This document discusses Verilog data types. There are two main groups: nets and variables. Nets like wire are used for connections and have a default value of Z. Variables like reg store values and have a default of X. Important net types are wire, tri, and trireg; wire is used for single-driver nets while tri is for multiple drivers. Variables include reg for storage in procedural blocks, integer for integers, and real for real numbers.





![NET DATA TYPES…
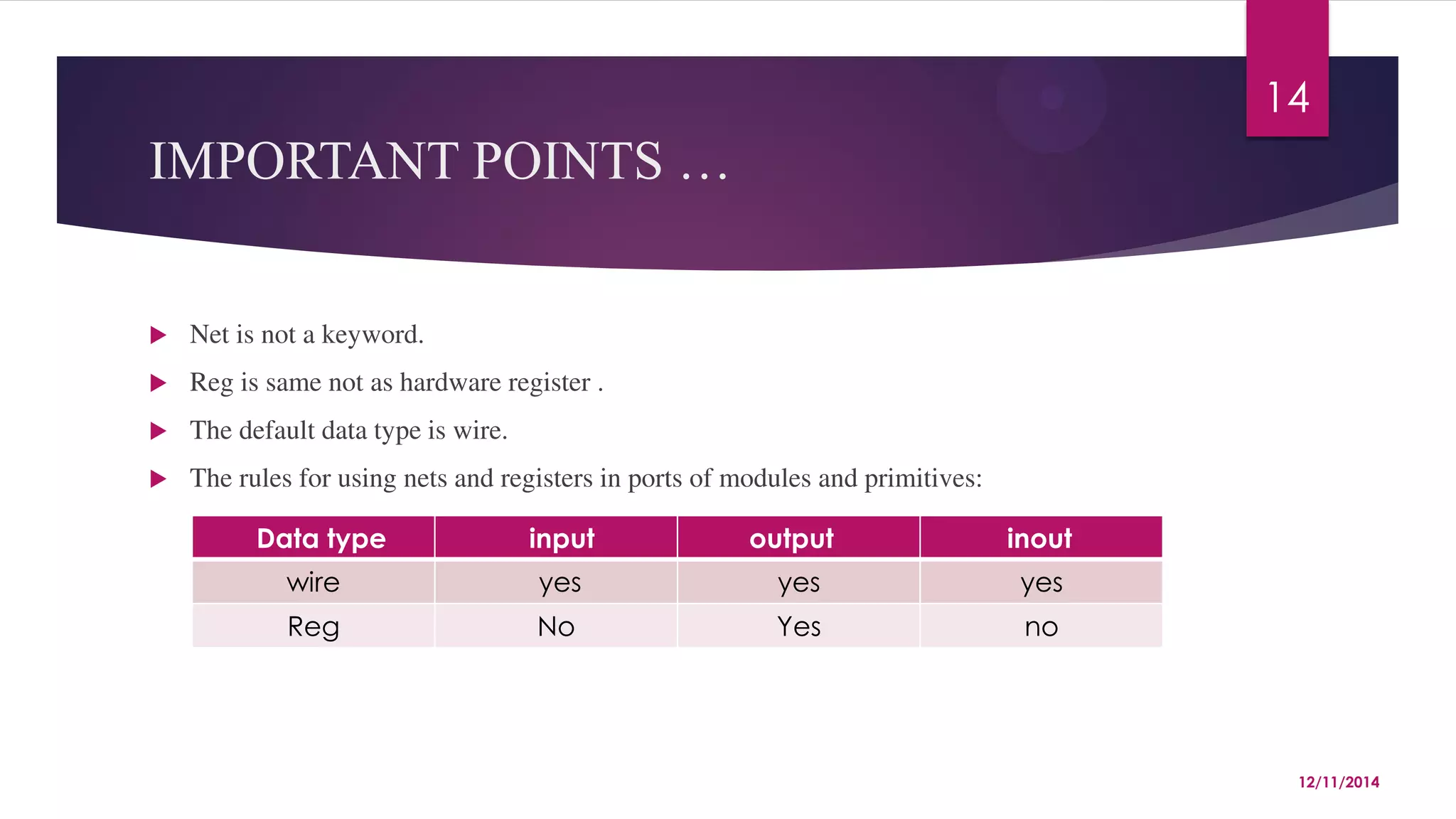
Example : tri [15:0] busa; // a tri-state 16-bit bus .
WIRED NETS :-
Wired nets are of type wor , wand , trior , and triand .
These are used to model wired logic configurations .
These will resolve the conflicts that result when multiple drivers drive the same net.
The wor and trior nets create wired or configurations, such that when any of the drivers is
1, the net is 1.
The wand and triand nets create wired and configurations, such that if any driver is 0, the
net is 0.
6
12/11/2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-141211001303-conversion-gate01/75/Data-types-in-verilog-6-2048.jpg)
![NET DATA TYPES…
EXAMPLES : wor w1 ,w2 ; // or operation .
Wand x,y ; // and operation .
Trior [2:0] bus ; //or operation.
Triand [3:0] bus ; // and operation.
7
12/11/2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-141211001303-conversion-gate01/75/Data-types-in-verilog-7-2048.jpg)
![NET DATA TYPES…
TRIREG :-
The trireg net stores a value and is used to model charge storage nodes. A trireg can be one
of two states:
The Driven State :- When at least one driver of a trireg has a value of 1, 0, or x, that value
propagates into the trireg and is the trireg’s driven value.
Capacitive State :- When all the drivers of a trireg net are at the high impedance value (z),
the trireg net retains its last driven value; the high impedance
value does not propagate from the driver to the trireg.
This is only data type in net which is used to store.
EXAMPLE : trireg [2:0] bus ; // a charge storage node .
8
12/11/2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-141211001303-conversion-gate01/75/Data-types-in-verilog-8-2048.jpg)

![VARIABLE DATA TYPES …
It is used to represent the data storage element.
The default value of variable data type is X.
Data types under the variable data type…
Reg , integer , real , time .
REG :-
This data type is used to represent the data storage element .
It holds the value , Until the a new value is assigned to it .
This reg is used when the variables are declared in the procedural blocks only (always and
initial block).
Example :- reg [2:0] out ; //where the out is used in the procedural block .
10
12/11/2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypes-141211001303-conversion-gate01/75/Data-types-in-verilog-10-2048.jpg)