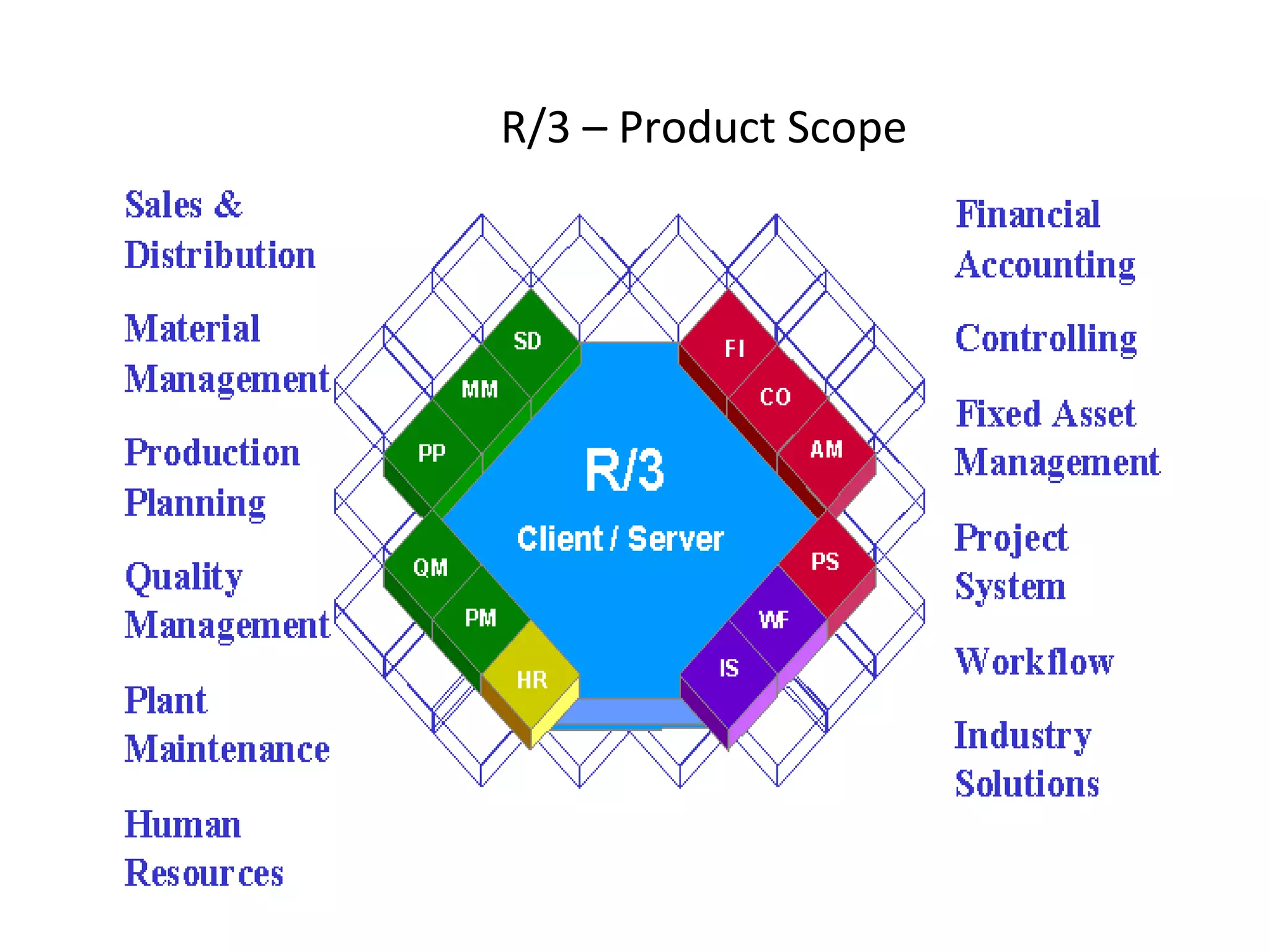
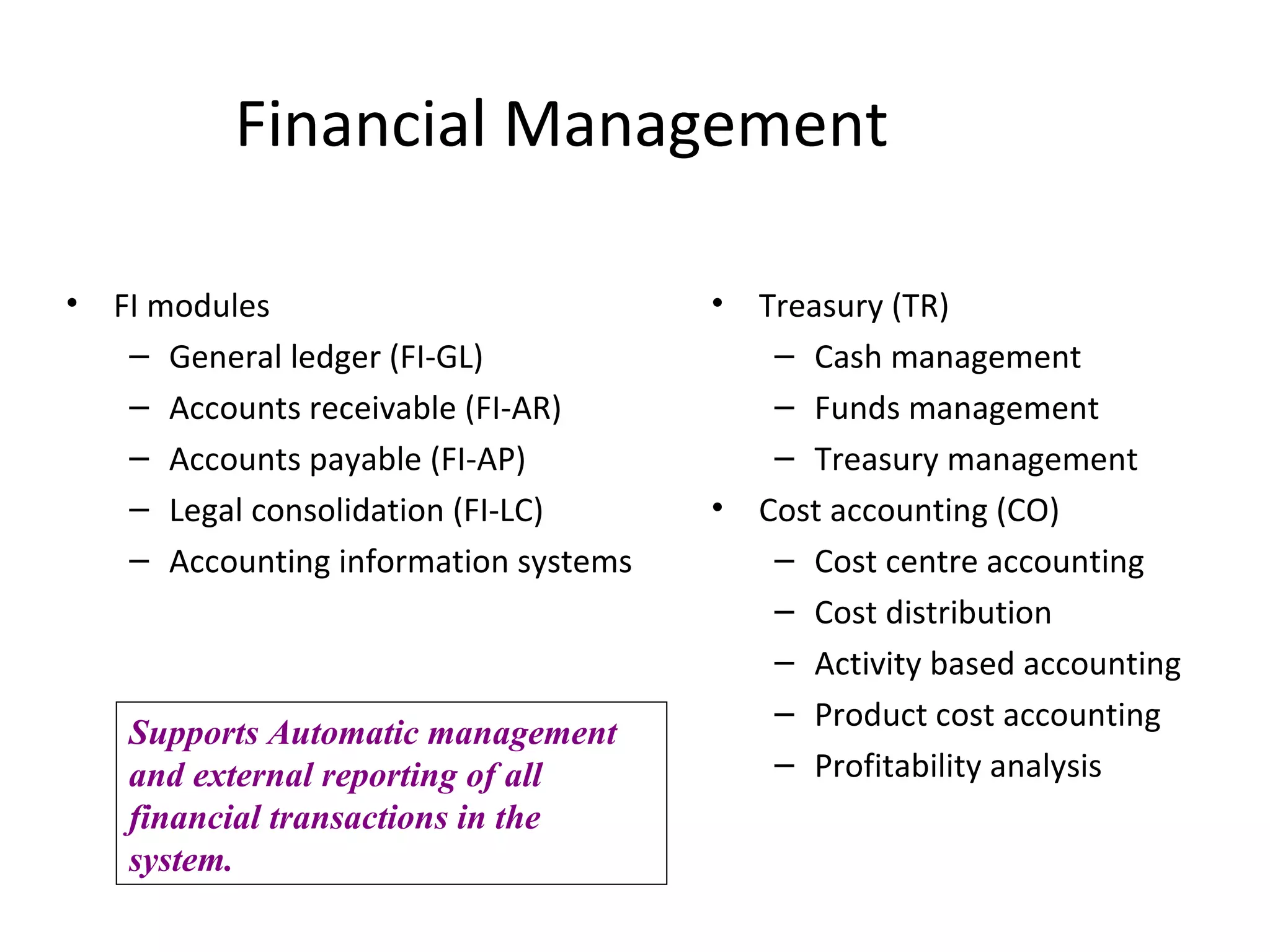
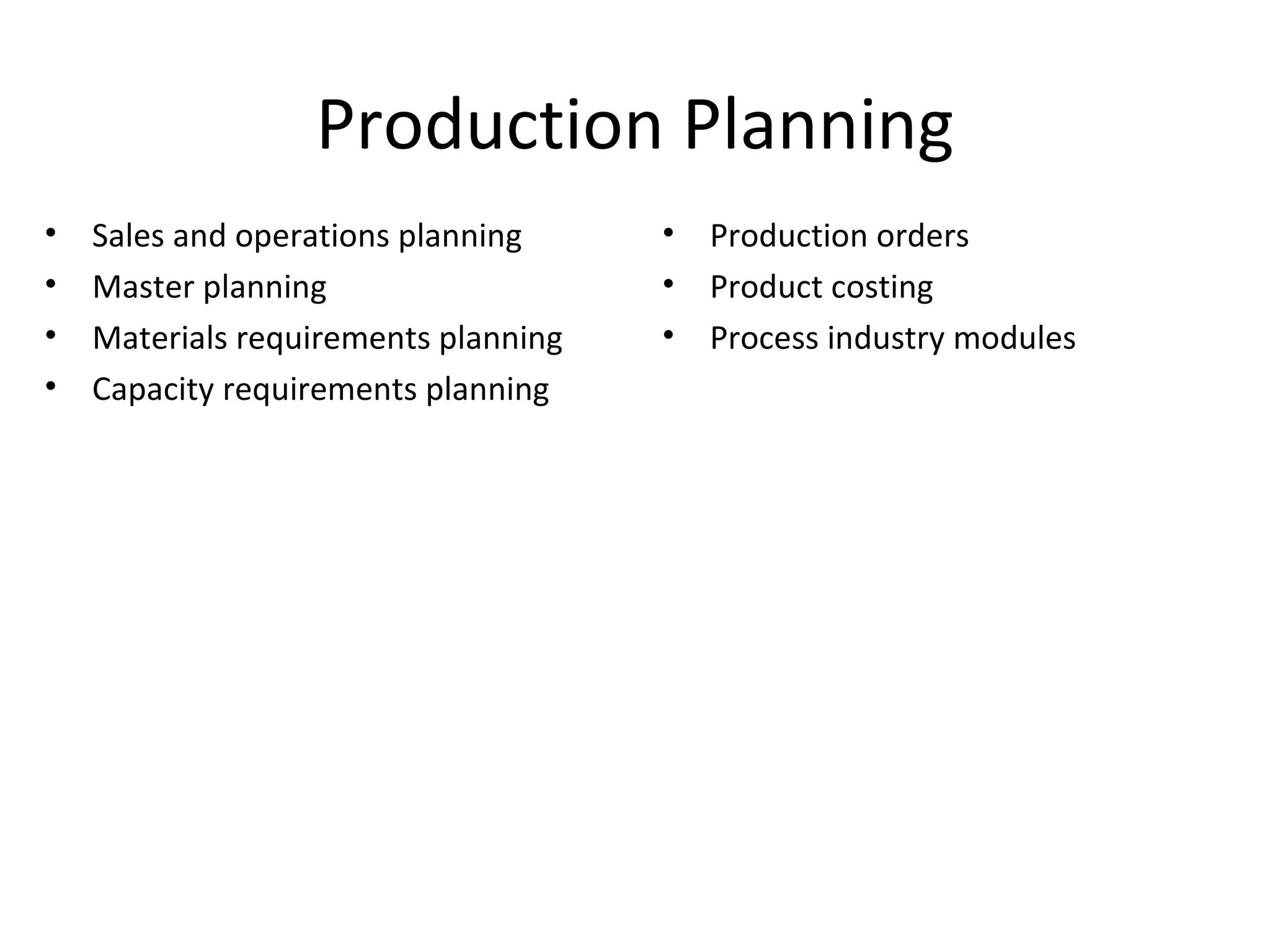
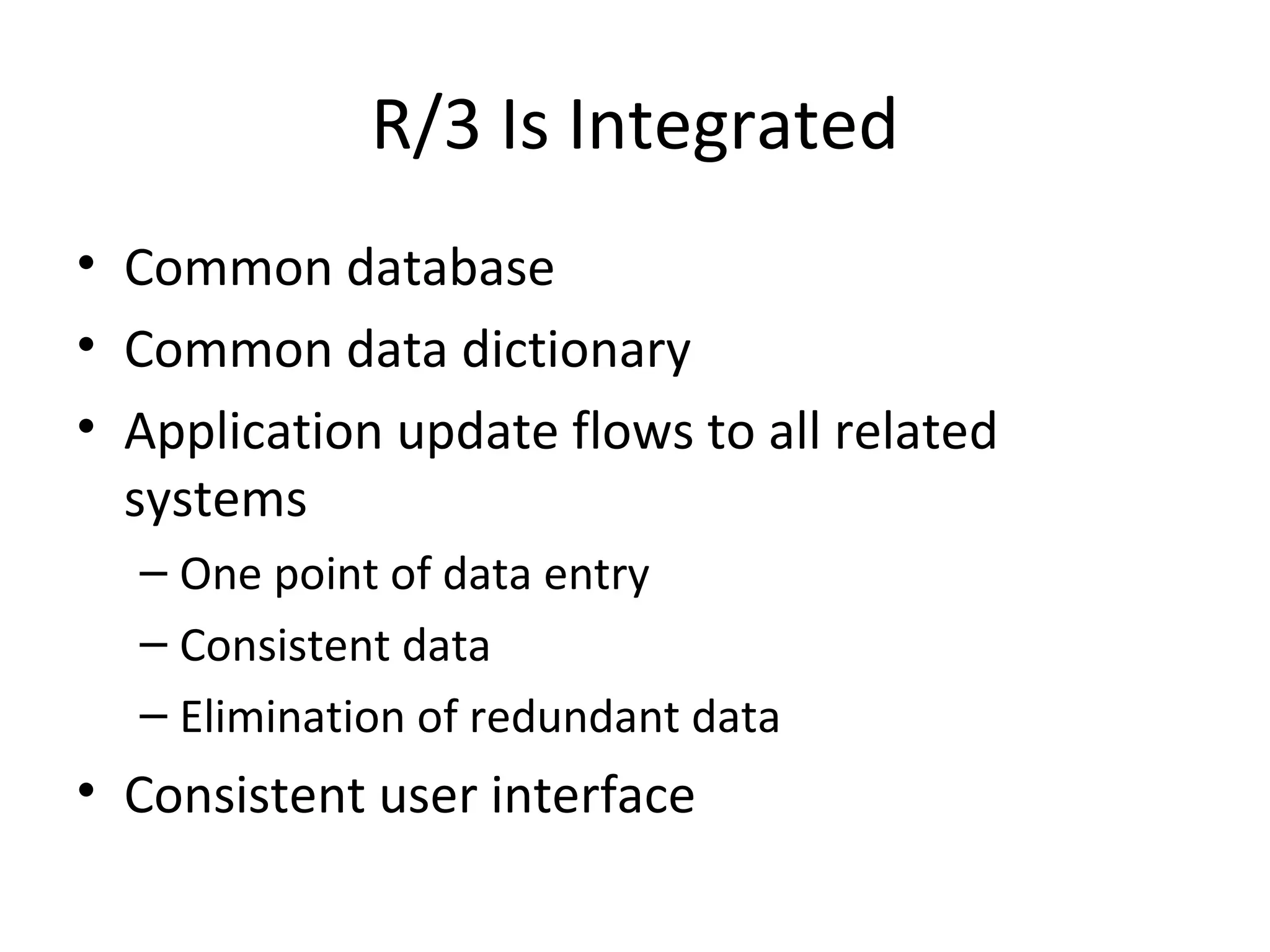
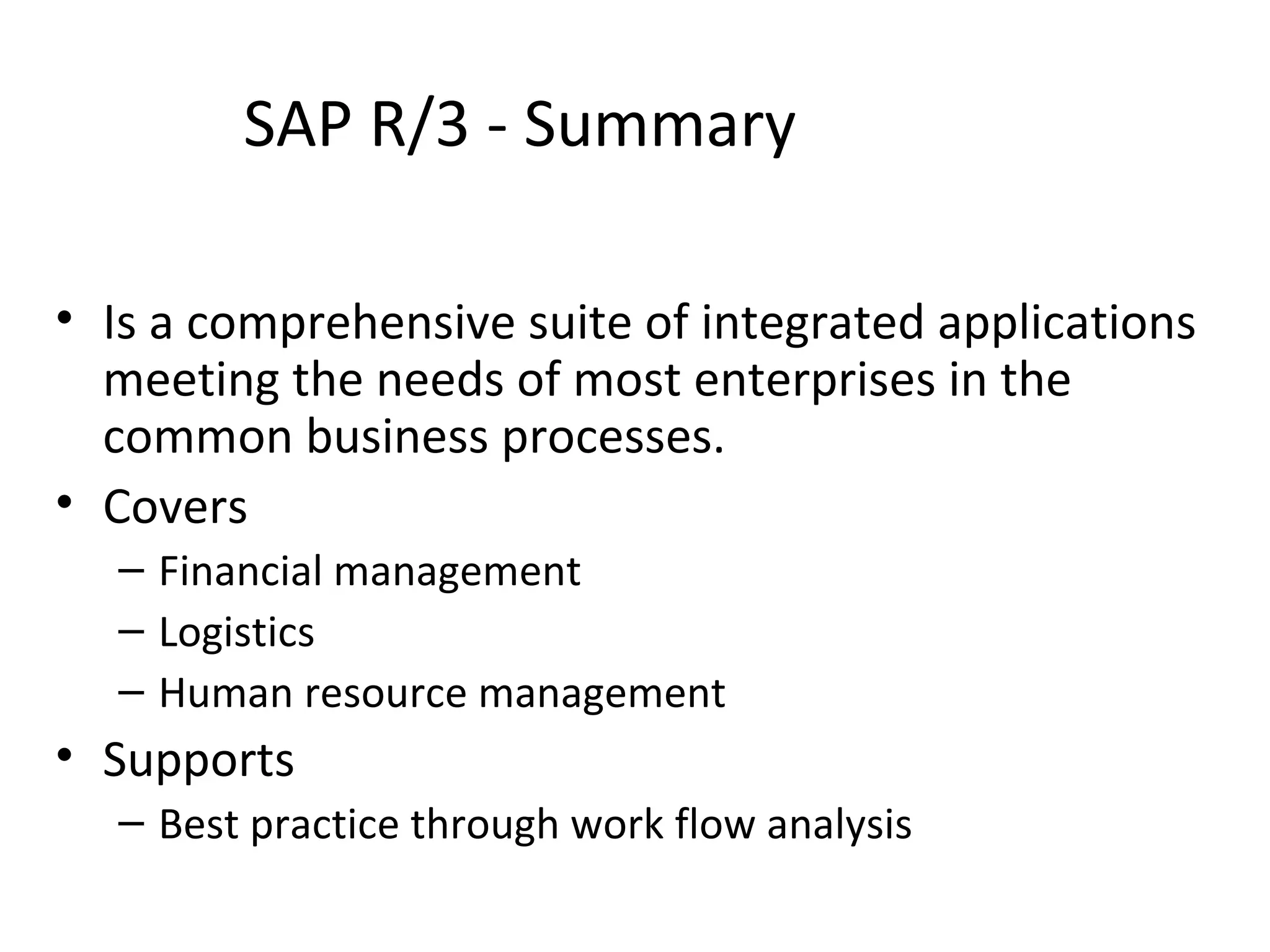
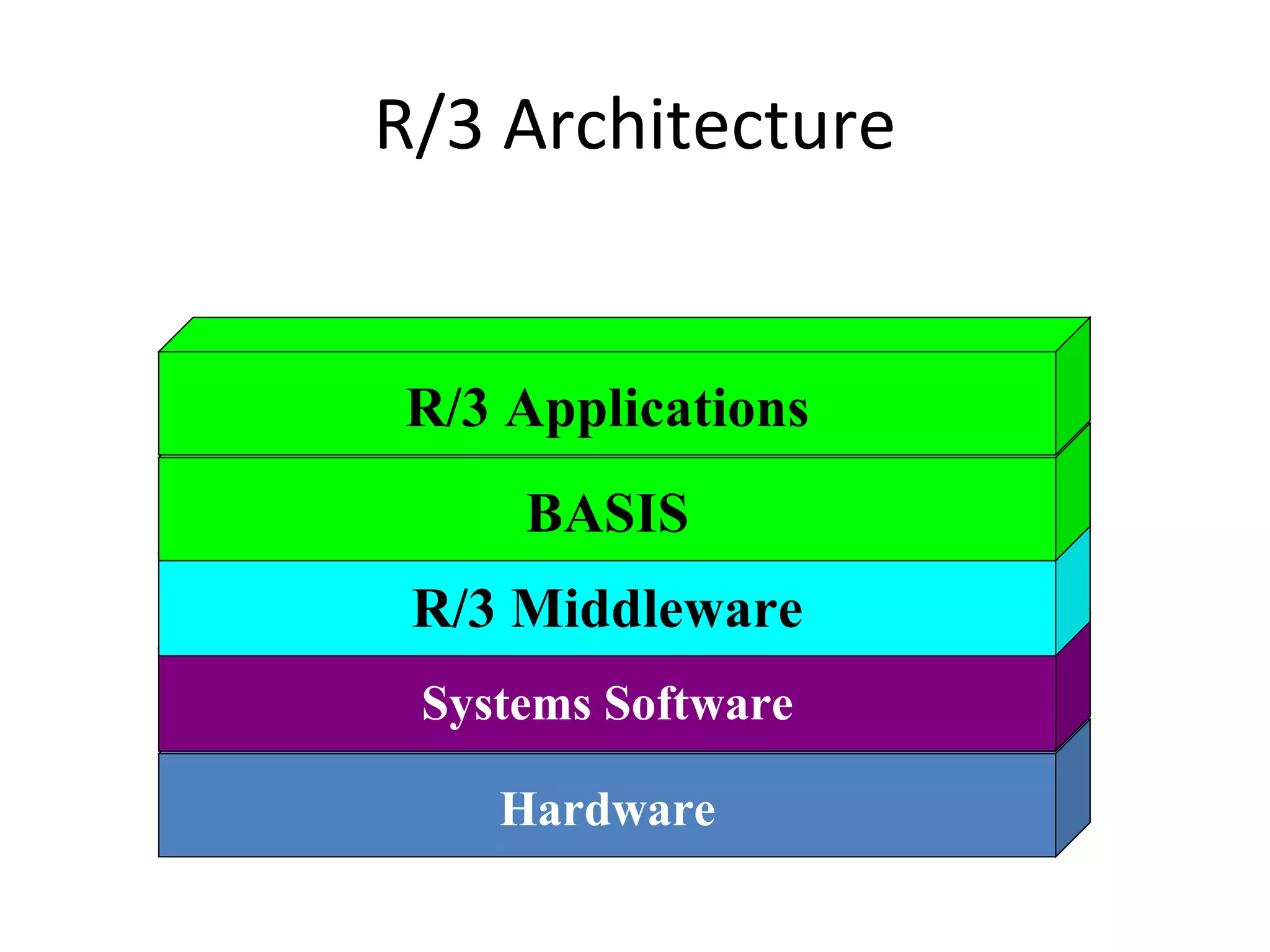
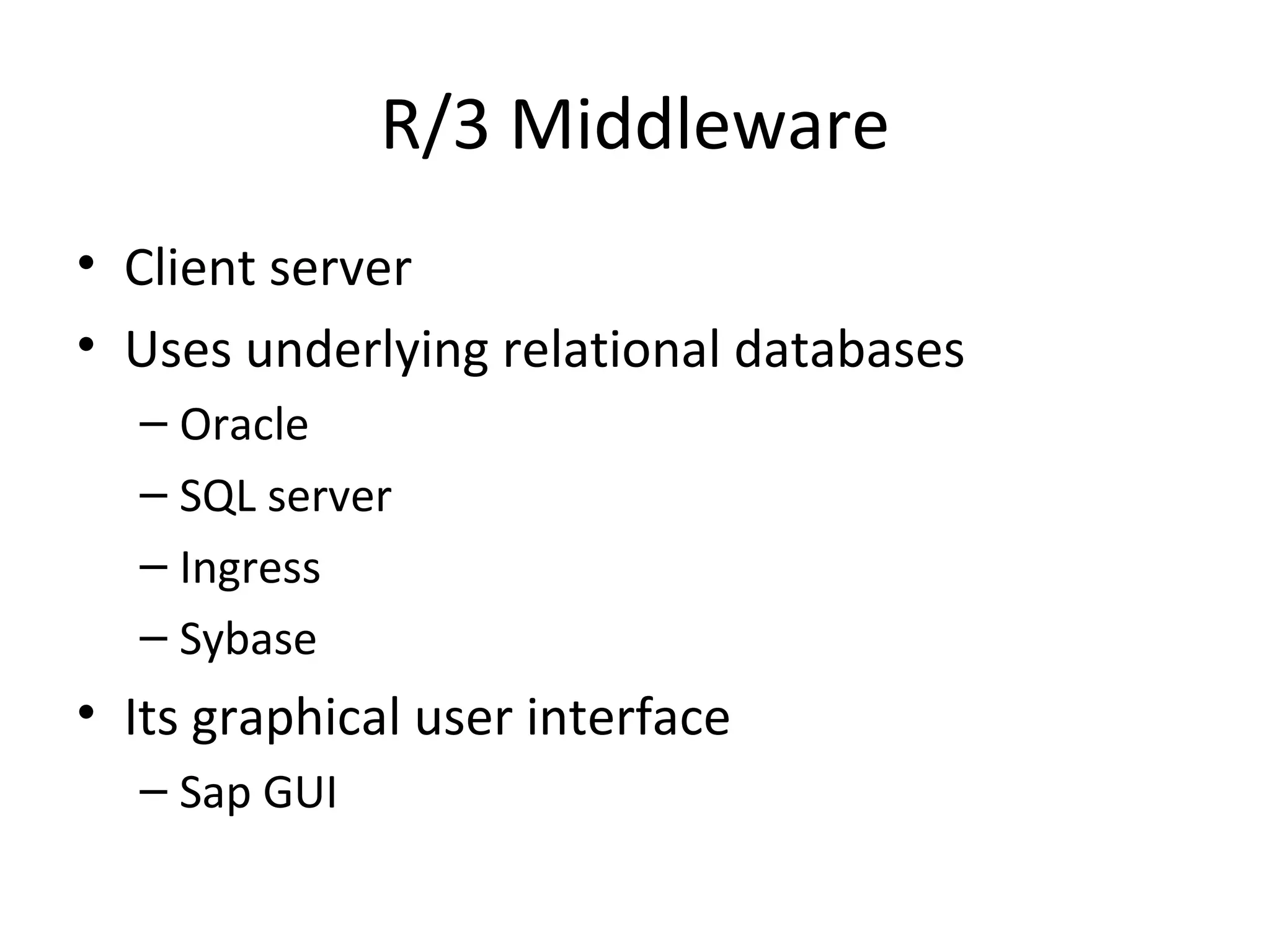
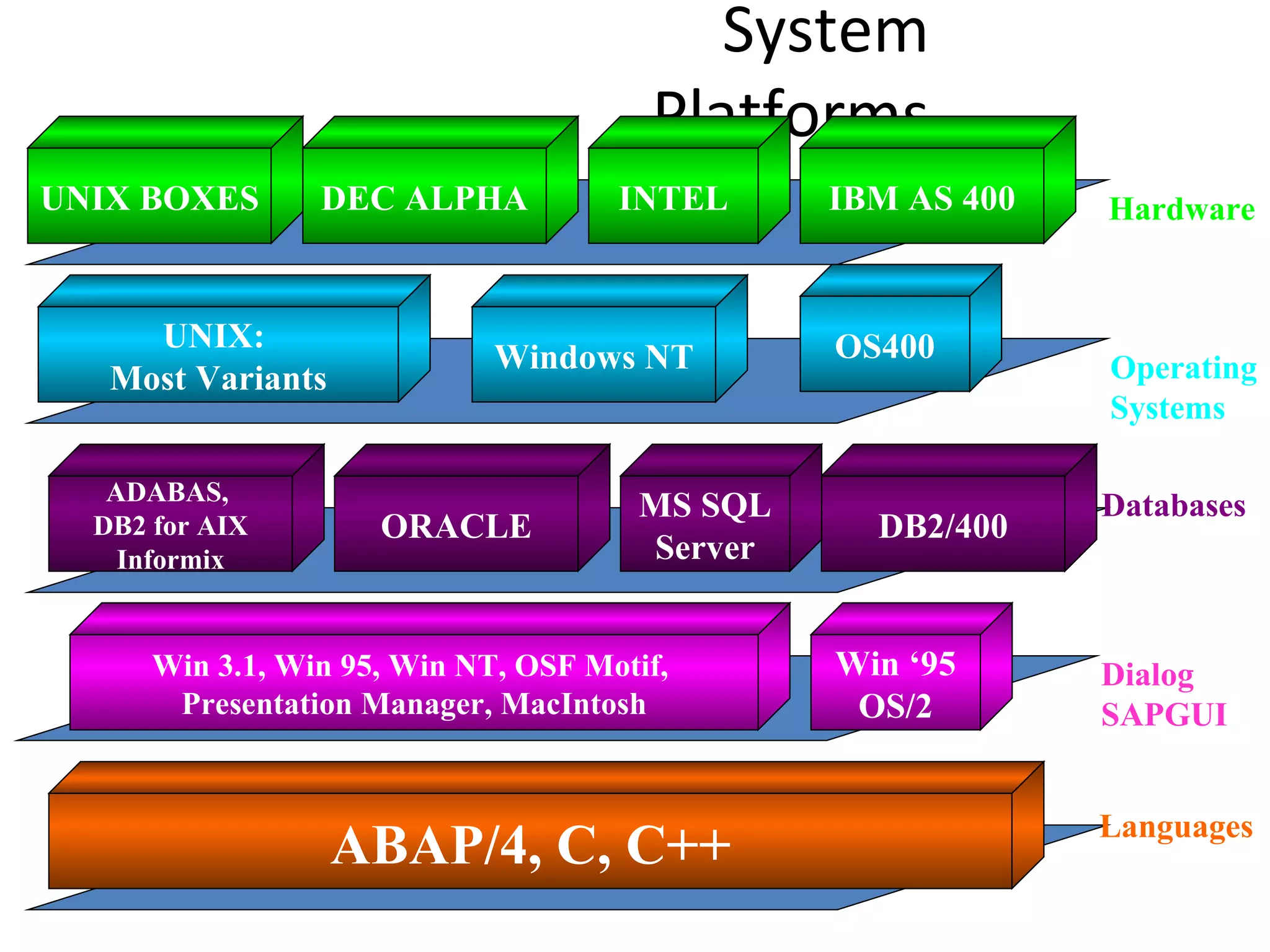
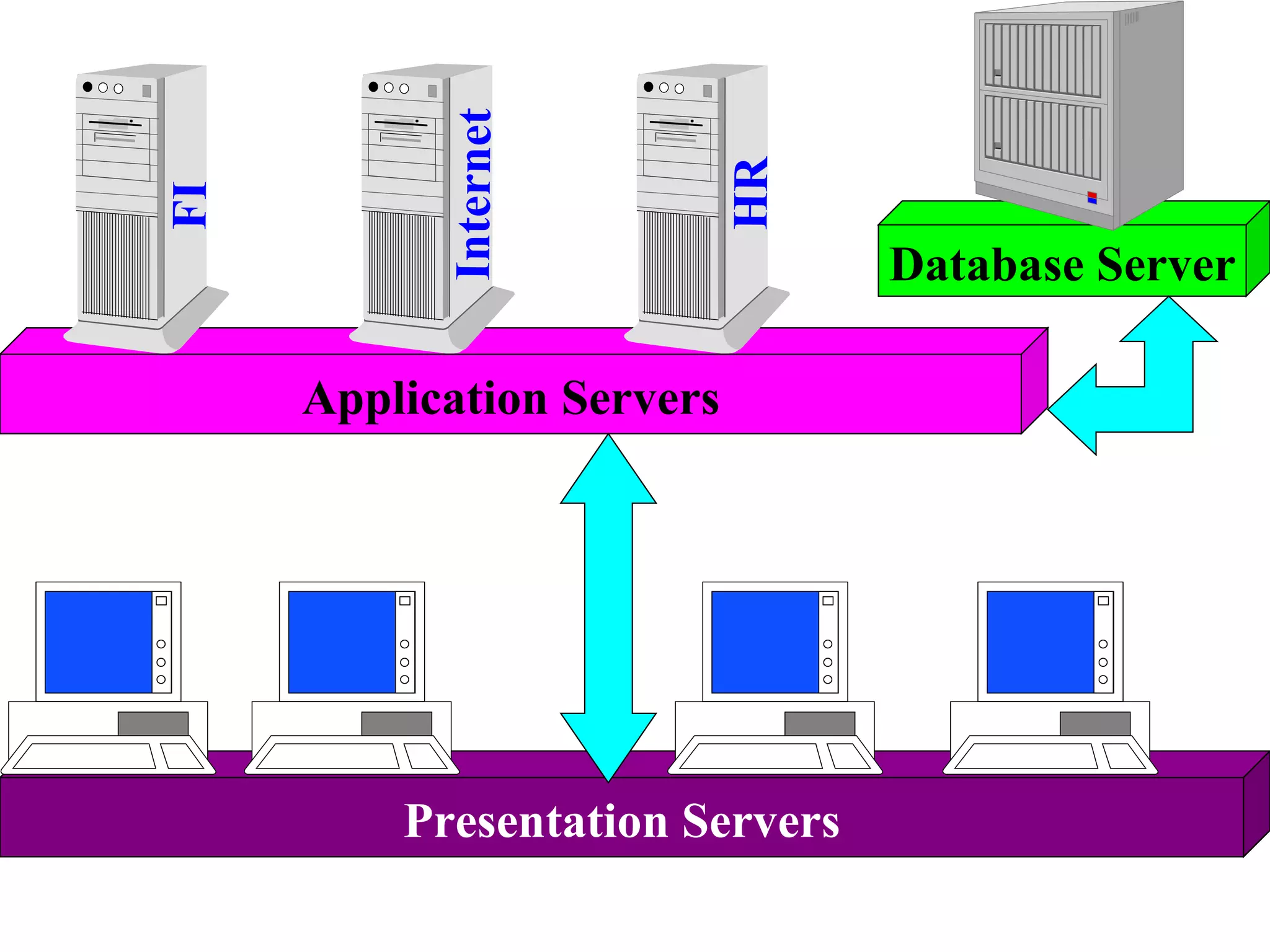
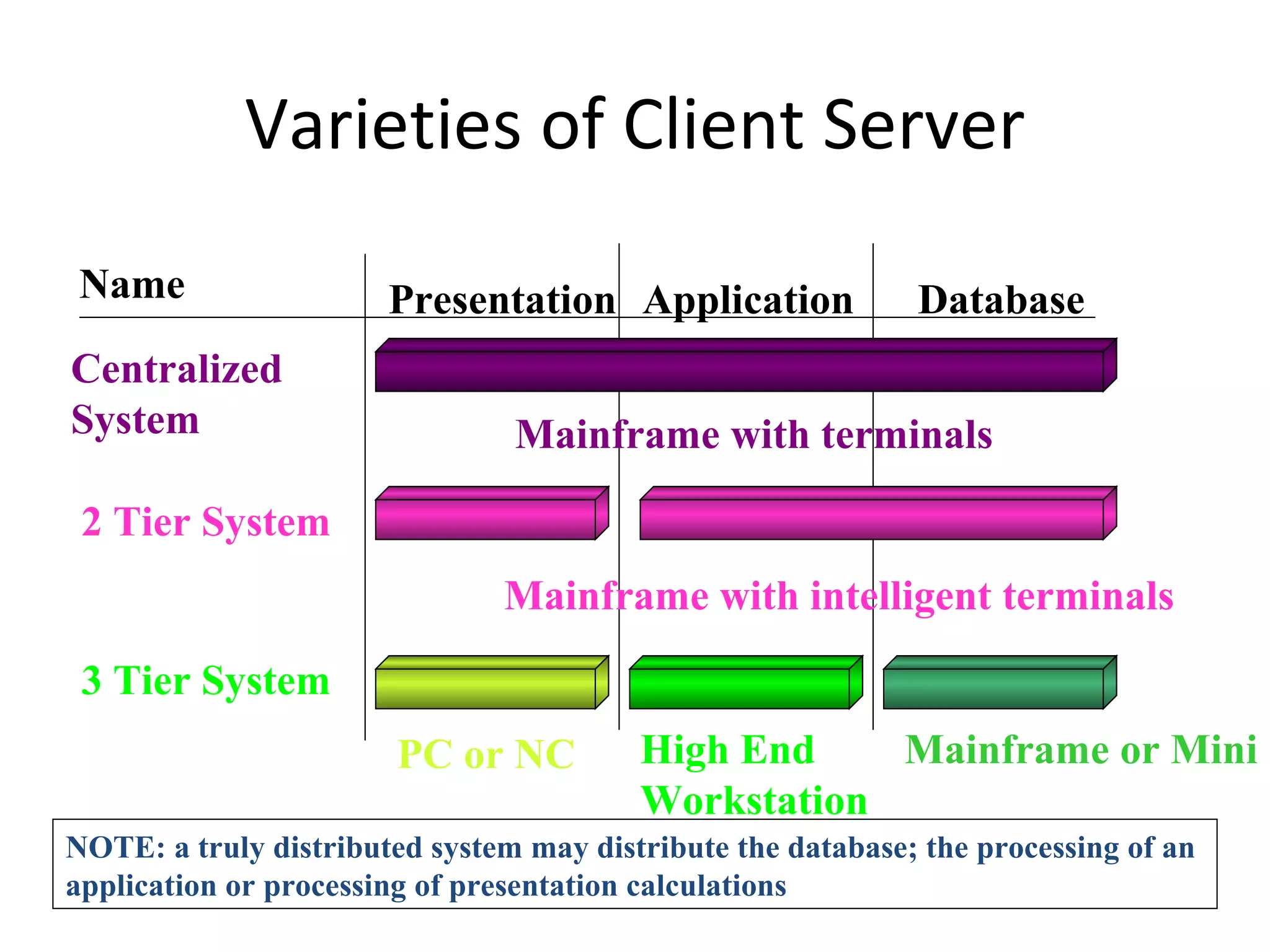
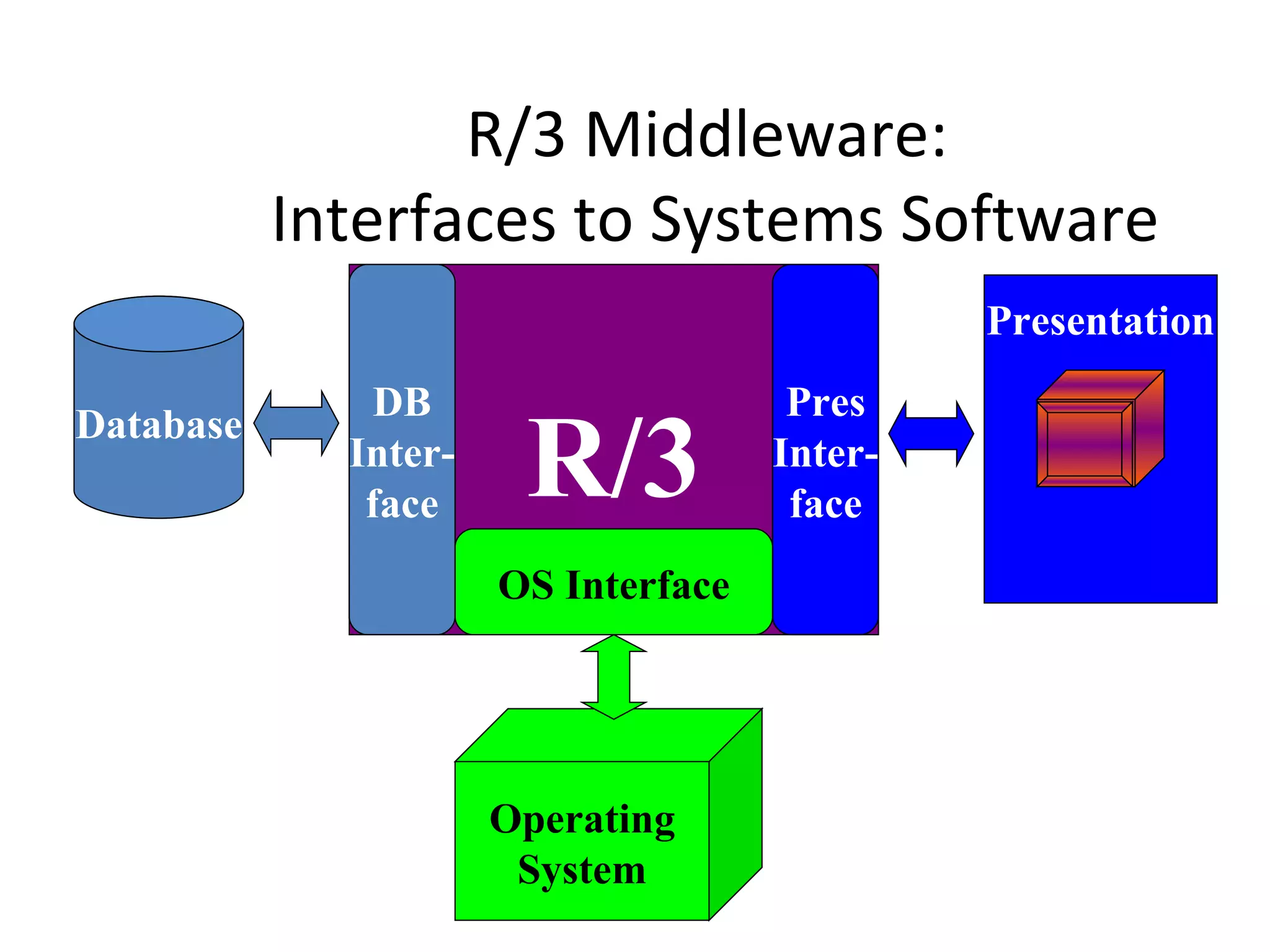
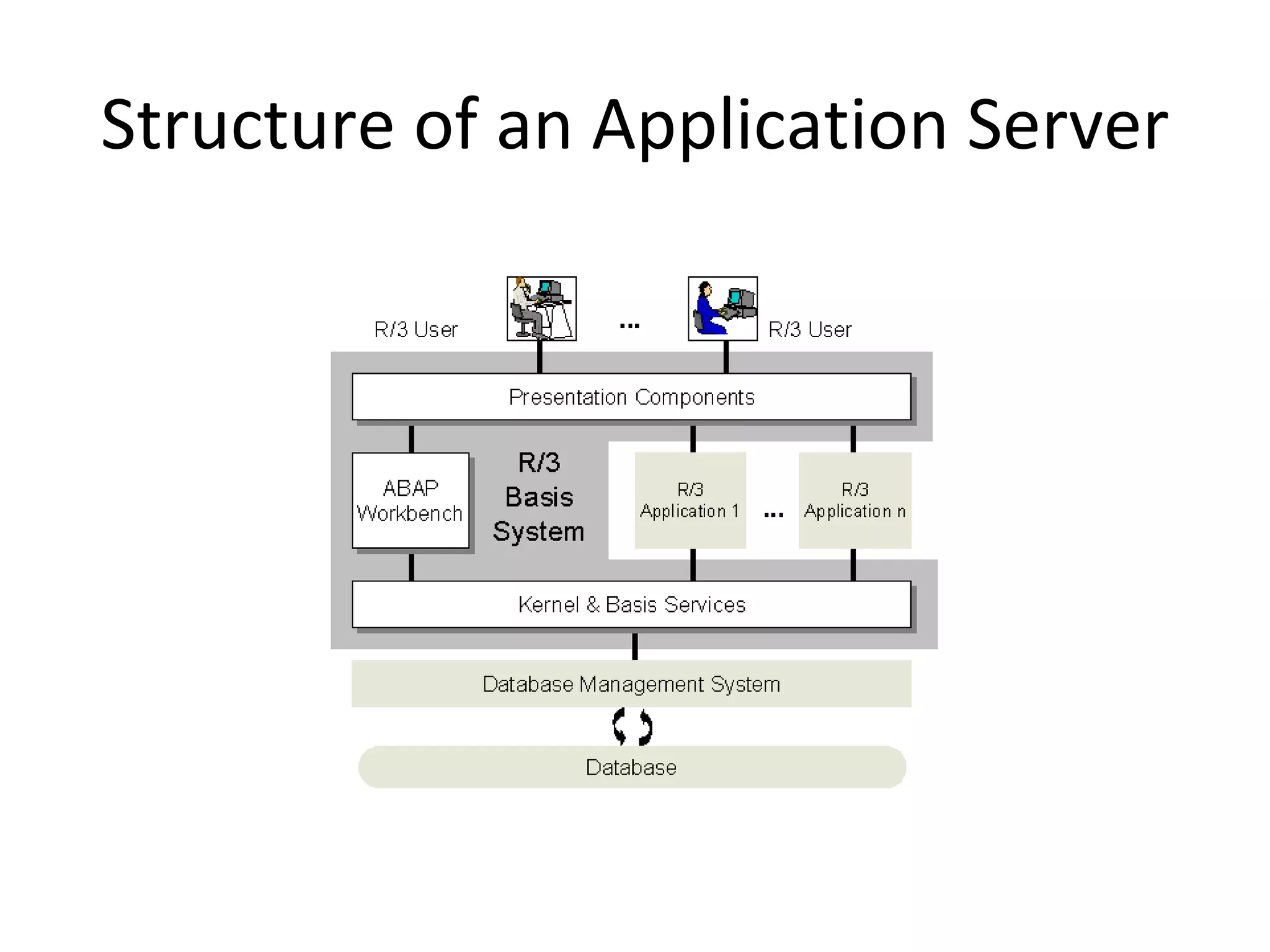
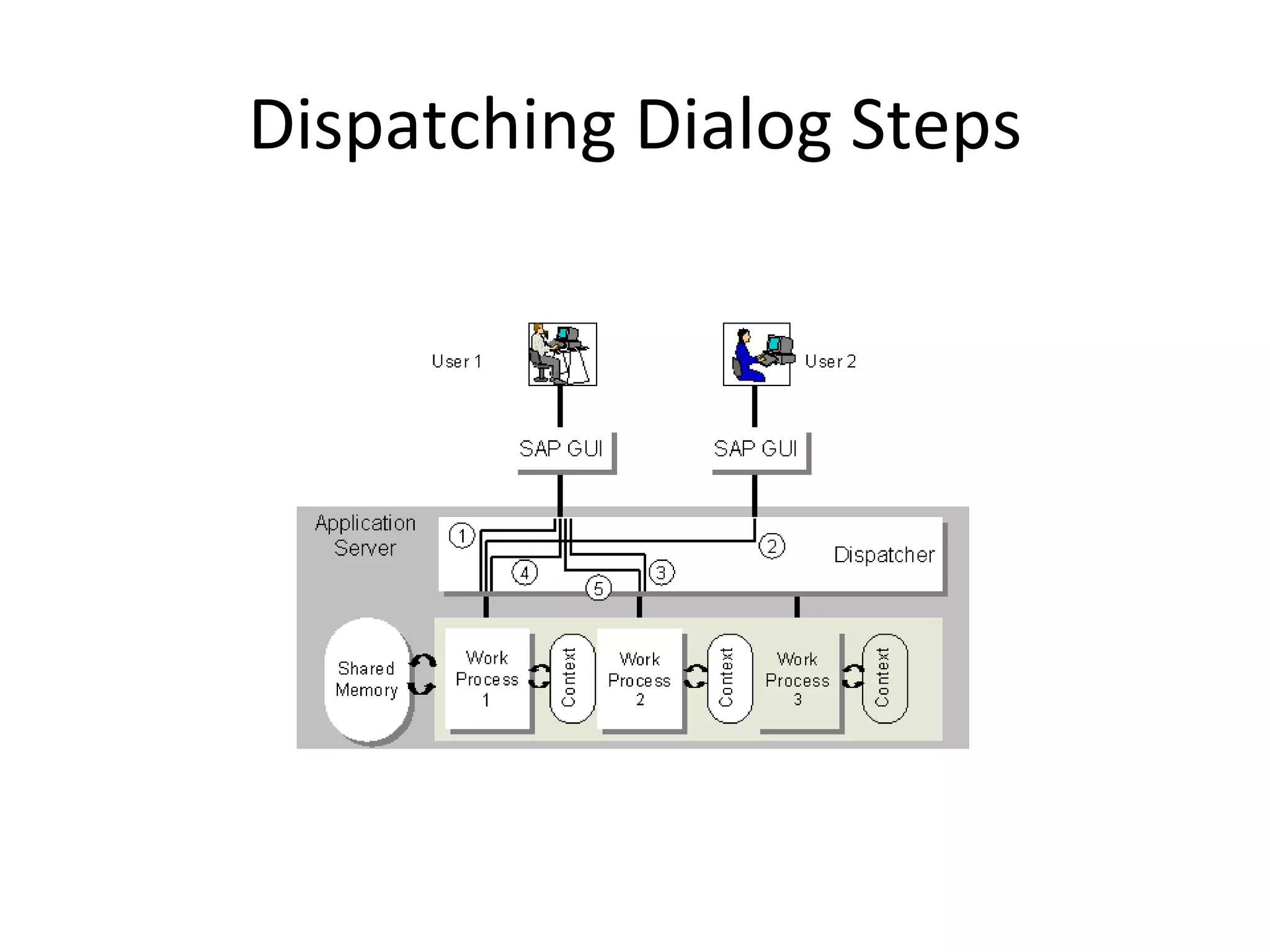
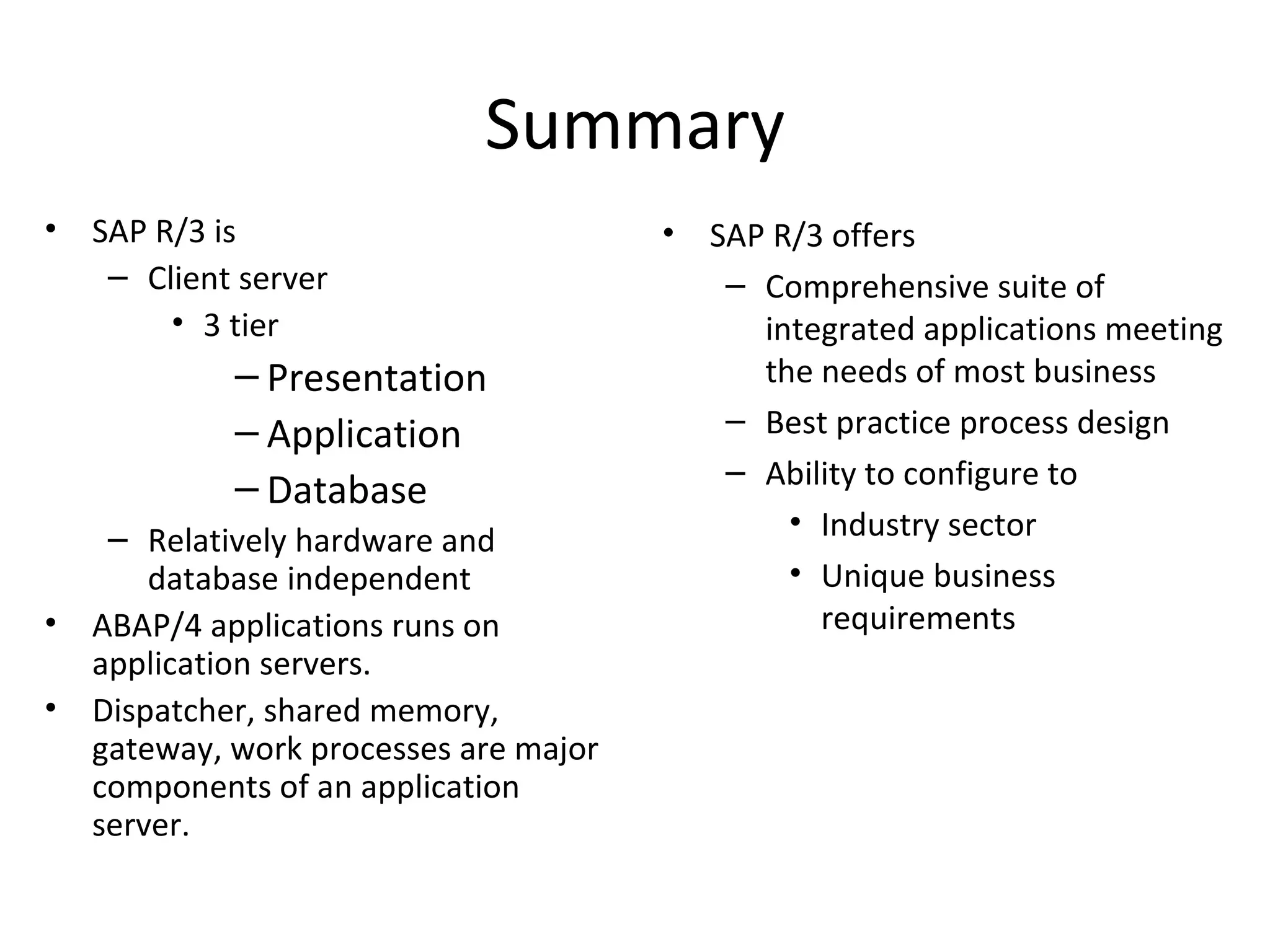
SAP R/3 is a comprehensive enterprise resource planning software that integrates common business functions across various modules. It consists of financial management, logistics, human resources management, and other key modules. The software takes a process-based approach and can be customized to meet a company's unique business needs and practices. It runs on a three-tier client-server architecture that is relatively independent of hardware and database platforms.
![ERP SAP R/3 Overview Last modified by: Bunty Jain – SAP ABAP, Delhi, India, IT SAP Training [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erpsapr3overviewintroduction-120131003707-phpapp01/75/Erp-sap-r3-overview-introduction-1-2048.jpg)
















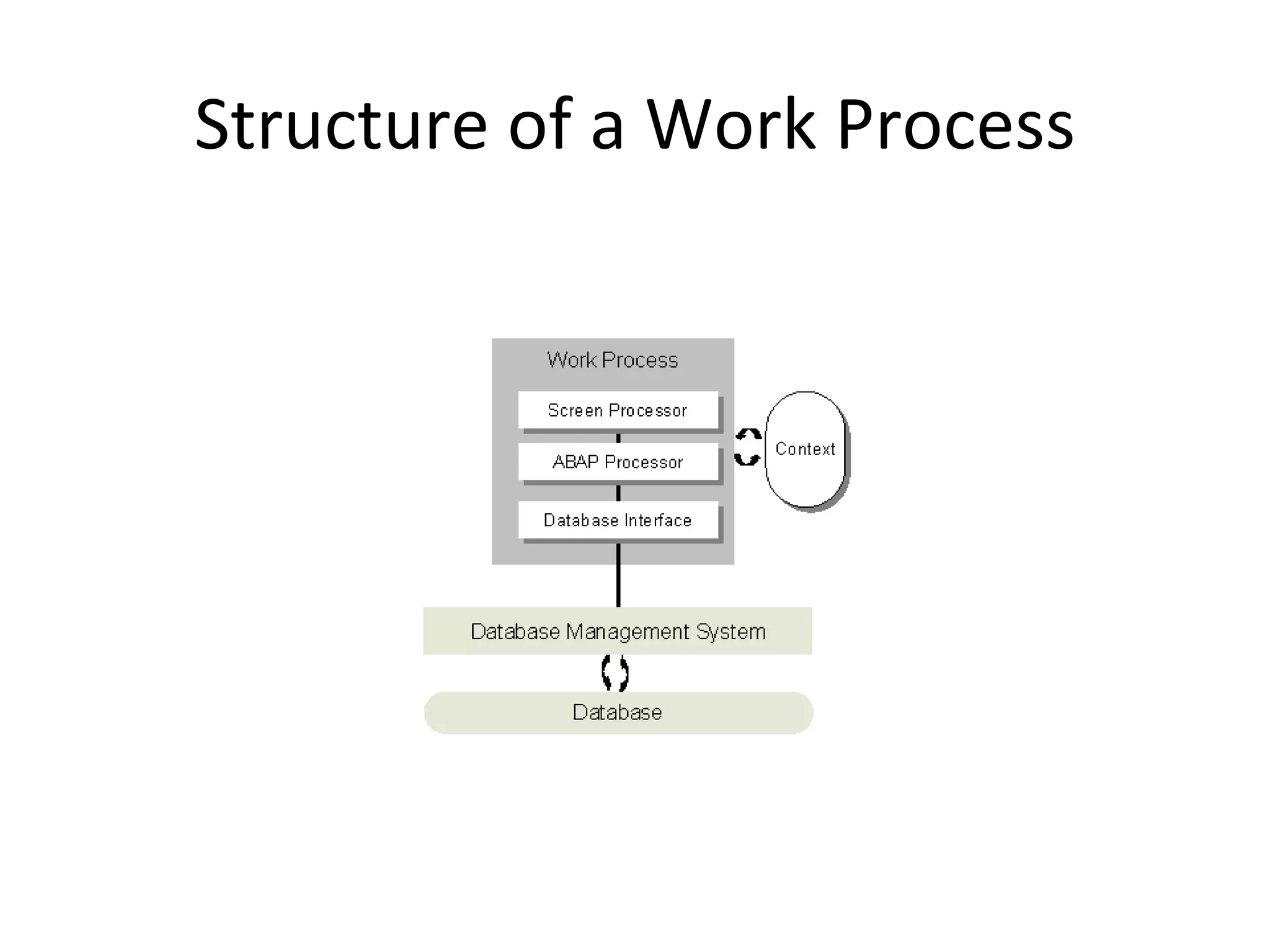


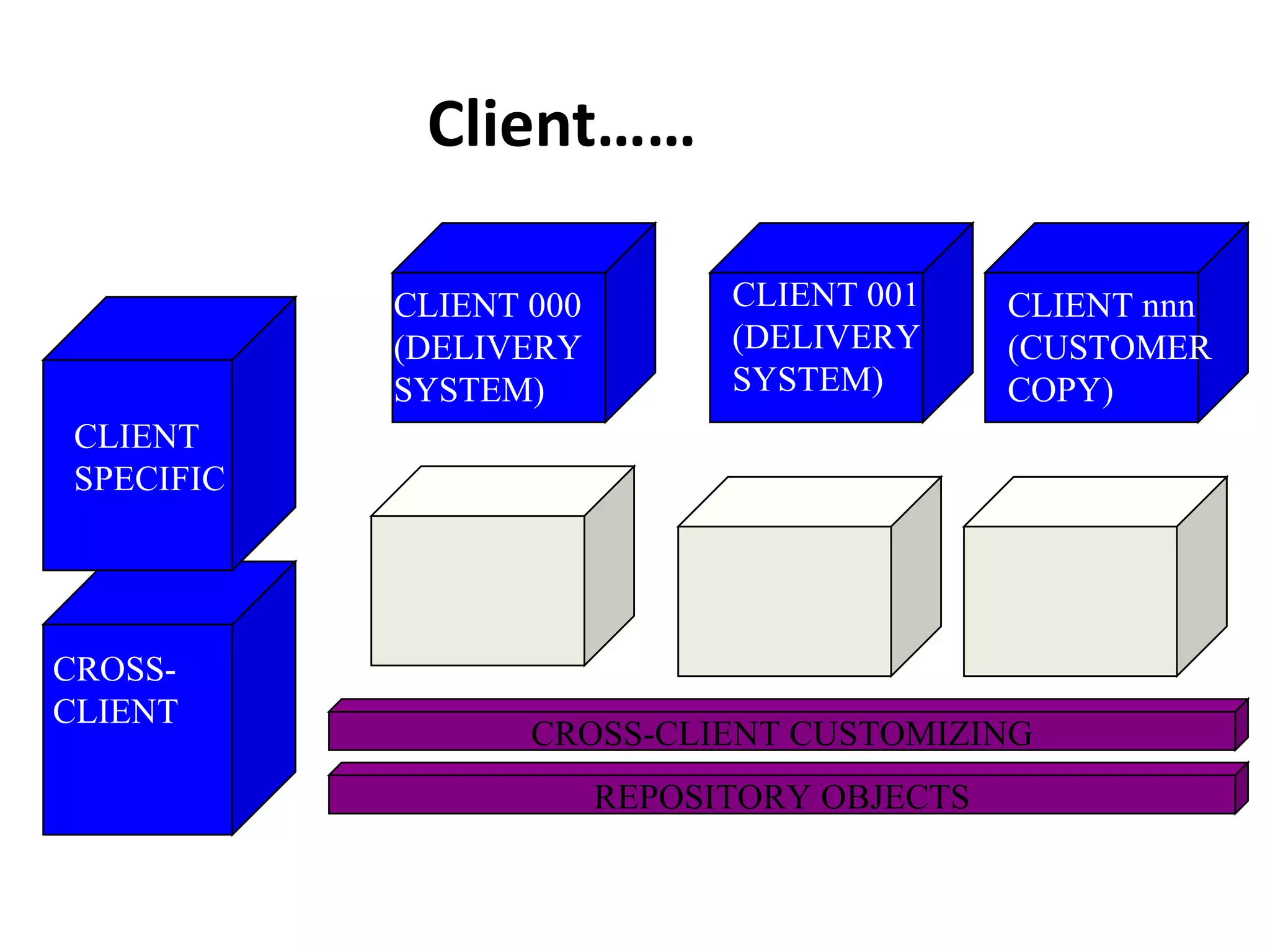
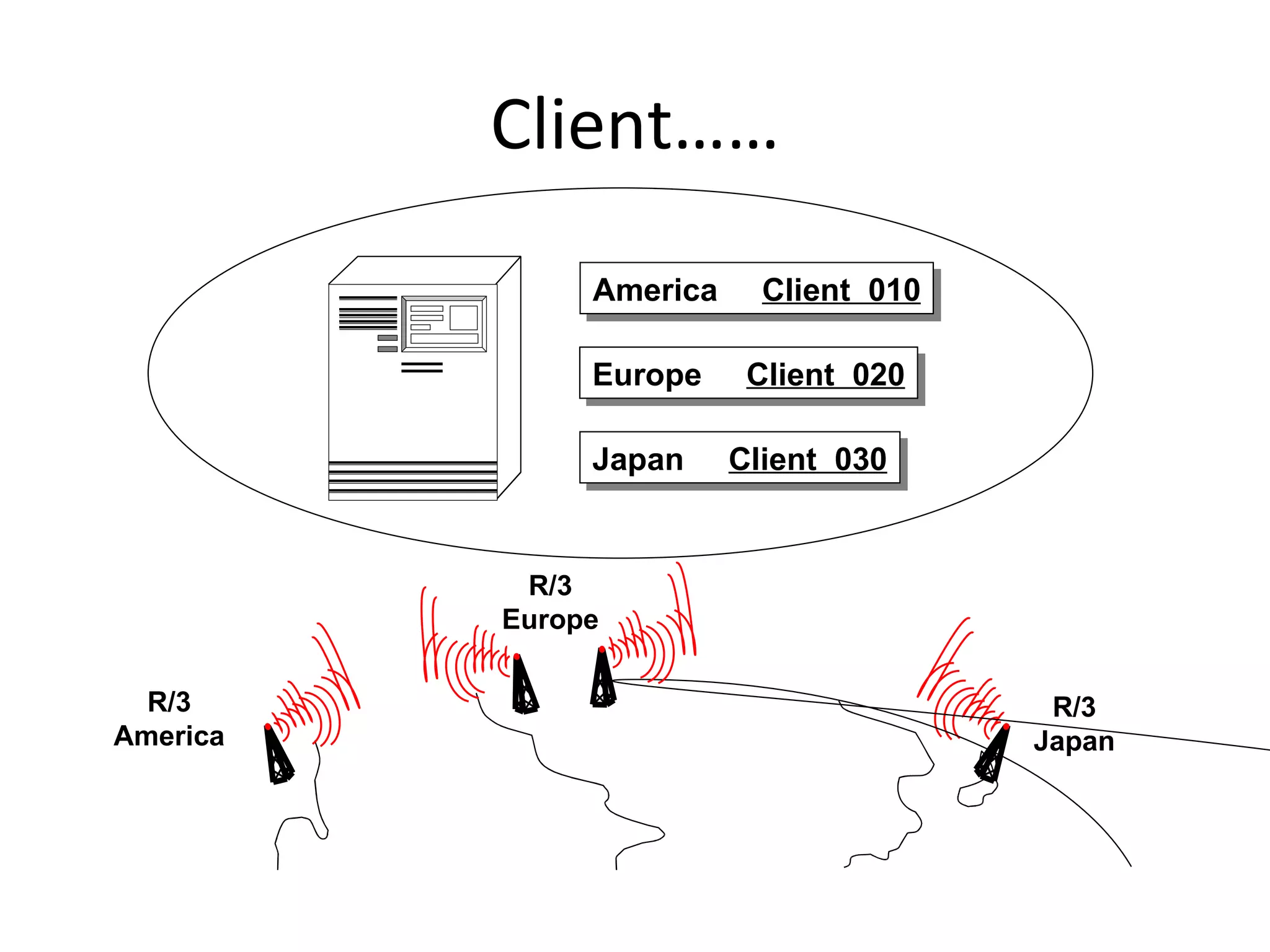
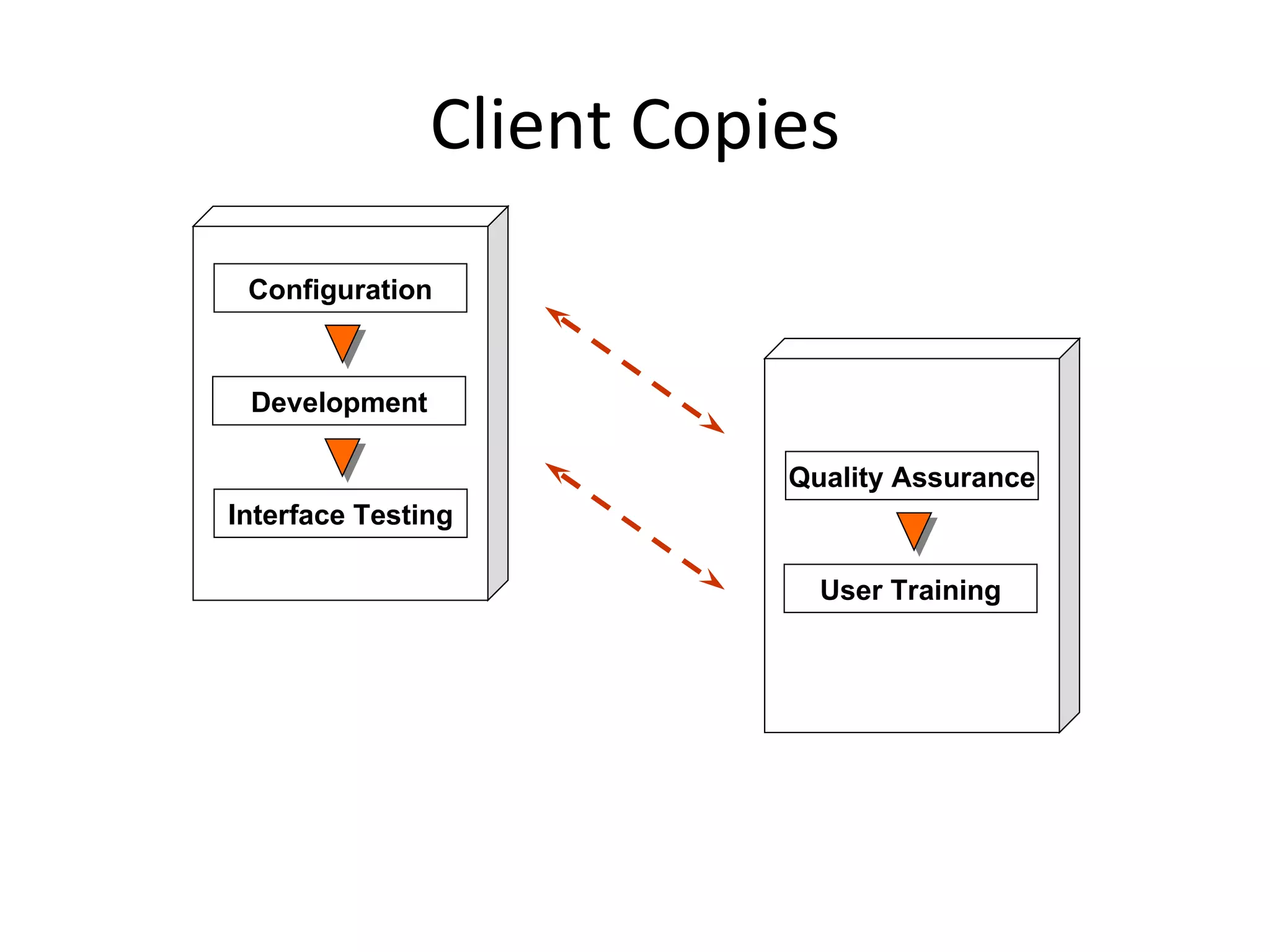

![End Last modified by: Bunty Jain – SAP ABAP, Delhi, India, IT SAP Training [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erpsapr3overviewintroduction-120131003707-phpapp01/75/Erp-sap-r3-overview-introduction-42-2048.jpg)