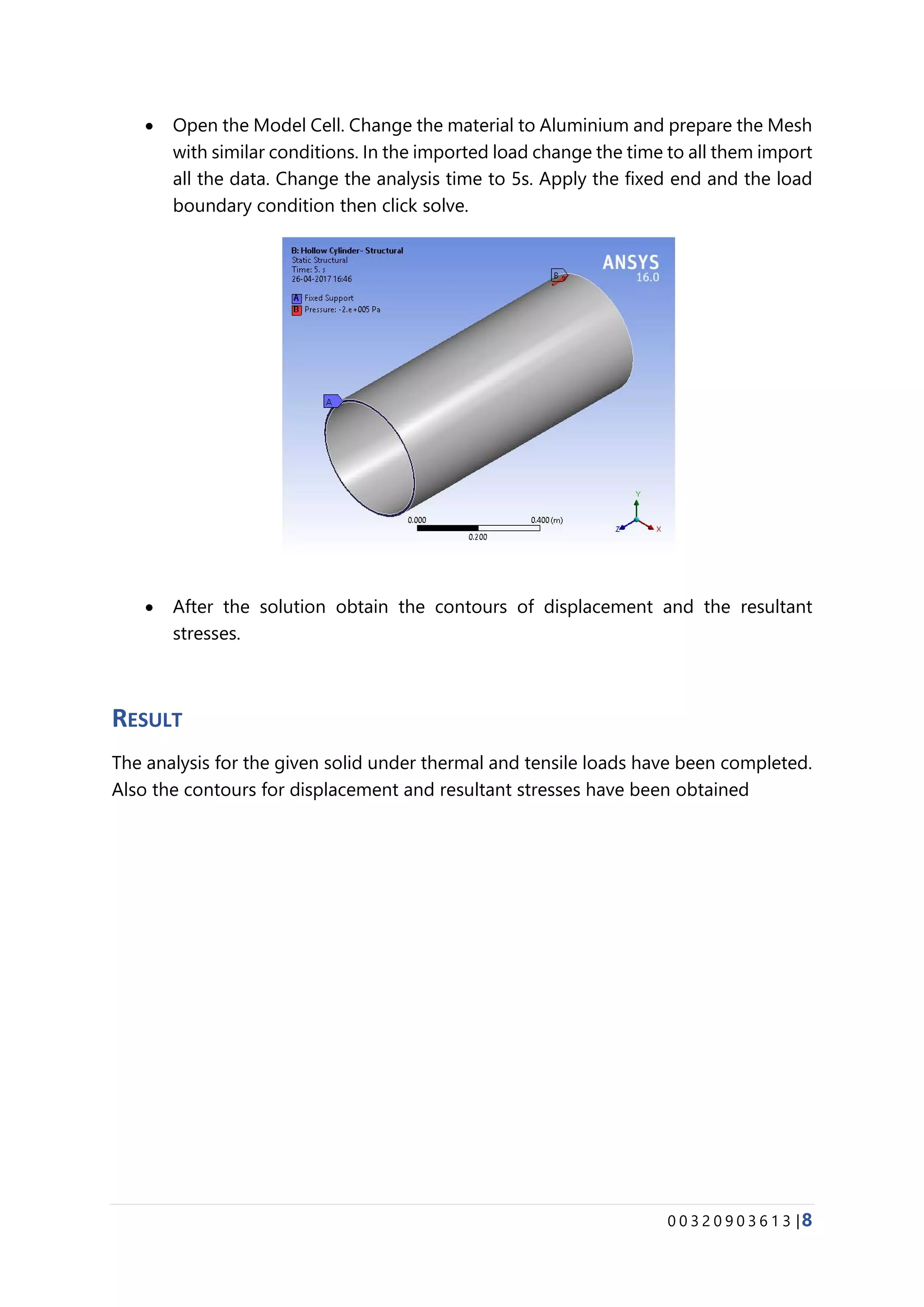
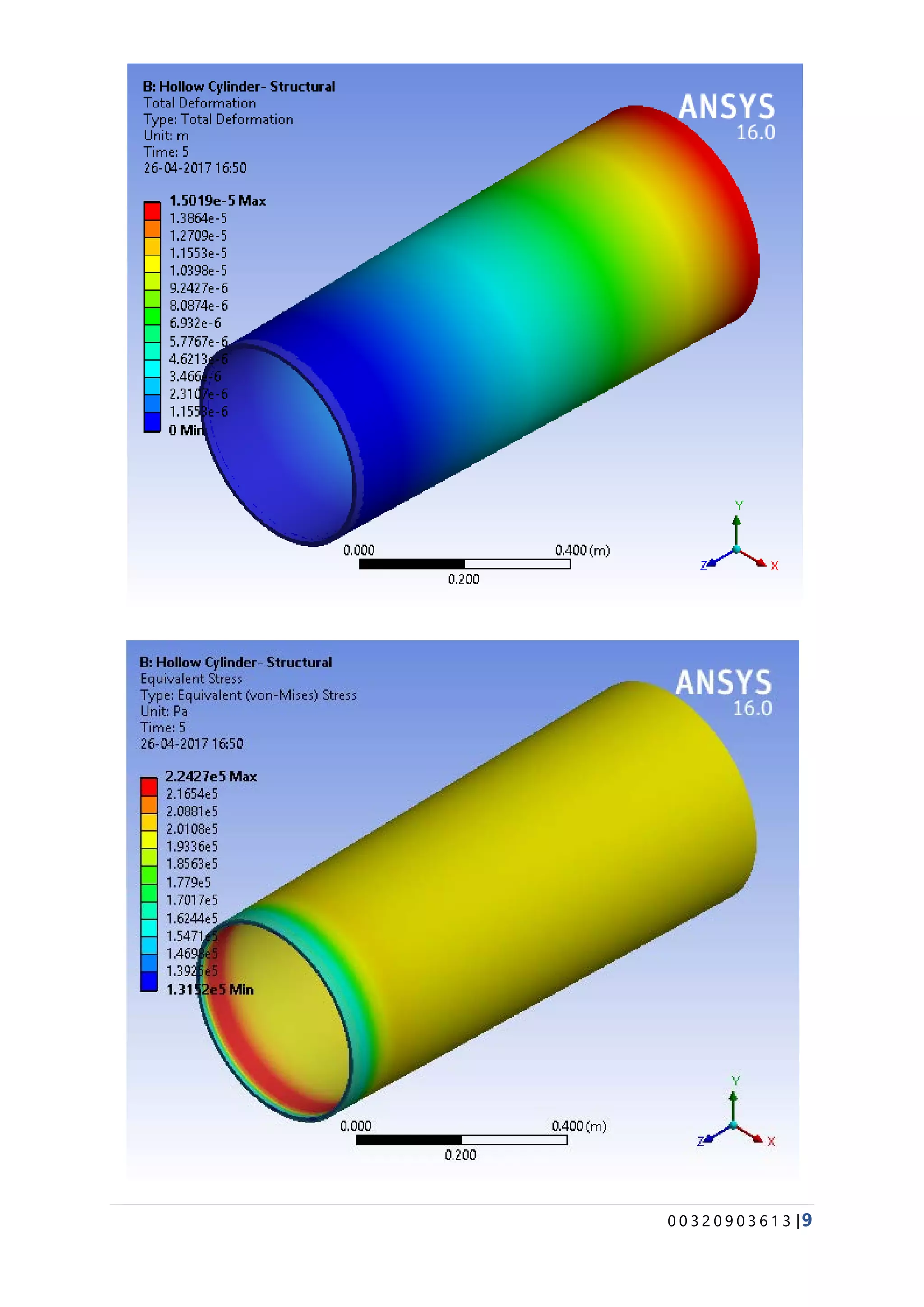
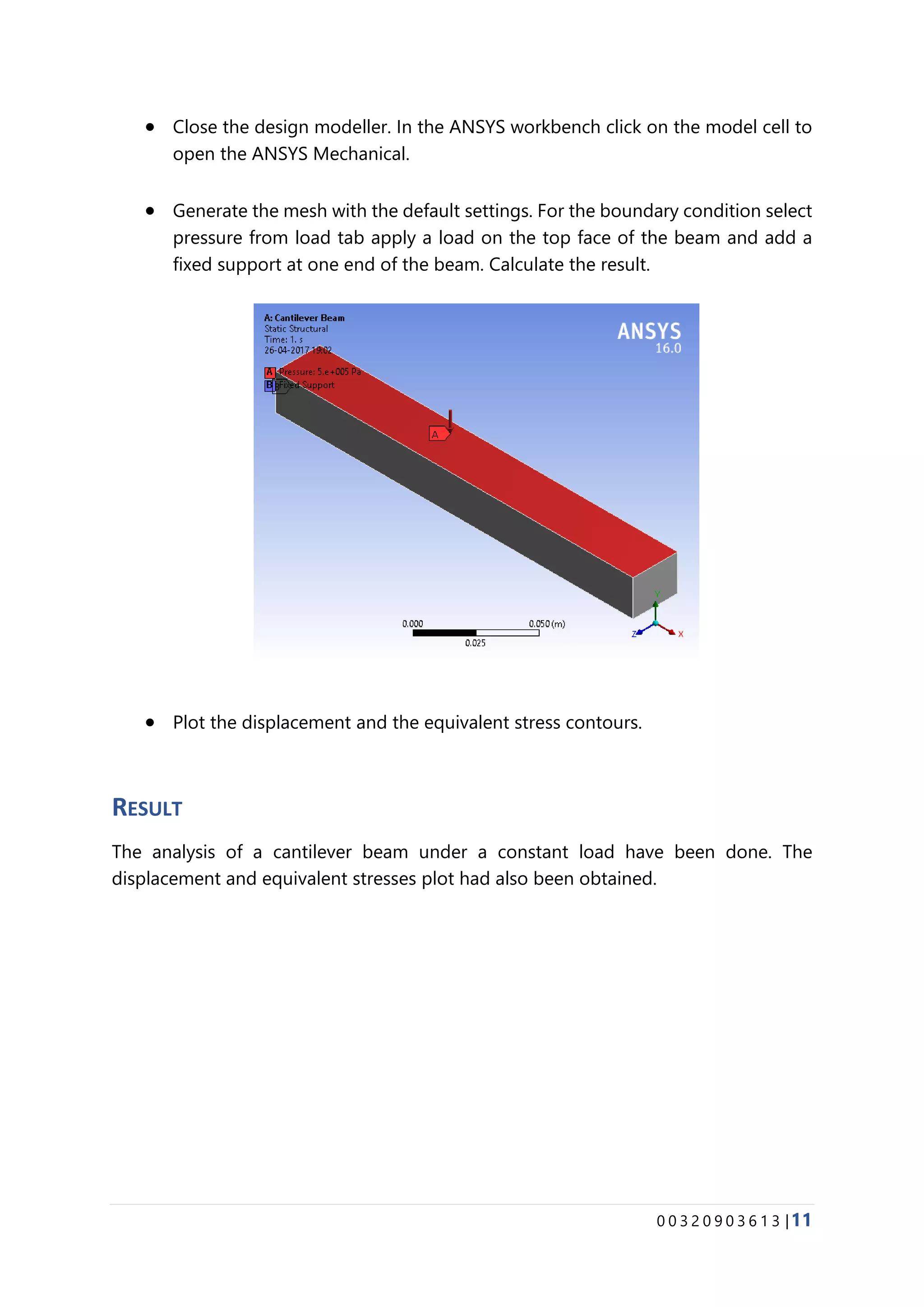
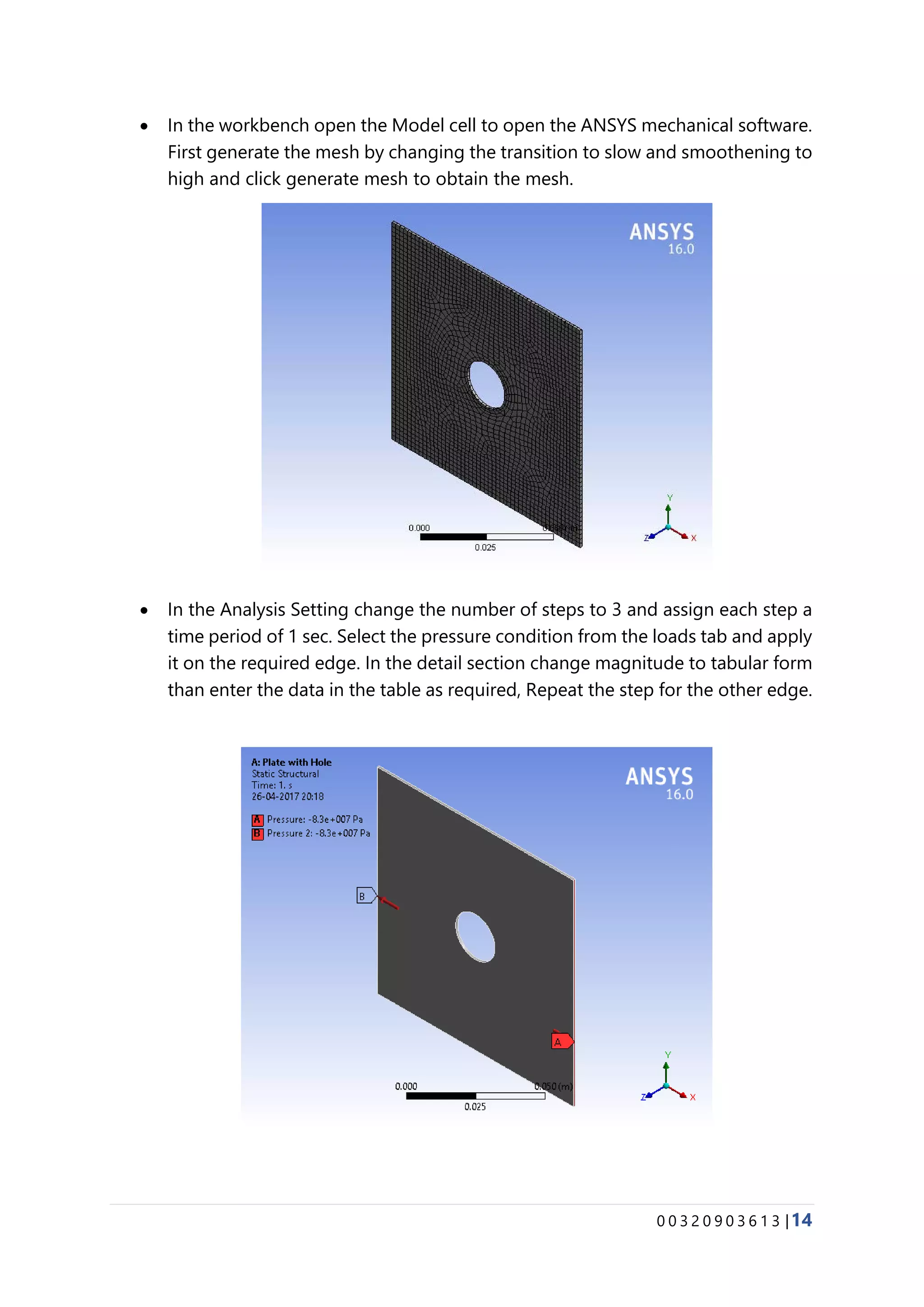
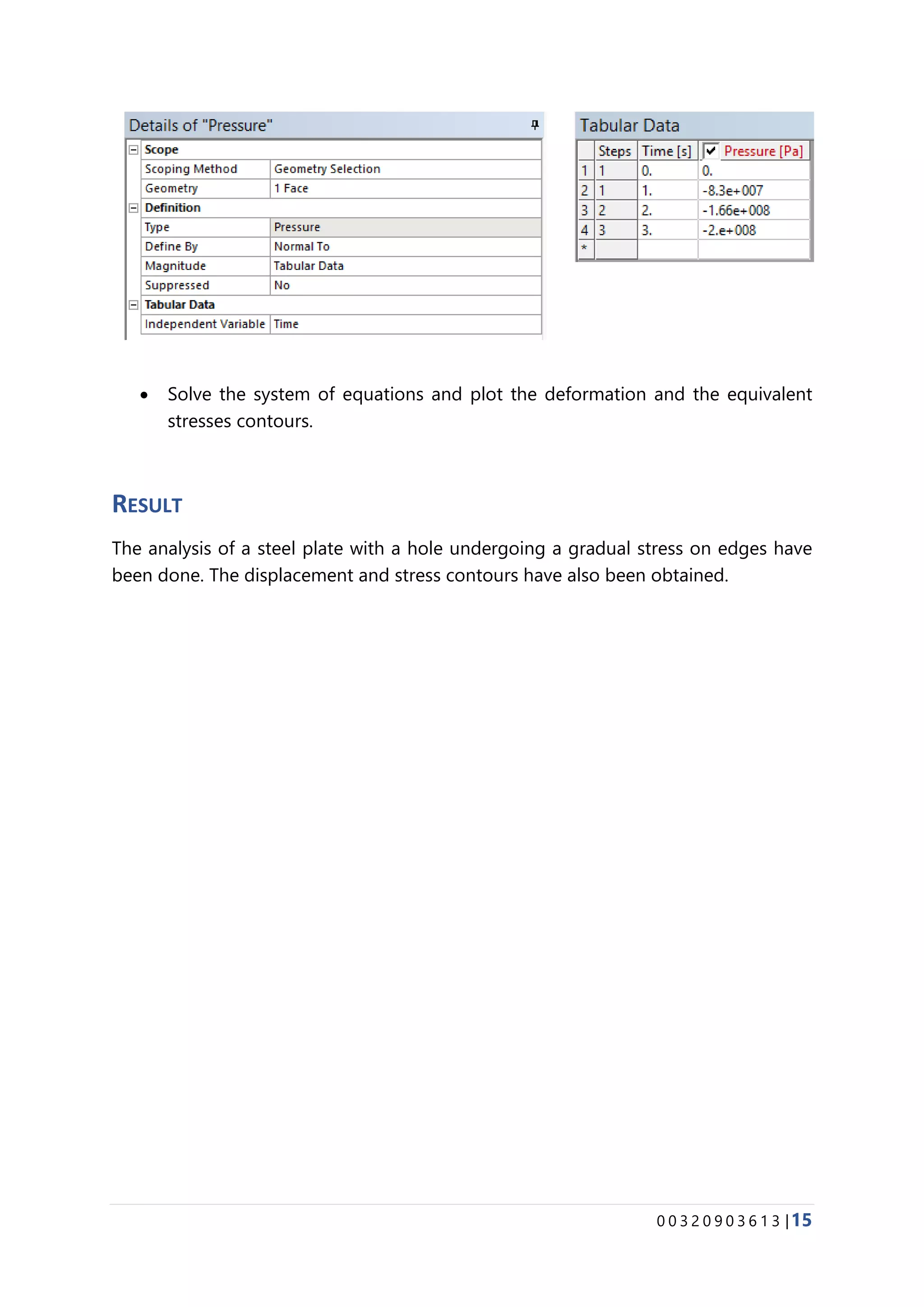
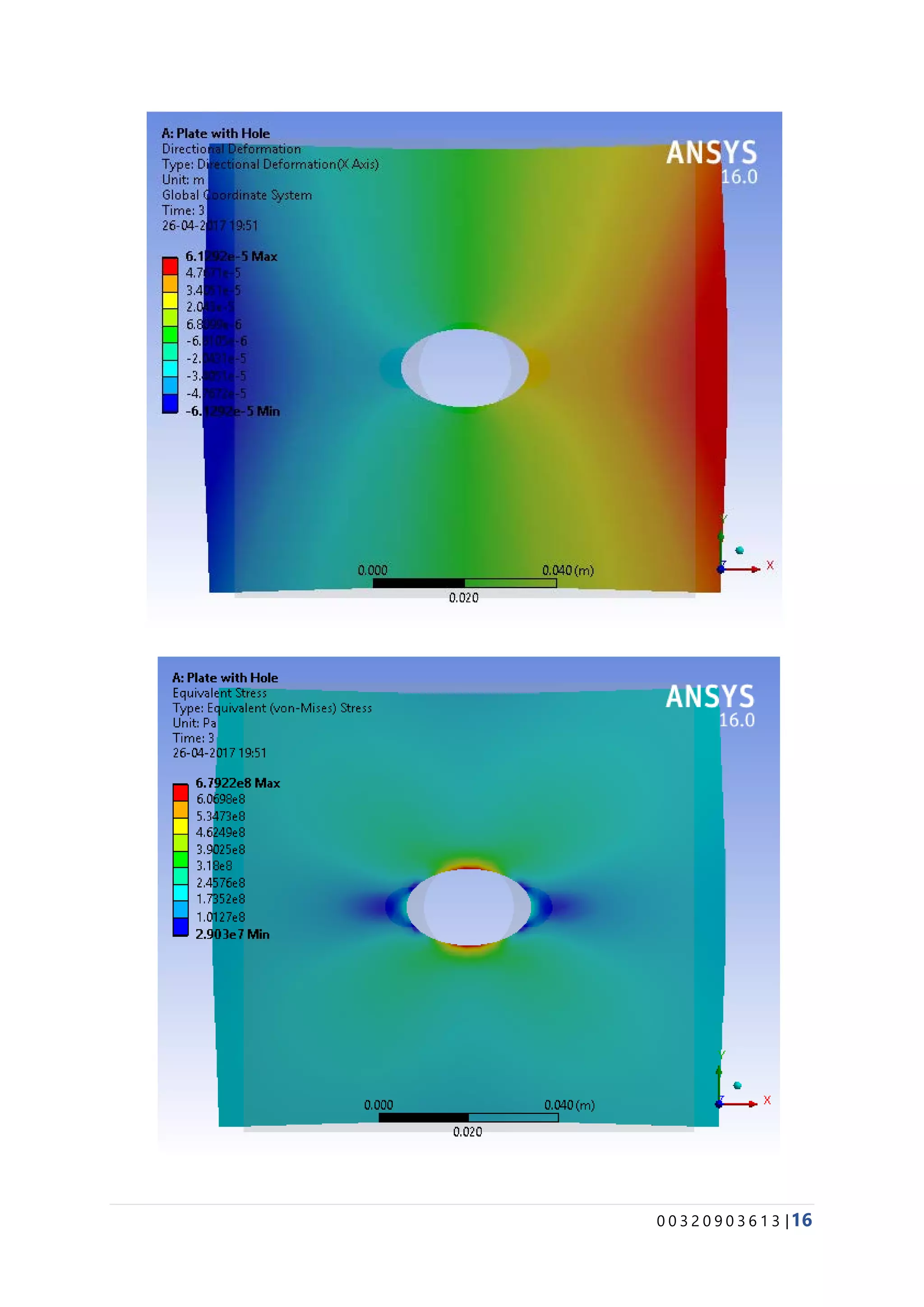
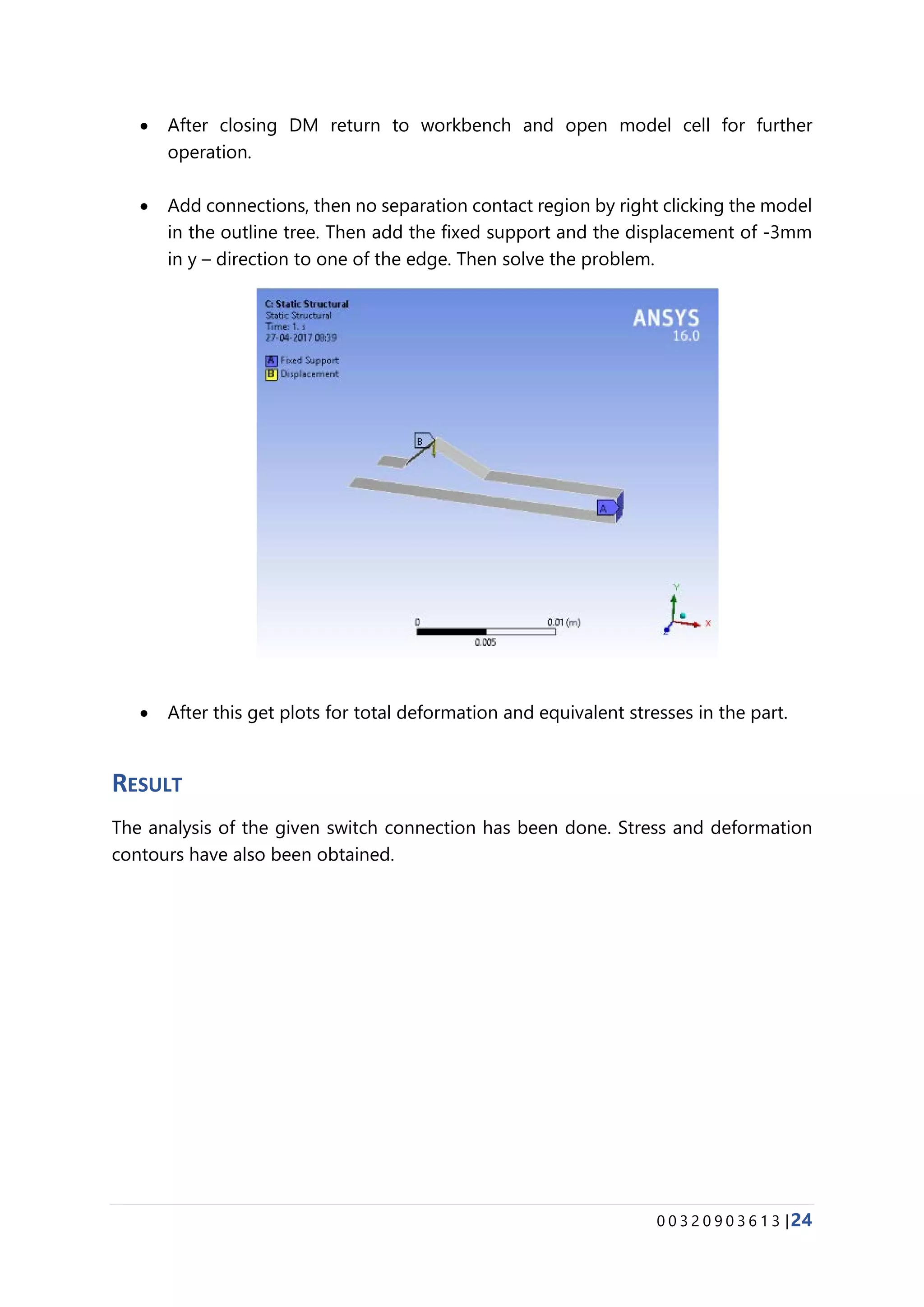
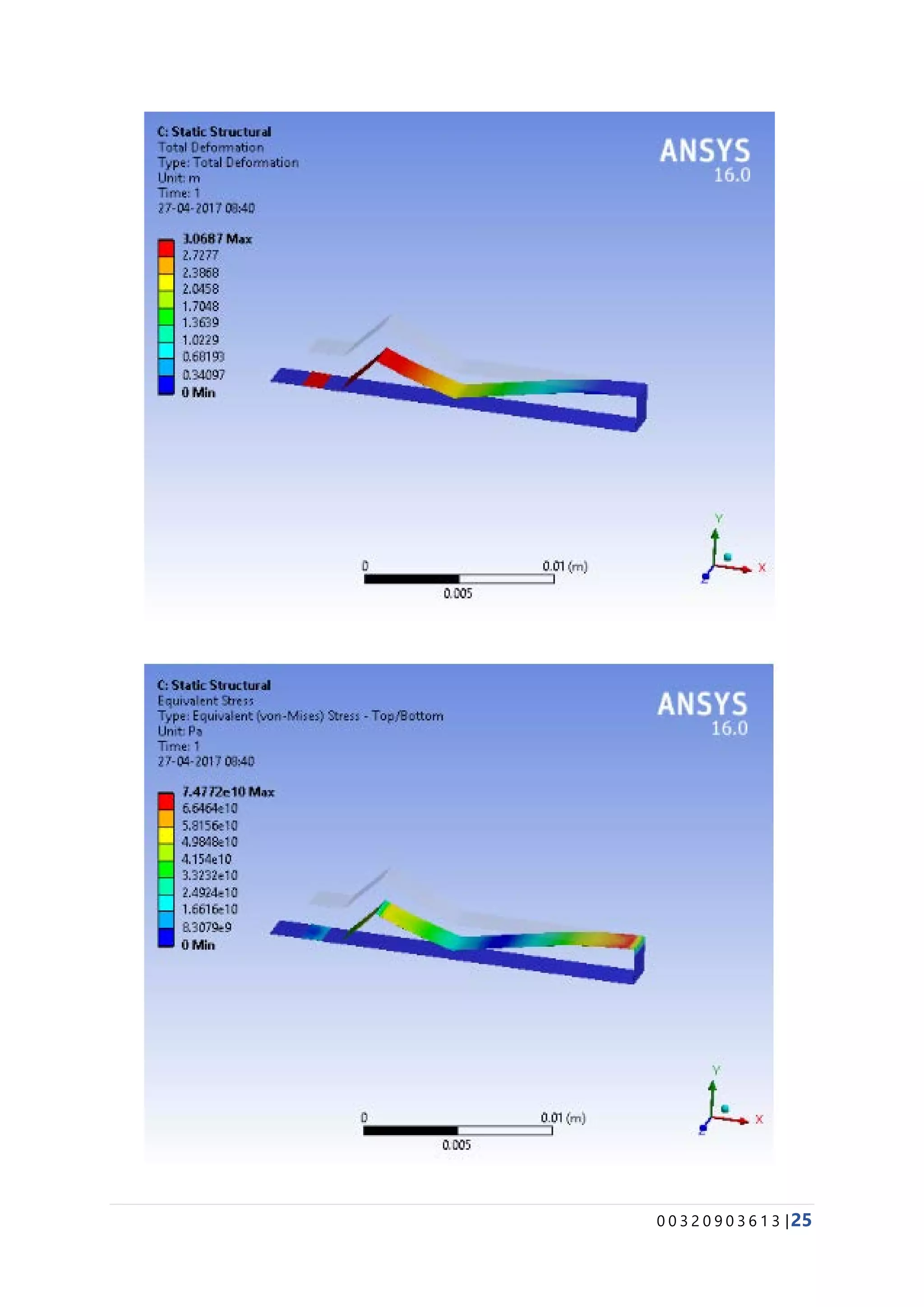
The document provides details about conducting various structural analysis simulations using ANSYS. It begins with an introduction to the basic functionalities of ANSYS structural modules for preprocessing, simulation, and postprocessing. It then presents the steps taken to analyze 7 different engineering problems using ANSYS, including a solid undergoing thermal expansion and mechanical loading, a cantilever beam under stress, a plate with a hole under increasing stress, a truss structure under load, a bar with varying diameter under load, and a mechanical switch interaction. For each problem, the document outlines the geometry creation, meshing, boundary conditions, and results obtained from the ANSYS simulation.