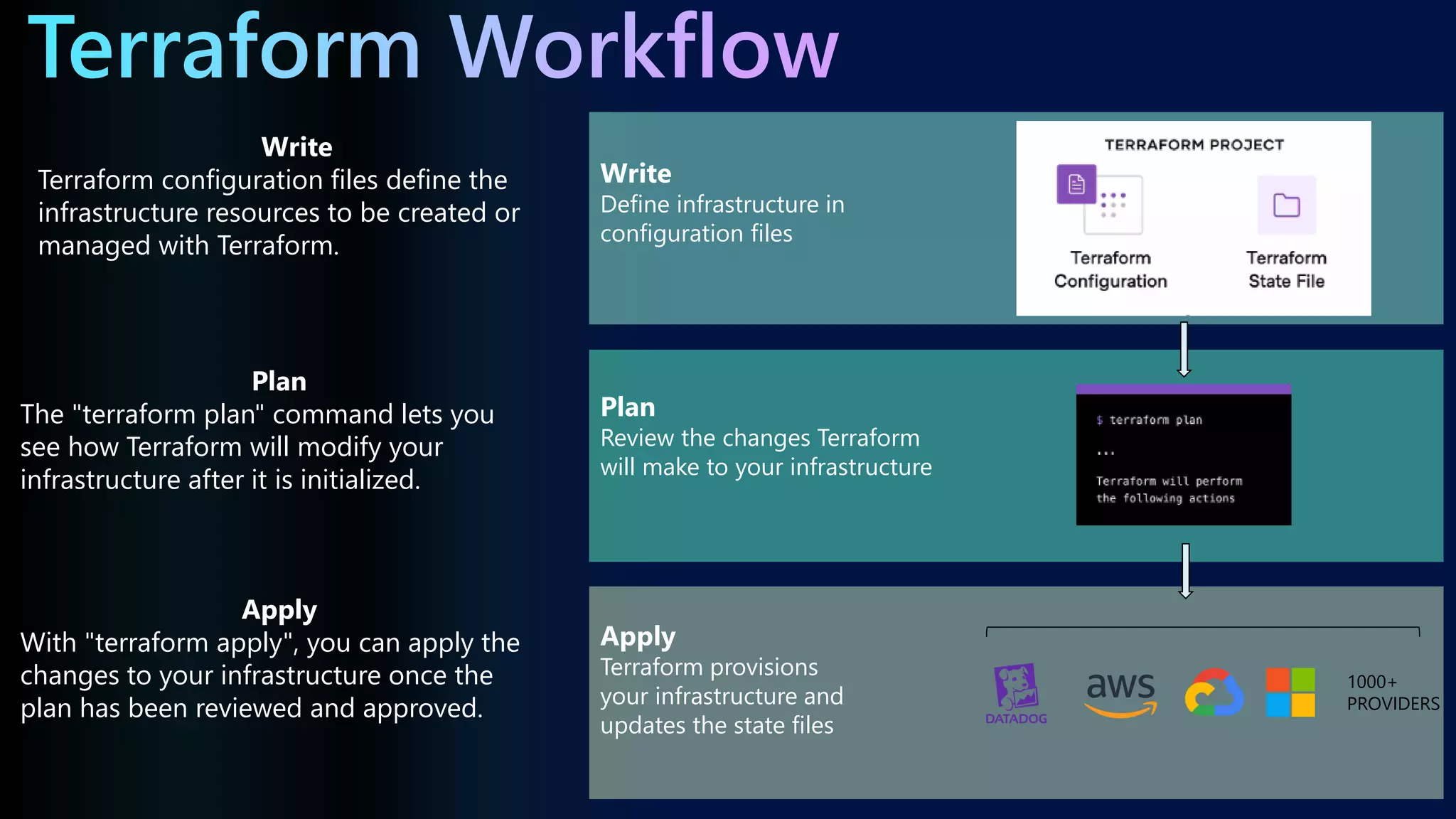
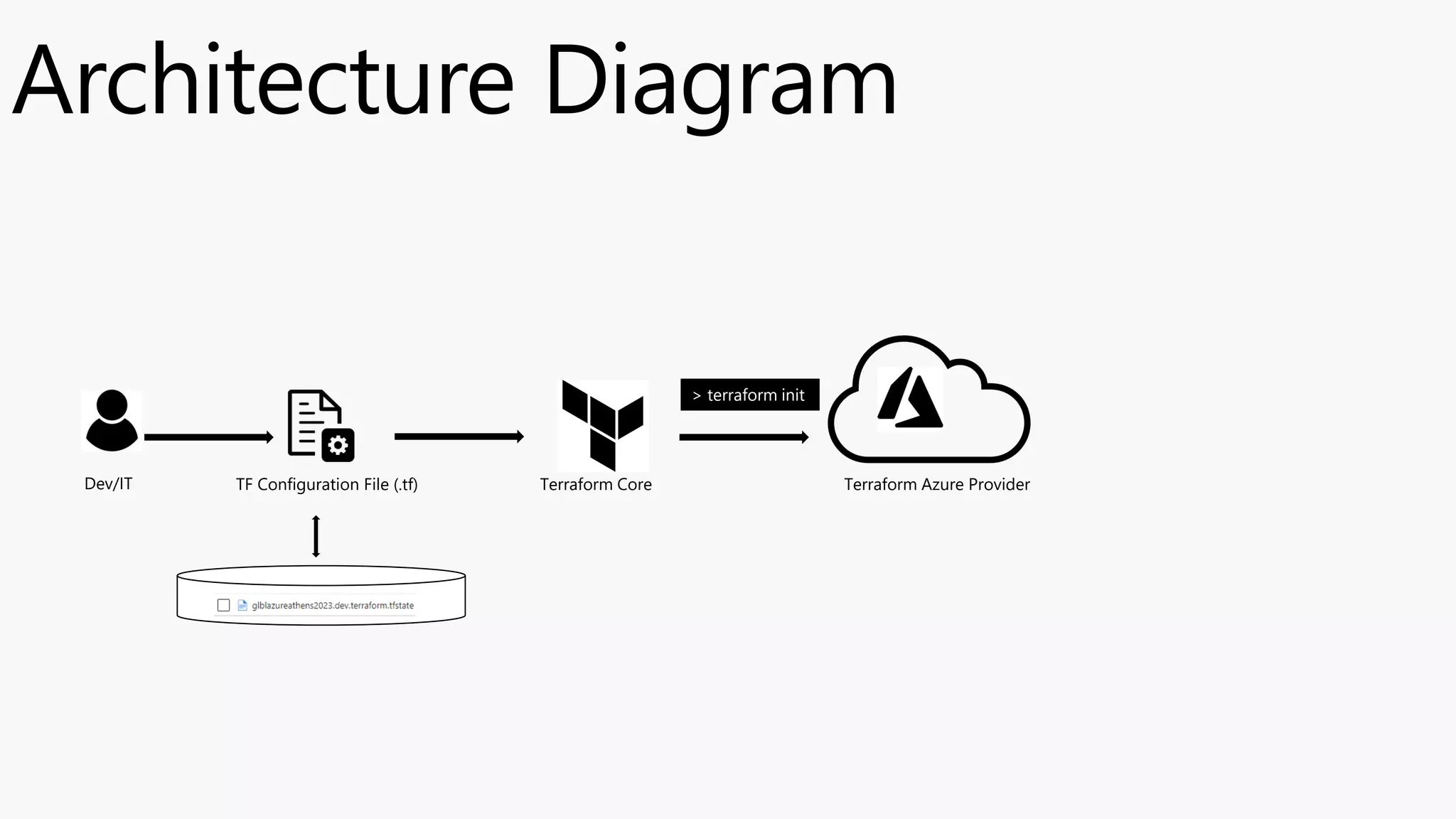
The document highlights the significance of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and Terraform within the context of the Global Azure Athens 2023 event, thanking sponsors for their support. It outlines the functionalities, commands, and benefits of Terraform, emphasizing its cloud-agnostic nature and ability to manage resources across multiple platforms efficiently. Additionally, it provides terminology related to Terraform and includes links for further exploration of the topics discussed.