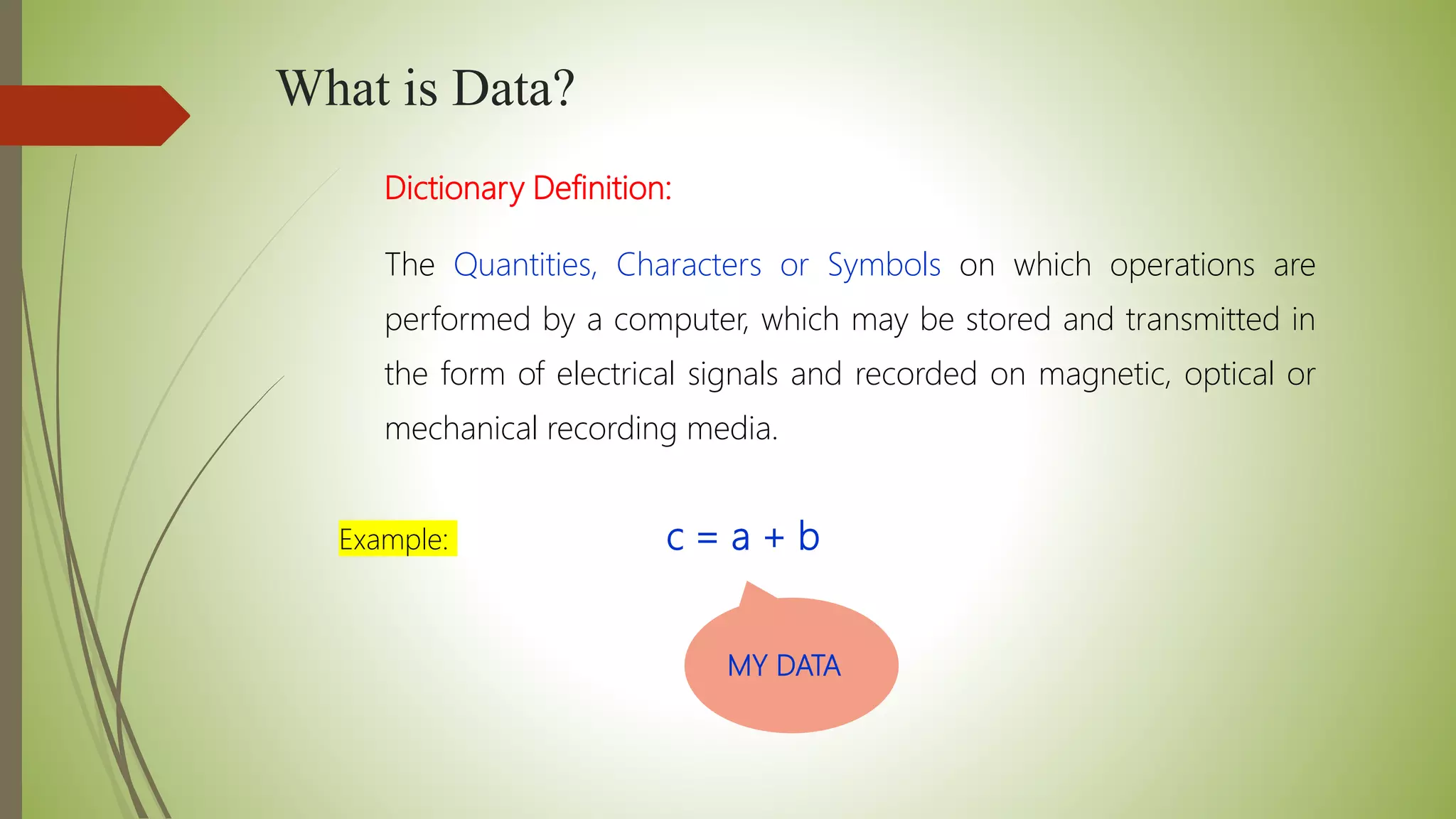
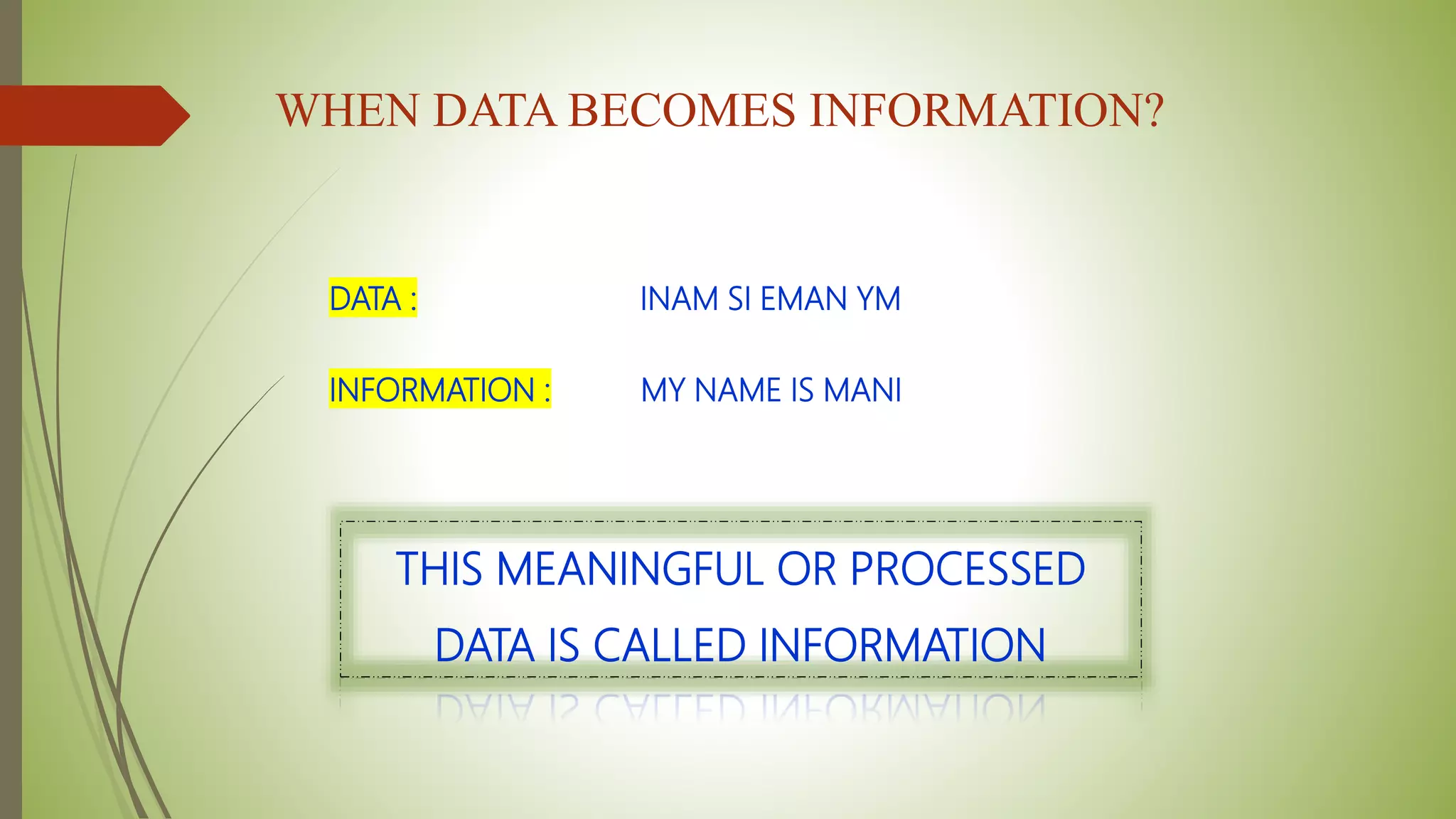
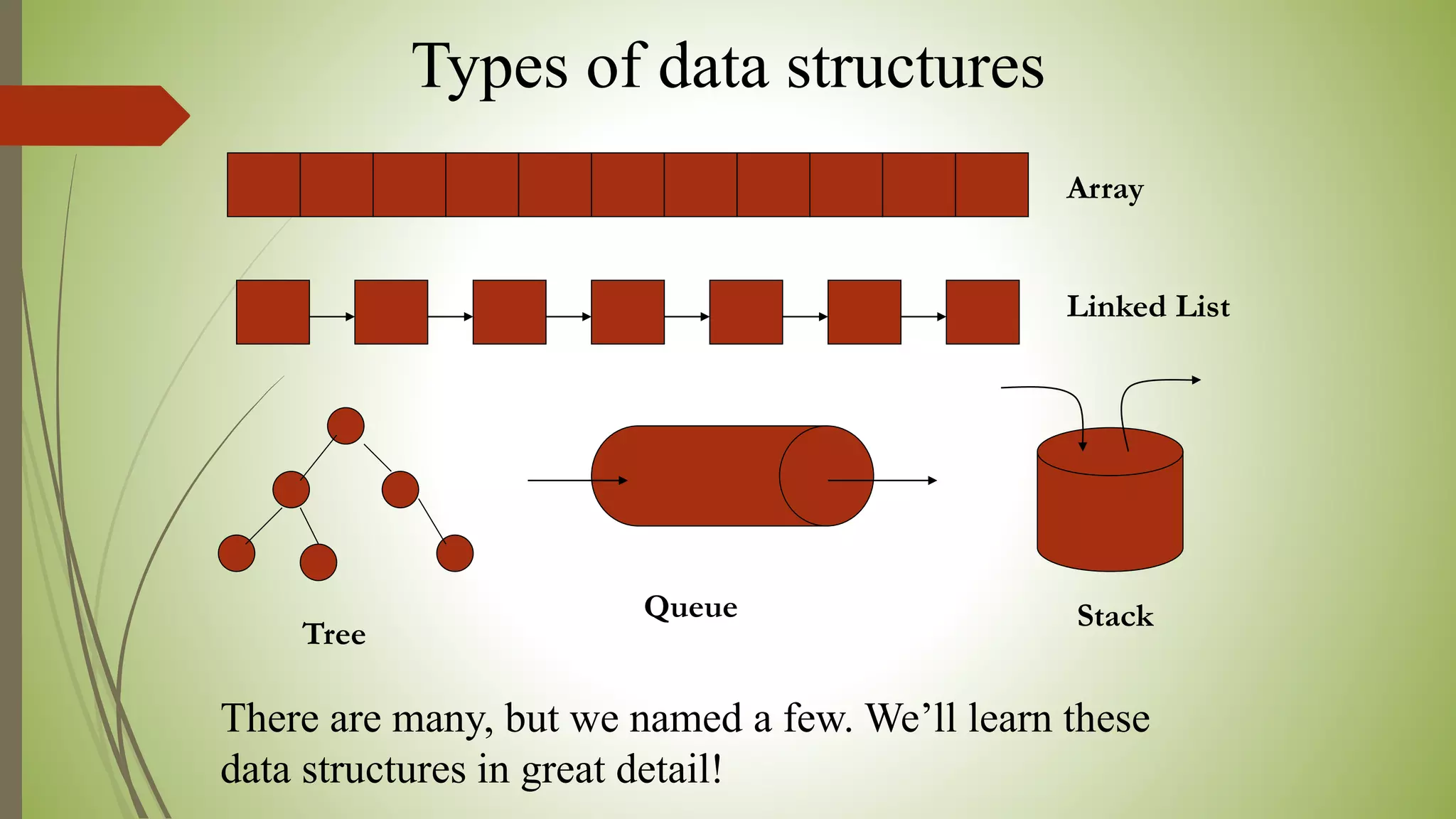
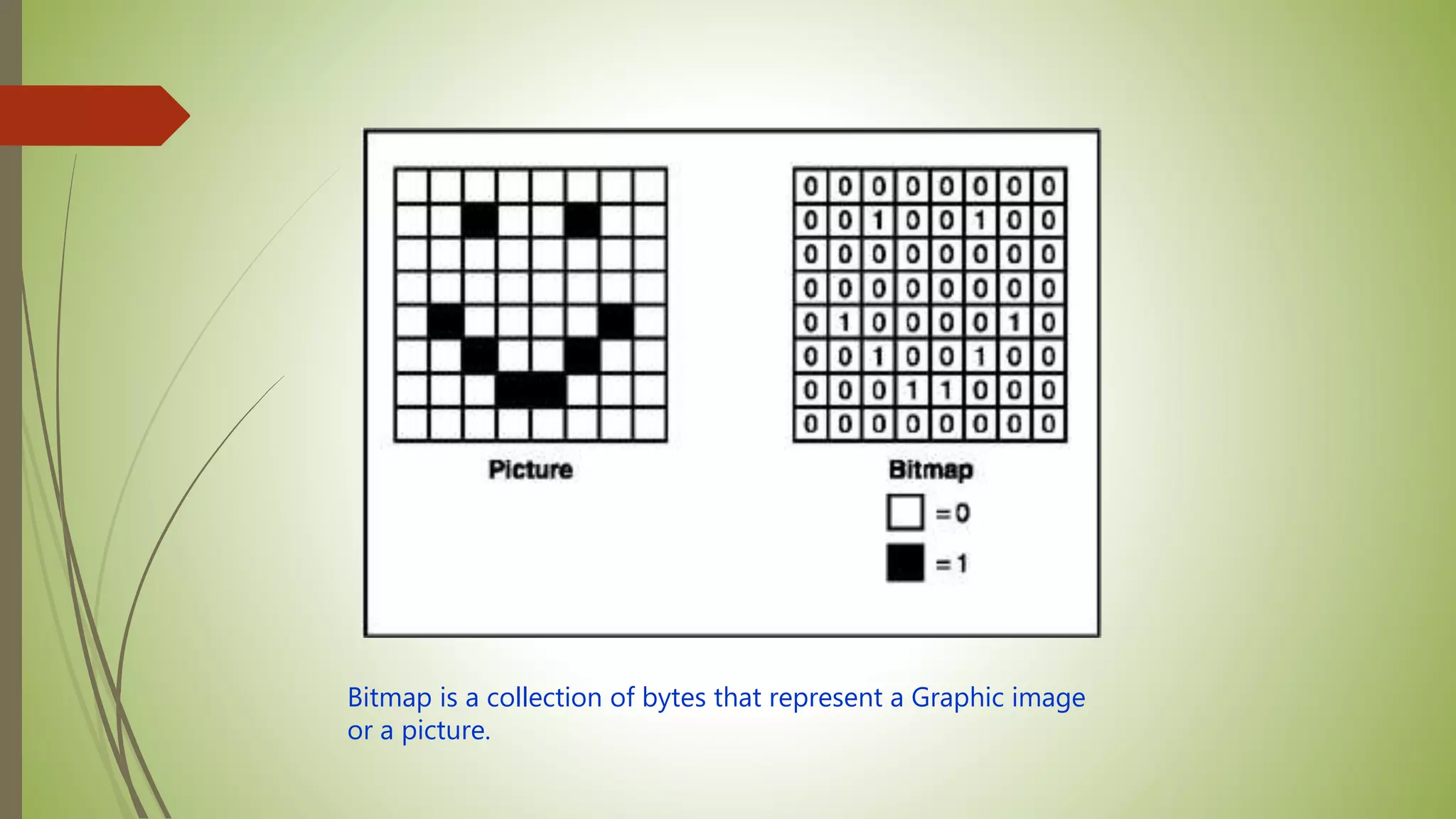
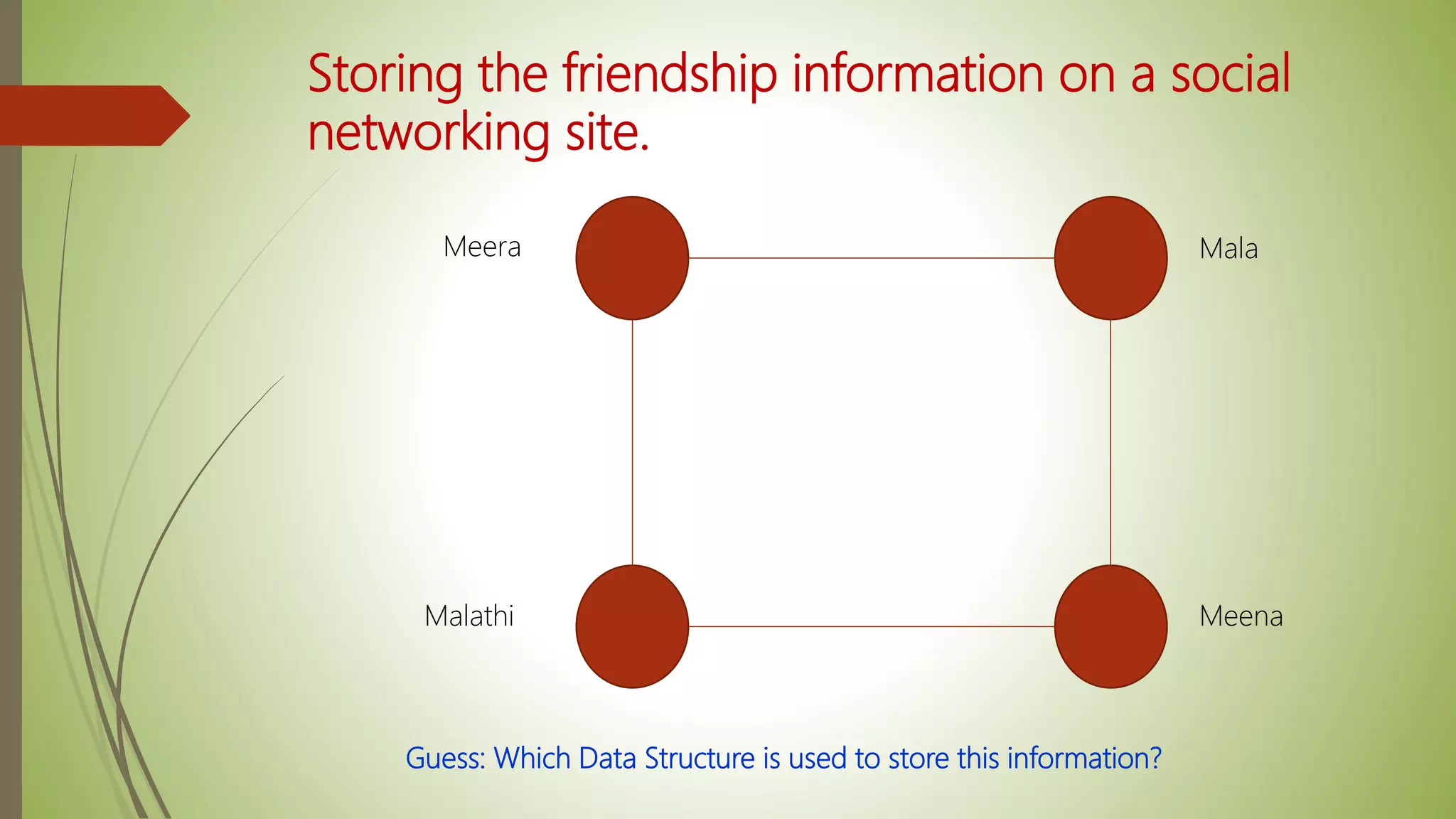
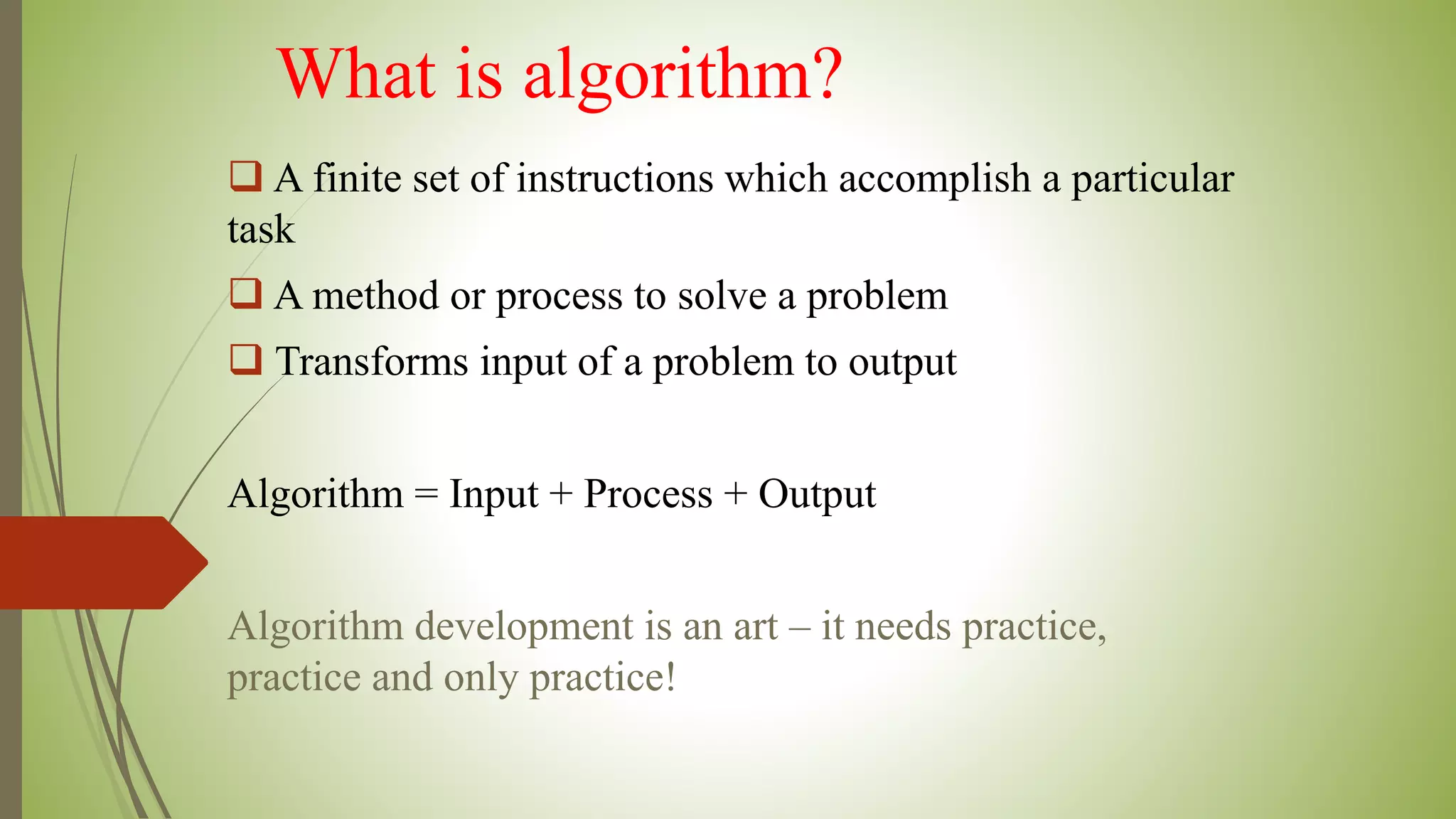
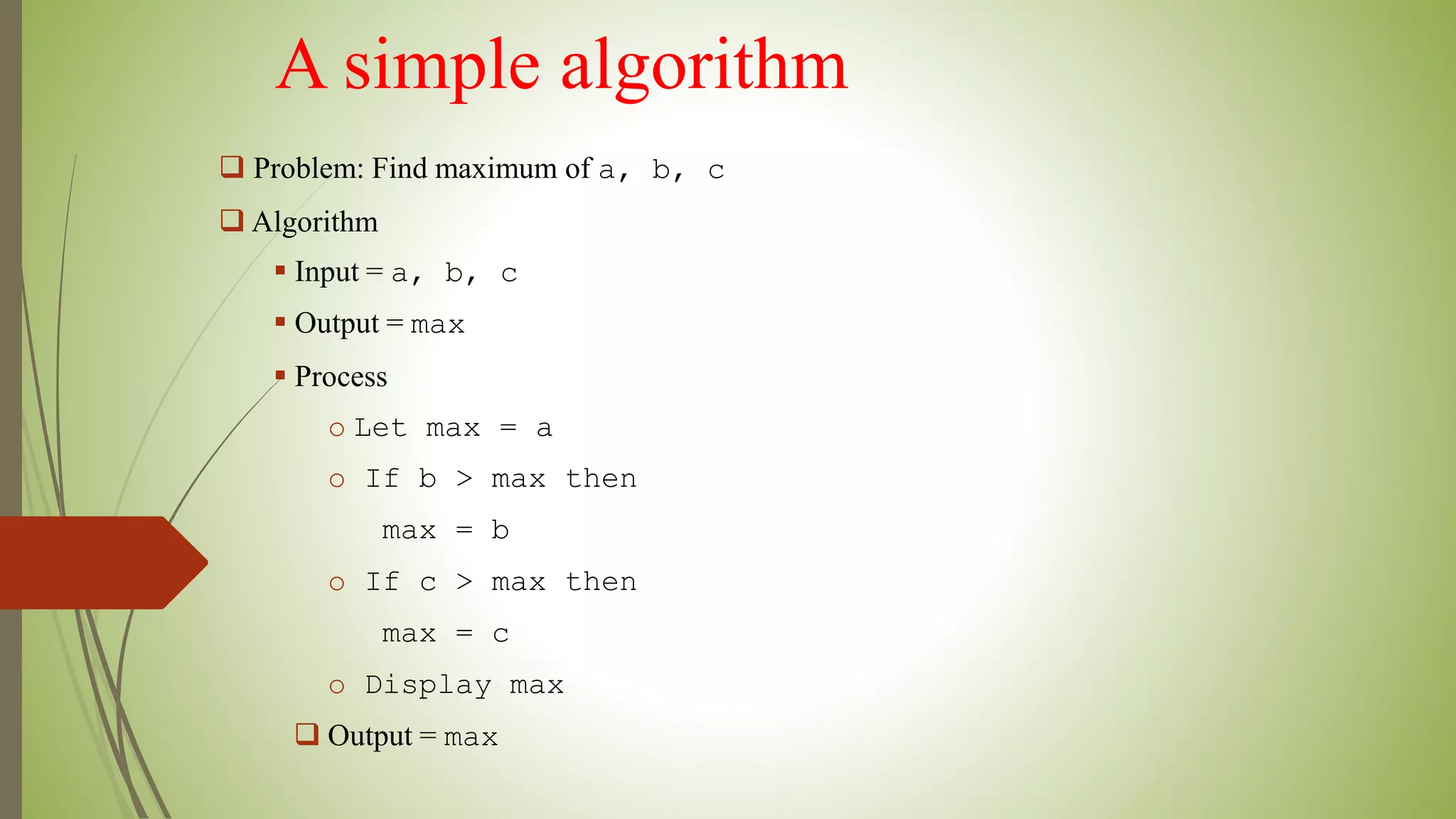
This document provides an introduction to data structures and algorithms. It defines data as quantities, characters, or symbols operated on by a computer. Data structures are described as organized ways to store and access data efficiently. Common data structures include arrays, linked lists, trees, stacks, and queues. Algorithms are sets of instructions to solve problems, taking input and producing output. Good algorithms are correct, unambiguous, and efficient. Examples demonstrate data structures like arrays and graphs, as well as a simple maximum-finding algorithm. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of data structures.