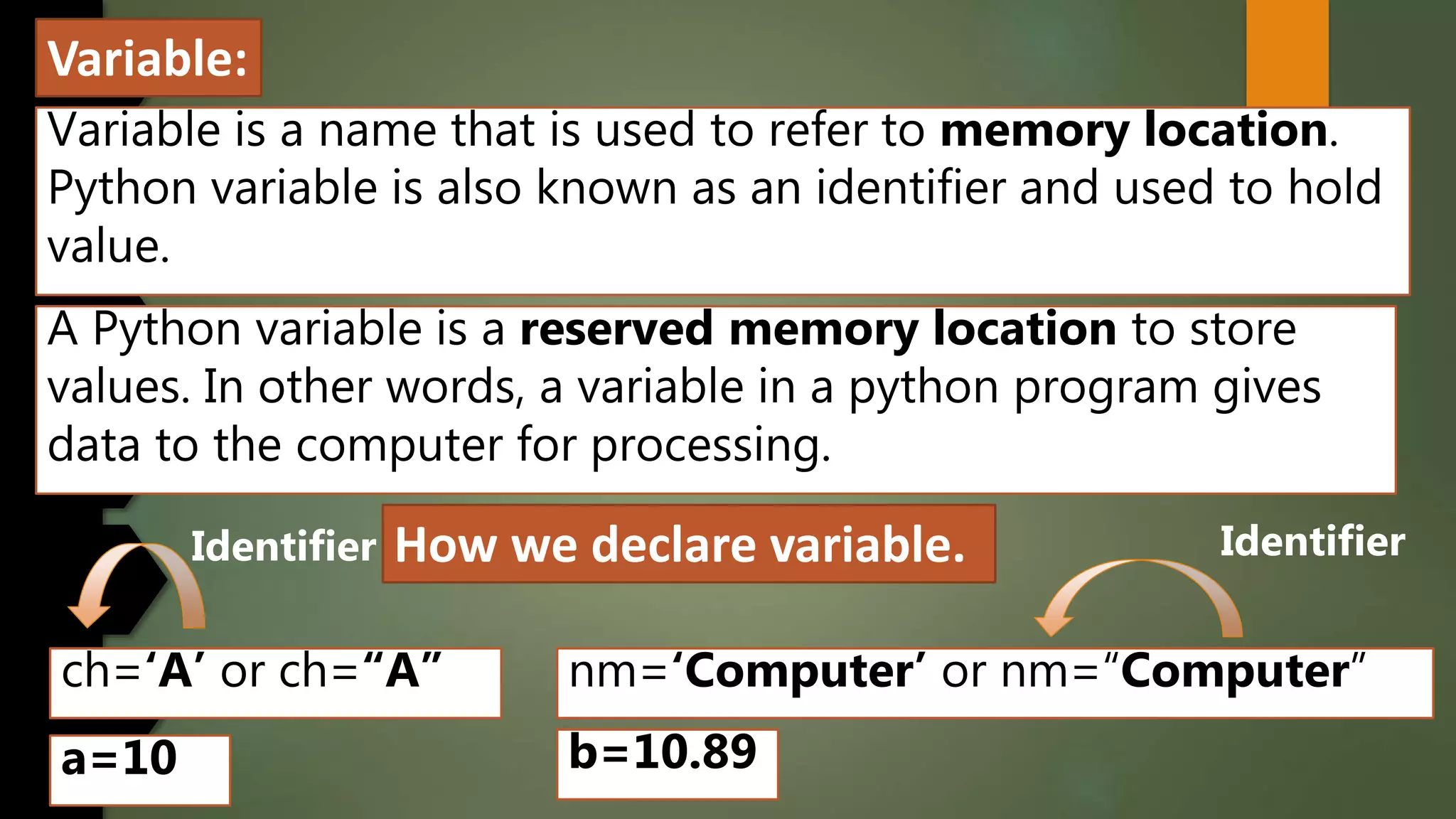
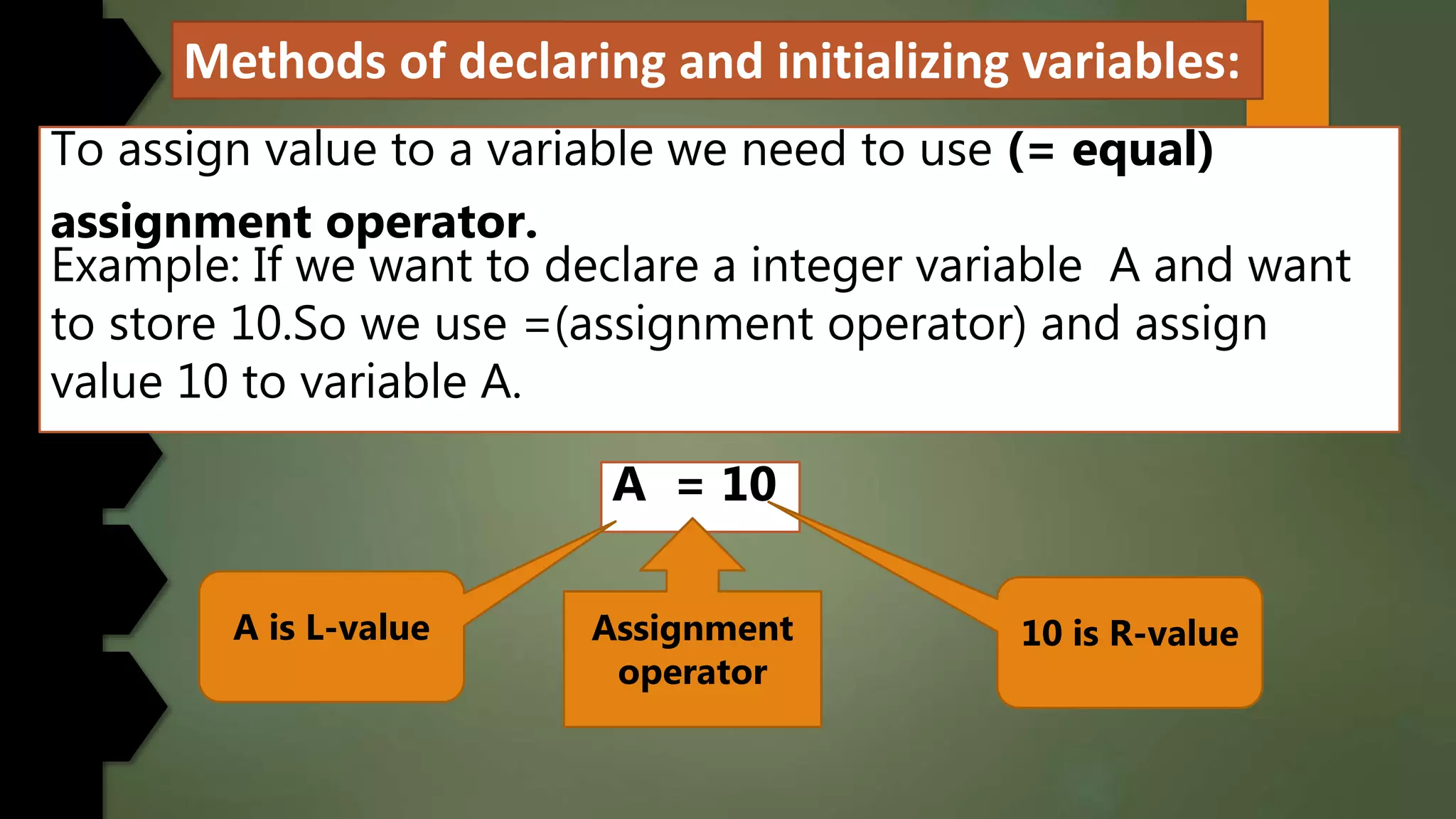
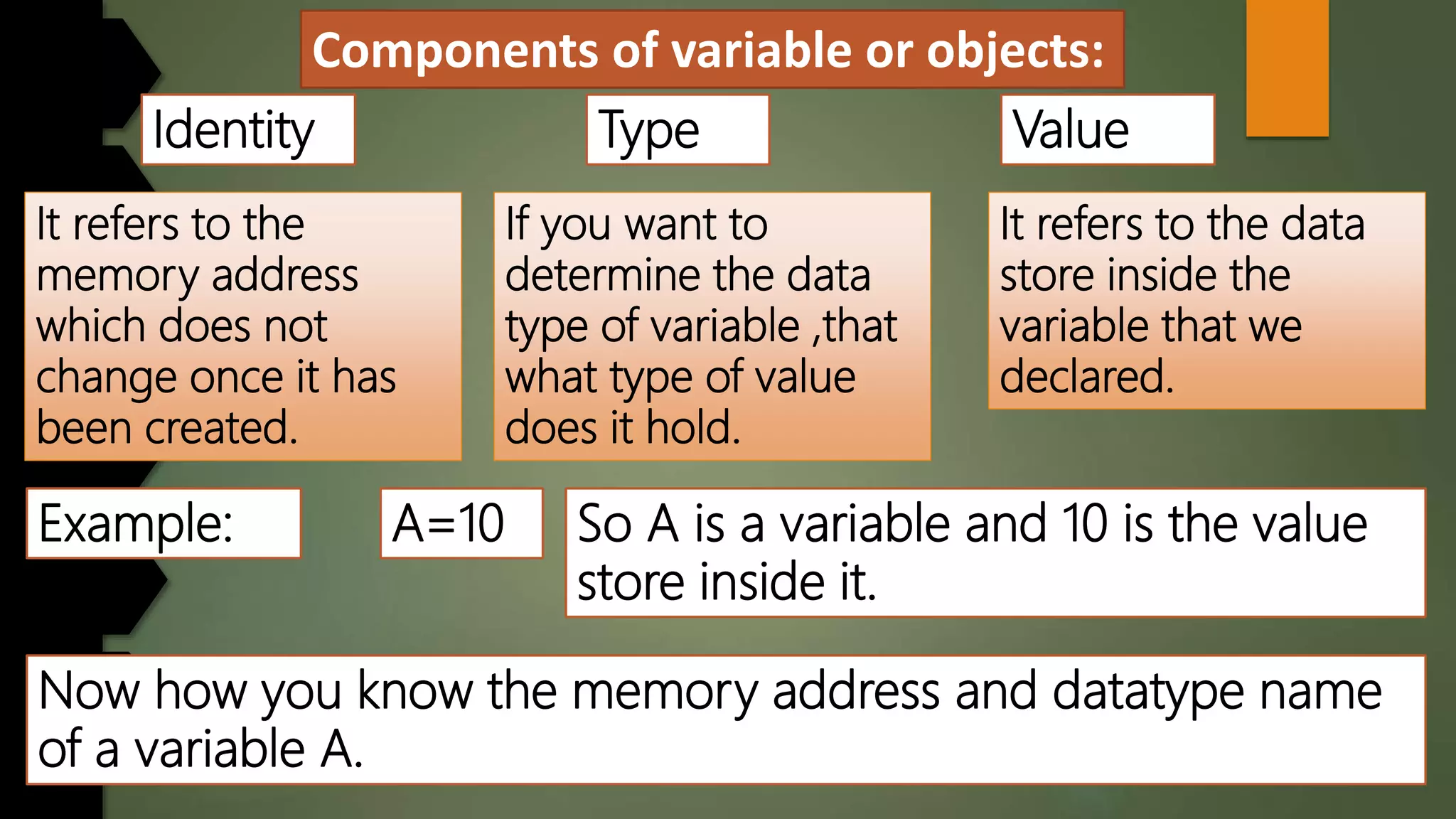
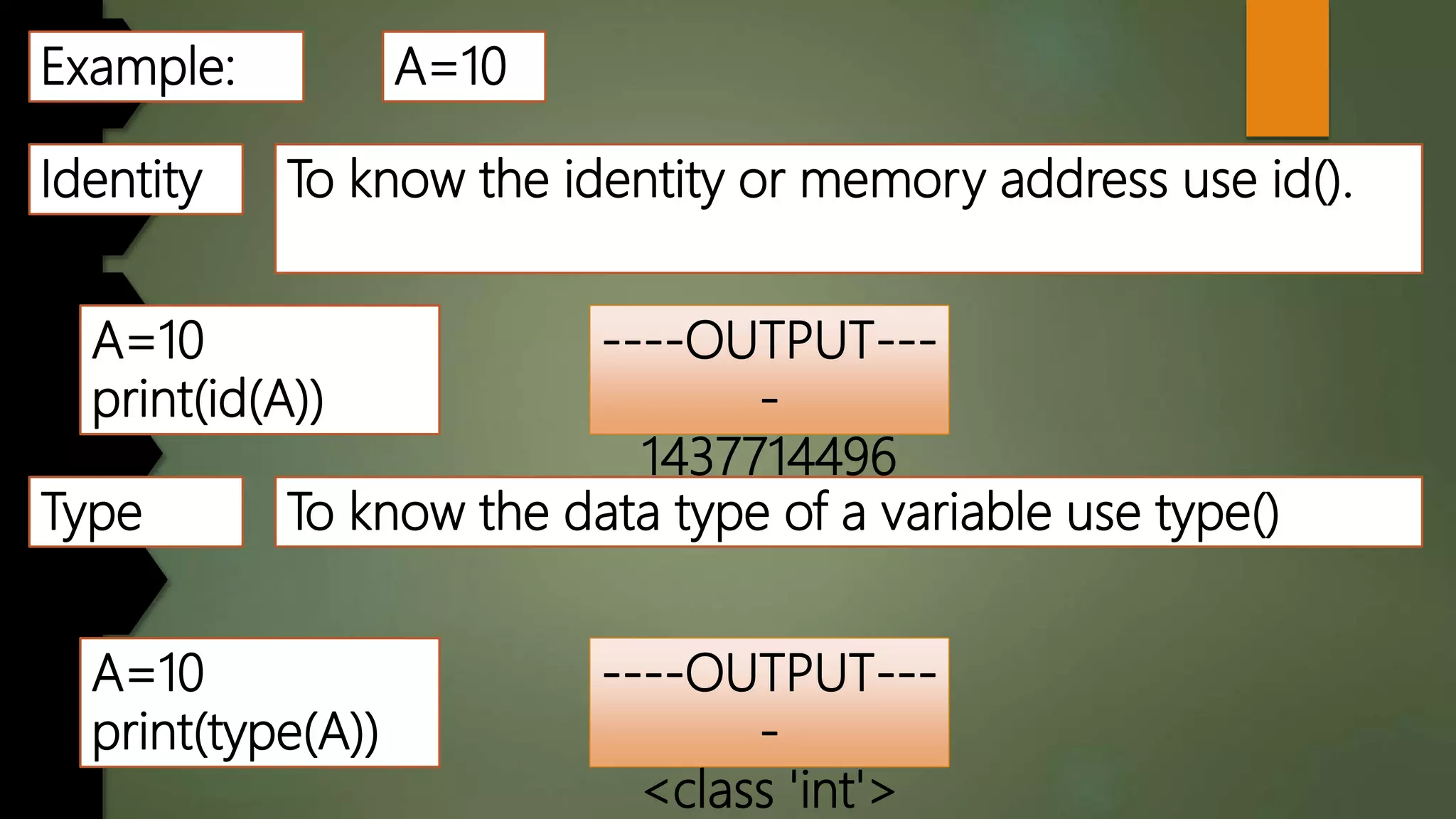
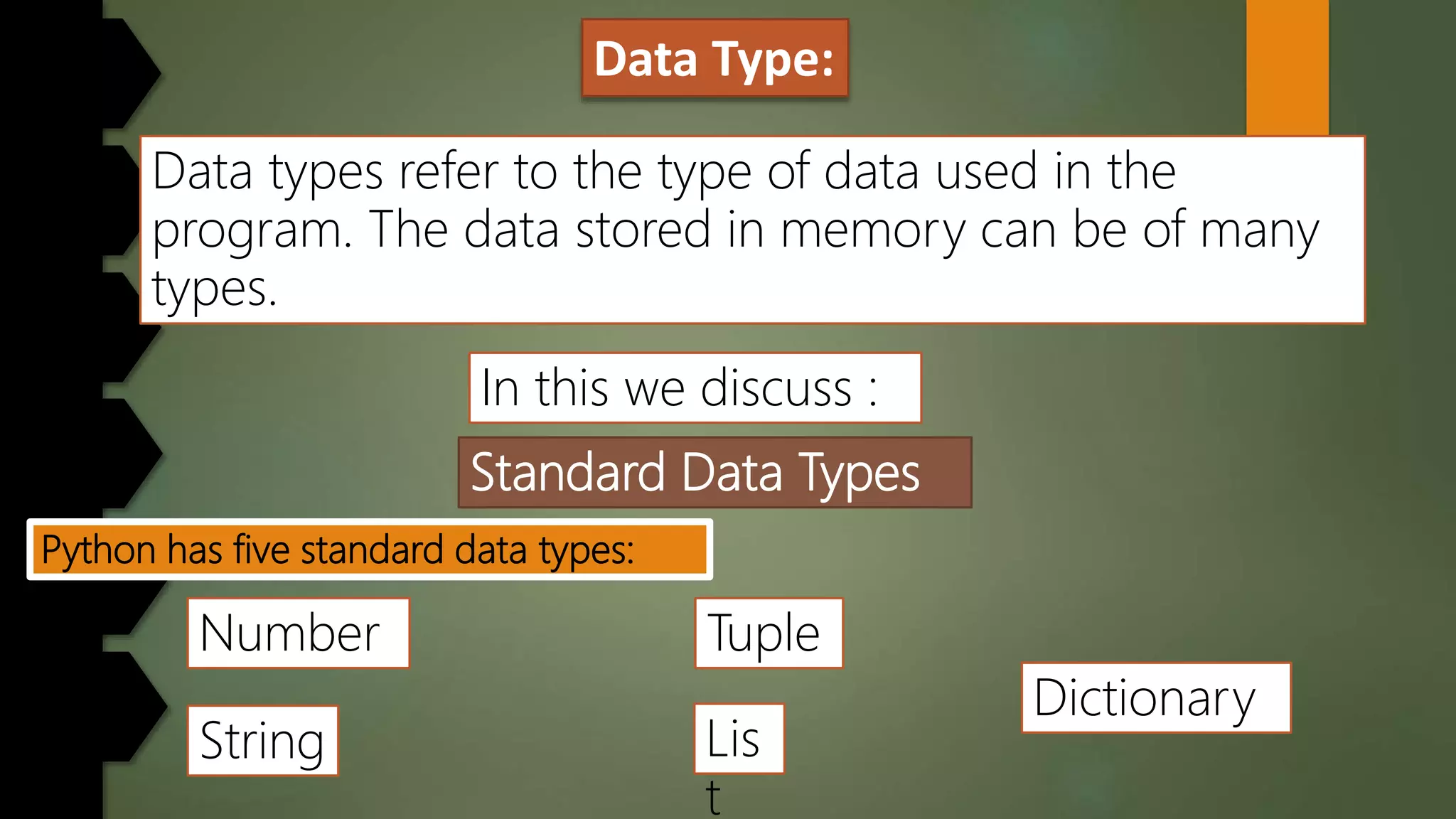
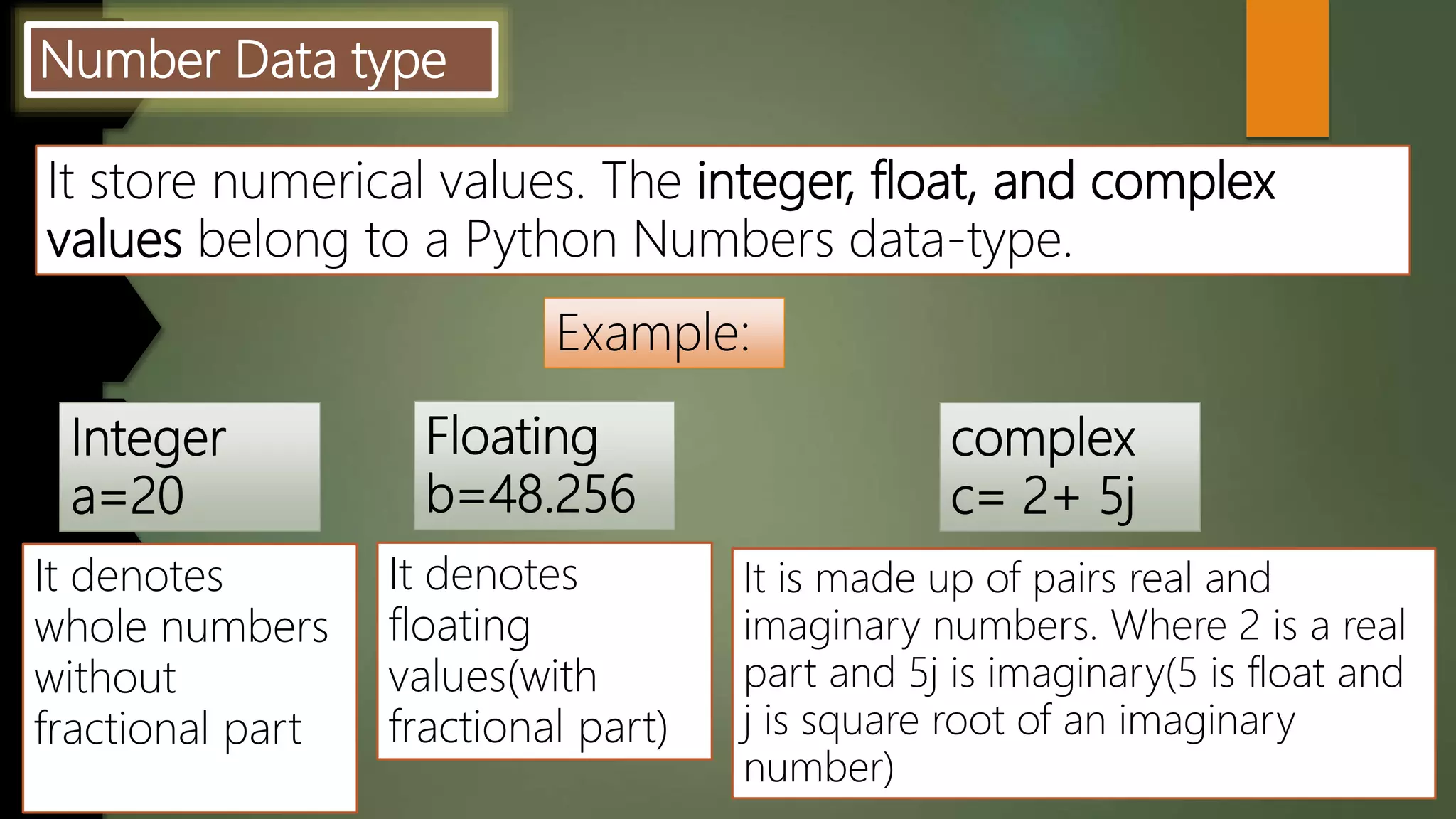
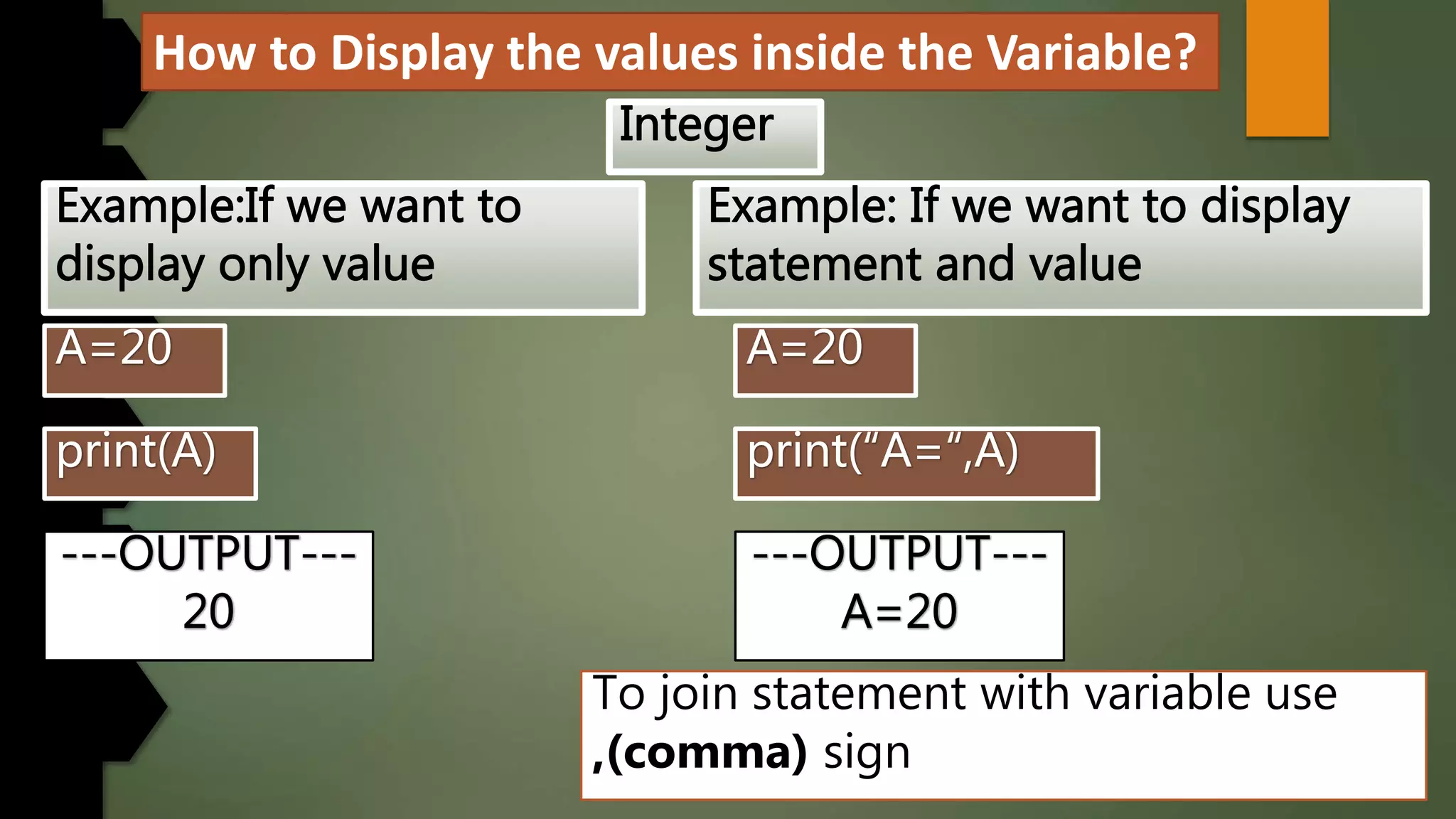
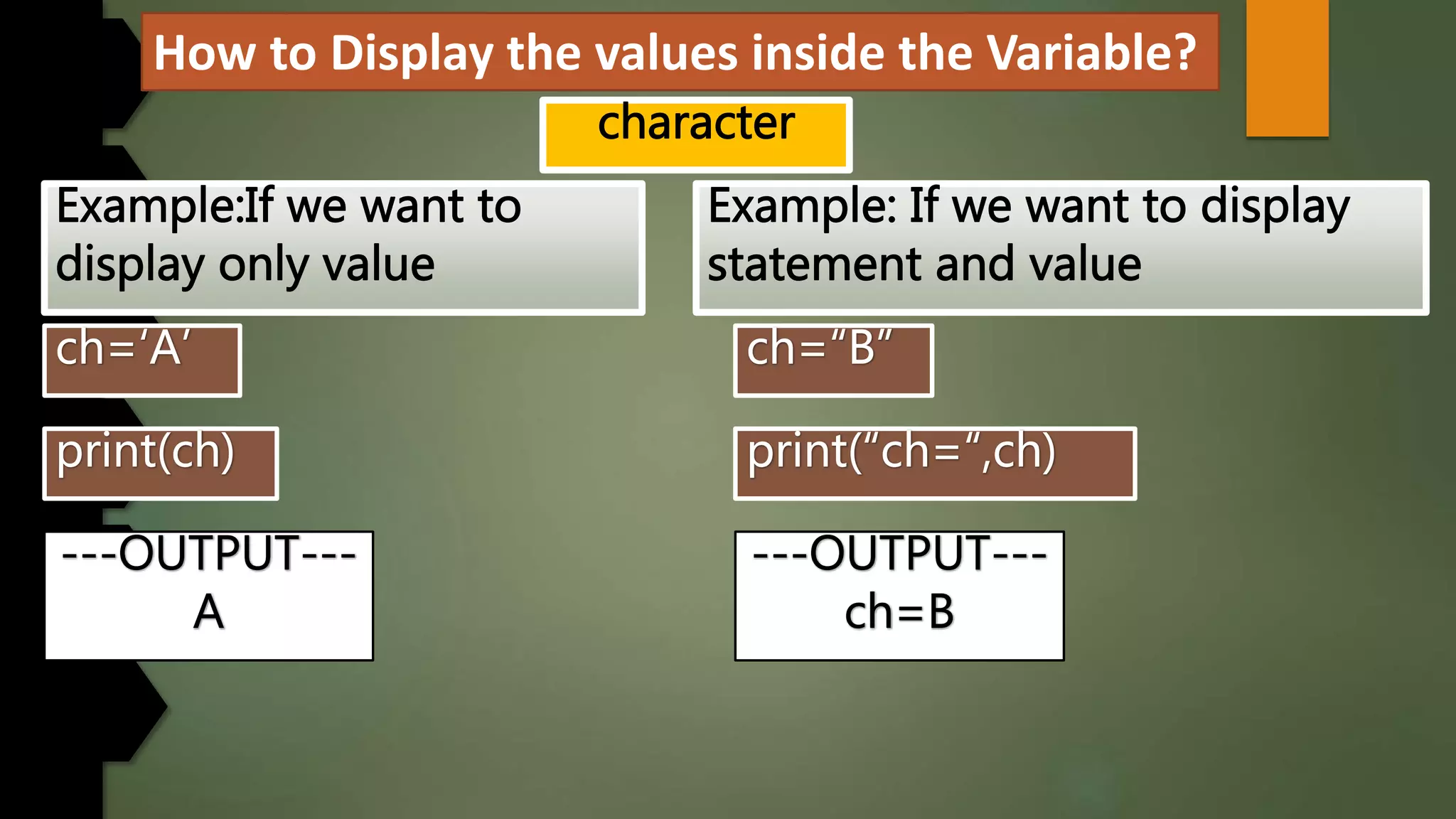
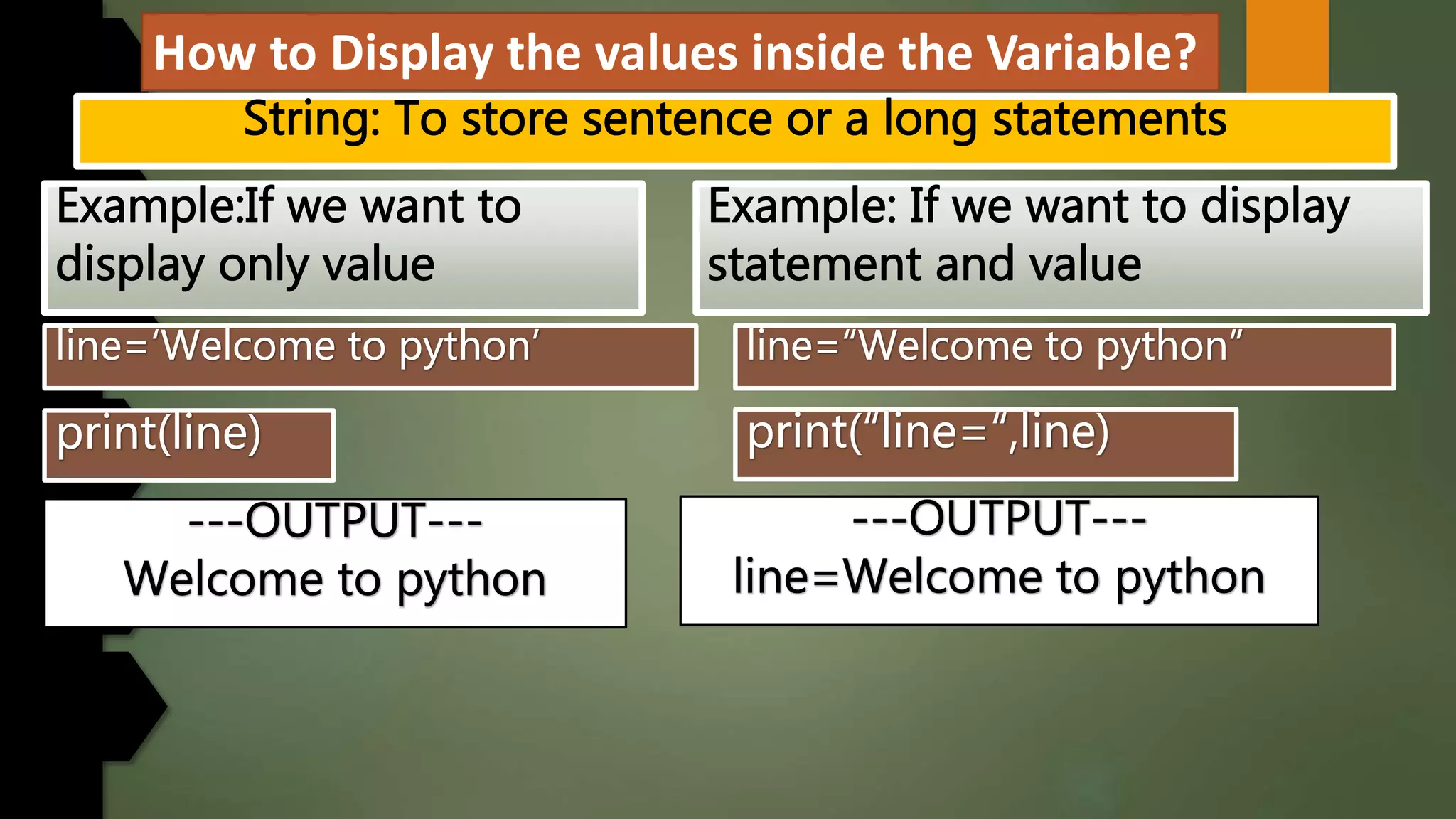
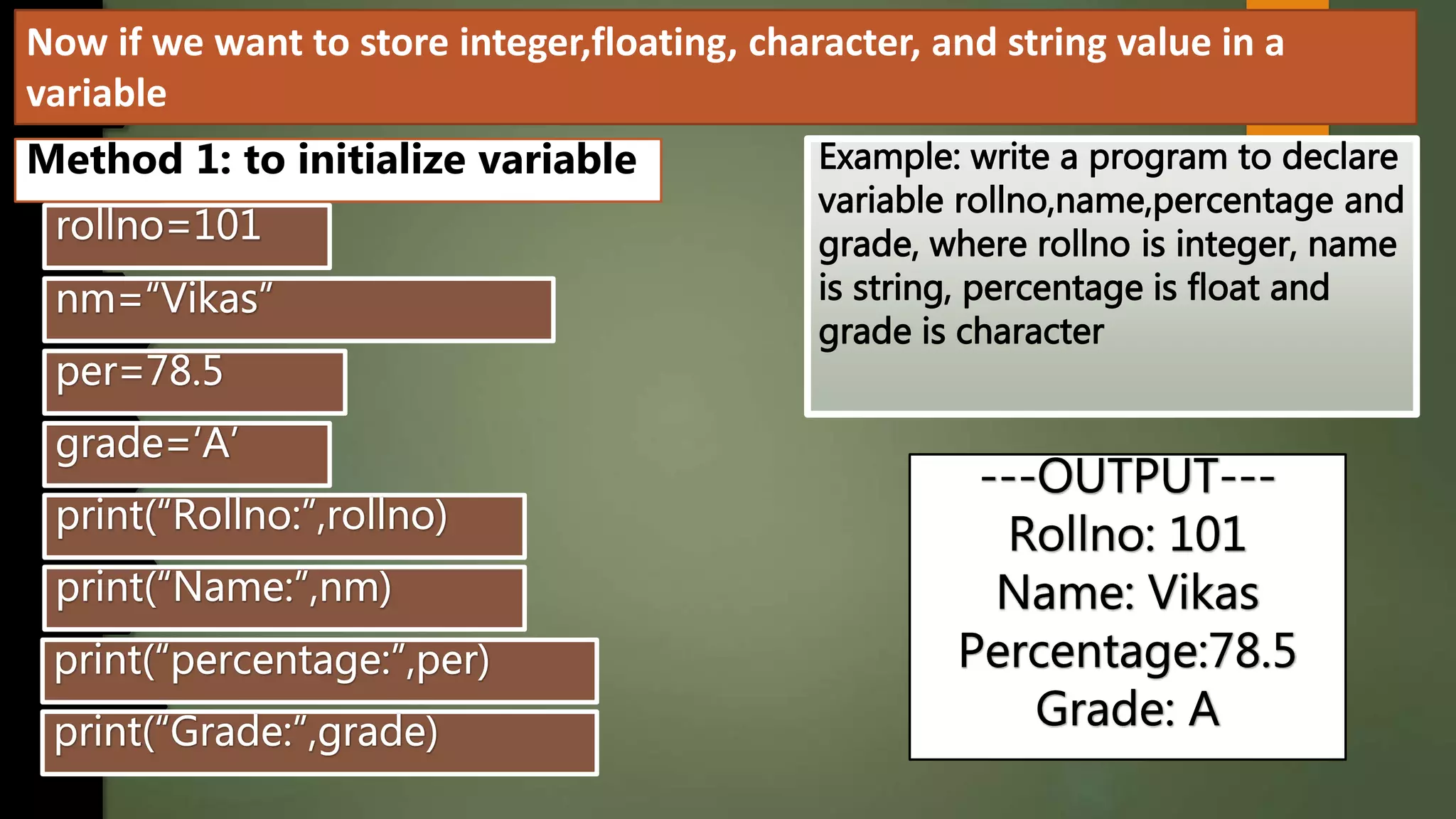
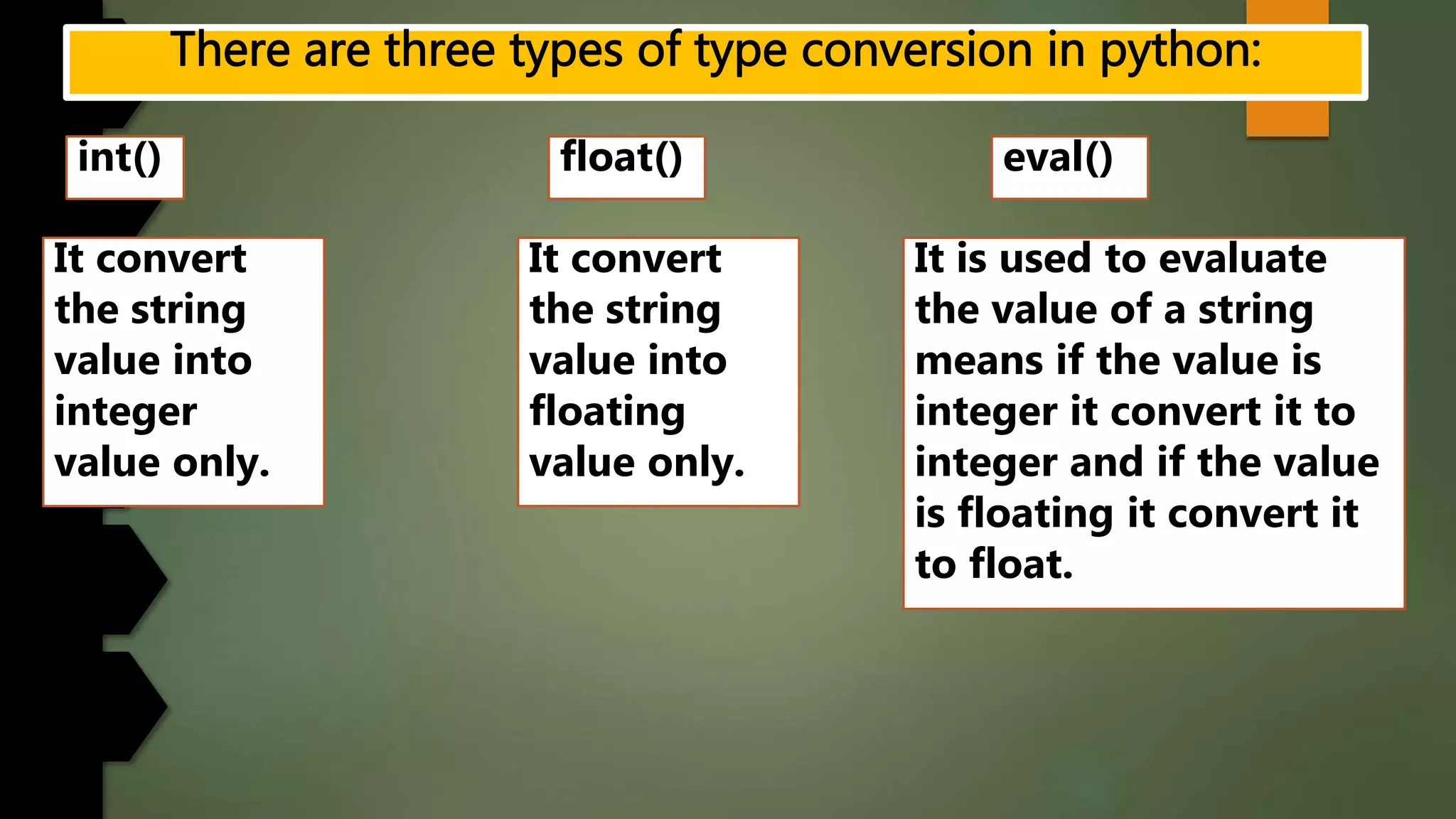
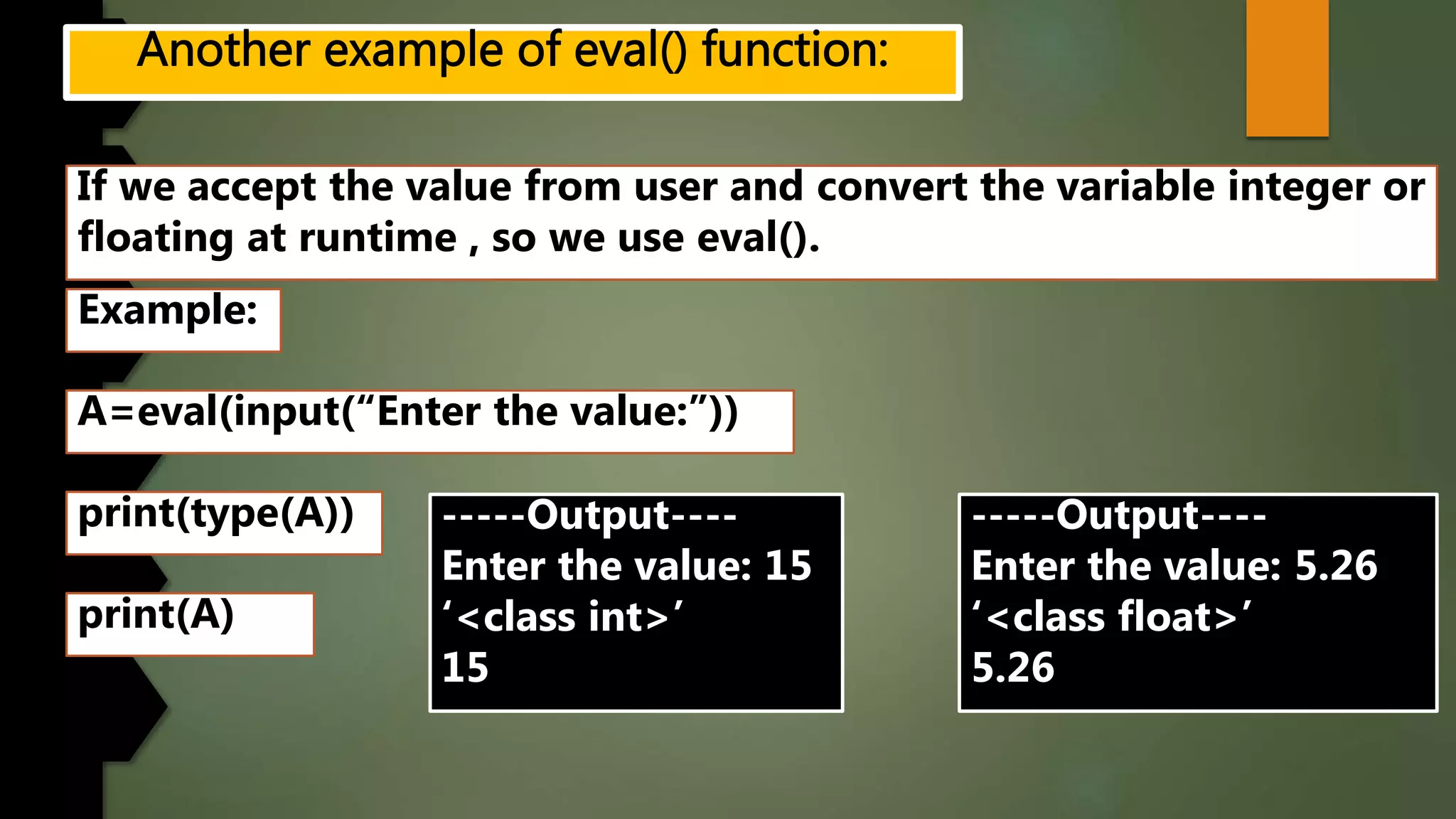
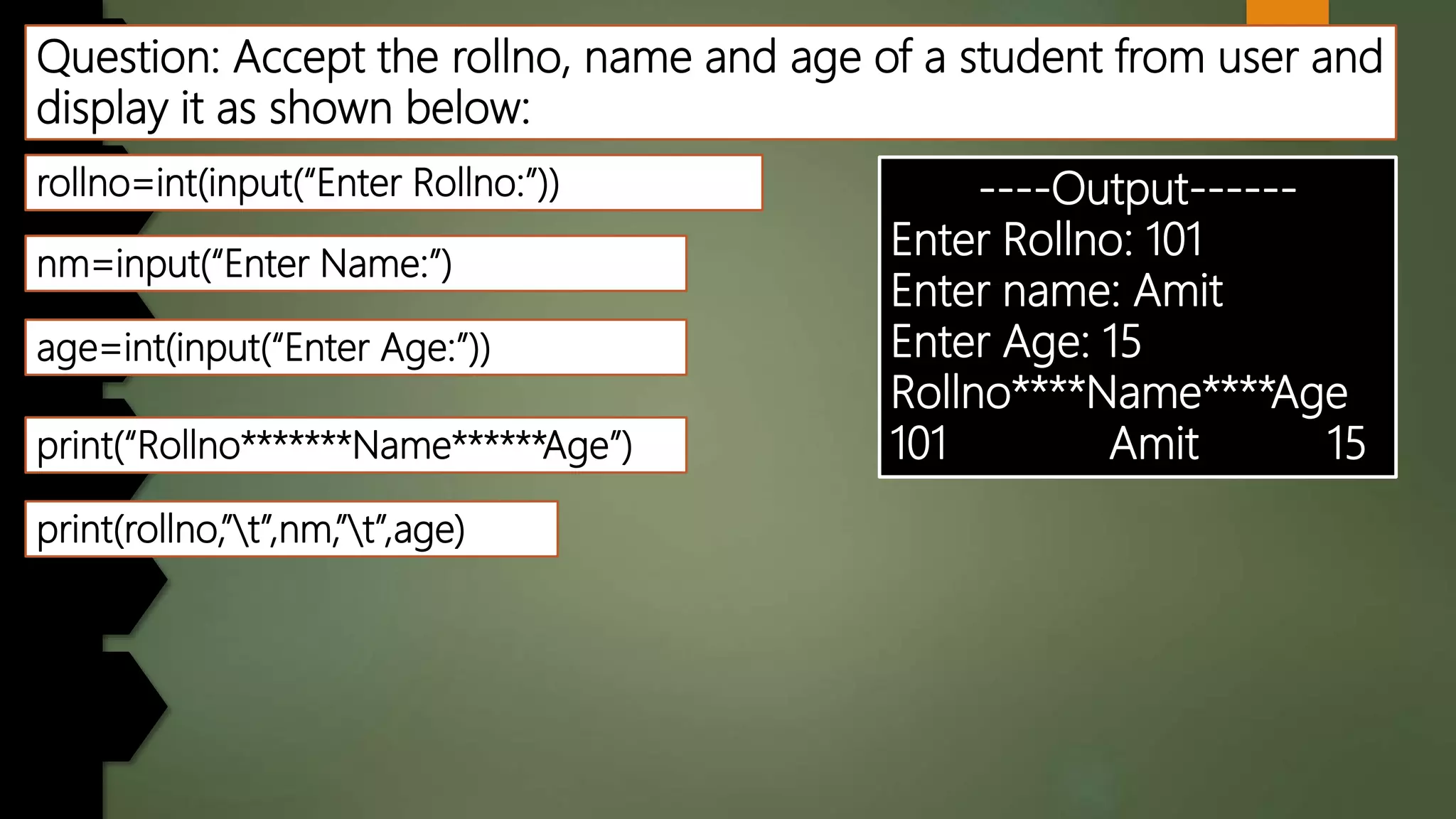
This document discusses data types and variables in Python. It explains that a variable is a name that refers to a memory location used to store values. The main data types in Python are numbers, strings, lists, tuples, and dictionaries. It provides examples of declaring and initializing different types of variables, including integers, floats, characters, and strings. Methods for assigning values, displaying values, and accepting user input are also demonstrated. The document also discusses type conversion using functions like int(), float(), and eval() when accepting user input.