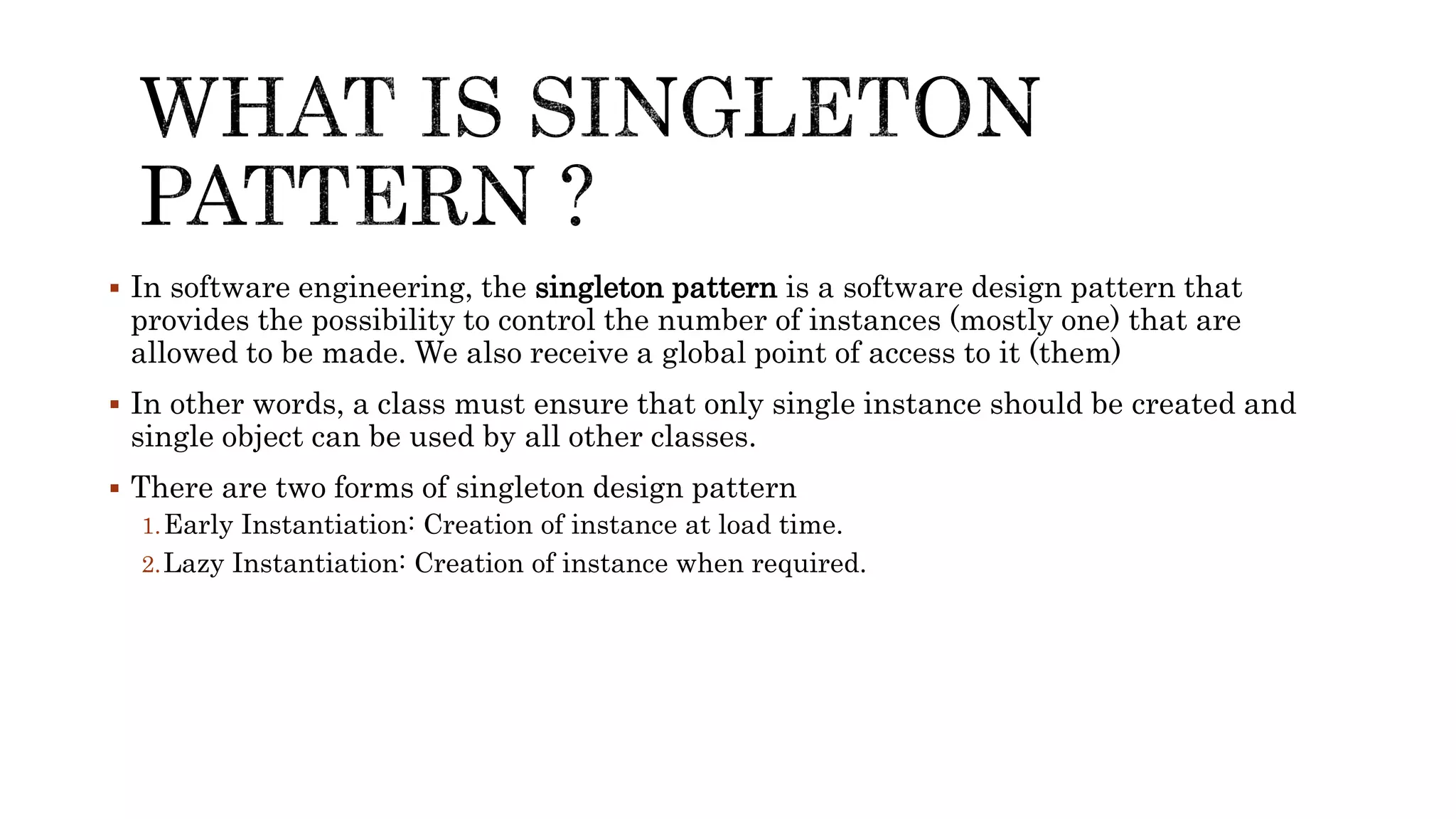
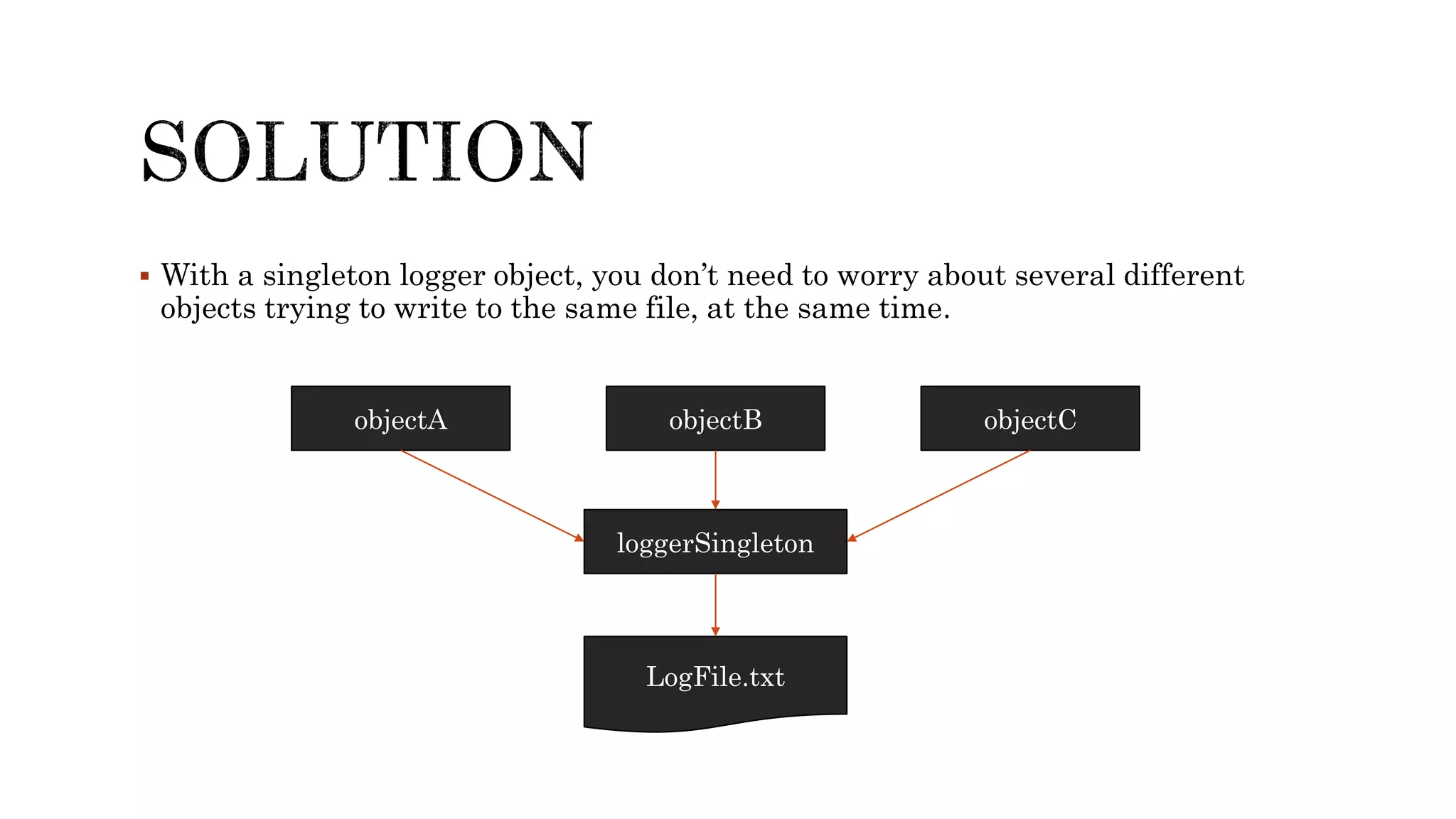
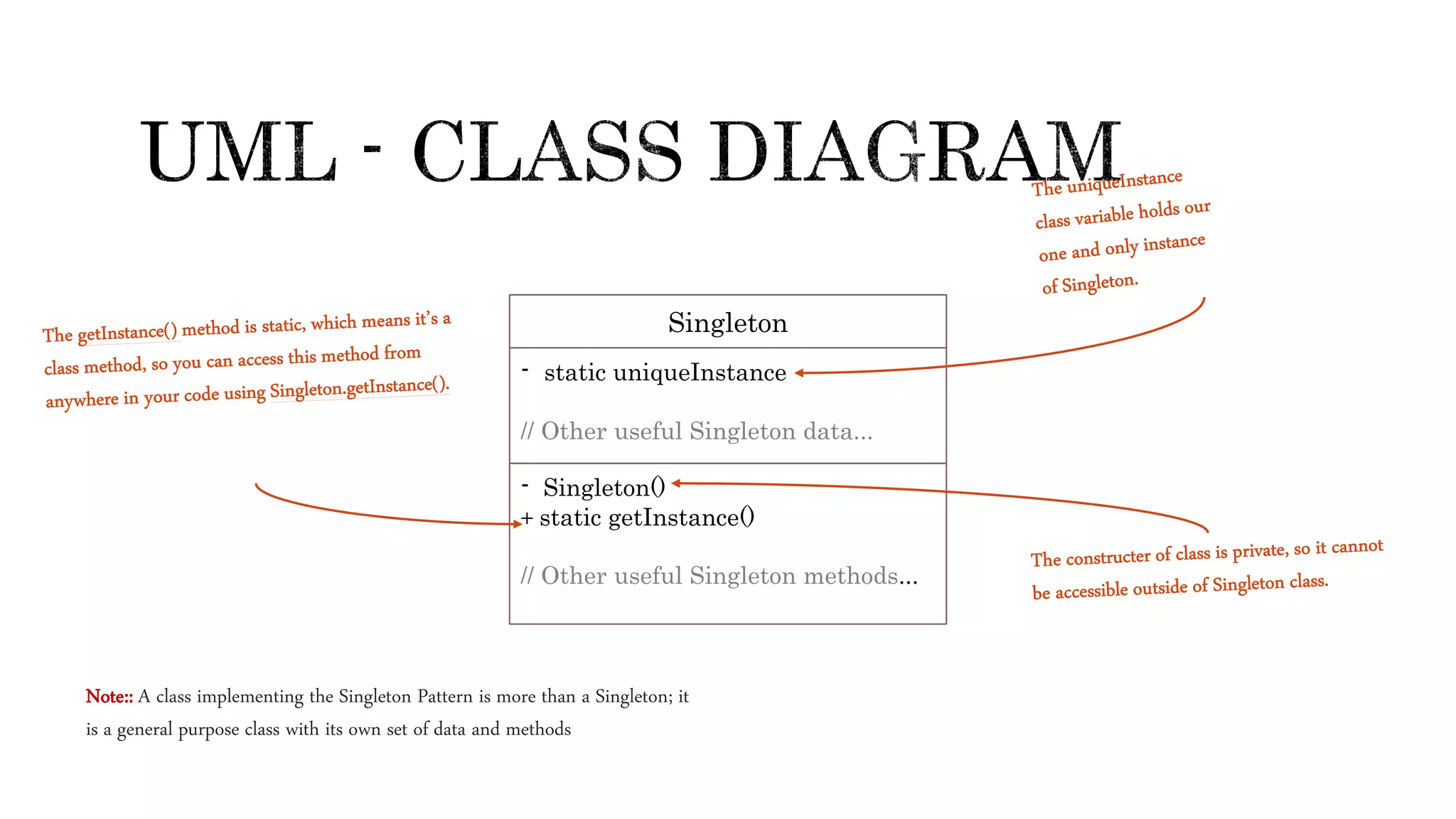
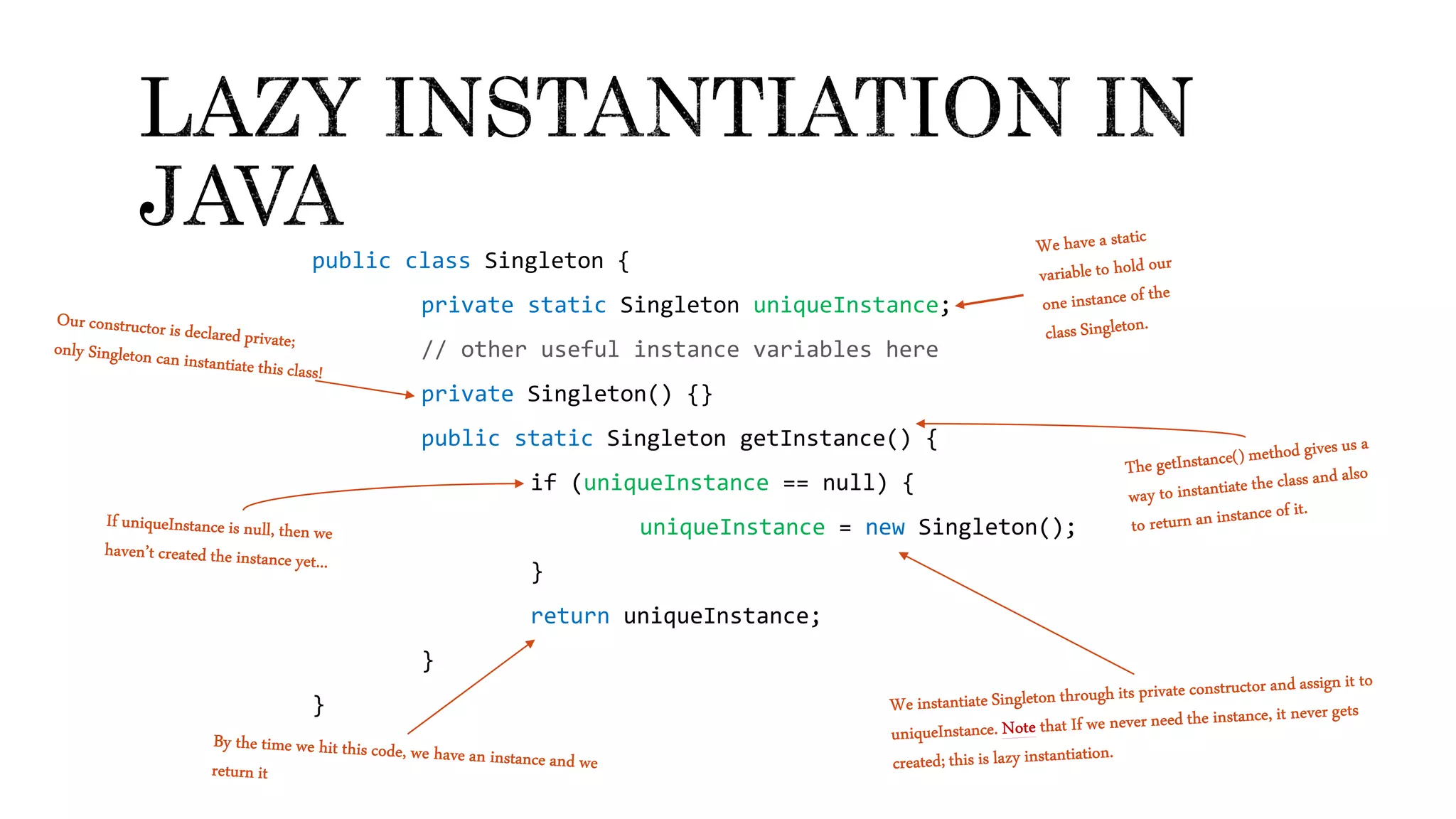
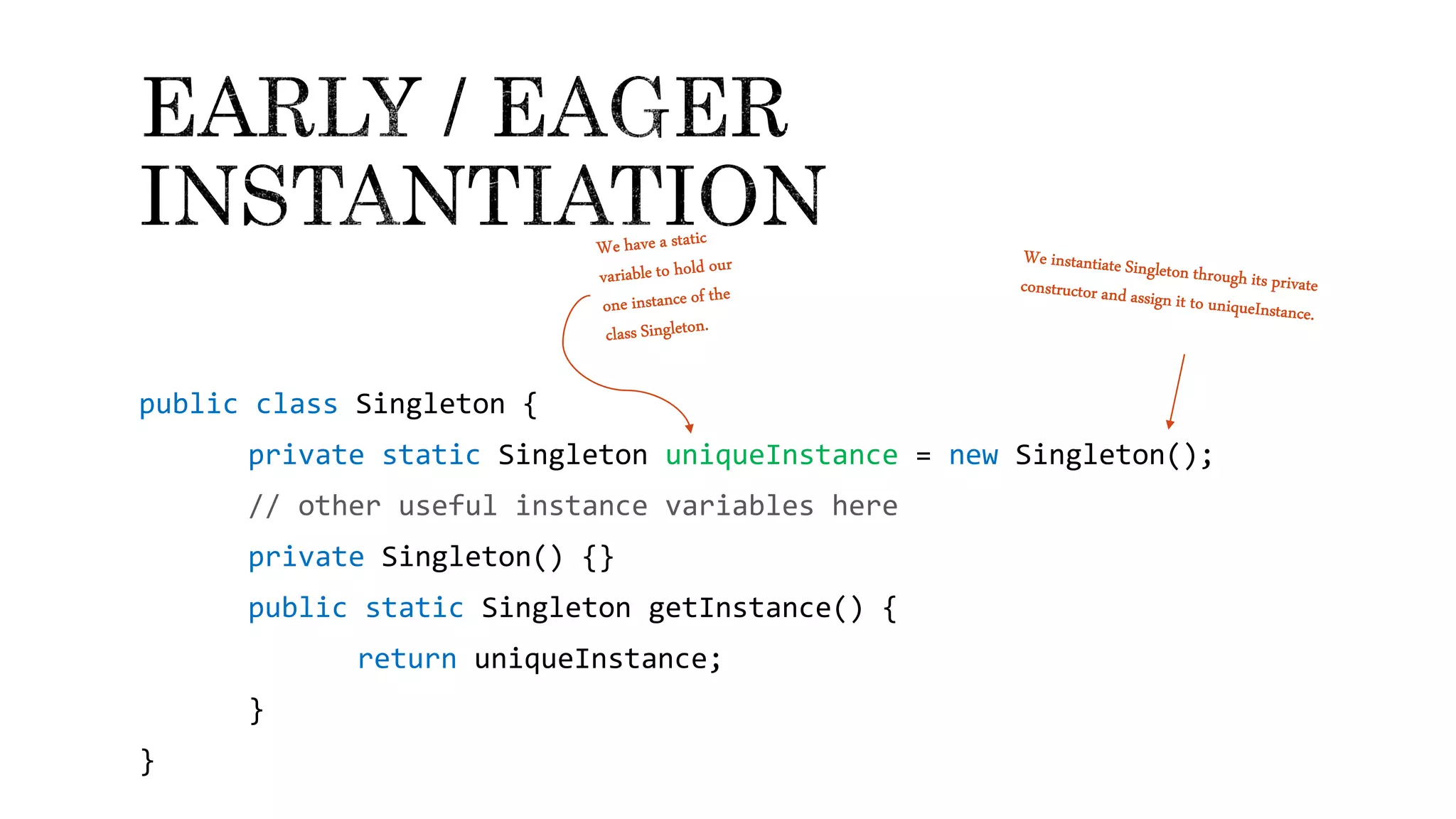
The document explains the singleton design pattern, a creational design pattern used in software engineering to control creation of instances, ensuring only one instance exists while providing global access to it. It discusses two forms of singleton instantiation: early and lazy instantiation, along with real-life analogies to illustrate its importance in avoiding complexity and resource conflicts. Additionally, the implementation details in Java are provided, emphasizing the need for a thread-safe approach in multi-threaded environments.






![public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton s = Singleton.getInstance();
Singleton r = Singleton.getInstance();
System.out.println (s);
System.out.println (r);
}
run:
15db9742
15db9742
BUILD SUCCESSFUL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singleton-design-pattern-190101132137/75/Singleton-Design-Pattern-Creation-Pattern-12-2048.jpg)

