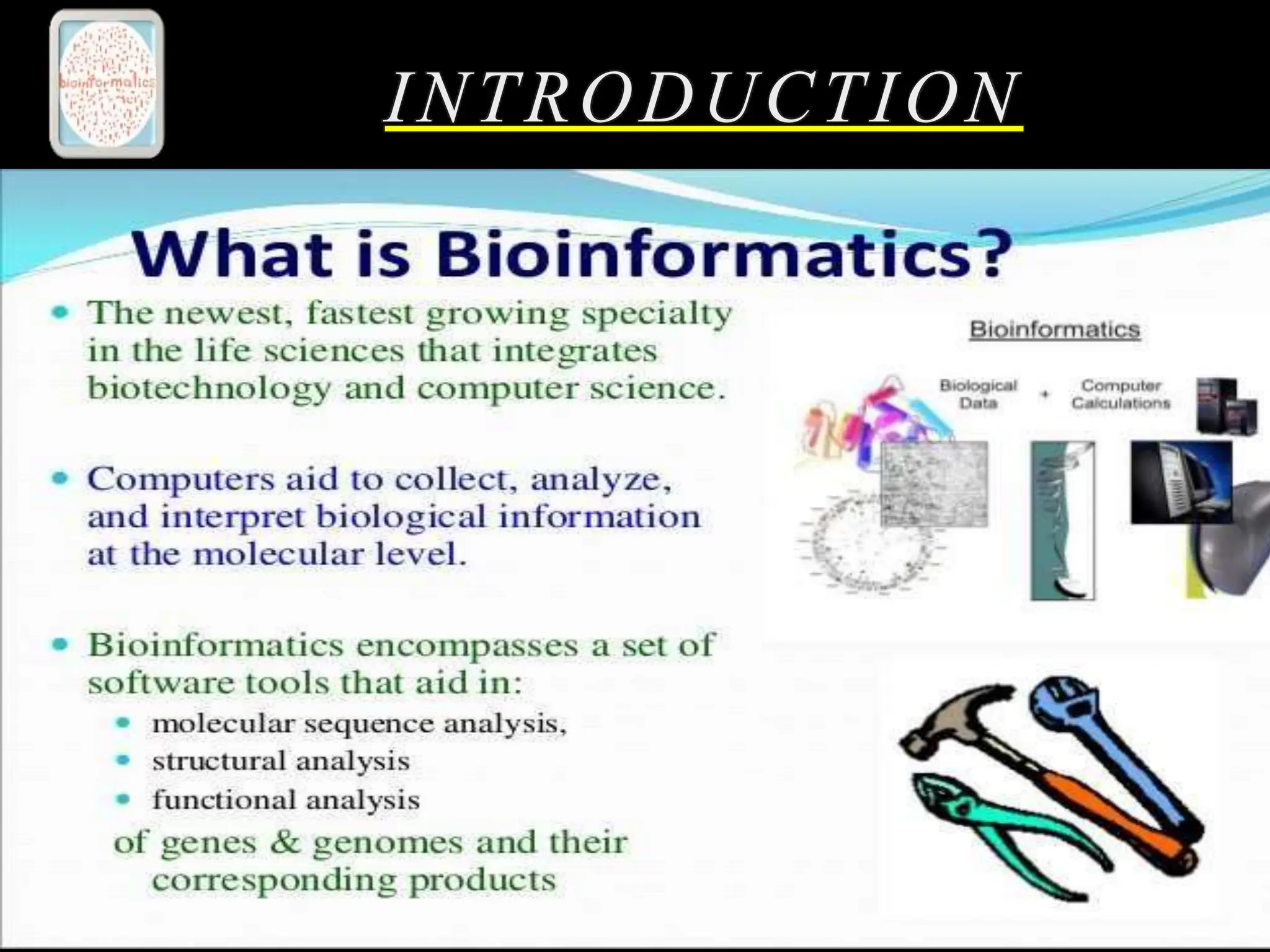
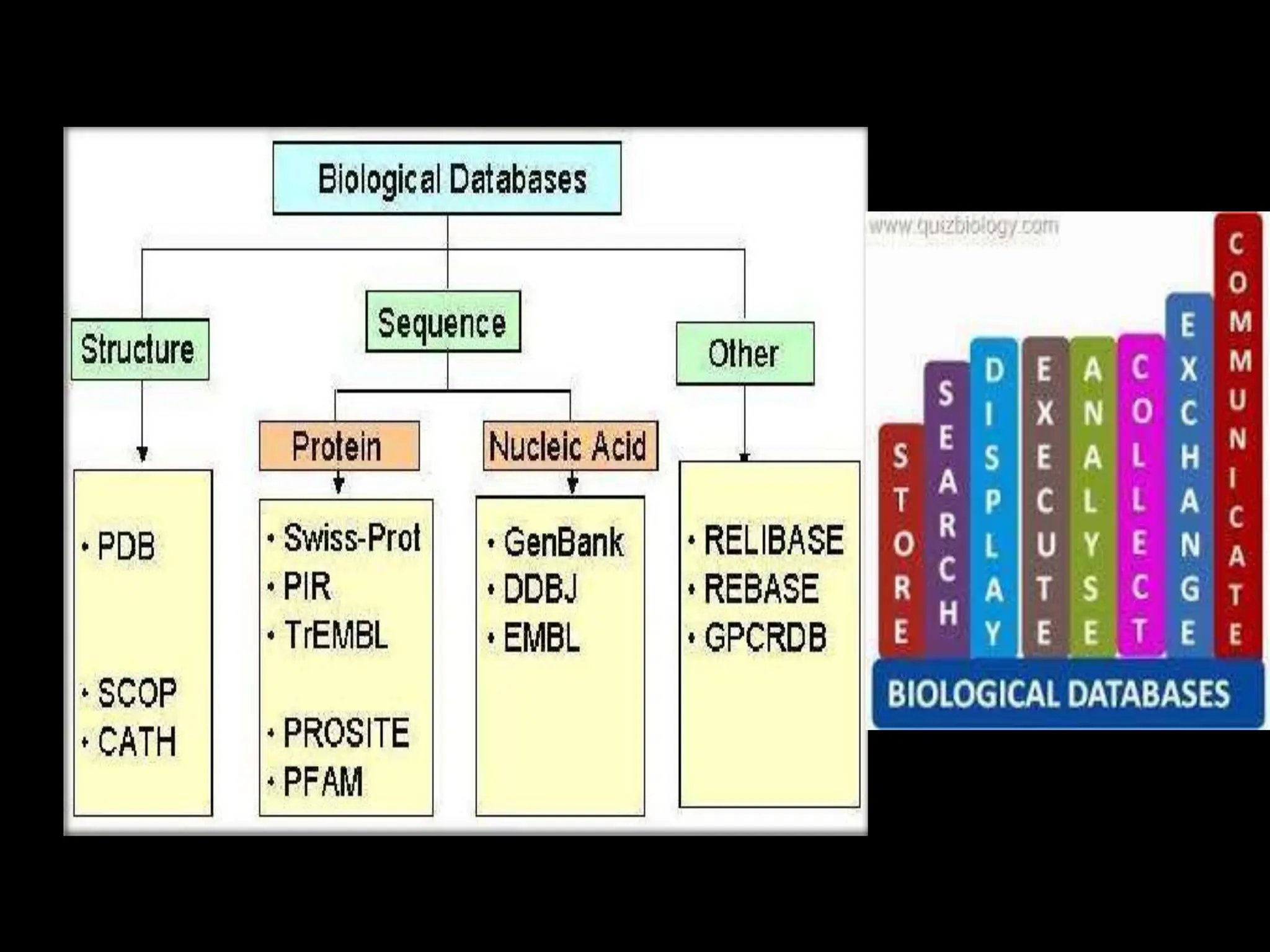
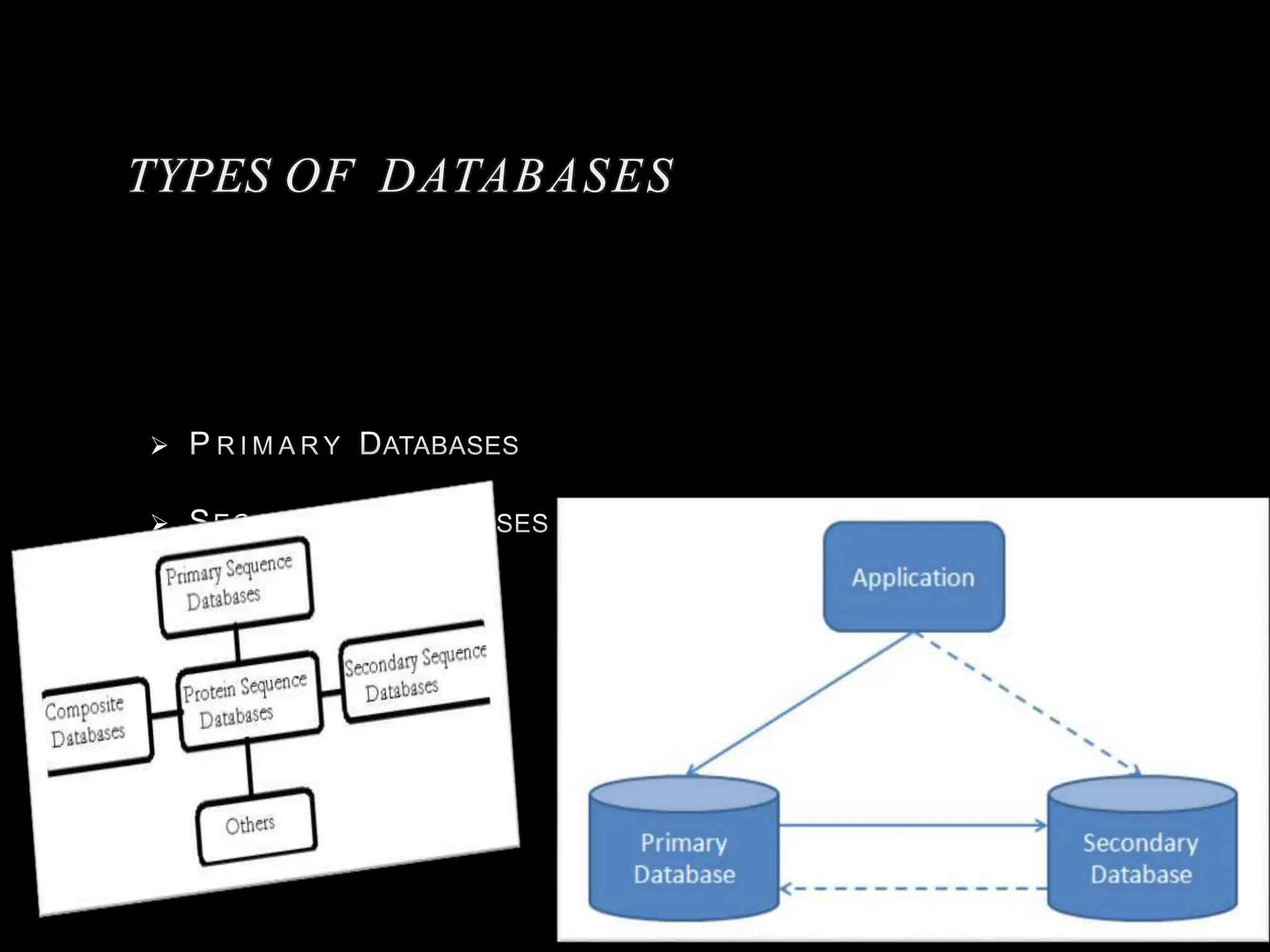
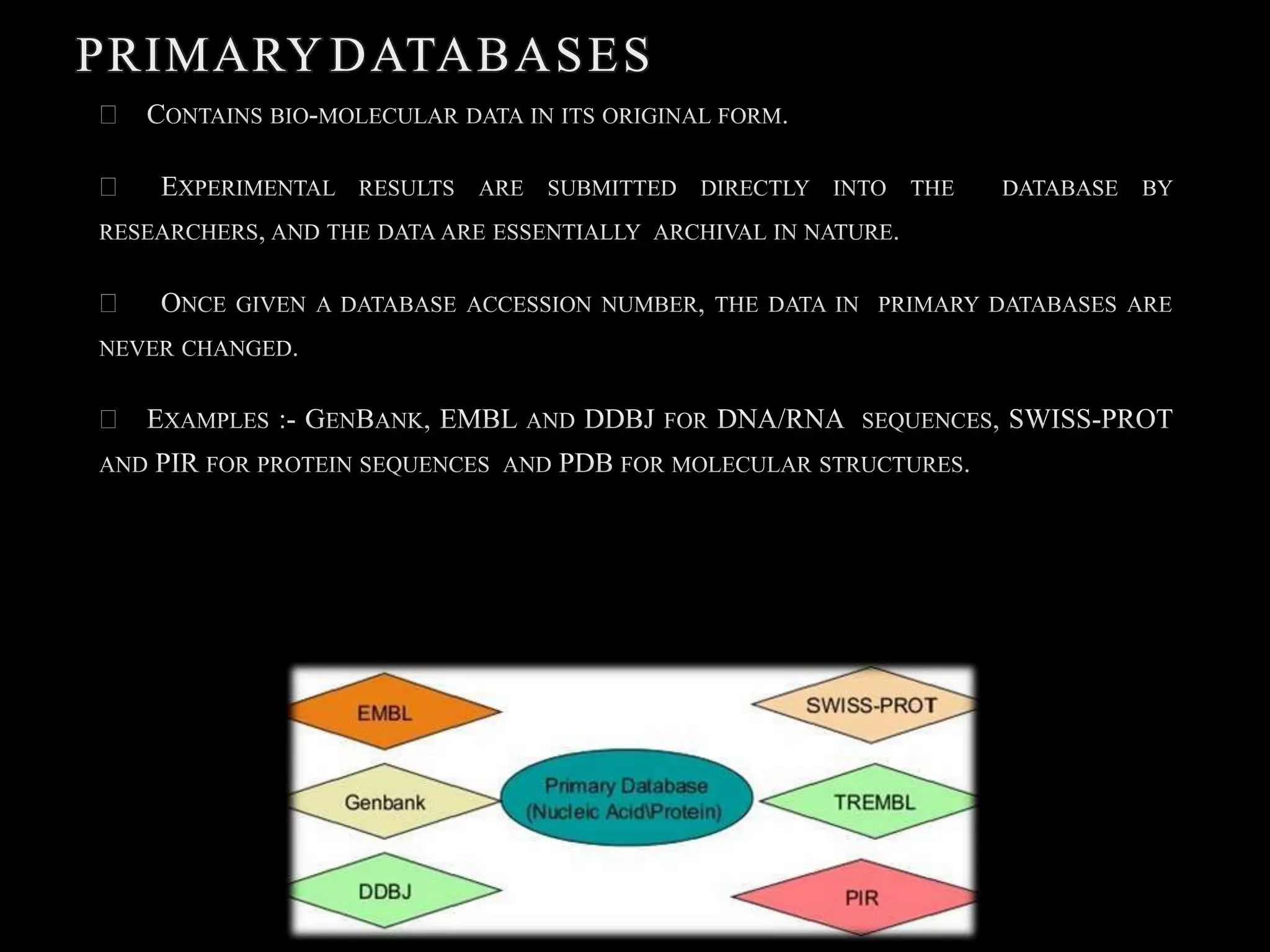
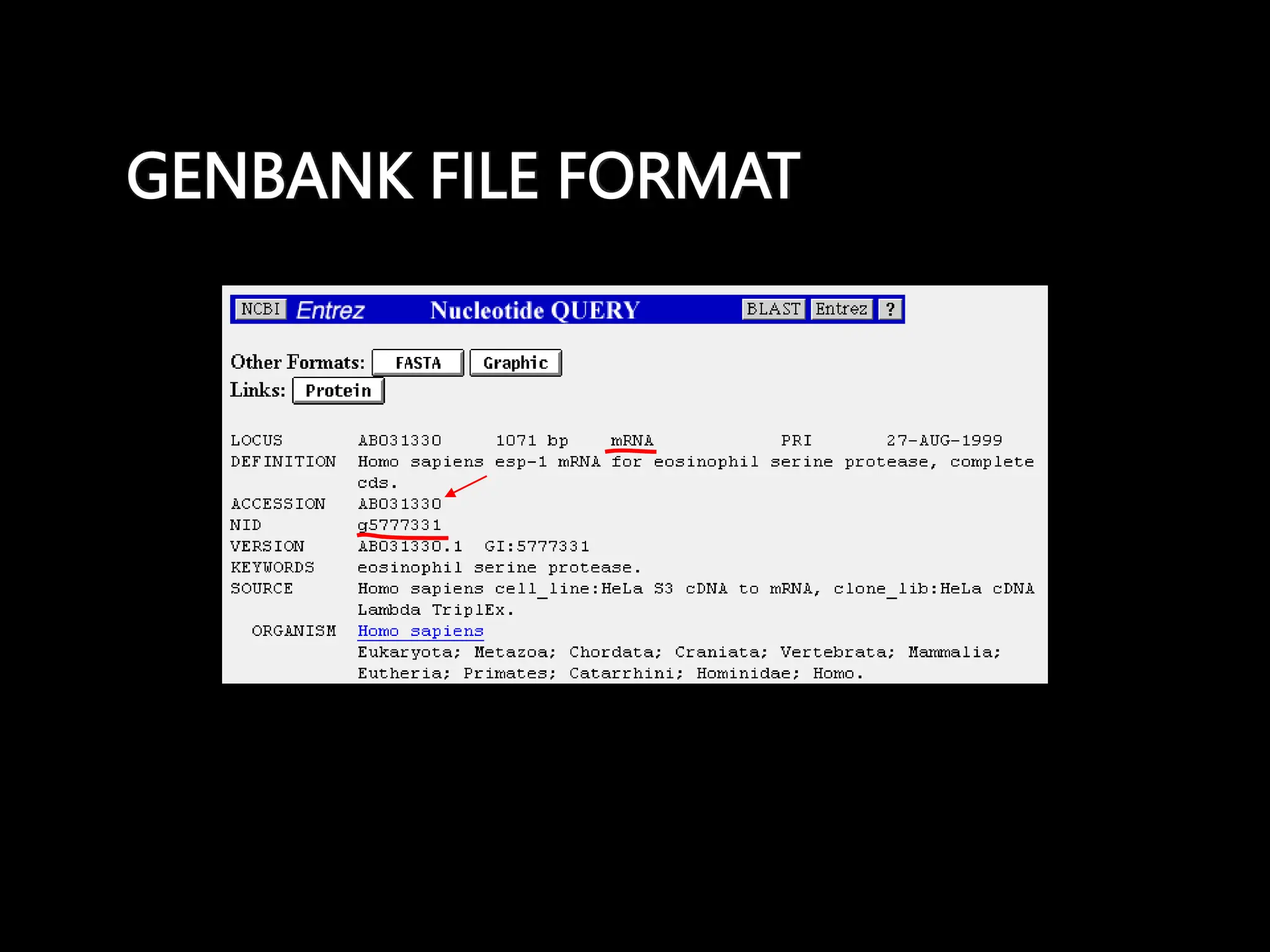
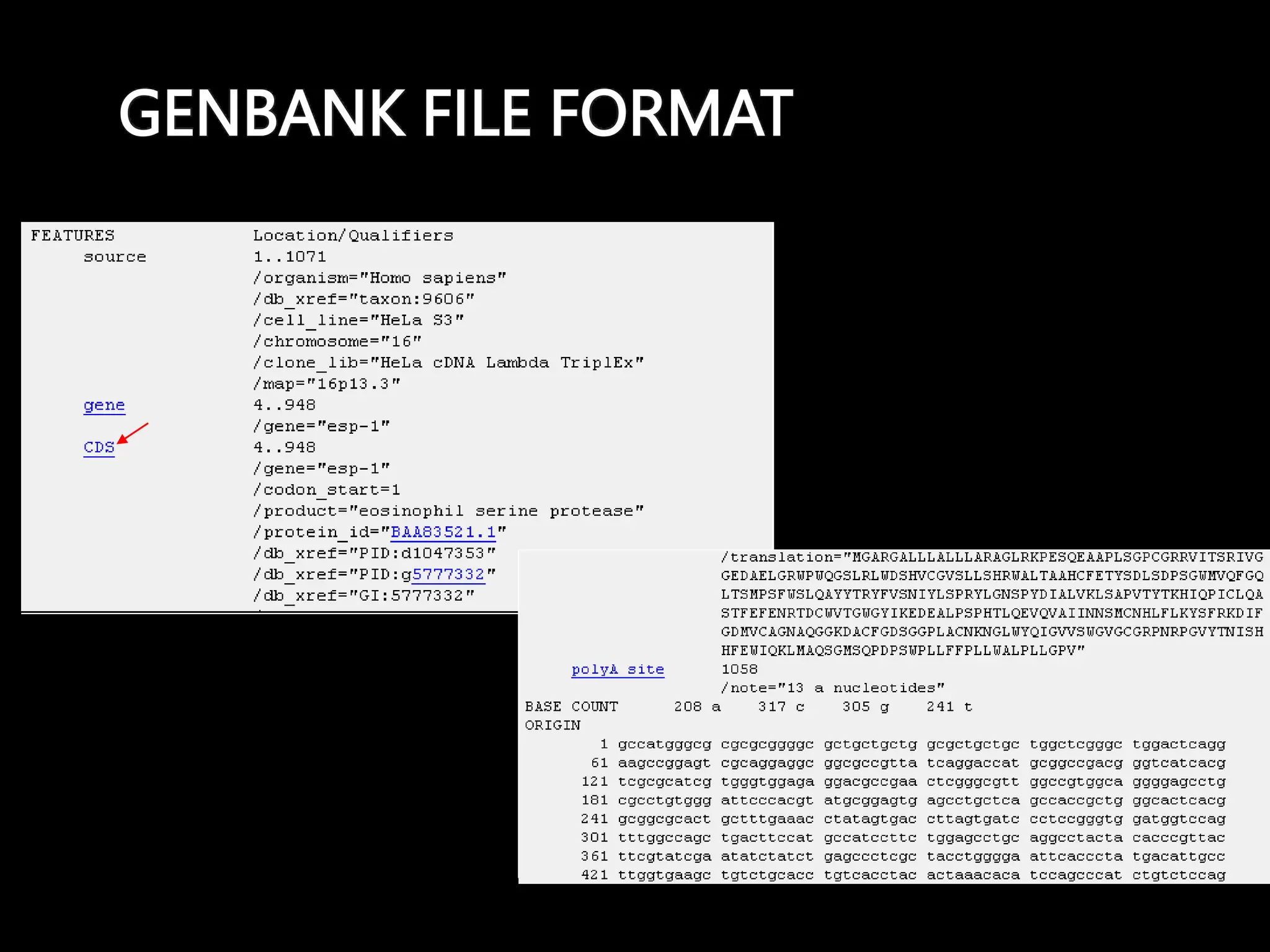
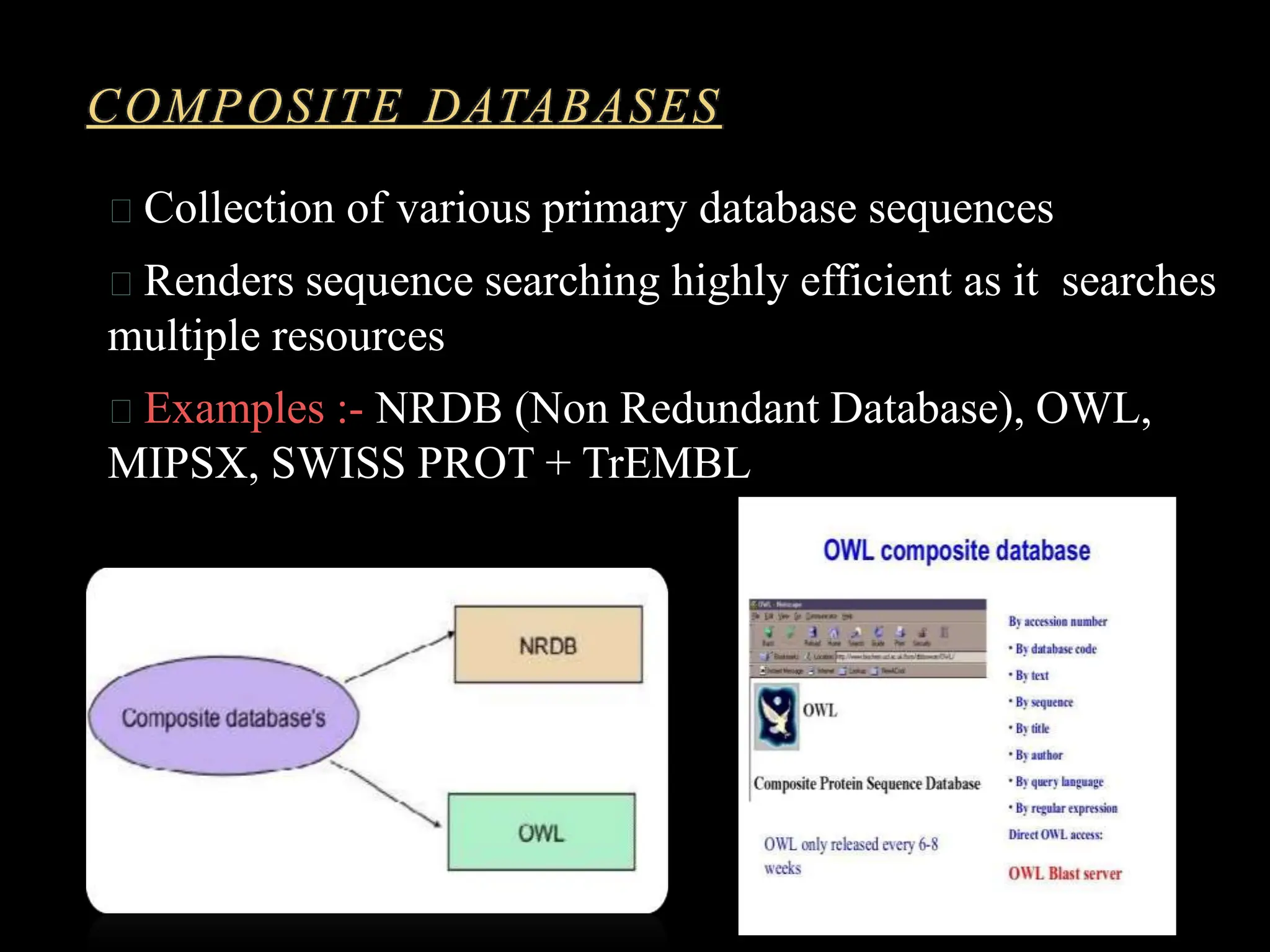
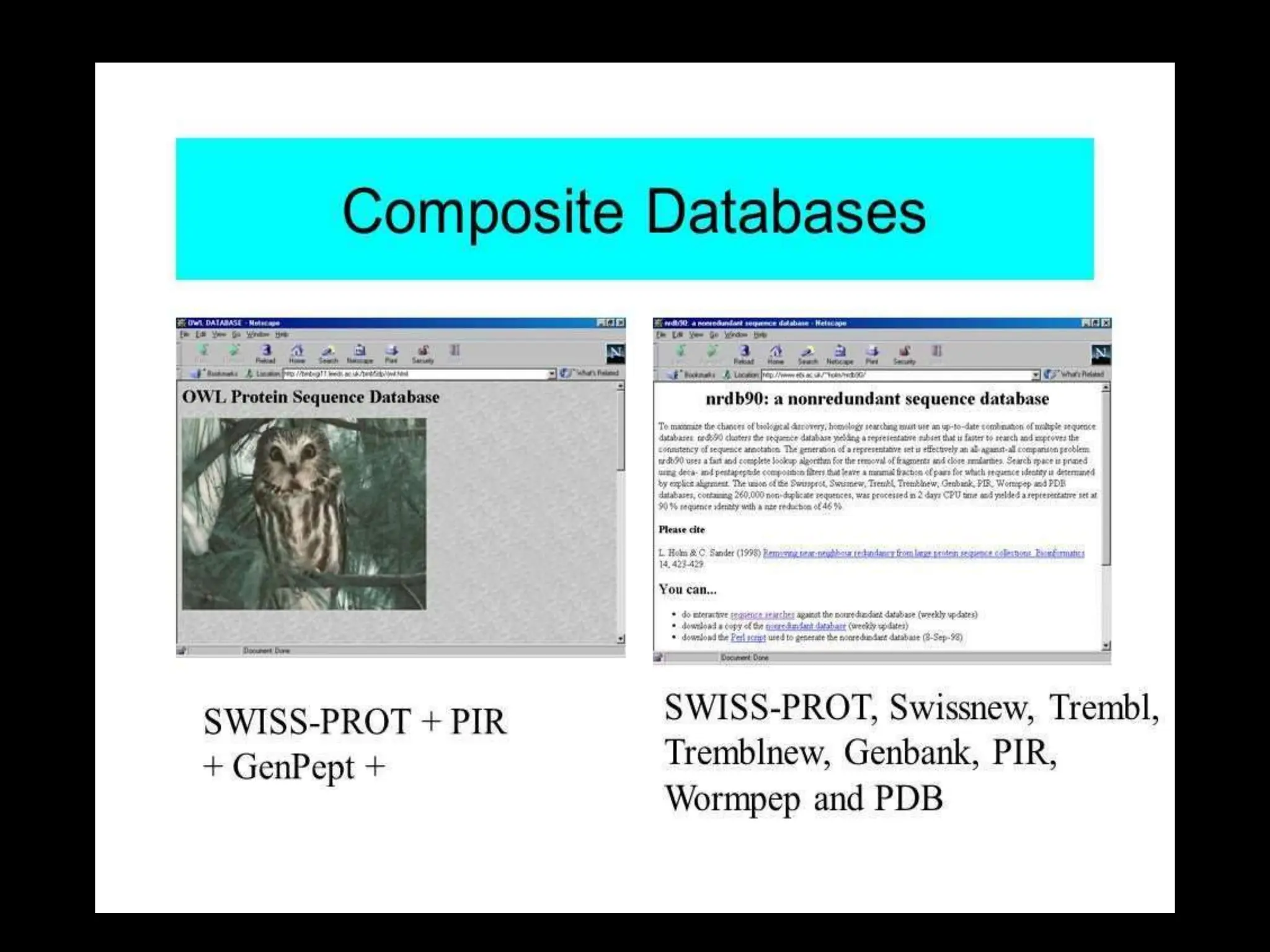
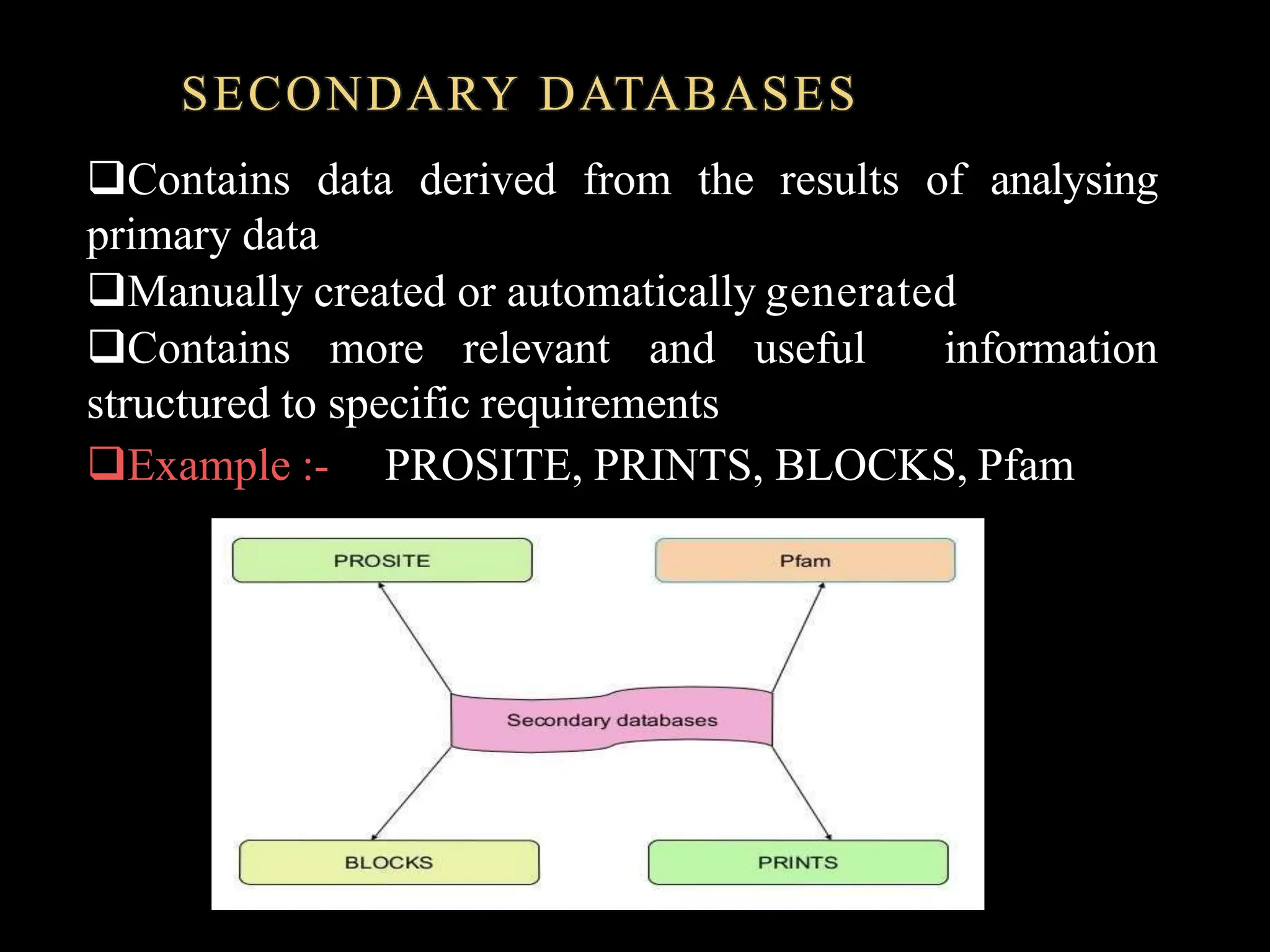
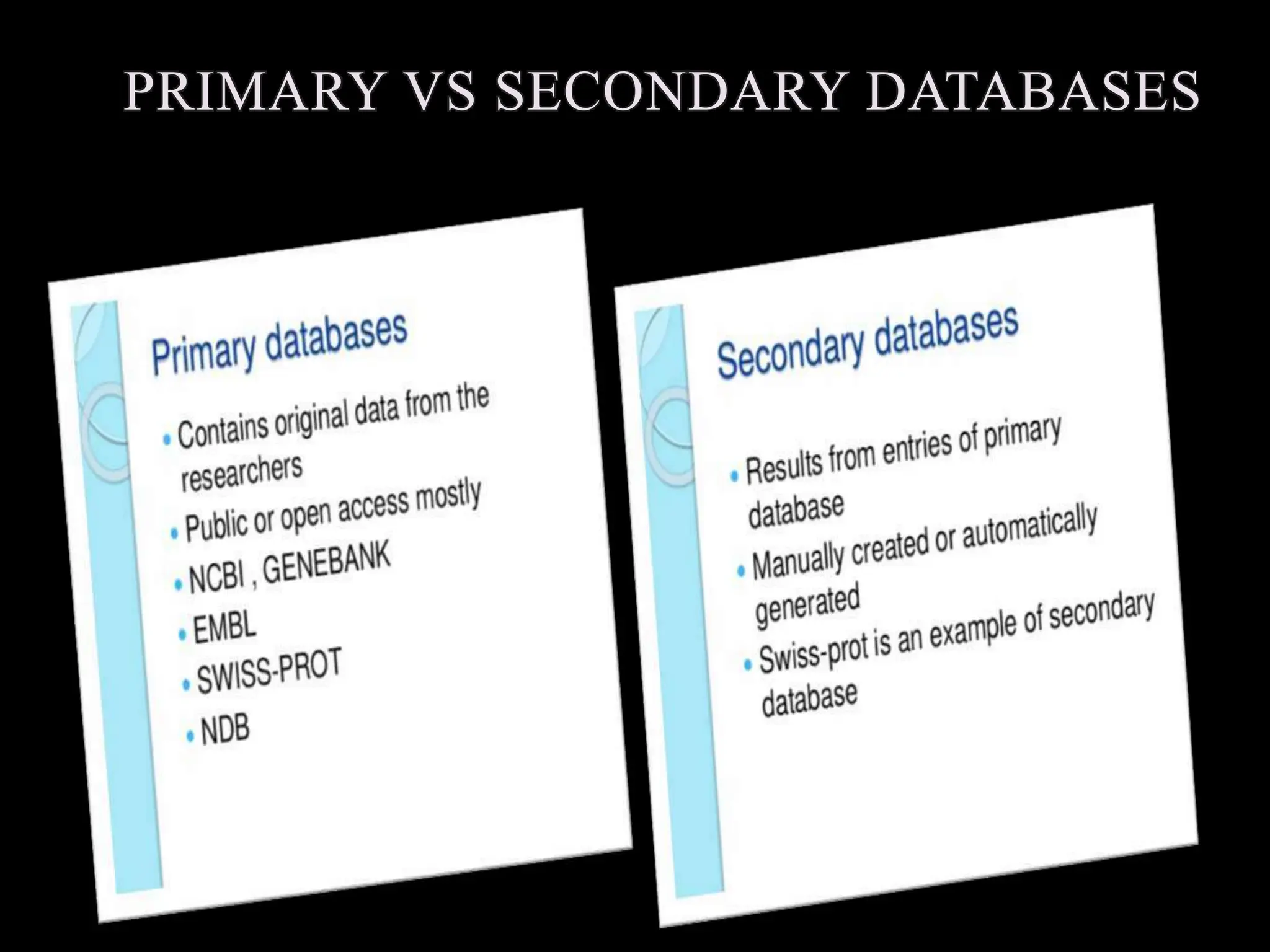
The document discusses biological databases, categorizing them into primary and secondary types. Primary databases like GenBank, EMBL, and Swiss-Prot provide raw sequence data, while secondary databases, such as Prosite and Pfam, derive from the analysis of primary data and offer more tailored information. It highlights various resources and their functionalities for searching genes, proteins, and protein families.