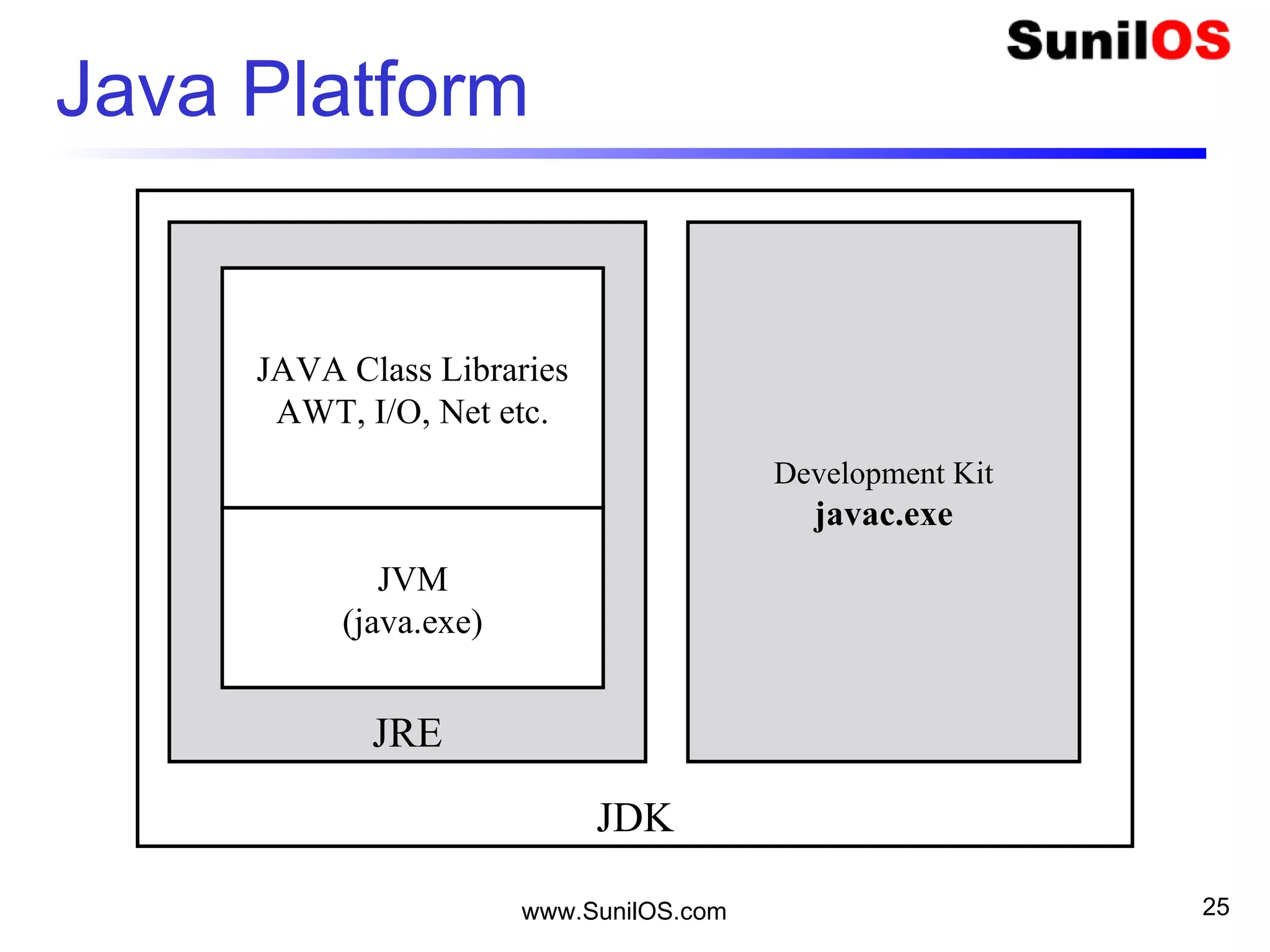
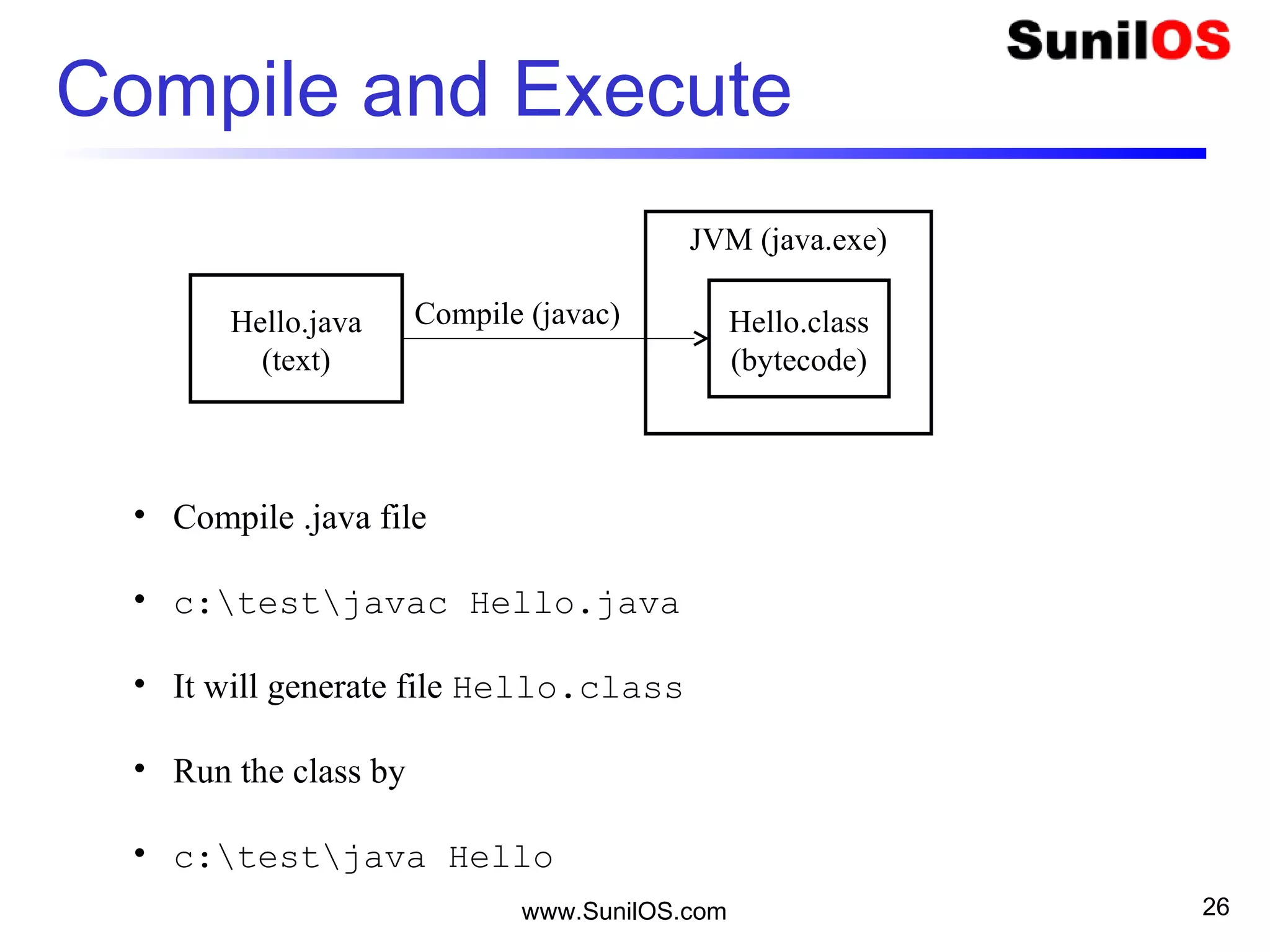
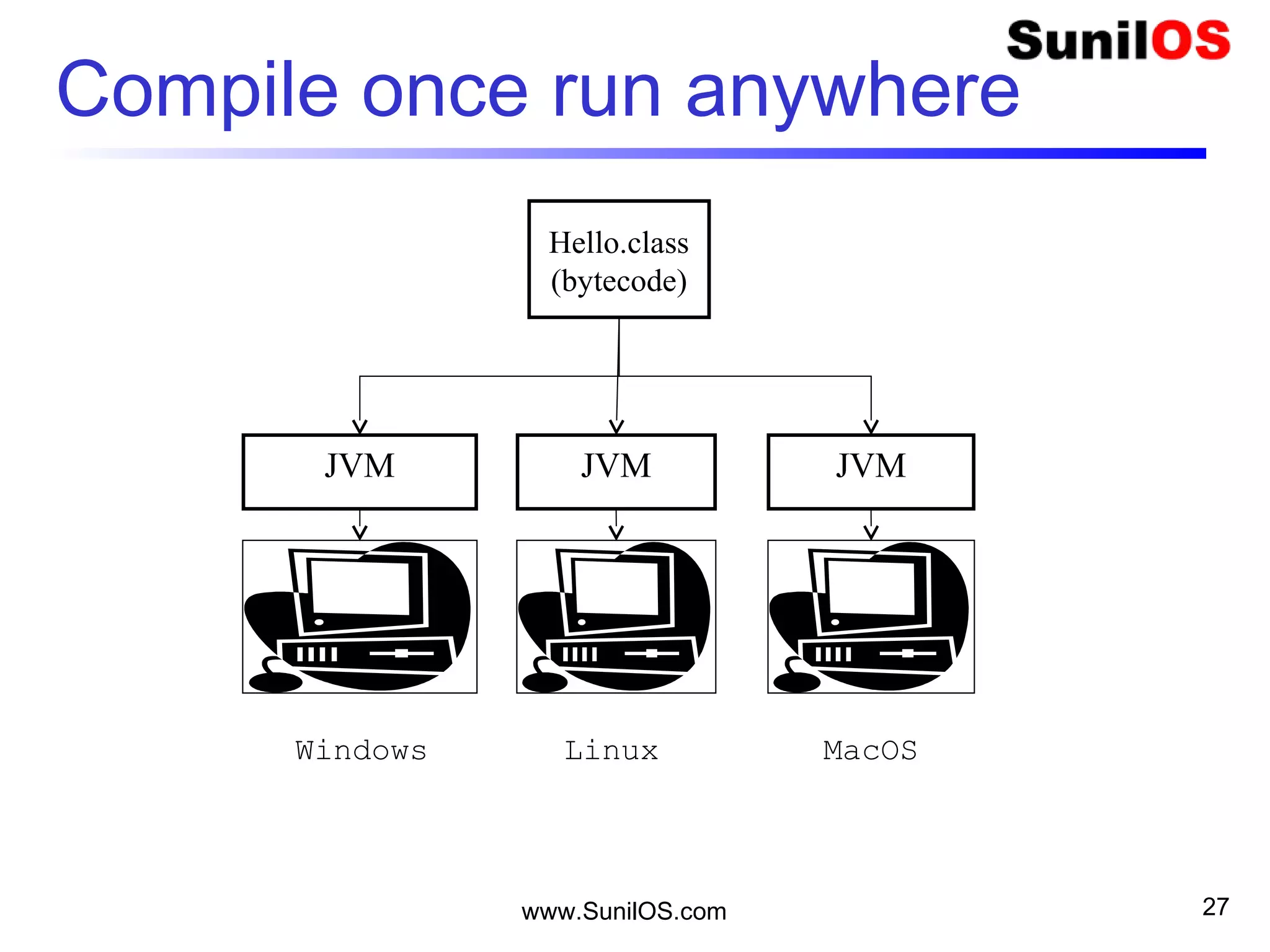
This document provides an overview of Java basics including:
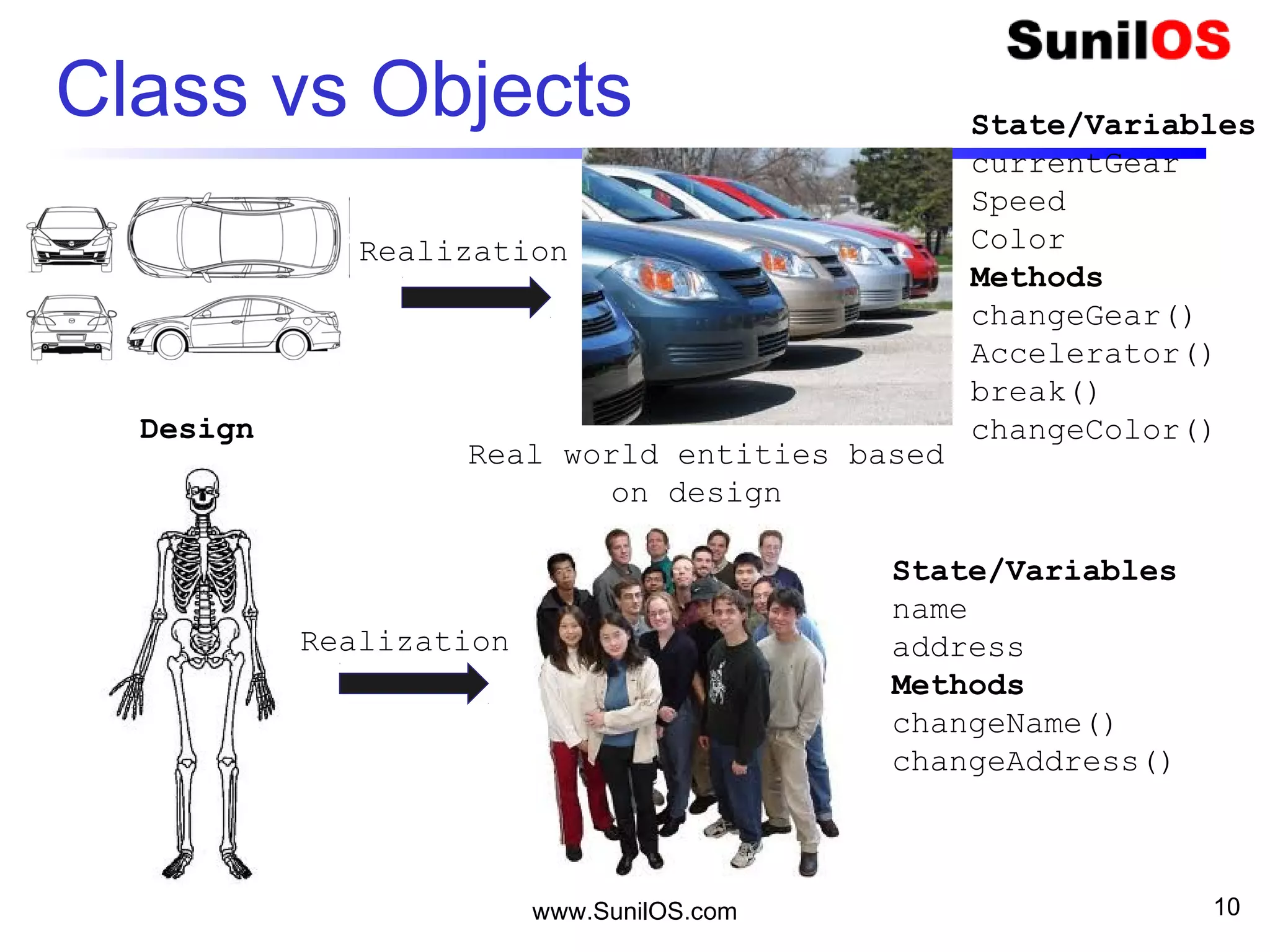
- Java is an object-oriented programming language like C++.
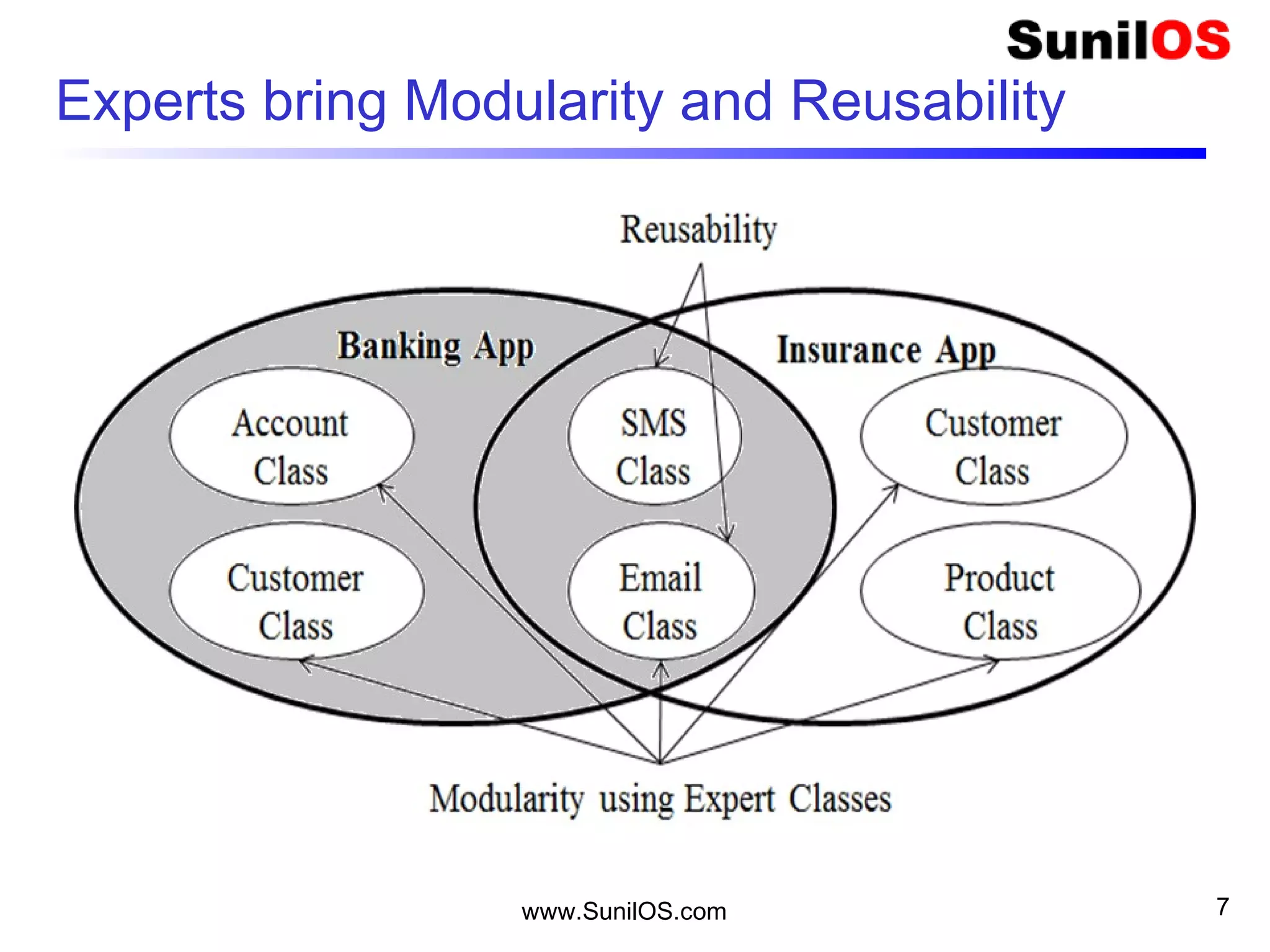
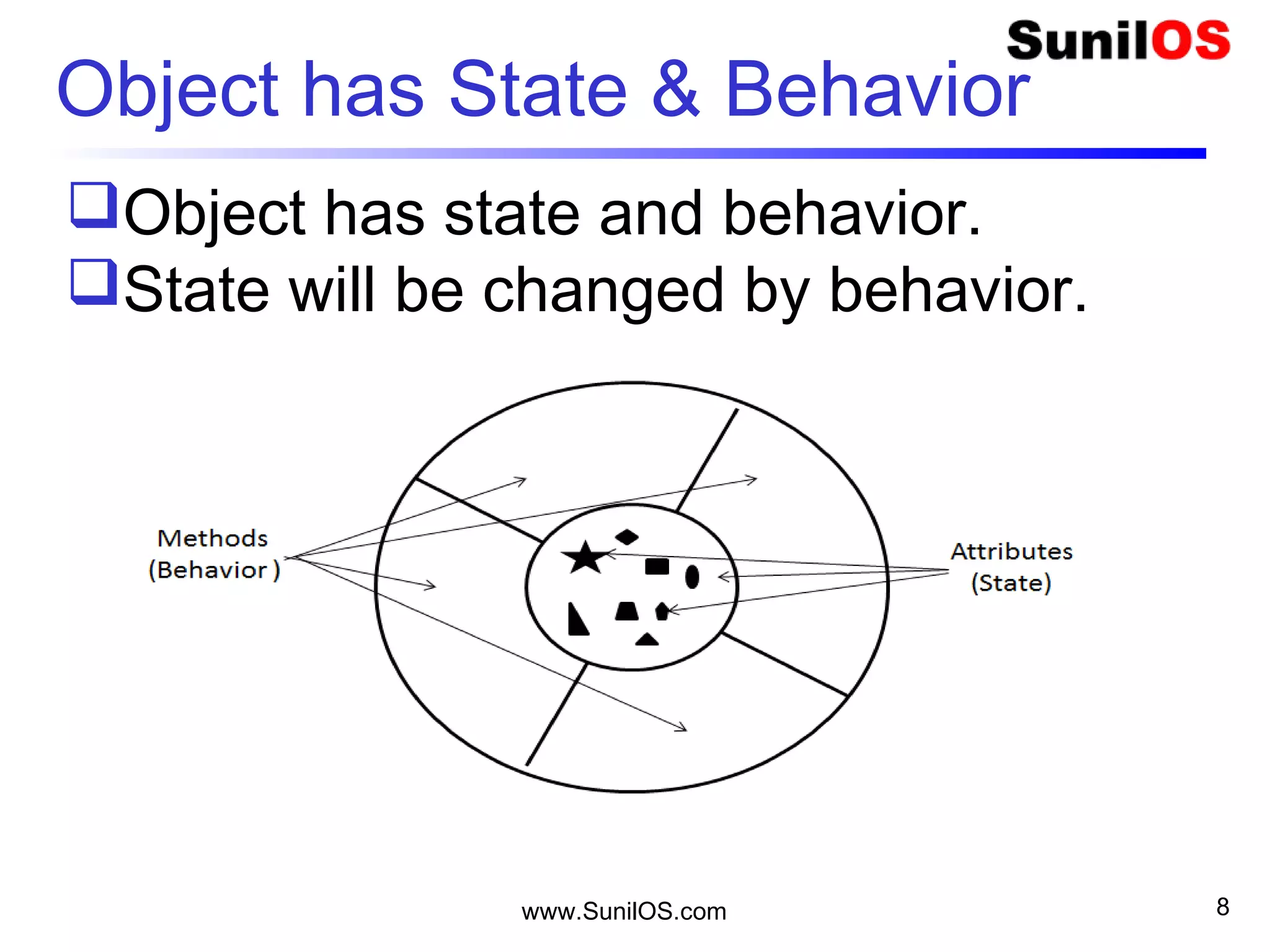
- The basic unit in Java is the object, which contains both state in the form of variables and behavior in the form of methods.
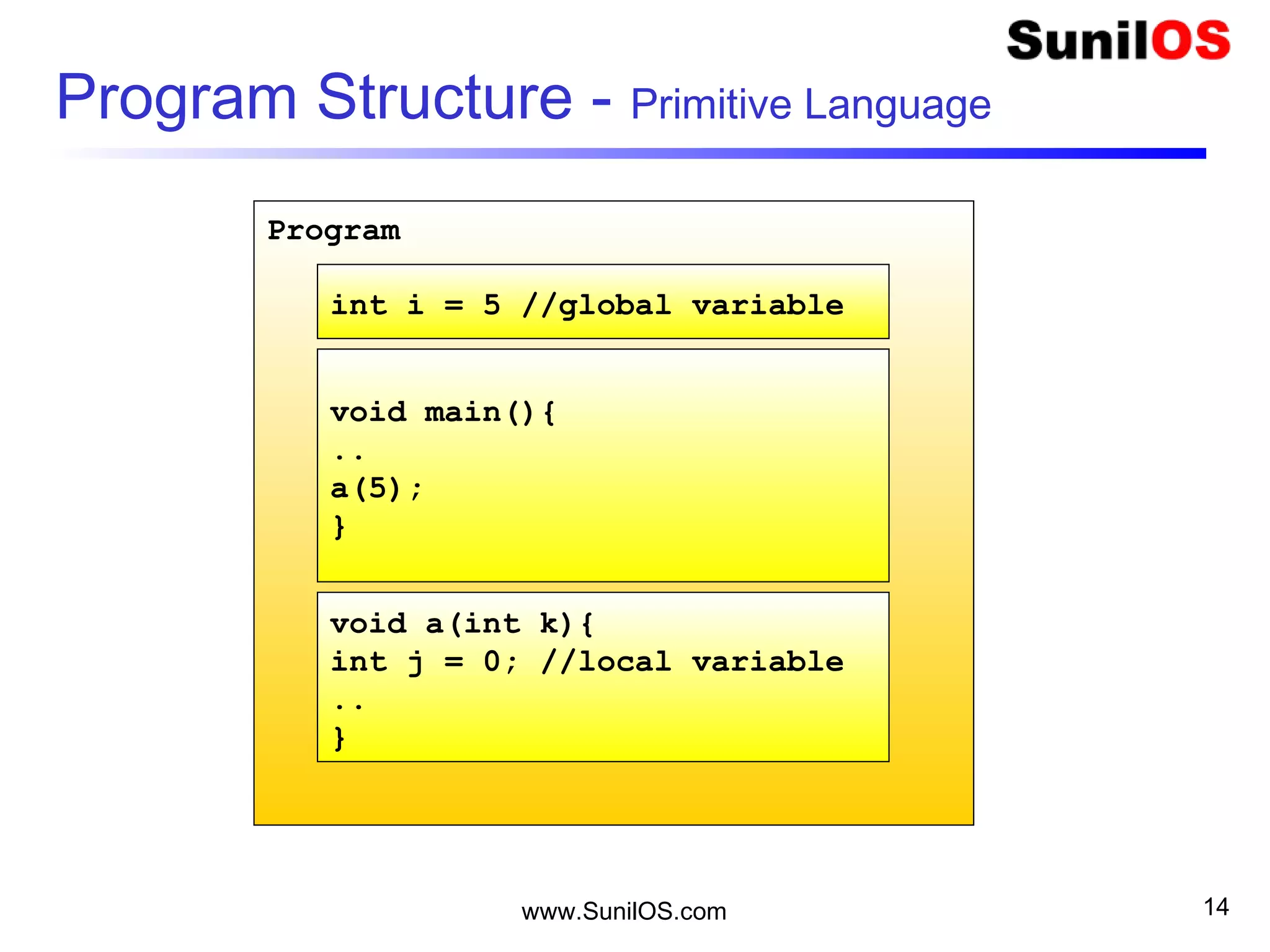
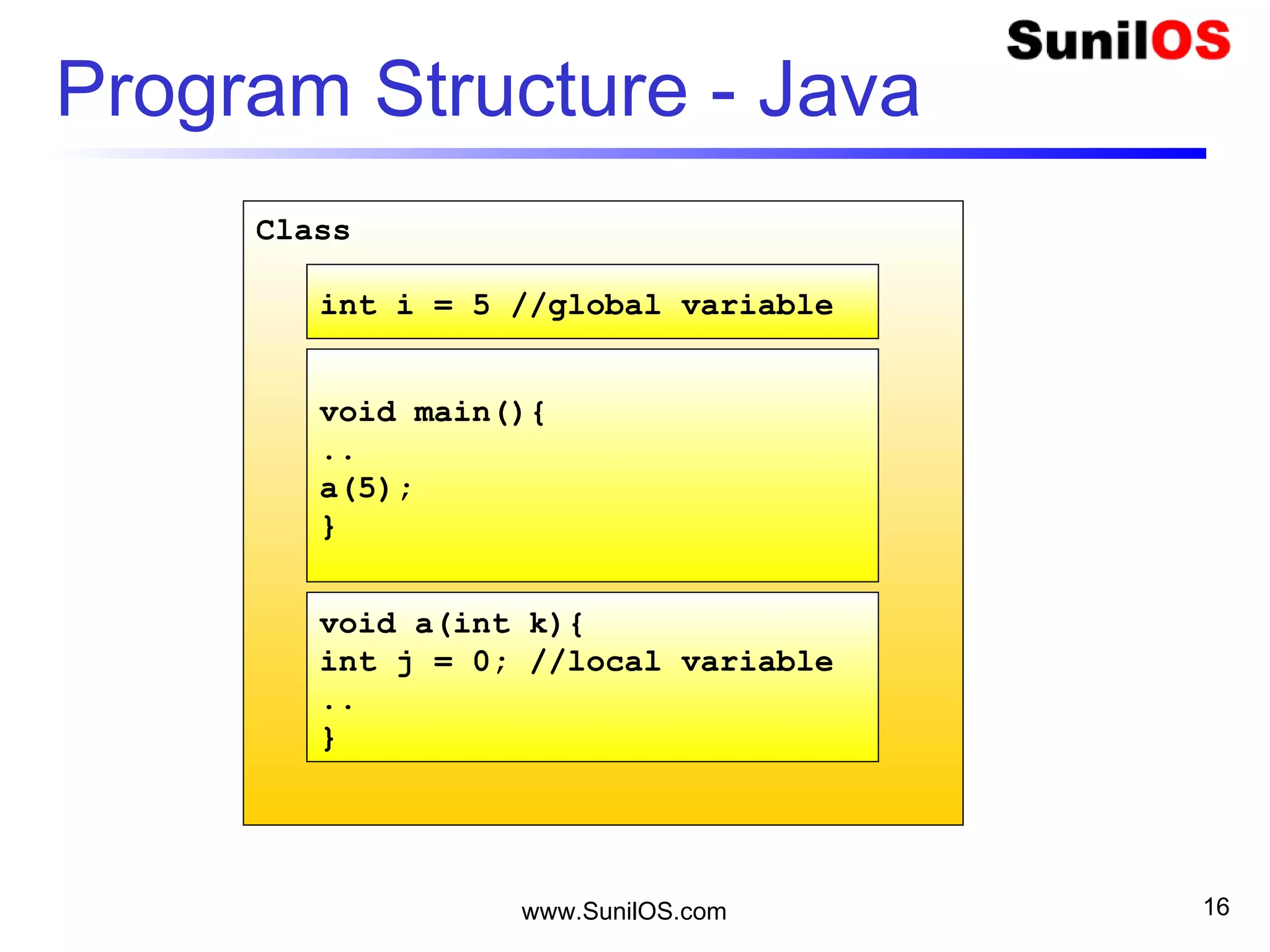
- Classes define the structure and behavior of objects through methods and variables. The main method is required to execute a Java program.





![www.SunilOS.com 20
My First Program - HelloJava
public class HelloJava {
opublic static void main(String[] args) {
o String name =“Vijay”;
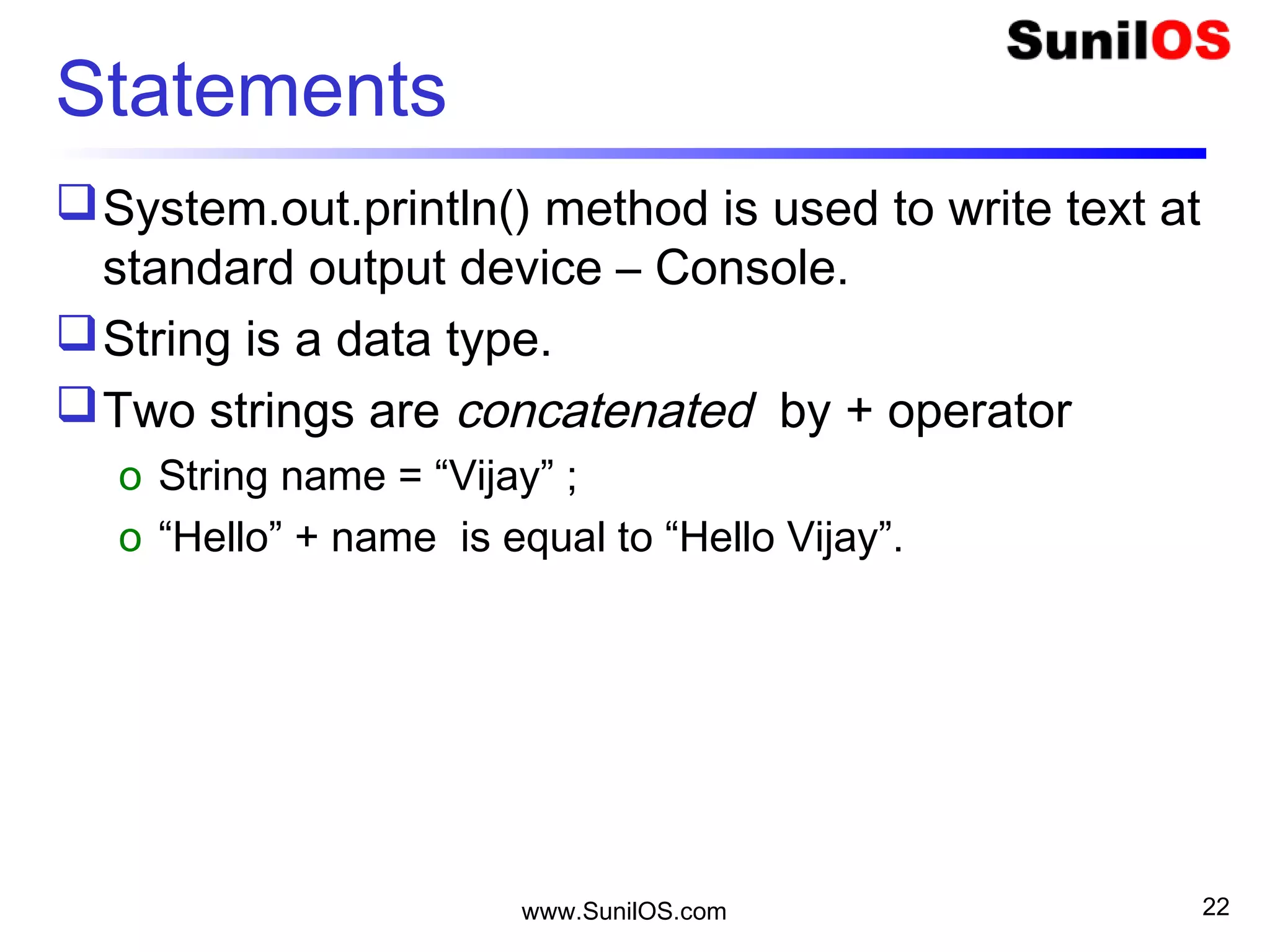
o System.out.println("Hello “ + name);
o}
}
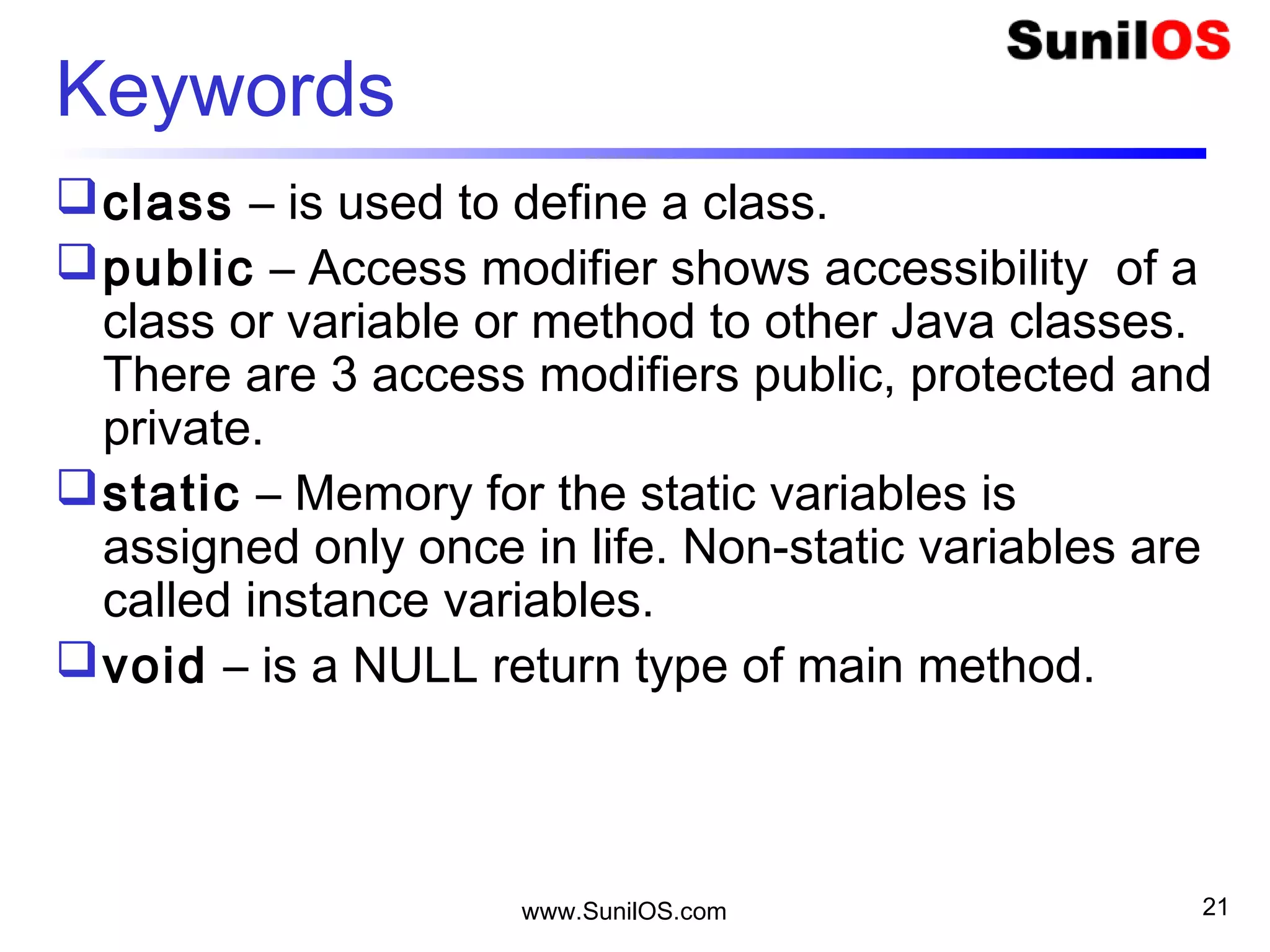
public, class, static, and void are keywords.
Keywords are always written in small letters.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-20-2048.jpg)

![www.SunilOS.com
While Loop
public class HelloWhile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
o boolean जबतकहेजान = true;
o int round = 0;
o while (जबतकहेजान ) {
System.out.println(“मै बसंती नाचूंगी !!!");
round++;
if(round>500 )
• जबतकहेजान = false;
}
}
}
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-30-2048.jpg)

![ public class HelloFor {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
o for (int shot=1; shot <= 5; shot++)
o {
System.out.println(i+“Shot Balloon");
o }
o }
}
www.SunilOS.com
For Loop – Five shots
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-32-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 33
Print Hello Java 5 times - for
public class HelloFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
o for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Hello Java ");
o }
o }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-33-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 34
Print Hello Java 5 times - while
public class HelloWhile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
o int i = 0;
o while (i < 5) {
System.out.println("Hello Java ");
i++; // i = i+1
o }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-34-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 35
Print Hello Java 5 times – do-while
public class HelloDoWhile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
o do {
System.out.println( i+ " Hello Java ");
i++;
o } while (i < 5);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-35-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 36
Foreach statement
public class HelloFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
o int[] table={ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10};
o for (int v : table) {
System.out.println(“Table “ + v);
o }
o }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-36-2048.jpg)
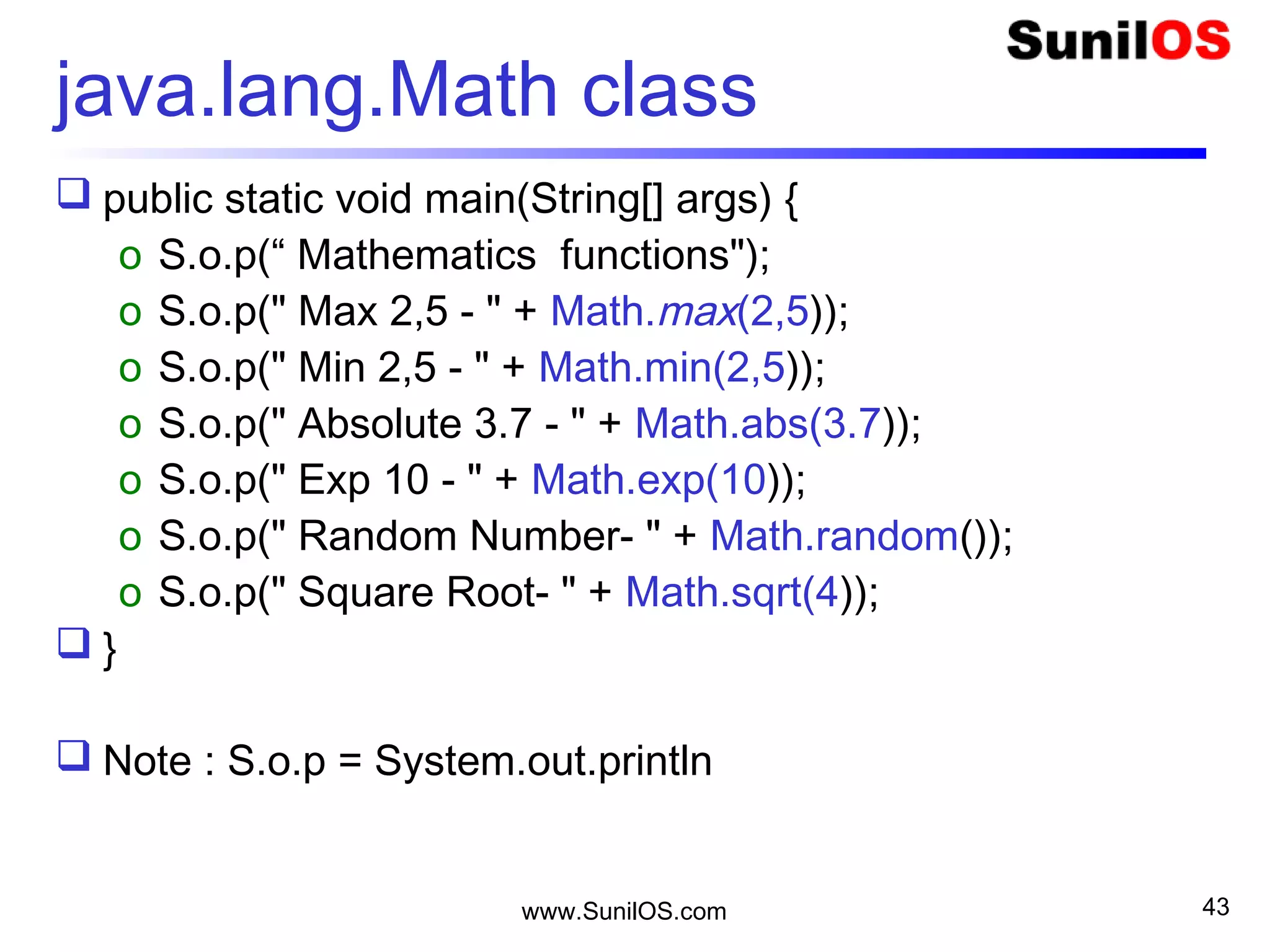
![www.SunilOS.com 37
Add.java
public class Add {
public static void main(String[] args) {
oint a = 5;
oint b = 10;
oint sum = a + b;
oSystem.out.println("Sum is " + sum);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-37-2048.jpg)
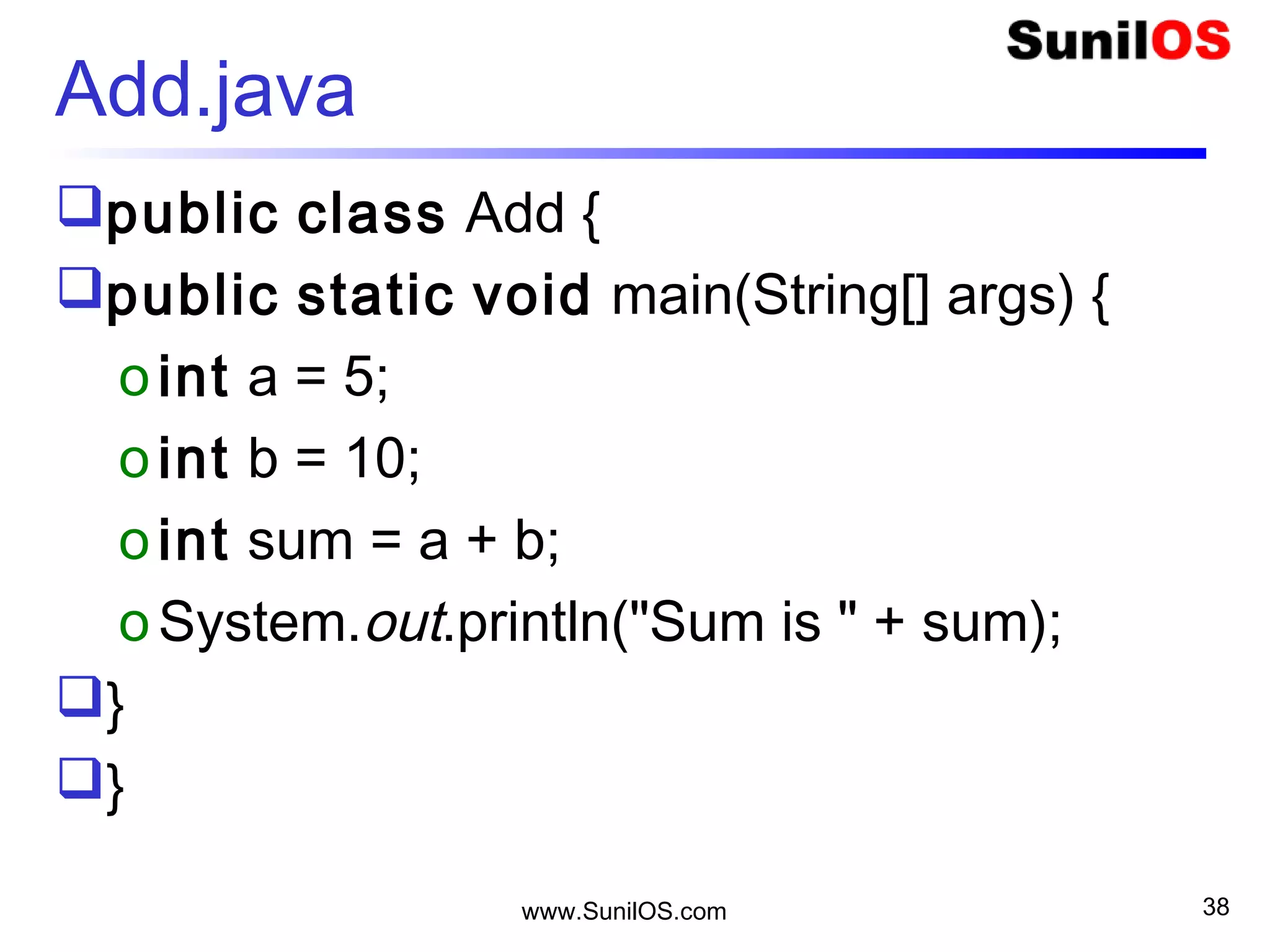

![www.SunilOS.com 40
Java.lang.StringBuffer class
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Vijay");
sb.append(“ Dinanath Chauhan");
S.o.p("Length : " + sb.length());
S.o.p("Capacity :" + sb.capacity());
S.o.p("Char at :" + sb.charAt(1));
S.o.p("Index Of : " + sb.indexOf("Dinanth"));
S.o.p("Replace : " + sb.replace(0, 5, "Jay "));
S.o.p("Reverse : " + sb.reverse());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-40-2048.jpg)
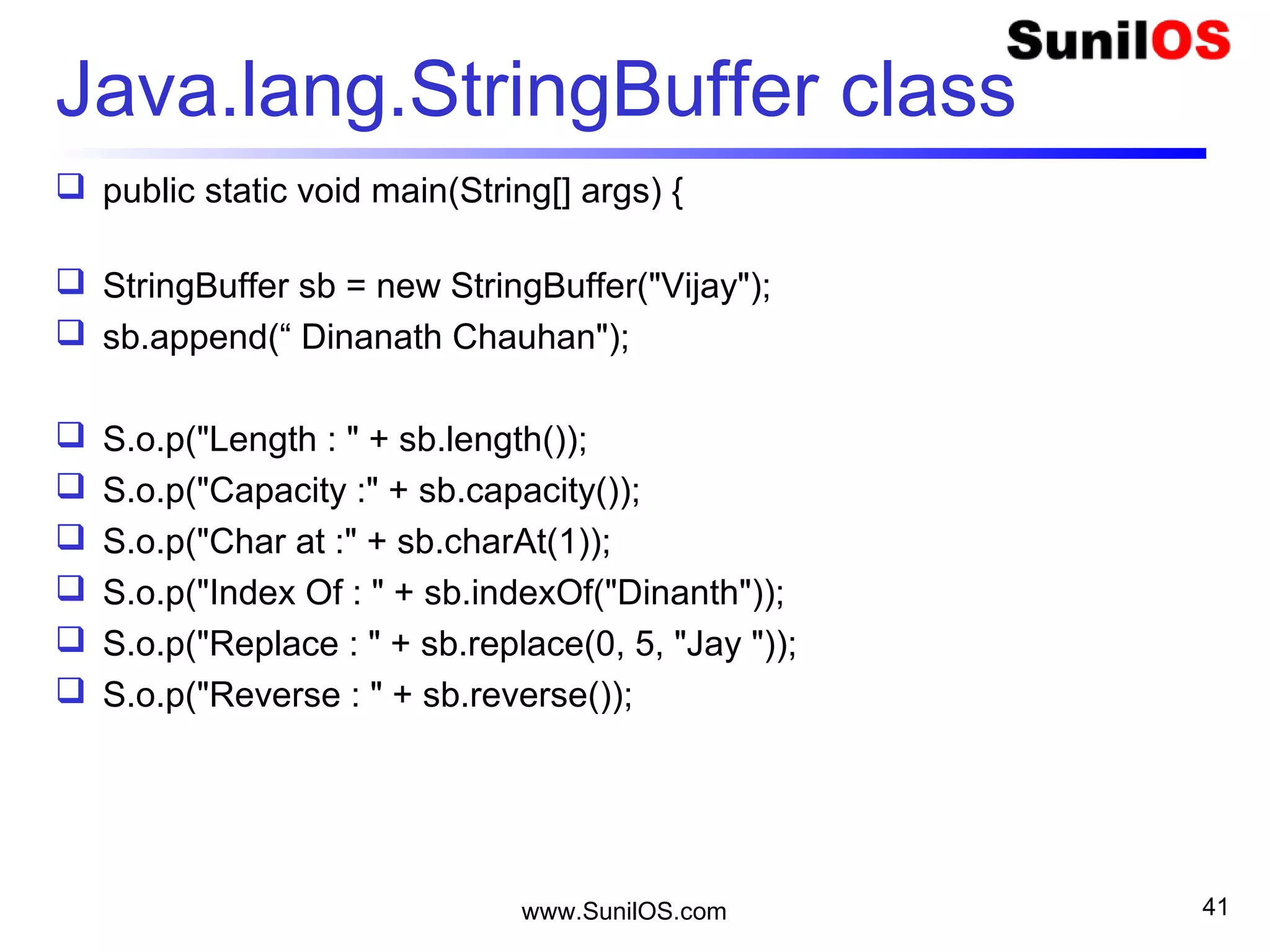
![www.SunilOS.com 42
java.lang.Math class
public static void main(String[] args) {
o S.o.p(“ Mathematics functions");
o S.o.p(" Max 2,5 - " + Math.max(2,5));
o S.o.p(" Min 2,5 - " + Math.min(2,5));
o S.o.p(" Absolute 3.7 - " + Math.abs(3.7));
o S.o.p(" Exp 10 - " + Math.exp(10));
o S.o.p(" Random Number- " + Math.random());
o S.o.p(" Square Root- " + Math.sqrt(4));
}
Note : S.o.p = System.out.println](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-42-2048.jpg)
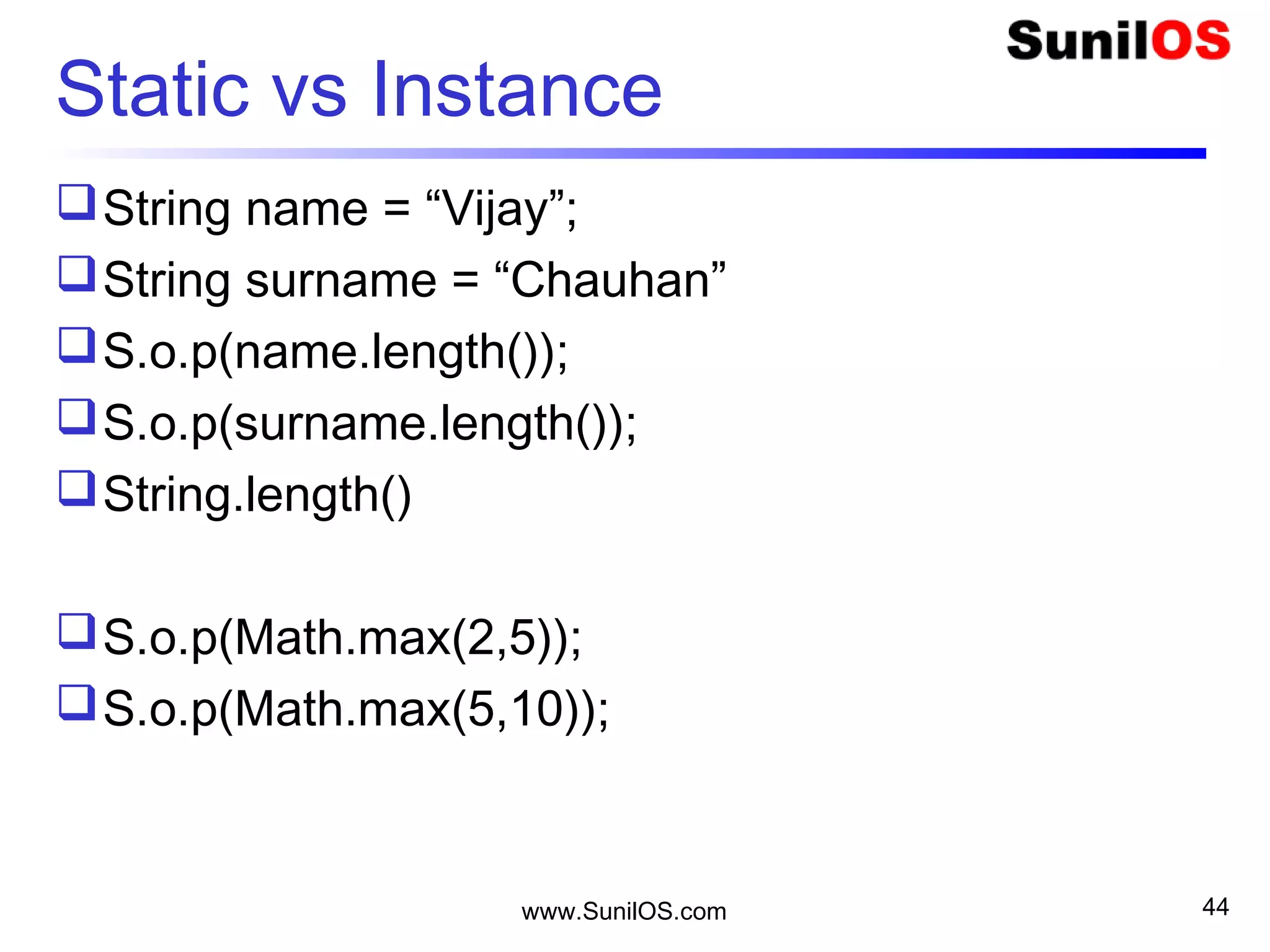
![www.SunilOS.com 45
Hello <Name>
public class HelloName {
o public static void main(String[] args) {
o System.out.println("Hello " + args[0]);
o }
}
C:>java HelloName Vijay Dinanath Chauhan
class args[0] args[1] args[2]
C:>java HelloName “Vijay Dinanath” Chauhan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-45-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 46
Hello Name – if <condition>
public class HelloName1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
o if (args.length == 1) {
System.out.println("Hello " + args[0]);
o } else {
System.out.println(“Parameter name is required");
o }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-46-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 47
Hello All
public class HelloAll {
public static void main(String[] args) {
o for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + " = Hello " + args[i]);
o }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-47-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 48
Hello All (Cond)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = args.length;
if (size == 0) {
o S.o.p("Usage : java HelloAll n1 n2 n3 .. ");
} else {
o for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
o S.o.p ( i+ " = Hello " + args[i]);
o }
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-48-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 49
Hello All - switch
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = args.length;
switch(size) {
case 0 :S.o.p("Usage : java HelloAll1 n1 n2 n3..");
o break;
case 1 : S.o.p(“Hello “ + args[0]); break;
default :
o for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
S.o.p(i + " = Hello " + args[i]);
o }//for
}//switch
}//method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-49-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 50
Add.java – Integer Arguments
public class Add {
public static void main(String[] args) {
oint a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
oint b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
oint sum = a + b;
oSystem.out.println("Sum is " + sum);
}
}
C:>java Add 10 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-50-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 51
Division
public class Division {
o public static void main(String[] args) {
o int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
o int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
o double div = a/b;
o System.out.println("Division is " + div);
o }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-51-2048.jpg)
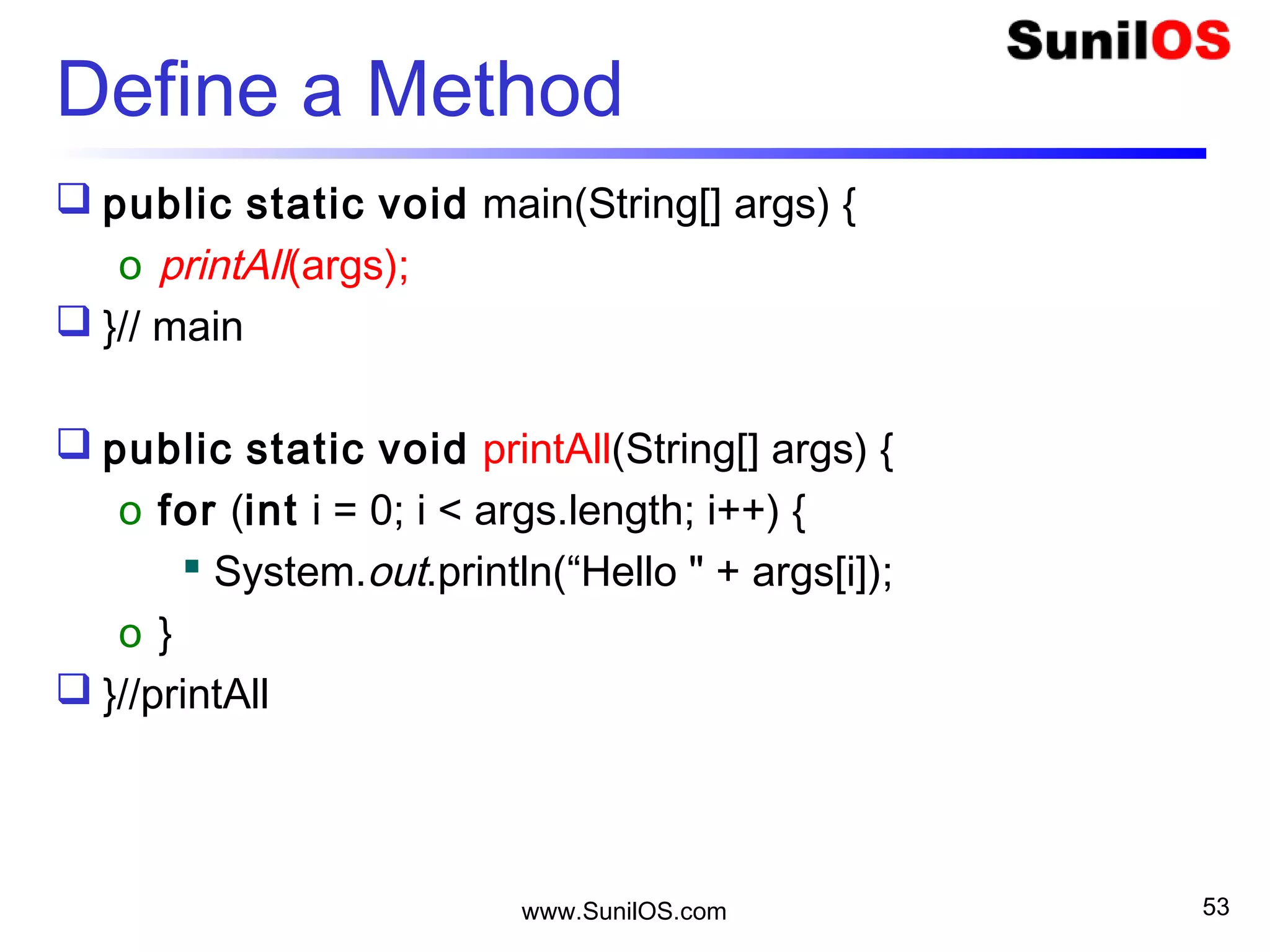
![www.SunilOS.com 52
Define a Method
public static void main(String[] args) {
o printAll(args);
}// main
public static void printAll(String[] args) {
o for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
System.out.println(“Hello " + args[i]);
o }
}//printAll](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-52-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 54
Command line Menu
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
int ch = System.in.read(); //Read data from keyboard
System.out.println( "Selected char ASCII Code " + ch);
if (ch == 'A' || ch == 'a') {
Add.main(args);
o } else if (ch == 'D' || ch == 'd') {
Division.main(args);
o } else {
S.o.p("Incorrect Choice ");
o }
o }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-54-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 55
10
One Dimension Array
20
[0]
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
length
int[] table = new int[10];
int a = table[4];
int a = table[2];
int size = table.length;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-55-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 56
10
Initialize an Array
20
[0]
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
length
int[] table = new int[10];
table[0] =2;
table[1] =4;
….
Or
int[] table =
{2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-56-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 57
Other Data Type Arrays
char[] chList = new char[5];
chList[0] = ‘A’….
o Or
char[] chList = {‘A’,’B’,’C’,’D’,’E’}
String[] strList = new String[5];
strList[0] = “A”
strList[1] = “Bee”
o Or
String[] strList = {“A”,”Bee”,”Cee”,”Dee”,”E”}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-57-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 58
Copy an Array
public static void main(String[] args) {
o char[] copyFrom = { 'd', 'e', 'c', 'a', 'f', 'f', 'e', 'i', 'n',
'a', 't', 'e', 'd' };
o char[] copyTo = new char[7];
o System.arraycopy(copyFrom, 2,
o copyTo, 0, 7);
o S.o.p(new String(copyTo));
}
Start
Index
Start
Index
No Of
Element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-58-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 59
One Dimension Array
int[] table;
table = new int[10];
table[0] =2;
table[1] =4;
4B
10
[0]
[1]
[9]
length
2
4
20
1000
1000
table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-59-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 60
10length
2D Array
[0]
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
…
[0] [1] [2] [7] [8]
9
9
..
9
9
9
9
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-60-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 61
int[][] table = new int[10][9];
table
1010
1000
1000
1011
1111
1010
1011
1111](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-61-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 62
Define an Array
int[][] table = new int[10][9];
table[1][5] = 5;
int size = table.length;
int size = table[0].length;
int[][] rows = new int[10][];
rows[0] = new int[9];
rows[1] = new int[19];
rows[2] = new int[29];
int[][][] xyz = new int[10][9][2];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-62-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 63
3D Array
20
[0]
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
[0] [1] [2] [8] [9]
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
…
[0]
[1]
[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-63-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 64
java.util.Date class
import java.util.*;
public class TestDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
o Date d = new Date();
o S.o.p("Date : " +d);
o S.o.p ("Long Time : " +d.getTime());
}
Output
o Date : Mon Jan 04 00:35:53 IST 2010
o Long Time : 1262545553156](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-64-2048.jpg)
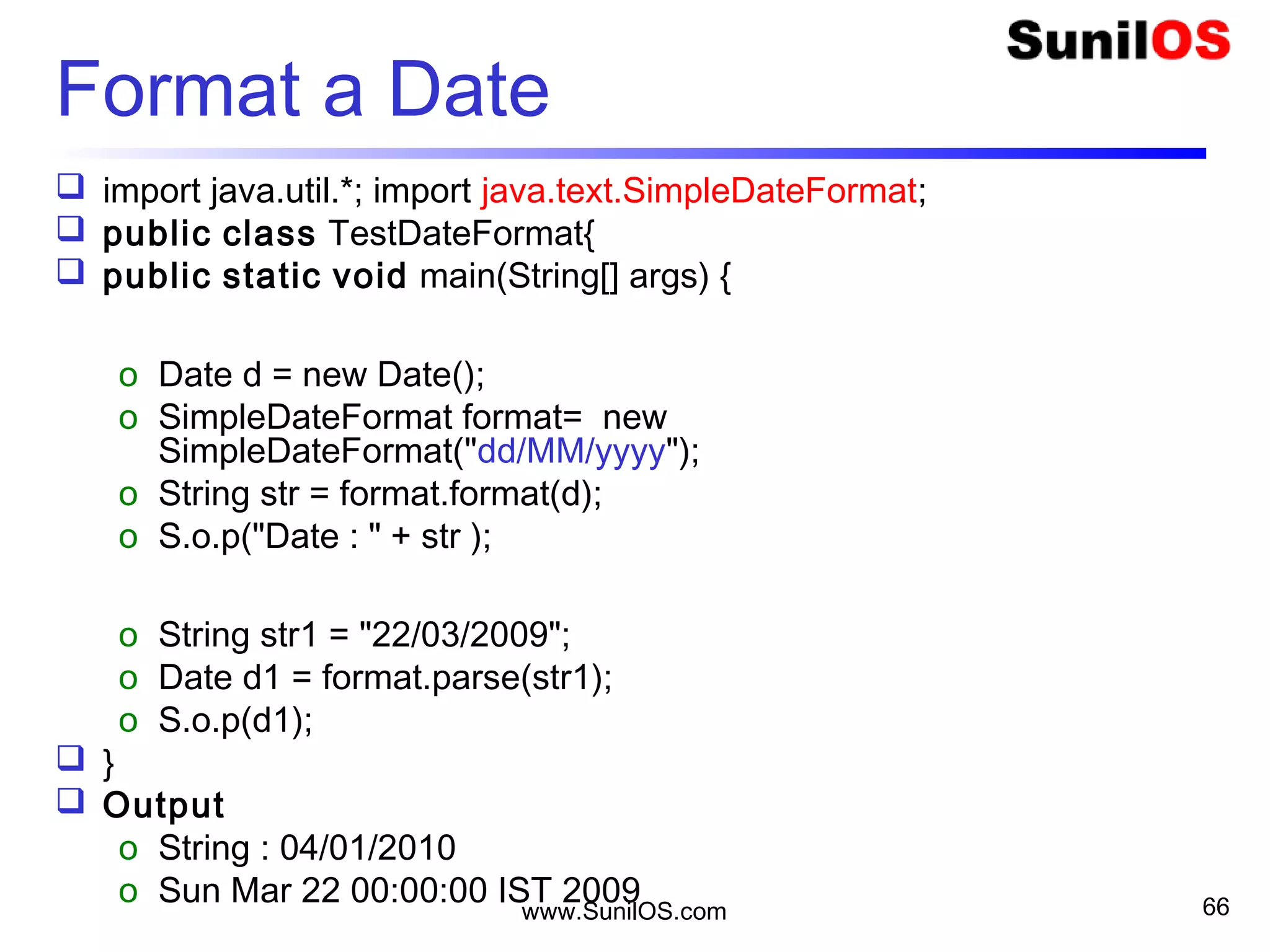
![www.SunilOS.com 65
Format a Date
import java.util.*; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class TestDateFormat{
public static void main(String[] args) {
o Date d = new Date();
o SimpleDateFormat format= new
SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
o String str = format.format(d);
o S.o.p("Date : " + str );
o String str1 = "22/03/2009";
o Date d1 = format.parse(str1);
o S.o.p(d1);
}
Output
o String : 04/01/2010
o Sun Mar 22 00:00:00 IST 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intialjavav2-151127095031-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Basics-65-2048.jpg)