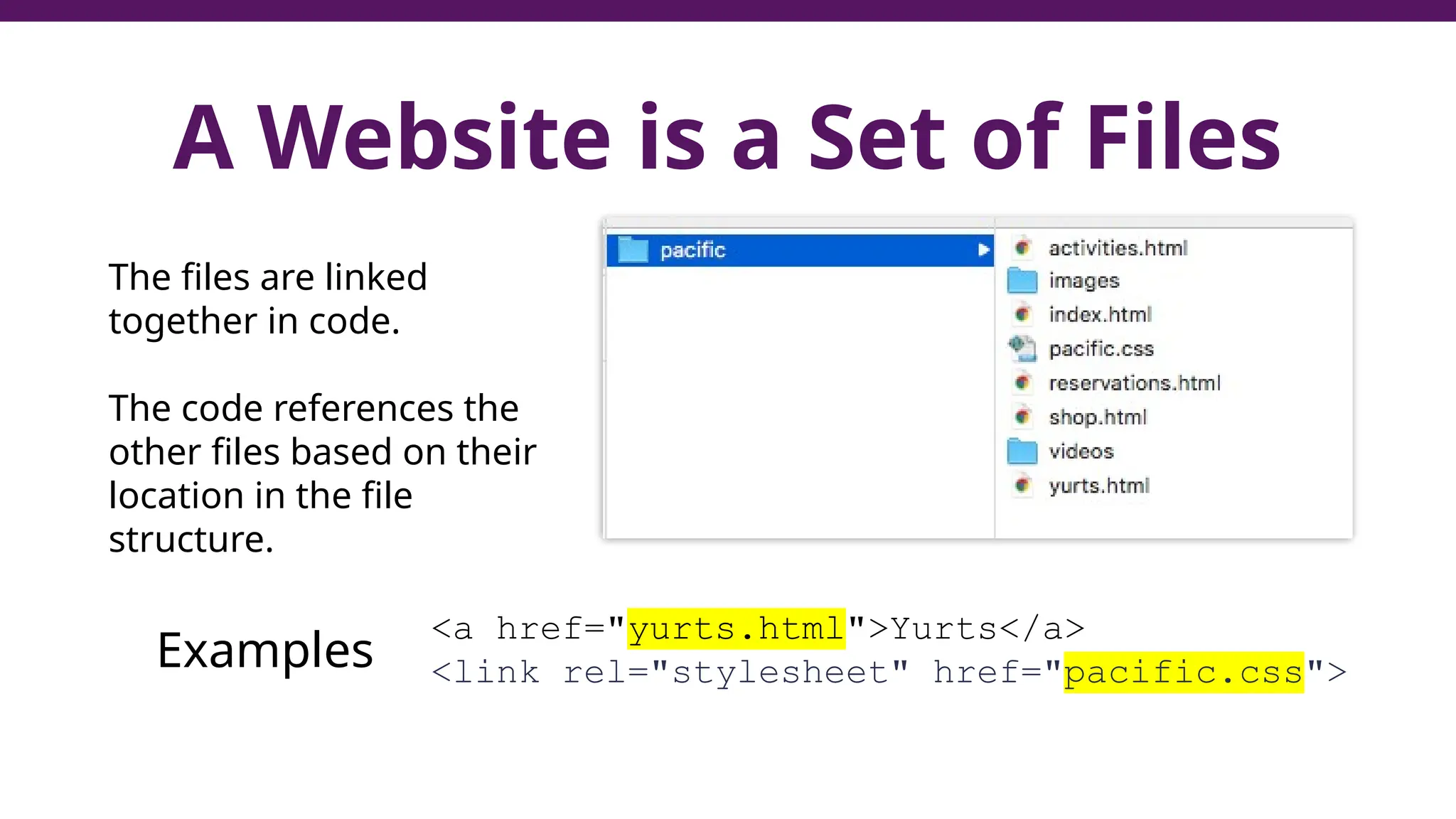
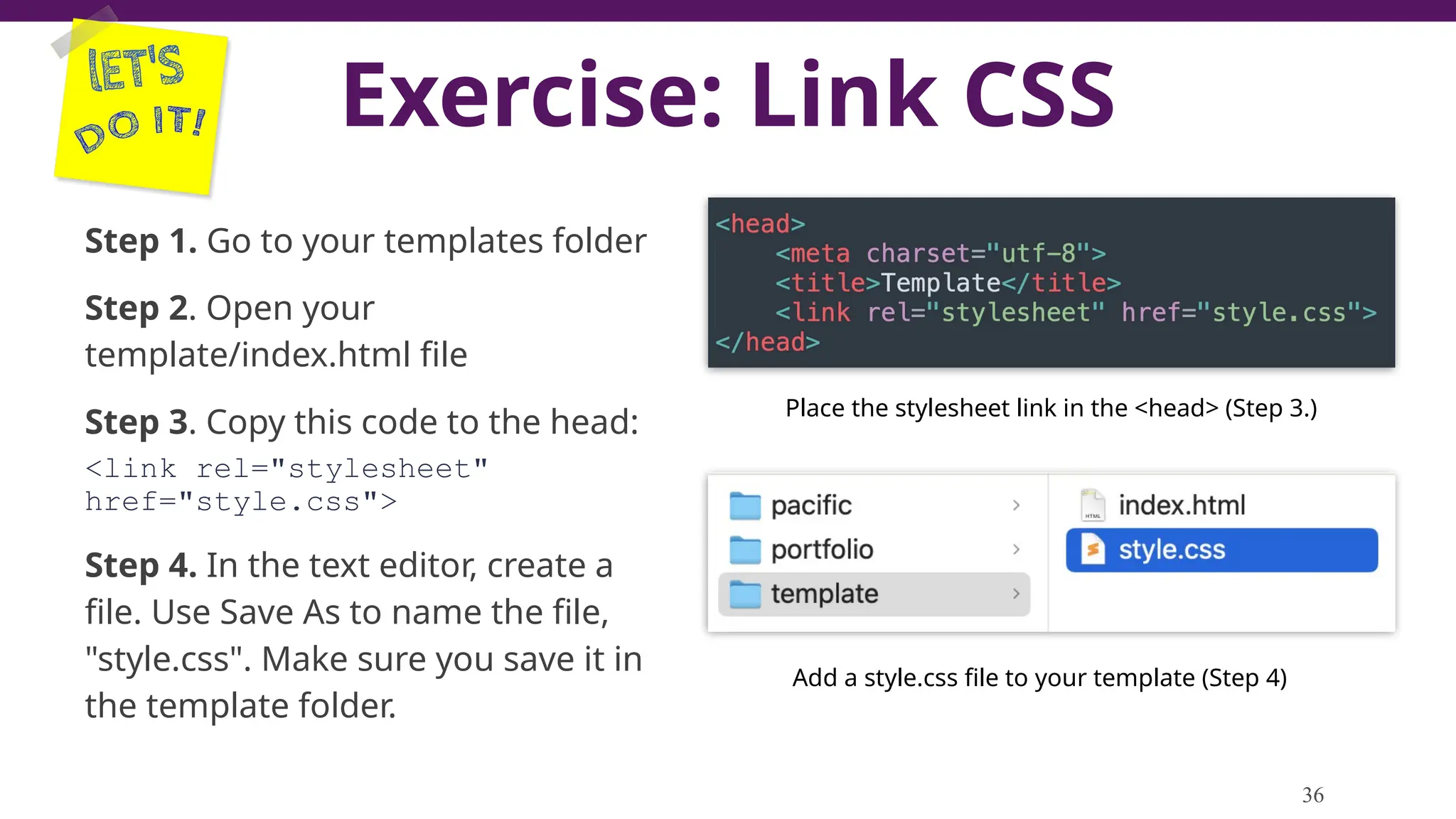
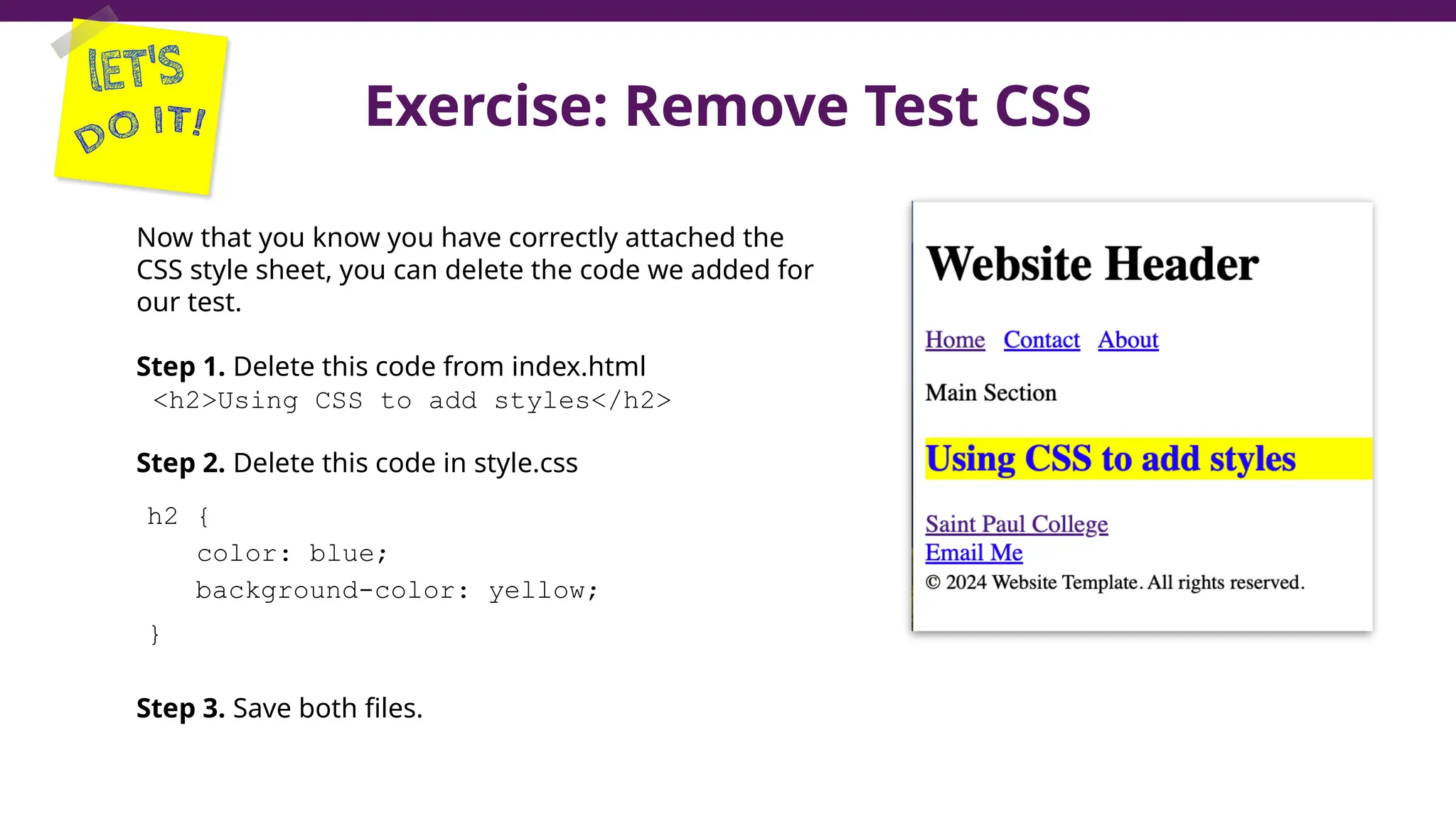
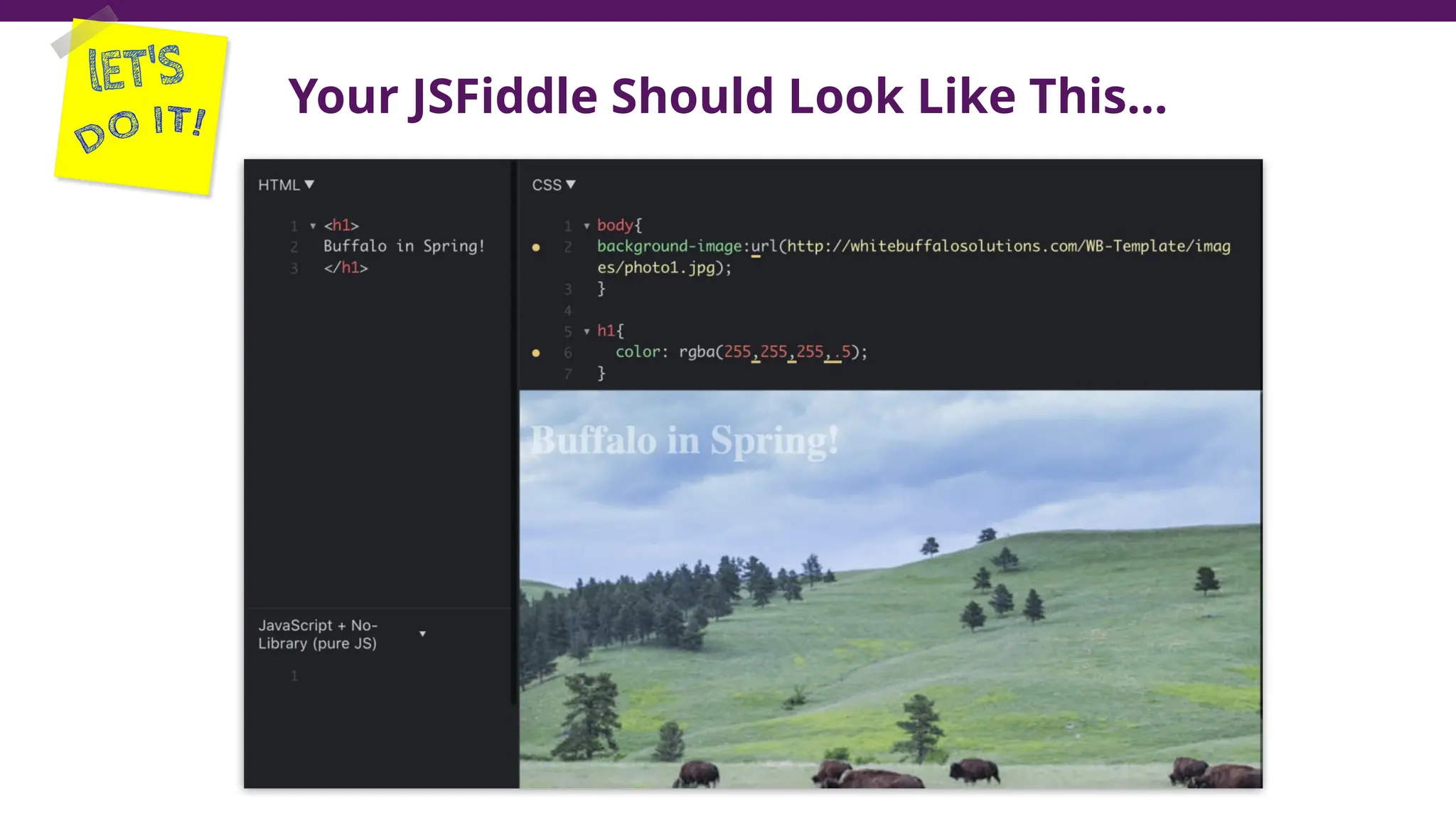
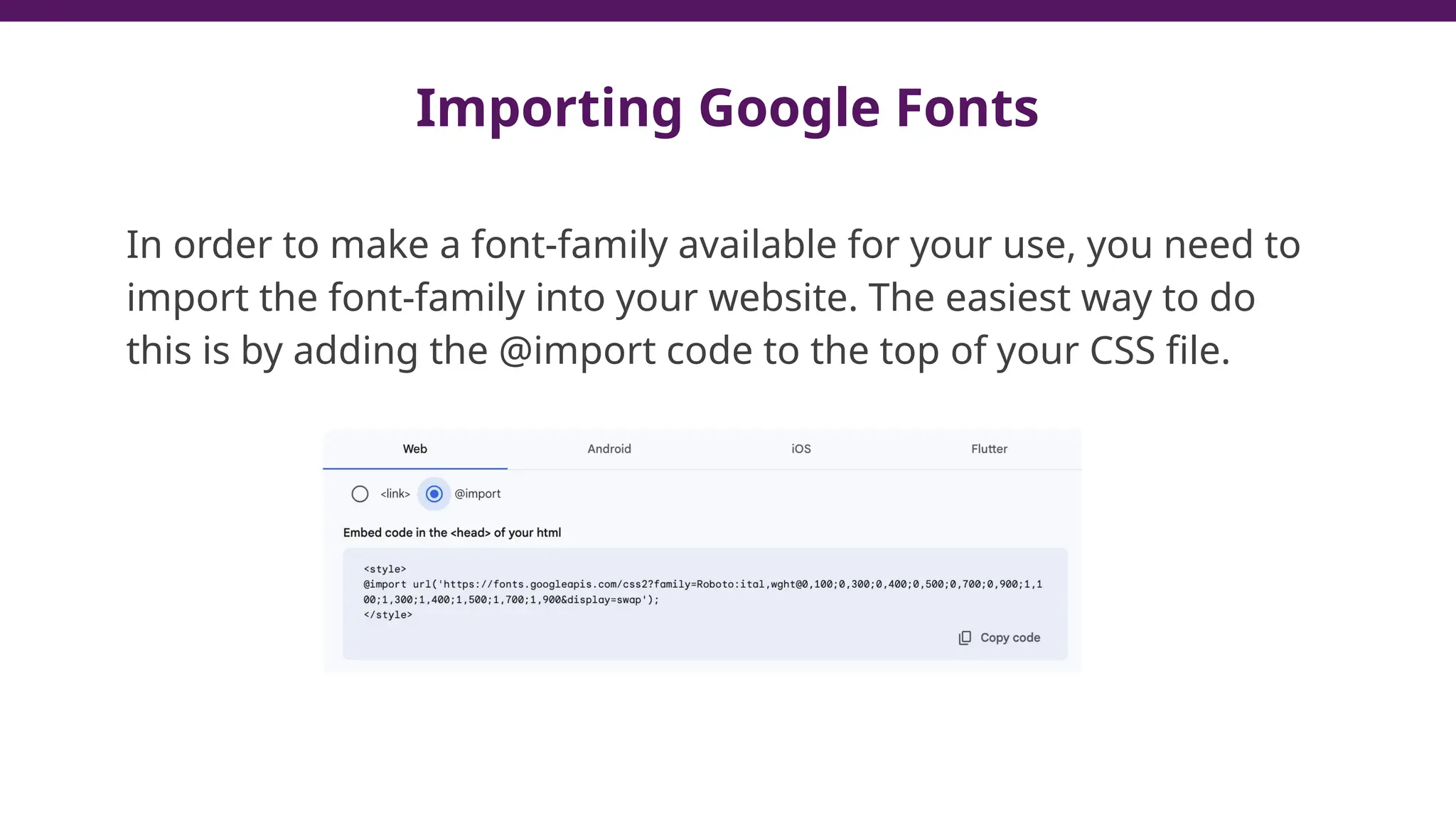
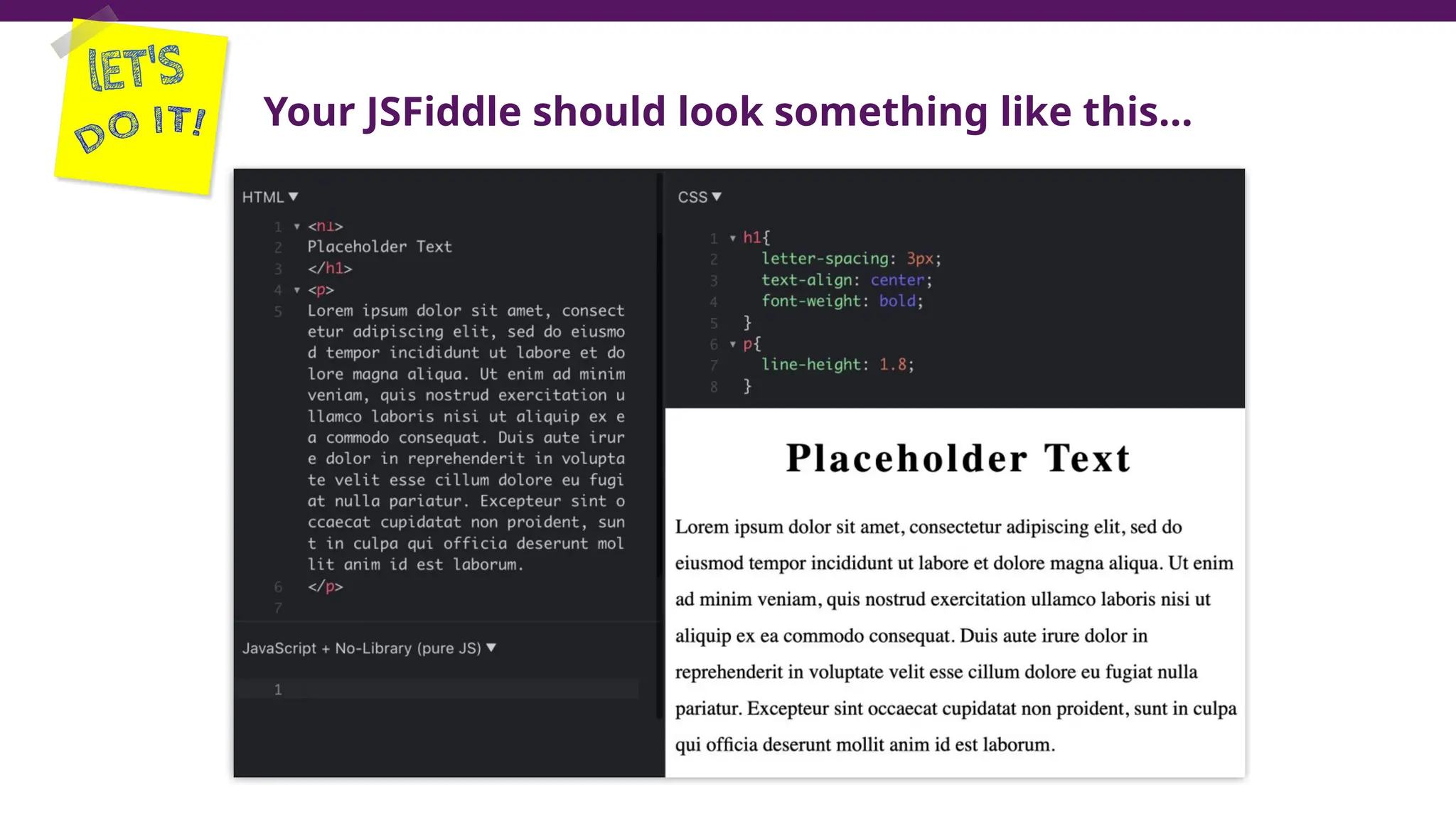
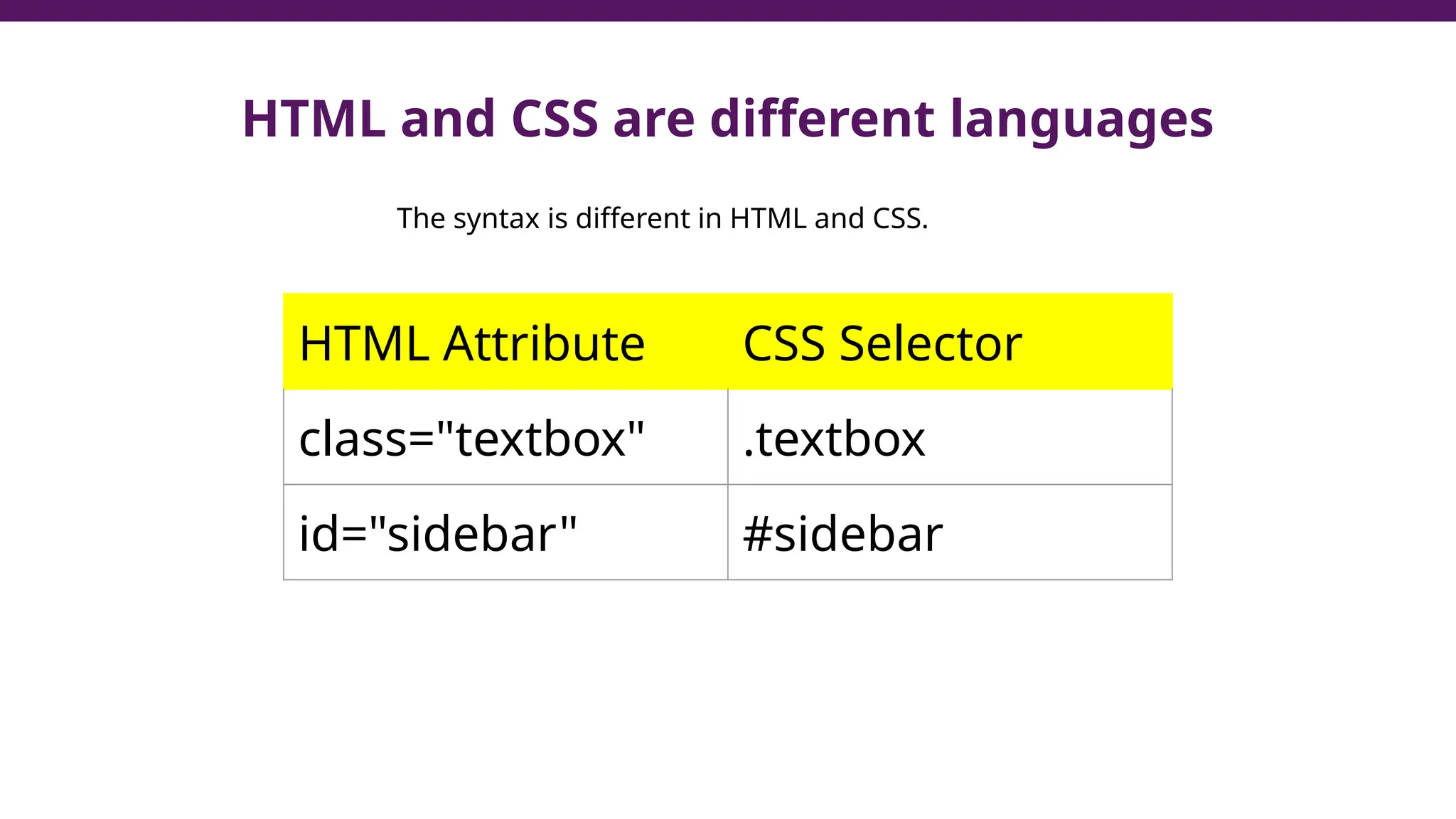
This document serves as a guide to introduce CSS in the context of web development, supplementing material from a specific textbook. It outlines the agenda for Module 3, covering CSS syntax, color properties, font-family usage, and different methods for incorporating CSS into webpages. The document also emphasizes the importance of maintaining a proper file structure and provides lab instructions and exercises related to template creation and the application of CSS styles.