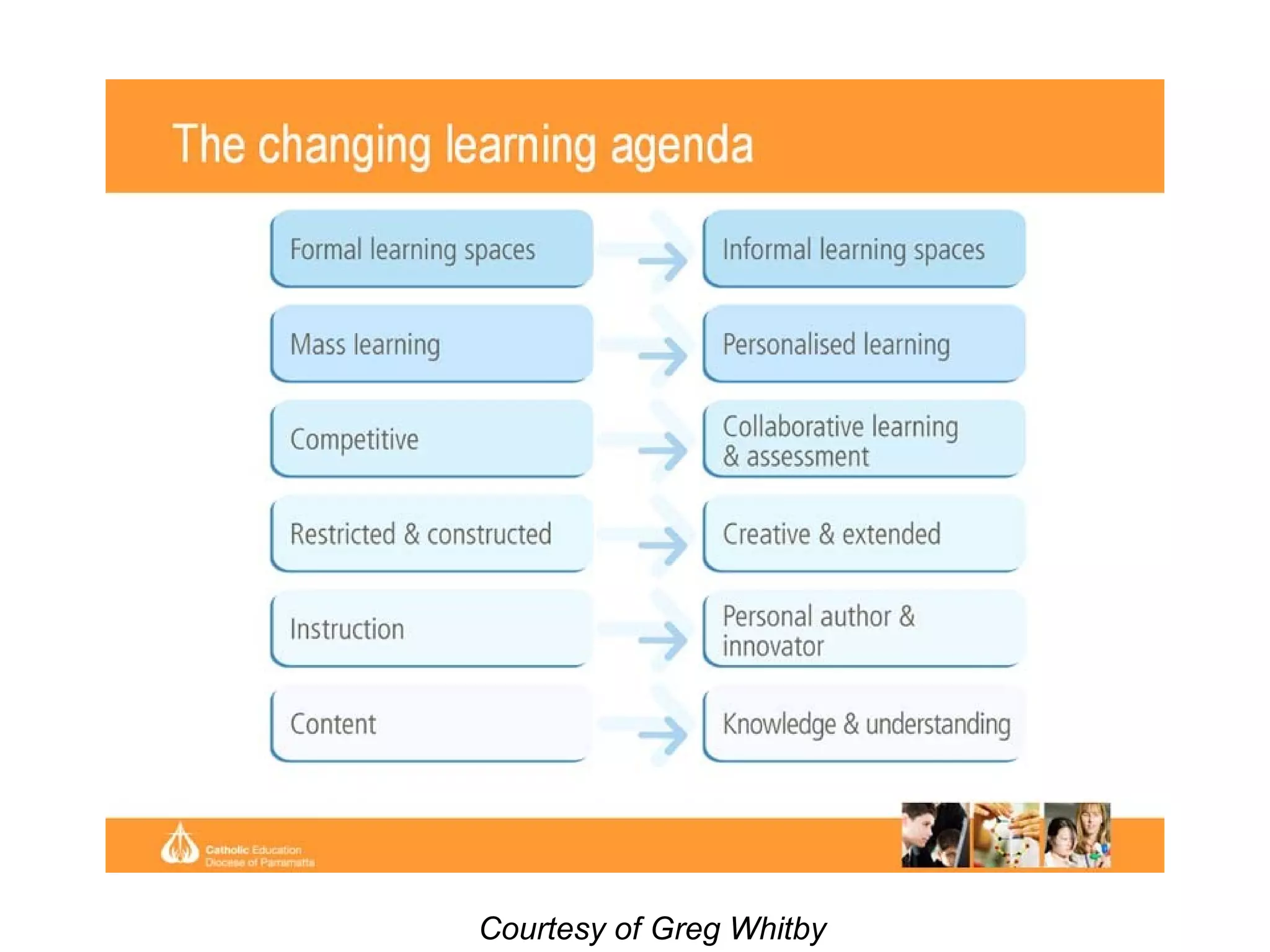
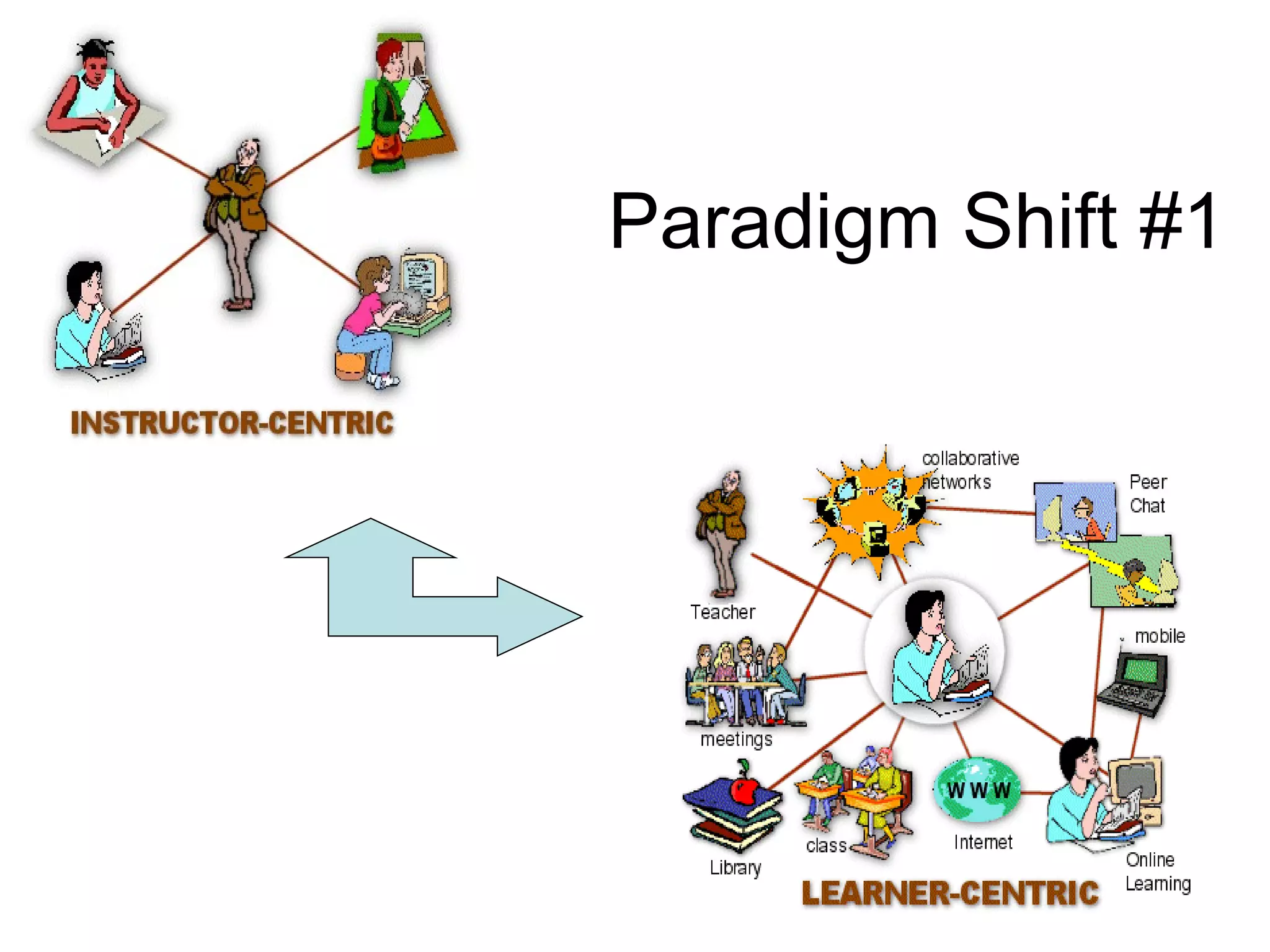
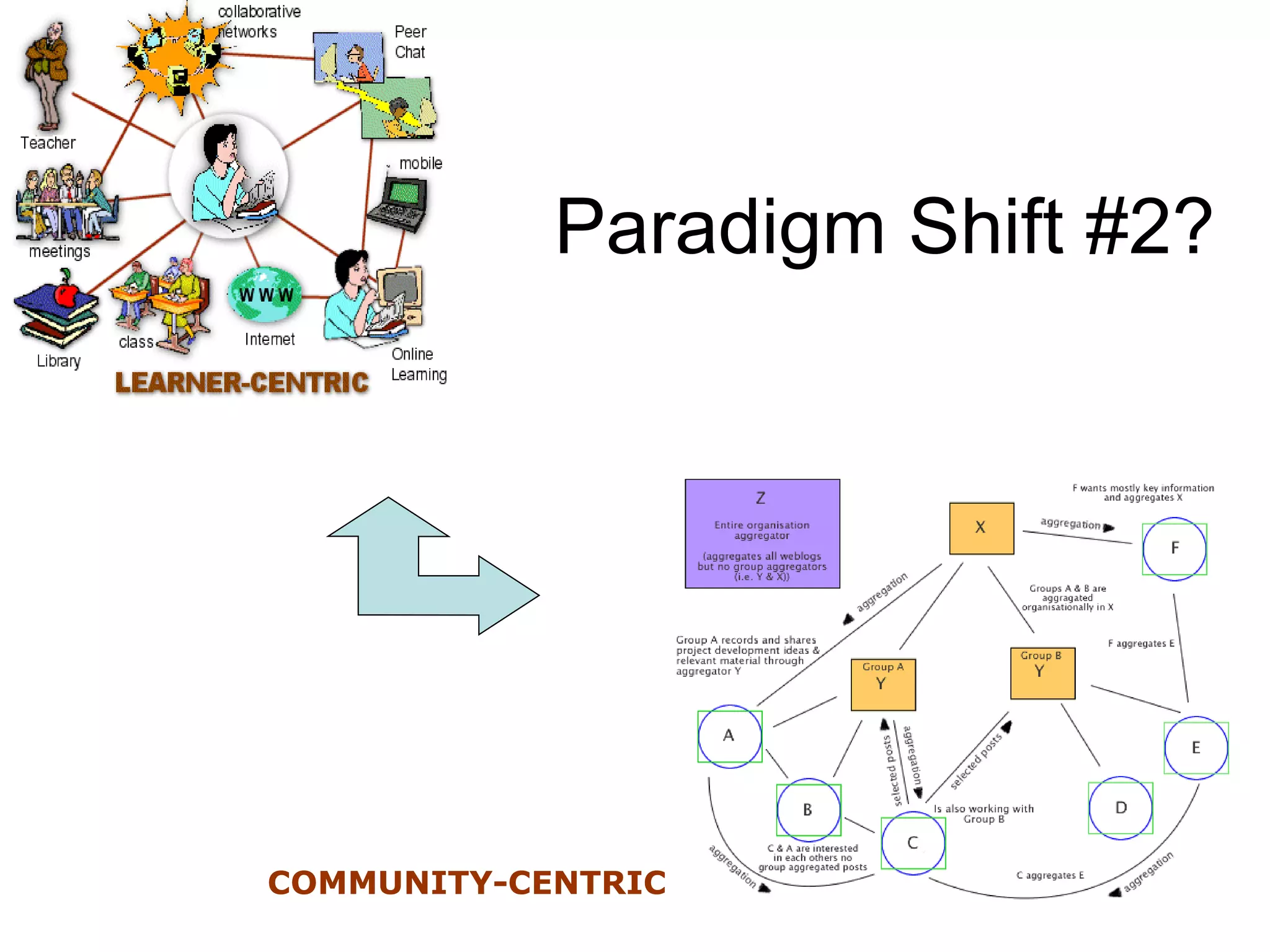
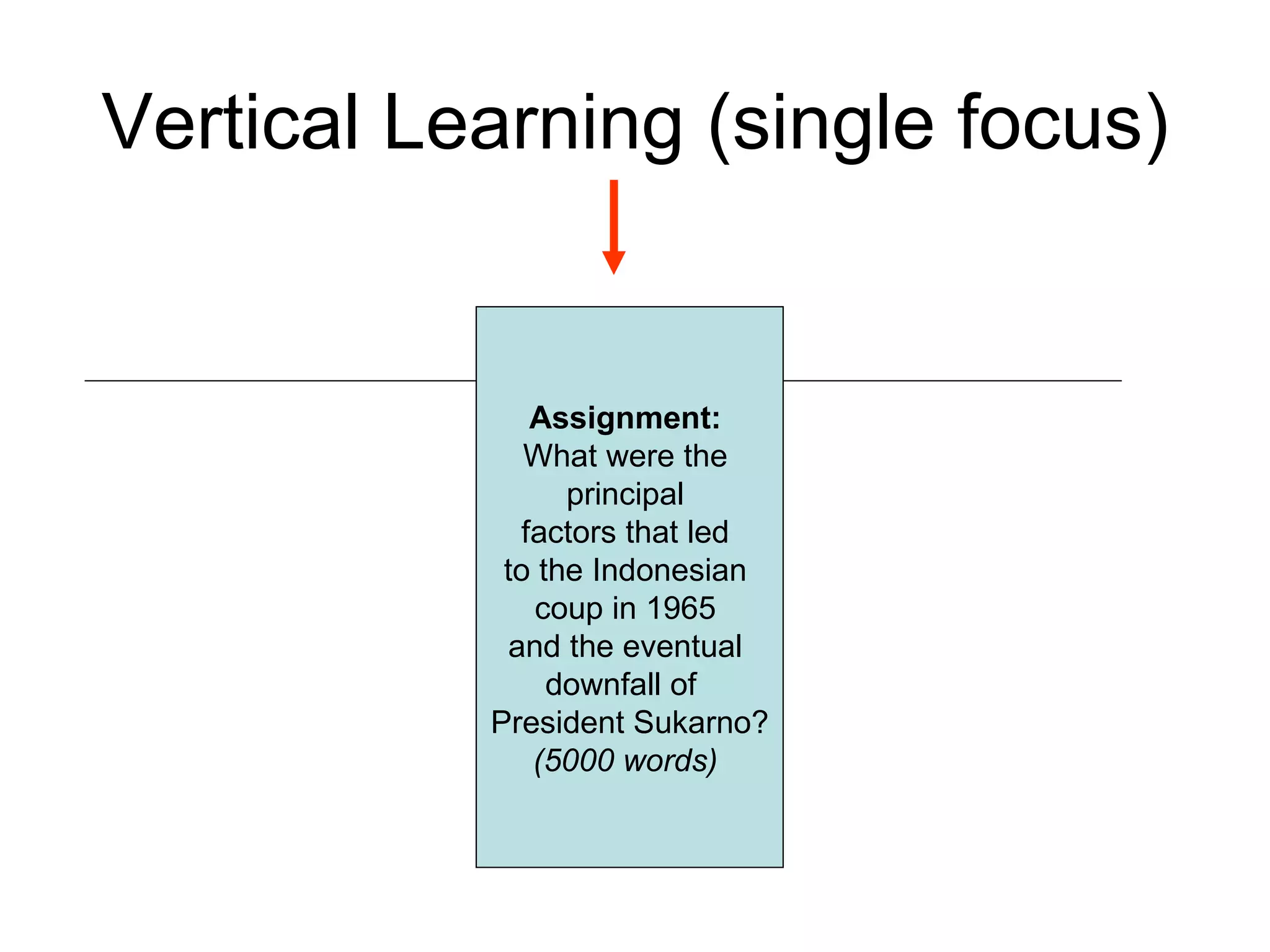
The document discusses the evolution from traditional eLearning (1.0) to a more interactive and user-centered eLearning (2.0) that utilizes social networking, allowing students to generate content and engage with peers and global sources. It emphasizes the paradigm shifts in education, focusing on connectivism and the need for educators to adapt to technology and participatory media to facilitate effective learning experiences. The text advocates for a model where learners actively construct knowledge rather than passively receive it, and highlights the importance of informal learning and community engagement.