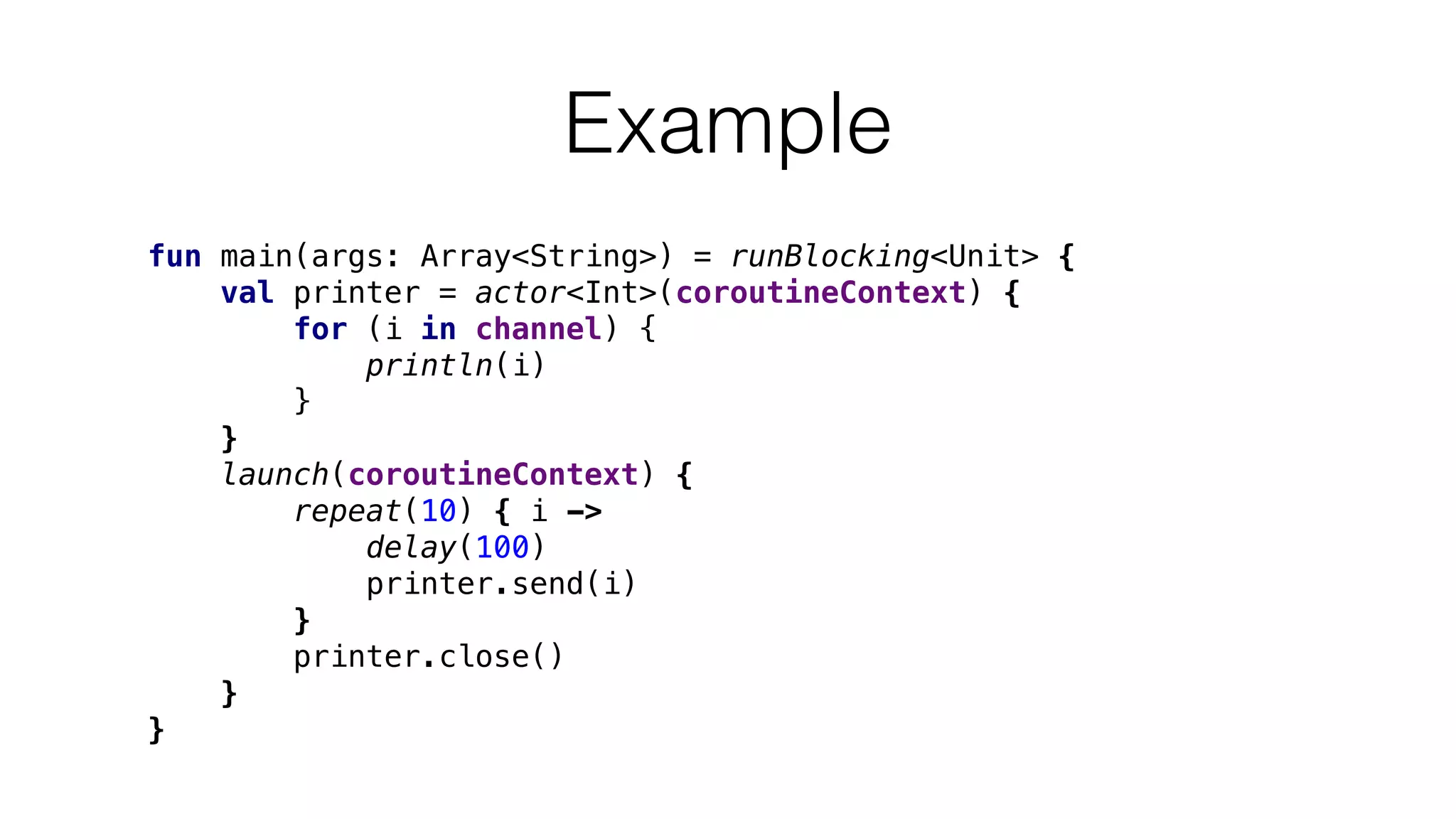
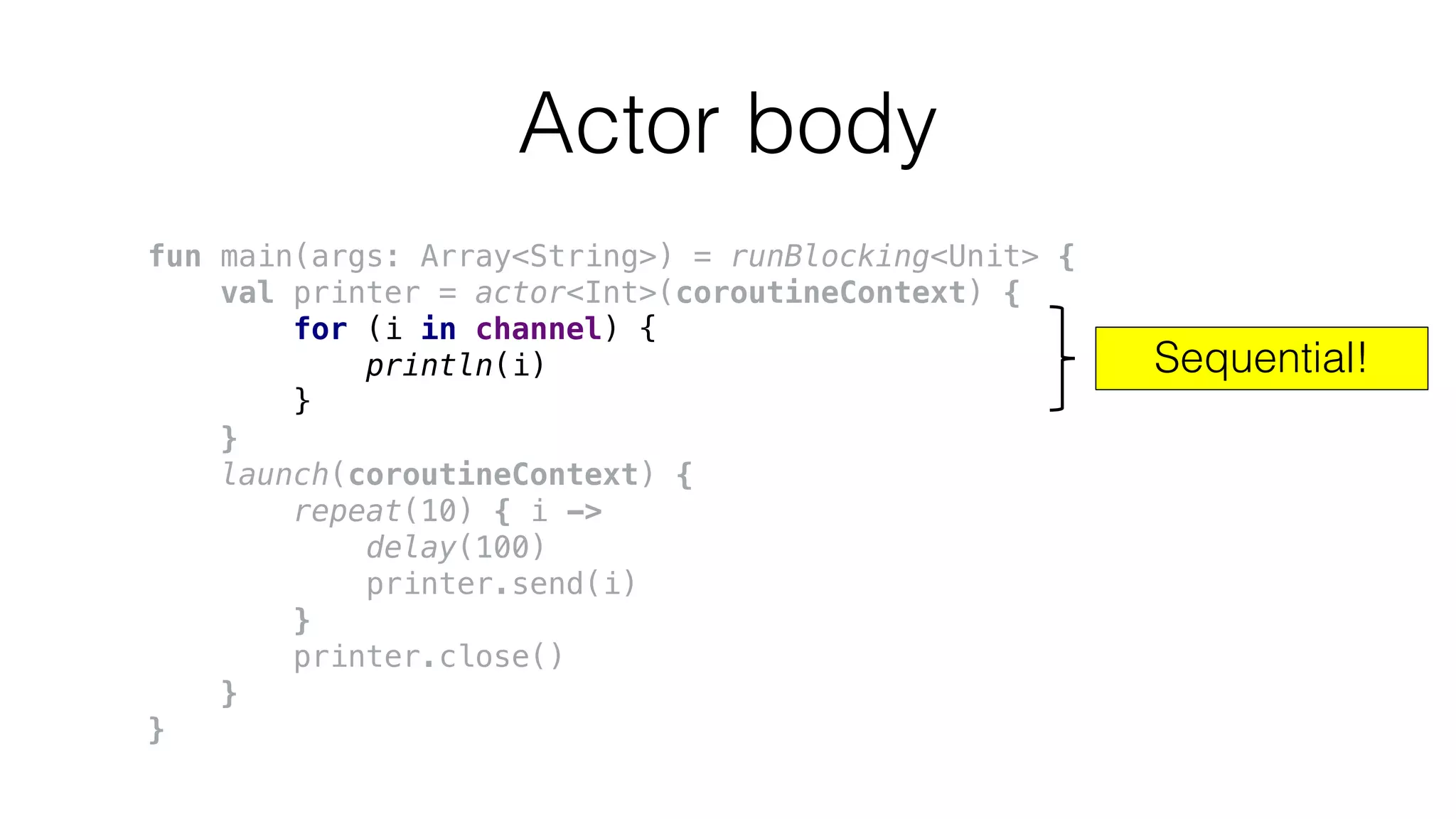
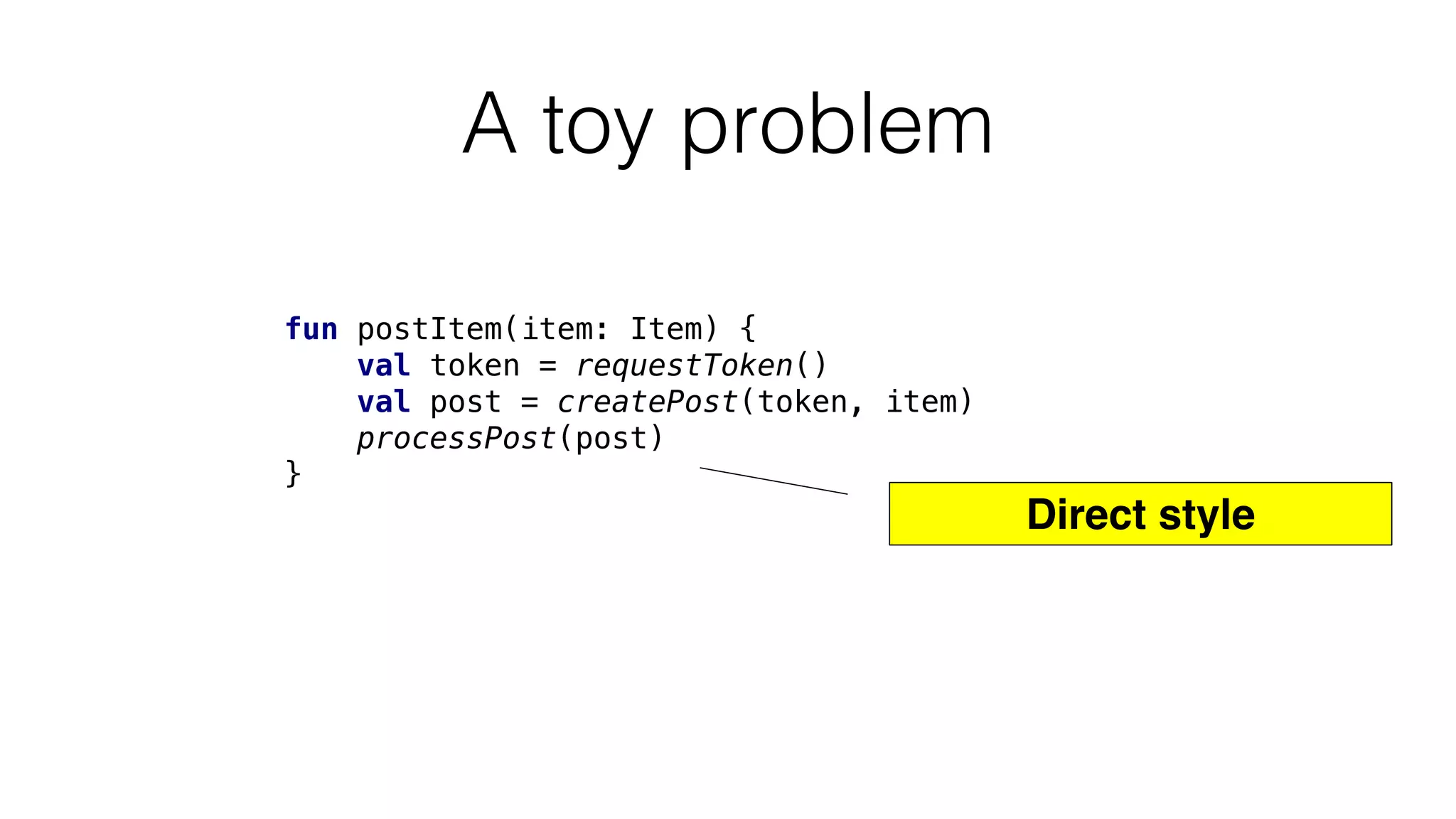
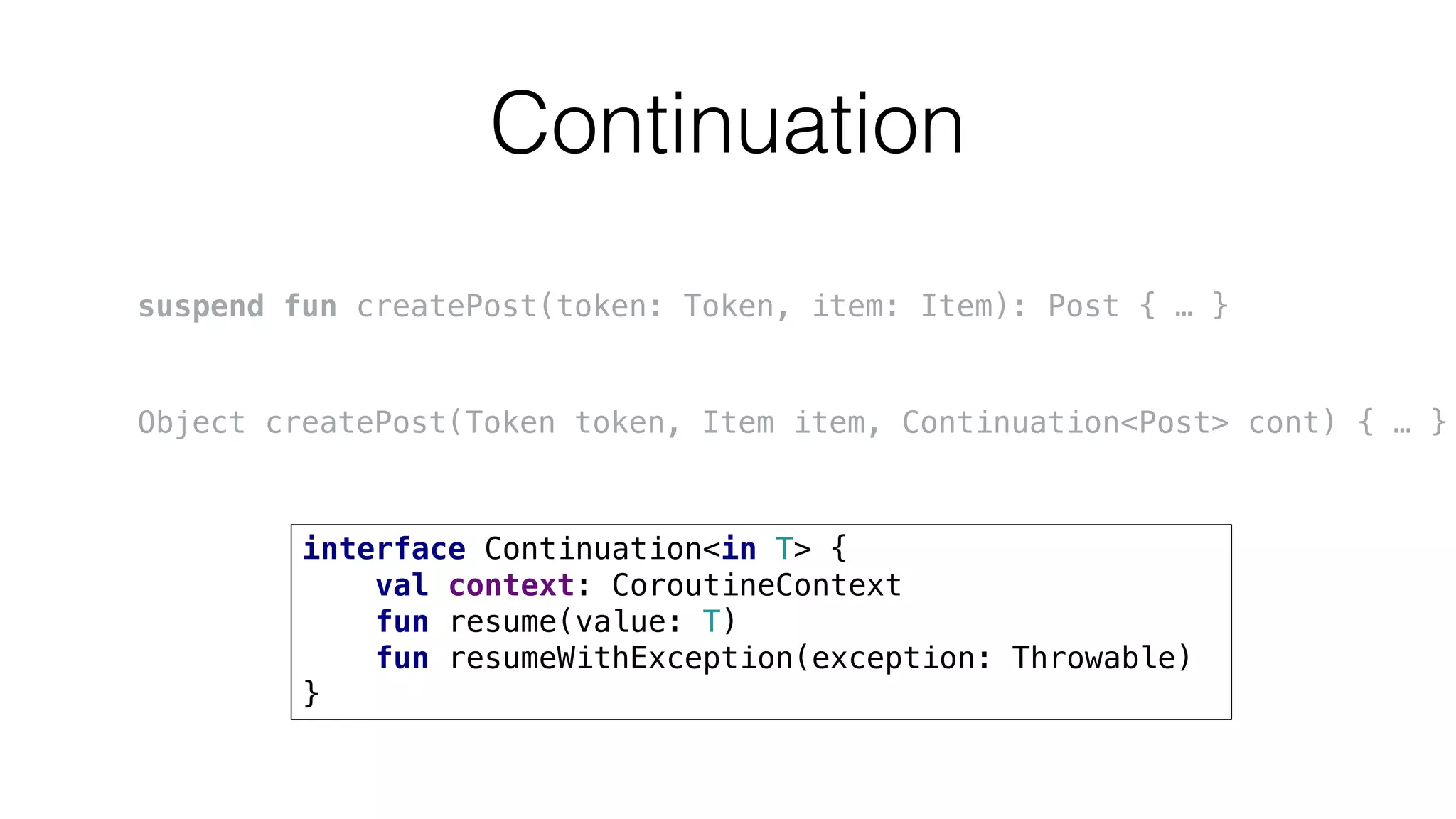
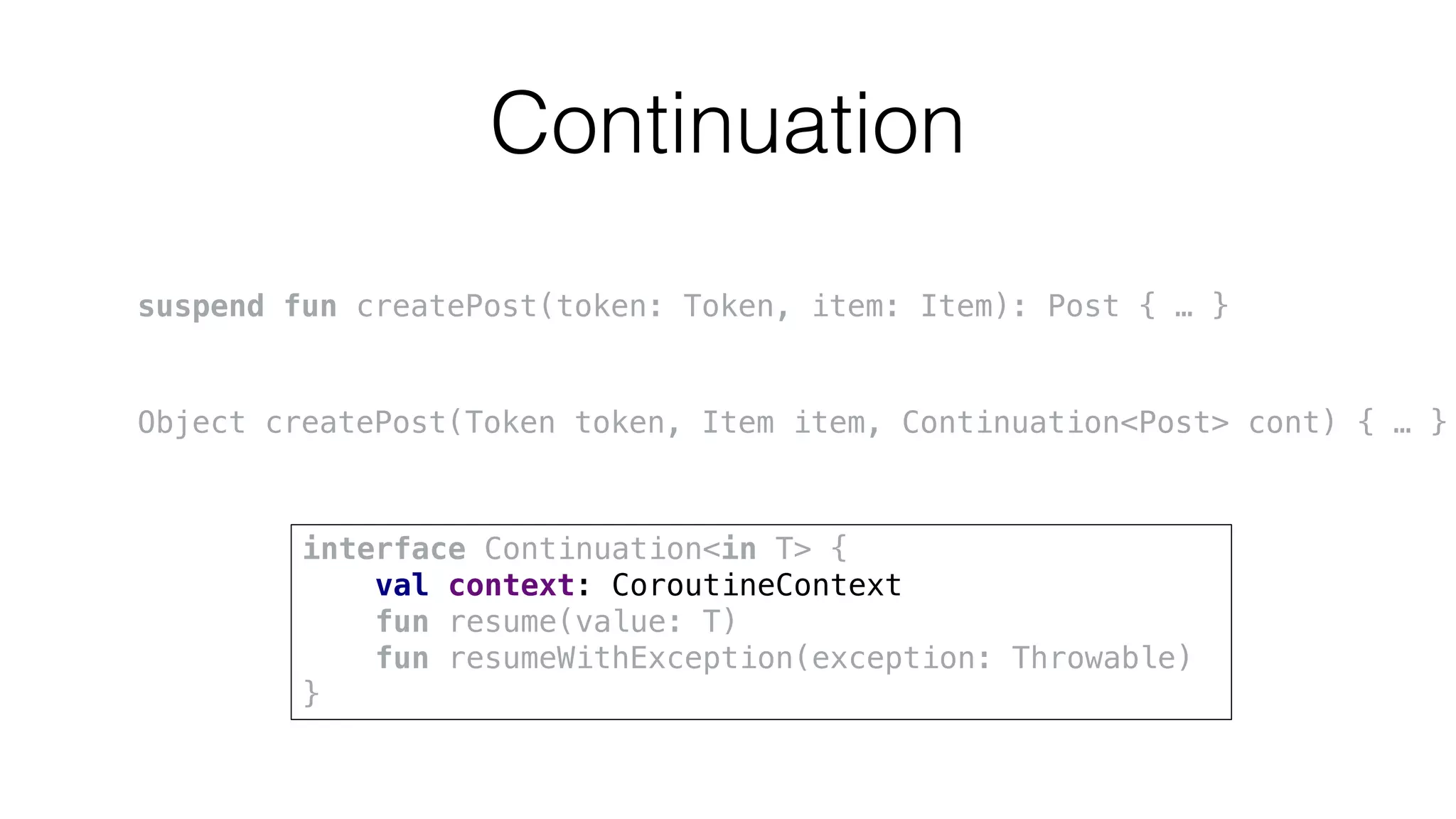
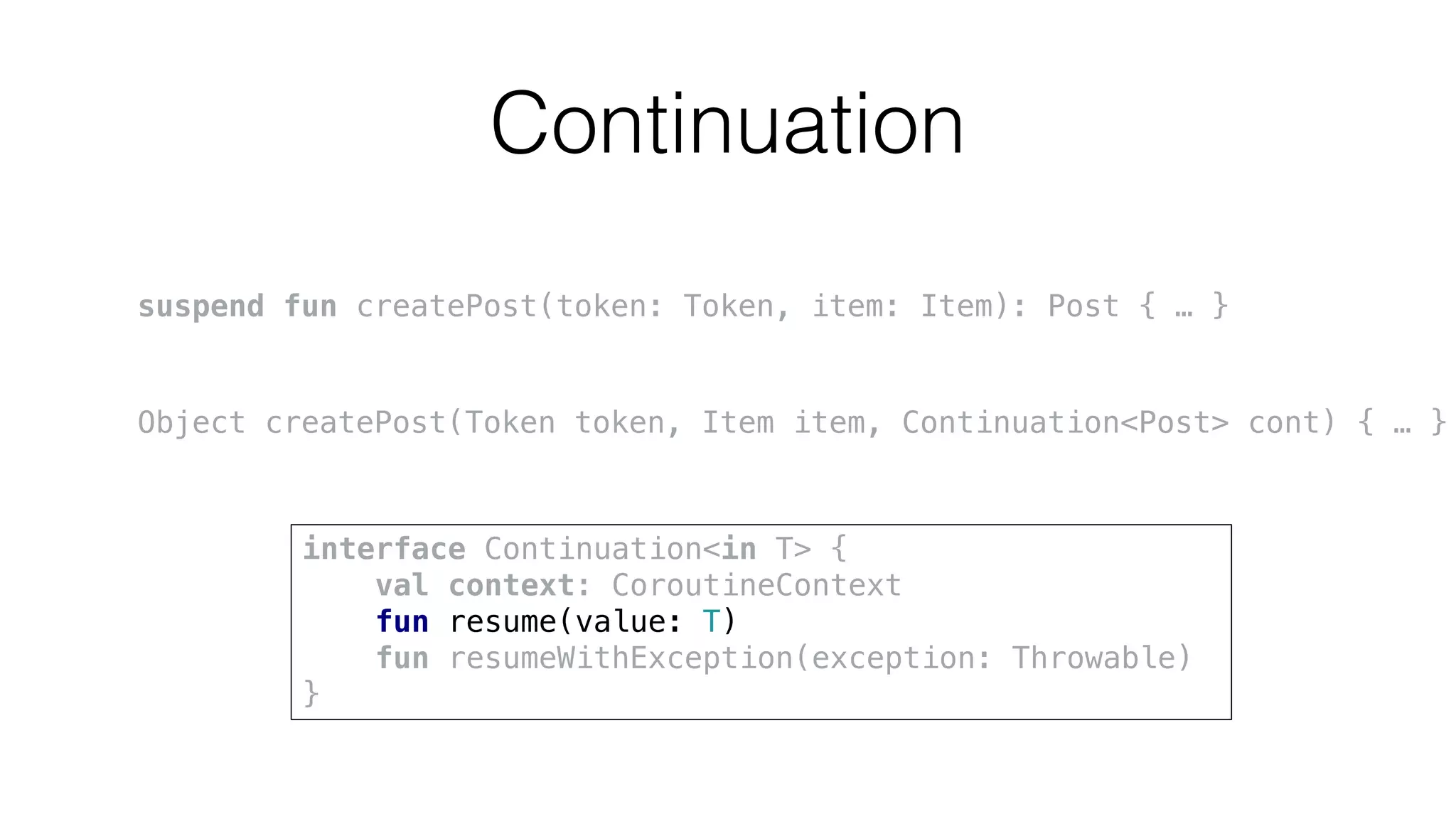
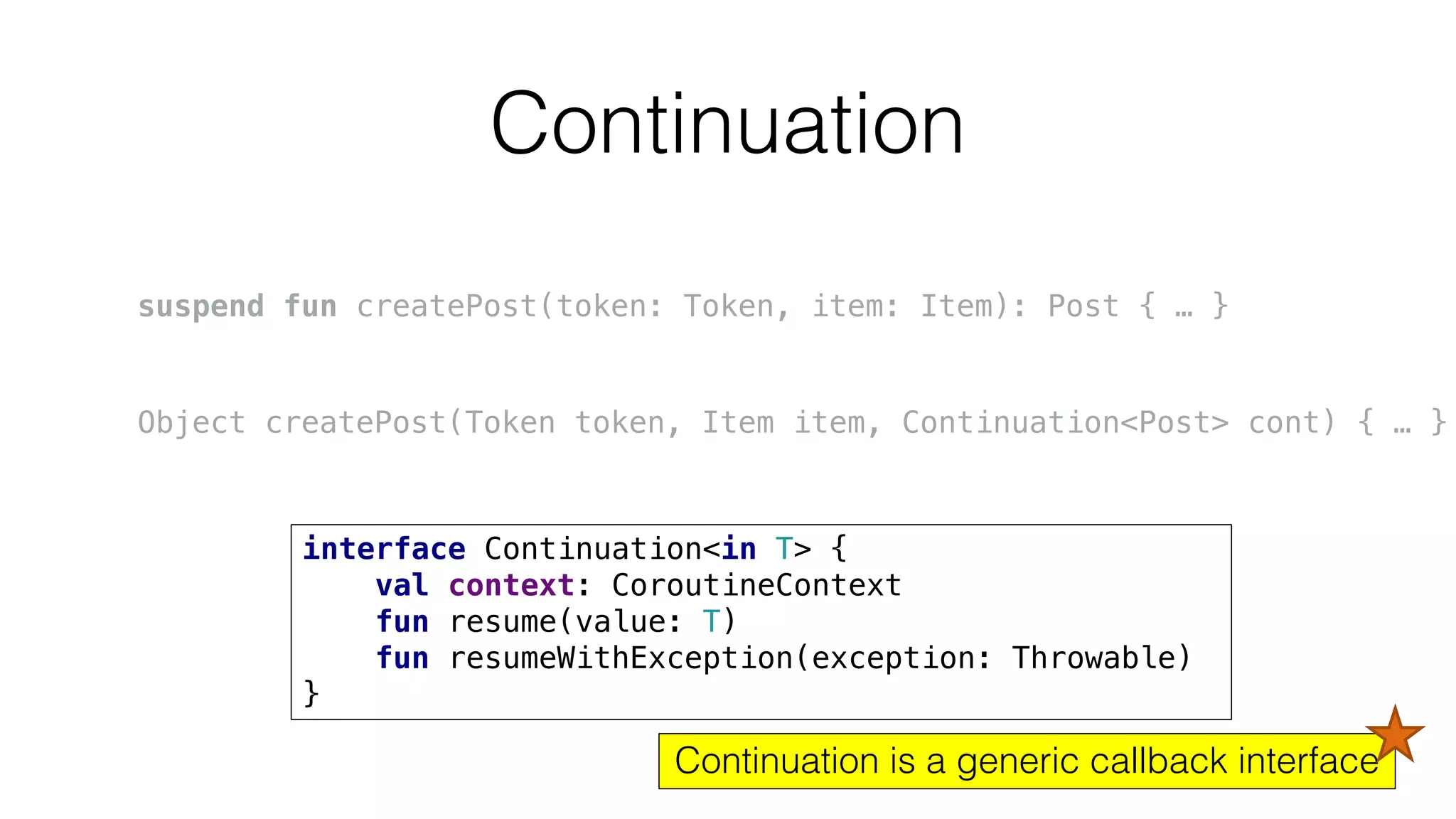
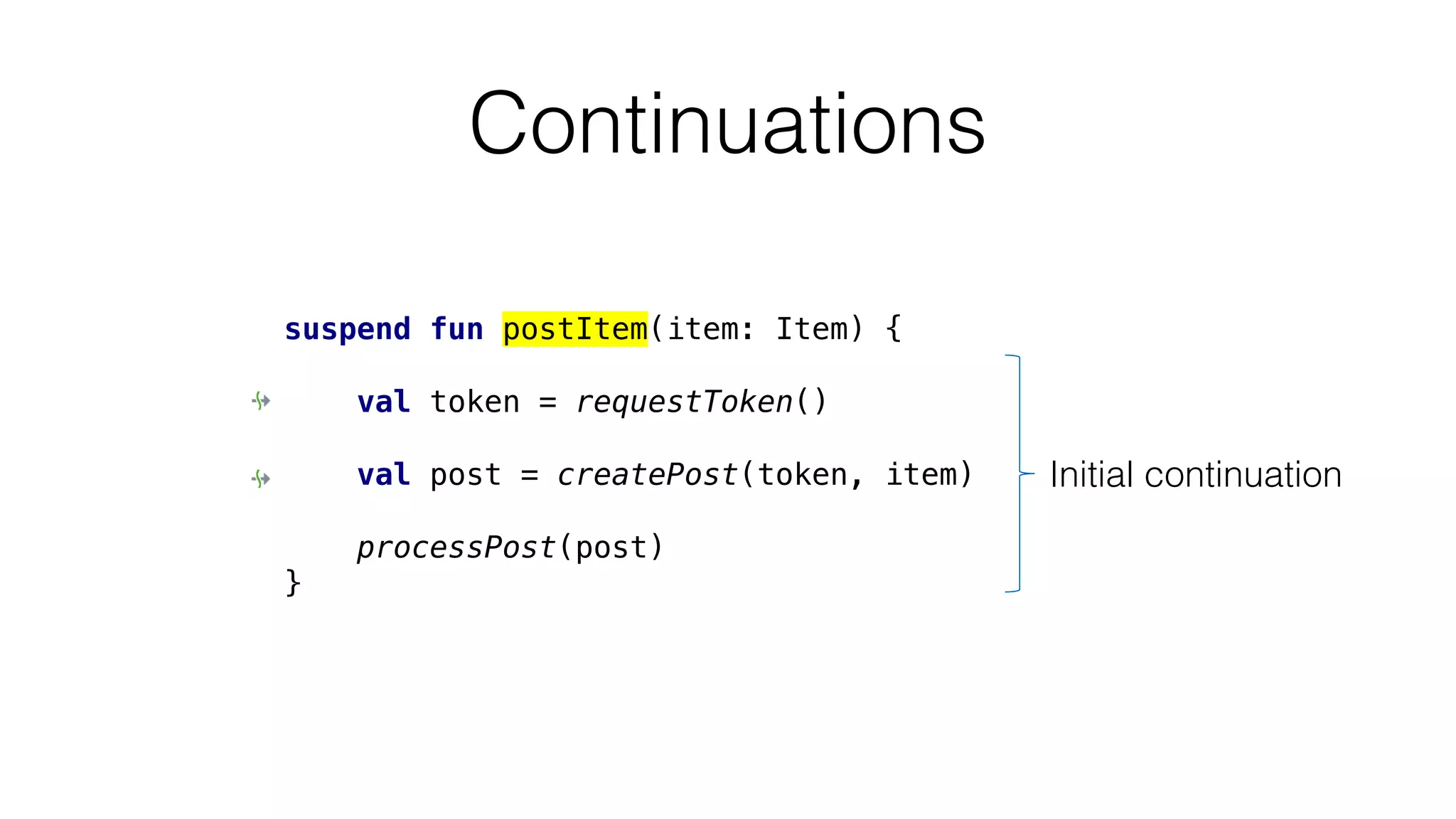
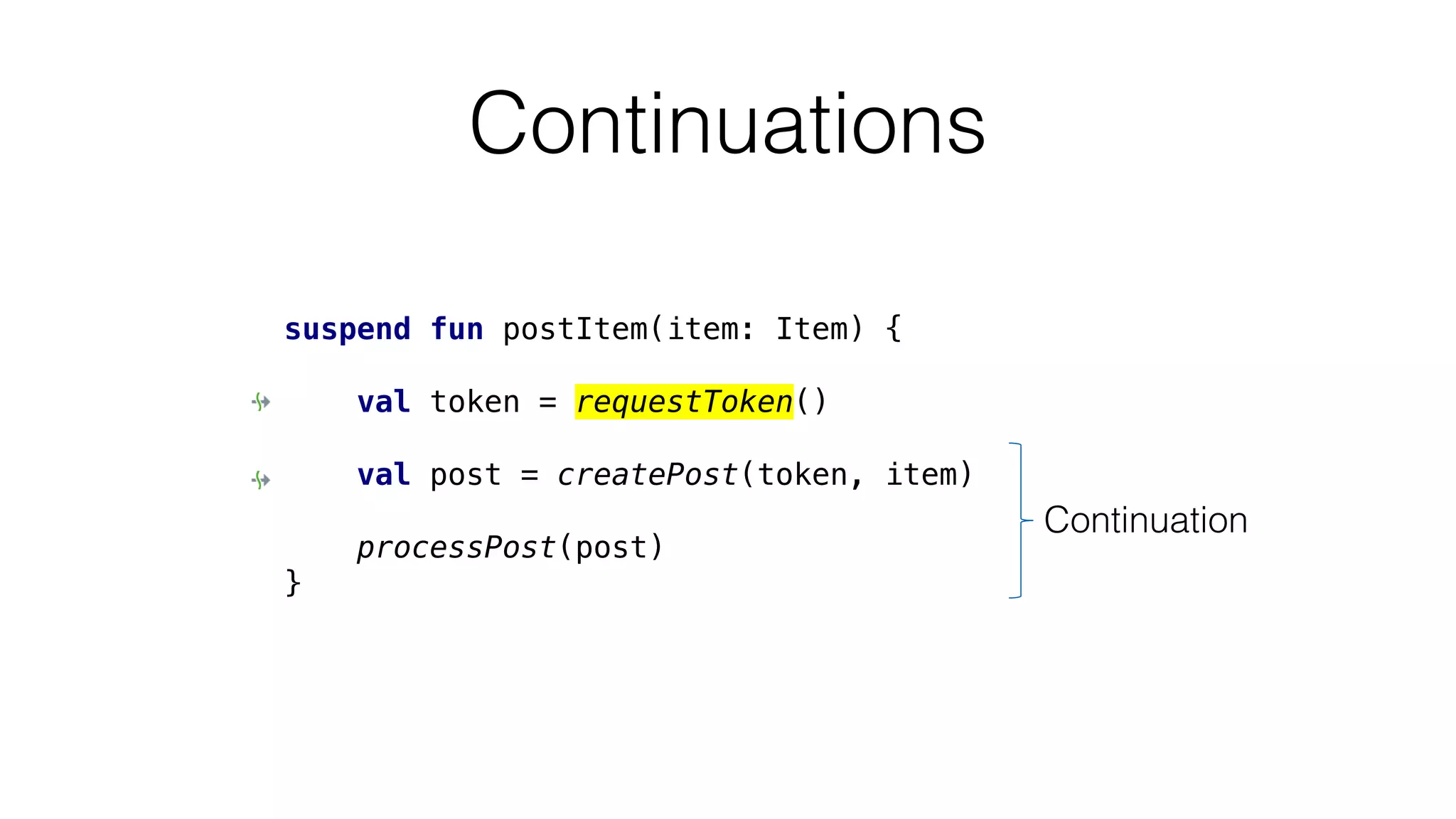
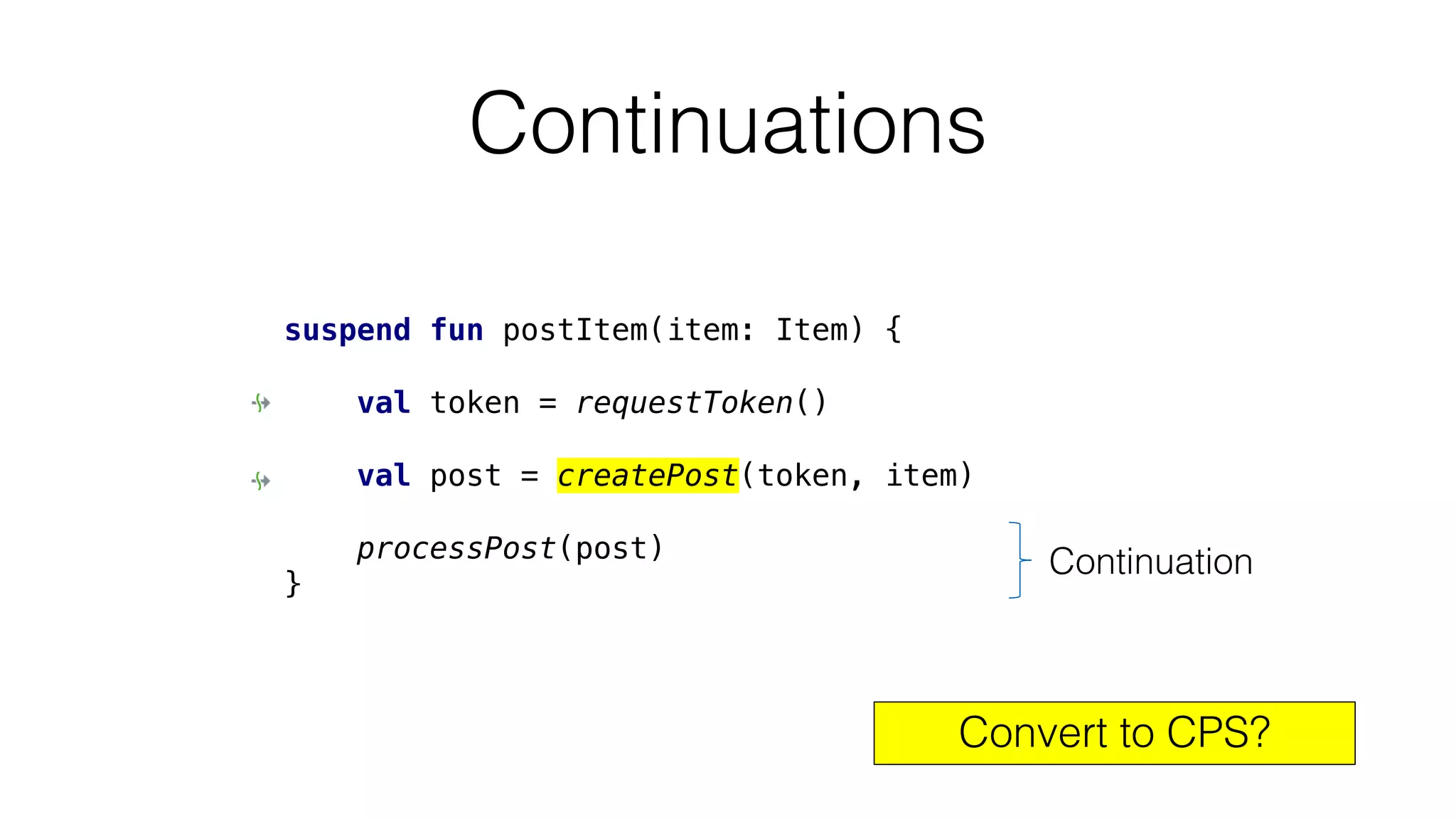
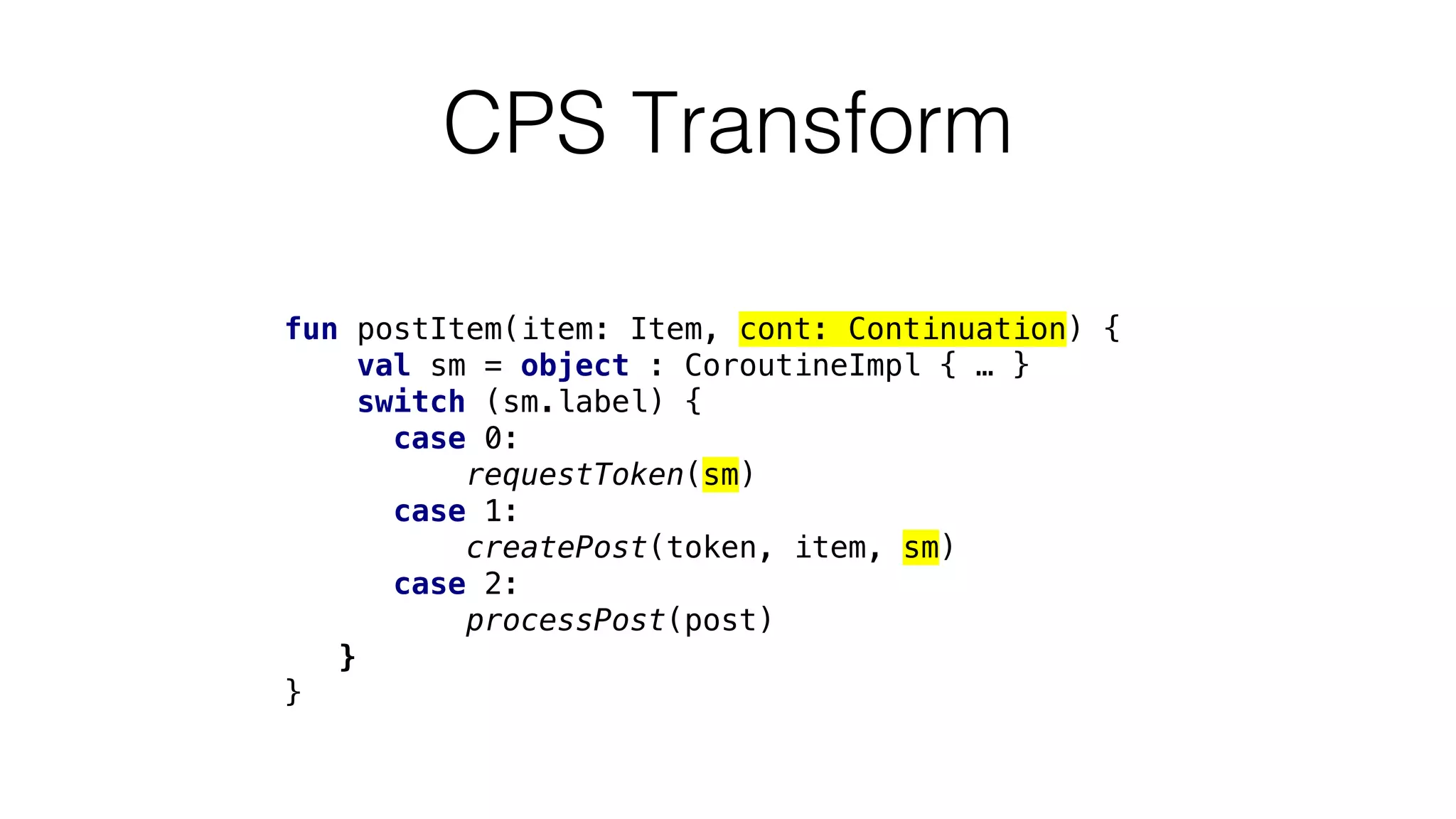
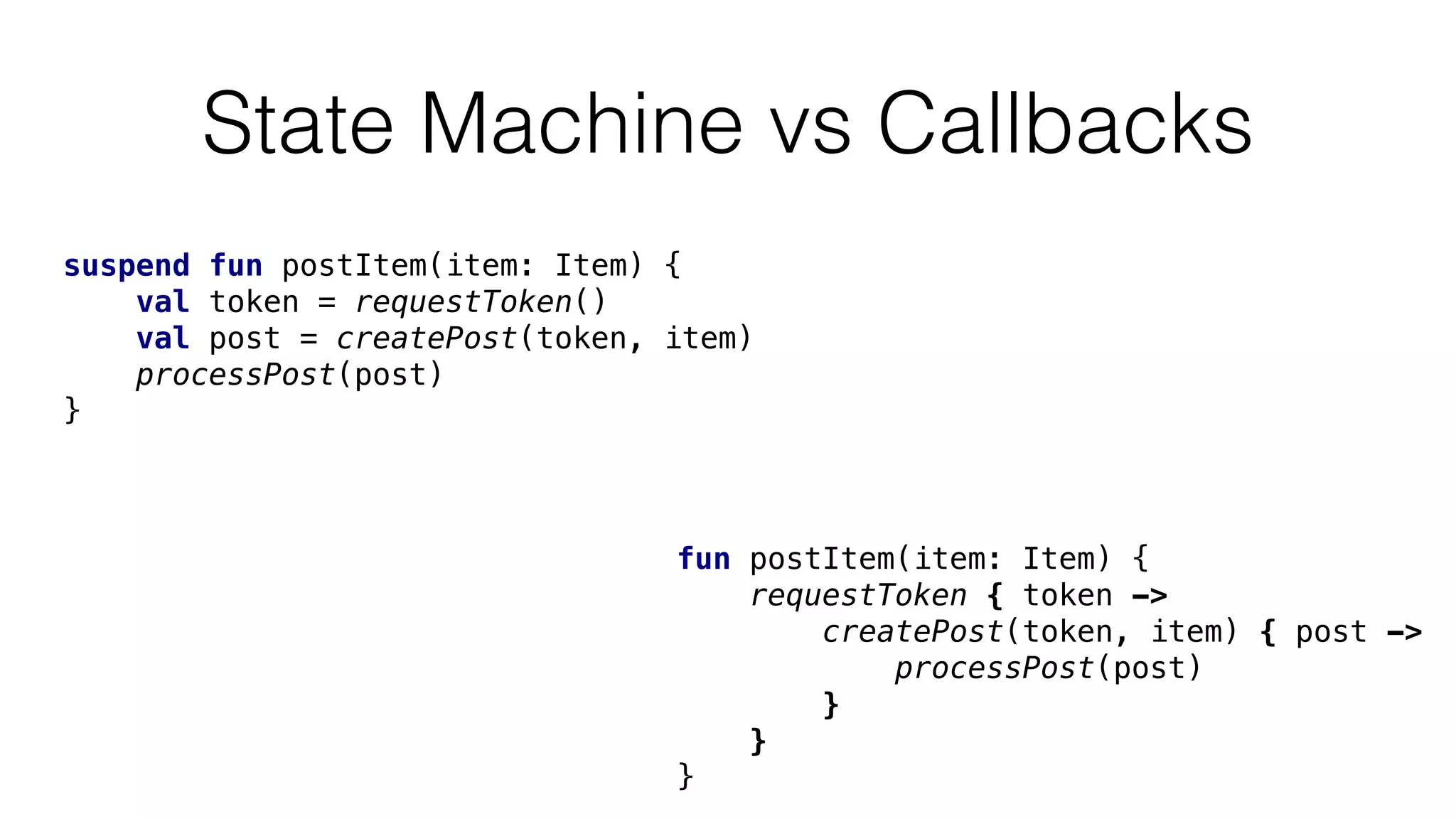
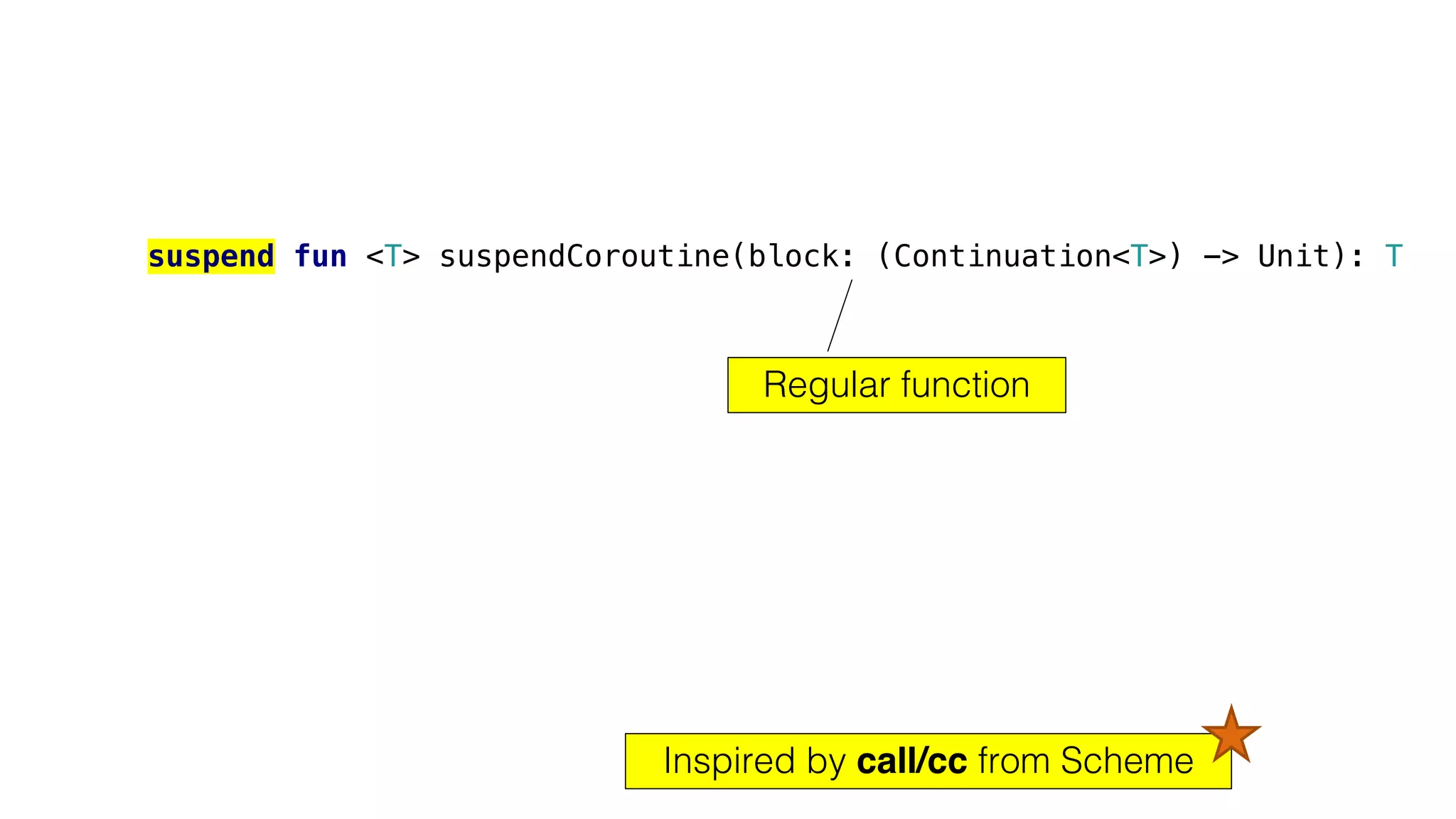
The document provides an in-depth exploration of coroutines in Kotlin, detailing various programming styles including direct style, continuation-passing style (CPS), and their transformations. It explains how Kotlin manages suspending functions, continuations, and the coroutine context, touching upon thread management and job cancellation. The content also addresses the use of callbacks, state machines, and integrates with frameworks like kotlinx-coroutines, showcasing practical examples and coding techniques.








































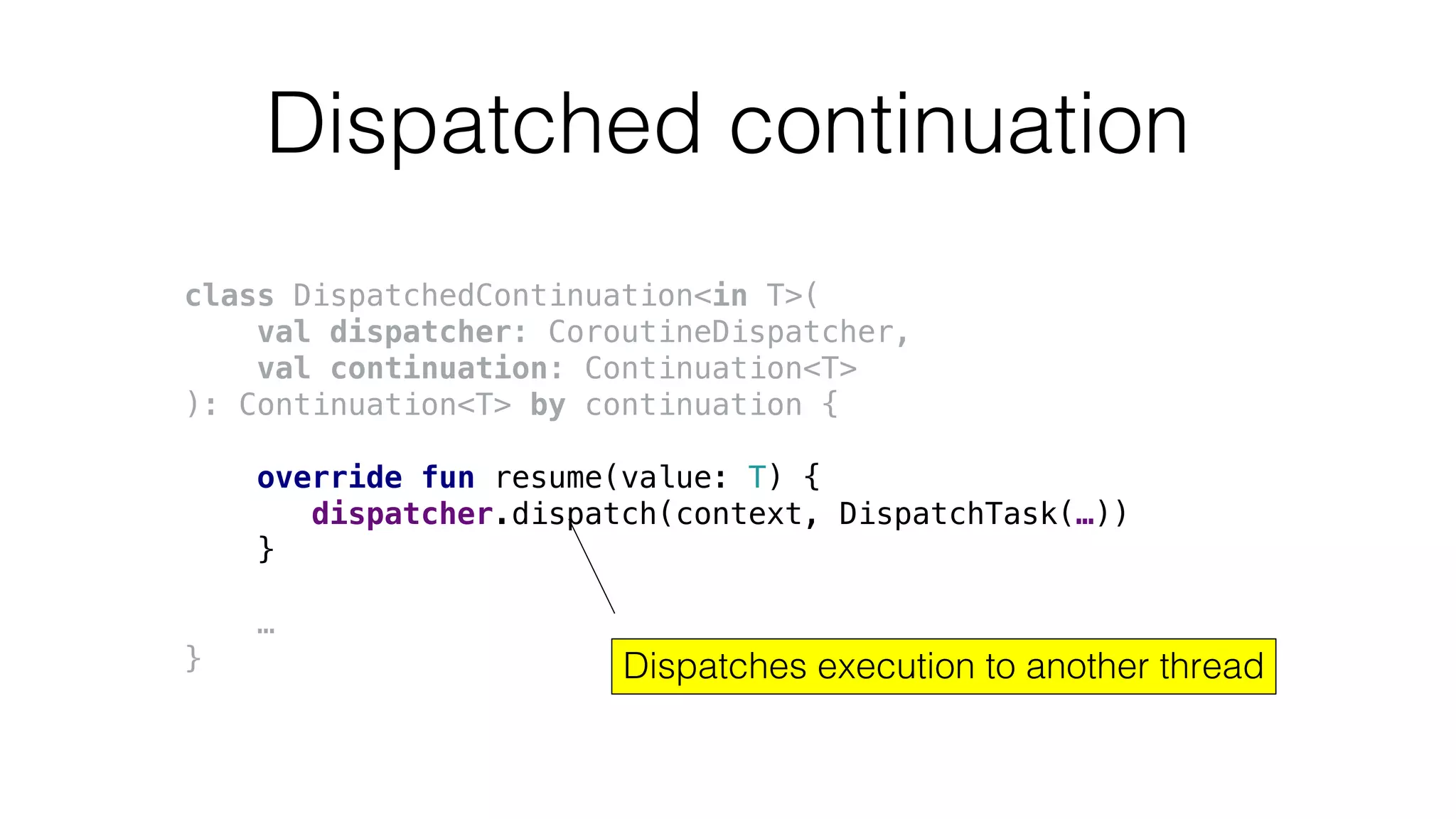


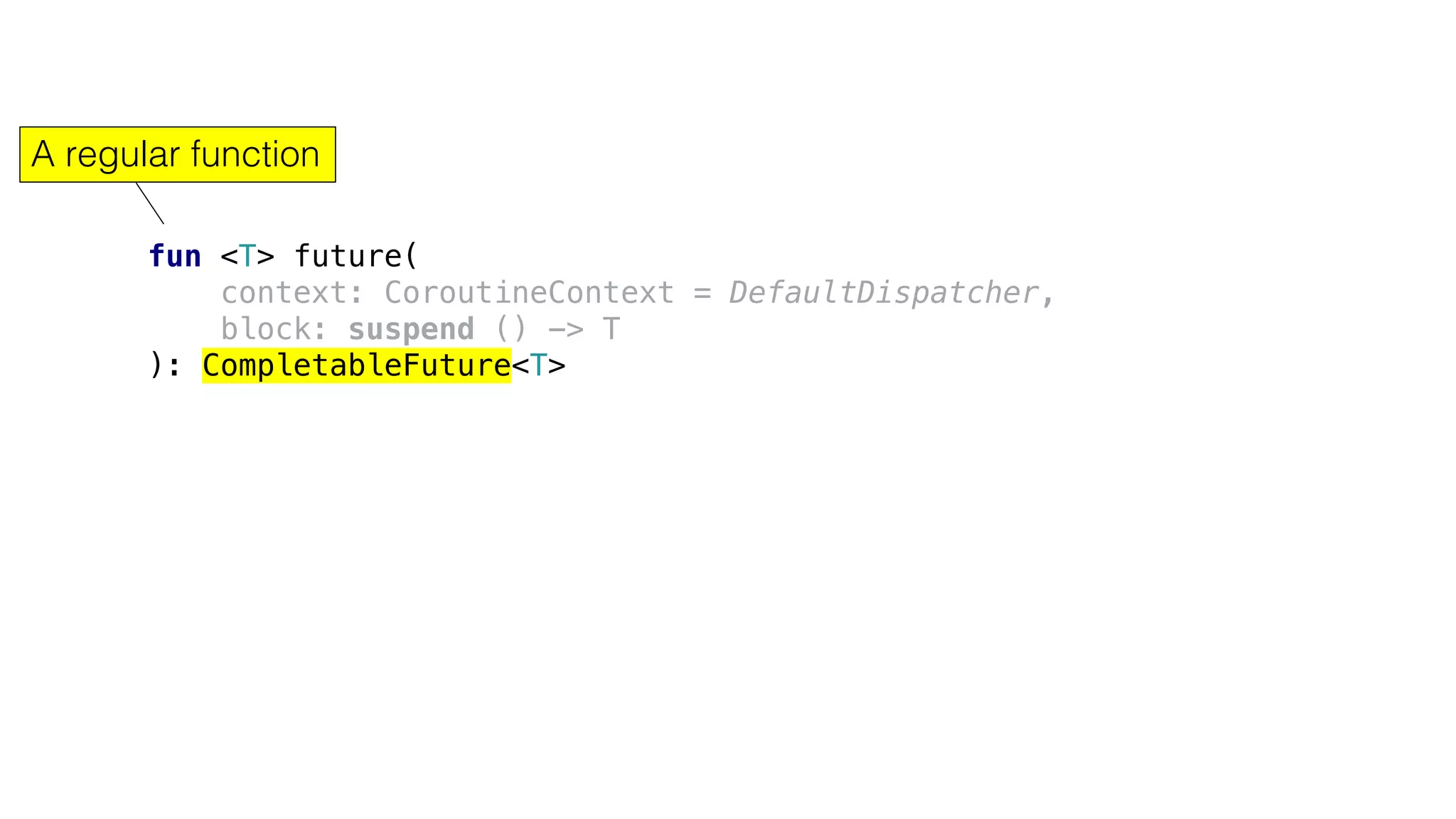




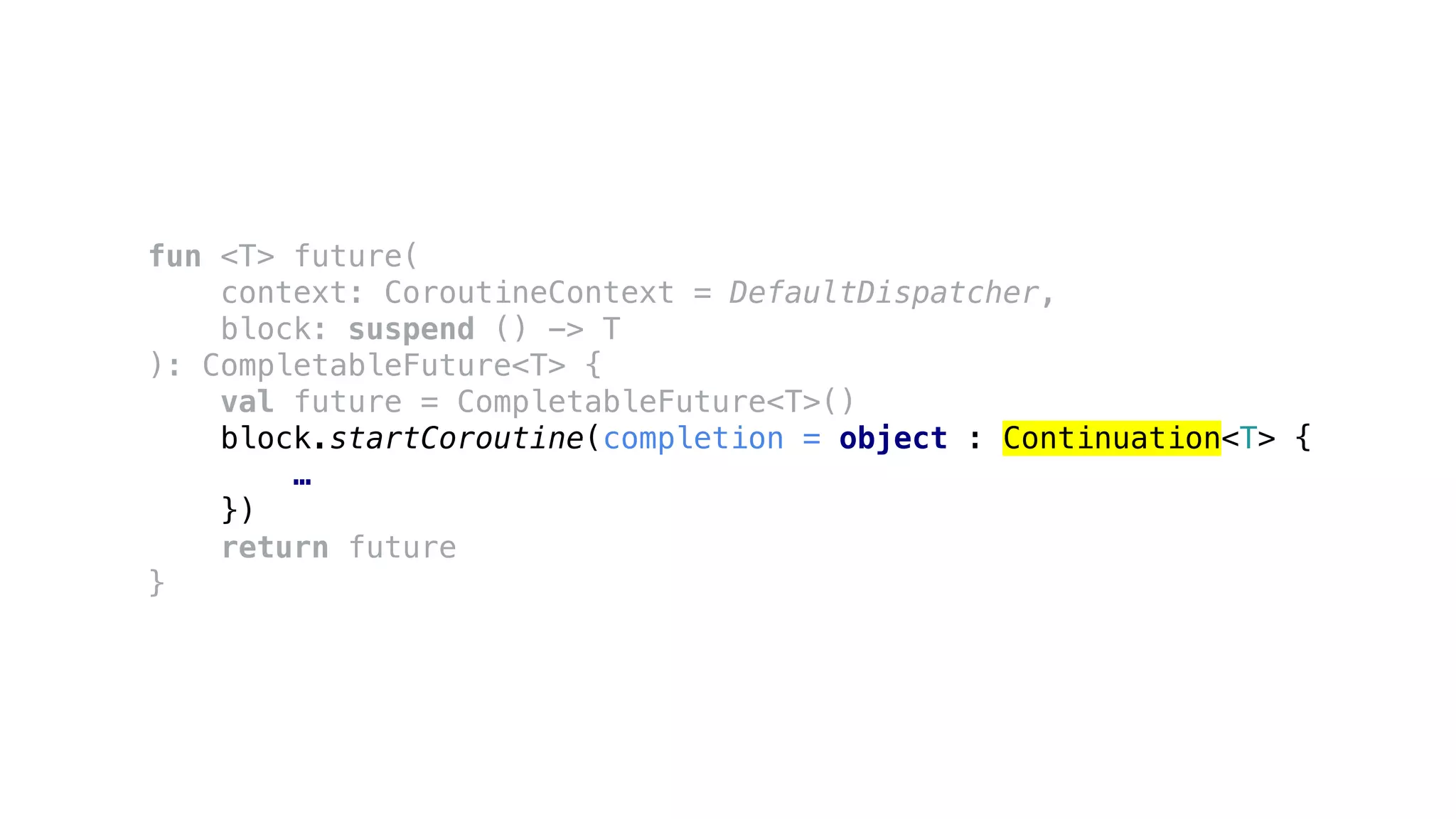

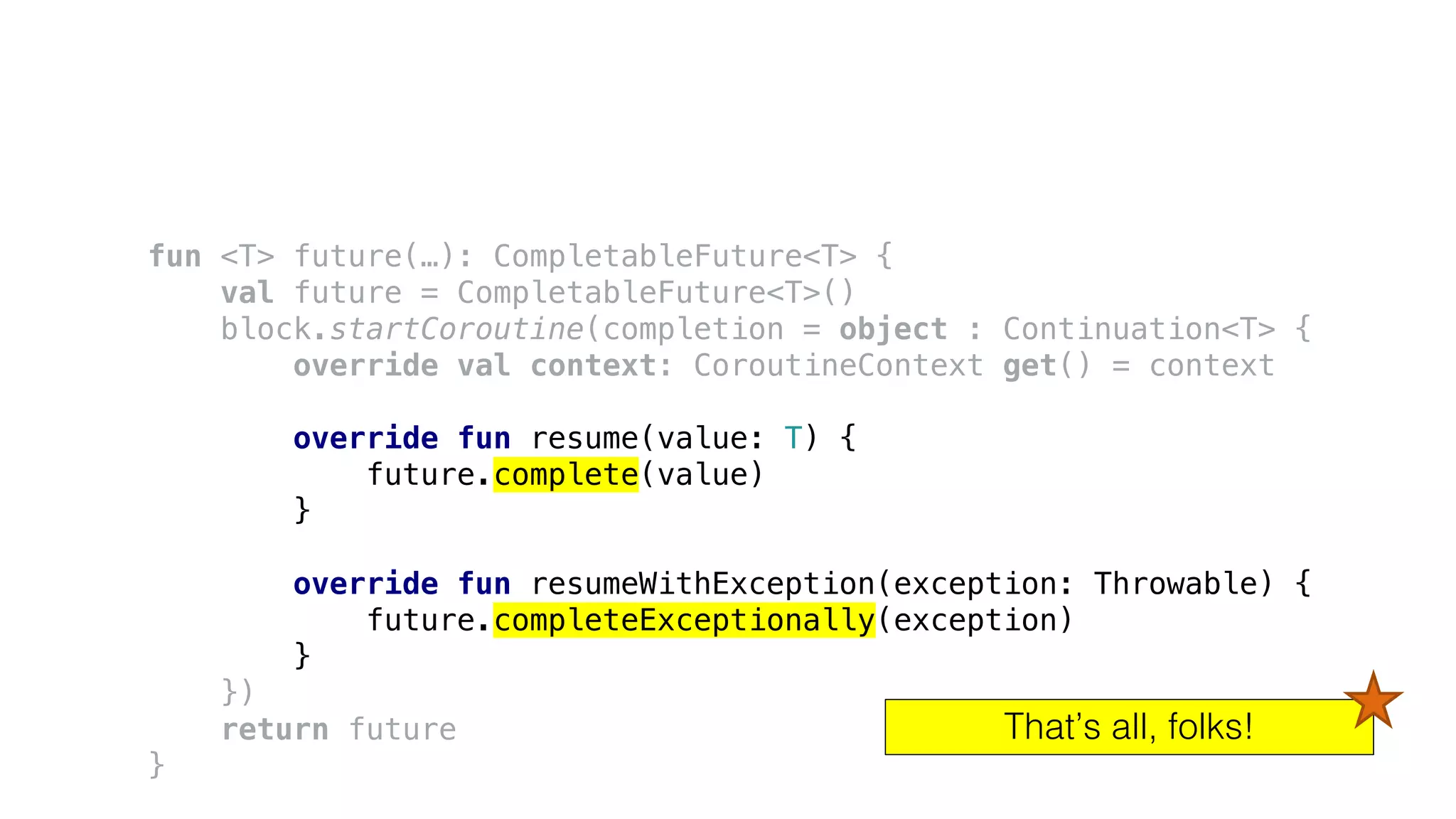






![Using coroutine context
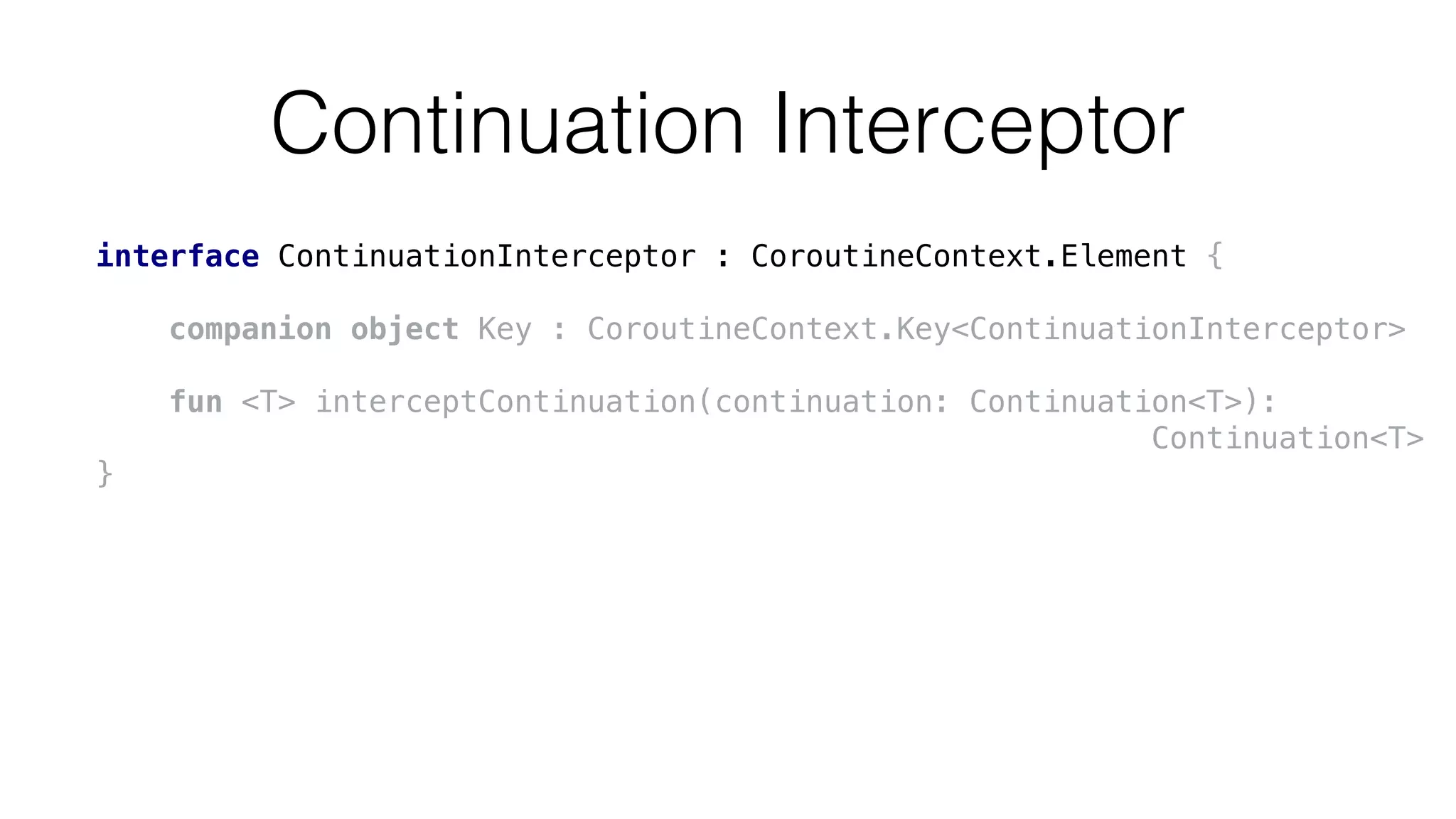
launch {
val job = coroutineContext[Job]!!
…
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017kotlinconf-deepdiveintocoroutinesonjvm-171115210433/75/Deep-dive-into-Coroutines-on-JVM-KotlinConf-2017-76-2048.jpg)
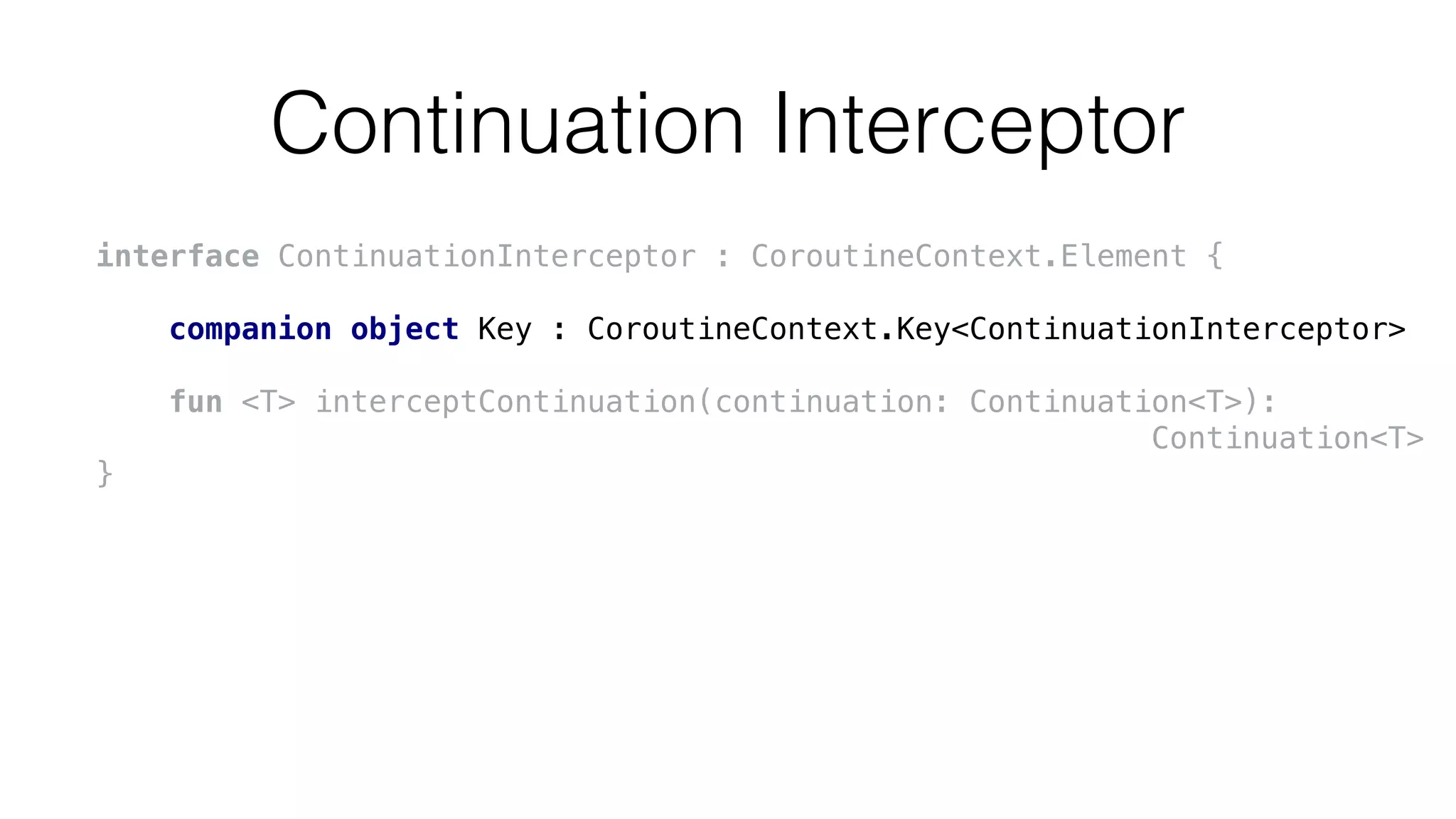
![Using coroutine context
launch {
val job = coroutineContext[Job]!!
val interceptor = coroutineContext[CoroutineInterceptor]!!
…
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017kotlinconf-deepdiveintocoroutinesonjvm-171115210433/75/Deep-dive-into-Coroutines-on-JVM-KotlinConf-2017-77-2048.jpg)