Database_Connectivity_PHP_MySQL_Presentation.pptx
Recommended
PDF
Connecting_to_Database(MySQL)_in_PHP (3).pdf
PPTX
Connecting_to_Database(MySQL)_in_PHP (3).pptx
PPTX
Connecting_to_Database(MySQL)_in_PHP.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
3-Chapter-Edit.pptx debre tabour university
DOCX
Module 6WEB SERVER AND SERVER SIDE SCRPTING, PART-2Chapte.docx
PPTX
Database Connectivity in PHP
PPTX
PHP DATABASE MANAGEMENT.pptx
PPTX
7. PHP and gaghhgashgfsgajhfkhshfasMySQL.pptx
DOCX
PPTX
Dadabase connection using PHP and MYsQL.pptx
PPTX
lecture 7 - Introduction to MySQL with PHP.pptx
PDF
PPTX
Basics of Working with PHP and MySQL.pptx
PPTX
Php and database functionality
PPTX
Php and database functionality
PPTX
PHP and database functionality
PPTX
PHP Database Programming Basics -- Northeast PHP
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
This slide show will brief about database handling
PPTX
PPTX
Connecting to my sql using PHP
PPTX
PPTX
Database Connectivity MYSQL by Dr.C.R.Dhivyaa Kongu Engineering College
PPTX
SRMS 5th Sem Minor project.pptx
PDF
PPT
PHP - Getting good with MySQL part II
PPTX
Exploring Entrepreneurial Qualities: A Curated Presentation for Grade 11 Busi...
PPTX
Capitol Webinar October 2025 Dr. Jha.pptx
More Related Content
PDF
Connecting_to_Database(MySQL)_in_PHP (3).pdf
PPTX
Connecting_to_Database(MySQL)_in_PHP (3).pptx
PPTX
Connecting_to_Database(MySQL)_in_PHP.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
3-Chapter-Edit.pptx debre tabour university
DOCX
Module 6WEB SERVER AND SERVER SIDE SCRPTING, PART-2Chapte.docx
PPTX
Database Connectivity in PHP
PPTX
PHP DATABASE MANAGEMENT.pptx
Similar to Database_Connectivity_PHP_MySQL_Presentation.pptx
PPTX
7. PHP and gaghhgashgfsgajhfkhshfasMySQL.pptx
DOCX
PPTX
Dadabase connection using PHP and MYsQL.pptx
PPTX
lecture 7 - Introduction to MySQL with PHP.pptx
PDF
PPTX
Basics of Working with PHP and MySQL.pptx
PPTX
Php and database functionality
PPTX
Php and database functionality
PPTX
PHP and database functionality
PPTX
PHP Database Programming Basics -- Northeast PHP
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
This slide show will brief about database handling
PPTX
PPTX
Connecting to my sql using PHP
PPTX
PPTX
Database Connectivity MYSQL by Dr.C.R.Dhivyaa Kongu Engineering College
PPTX
SRMS 5th Sem Minor project.pptx
PDF
PPT
PHP - Getting good with MySQL part II
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Exploring Entrepreneurial Qualities: A Curated Presentation for Grade 11 Busi...
PPTX
Capitol Webinar October 2025 Dr. Jha.pptx
PPTX
How to Create a Manifest File in Odoo 18
PPTX
THERAPEUTIC ENVIORNMENT.............pptx
PDF
Slit lamp parts 2/ppt/notes/download.pdf
PPTX
Capital Budgeting - Risk Analysis Using Payback Period Method
PDF
Admin Slides for Oct'25 semester - PB1_MC5.pdf
PDF
Total Quality Management : A presentation by a third year student.
PDF
Yaksha Prashna | General Quiz at RLAC | Amlan Sarkar | Full Set
PPTX
Nerve lecture 2:strength-duration curve and an introduction to action potential
PDF
Nernst Distribution Law and factors affecting distribution constant
PDF
Admin Slides for Oct'25 semester (Progression)
PPTX
Safety Needs and Prevention of environmental hazards.pptx
PPTX
Basics for Conducting Bibliometric Analysis - Dr Ahsan Riaz
PPTX
Common problems or challenges faced by Indian adolescents
PDF
Phase Equilibria and Colligative Properties.pdf
PPTX
Project Dashboard in Odoo 18 Project
PPTX
DPSM-BITDA Introduction Presentation Slides
PPTX
DBP - BITA Introduction Slides Oct 202526
PDF
BUSINESS ETHICS – UNIT I: Introduction to Business Ethics
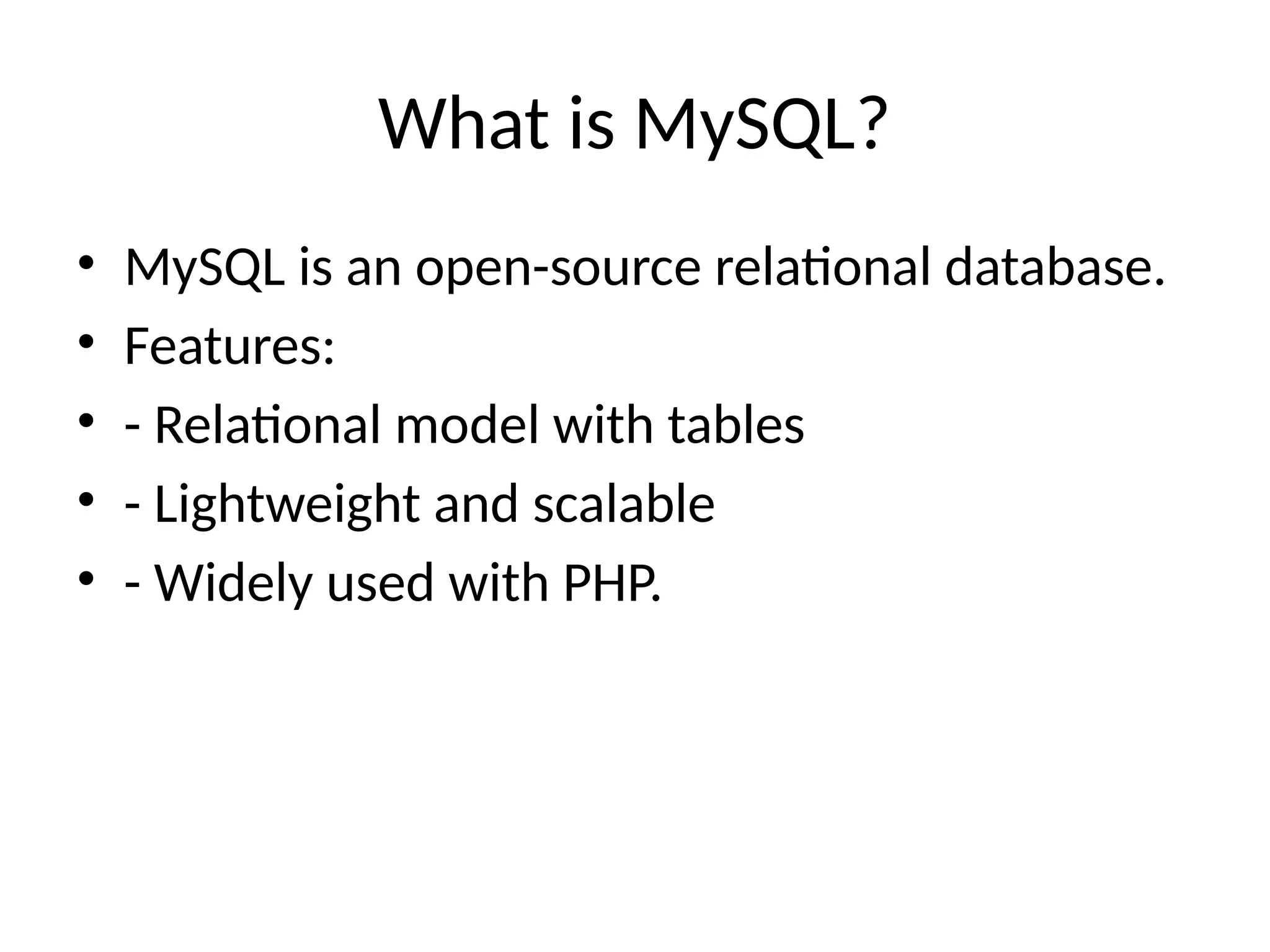
Database_Connectivity_PHP_MySQL_Presentation.pptx 1. 2. 3. What is MySQL?
• MySQL is an open-source relational database.
• Features:
• - Relational model with tables
• - Lightweight and scalable
• - Widely used with PHP.
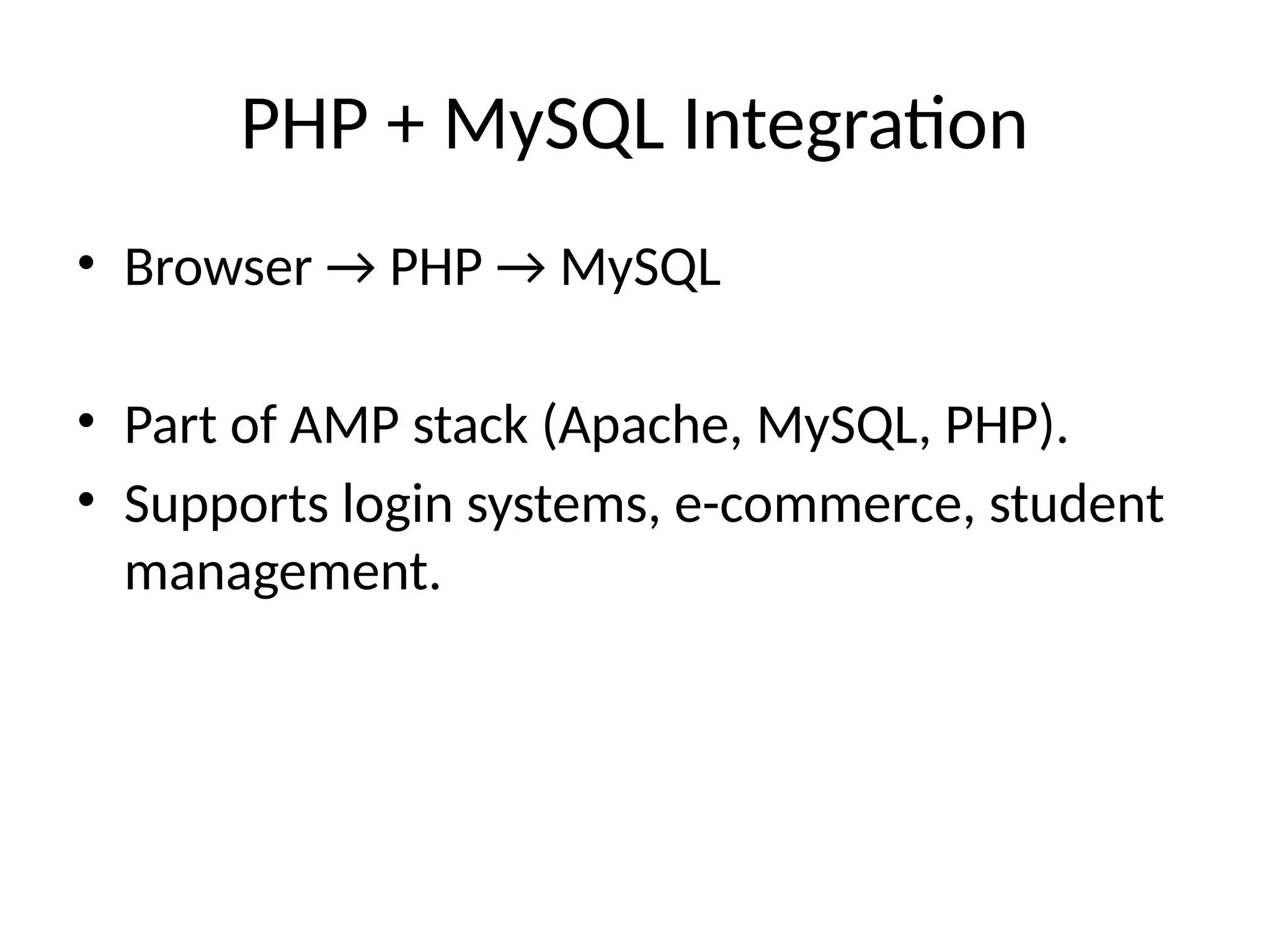
4. PHP + MySQL Integration
• Browser → PHP → MySQL
• Part of AMP stack (Apache, MySQL, PHP).
• Supports login systems, e-commerce, student
management.
5. Database Connection
<?php
$host = "localhost";
$user = "root";
$pass = "";
$db = "college";
$conn = mysqli_connect($host, $user, $pass, $db);
if ($conn) {
echo "Connected Successfully!";
} else {
echo "Connection Failed!";
}
• ?>
6. 7. Insert Example
$sql = "INSERT INTO students (name, course) VALUES ('Ankit', 'B.Tech
CSE')";
• mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
8. Read Example
$result = mysqli_query($conn, "SELECT * FROM students");
while($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)){
echo $row['name']." - ".$row['course']."<br>";
• }
9. 10. 11. Security Best Practices
• • Prevent SQL injection using prepared
statements
• • Validate inputs
• • Use PDO/MySQLi
• • Prefer HTTPS
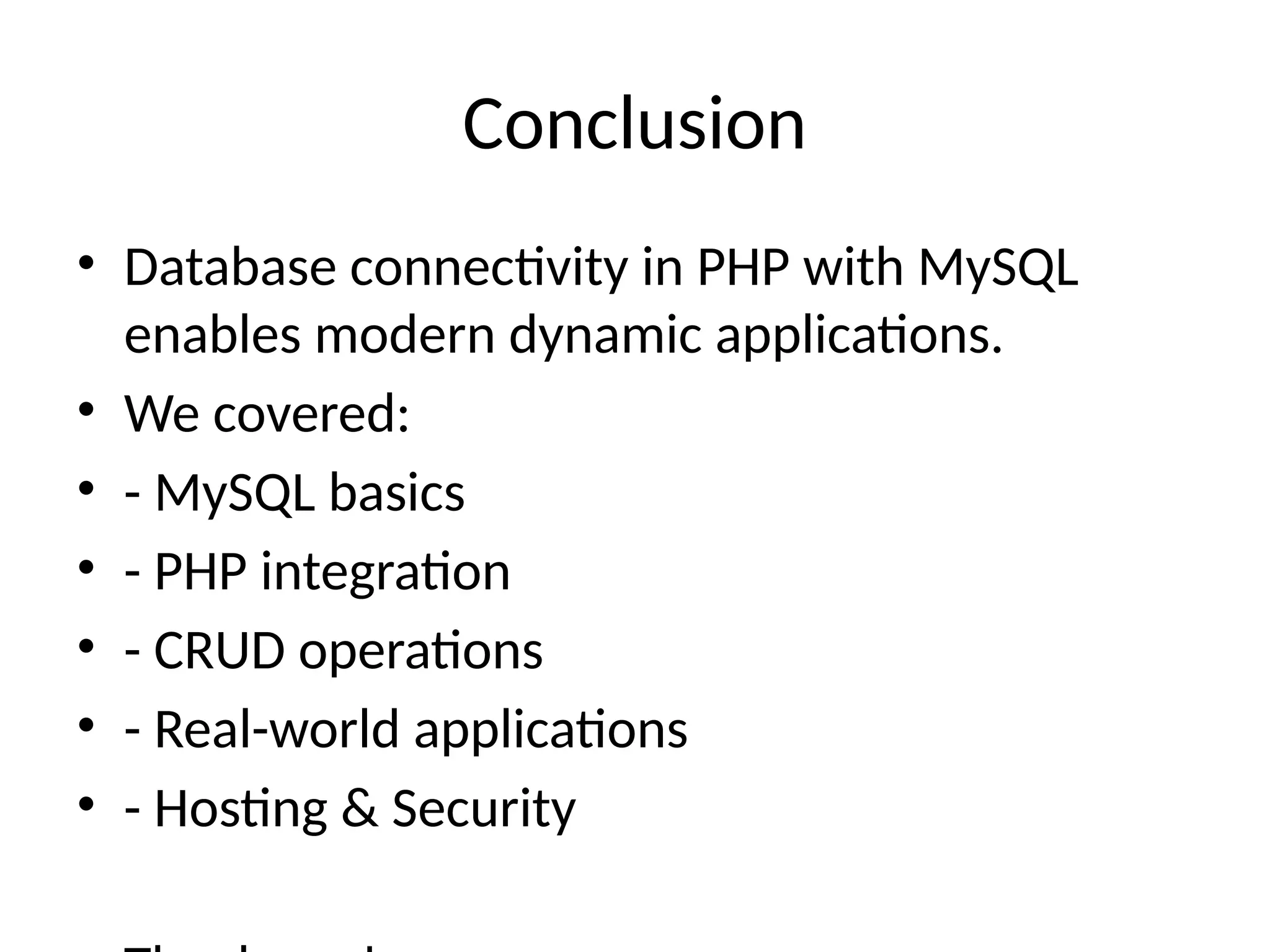
12. Conclusion
• Database connectivity in PHP with MySQL
enables modern dynamic applications.
• We covered:
• - MySQL basics
• - PHP integration
• - CRUD operations
• - Real-world applications
• - Hosting & Security





![Read Example
$result = mysqli_query($conn, "SELECT * FROM students");
while($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($result)){
echo $row['name']." - ".$row['course']."<br>";
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databaseconnectivityphpmysqlpresentation-250910083428-873d6be4/75/Database_Connectivity_PHP_MySQL_Presentation-pptx-8-2048.jpg)