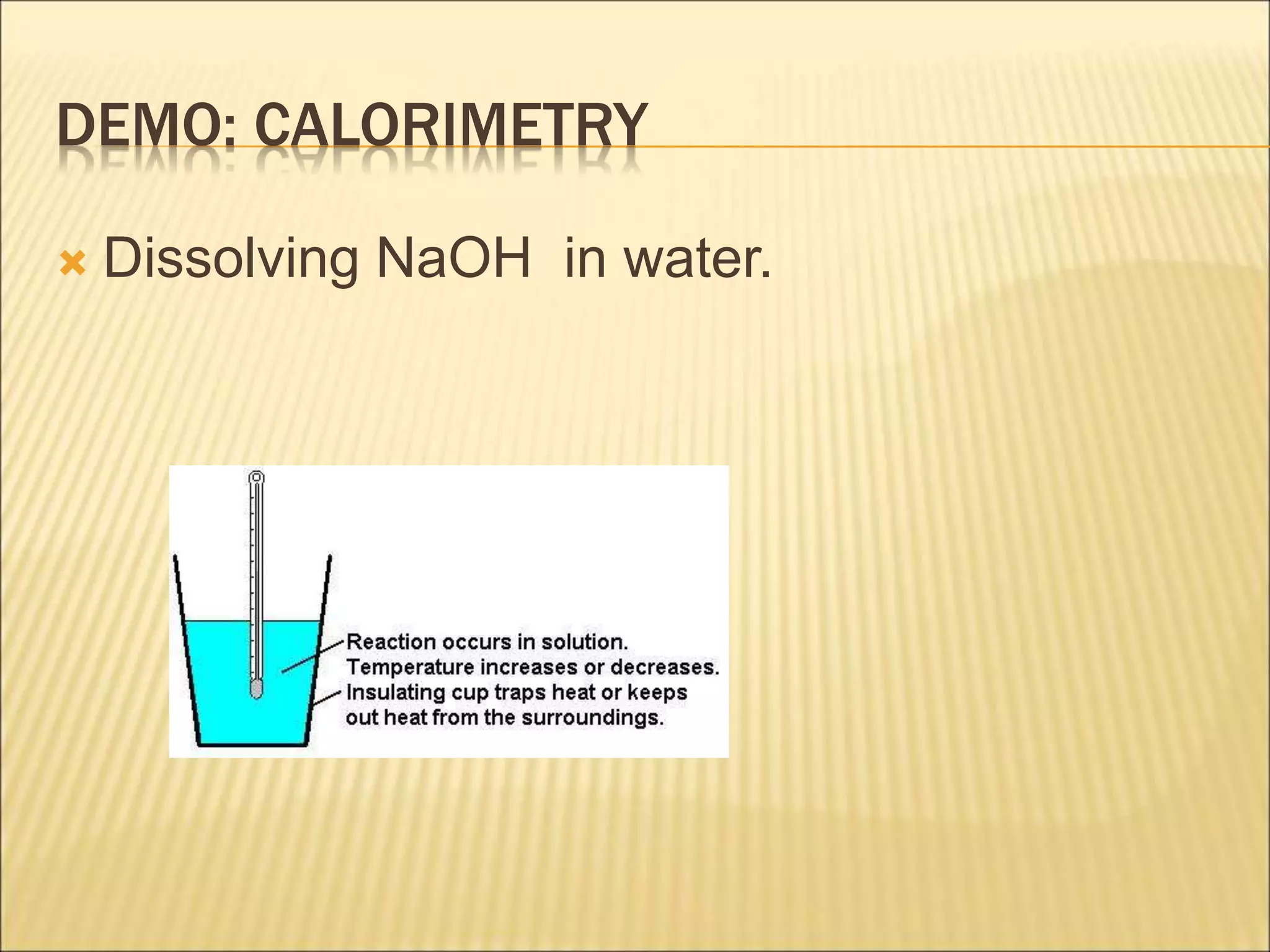
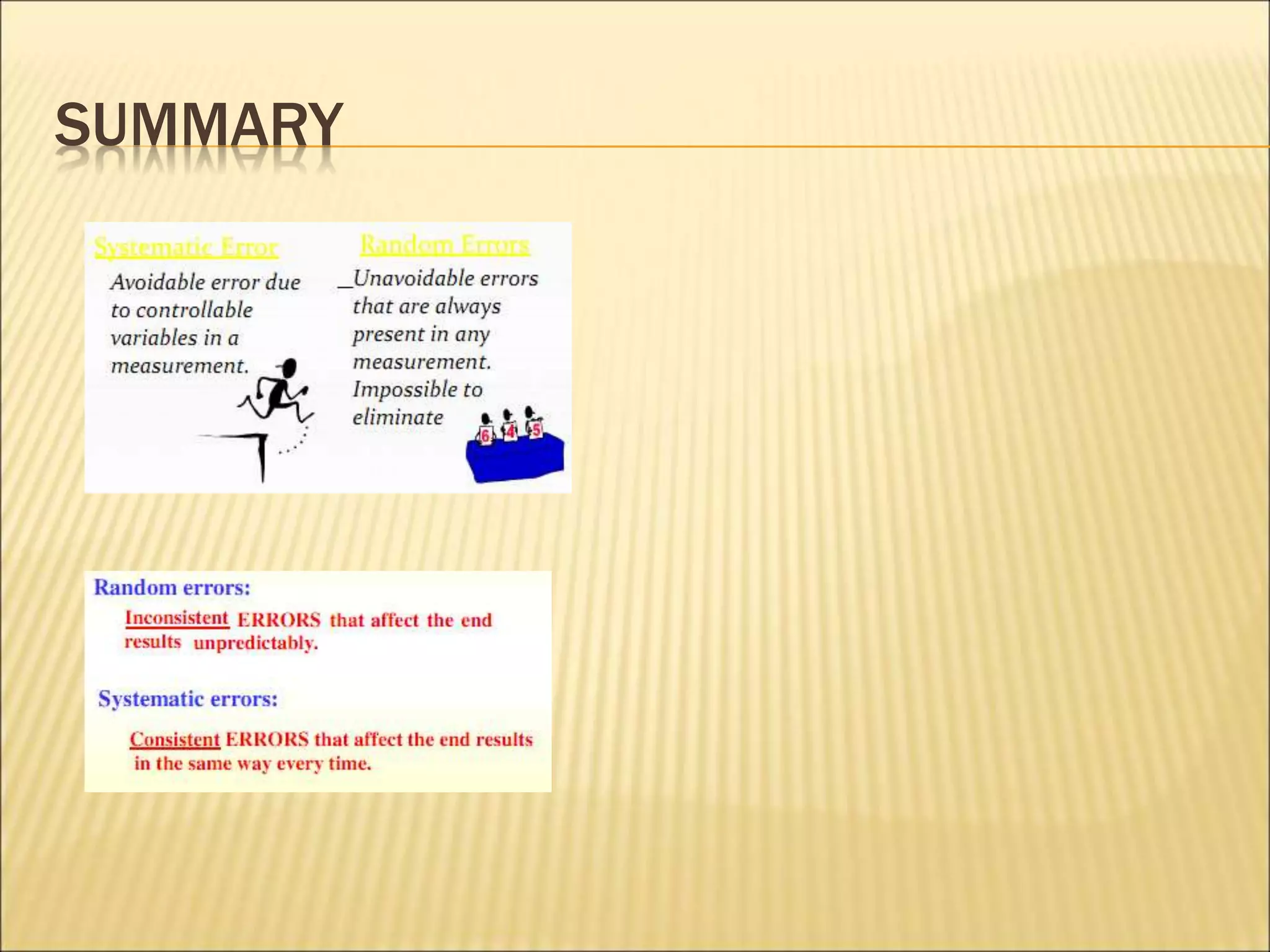
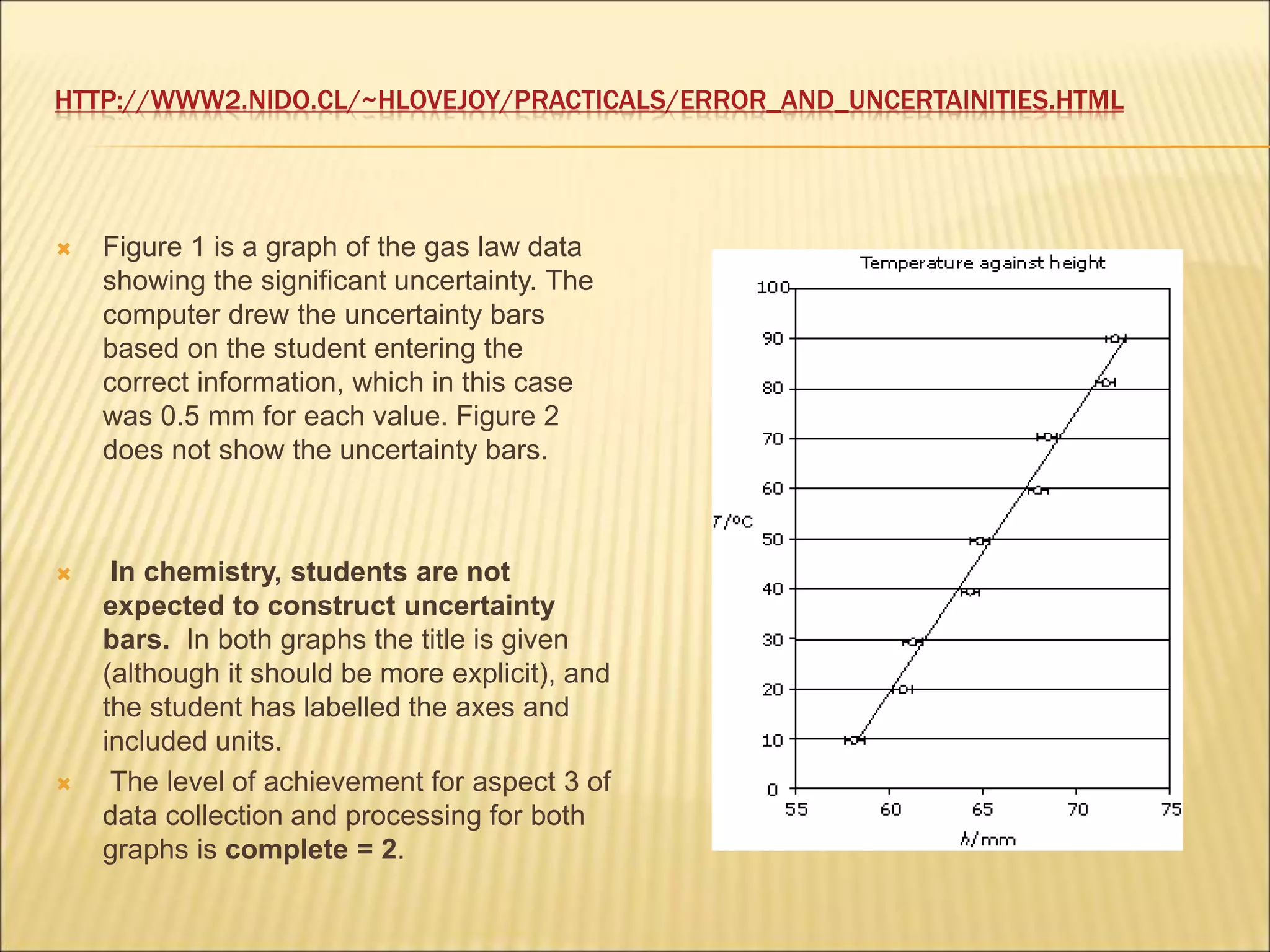
- Random uncertainties arise from imprecision in measurements and can cause readings to be above or below the true value. They can be reduced by more precise instruments or repeating measurements.
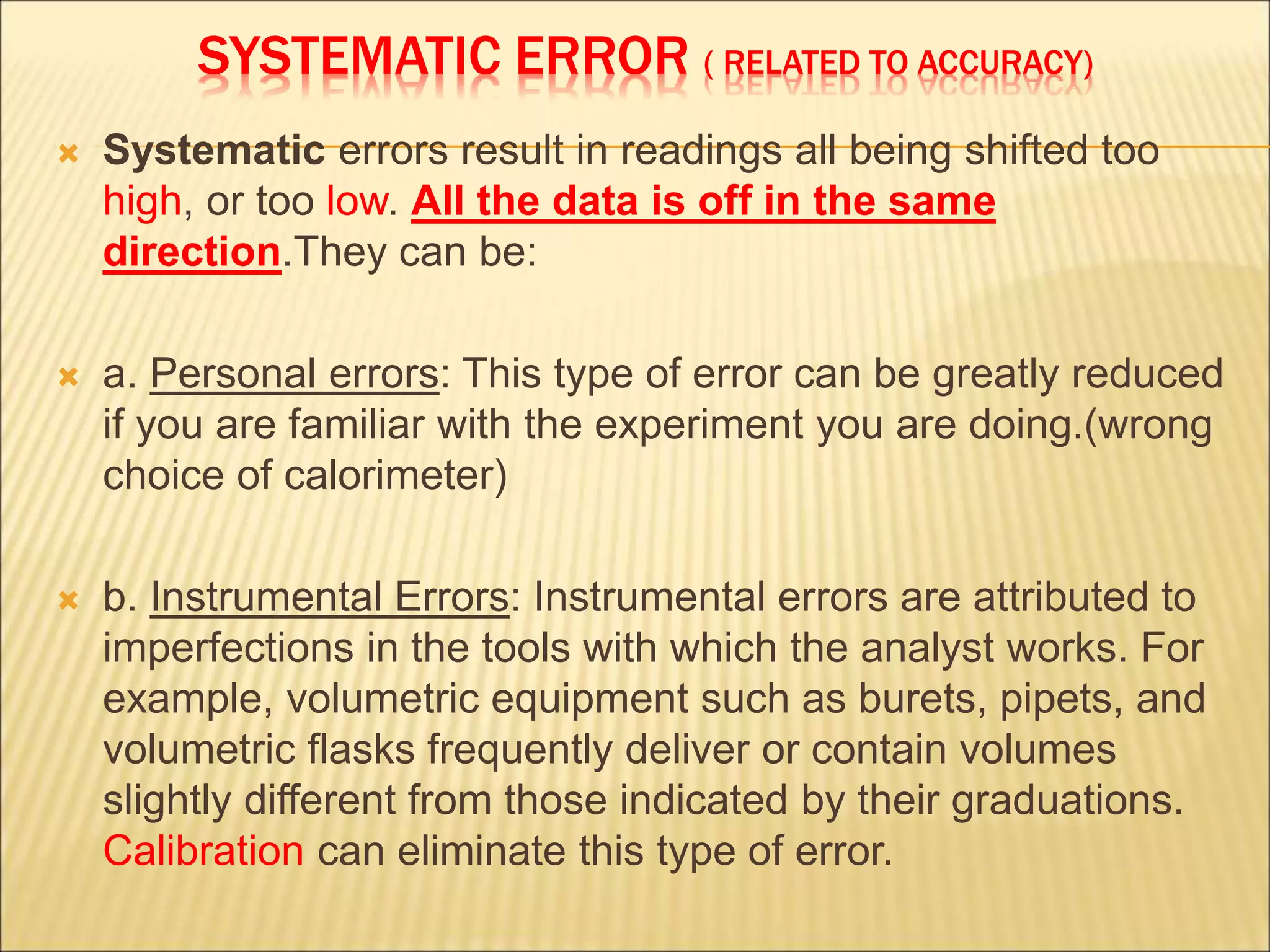
- Systematic uncertainties result in all readings being consistently too high or too low. They may be due to instrumentation errors or experimental technique and can sometimes be addressed through calibration.
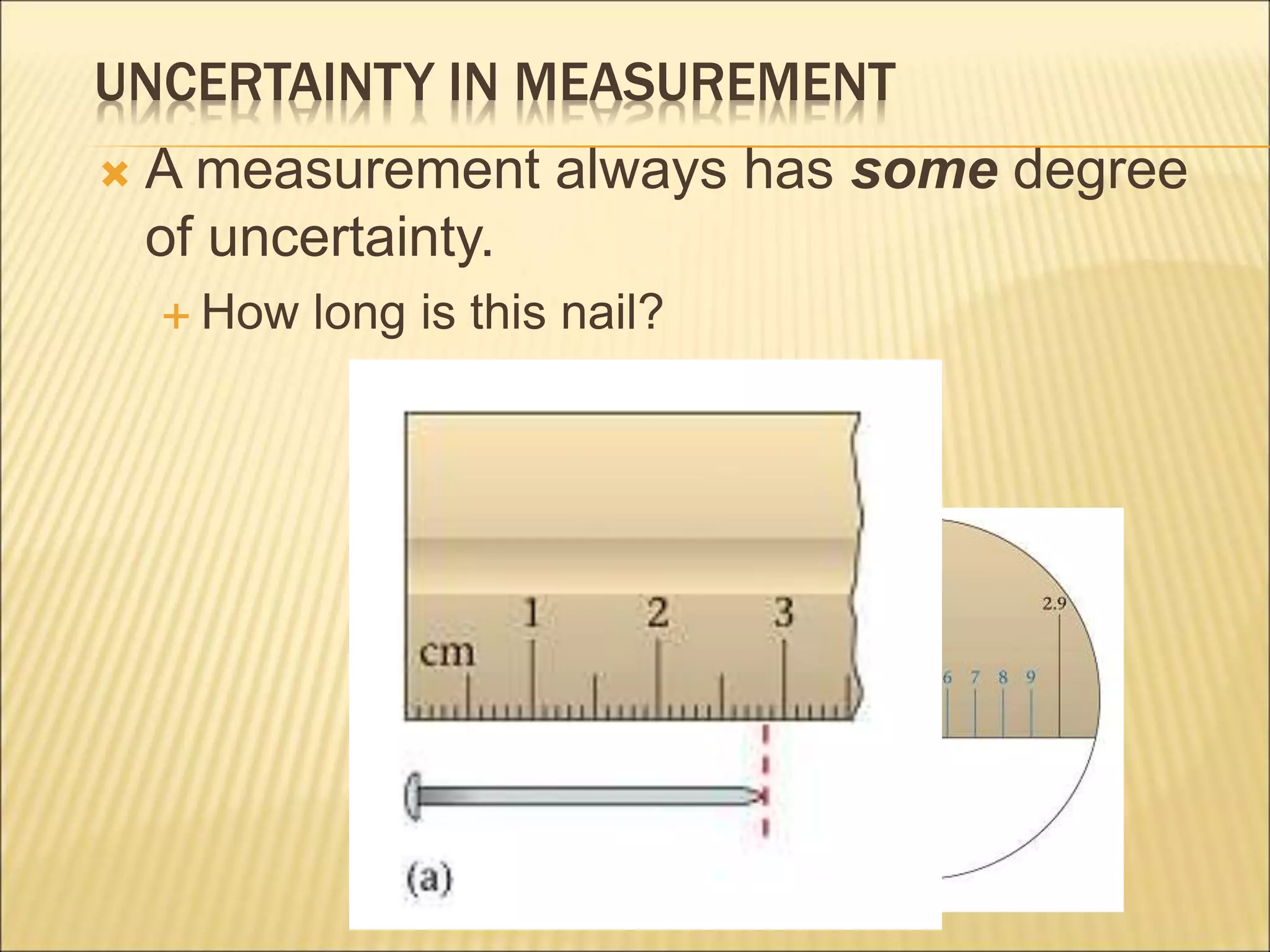
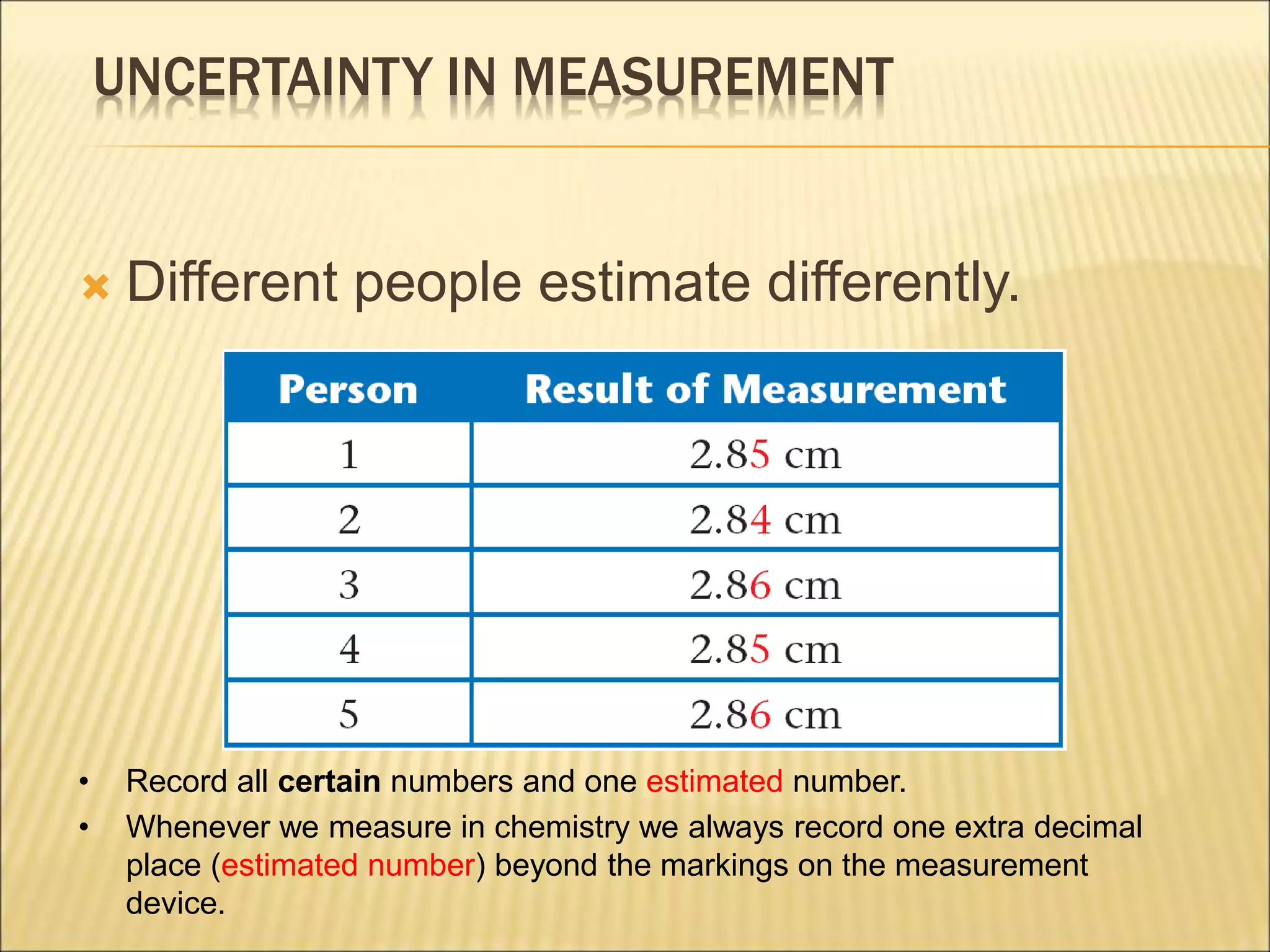
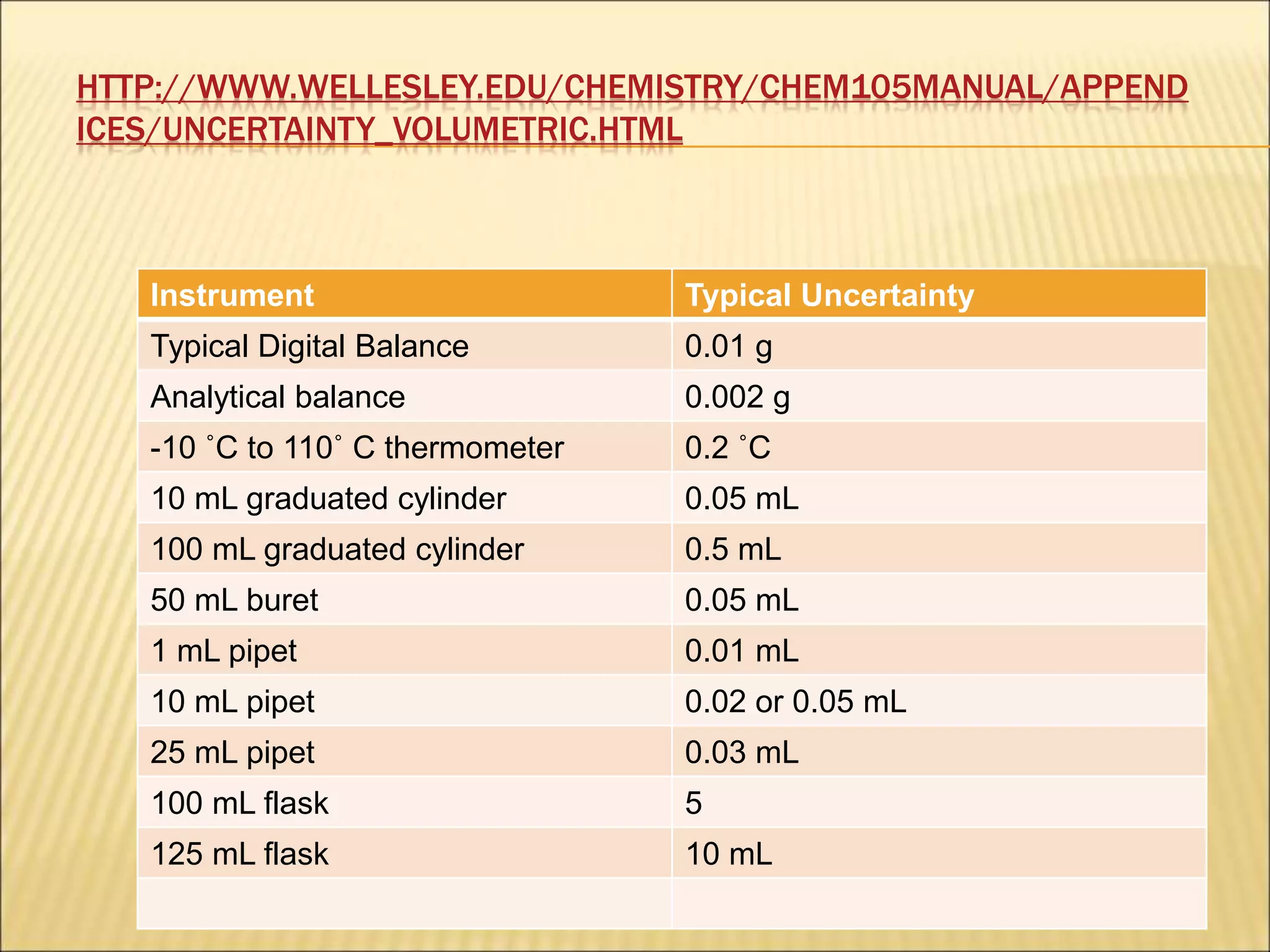
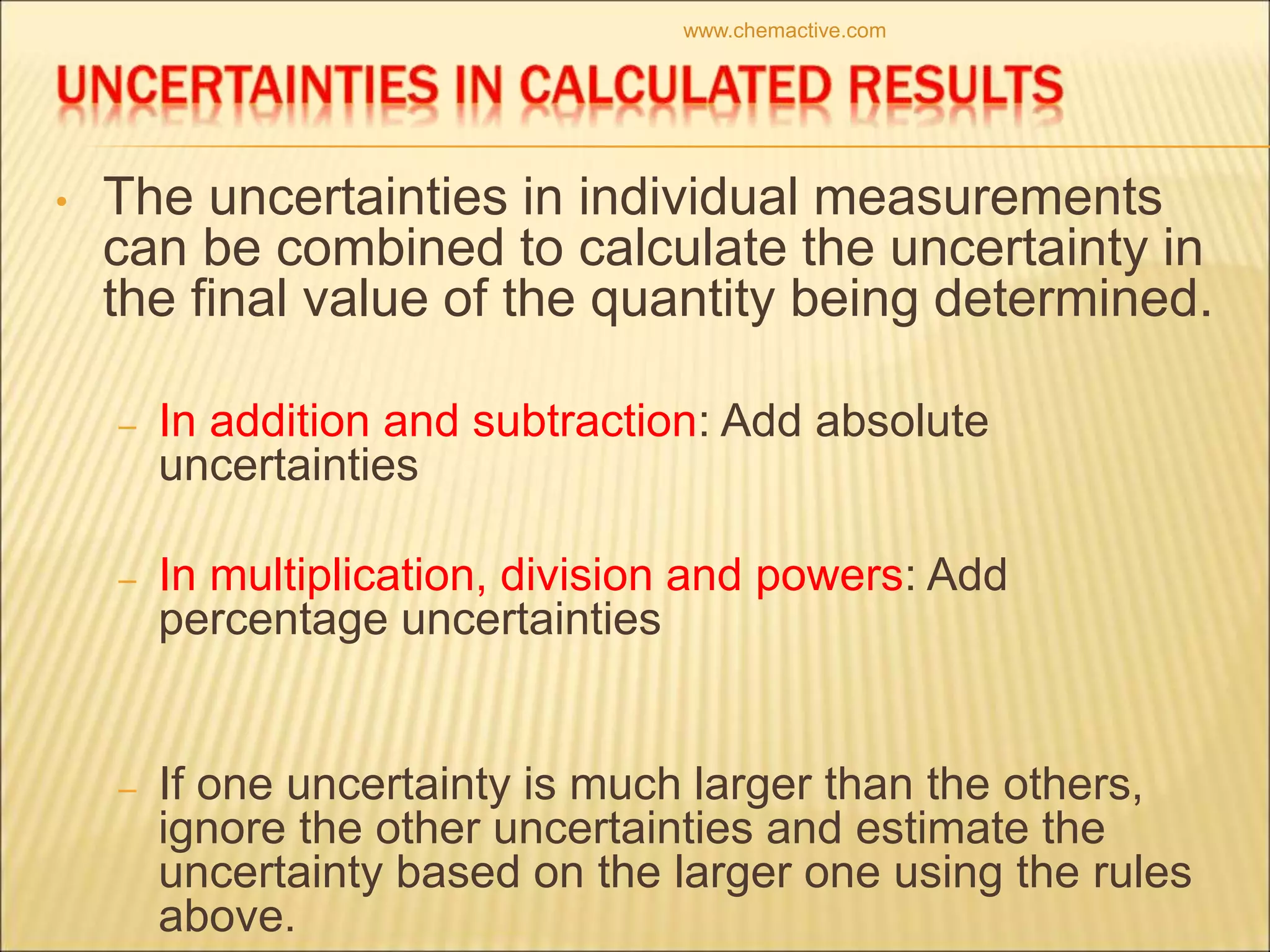
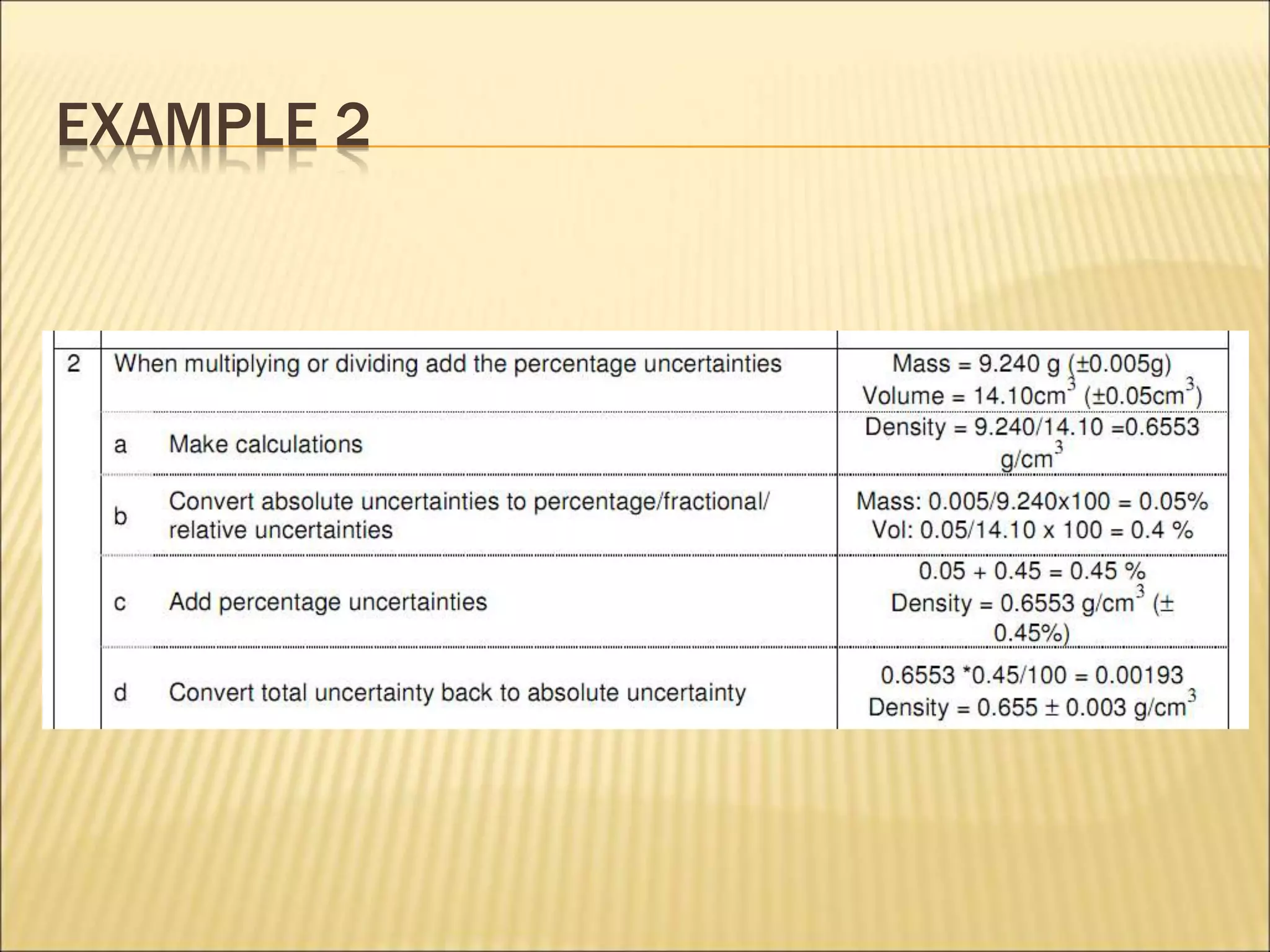
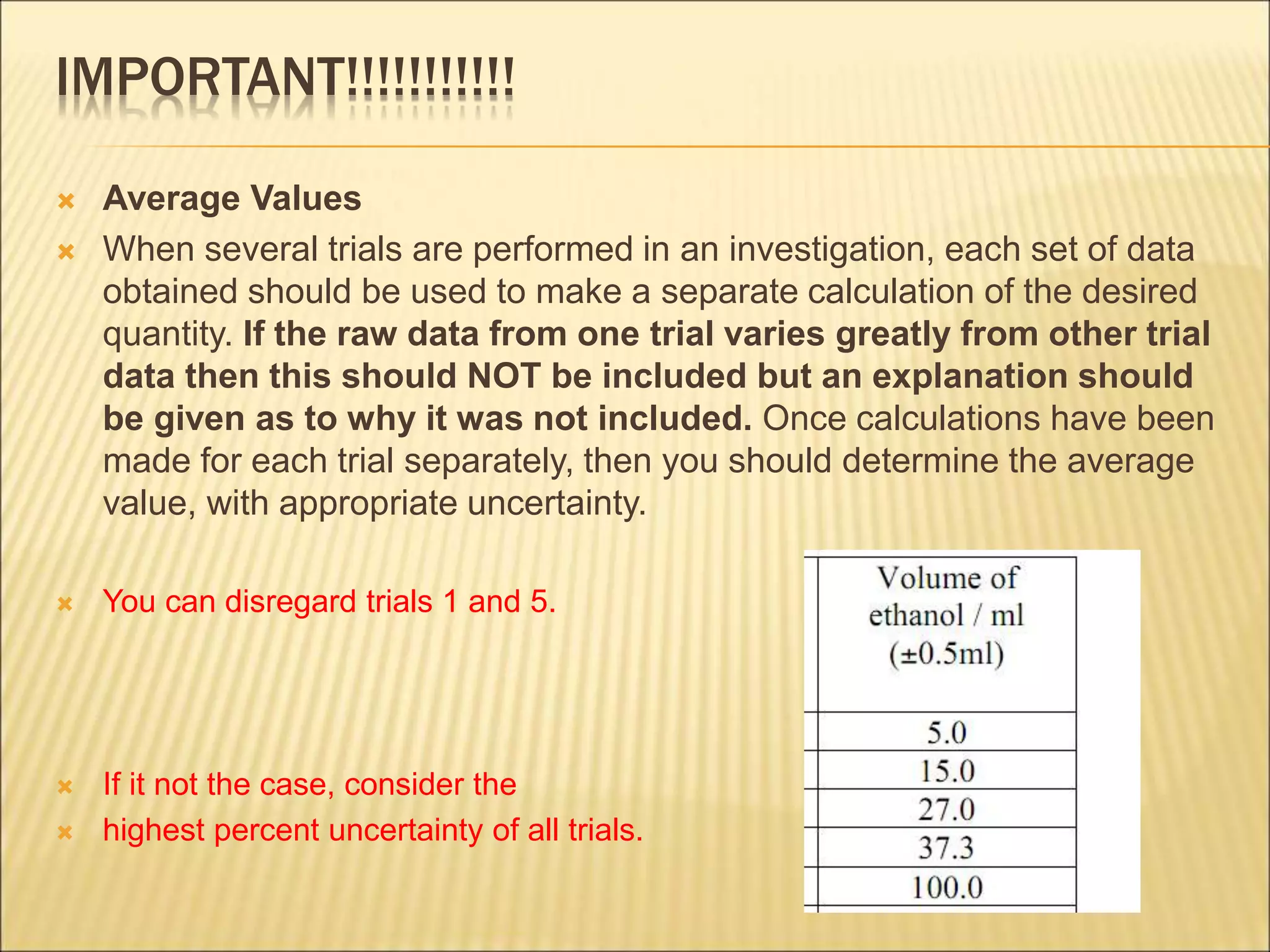
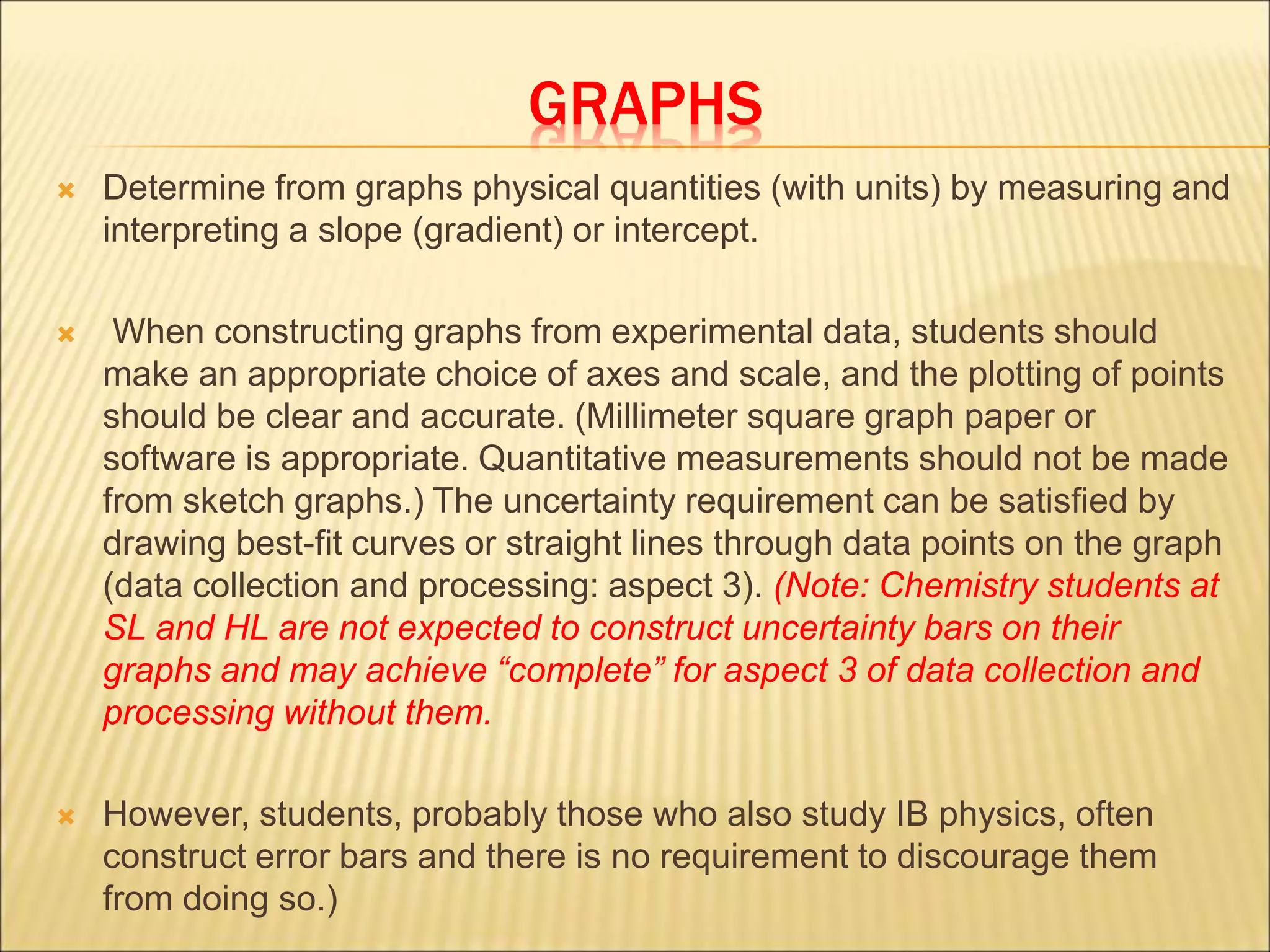
- Uncertainty is incorporated into measurements as a range rather than a single value, and it is important to propagate uncertainties through calculations.