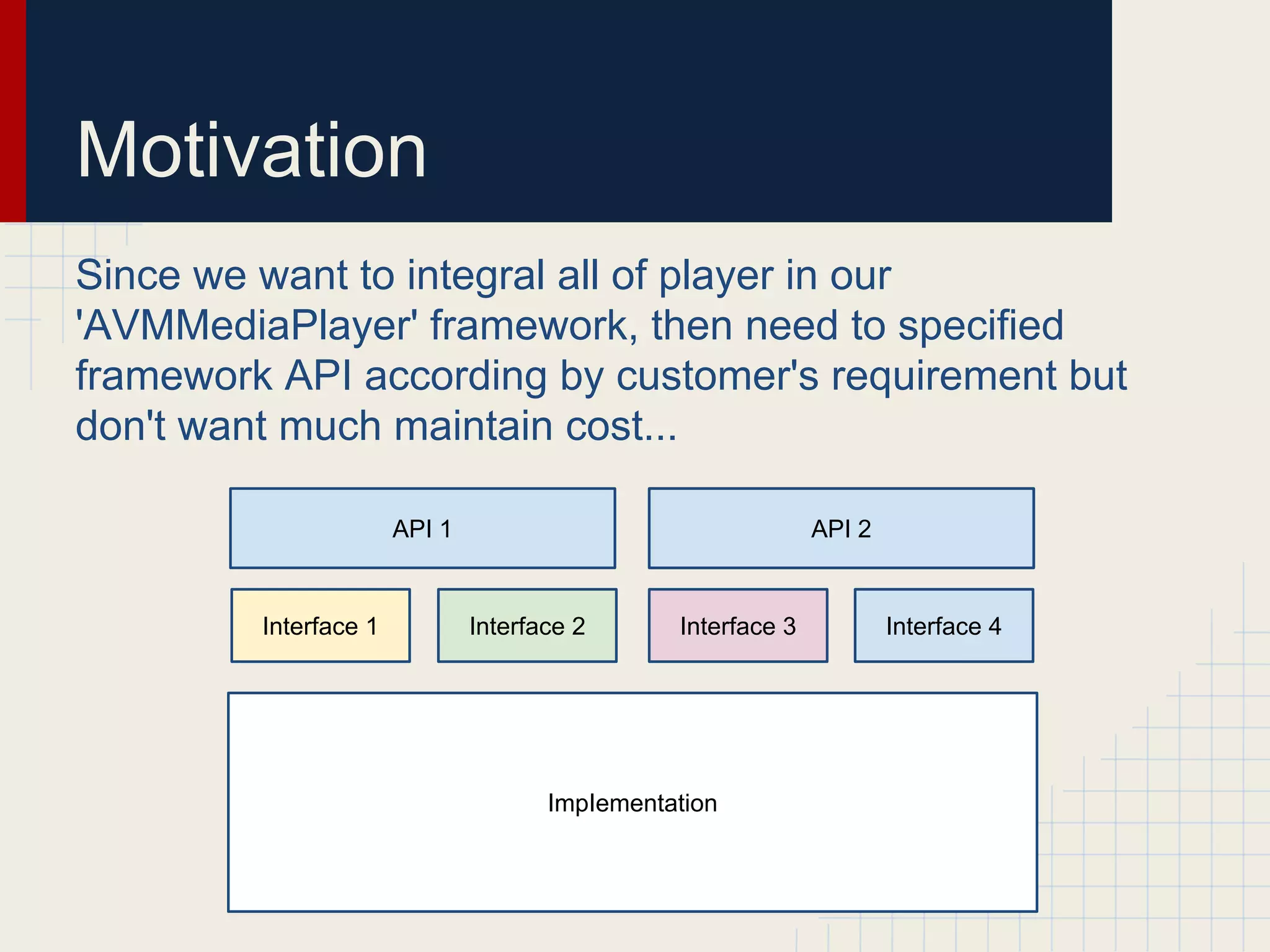
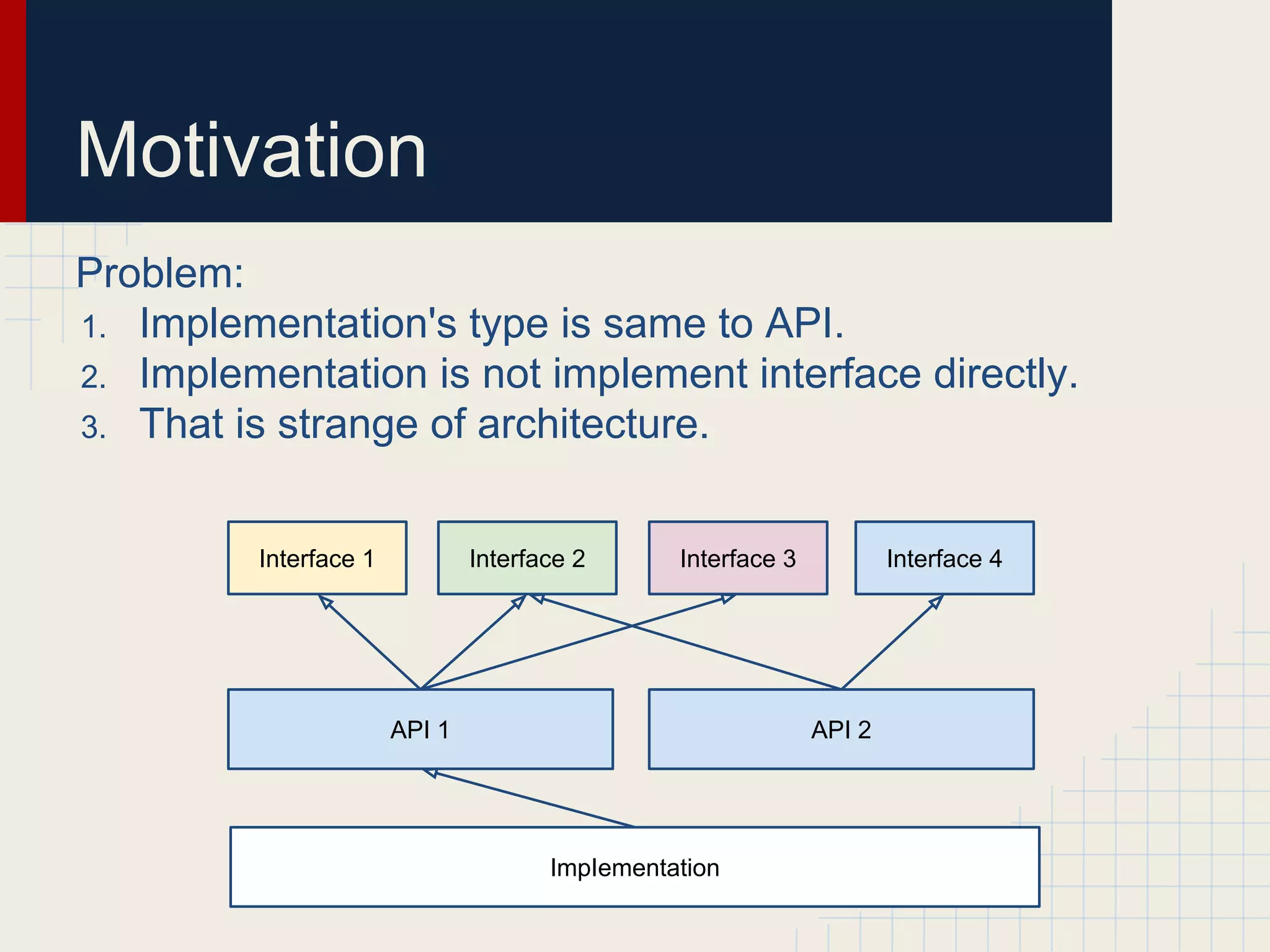
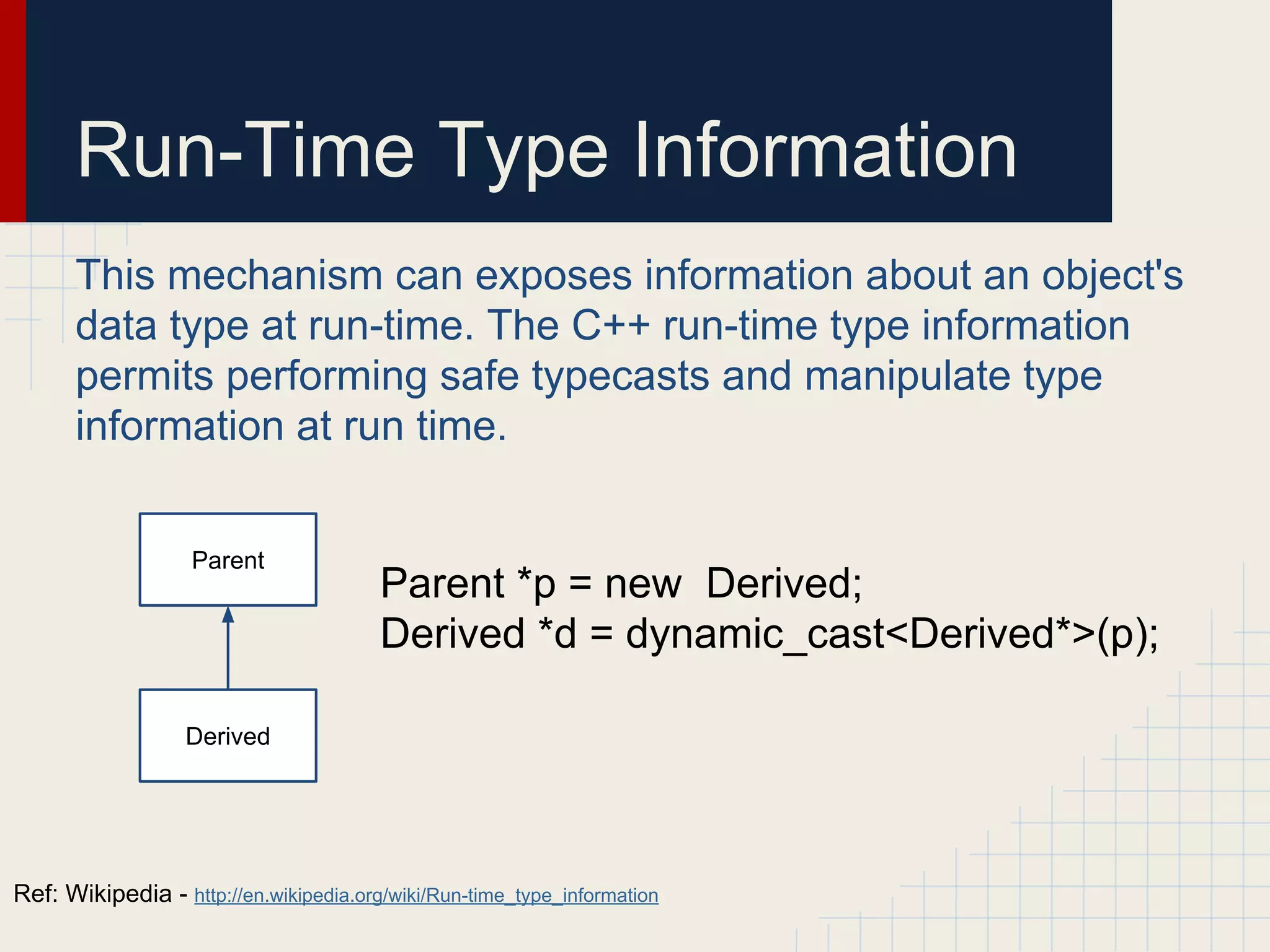
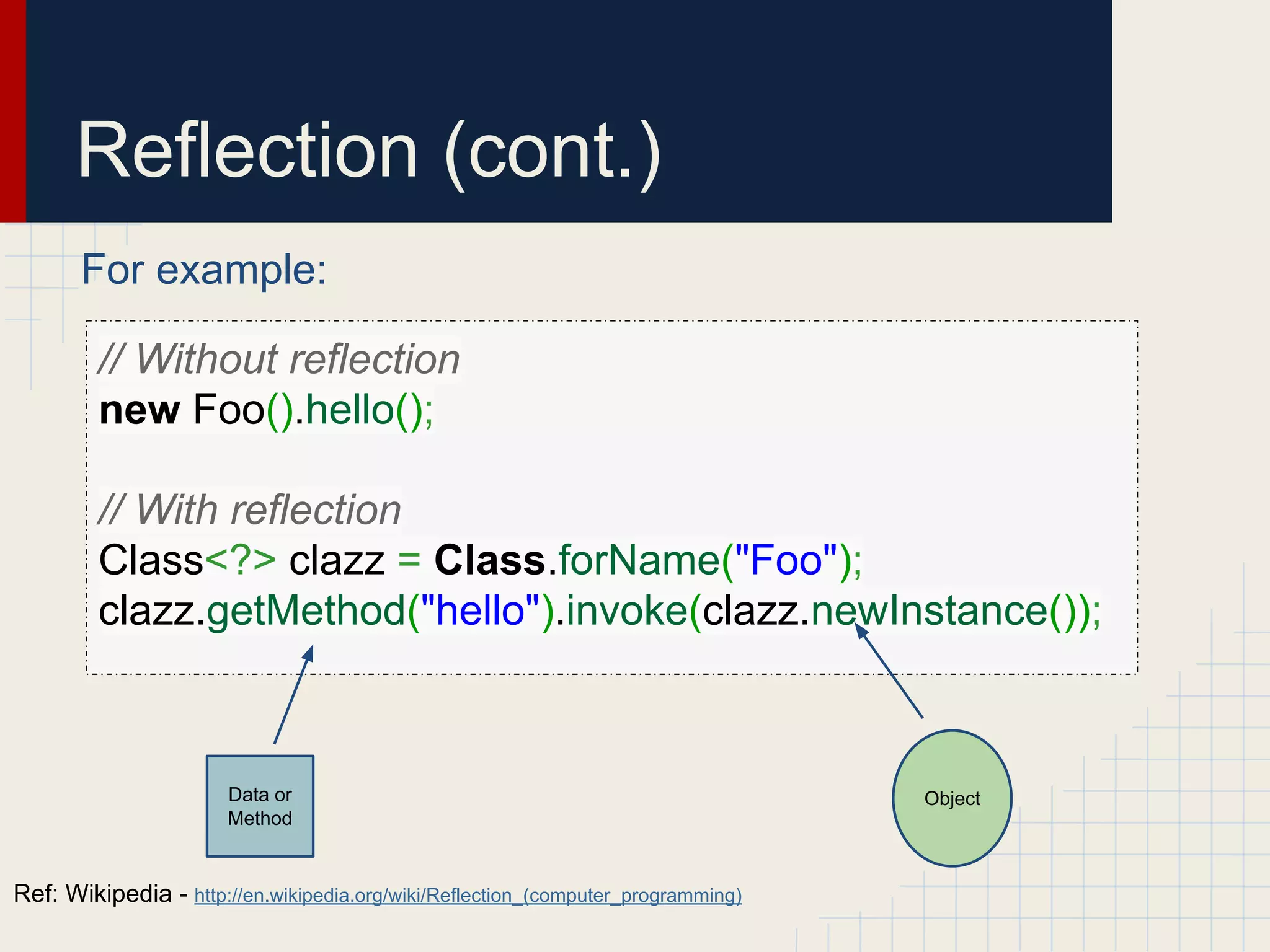
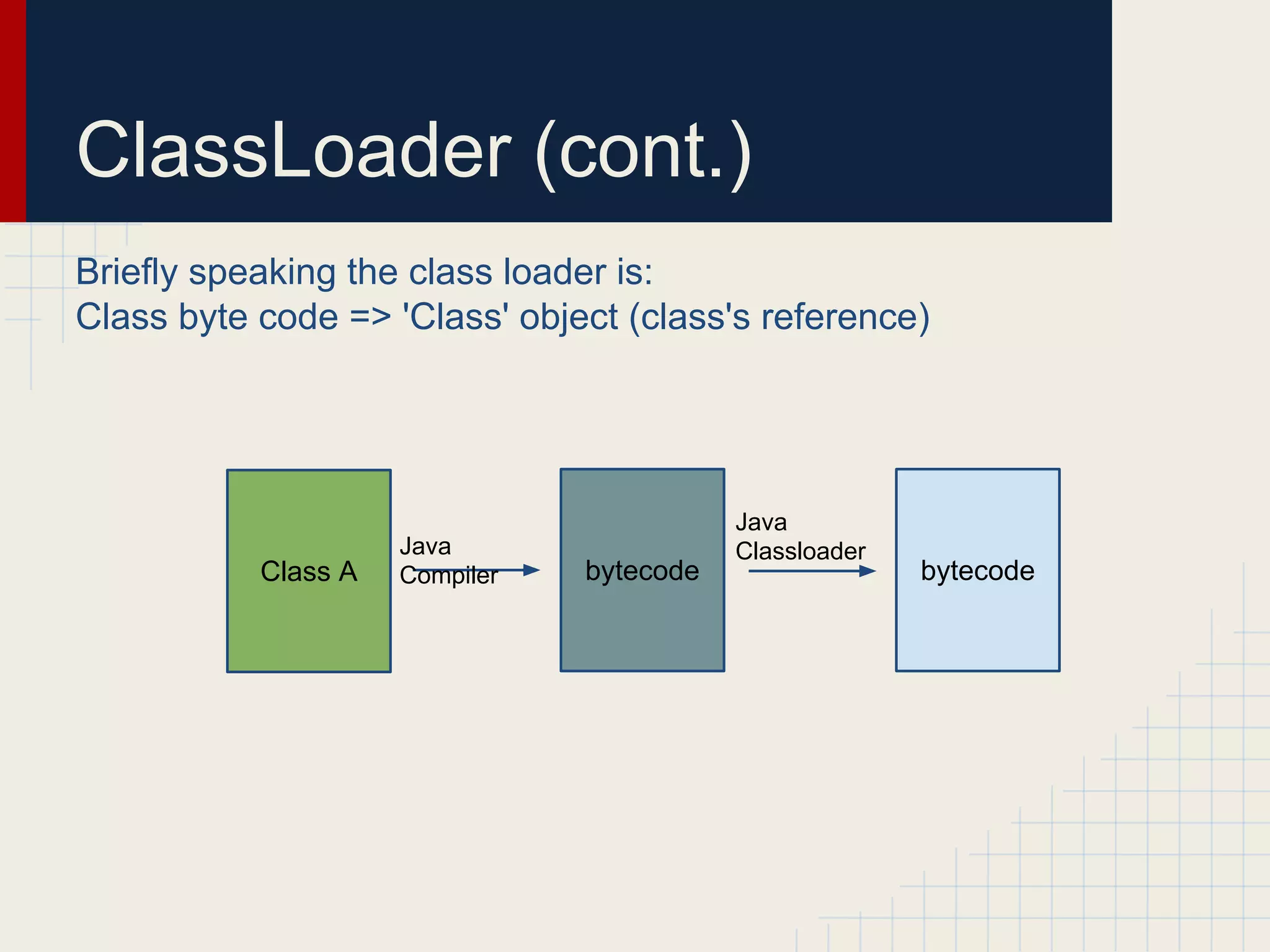
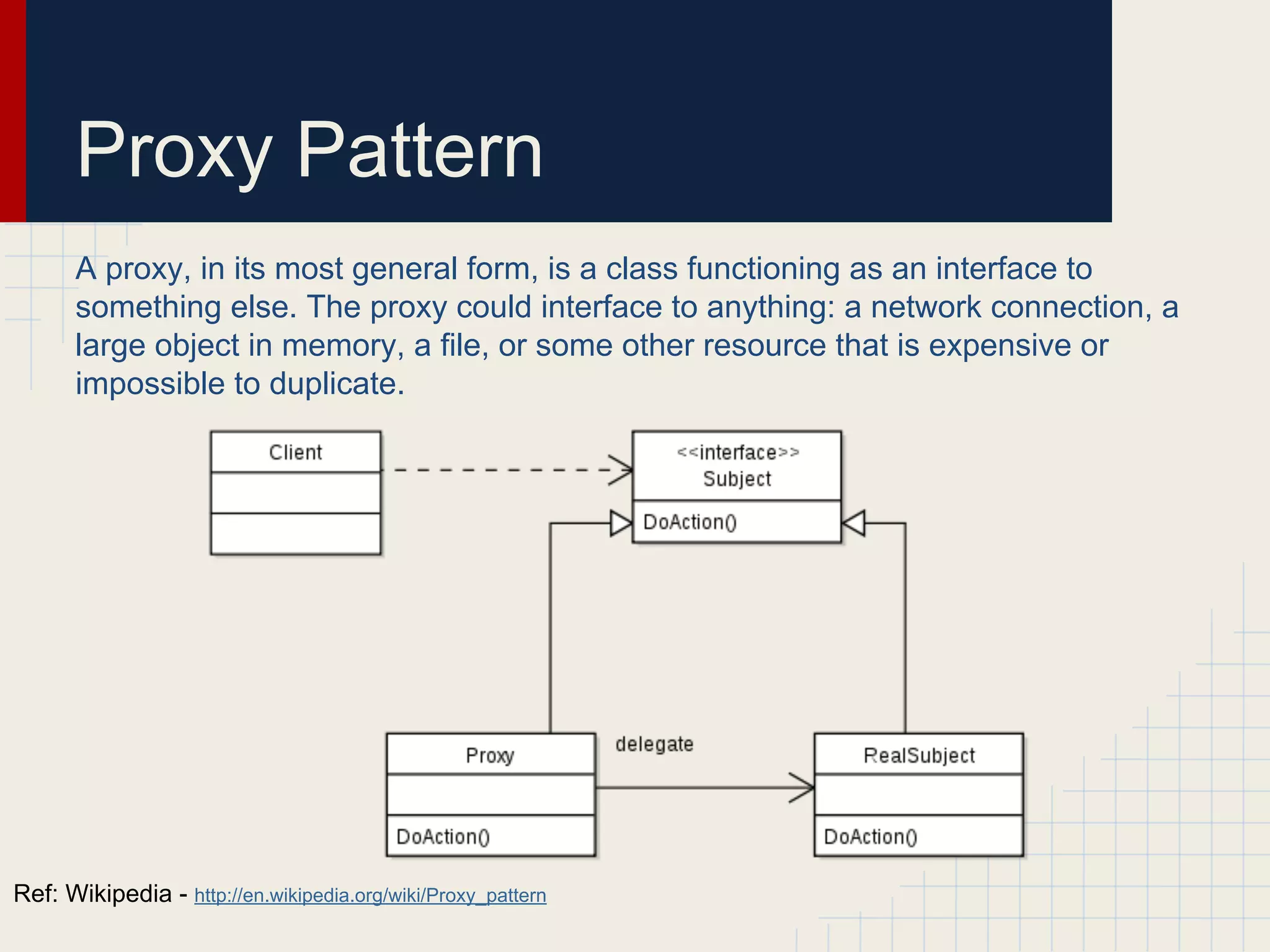
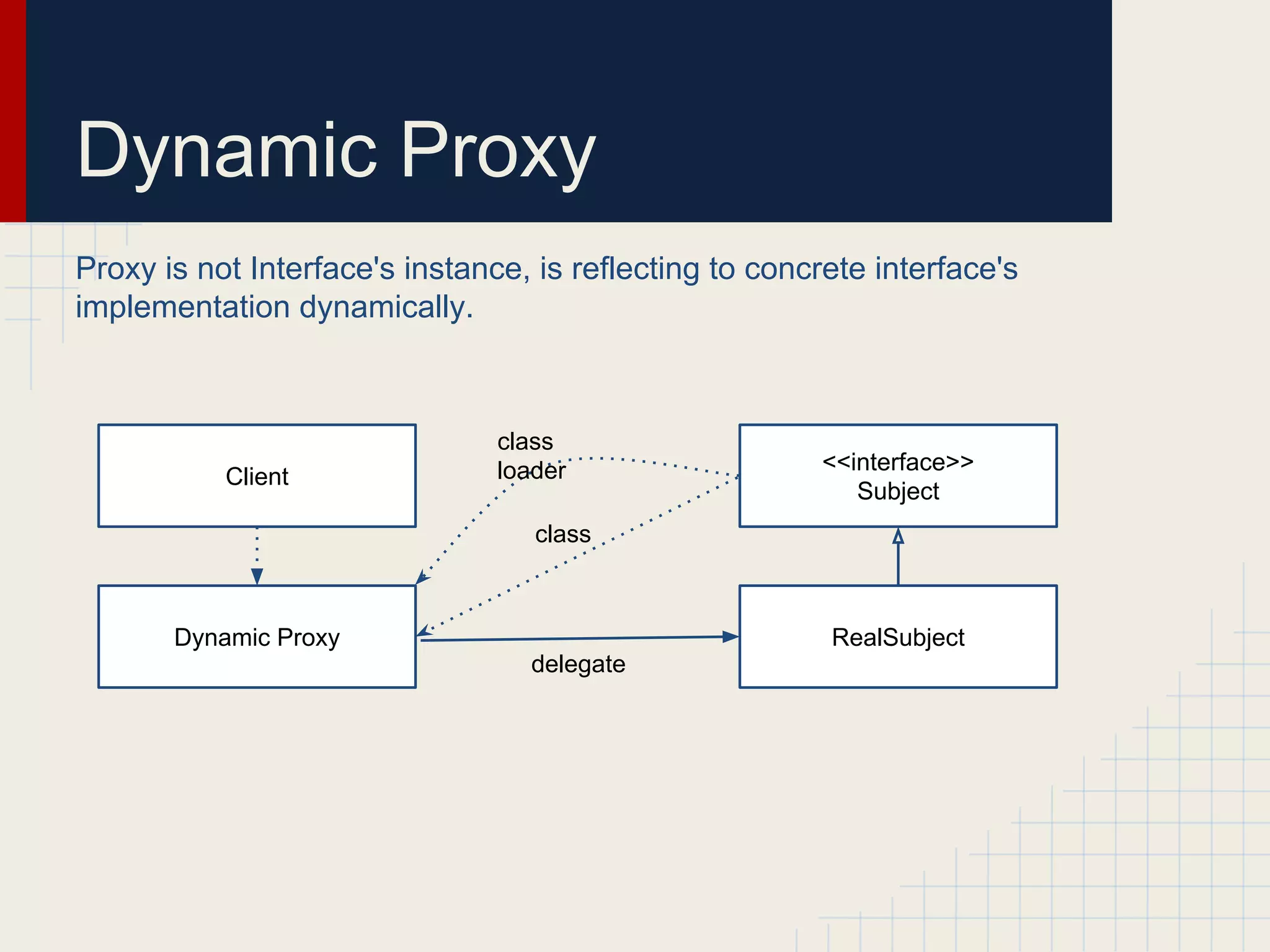
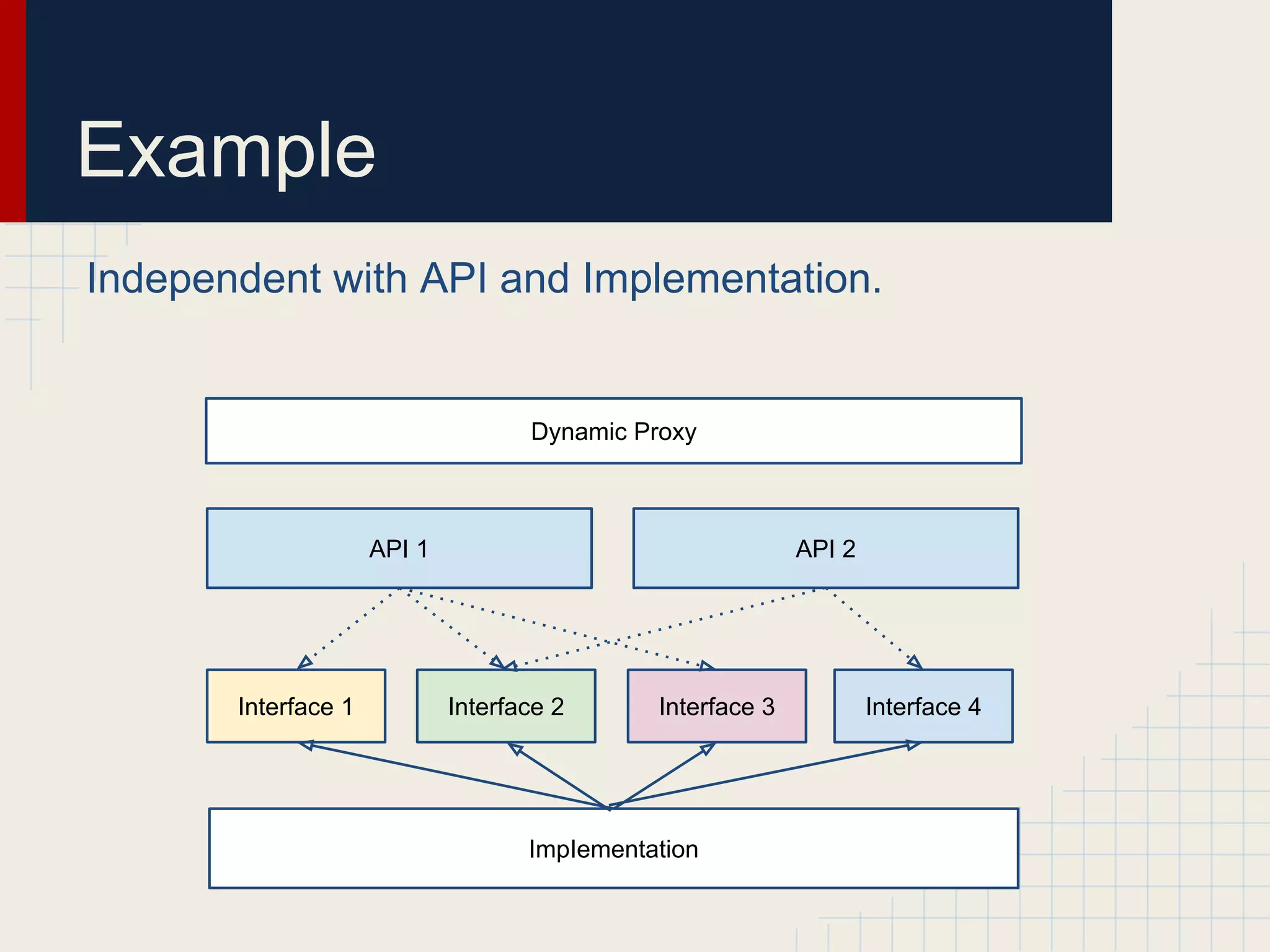
Dynamic proxies in Java allow an object to dynamically implement interfaces at runtime through reflection and runtime type information. This avoids tight coupling between interfaces and their implementations. Proxies delegate method calls to a real subject object behind the scenes, making it possible to implement interfaces without the implementation class directly implementing them.