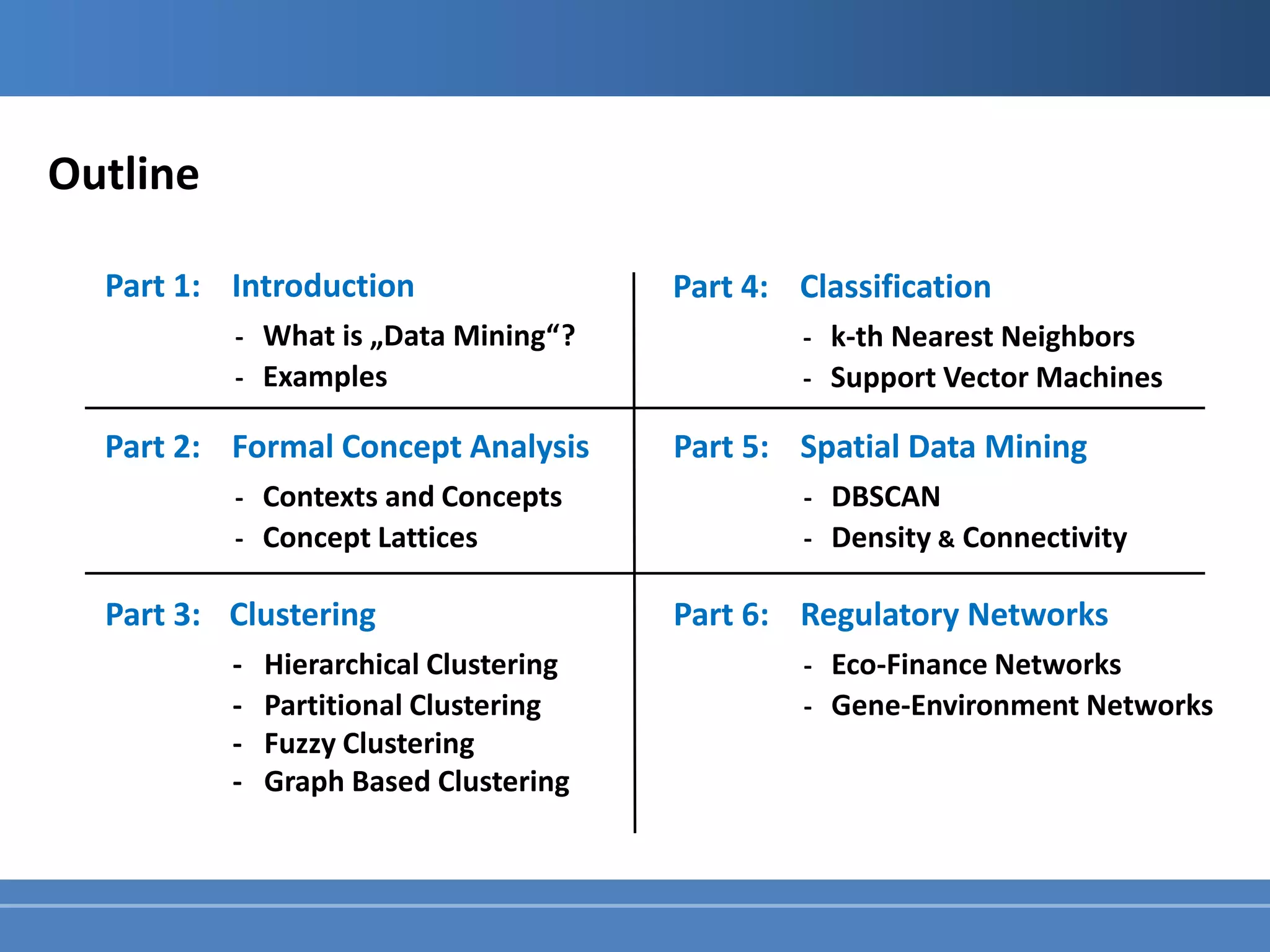
This document outlines topics in data mining and knowledge discovery in large databases. It discusses hierarchical, divisive, and density-based clustering techniques. It also mentions k-nearest neighbors and support vector machines classification algorithms. Additionally, it notes DBSCAN and density/connectivity for spatial data mining and regulatory networks for eco-finance and gene-environment applications. The document provides an introduction to data mining concepts and examples of analyzing retail, banking, and telecommunications customer data.