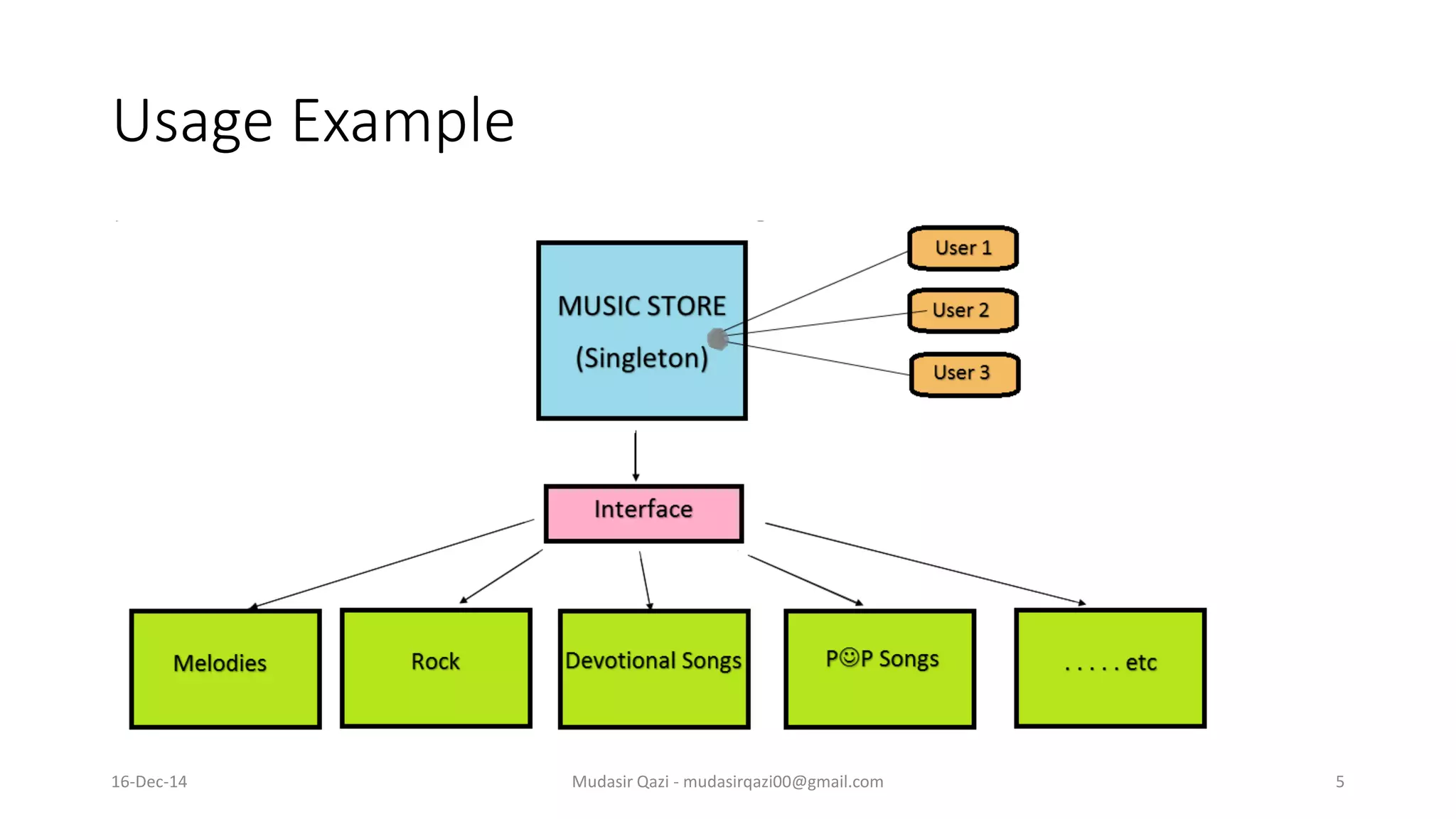
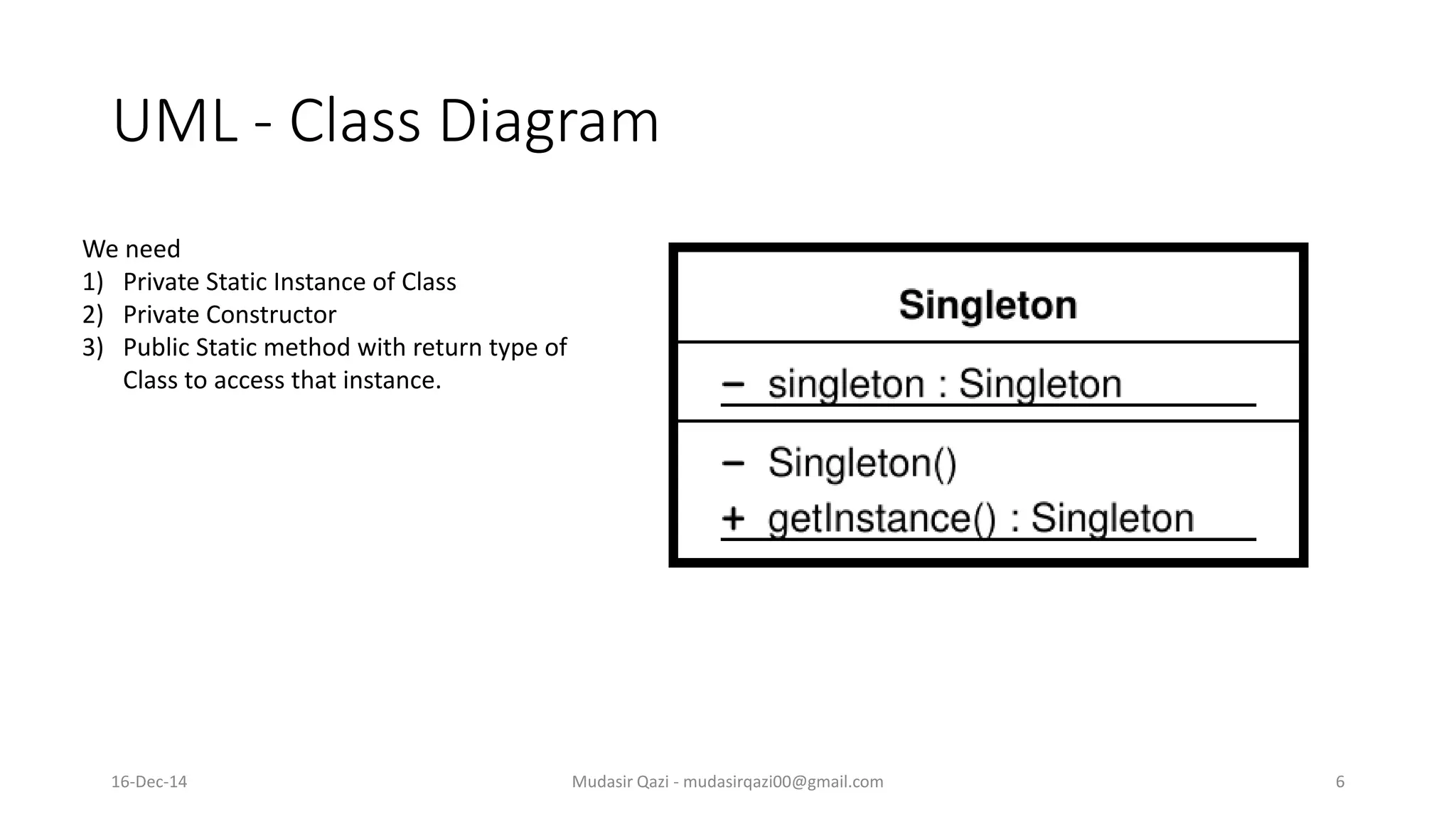
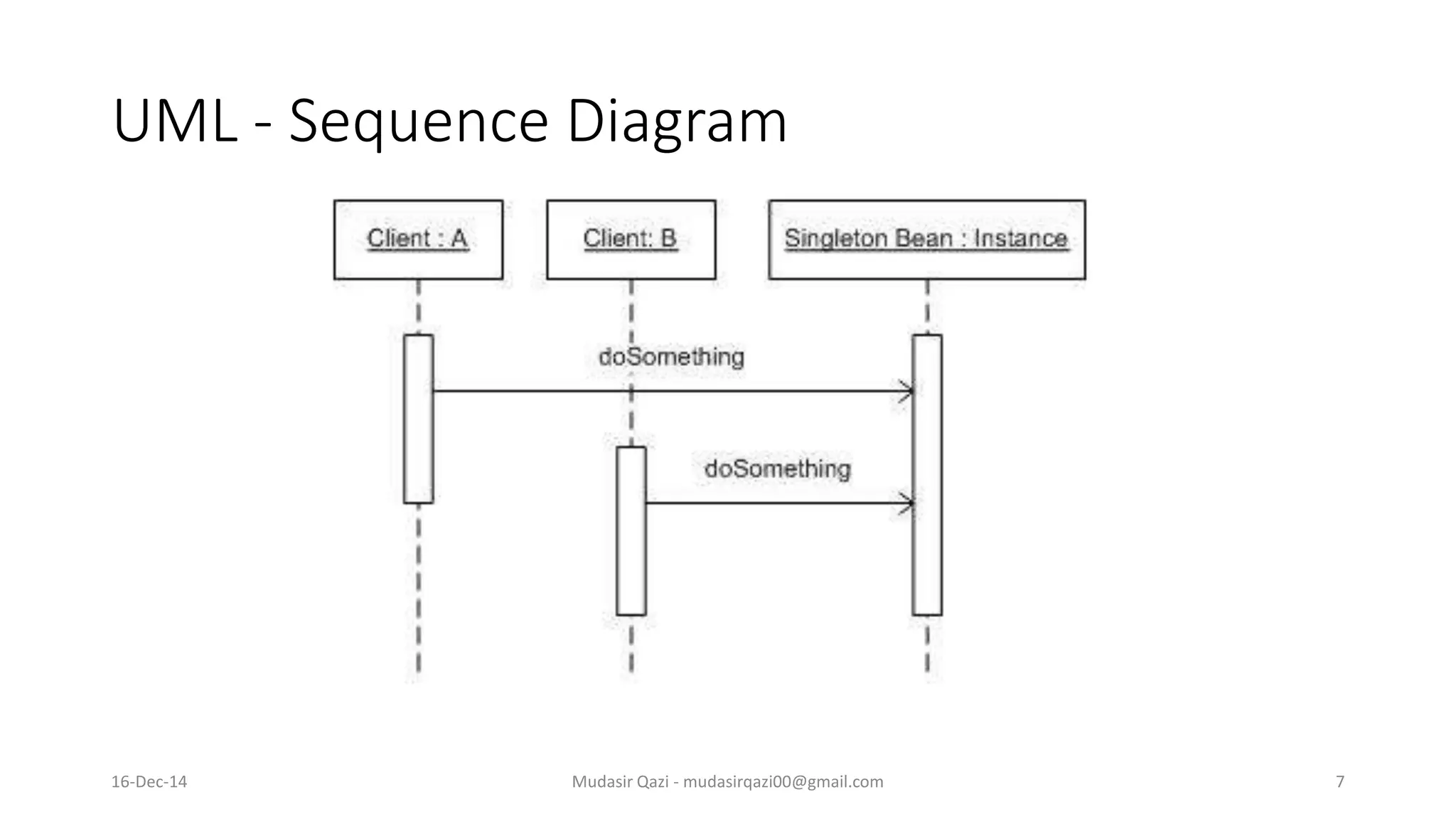
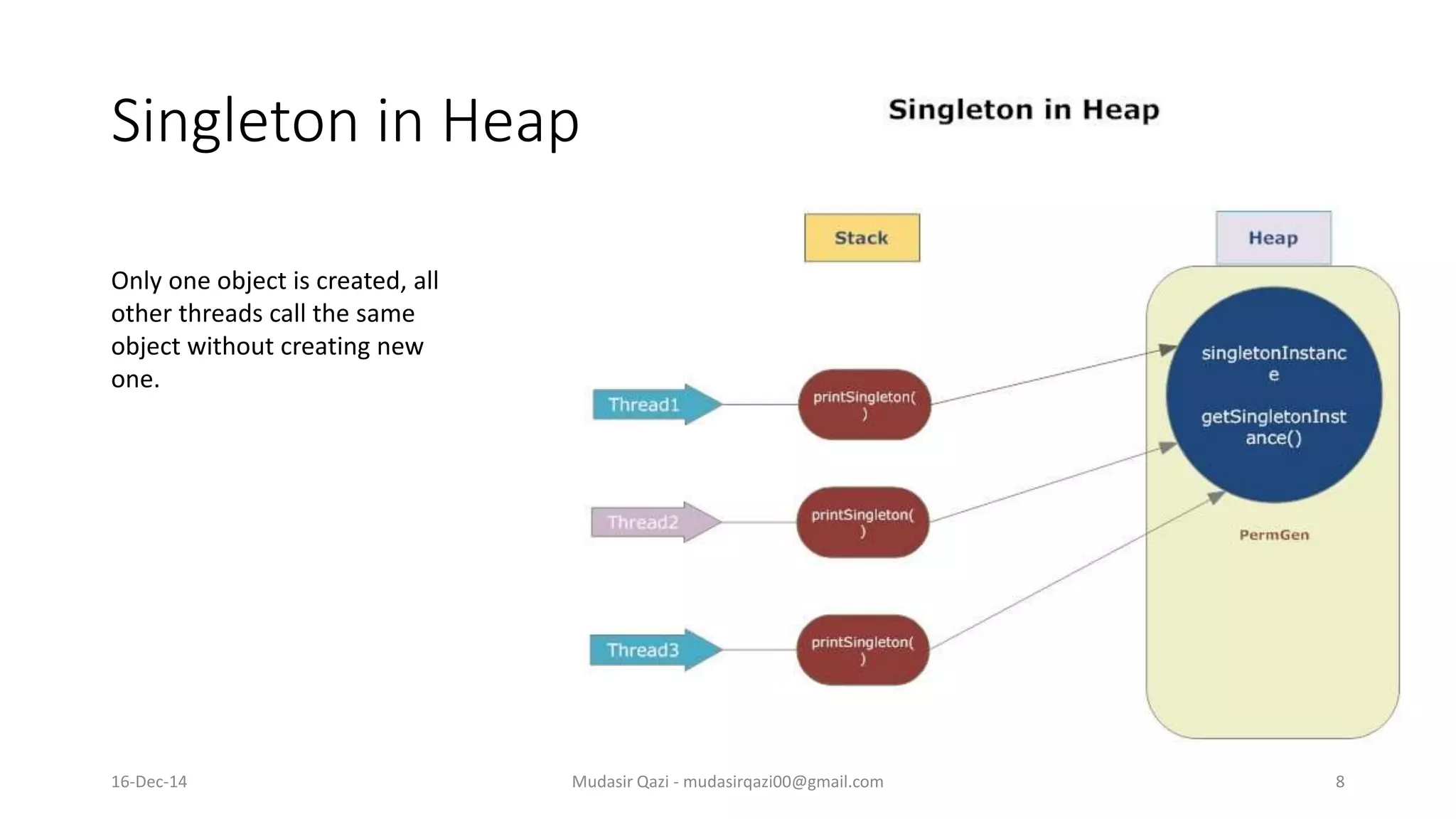
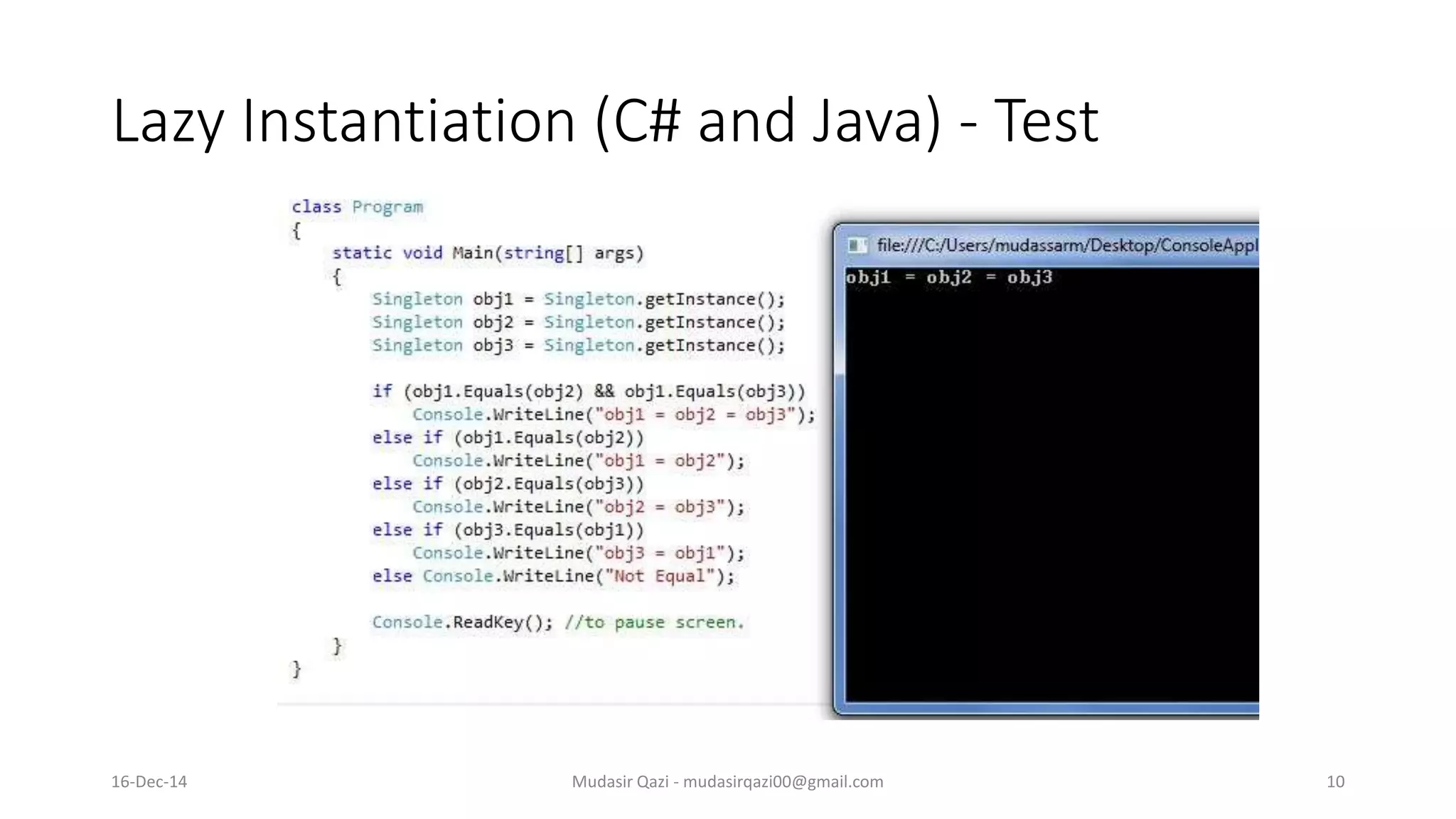
The document provides an in-depth overview of the Singleton Design Pattern, defining it as a pattern that ensures a class has only one instance while offering a global point of access to it. It discusses various implementation strategies including early and lazy instantiation, thread-safe methods, and n-singleton variations, along with their advantages and best use cases in multi-threaded applications. Additionally, it includes UML diagrams to illustrate class and sequence structures relevant to the Singleton pattern.