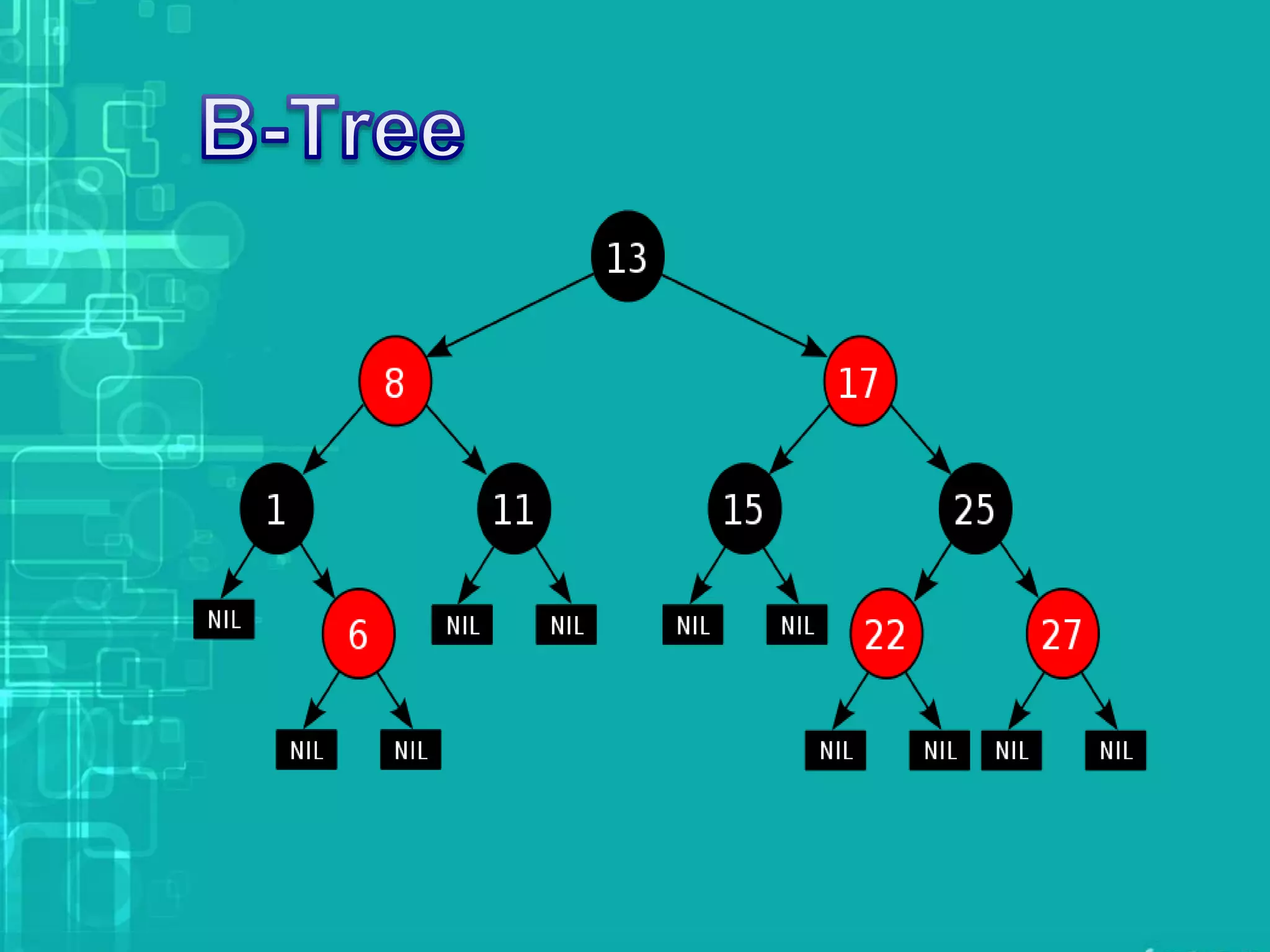
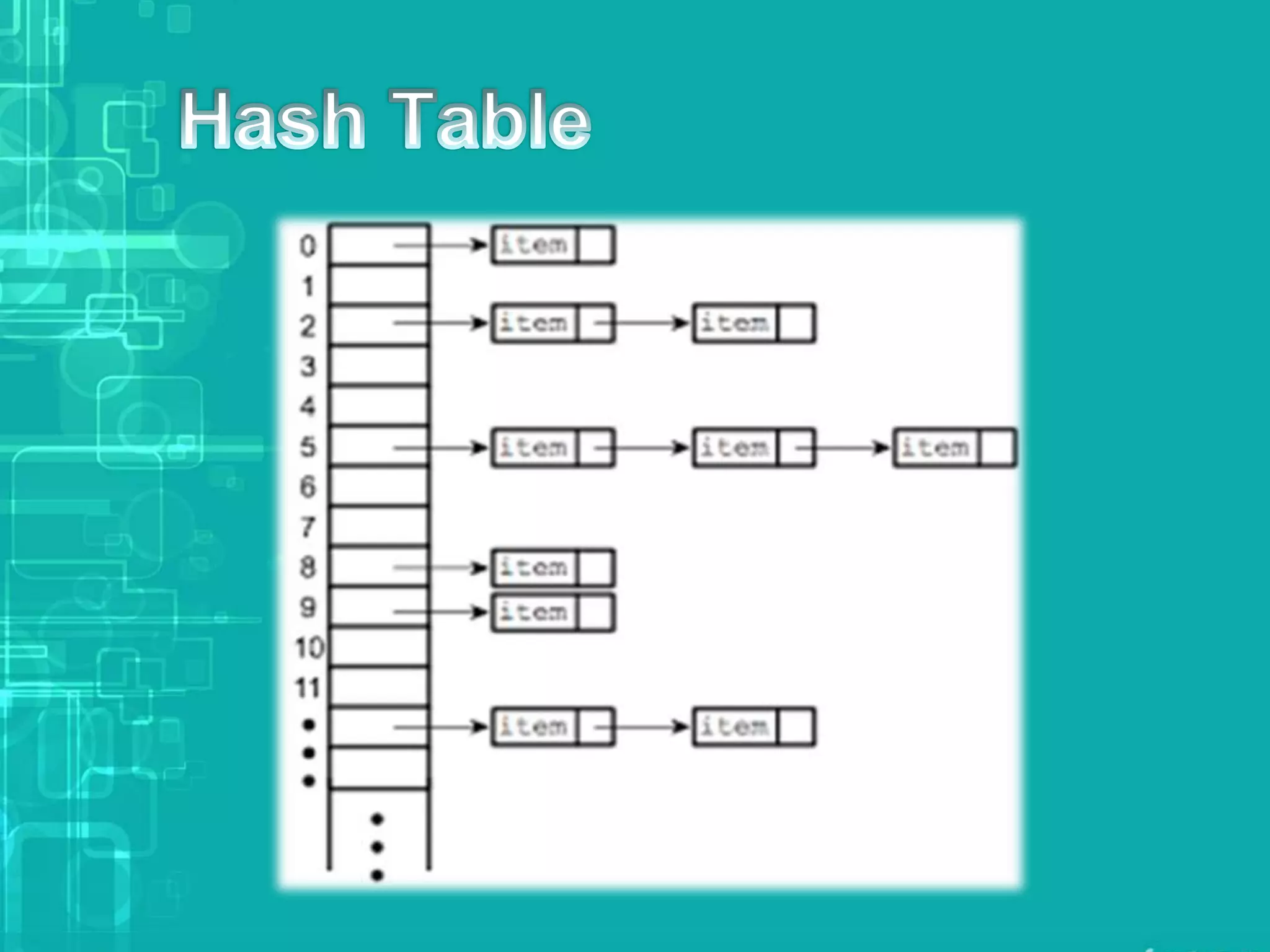
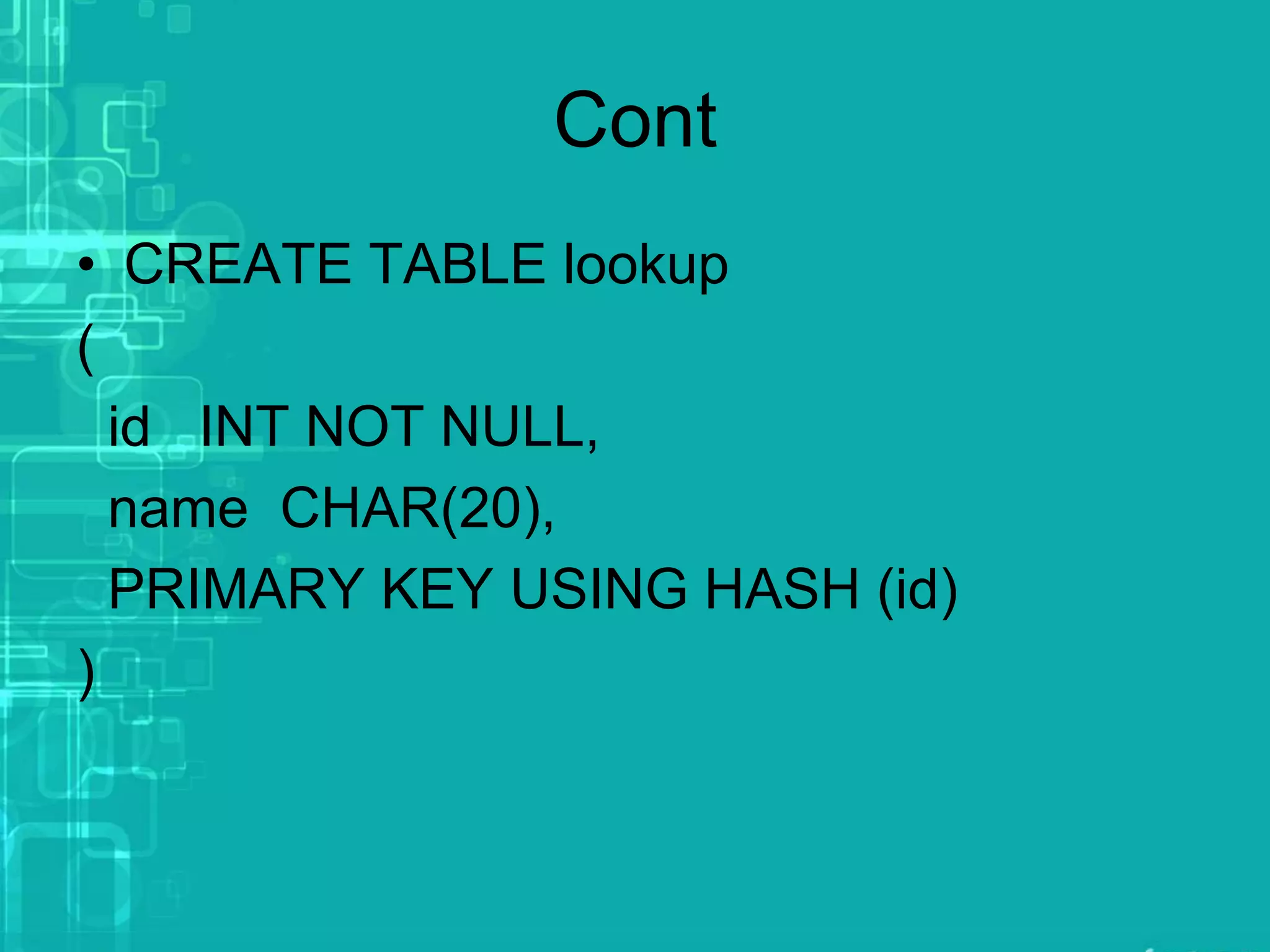
A database index is a data structure that enhances data retrieval speed at the expense of additional storage and write operations. Common types include B-trees and hash tables, with B-trees allowing efficient data manipulation while hash tables are limited to key-value lookups. Indexes store pointers to table rows and must be maintained with any table modifications to ensure data integrity.