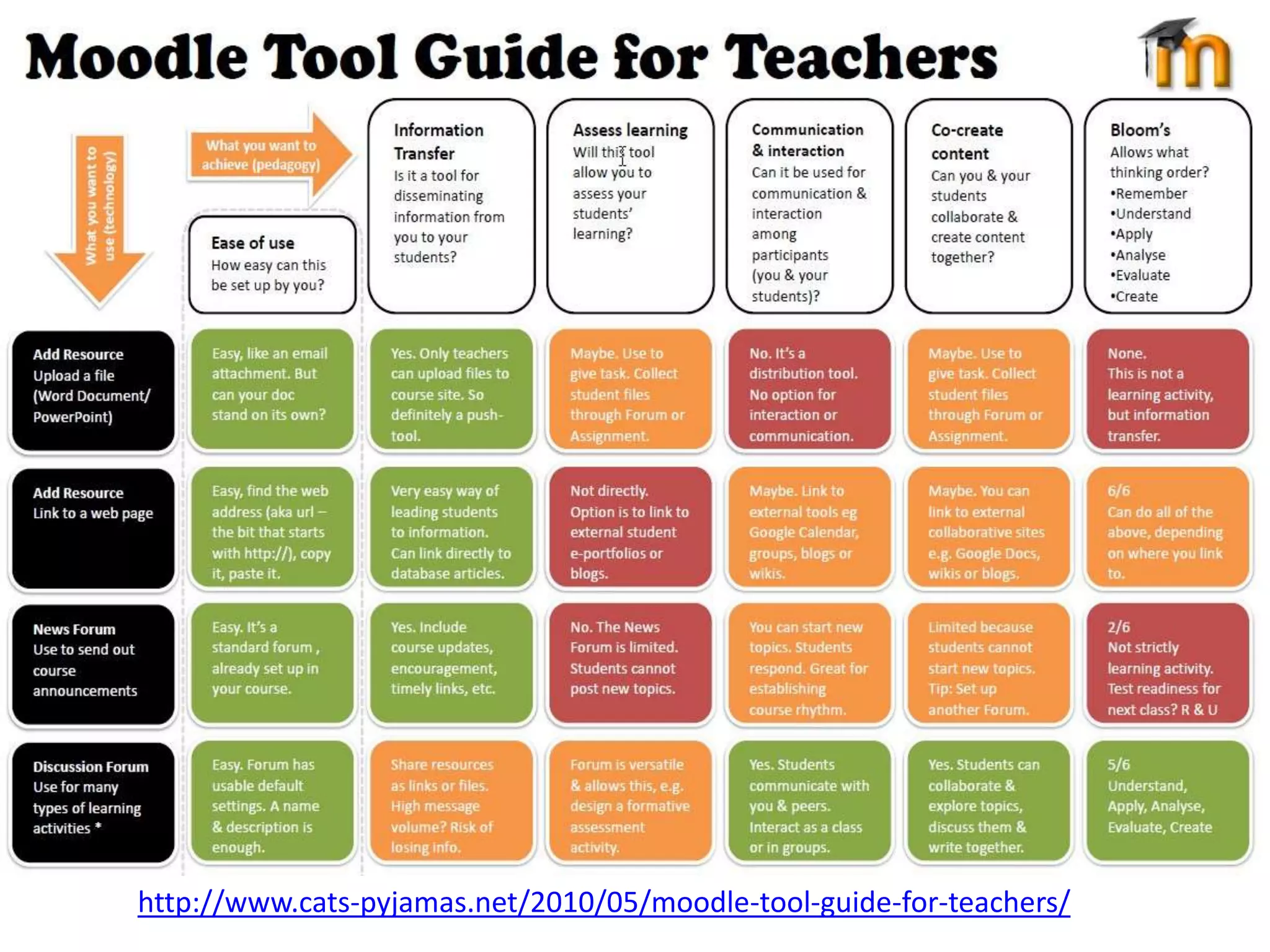
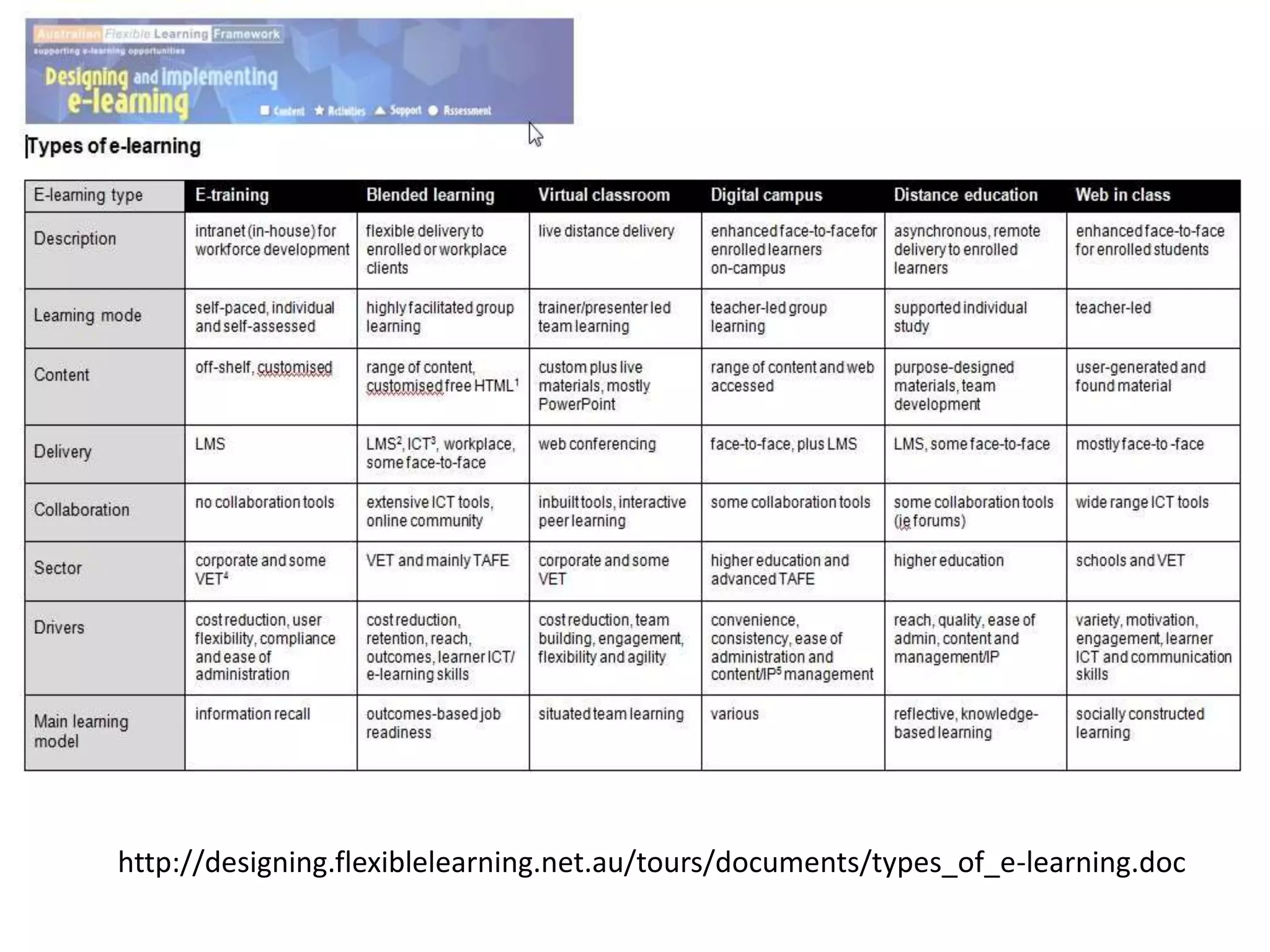
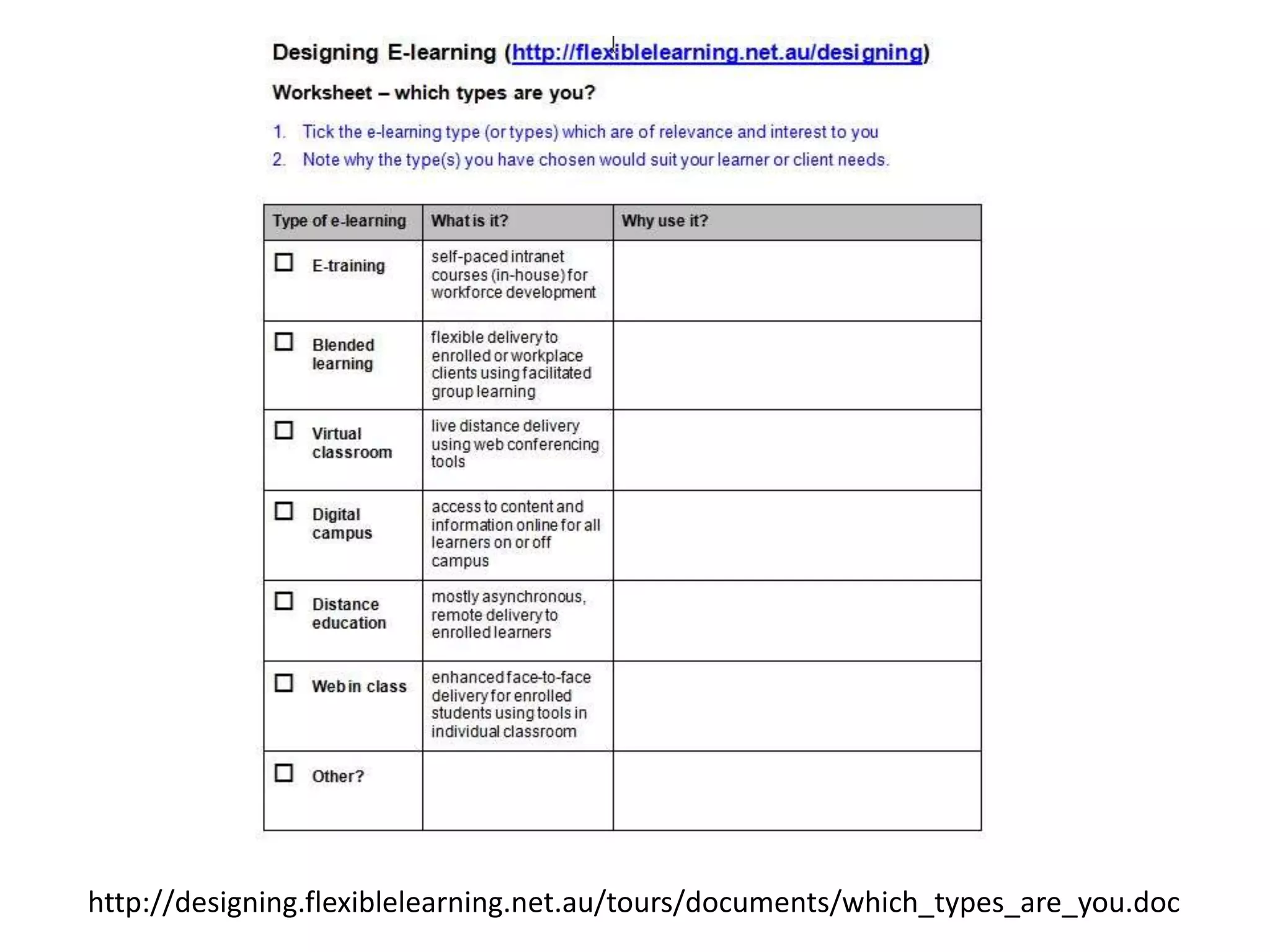
The document discusses different models of elearning and provides guidance on choosing the right model. It outlines 8 common elearning models: etraining, distance education, blended learning types 1 and 2, virtual classrooms types 1 and 2, communities of practice, MOOCs, and flipped classroom. It also discusses the extremes of self-paced vs facilitated elearning and notes facilitated has benefits like regular teacher presence and a richer learning experience but requires more resources. Overall, the document provides tips for designing an effective online course, including breaking content into bite-sized chunks, using a variety of tasks and activities, and providing regular feedback.