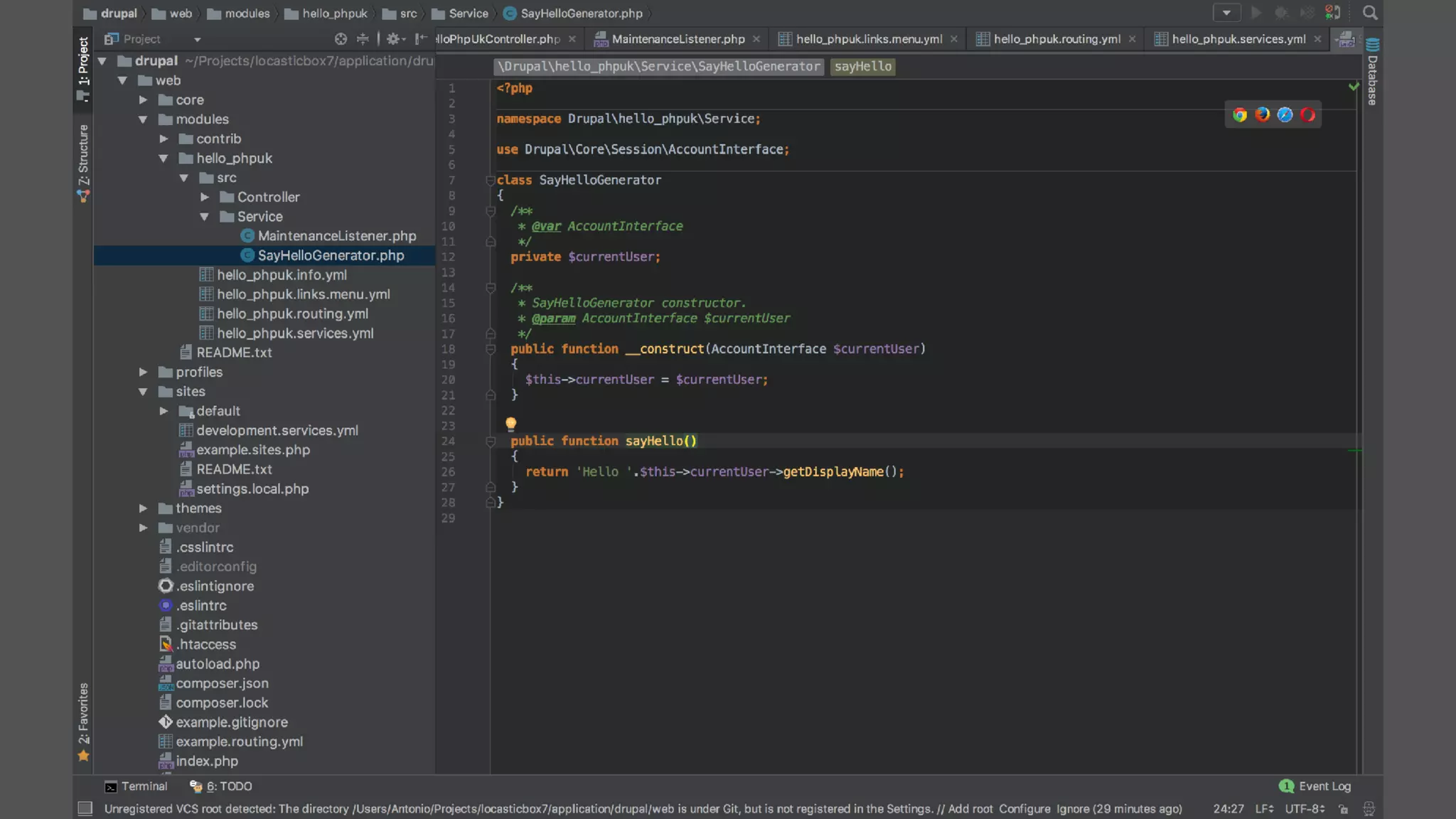
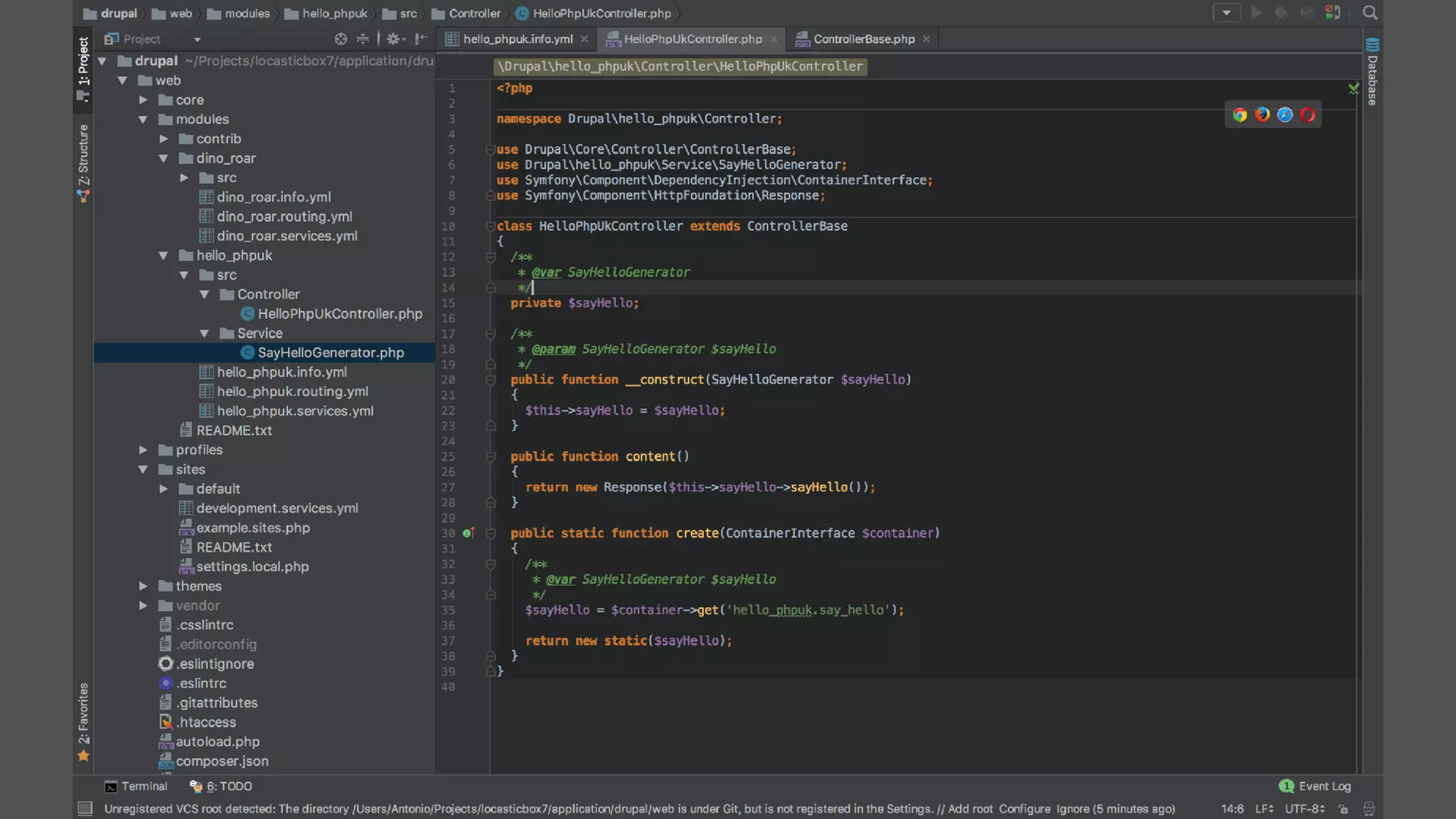
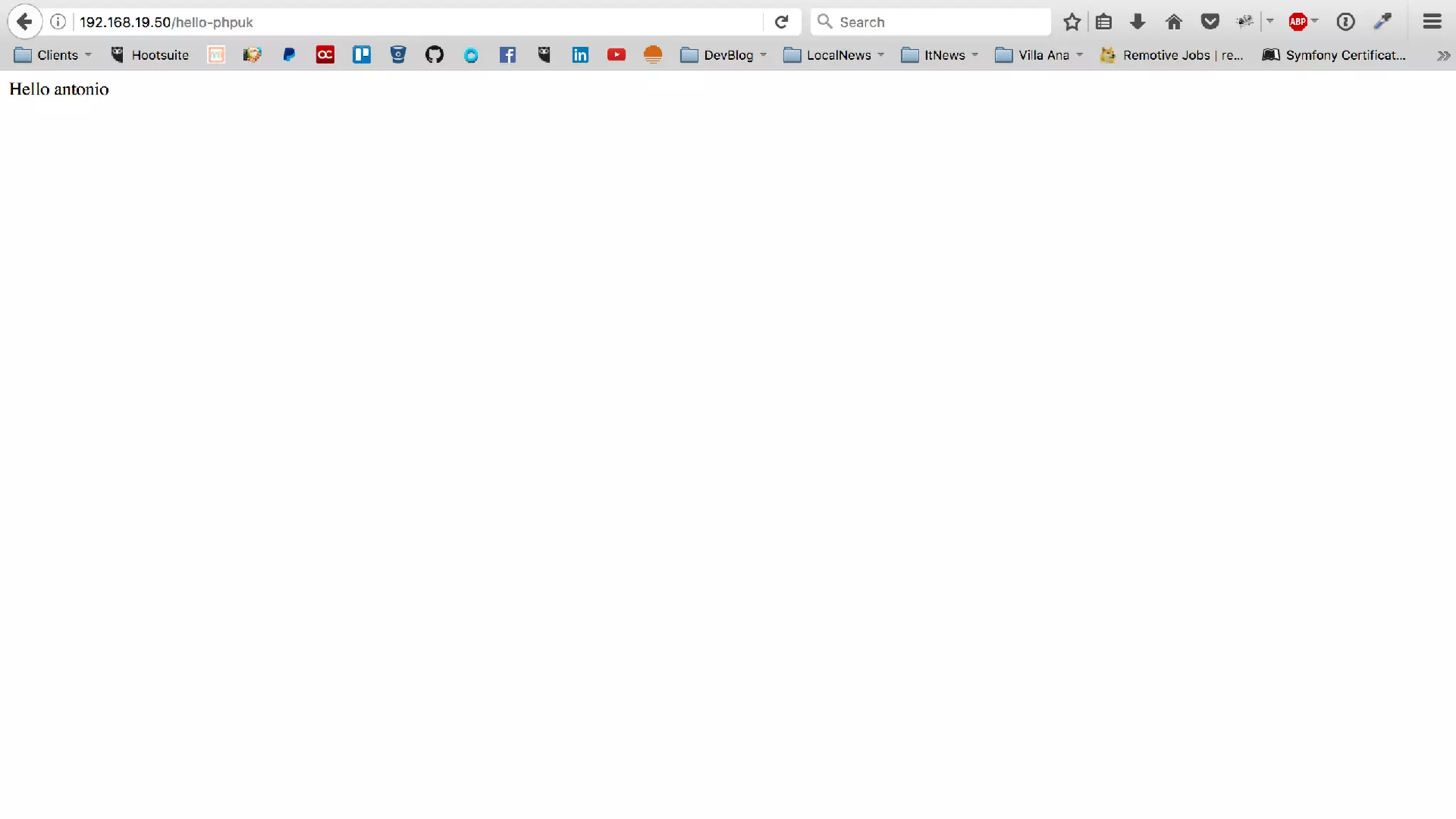
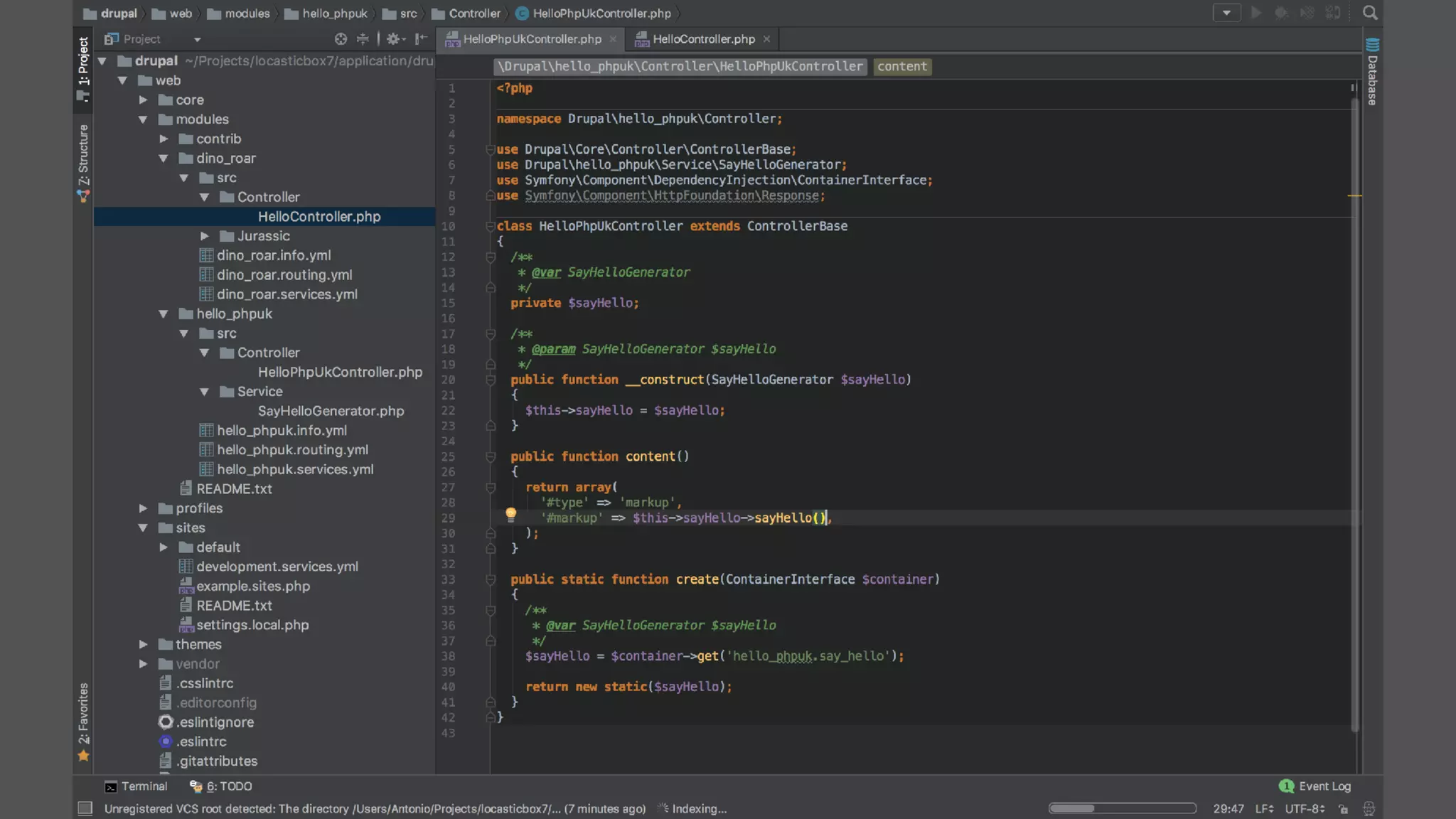
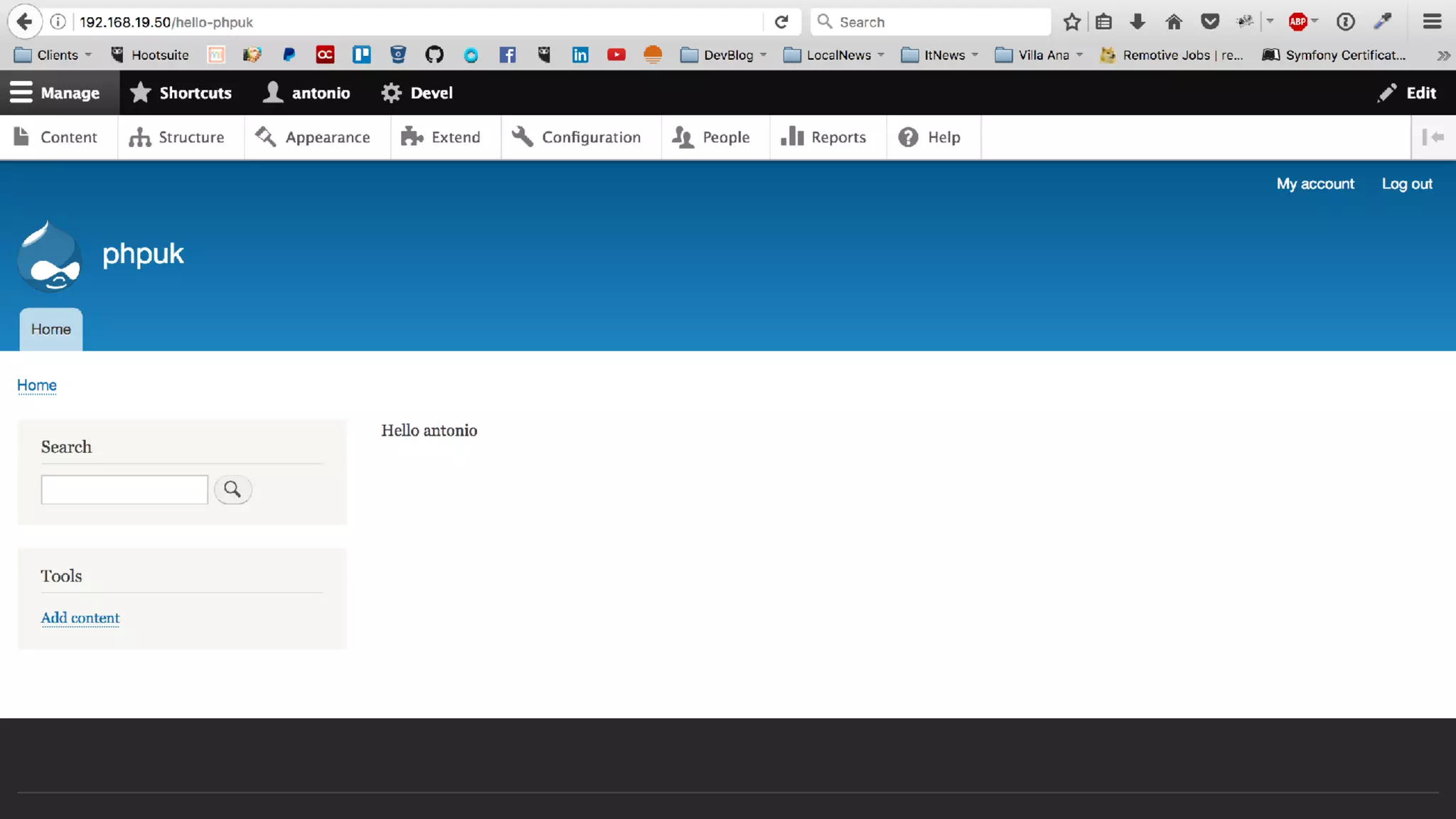
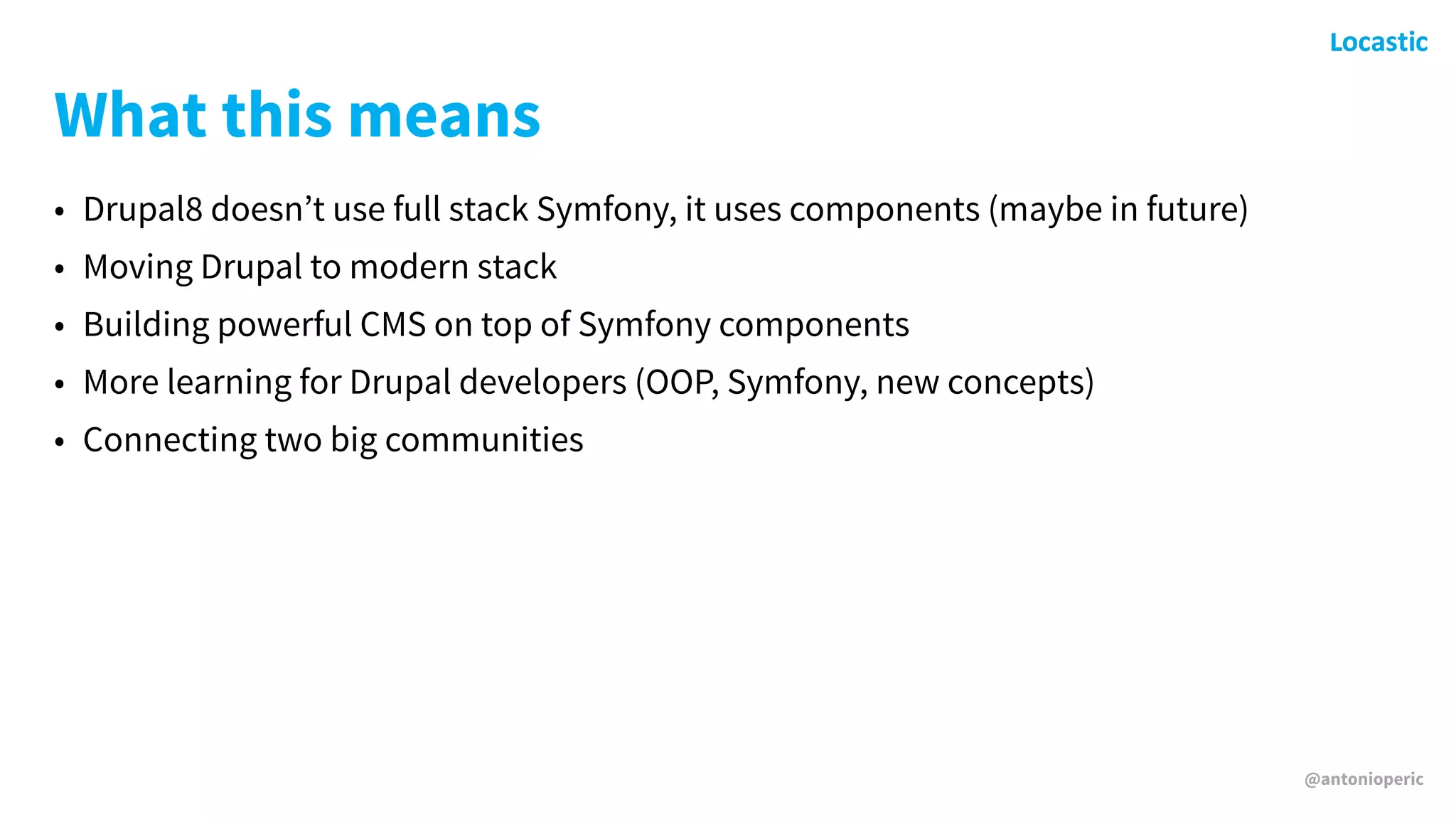
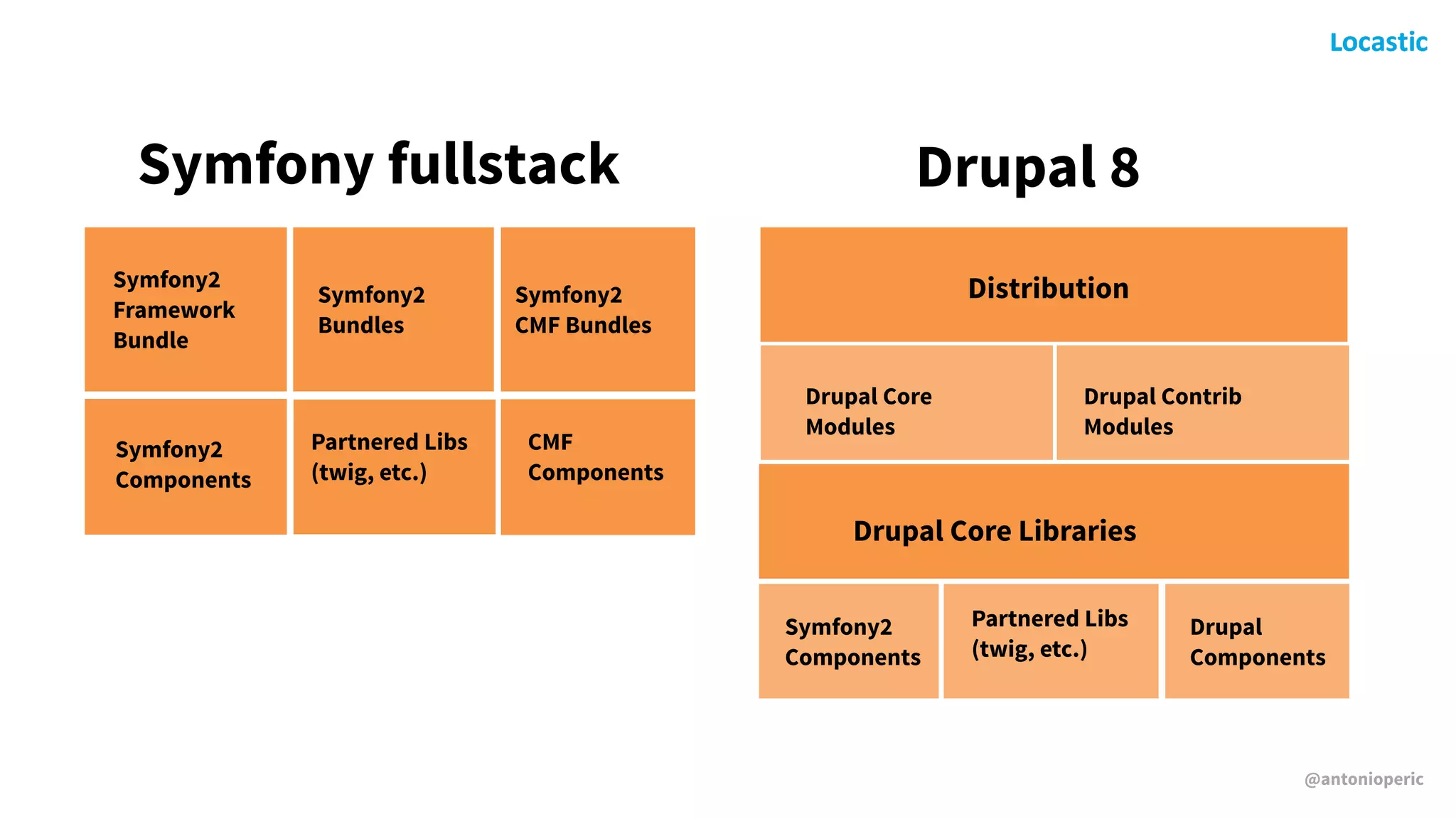
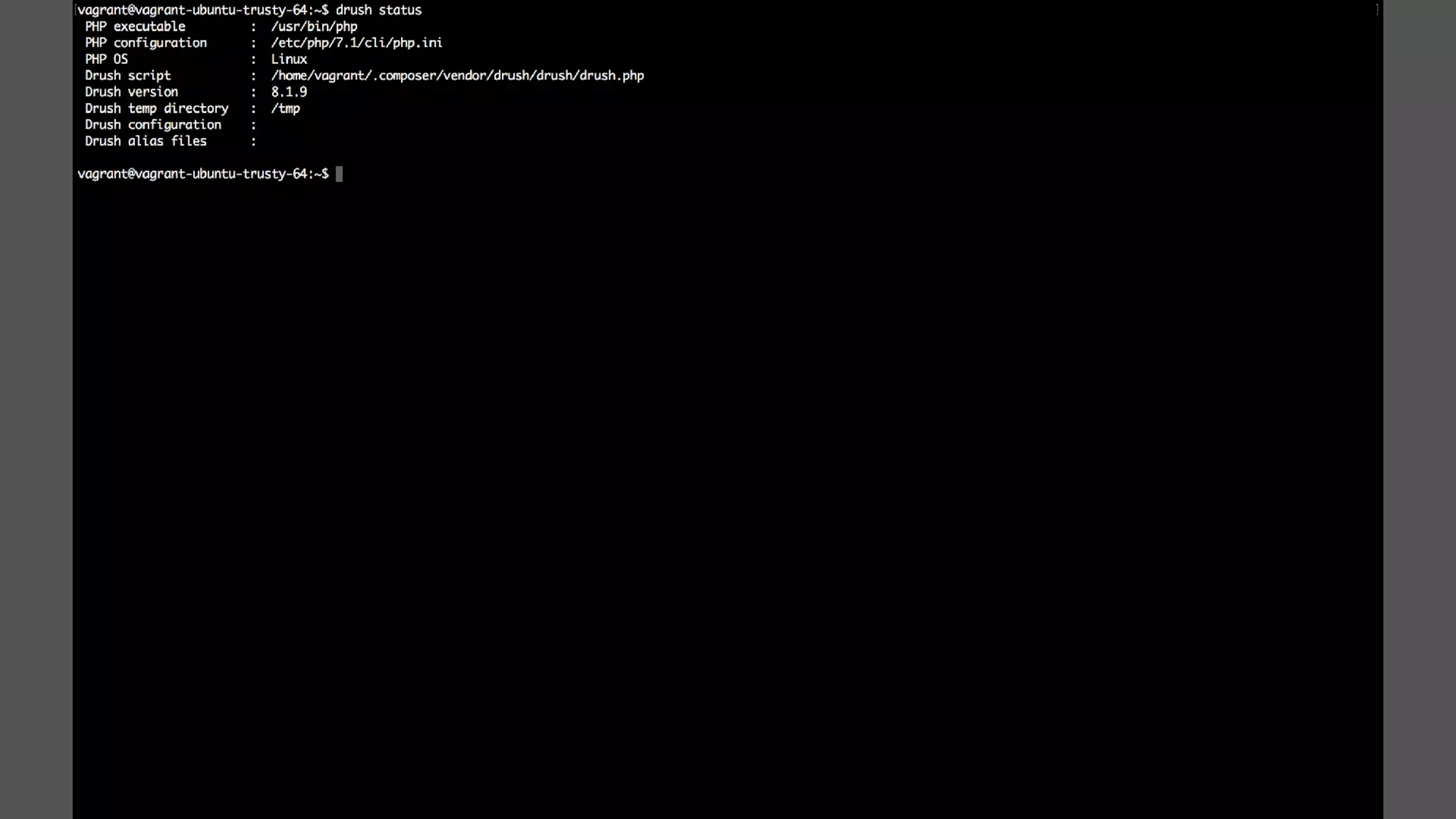
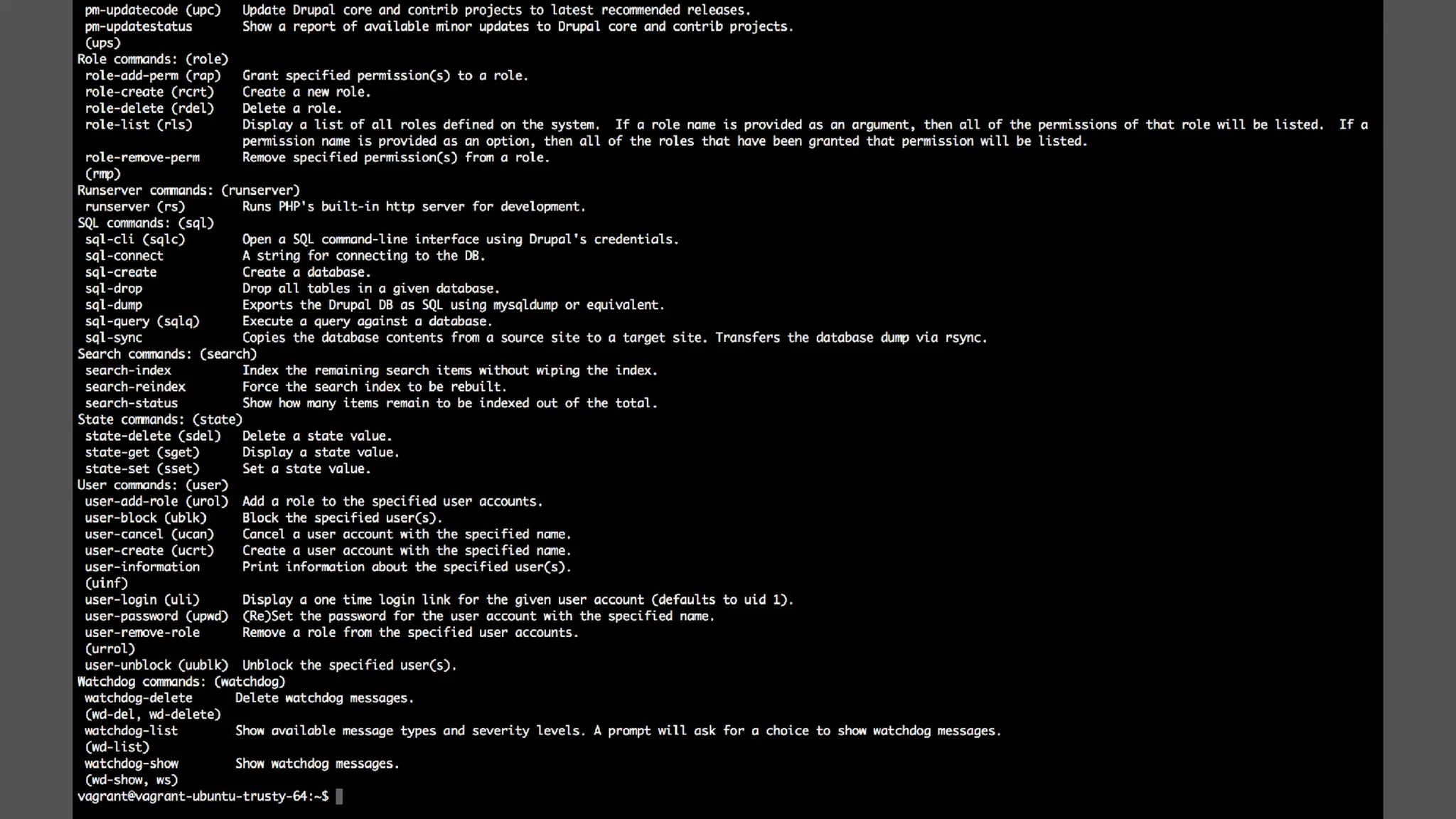
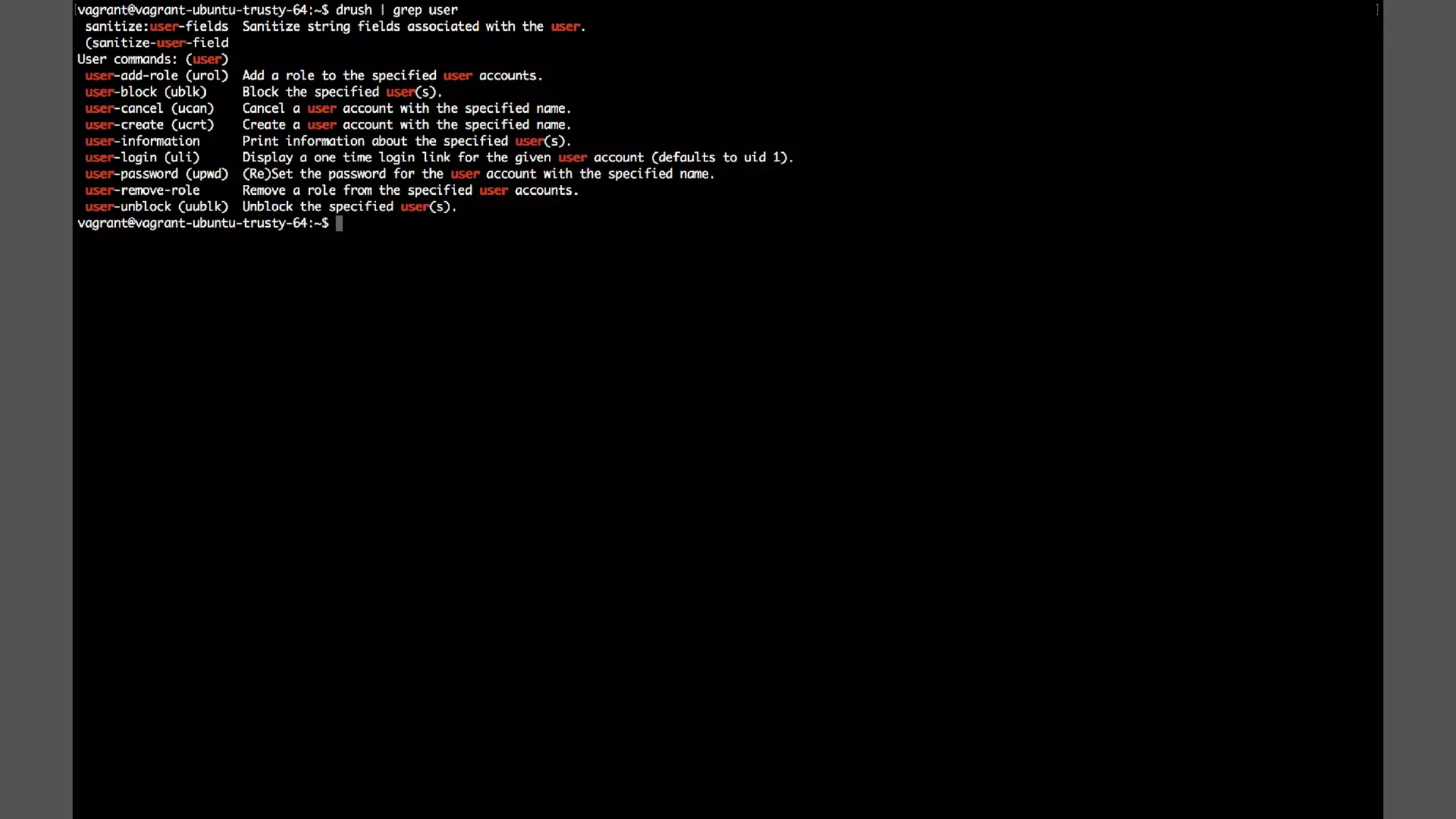
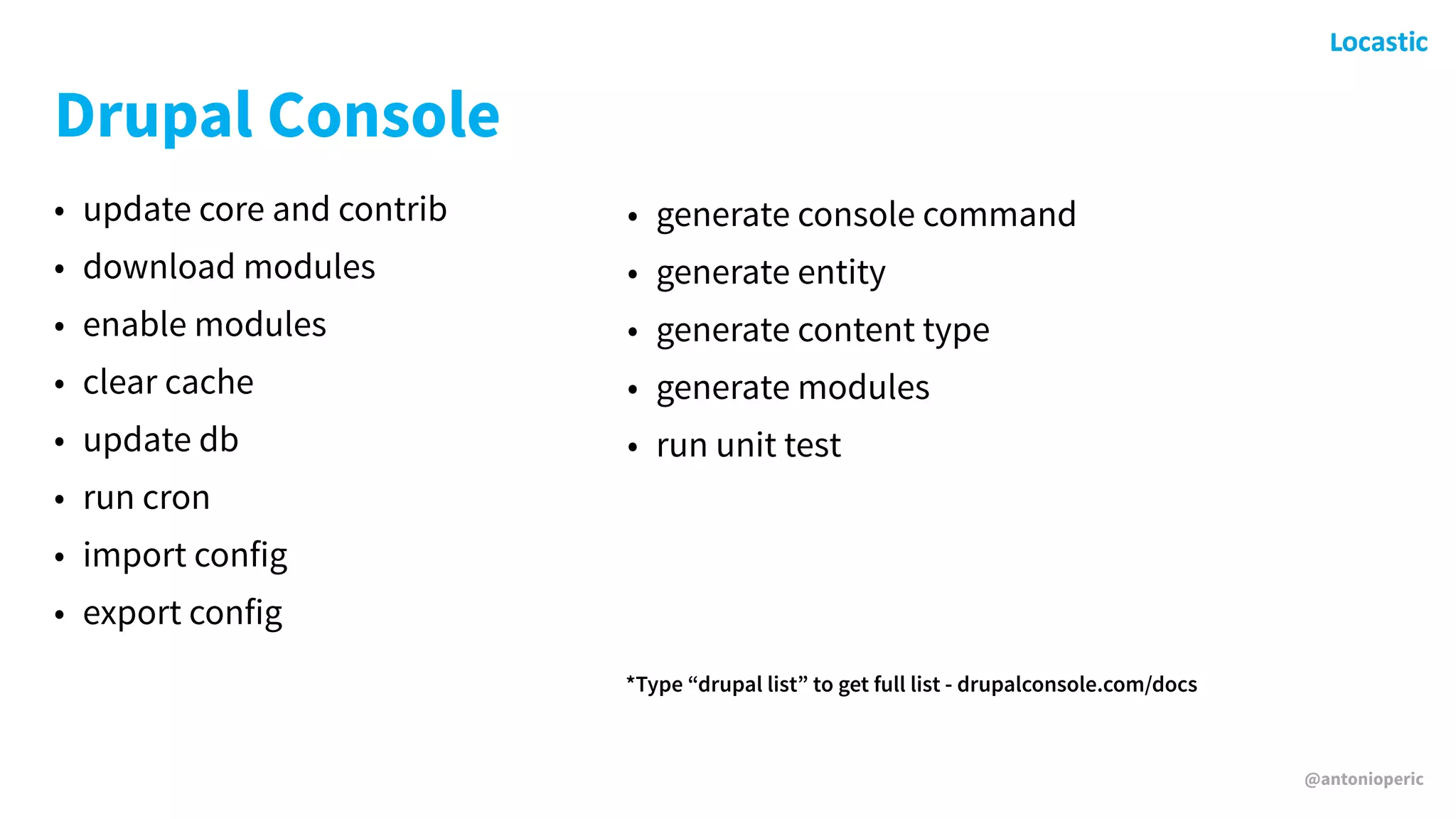
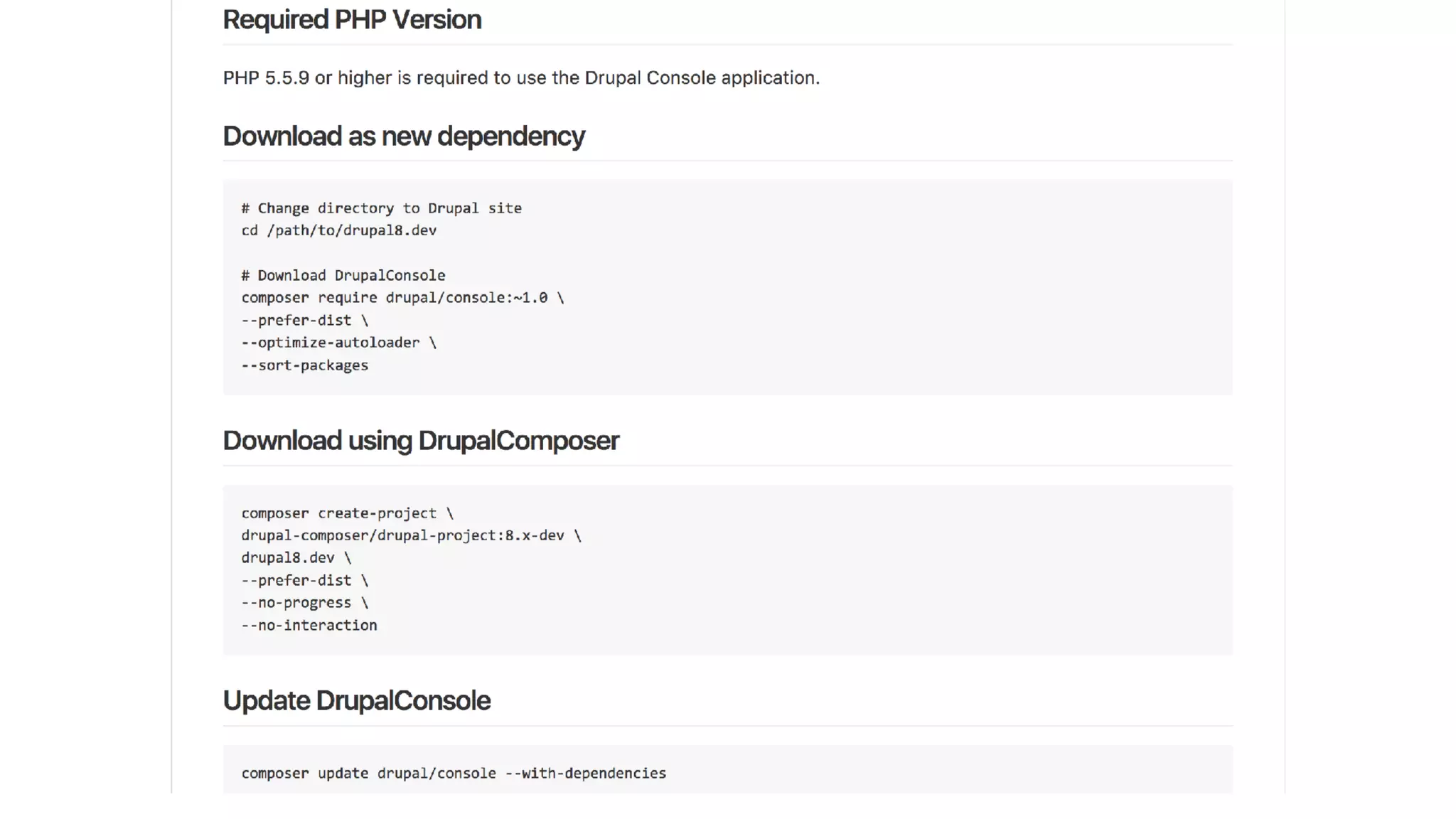
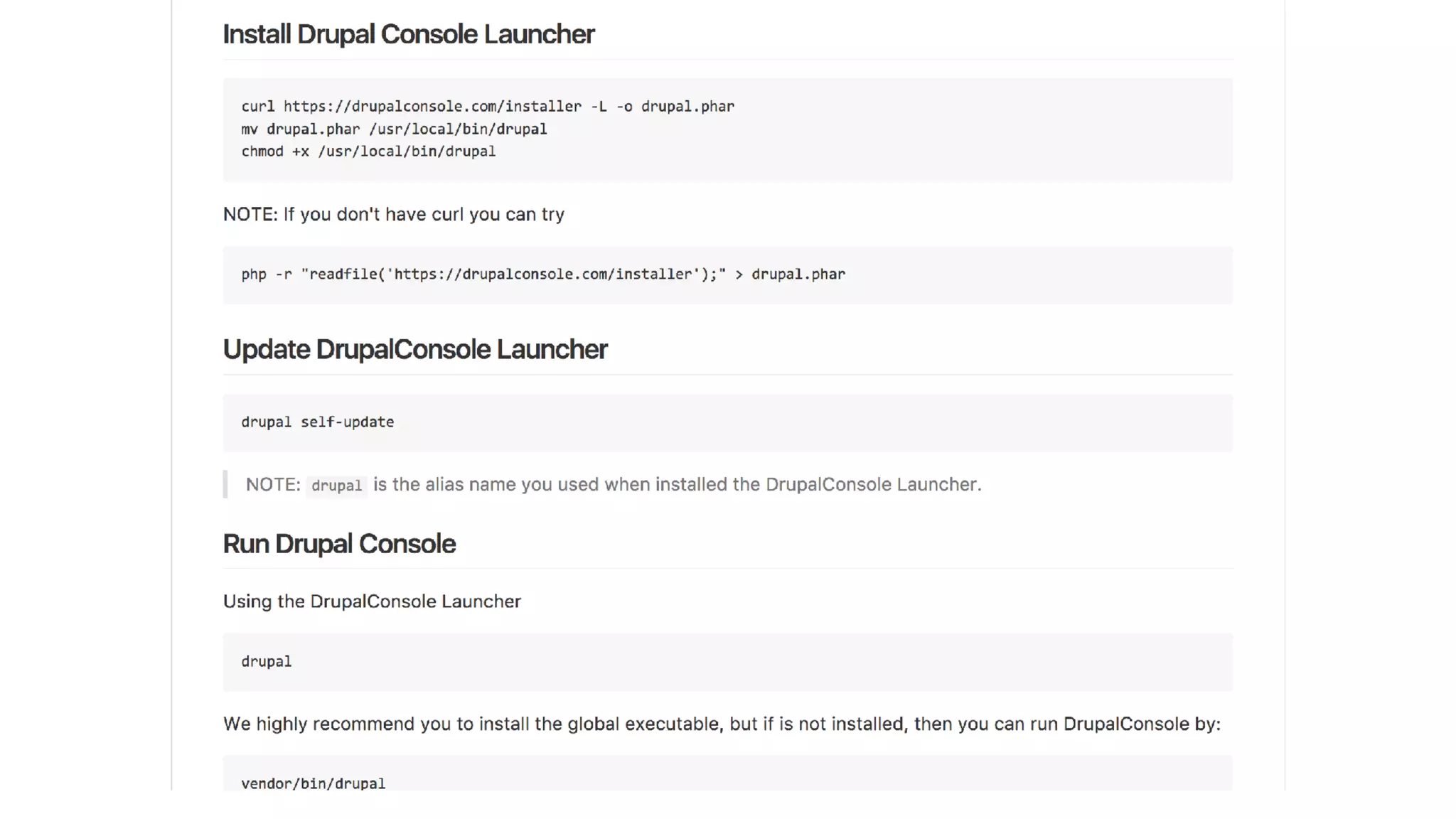
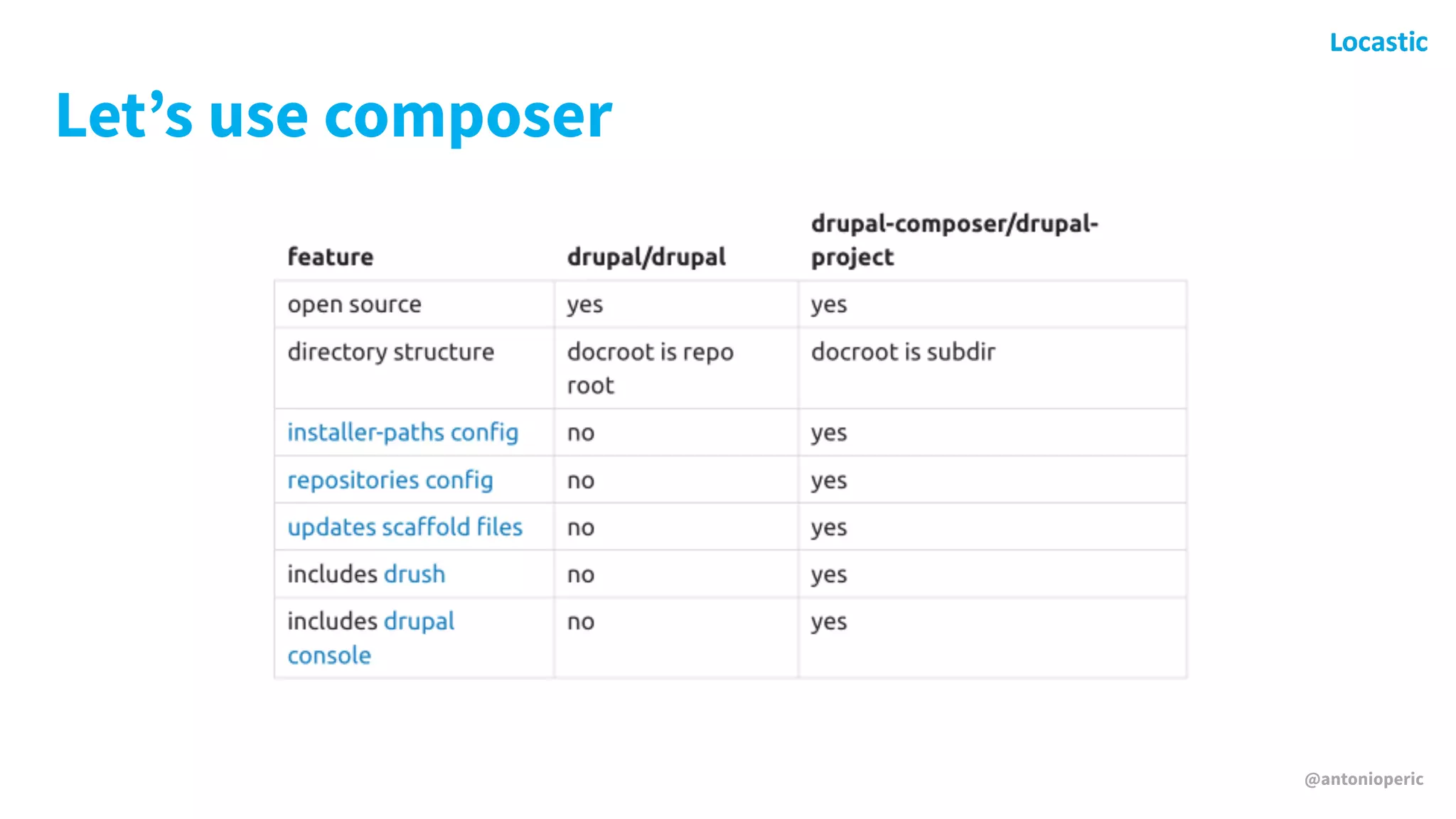
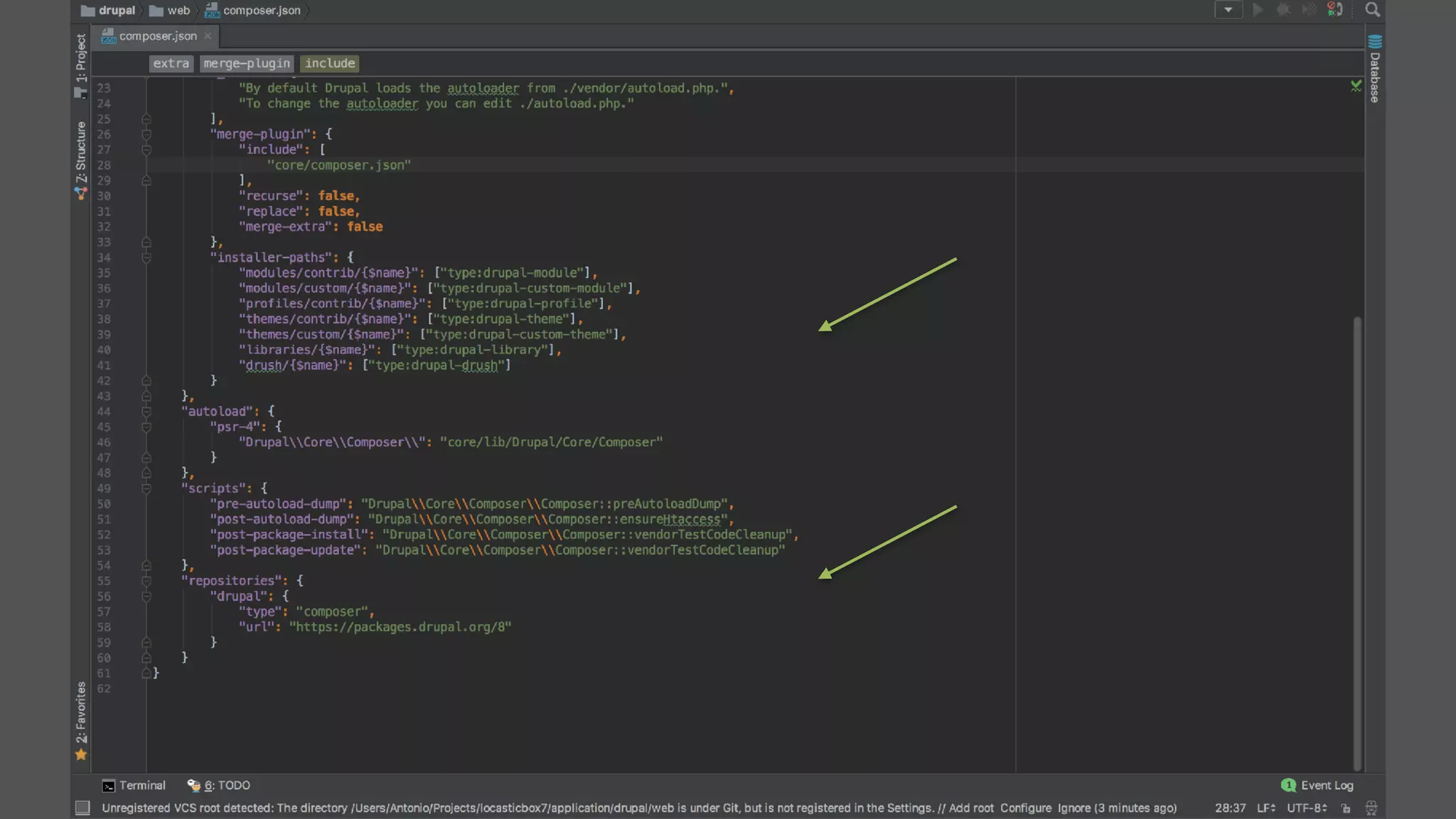
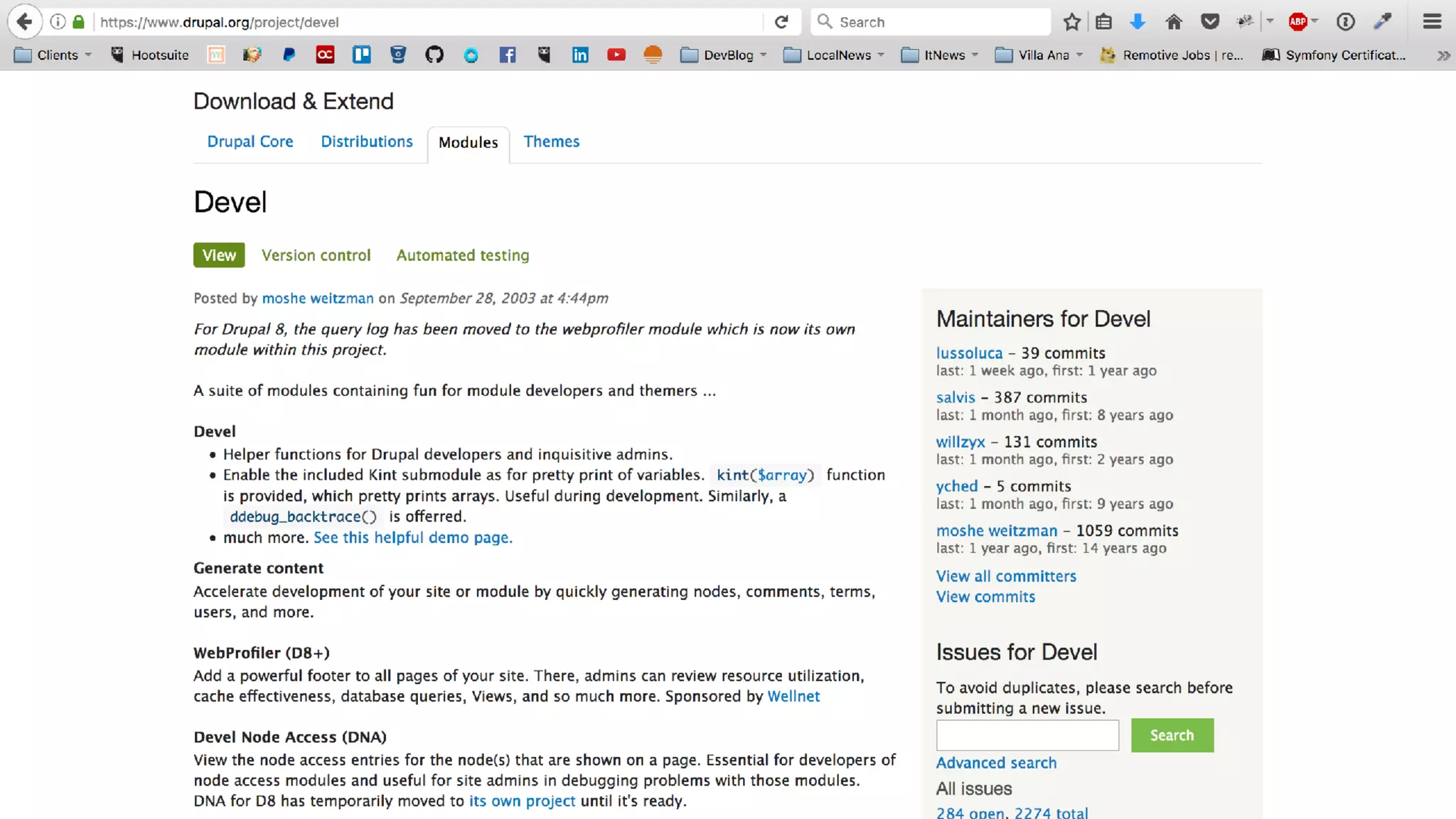
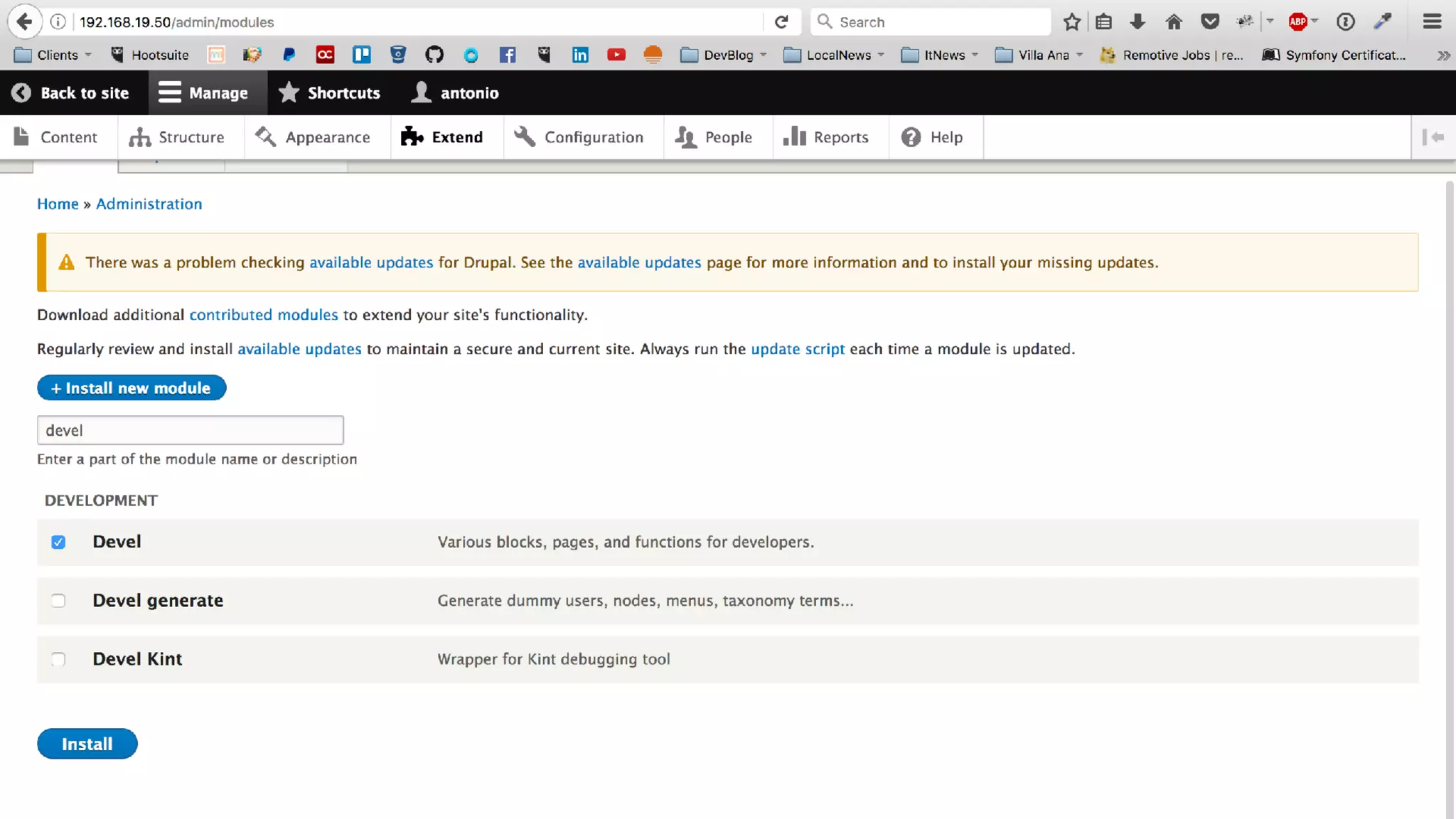
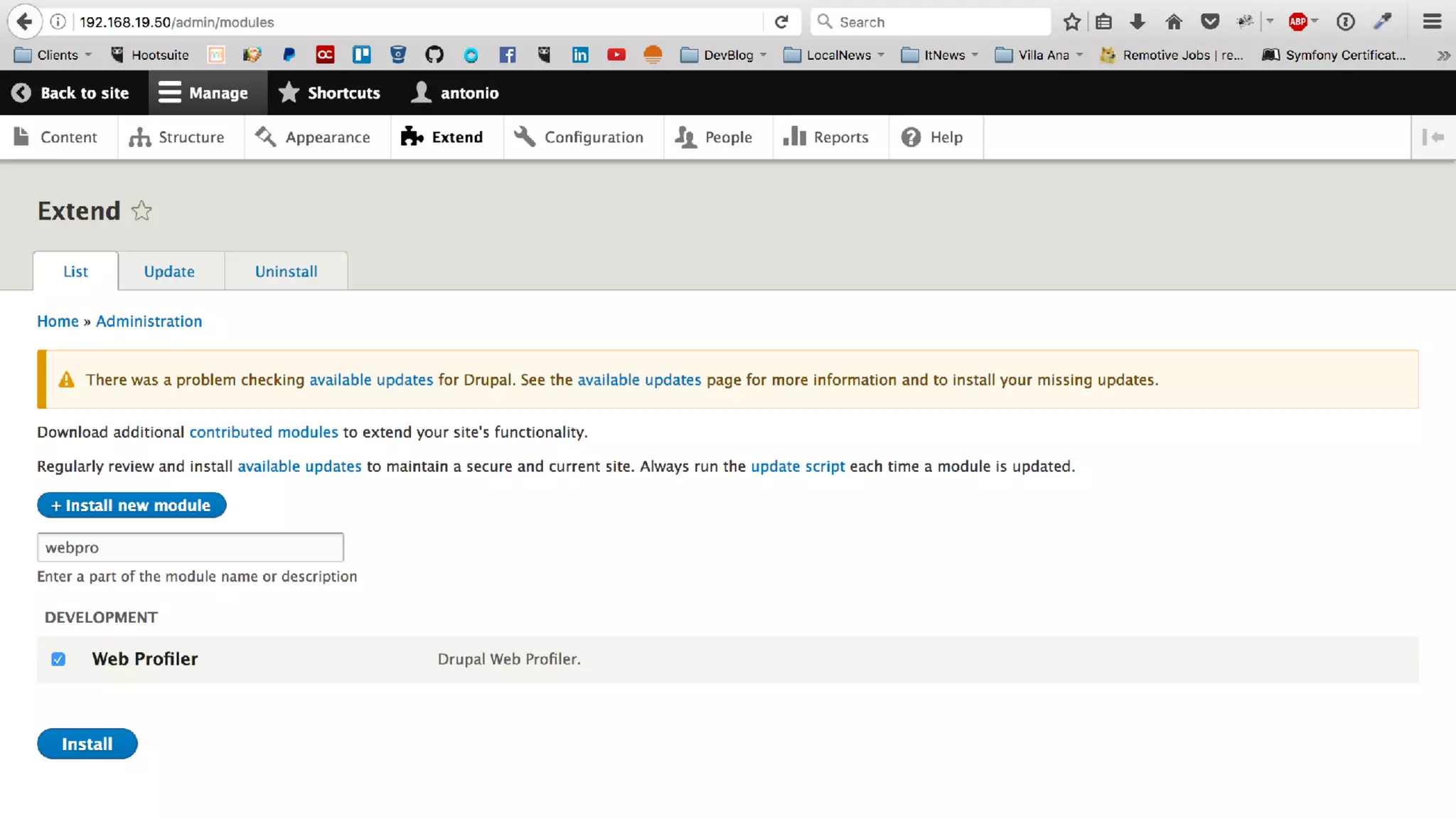
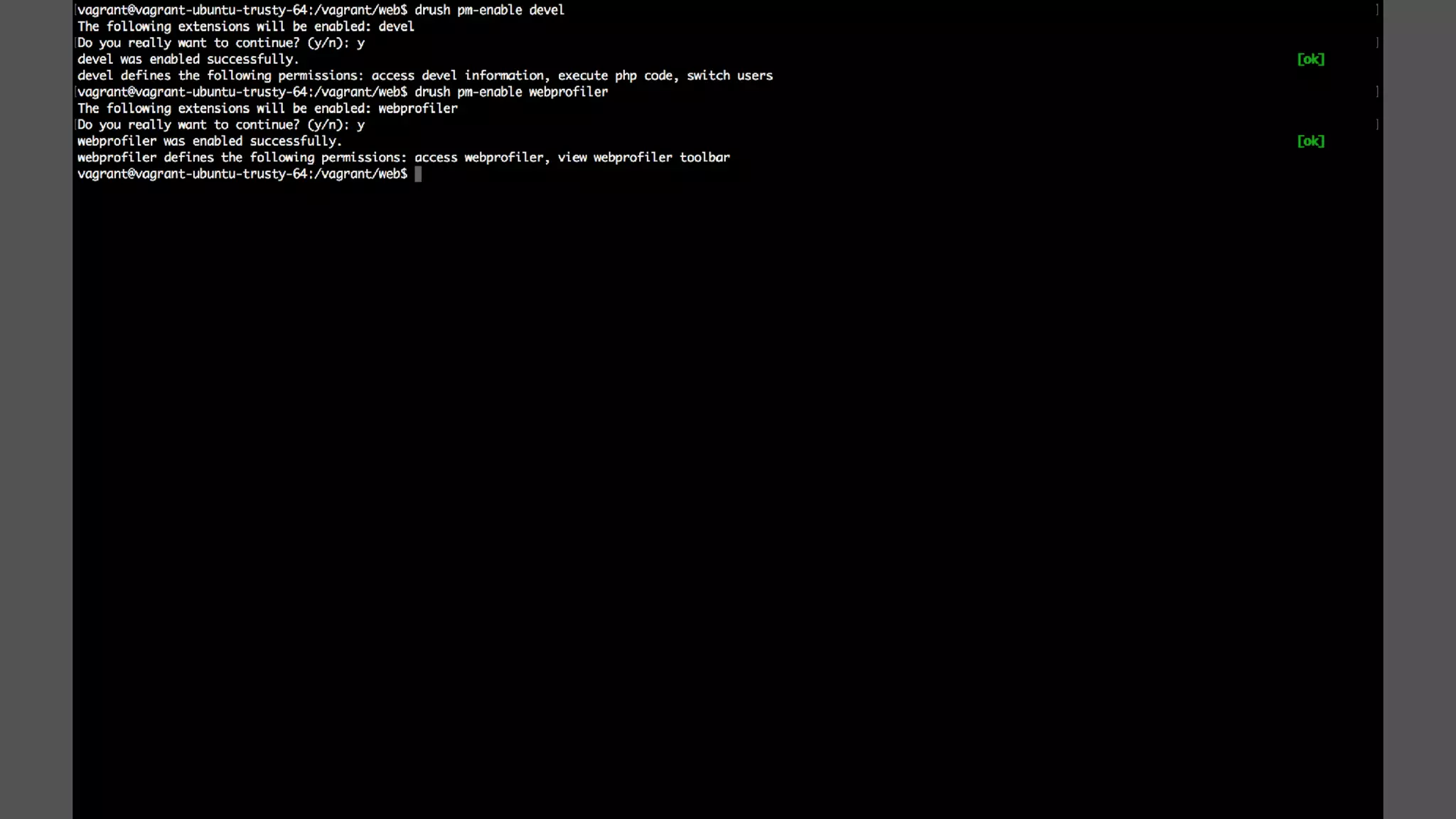
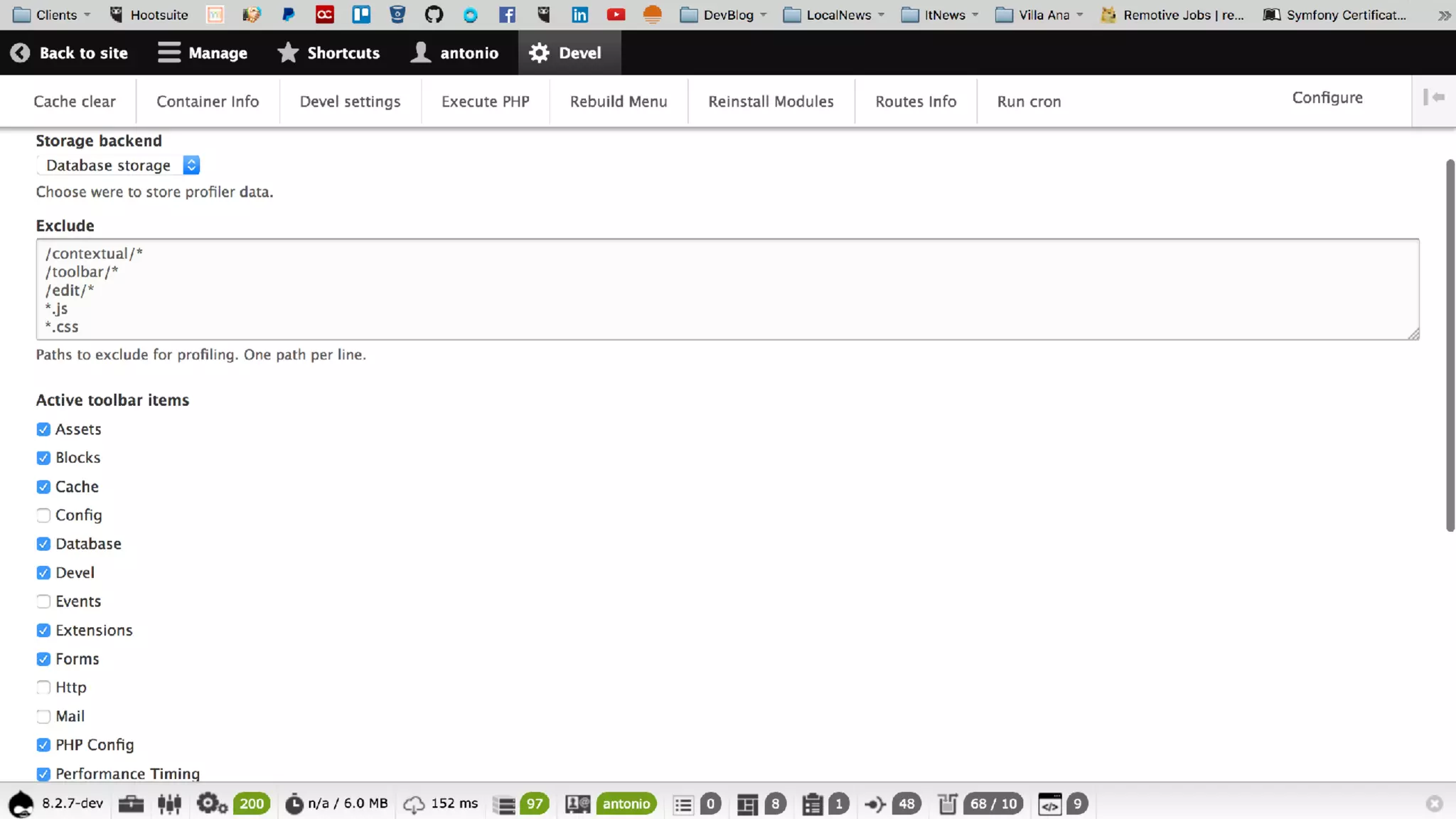
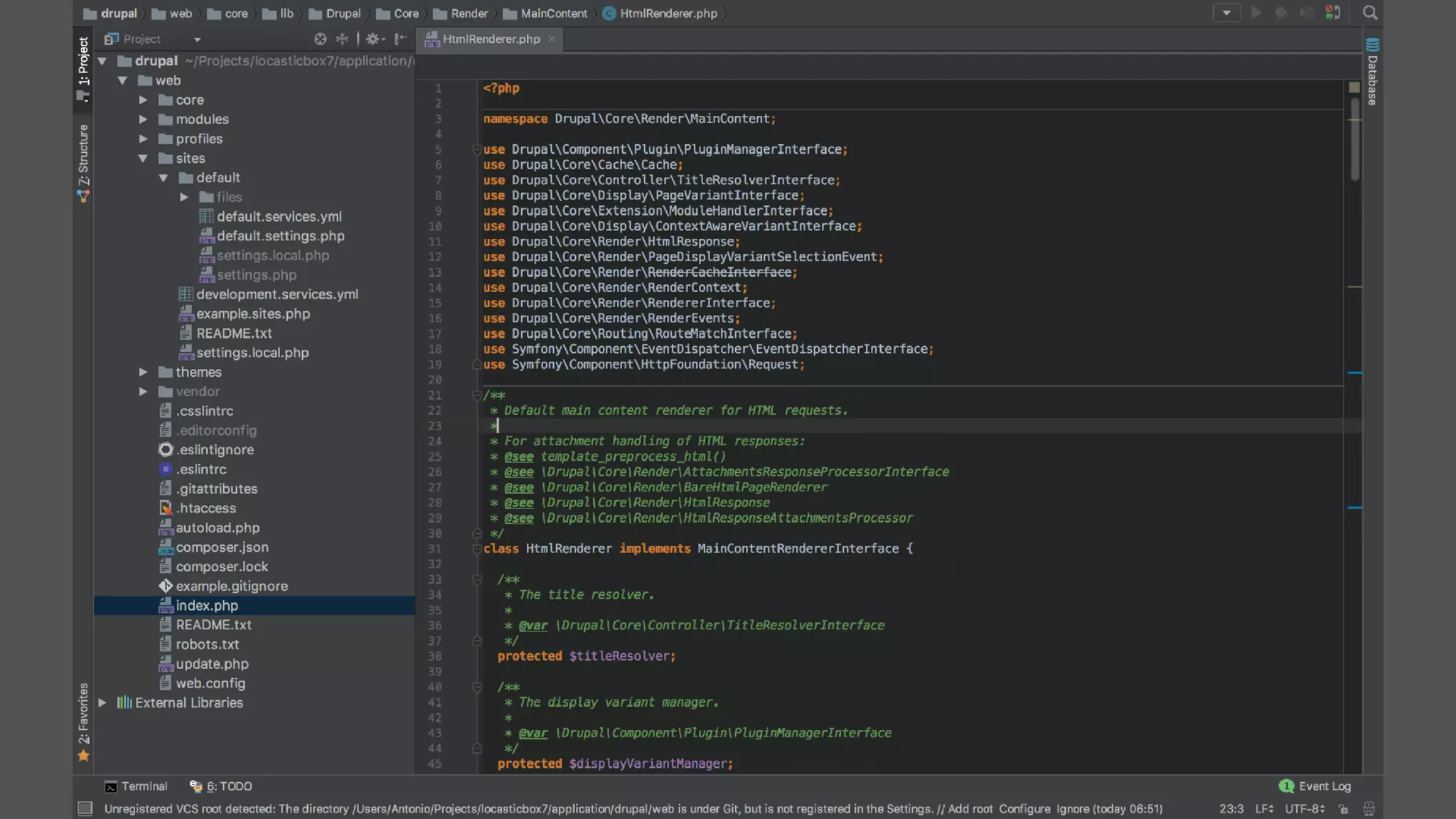
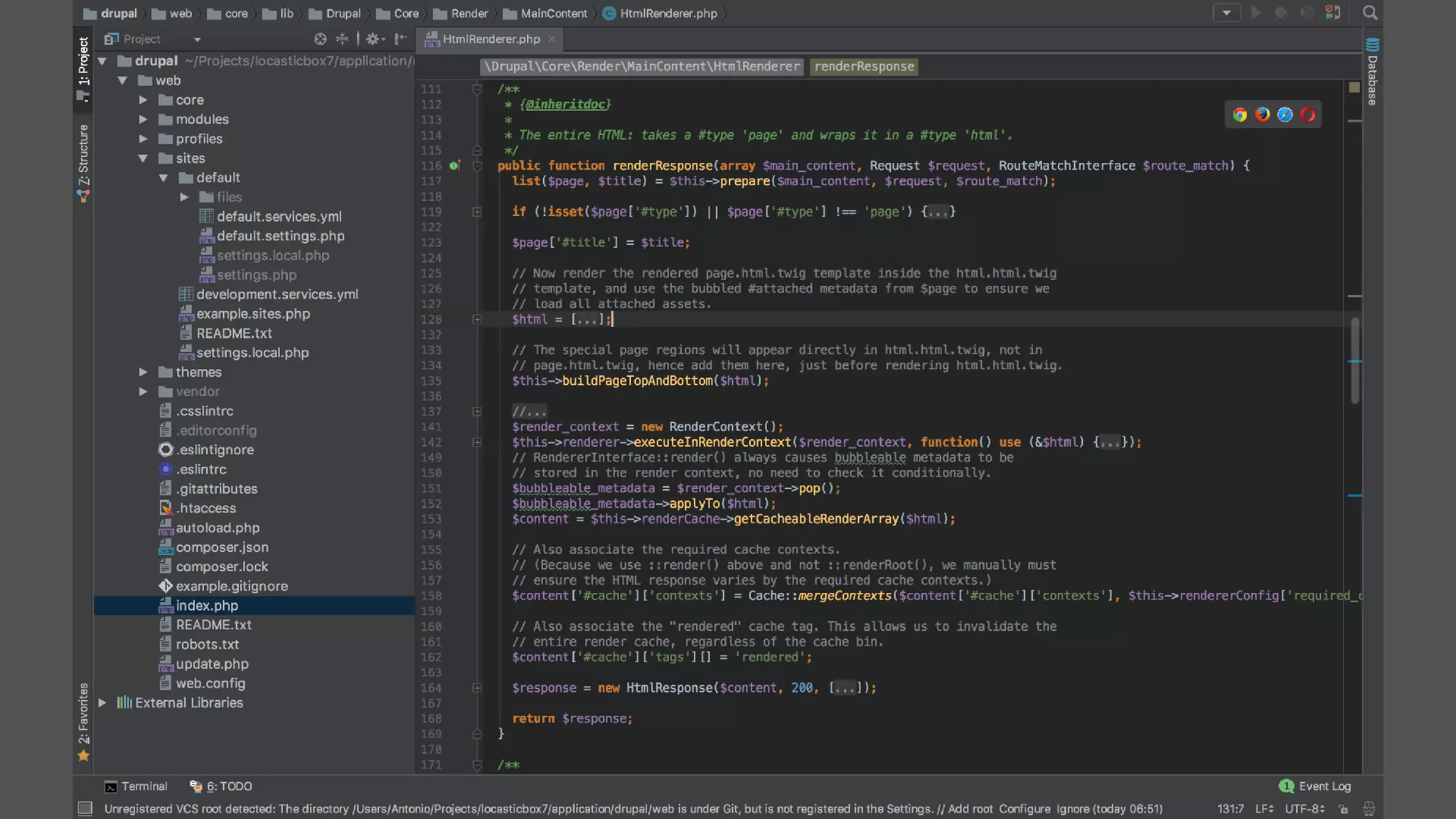
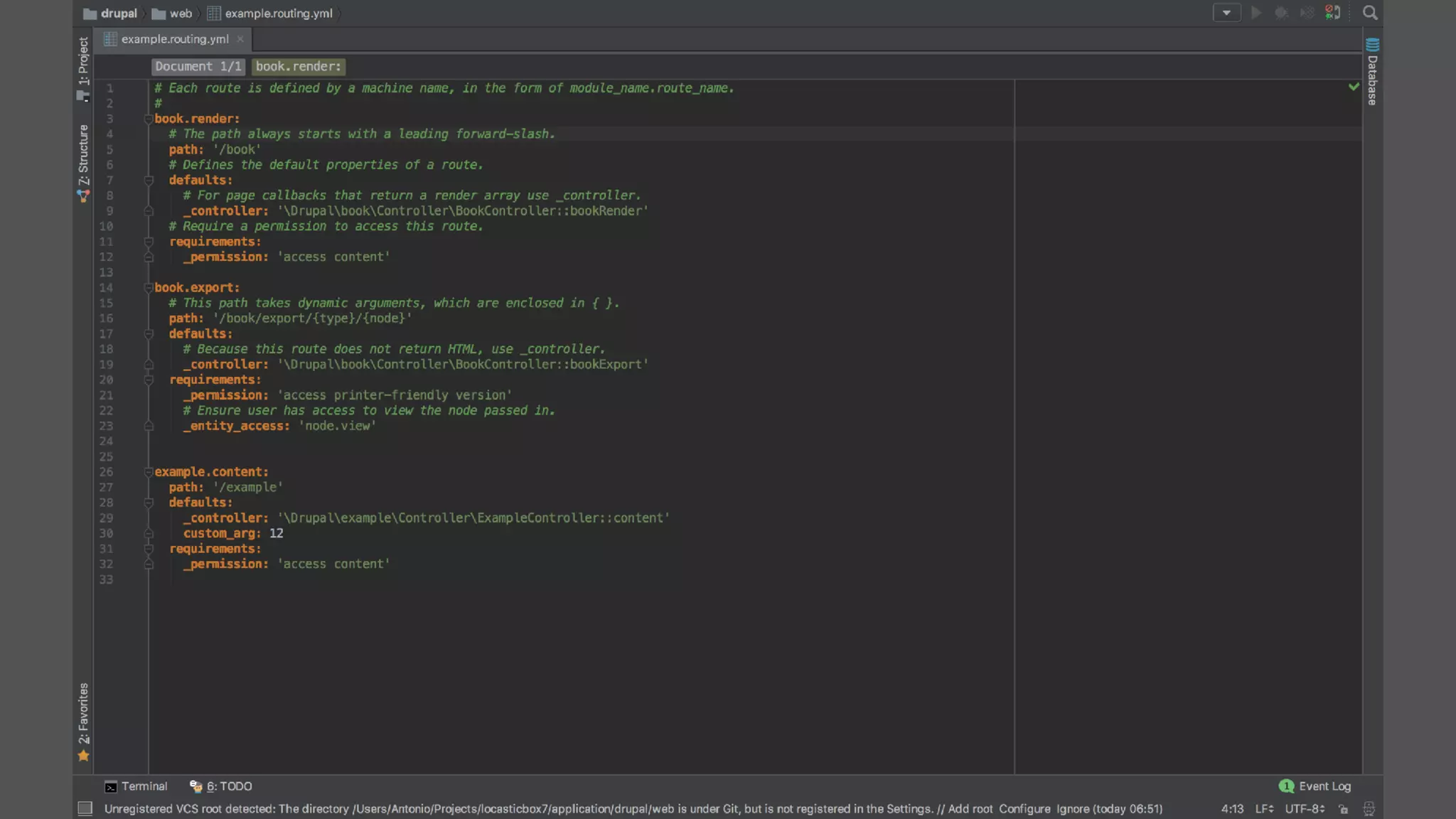
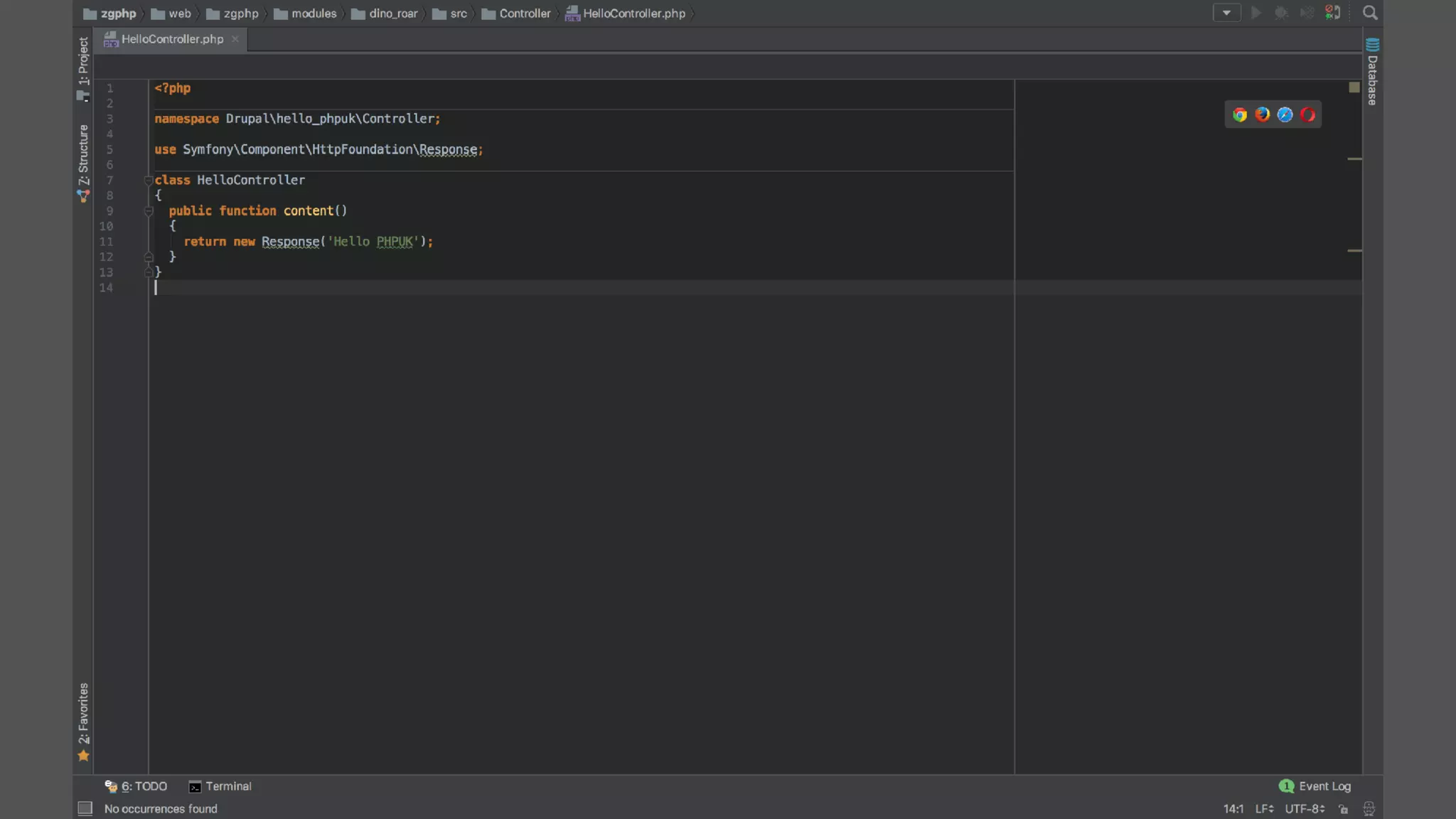
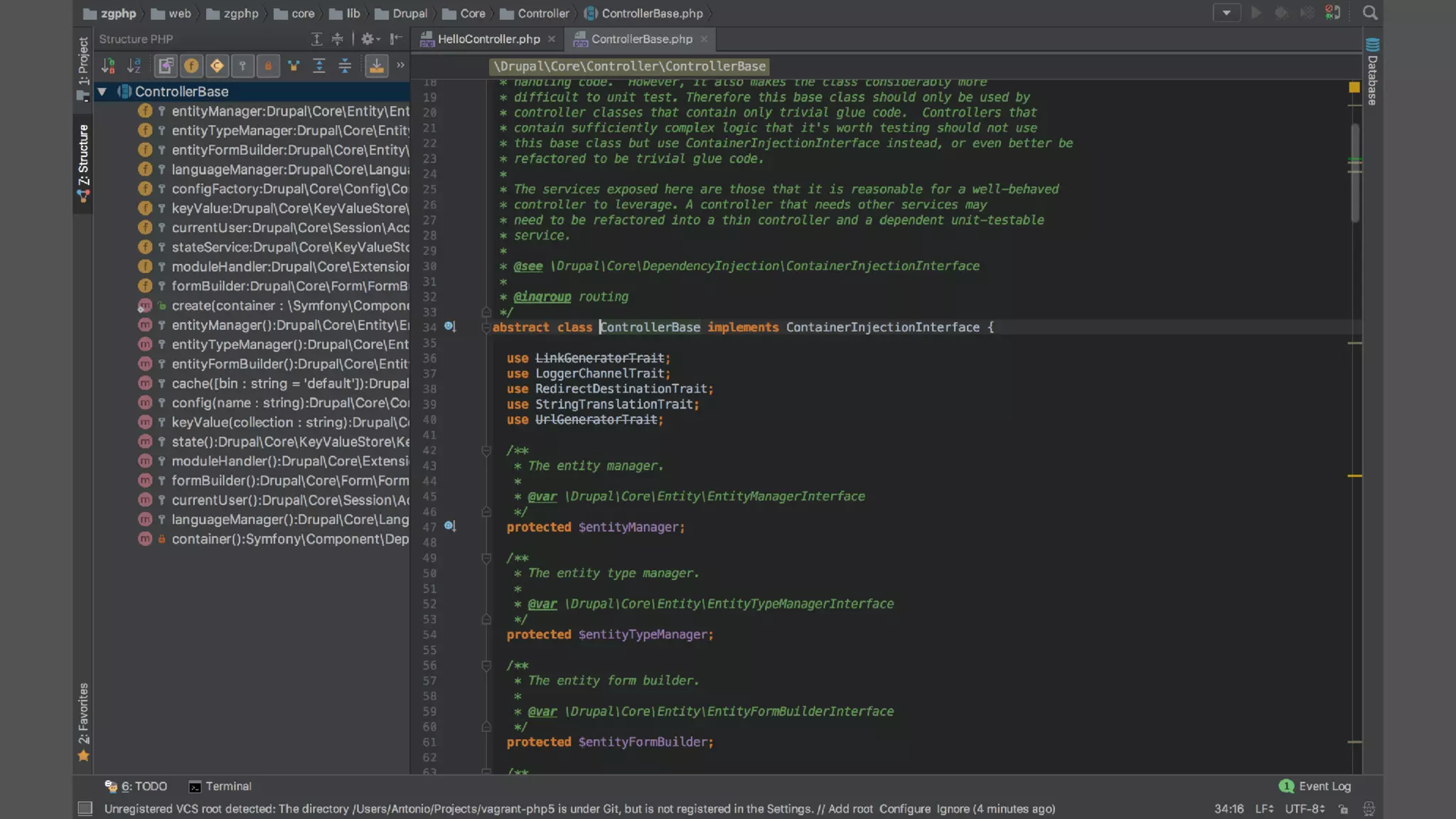
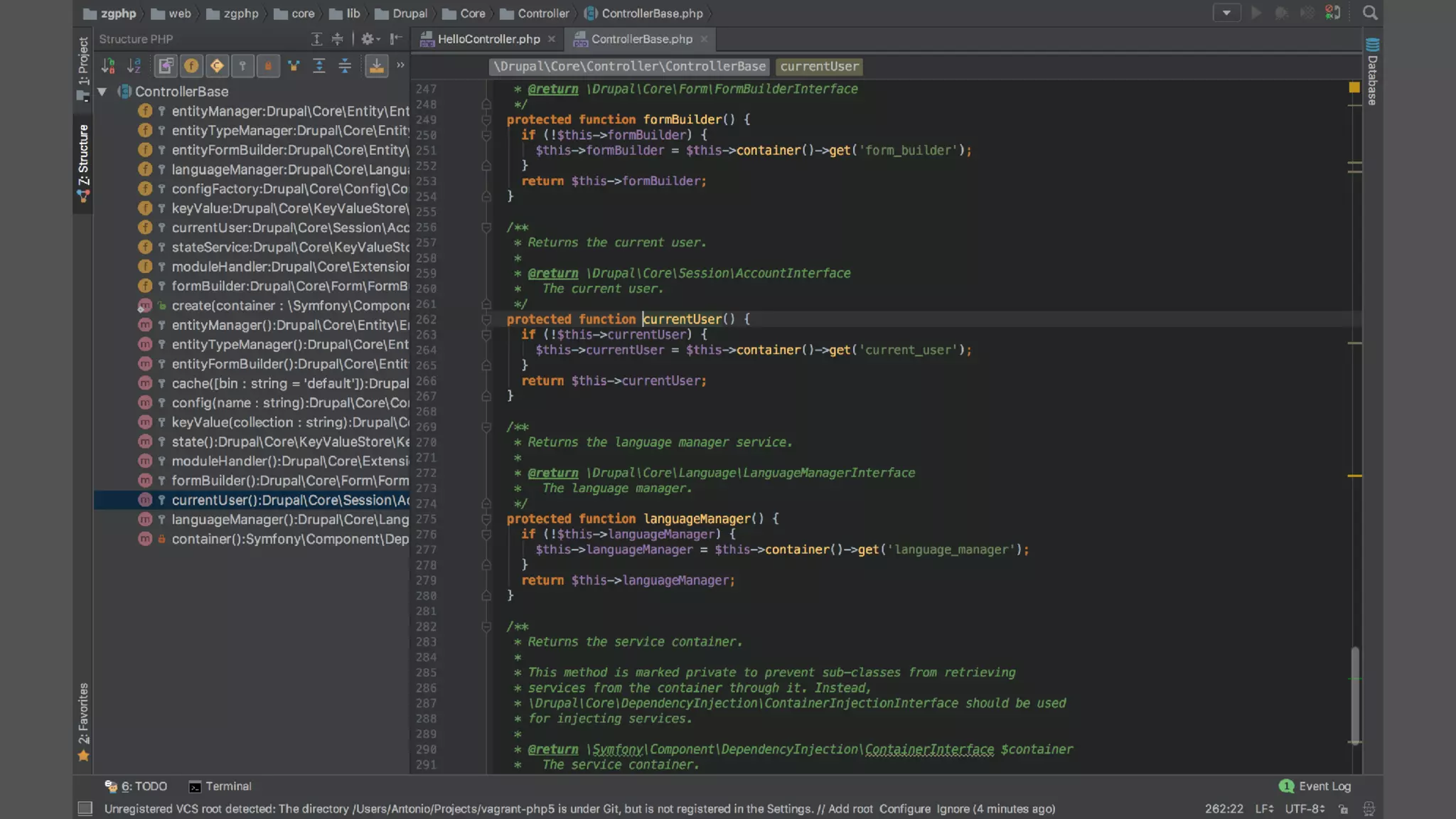
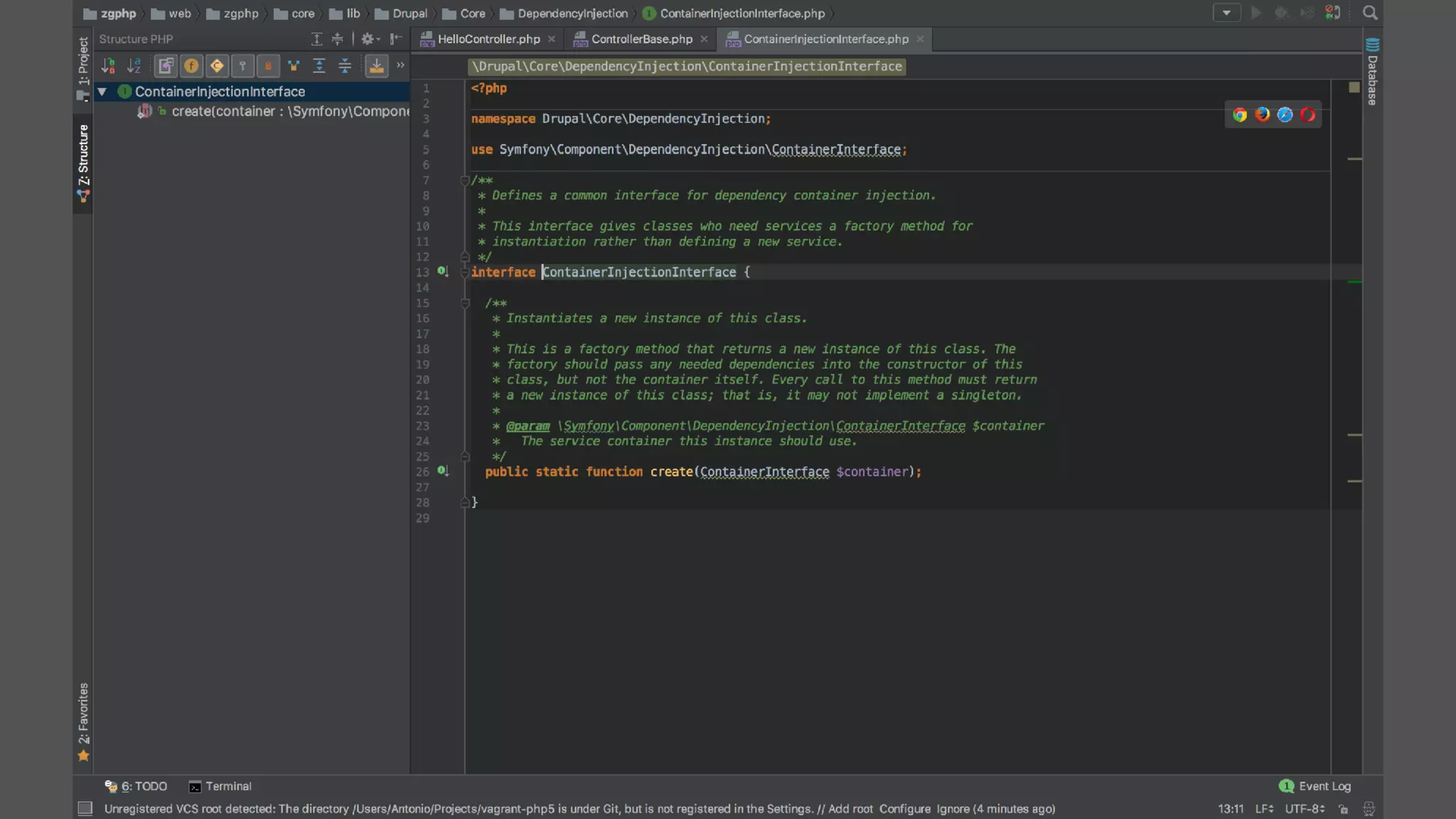
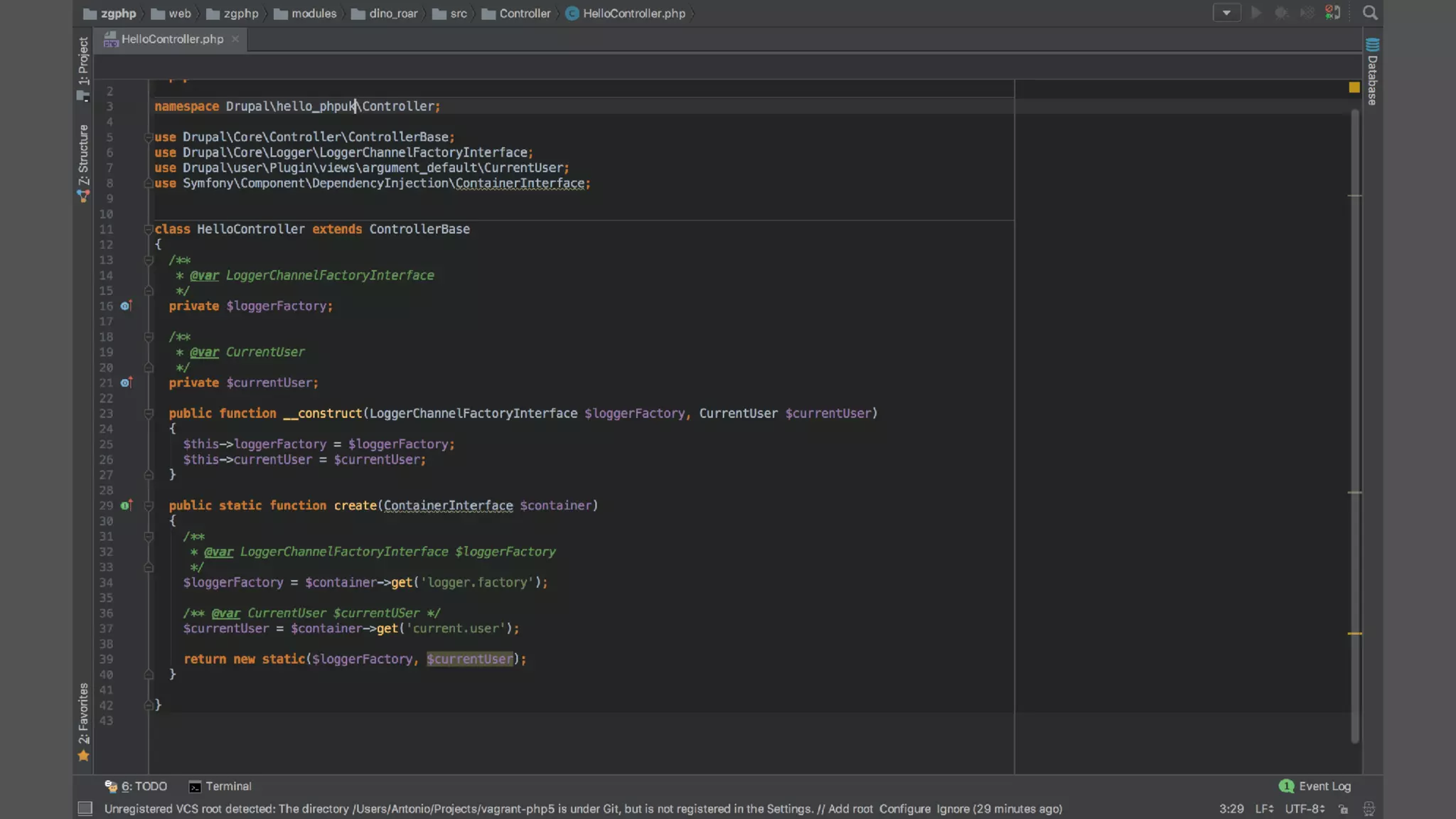
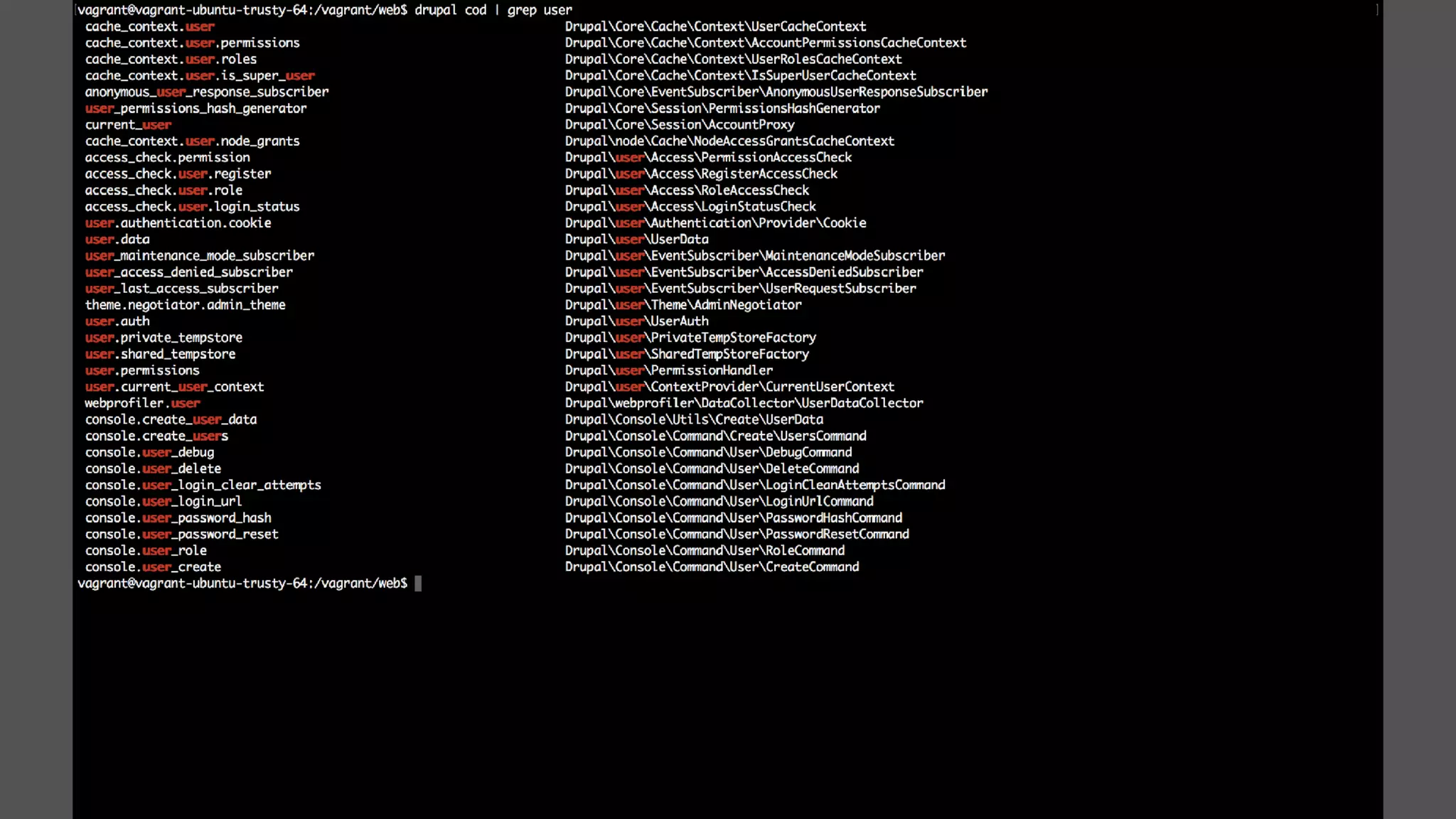
Antonio Perić-Mažar's presentation discusses integrating Symfony components within Drupal 8, highlighting how Drupal 8 employs a modern stack to enhance its CMS capabilities. The talk covers Drupal 8's development environment, tools like Drush and Drupal Console, installation via Composer, and the architecture involved in request handling. Perić-Mažar emphasizes the need for Symfony knowledge to effectively work with Drupal 8, and encourages developers from both communities to collaborate and learn together.















































![@antonioperic
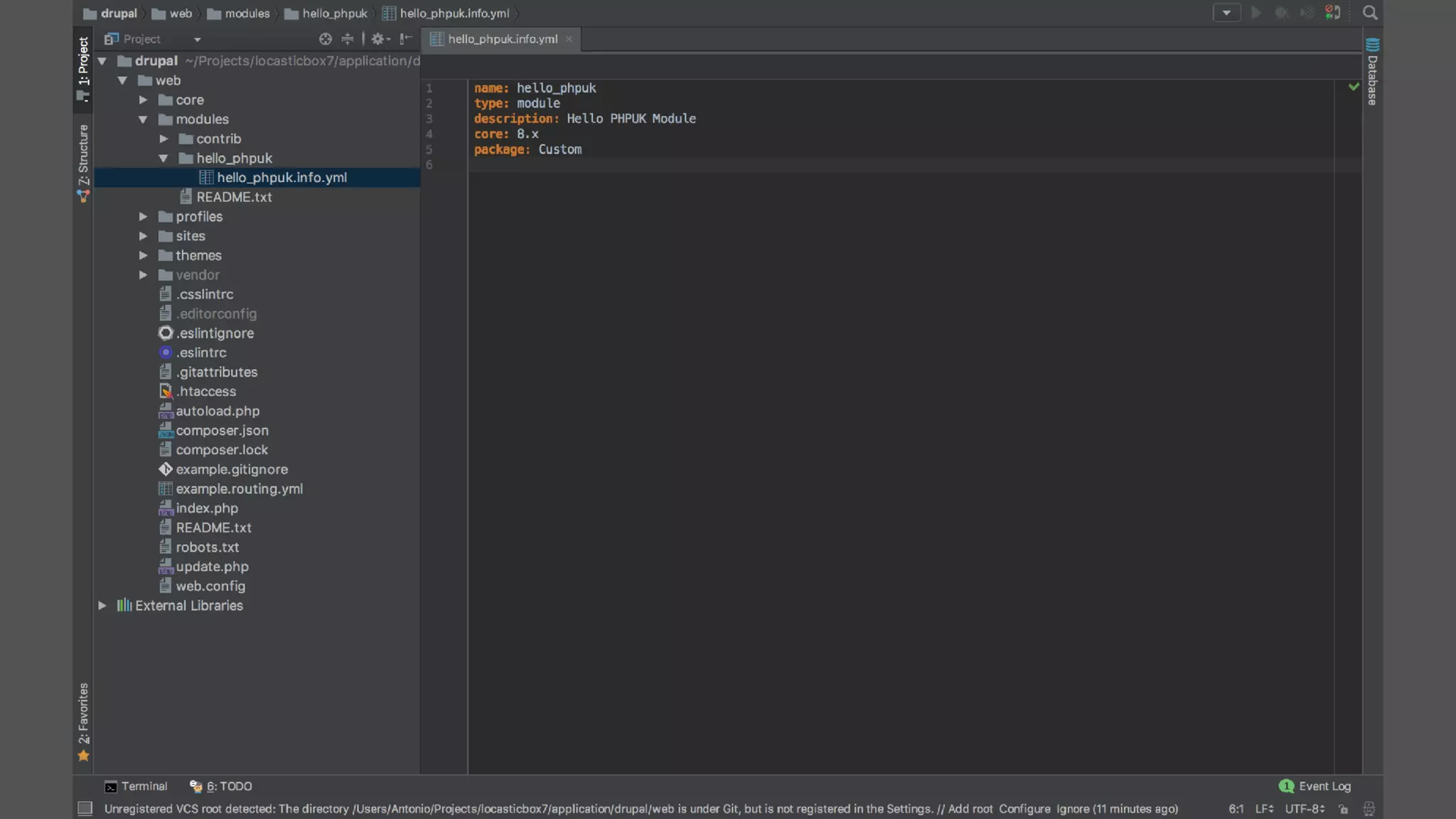
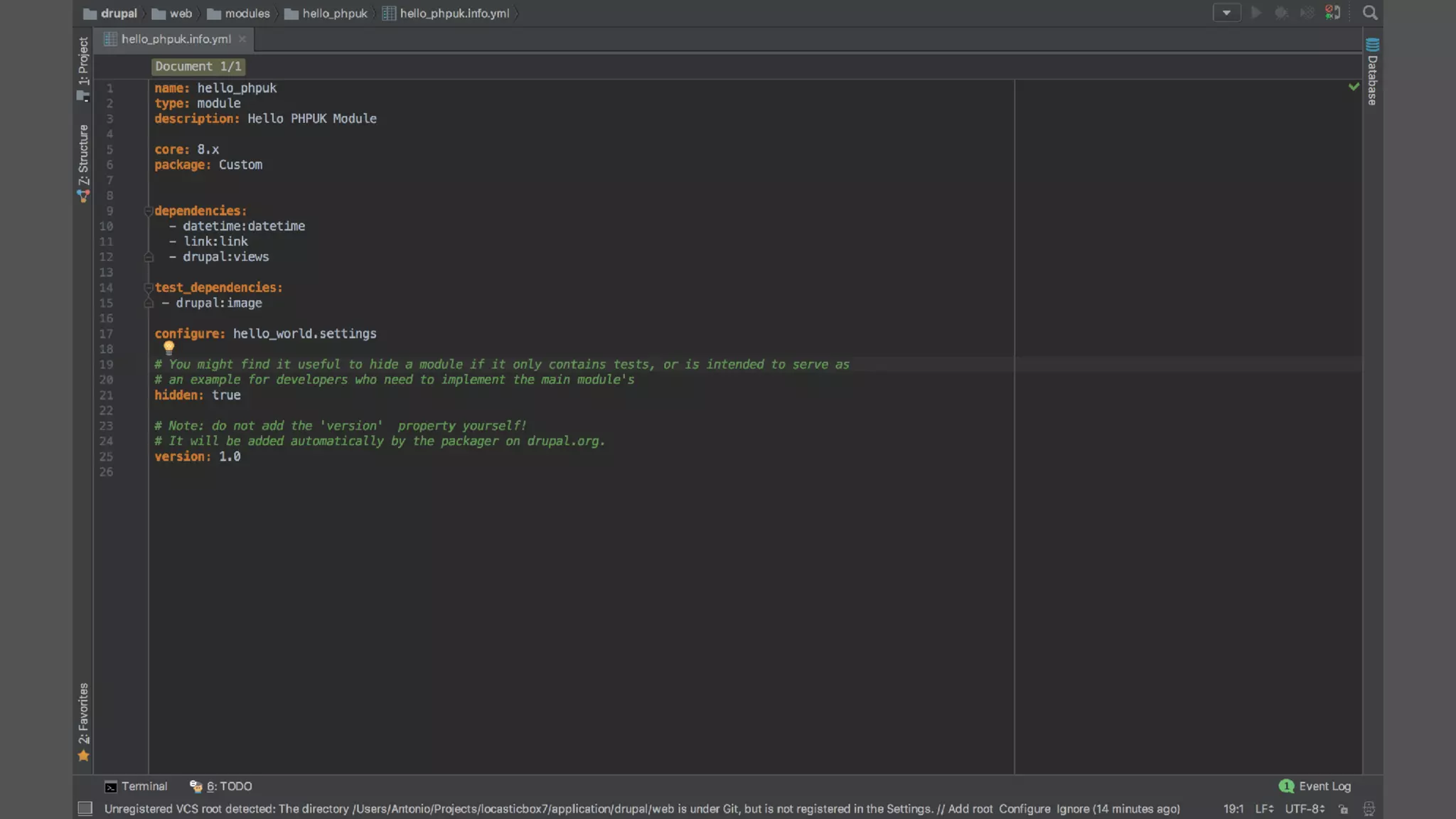
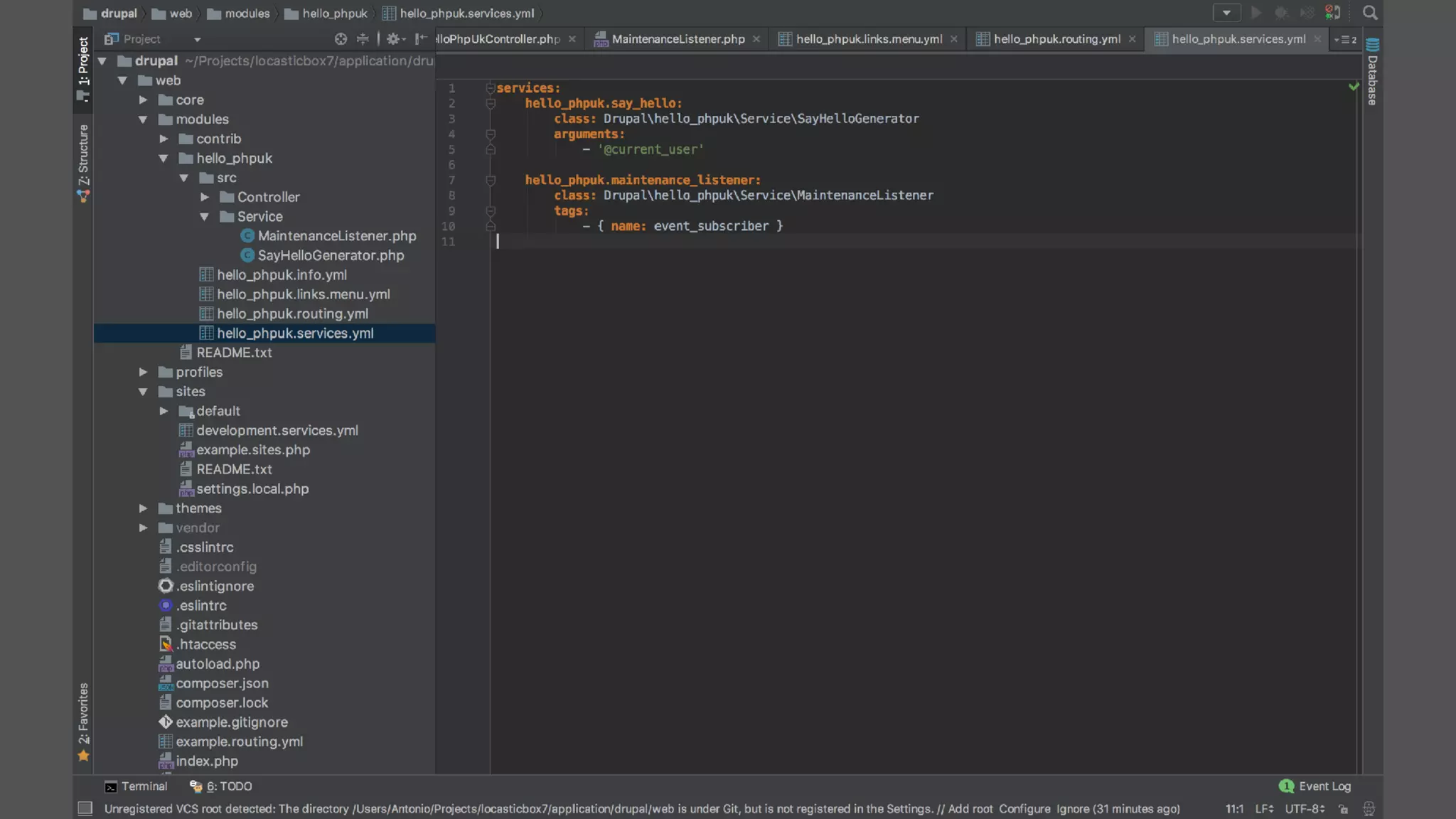
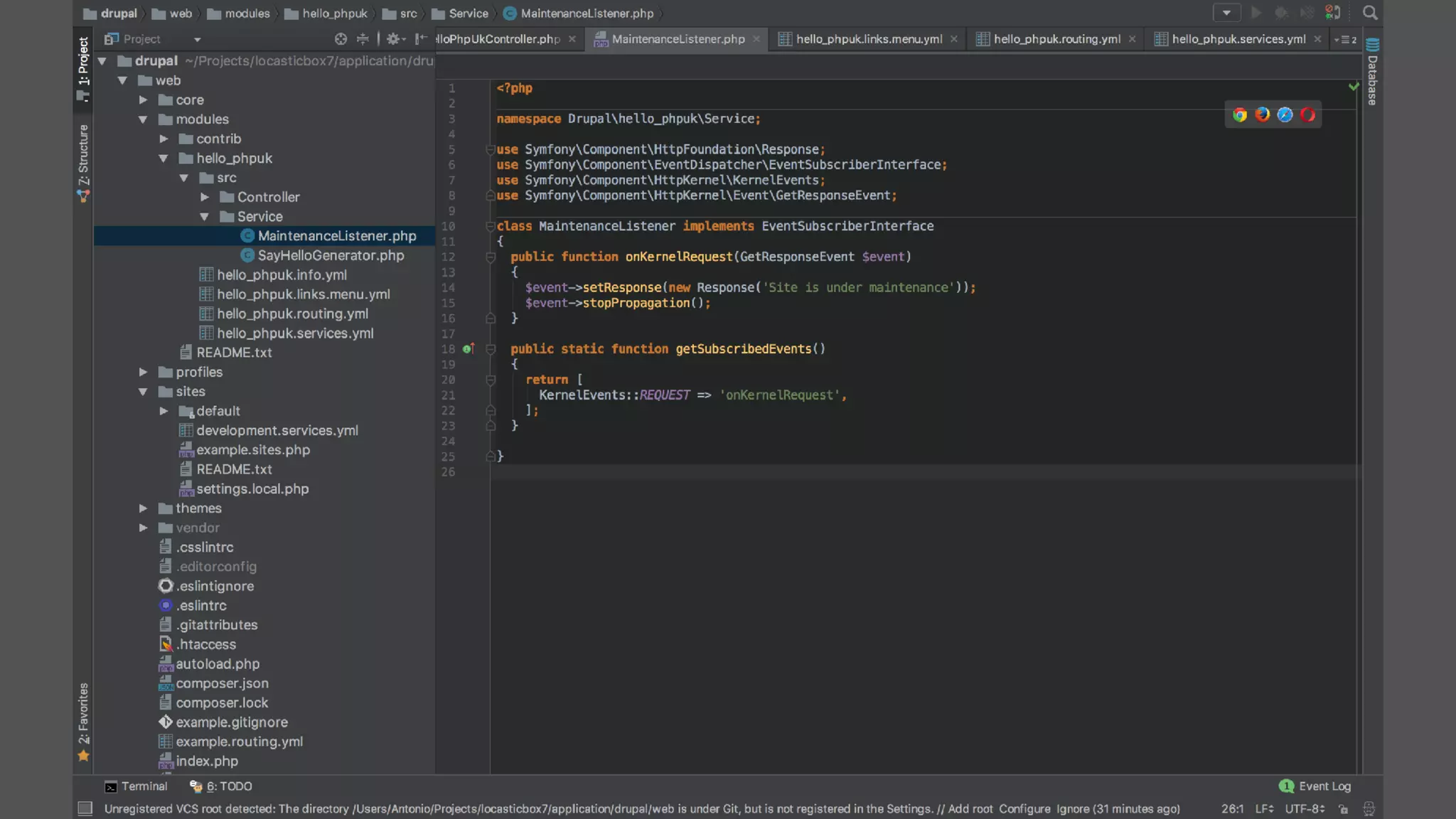
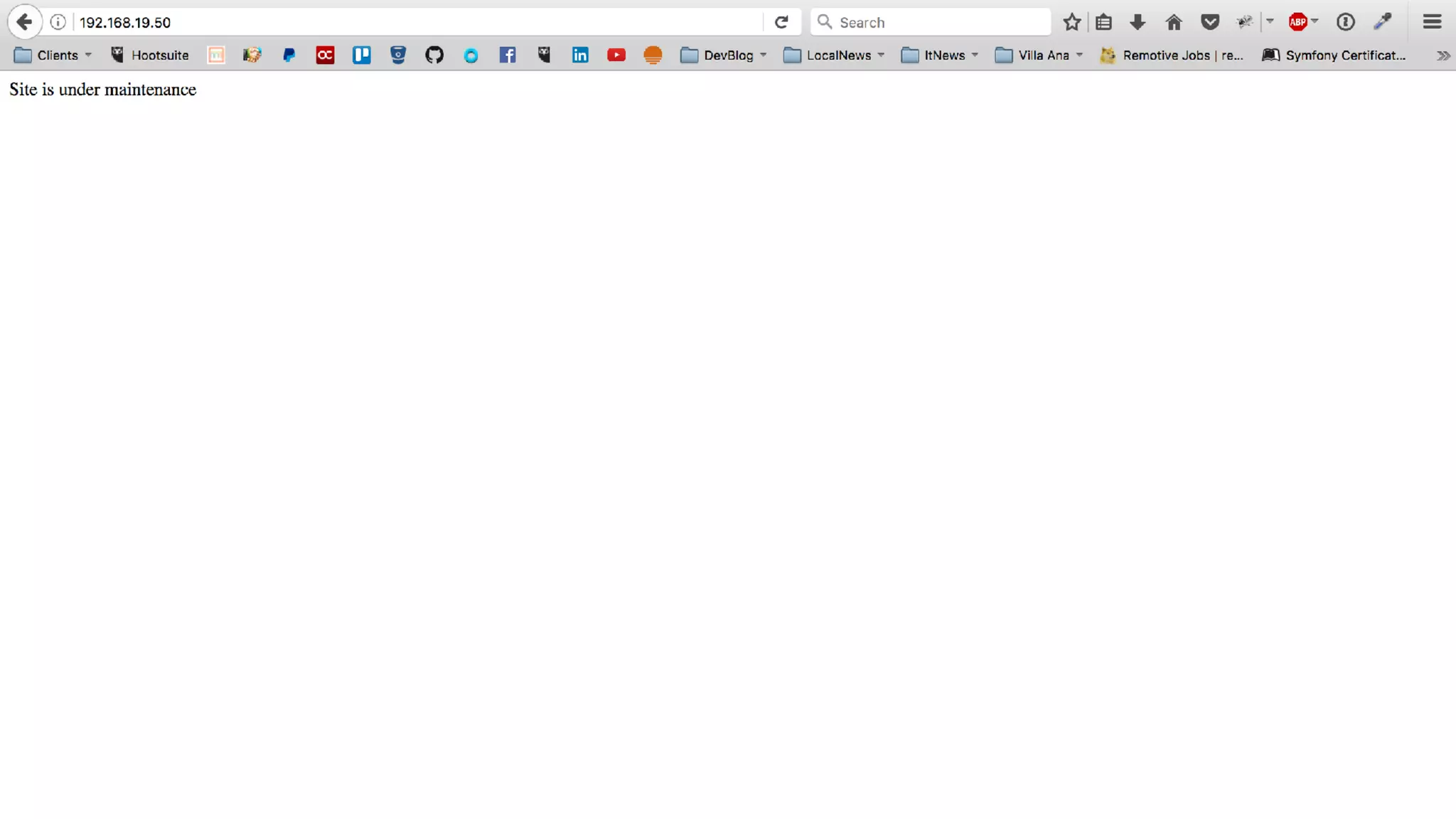
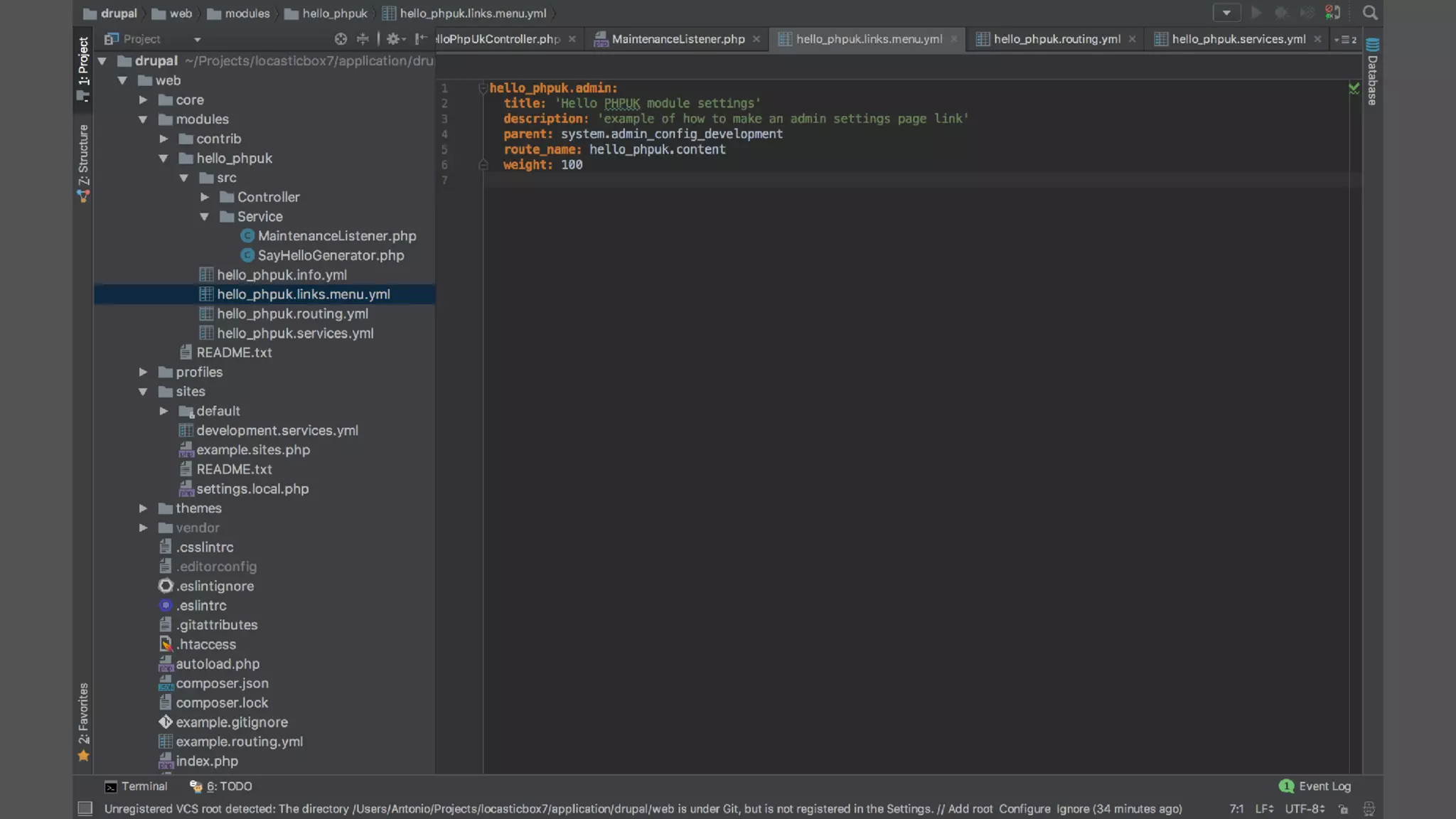
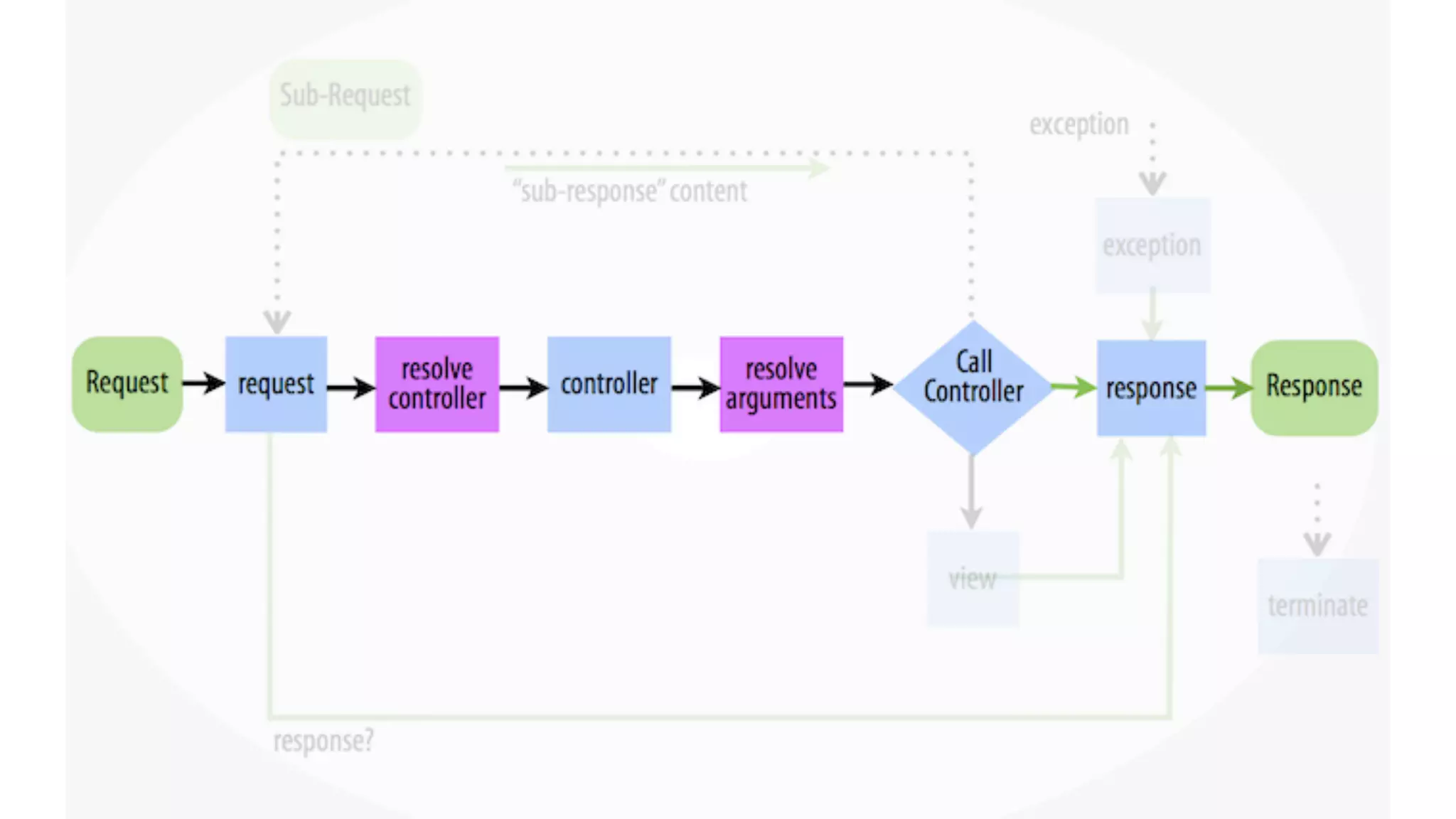
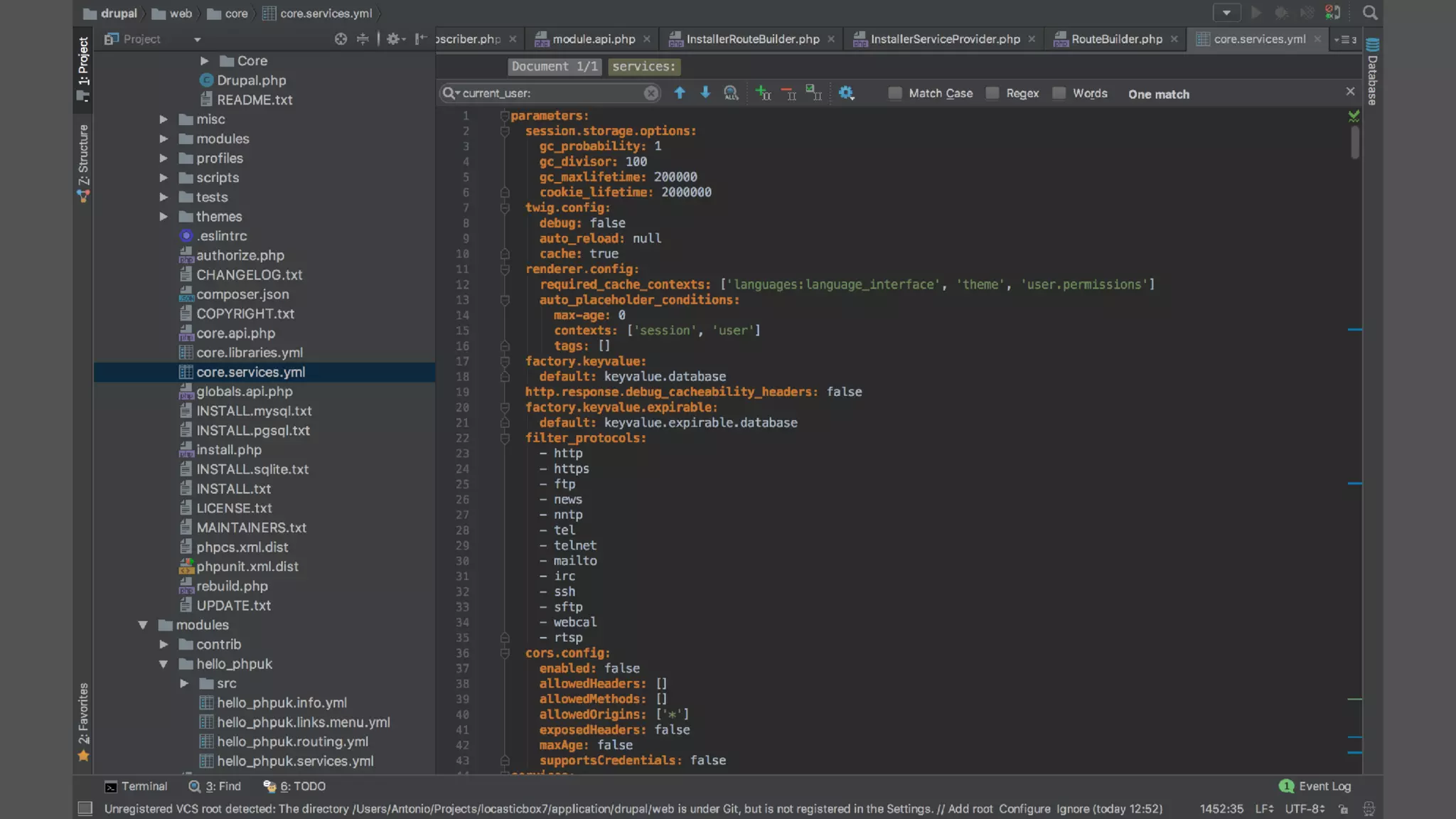
Registering event subscribers
Here are the steps to register an event subscriber:
Define a service in your module, tagged with 'event_subscriber' (see the Services topic for instructions).
Define a class for your subscriber service that implements SymfonyComponentEventDispatcherEventSubscriberInterface
In your class, the getSubscribedEvents method returns a list of the events this class is subscribed to, and which methods on the class
should be called for each one. Example:
public static function getSubscribedEvents() {
// Subscribe to kernel terminate with priority 100.
$events[KernelEvents::TERMINATE][] = array('onTerminate', 100);
// Subscribe to kernel request with default priority of 0.
$events[KernelEvents::REQUEST][] = array('onRequest');
return $events;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20170218phpukdrupal8forsymfonydevelopersv5-final-170515203506/75/Drupal8-for-Symfony-Developers-PHP-Day-Verona-2017-104-2048.jpg)